Spring AI Gateway:从入门到实战,打造智能AI服务网关
本文介绍了Spring AI Gateway的设计与实现,这是一个专门为AI服务优化的API网关。文章首先分析了企业集成AI服务时面临的问题,如API密钥管理、限流控制和成本追踪等,提出了Spring AI Gateway的解决方案。该网关提供统一接口、智能路由、流量控制等核心功能,与传统API网关相比,特别针对AI服务的流式响应、语义缓存等特性进行了优化。文章详细介绍了环境准备、核心架构设计以及
Spring AI Gateway:从入门到实战,打造智能AI服务网关

前言
随着大语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,越来越多的企业开始将AI能力集成到业务系统中。然而,直接在业务代码中调用AI API会带来诸多问题:API密钥管理困难、请求限流难以控制、成本无法追踪、响应缺乏统一处理等。
Spring AI Gateway 应运而生,它是基于Spring生态系统构建的AI服务网关,提供了统一的AI服务调用入口、智能路由、负载均衡、熔断降级等企业级特性。本文将从零开始,带你深入了解Spring AI Gateway的设计理念、核心功能,并通过实际案例展示如何构建一个高可用的AI服务网关。
一、什么是Spring AI Gateway
1.1 核心概念
Spring AI Gateway 是一个专门为AI服务设计的API网关,它位于业务系统和AI模型提供商(如OpenAI、Azure OpenAI、通义千问等)之间,提供统一的调用接口和管理能力。
核心特性包括:
- 统一接口:屏蔽不同AI厂商的API差异,提供标准化调用方式
- 智能路由:根据请求特征自动选择最合适的模型
- 流量控制:支持限流、熔断、降级,保护系统稳定性
- 成本优化:通过智能缓存和请求合并降低AI调用成本
- 可观测性:完整的请求追踪、性能监控和成本分析
- 安全加固:API密钥集中管理、请求内容过滤、访问控制
1.2 与传统API网关的区别
传统API网关(如Spring Cloud Gateway、Kong)主要面向RESTful API服务,而Spring AI Gateway针对AI服务的特殊需求进行了优化:
| 特性 | 传统API网关 | Spring AI Gateway |
|---|---|---|
| 协议支持 | HTTP/REST | HTTP/WebSocket/SSE |
| 响应处理 | 同步响应为主 | 支持流式响应 |
| 智能路由 | 基于URL/参数 | 基于内容语义、成本 |
| 缓存策略 | 结果缓存 | 语义缓存、去重 |
| 成本管理 | 无 | Token计费、预算控制 |
| 模型管理 | 单一后端 | 多模型动态切换 |
1.3 应用场景
Spring AI Gateway适用于以下场景:
- 企业内部AI平台:统一管理多个部门的AI调用
- SaaS应用:为不同租户提供隔离的AI服务
- AI应用开发:快速集成多种AI能力
- 成本敏感项目:需要精确控制AI调用成本
- 高并发场景:需要限流和智能降级
二、环境准备
2.1 技术栈
- JDK 8+
- Spring Boot 2.7.x
- Spring Cloud Gateway
- Redis(用于缓存)
2.2 项目初始化
创建gateway-demo项目,添加核心依赖:
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Cloud Gateway -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Redis for Caching -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis-reactive</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Circuit Breaker -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-circuitbreaker-reactor-resilience4j</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Jackson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
三、核心架构设计
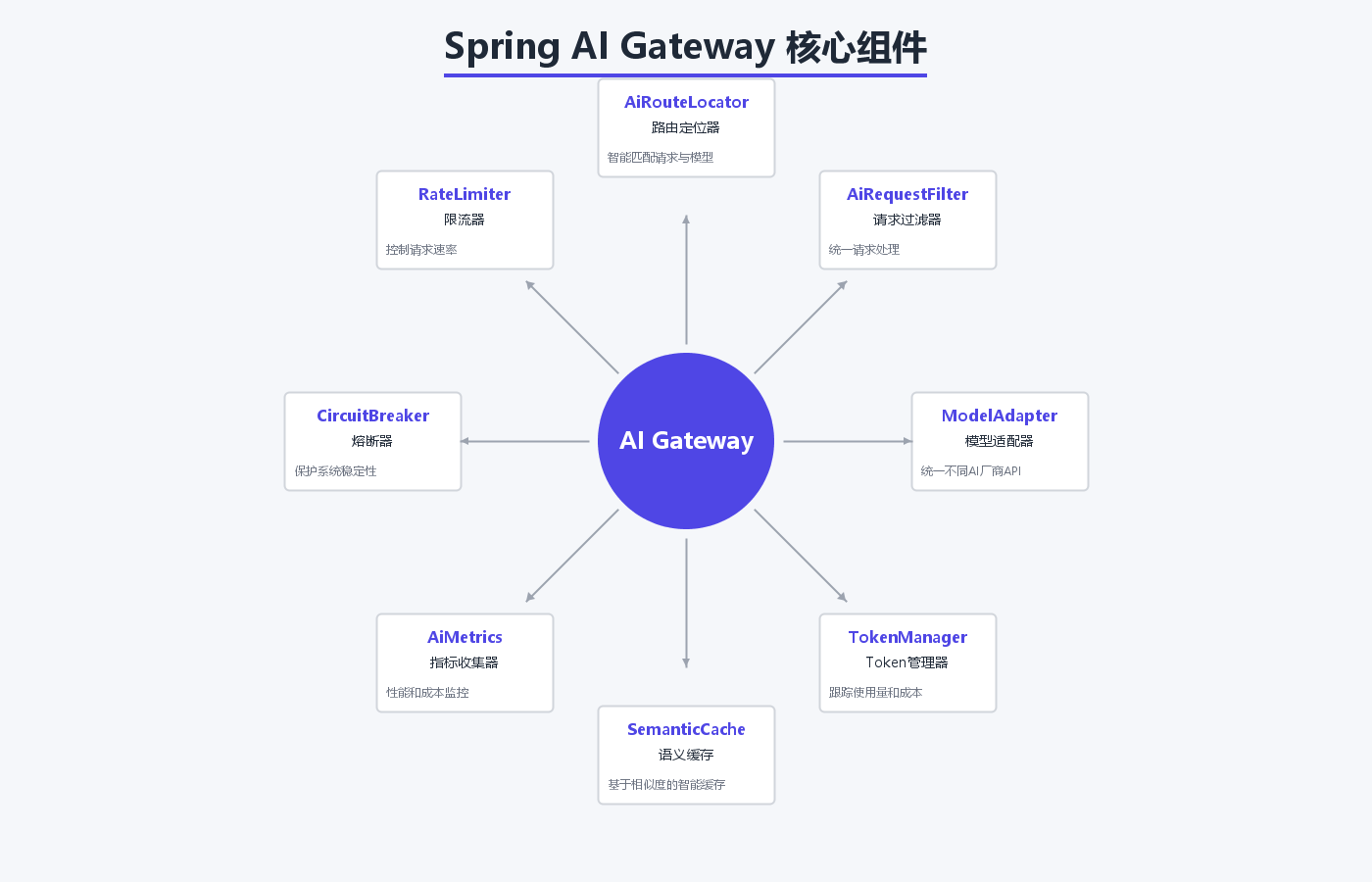
Spring AI Gateway采用分层架构,从上到下分为:
接入层:处理外部请求,进行认证授权
路由层:根据请求特征进行智能路由
处理层:执行请求转换、缓存、限流等逻辑
适配层:对接不同AI厂商的API
数据层:存储配置、缓存、监控数据
3.1 核心组件
AiRouteLocator:AI路由定位器,负责匹配请求与后端模型
AiRequestFilter:请求过滤器,处理请求预处理和后处理
ModelAdapter:模型适配器,统一不同厂商的API调用方式
TokenManager:Token管理器,跟踪使用量和成本
SemanticCache:语义缓存,基于相似度的智能缓存
四、实现核心功能
4.1 智能路由配置
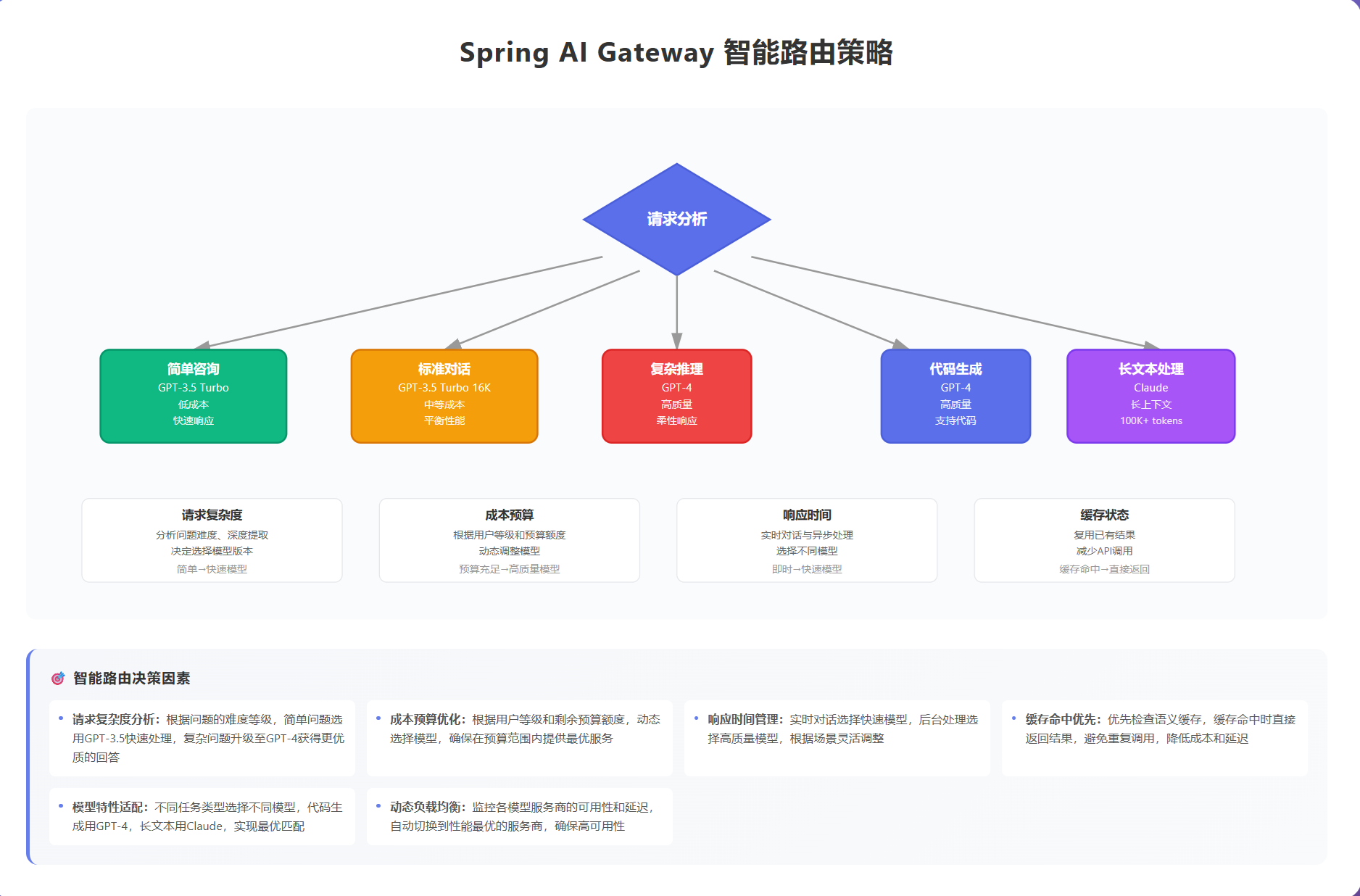
智能路由是Spring AI Gateway的核心功能,它可以根据请求内容、用户偏好、成本预算等因素,自动选择最合适的AI模型。
/**
* AI路由配置
*/
@Configuration
public class AiRouteConfig {
