LangChain使用
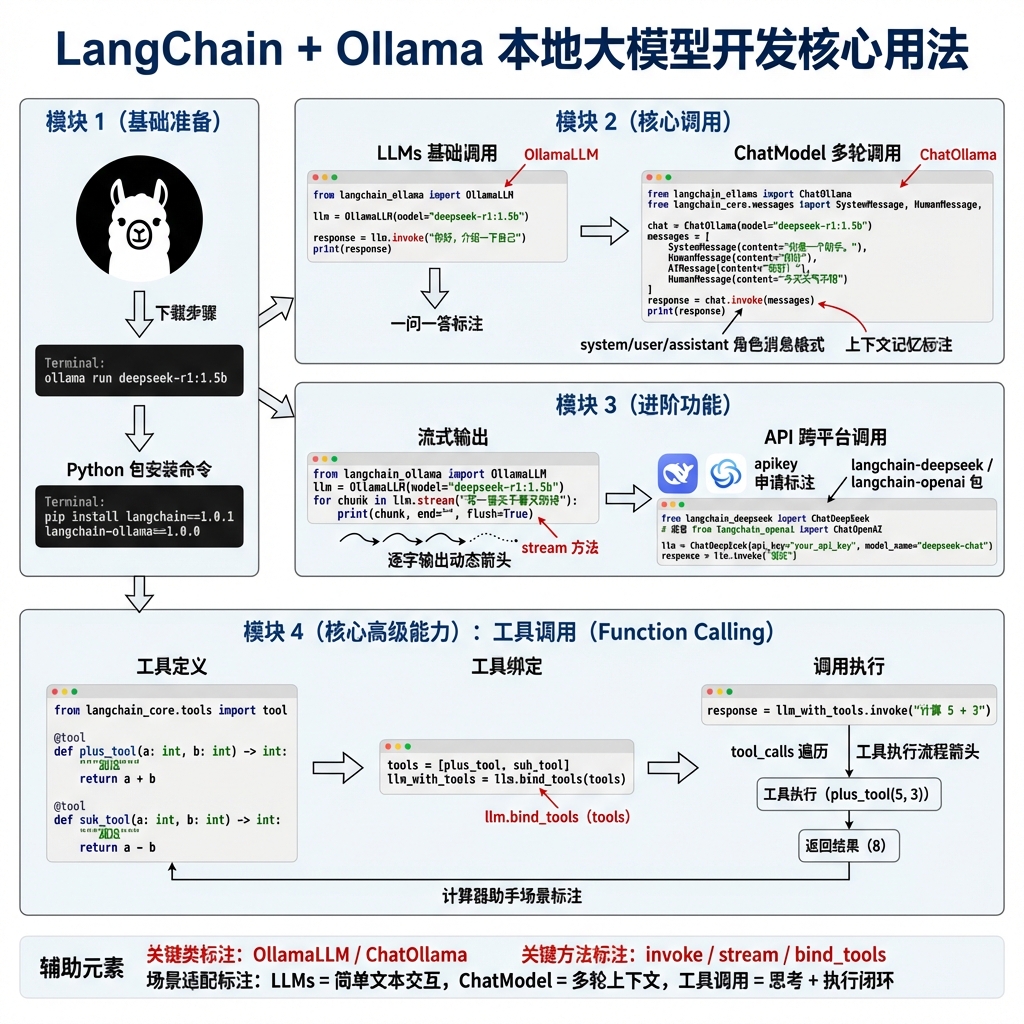
本文介绍了本地和云端大模型的调用方法及选择策略。首先详细说明了如何通过Ollama和LangChain调用DeepSeek本地模型,以及如何通过API调用DeepSeek和阿里云大模型。文章对比了基础LLMs和ChatModel的特点及适用场景,LLMs适合简单问答,ChatModel支持多轮对话。同时讲解了消息格式规范、流式输出实现方法,以及如何通过工具调用扩展大模型能力。最后演示了如何定义并绑
首先我们需要安装ollama,官方网站为:https://ollama.com/
下载好了以后,我们需要下载deepseek模型,可以使用 ollama run deepseek-r1:1.5b
完成前面两部准备工作以后,我们就可以开启langchain的学习之路了。
本地大模型调用方法
首先我们需要安装langchain包
pip install langchain ==1.0.1然后需要安装ollama集成库
pip install langchain-ollama==1.0.0调用代码实例
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
# 初始化大模型
llm =ChatOllama(
model="deepseek-r1:1.5b",
base_url = "http://127.0.0.1:11434",
temperature=0.7,
)
# 调用大模型
res = llm.invoke("你好,你是谁")
print(res.content)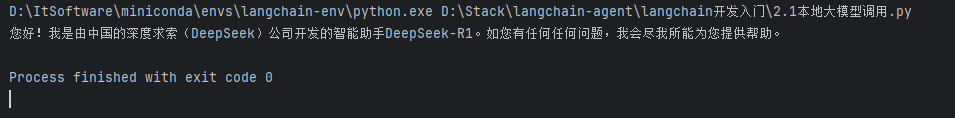
通过API调用大模型
首先我们需要安装langchain与deepseek的集成包
pip install langchain-deepseek==1.0.0调用deepseek
我们需要去deepseek官网(https://www.deepseek.com/)去申请一个apikey并且放到我们的环境变量当中
from langchain_deepseek import ChatDeepSeek
import os
# 初始化大模型
llm = ChatDeepSeek(
model="deepseek-chat",
api_key=os.environ["DEEPSEEK_API_KEY"],
)
# 调用模型
print(llm.invoke("你好,你是?").content)
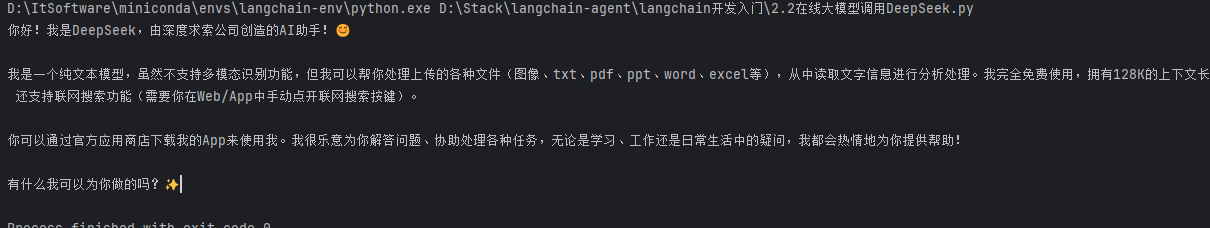
调用阿里大模型
我们需要去阿里百炼获取apikey:https://bailian.console.aliyun.com/
此外我们还需要安装langchain-openai库
pip install langchain-openaifrom langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
import os
llm = ChatOpenAI(
base_url="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",
model="qwen-plus",
api_key=os.environ["DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"],
)
print(llm.invoke("1+1等于多少").content)
大模型选择策略LLMs
LLMs特点:功能简单,仅支持一问一答的纯文本交互,不支持工具调用、结构化输出。
应用场景(适用于无复杂逻辑的文本交互场景):
- 日常闲聊(如讲笑话、聊生活);
- 基础知识问答(如“地球周长是多少”);
- 短文本创作(如写打油诗、小段子)。
from langchain_ollama import OllamaLLM
