【IO】 IO核心机制全解析
本文系统介绍Java IO技术,涵盖字节流/字符流/缓冲流操作、装饰器/适配器/观察者设计模式,详解BIO/NIO/AIO三种模型及操作系统五种IO模型,深入NIO核心组件(Buffer、Channel、Selector)、零拷贝与多路复用机制(select/poll/epoll),通过代码示例对比各模型优缺点,为Java开发者提供全面的IO编程指南。
>IO是计算机与外部世界交换数据的过程
目录
一、IO操作
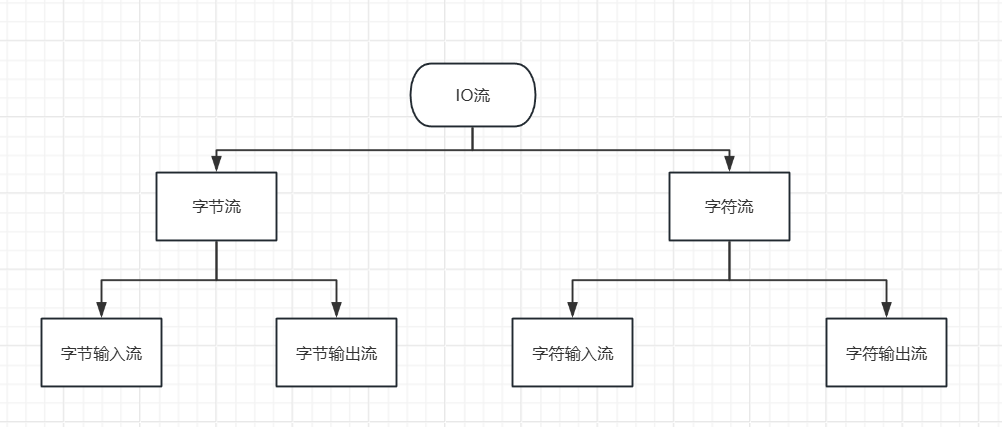
1.1 字节流操作
FileInputStream:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassLoader classLoader = ByteDemo01.class.getClassLoader();
String path = Objects.requireNonNull(classLoader.getResource("file/byte.txt")).getPath();
// 字节输入流
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path)) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int mark = 0;
while ((mark = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(buffer, 0, mark));
}
}
}BufferedInputStream:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(PATH);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis)) {
int mark = 0;
while ((mark = bis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) mark);
}
}
}DataOutputStream:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String PATH = Objects.requireNonNull(ByteDemo01.class.getClassLoader().getResource("file/byte.bin")).getPath();
PATH = PATH.substring(1);
try (DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(Files.newOutputStream(Paths.get(PATH)))) {
dos.writeBoolean(true);
dos.writeInt(123);
dos.writeUTF("你好,世界");
}
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(PATH);
DataInputStream bis = new DataInputStream(fis)) {