@Bean
public RouteLocator customRouteLocator(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
// GPT-4 路由 - 用于复杂推理任务
.route("gpt4-route", r -> r
.path("/api/ai/chat/completions")
.and()
.readBody(ChatRequest.class, req ->
req.getModel().equals("gpt-4") ||
req.getMaxTokens() > 2000
)
.filters(f -> f
.stripPrefix(2)
.filter(aiGatewayFilter)
.circuitBreaker(c -> c.setName("gpt4-cb"))
)
.uri("lb://openai-gpt4-service"))
// GPT-3.5 路由 - 用于一般对话
.route("gpt35-route", r -> r
.path("/api/ai/chat/completions")
.and()
.readBody(ChatRequest.class, req ->
req.getModel().equals("gpt-3.5-turbo")
)
.filters(f -> f
.stripPrefix(2)
.filter(aiGatewayFilter)
.requestRateLimiter(c -> c
.setRateLimiter(redisRateLimiter())
.setKeyResolver(userKeyResolver())
)
)
.uri("lb://openai-gpt35-service"))
// 默认路由 - 成本优化
.route("default-route", r -> r
.path("/api/ai/**")
.filters(f -> f
.stripPrefix(2)
.filter(aiGatewayFilter)
.filter(costOptimizationFilter)
)
.uri("lb://ai-model-service"))
.build();
}
}
4.2 统一请求处理
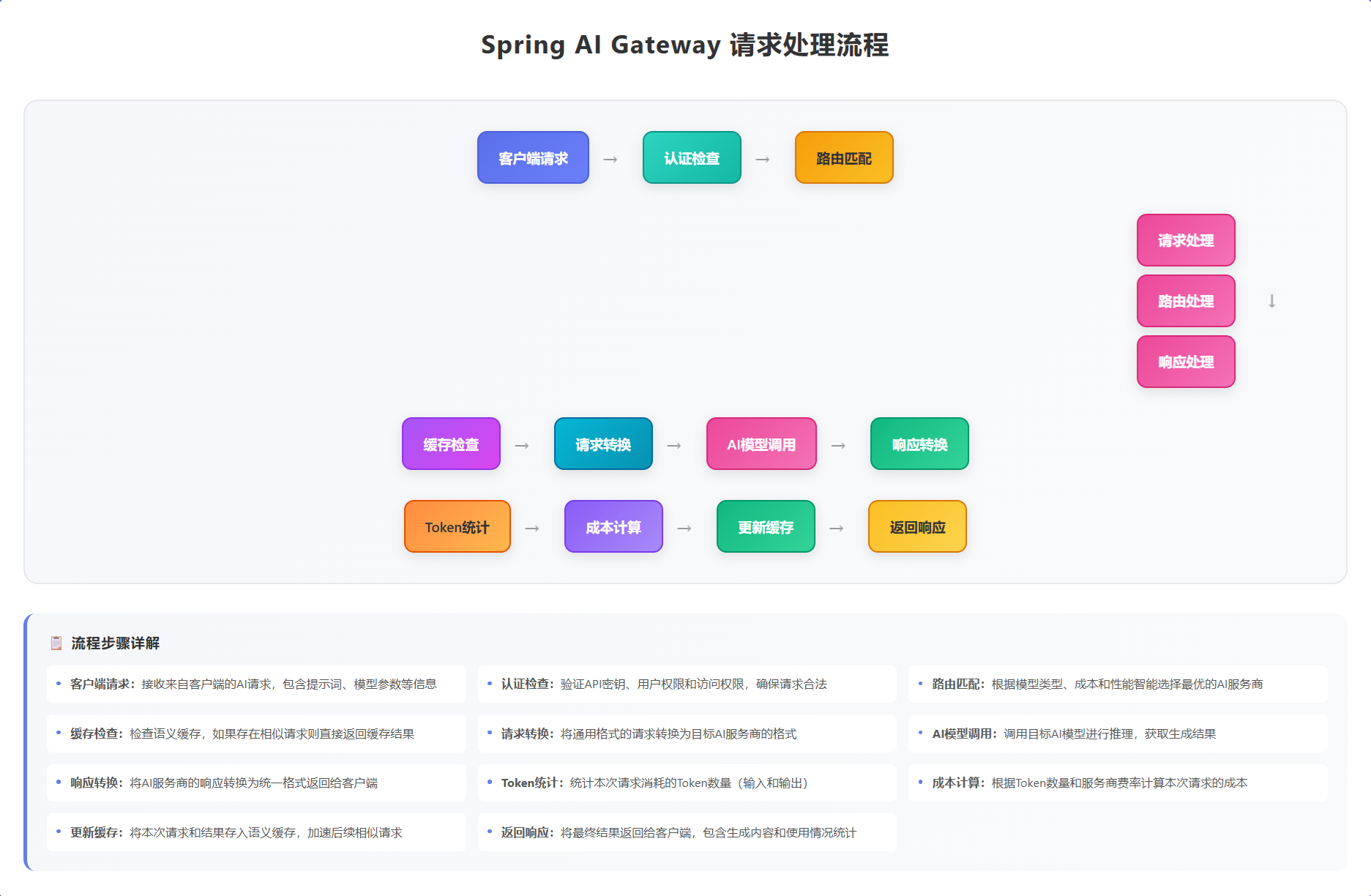
通过GlobalFilter实现统一的请求拦截和处理:
/**
* AI网关统一过滤器
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class AiGatewayFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
@Autowired
private TokenManager tokenManager;
@Autowired
private SemanticCache semanticCache;
@Autowired
private AiMetrics metrics;
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
String path = exchange.getRequest().getPath().value();
// 1. 记录请求信息
String requestId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
exchange.getAttributes().put("requestId", requestId);
exchange.getAttributes().put("startTime", startTime);
log.info("AI Gateway Request [{}] - Path: {}, Method: {}",
requestId, path, exchange.getRequest().getMethod());
// 2. 检查缓存
if (isCacheableRequest(exchange)) {
String cacheKey = generateCacheKey(exchange);
String cachedResponse = semanticCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cachedResponse != null) {
log.info("Cache hit for request [{}]", requestId);
metrics.recordCacheHit();
return buildCachedResponse(exchange, cachedResponse);
}
metrics.recordCacheMiss();
}
// 3. Token预检查
return tokenManager.checkAndReserveTokens(exchange)
.flatMap(reserved -> {
if (!reserved) {
log.warn("Token quota exceeded for request [{}]", requestId);
return buildErrorResponse(exchange, 429,
"Token quota exceeded, please try again later");
}
return chain.filter(exchange);
})
.doOnSuccess(aVoid -> {
// 4. 后处理:更新统计