# 初始化大模型
llm =OllamaLLM(
model="deepseek-r1:1.5b",
base_url = "http://127.0.0.1:11434",
temperature=0.7,
)
result = llm.invoke("你好,你是?")
print(result)
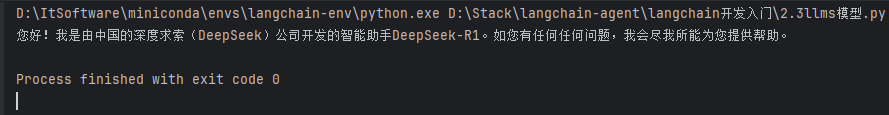
LLMs因功能局限,目前实际开发中较少使用,复杂场景建议选择支持工具调用、结构化输出的大模型类型。
大模型选择策略ChatModel
ChatModel特点:支持多轮对话,采用结构化消息格式(区分system/user/assistant角色),可保留上下文语境,比基础LLMs更适合交互场景。
应用场景(适用于需要上下文记忆的交互场景):
- 智能客服(记住用户历史问题,连贯解答);
- 聊天机器人(多轮闲聊、主题对话);
- 任务引导(分步指导用户完成操作,如注册流程)。
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
# 初始化大模型
llm =ChatOllama(
model="deepseek-r1:1.5b",
base_url = "http://127.0.0.1:11434",
temperature=0.7,
)
# 多轮消息列表(含上下文)
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "你是贴心助手,需记住用户偏好"},
{"role": "user", "content": "我喜欢科幻电影"},
{"role": "user", "content": "推荐几部类似的"}
]
response = llm.invoke( messages)
print(response.content) # 会基于“喜欢科幻电影”的上下文推荐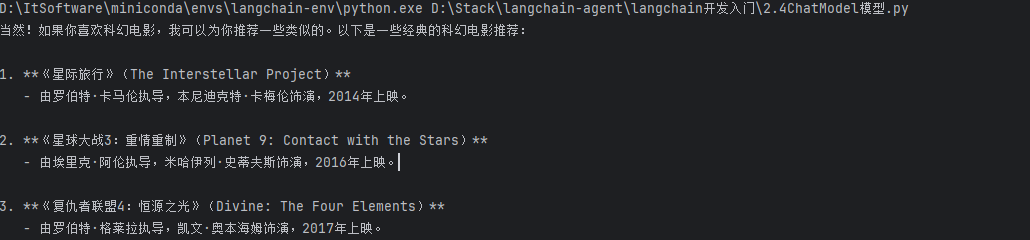
大模型消息格式
作用:标准化多轮对话的上下文传递,明确角色(系统、用户、助手)与内容,保证大模型交互的连贯性和准确性。
类型
- SystemMessage:定义大模型的角色、规则(如“你是C/C++语言专家”)。
- HumanMessage:用户的输入内容。
- AIMessage:大模型的输出内容(调用时一般无需手动构造,接收回复时使用)。
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage, HumanMessage
# 初始化大模型
llm = ChatOllama(
model="deepseek-r1:1.5b",
base_url="http://127.0.0.1:11434",
temperature=0.7,
)
# 构造消息列表
langchain_messages = [
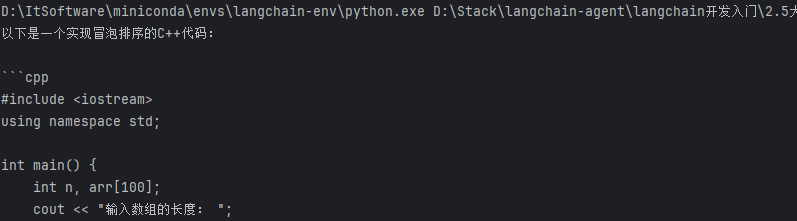
SystemMessage(content="你是一个C/C++语言专家"),
HumanMessage(content="帮我用C++语言写一个冒泡排序算法")
]
# 调用模型
result = llm.invoke(langchain_messages)
print(result.content)
- 消息需严格区分角色类型(SystemMessage/HumanMessage/AIMessage),不可混淆。
- 多轮对话时,消息列表需按“系统 → 用户 → 助手 → 用户 → 助手...”的逻辑顺序排列,保证上下文连贯。
大模型流式输出
传统 lvm.invoke 需等大模型生成全部内容后才输出,流式输出(lvm.stream)可逐字/逐段返回结果,提升交互实时性,适合聊天、实时内容展示等场景。
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage, HumanMessage