boolean isEnable = bis.readBoolean();
int readInt = bis.readInt();
String readUTF = bis.readUTF();
System.out.println("isEnable = " + isEnable + ", readInt = " + readInt + ", readUTF = " + readUTF);
}
}ObjectInputStream:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String PATH = Objects.requireNonNull(ByteDemo01.class.getClassLoader().getResource("file/byte.txt")).getPath();
PATH = PATH.substring(1);
User user = new User();
user.setName("theonefx");
user.setAge(666);
try (ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(Files.newOutputStream(Paths.get(PATH)))) {
oos.writeObject(user);
}
try(ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(Files.newInputStream(Paths.get(PATH)))) {
Object object = ois.readObject();
System.out.println((User)object);
}
}BufferedOutputStream:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = ByteDemo01.class.getClassLoader().getResource("file/byte.txt").getPath();
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(path);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos)) {
String context = "hello world!!!";
bos.write(context.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
bos.flush();
System.out.println("写入成功!");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("写入失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}在使用output流时,如果项目是Maven项目,需要注意src/main是源码目录,当程序编译后,会将resource目录下面的文件复制到target目录下面。
1.2 字符流操作
FileReader:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try(FileReader fr = new FileReader(path)) {
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
int mark = 0;
while ((mark = fr.read(buffer)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(buffer, 0, mark));
}
}
}FileWriter:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try(FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(path)) {
String context = "你好,世界!";
fw.write(context);
}
}当使用try-with-resources时,会在自动调用close()时自动再flush()
BufferedReader:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try(BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path))) {
String readLine;
while ((readLine = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(readLine);
}
}
}1.3 缓冲流操作
默认的缓冲区都是8kb
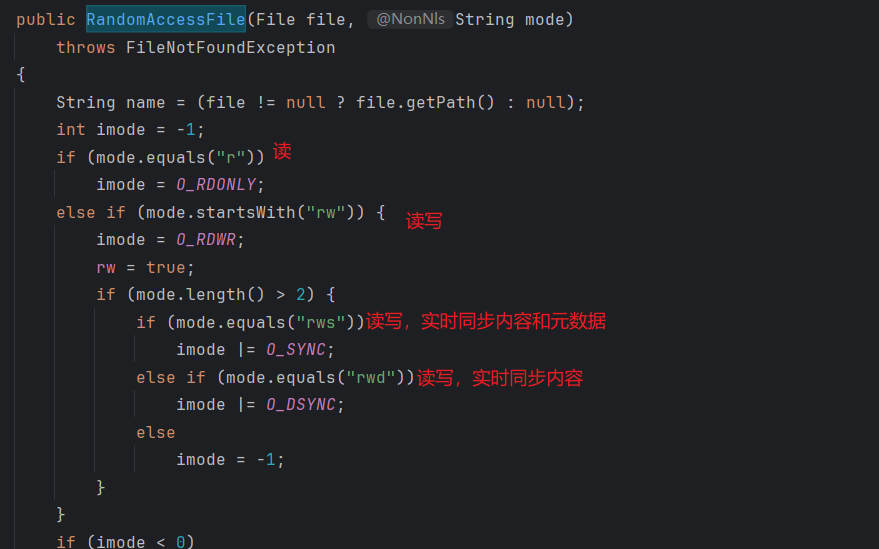
RandomAccessFile:随机访问流
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try(RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(path, "rws")) {
System.out.println(raf.getFilePointer());
int read = raf.read();
System.out.println((char) read);
raf.seek(2);
System.out.println(raf.getFilePointer());
int read1 = raf.read();
System.out.println((char) read1);
raf.write('a');
}
}
总结:字节流适合处理二进制,如图片和视频等;字符流适合处理文本数据,自动处理编码问题;
打印流适合格式化输出内容,随机访问流适合断点续传等高级功能。
二、IO设计模式
2.1 装饰器模式

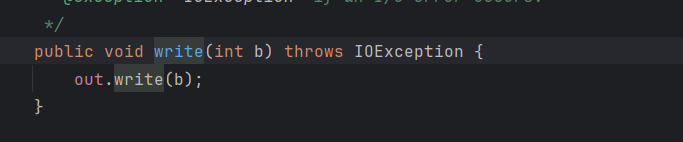
2.2 适配器模式
new InputStreamReader(Files.newInputStream(Paths.get(path)));
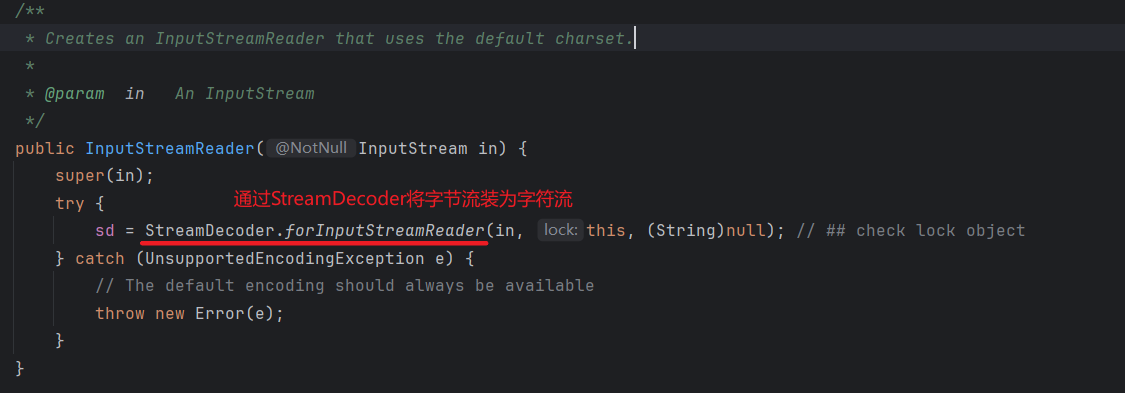
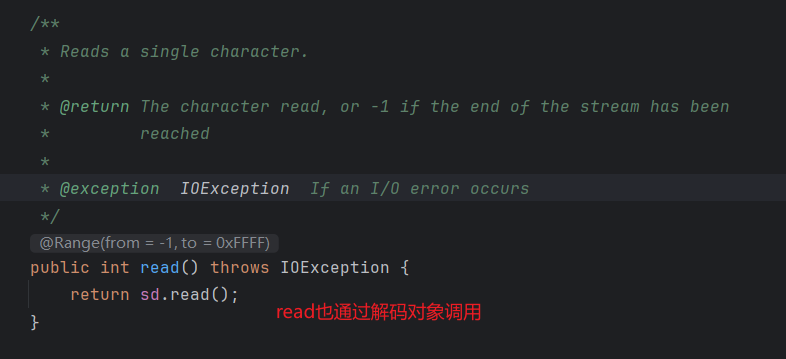