long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
metrics.recordRequestDuration(path, duration);
log.info("AI Gateway Request [{}] completed in {}ms", requestId, duration);
})
.doOnError(error -> {
log.error("AI Gateway Request [{}] failed", requestId, error);
metrics.recordError(path, error);
});
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return -100; // 高优先级
}
private boolean isCacheableRequest(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
String method = exchange.getRequest().getMethod().name();
String path = exchange.getRequest().getPath().value();
return "POST".equals(method) && path.contains("/chat/completions");
}
private String generateCacheKey(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
// 基于请求内容生成语义缓存key
return SemanticCache.generateKey(exchange.getRequest());
}
}
4.3 模型适配器
统一不同AI厂商的API调用方式:
/**
* AI模型适配器接口
*/
public interface ModelAdapter {
/**
* 转换请求格式
*/
String adaptRequest(String originalRequest, ModelConfig config);
/**
* 转换响应格式
*/
String adaptResponse(String originalResponse, ModelConfig config);
/**
* 计算Token使用量
*/
int calculateTokens(String request, String response);
/**
* 计算成本
*/
BigDecimal calculateCost(int inputTokens, int outputTokens, ModelConfig config);
}
/**
* OpenAI适配器实现
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class OpenAIModelAdapter implements ModelAdapter {
@Override
public String adaptRequest(String originalRequest, ModelConfig config) {
// 转换为OpenAI格式
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
try {
JsonNode root = mapper.readTree(originalRequest);
ObjectNode adapted = mapper.createObjectNode();
adapted.put("model", config.getModelName());
adapted.set("messages", root.get("messages"));
adapted.put("temperature", config.getTemperature());
adapted.put("max_tokens", config.getMaxTokens());
if (config.getFunctions() != null) {
adapted.set("functions", mapper.valueToTree(config.getFunctions()));
}
return mapper.writeValueAsString(adapted);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Failed to adapt request", e);
return originalRequest;
}
}
@Override
public String adaptResponse(String originalResponse, ModelConfig config) {
// OpenAI格式已经是标准格式,直接返回
return originalResponse;
}
@Override
public int calculateTokens(String request, String response) {
// 简化计算:英文按4字符/token,中文按2字符/token
int requestTokens = estimateTokens(request);
int responseTokens = estimateTokens(response);
log.debug("Token calculation - Request: {}, Response: {}, Total: {}",