# 构造消息
langchain_messages = [
SystemMessage(content="你是一个C/C++语言专家"),
HumanMessage(content="帮我用C++语言写一个冒泡排序算法")
]
# 初始化大模型
llm =ChatOllama(
model="deepseek-r1:1.5b",
base_url = "http://127.0.0.1:11434",
temperature=0.7,
)
# 流式输出调用
for chunk in llm.stream(input=langchain_messages):
print(chunk.content, end="")
- 流式输出返回的是生成器对象,需通过循环迭代获取每段输出;
- 部分大模型对流式支持存在差异,需确认所使用的模型是否兼容流式调用。
工具调用(Function Calling)
大模型虽智能,但无法直接执行发送邮件、网页数据抓取、复杂计算等操作。Function Calling可让大模型自主选择并调用外部工具(函数),拓展其能力边界,实现“思考 + 执行”的闭环。
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, ToolMessage
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.tools import tool
# 定义工具函数
@tool
def plus_tool(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""
计算两数相加
@参数1:a整数
@参数2:b整数
"""
print(f"调用工具:plus_tool,参数:a={a}, b={b}")
return a + b
@tool
def sub_tool(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""计算两数相减"""
print(f"调用工具:sub_tool,参数:a={a}, b={b}")
return a - b
# 工具绑定:将工具与大模型关联
tools = [plus_tool, sub_tool]
# 初始化大模型
llm =ChatOllama(
model="qwen3:4b",
base_url = "http://127.0.0.1:11434",
temperature=0.7,
)
tools_with_llm = llm.bind_tools(tools)
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个计算器助手"},
{"role": "user", "content": "帮我计算2+3等于多少"}]
# 调用带工具的大模型
response: AIMessage = tools_with_llm.invoke(messages)
# 执行所有工具调用参数
# 获取大模型返回的工具
for tool_call in response.tool_calls:
tool_call_name = tool_call.get("name")
tool_call_id = tool_call.get("id")
tool_call_args = tool_call.get("args")
print(f"调用工具:{tool_call_name}, 参数:{tool_call_args}")
# 执行工具
for tool in tools:
if tool.name == tool_call_name:
result = tool.invoke(tool_call_args)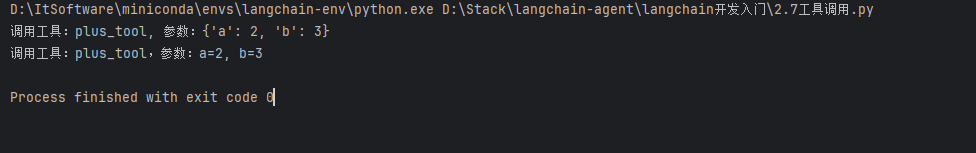
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献24条内容
已为社区贡献24条内容






所有评论(0)