2.3 观察者模式
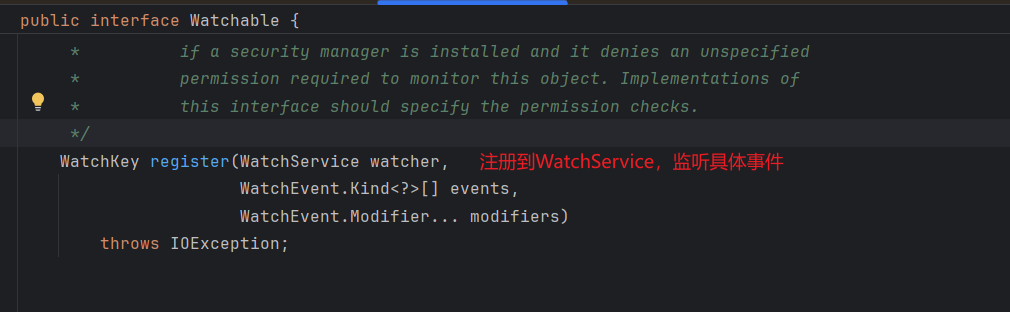
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
WatchService watchService = FileSystems.getDefault().newWatchService();
// 修改这里:获取的是目录而不是文件
Path configDir = Paths.get(WatchDemo01.class.getClassLoader().getResource("file").toURI());
configDir.register(watchService,
StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_CREATE,
StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_MODIFY,
StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_DELETE);
WatchKey watchKey;
while((watchKey = watchService.take()) != null) {
for (WatchEvent<?> pollEvent : watchKey.pollEvents()) {
WatchEvent.Kind<?> kind = pollEvent.kind();
Path fileName = (Path)pollEvent.context();
if (kind == StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_CREATE) {
System.out.println("创建: " + fileName);
} else if (kind == StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_MODIFY) {
System.out.println("修改: " + fileName);
} else if (kind == StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_DELETE) {
System.out.println("删除: " + fileName);
}
}
watchKey.reset();
}
}
三、IO模型
3.1 五种IO模型(操作系统)
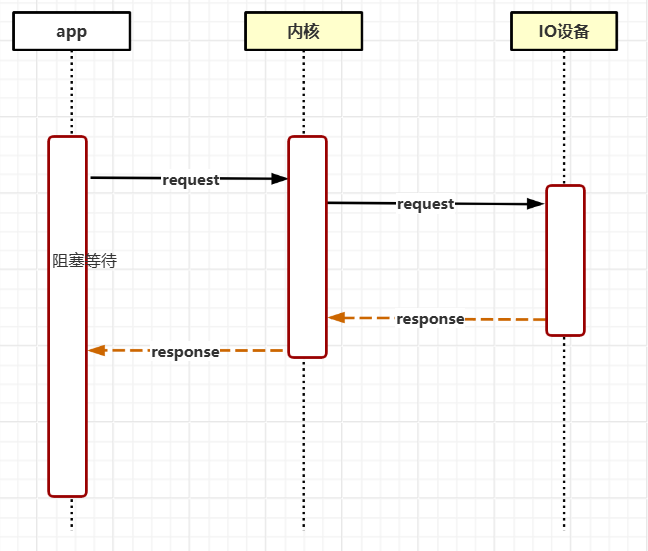
同步阻塞IO(BIO)
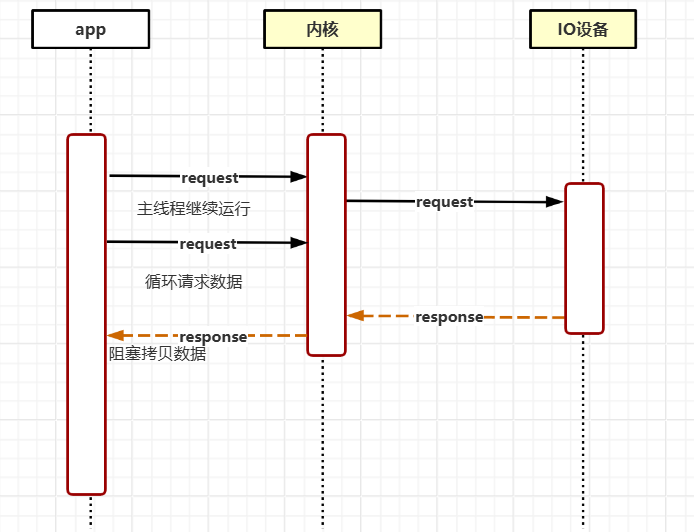
同步非阻塞IO(NIO)
IO多路复用
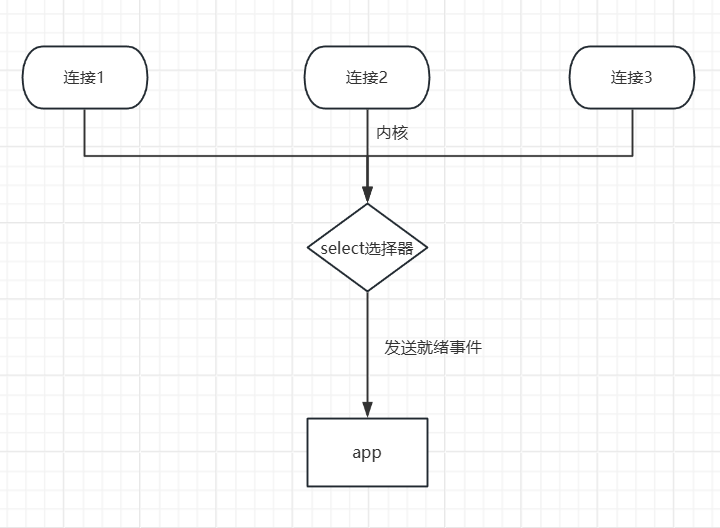
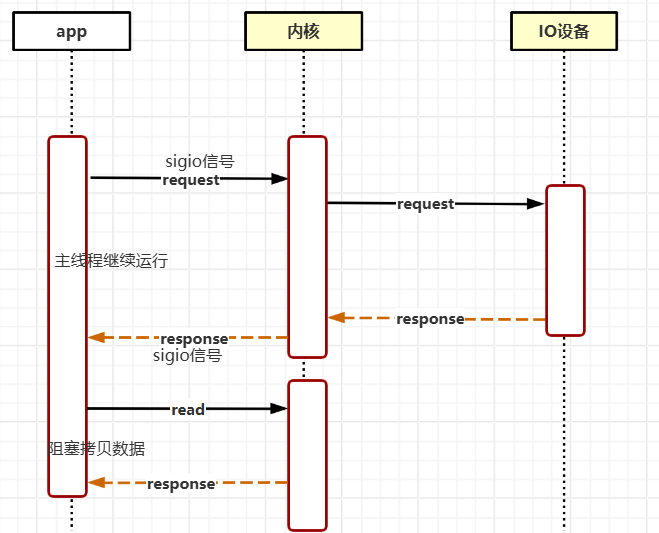
信号驱动IO
应用注册信号处理函数,数据准备好后,内核再发送信号通知来处理数据。
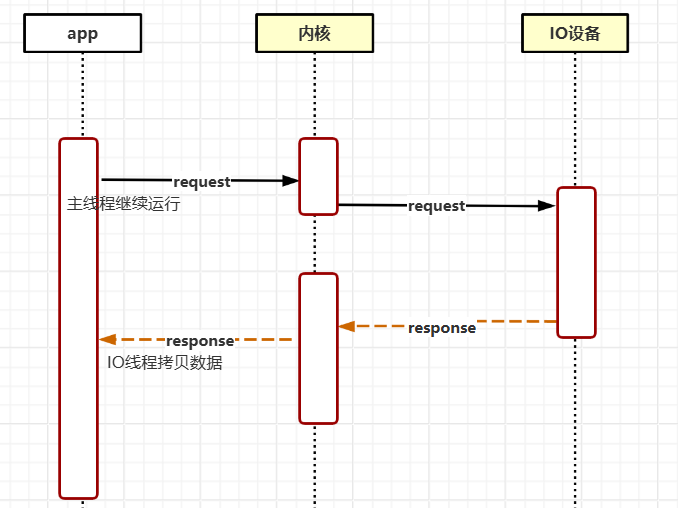