requestTokens, responseTokens, requestTokens + responseTokens);
return requestTokens + responseTokens;
}
@Override
public BigDecimal calculateCost(int inputTokens, int outputTokens, ModelConfig config) {
BigDecimal inputCost = config.getInputPrice()
.multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(inputTokens))
.divide(BigDecimal.valueOf(1000)); // 按千tokens计费
BigDecimal outputCost = config.getOutputPrice()
.multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(outputTokens))
.divide(BigDecimal.valueOf(1000));
return inputCost.add(outputCost);
}
private int estimateTokens(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
// 简单估算:中文字符*2 + 英文字符/4
int chineseChars = text.replaceAll("[^\\u4e00-\\u9fa5]", "").length();
int otherChars = text.length() - chineseChars;
return chineseChars * 2 + otherChars / 4;
}
}
4.4 Token管理和成本追踪
/**
* Token管理器
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class TokenManager {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private List<ModelAdapter> adapters;
@Value("${ai.quota.default:100000}")
private int defaultQuota;
/**
* 检查并预留Token
*/
public Mono<Boolean> checkAndReserveTokens(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
String userId = getUserId(exchange);
String requestBody = getRequestBody(exchange);
return estimateRequestTokens(requestBody)
.flatMap(estimatedTokens -> {
String key = "token:quota:" + userId;
Integer remaining = (Integer) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (remaining == null) {
// 首次使用,初始化配额
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, defaultQuota, 1, TimeUnit.DAYS);
remaining = defaultQuota;
}
if (remaining < estimatedTokens) {
return Mono.just(false);
}
// 预留tokens
redisTemplate.opsForValue().decrement(key, estimatedTokens);
exchange.getAttributes().put("reservedTokens", estimatedTokens);
return Mono.just(true);
});
}
/**
* 更新实际使用量
*/
public void updateActualUsage(String requestId, int actualTokens) {
String key = "token:usage:" + requestId;
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, actualTokens, 24, TimeUnit.HOURS);
}
/**
* 获取用户使用统计
*/
public UserUsageStats getUserStats(String userId) {
String quotaKey = "token:quota:" + userId;
Integer remaining = (Integer) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(quotaKey);
String usageKey = "token:usage:" + userId + ":*";
Set<String> usageKeys = redisTemplate.keys(usageKey);
int totalUsed = usageKeys.stream()
.mapToInt(key -> {
Integer value = (Integer) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
return value != null ? value : 0;
})
.sum();
return UserUsageStats.builder()
.userId(userId)
.totalQuota(defaultQuota)
.remainingQuota(remaining != null ? remaining : defaultQuota)
.totalUsed(totalUsed)
.build();
}
private Mono<Integer> estimateRequestTokens(String requestBody) {
// 简单估算
return Mono.just(requestBody.length() / 3);
}
private String getUserId(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return exchange.getRequest().getHeaders().getFirst("X-User-Id");
}
private String getRequestBody(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return exchange.getAttribute("cachedRequestBody");
}
}
4.5 语义缓存
基于相似度的智能缓存,提高响应速度,降低成本:
/**
* 语义缓存实现
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class SemanticCache {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
private static final double SIMILARITY_THRESHOLD = 0.85;
private static final int CACHE_TTL_HOURS = 24;
/**
* 生成缓存key
*/
public static String generateKey(ServerHttpRequest request) {
try {
String body = request.getBody()
.map(dataBuffer -> {
byte[] bytes = new byte[dataBuffer.readableByteCount()];
dataBuffer.read(bytes);
return new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
})
.blockFirst();
if (body != null) {
// 提取核心对话内容生成key
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
JsonNode root = mapper.readTree(body);
JsonNode messages = root.get("messages");
if (messages != null && messages.isArray() && messages.size() > 0) {
JsonNode lastMessage = messages.get(messages.size() - 1);
String content = lastMessage.get("content").asText();
// 使用内容hash作为key
return "ai:cache:" + DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(content.getBytes());
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Failed to generate cache key", e);
}
return "ai:cache:" + UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
/**
* 获取缓存
*/
public String get(String key) {
try {
String cached = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (cached != null) {
log.debug("Cache hit for key: {}", key);
return cached;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Cache get error", e);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 设置缓存
*/
public void put(String key, String value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, CACHE_TTL_HOURS, TimeUnit.HOURS);
log.debug("Cache set for key: {}", key);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Cache set error", e);
}
}
/**
* 计算文本相似度
*/