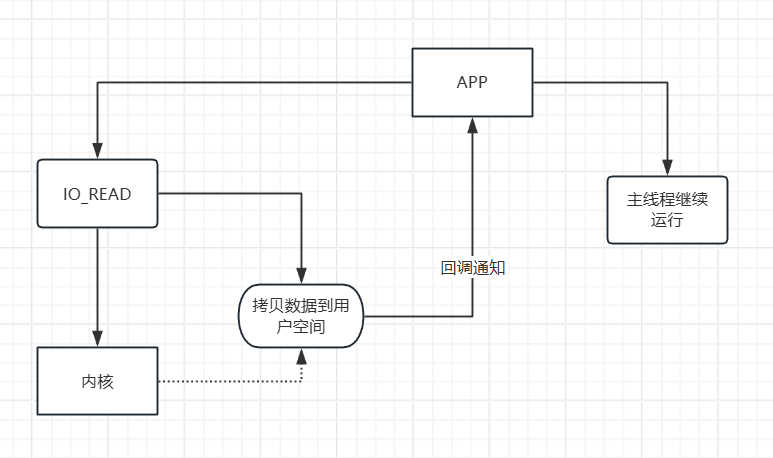
异步非阻塞IO(AIO)
在并发情况下,如果任务是IO密集型采用IO多路复用,如果是CPU密集型采用多线程。 最佳实践为IO多路复用接受任务,多线程同步处理任务。
3.3 三中IO模型(Java)
BIO:每个连接都会去创建一个线程,在并发情况下会存在严重的内存占用问题。
NIO:类似IO多路复用模型
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel.open()
.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080))
.configureBlocking(false)
.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("Server is listening on port 8080");
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (true) {
selector.select();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
keyIterator.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
System.out.println("Client connected");
ServerSocketChannel serverSocket = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
clientSocket.configureBlocking(false);
clientSocket.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
System.out.println("Reading from client");
SocketChannel clientSocket = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int bytesRead = clientSocket.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead == -1) {
clientSocket.close();
}
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
System.out.println("Received: " + new String(buffer.array(), 0, bytesRead));
}
if (key.isWritable()) {
System.out.println("Writing to client");
SocketChannel clientSocket = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("Server response".getBytes());
clientSocket.write(byteBuffer);