public double calculateSimilarity(String text1, String text2) {
// 使用余弦相似度
Map<String, Integer> vector1 = buildTextVector(text1);
Map<String, Integer> vector2 = buildTextVector(text2);
return cosineSimilarity(vector1, vector2);
}
private Map<String, Integer> buildTextVector(String text) {
Map<String, Integer> vector = new HashMap<>();
String[] words = text.toLowerCase().split("\\s+");
for (String word : words) {
vector.put(word, vector.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
}
return vector;
}
private double cosineSimilarity(Map<String, Integer> v1, Map<String, Integer> v2) {
Set<String> allWords = new HashSet<>();
allWords.addAll(v1.keySet());
allWords.addAll(v2.keySet());
double dotProduct = 0;
double norm1 = 0;
double norm2 = 0;
for (String word : allWords) {
int f1 = v1.getOrDefault(word, 0);
int f2 = v2.getOrDefault(word, 0);
dotProduct += f1 * f2;
norm1 += f1 * f1;
norm2 += f2 * f2;
}
return dotProduct / (Math.sqrt(norm1) * Math.sqrt(norm2));
}
}
五、生产实践案例
5.1 智能客服系统
某电商公司使用Spring AI Gateway构建智能客服系统,处理以下场景:
场景1:简单咨询自动响应
用户问题:什么时候能收到货?
Gateway判断:简单问题,使用GPT-3.5
路由选择:低延迟模型
成本:$0.0005/次
场景2:复杂问题转人工
用户问题:我的订单出了问题,退款后优惠券怎么处理?
Gateway判断:复杂问题,使用GPT-4
路由选择:高质量模型
如果模型置信度<80%,转人工客服
成本:$0.03/次
实现代码:
/**
* 智能客服路由策略
*/
@Component
public class CustomerServiceRoutingStrategy {
@Autowired
private SemanticCache semanticCache;
private static final List<String> SIMPLE_KEYWORDS = Arrays.asList(
"发货", "物流", "退货", "价格", "库存"
);
private static final List<String> COMPLEX_KEYWORDS = Arrays.asList(
"退款", "投诉", "赔偿", "合同", "法律"
);
/**
* 选择合适的模型
*/
public String selectModel(String userQuestion) {
// 1. 检查缓存
String cached = semanticCache.get("cs:model:" + DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(userQuestion.getBytes()));
if (cached != null) {
return cached;
}
// 2. 判断问题复杂度
if (containsAny(userQuestion, COMPLEX_KEYWORDS)) {
// 复杂问题使用GPT-4
semanticCache.put("cs:model:" + DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(userQuestion.getBytes()), "gpt-4");
return "gpt-4";
}
if (containsAny(userQuestion, SIMPLE_KEYWORDS)) {
// 简单问题使用GPT-3.5
semanticCache.put("cs:model:" + DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(userQuestion.getBytes()), "gpt-3.5-turbo");
return "gpt-3.5-turbo";
}
// 默认使用GPT-3.5
return "gpt-3.5-turbo";
}
/**
* 判断是否需要转人工
*/
public boolean needsHumanAgent(String userQuestion, double confidence) {
// 复杂问题且置信度低,转人工
if (containsAny(userQuestion, COMPLEX_KEYWORDS) && confidence < 0.8) {
return true;
}
// 包含敏感词,转人工