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
}
}AIO:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open()
.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 接受连接
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object>() {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel client, Object attachment) {
// 继续接受下一个连接
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, this);
// 处理当前连接
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 异步读取数据
client.read(buffer, buffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
if (result > 0) {
// 切换读模式
attachment.flip();
String msg = new String(attachment.array(), 0, result);
System.out.println("收到消息:" + msg);
// 异步回写数据
ByteBuffer response = ByteBuffer.wrap(("服务器收到:" + msg).getBytes());
client.write(response, response, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
System.out.println("回写数据:" + new String(attachment.array(), 0, result));
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 阻塞,防止程序退出
System.in.read();
}四、NIO核心
4.1 Buffer缓冲
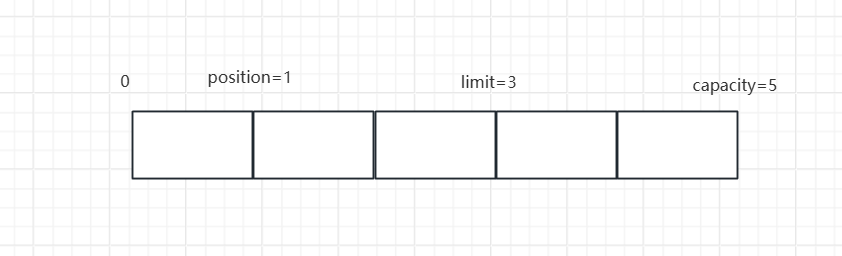
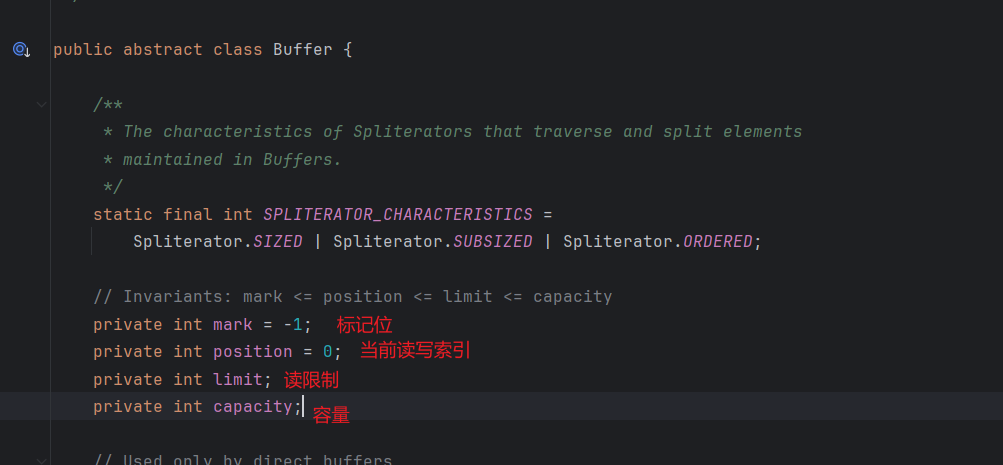
Buffer创建后默认是写模式,需要通过flip()方法切换为读模式;通过clear()和compact()方法切换为写模式。compact表示压缩剩余未读取数据到开头后继续写入。
4.2 Channel通道
FileChannel示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String sourceName = "source.txt";
String targetName = "target.txt";
try (RandomAccessFile sourceFile = new RandomAccessFile(sourceName, "r");