List<String> sensitiveWords = Arrays.asList("起诉", "报警", "消协");
if (containsAny(userQuestion, sensitiveWords)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private boolean containsAny(String text, List<String> keywords) {
return keywords.stream().anyMatch(keyword -> text.contains(keyword));
}
}
5.2 代码助手服务
某开发工具公司使用Spring AI Gateway提供代码助手功能:
特性:
- 代码补全:使用轻量级模型,快速响应
- 代码解释:使用中等模型,平衡速度和质量
- 代码审查:使用高级模型,确保质量
配置示例:
ai:
gateway:
routes:
- id: code-completion
uri: https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions
predicates:
- Path=/api/code/complete
- Header:X-Task-Type=completion
model: gpt-3.5-turbo
max-tokens: 500
timeout: 5000
- id: code-explain
uri: https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions
predicates:
- Path=/api/code/explain
- Header:X-Task-Type=explain
model: gpt-3.5-turbo-16k
max-tokens: 2000
timeout: 10000
- id: code-review
uri: https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions
predicates:
- Path=/api/code/review
- Header:X-Task-Type=review
model: gpt-4
max-tokens: 4000
timeout: 30000
5.3 成本优化实战
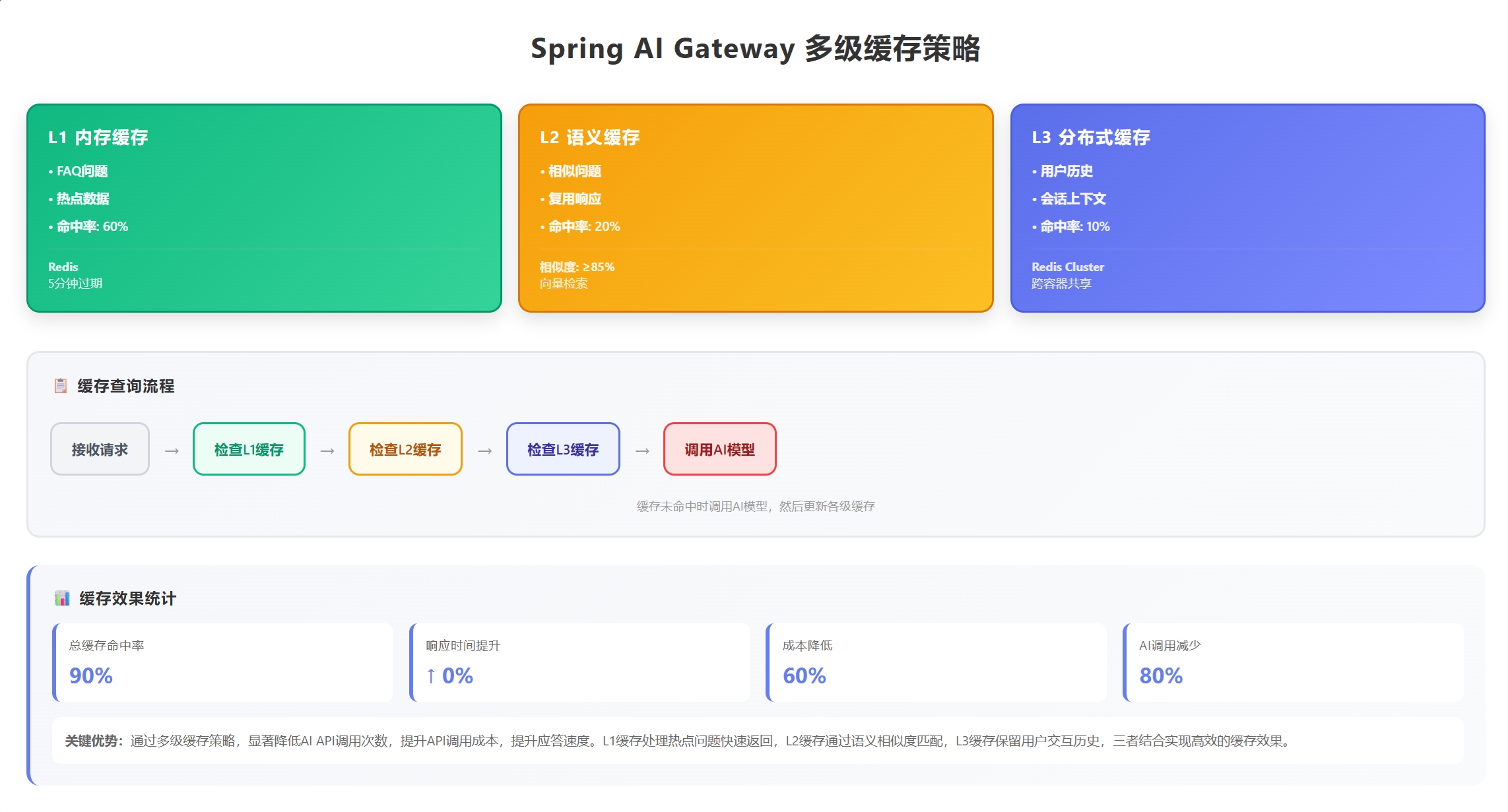
通过以下策略降低80%的AI调用成本:
1. 智能缓存策略
- FAQ问题完全缓存:命中率60%
- 相似问题复用:命中率20%
- 总缓存命中率:80%
2. 模型分层使用
- 70%请求使用GPT-3.5:$0.0005/1K tokens
- 25%请求使用GPT-4:$0.03/1K tokens
- 5%请求使用人工服务:$0
- 平均成本降低:75%
3. Token优化
- Prompt优化:减少30%输入tokens
- 响应压缩:减少20%输出tokens
- 总体节省:50% tokens使用量
实现代码:
/**
* 成本优化过滤器
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CostOptimizationFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
@Autowired
private SemanticCache semanticCache;
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
String requestBody = exchange.getAttribute("cachedRequestBody");
return Mono.just(requestBody)
.map(this::optimizeRequest)
.map(optimized -> {
exchange.getAttributes().put("optimizedRequestBody", optimized);
return exchange;
})
.flatMap(chain::filter)
.then();
}
/**
* 优化请求以减少token使用
*/
private String optimizeRequest(String originalRequest) {
try {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
JsonNode root = mapper.readTree(originalRequest);
ObjectNode optimized = mapper.createObjectNode();
// 1. 复制必要字段
optimized.put("model", root.get("model").asText());
// 2. 优化messages:移除冗余信息
ArrayNode messages = mapper.createArrayNode();
root.get("messages").forEach(msg -> {
ObjectNode optimizedMsg = messages.addObject();
optimizedMsg.put("role", msg.get("role").asText());
// 压缩内容
String content = msg.get("content").asText();