RandomAccessFile targetFile = new RandomAccessFile(targetName, "rw")) {
FileChannel sourceFileChannel = sourceFile.getChannel();
FileChannel targetFileChannel = targetFile.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (sourceFileChannel.read(byteBuffer) != -1) {
byteBuffer.flip();
targetFileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
}
}4.3 Selector选择器
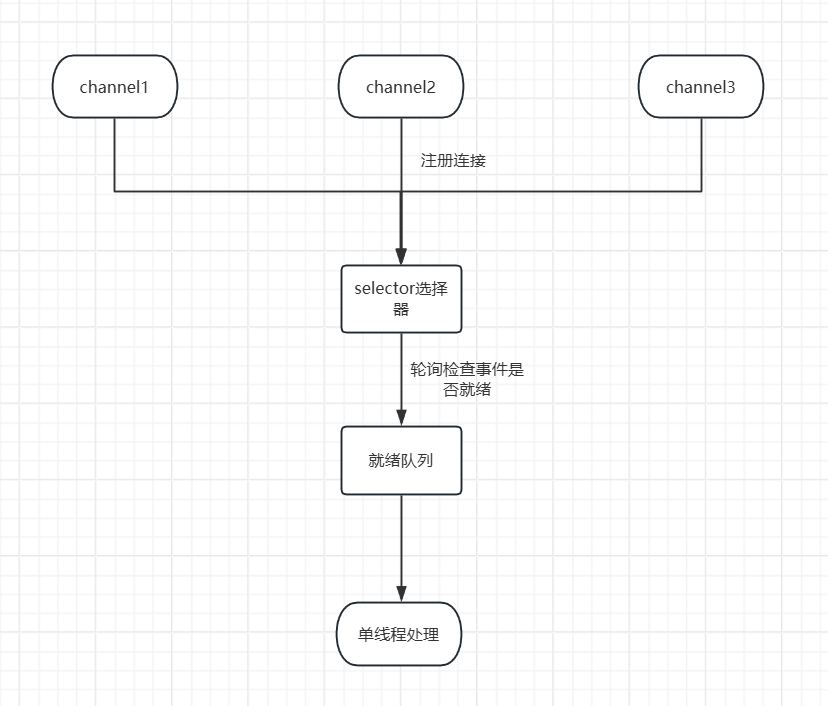
4.4 零拷贝
传统的IO操作流程:
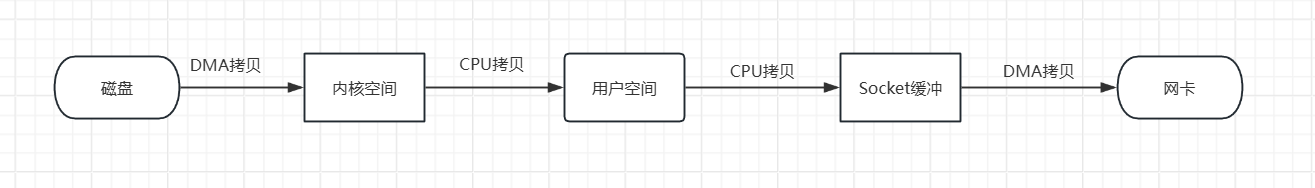
零拷贝就是不需要多次复制,第一种方式是直接内核空间到Socket缓冲的拷贝,少了用户空间;第二种是sendfile,少了用户空间和Socket缓冲,直接到内核空间到网卡。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String sourceName = "source.txt";
String targetName = "target.txt";
try (RandomAccessFile sourceFile = new RandomAccessFile(sourceName, "r");
RandomAccessFile targetFile = new RandomAccessFile(targetName, "rw")) {
FileChannel sourceFileChannel = sourceFile.getChannel();
FileChannel targetFileChannel = targetFile.getChannel();
sourceFileChannel.transferTo(0, sourceFileChannel.size(),
targetFileChannel);
}
}五、IO多路复用
5.1 三种机制
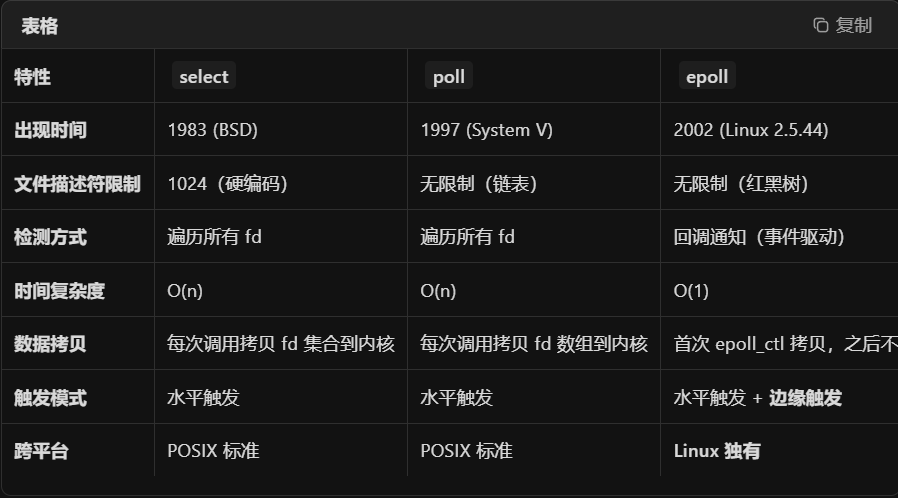
select的fd上限是1024,每次调用都需要拷贝整个fd_set到内核,遍历所有的fd;poll只是在select的基础上取消了fd的上限;epoll分为三个步骤:注册阶段(fd写入内核),事件就绪(内核回调,将就绪fd放入链表返回),epoll_wait(直接返回就绪的链表)
epoll的优化:

5.2 触发模式
水平模式LT:会持续处理未完成的fd,垂直模式ET:只会在fd变化时通知一次,如果应用程序没有一次性处理完,后续将不会再通知该事件。
面试口诀:
select和poll都是轮询O(n),epoll是事件驱动O(1);select有1024限制,poll和epoll没有限制,epoll支持ET模式。

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)