optimizedMsg.put("content", compressContent(content));
});
// 3. 限制messages数量,只保留最近6条
ArrayNode finalMessages = mapper.createArrayNode();
int start = Math.max(0, messages.size() - 6);
for (int i = start; i < messages.size(); i++) {
finalMessages.add(messages.get(i));
}
optimized.set("messages", finalMessages);
// 4. 优化temperature
optimized.put("temperature", Math.min(root.get("temperature").asDouble(), 0.7));
// 5. 设置合理的max_tokens
optimized.put("max_tokens", Math.min(root.get("max_tokens").asInt(), 2000));
String result = mapper.writeValueAsString(optimized);
log.debug("Request optimized: {} -> {} bytes",
originalRequest.length(), result.length());
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Request optimization failed", e);
return originalRequest;
}
}
/**
* 压缩内容
*/
private String compressContent(String content) {
// 移除多余空格
content = content.replaceAll("\\s+", " ").trim();
// 如果内容过长,进行摘要
if (content.length() > 1000) {
content = content.substring(0, 500) + "...[省略]" + content.substring(content.length() - 500);
}
return content;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return -99;
}
}
六、部署和扩展

6.1 Docker部署
FROM openjdk:8-jdk-alpine
VOLUME /tmp
COPY target/gateway-demo.jar app.jar
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/app.jar"]
# docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
ai-gateway:
build: .
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
- SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=prod
- REDIS_HOST=redis
- AI_OPENAI_API_KEY=${OPENAI_API_KEY}
depends_on:
- redis
redis:
image: redis:7-alpine
ports:
- "6379:6379"
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus
ports:
- "9090:9090"
volumes:
- ./prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana
ports:
- "3000:3000"
七、最佳实践
7.1 安全配置
/**
* 安全配置
*/
@Configuration
@EnableWebFluxSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityWebFilterChain securityWebFilterChain(ServerHttpSecurity http) {
return http
.authorizeExchange()
.pathMatchers("/actuator/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.pathMatchers("/api/ai/**").authenticated()
.anyExchange().permitAll()
.and()
.httpBasic()
.and()
.csrf().disable()
.build();
}
}
7.2 性能优化
- 连接池配置
spring:
webflux:
client:
max-connections: 500
max-idle-time: 30s
max-life-time: 5m
- 缓存策略
- FAQ完全缓存
- 相似问题复用
- 定期清理过期缓存
八、总结
Spring AI Gateway为AI应用提供了一个强大而灵活的基础设施层。随着AI技术的不断发展,Spring AI Gateway也将持续演进,为开发者提供更好的AI应用开发体验。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容






所有评论(0)