Java IO、NIO、AIO 演进:从阻塞到异步,一文读懂!
本文系统介绍了Java IO模型的演进历程,从传统阻塞式IO到非阻塞NIO,再到异步AIO。传统IO采用同步阻塞模式,每个连接需要独立线程;NIO引入通道、缓冲区和选择器,实现非阻塞IO和多路复用;AIO则基于事件回调机制实现真正的异步IO。文章通过代码示例展示了三种模型的实际应用,帮助开发者理解不同IO模型的原理、特点和适用场景,为高并发应用开发提供技术选型参考。
·
Java IO、NIO、AIO 演进:从阻塞到异步,一文读懂!

每个Java开发者都必须掌握的IO知识,你真的了解吗?
引言:IO演进的必然性
在当今高并发互联网时代,传统的阻塞式IO已经无法满足性能需求。从Java 1.0到Java 7,再到如今的Java 11,IO模型经历了翻天覆地的变化。本文将带你循序渐进地了解Java IO的演进之路,从传统IO到NIO,再到AIO,让你彻底理解不同IO模型的原理和应用场景。
Java IO 基础
什么是IO?
IO(Input/Output)即输入输出,指的是计算机与外部世界或者一个程序与另一程序的通信。Java中的IO主要是通过流(Stream)来实现,流是Java IO的核心概念。
传统IO的特点
- 阻塞式:线程在IO操作时会阻塞,直到操作完成
- 同步式:需要等待IO操作完成后才能继续执行
- 一对一:每个连接需要一个独立的线程
传统IO代码示例
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class TraditionalEchoServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
System.out.println("服务器启动,监听端口8080...");
while (true) {
// 阻塞等待客户端连接
Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("客户端连接: " + clientSocket.getInetAddress());
// 为每个客户端创建一个线程
new Thread(new ClientHandler(clientSocket)).start();
}
}
static class ClientHandler implements Runnable {
private Socket clientSocket;
public ClientHandler(Socket socket) {
this.clientSocket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try (
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(clientSocket.getInputStream()));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(
clientSocket.getOutputStream(), true);
) {
String inputLine;
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println("收到客户端消息: " + inputLine);
out.println("服务器回复: " + inputLine);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
clientSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
文件IO示例
import java.io.*;
public class TraditionalFileIO {
// 字节流读写
public static void byteStreamCopy(String source, String target) throws IOException {
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(source);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(target)) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = in.read(buffer)) != -1) {
out.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
}
}
// 字符流读写
public static void charStreamCopy(String source, String target) throws IOException {
try (Reader in = new FileReader(source);
Writer out = new FileWriter(target)) {
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
int charsRead;
while ((charsRead = in.read(buffer)) != -1) {
out.write(buffer, 0, charsRead);
}
}
}
// 带缓冲的读写
public static void bufferedCopy(String source, String target) throws IOException {
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(source));
BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(target))) {
String line;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
out.write(line);
out.newLine();
}
}
}
}
NIO:非阻塞IO的革命
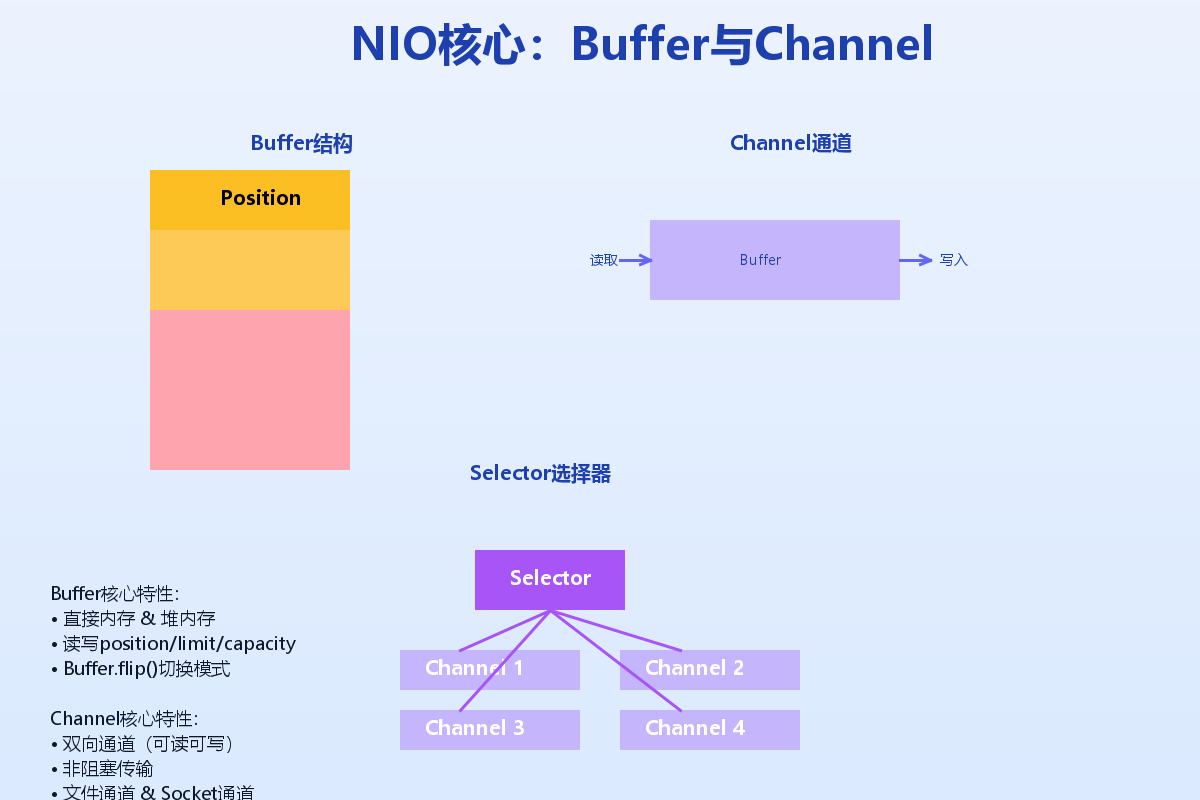
NIO核心概念
Java NIO(New IO)是在Java 1.4中引入的,提供了与传统IO不同的IO操作方式。核心组件包括:
- Channel(通道):类似流,但双向读写
- Buffer(缓冲区):数据容器,读写必须通过缓冲区
- Selector(选择器):多路复用器,用于监控多个Channel
- ByteBuffer:最常用的缓冲区实现
Buffer和Channel详解
Buffer是NIO的核心,它是一个线性的数据容器。以下是Buffer的核心属性:
// Buffer的三个重要属性
private int position = 0; //当前位置
private int limit; //缓冲区界限
private int capacity; //缓冲区容量
NIO代码实现
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.*;
public class NIOEchoServer {
private static final int PORT = 8080;
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建Selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 创建ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
// 将ServerSocketChannel注册到Selector
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("NIO服务器启动,监听端口: " + PORT);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER_SIZE);
while (true) {
// 阻塞等待事件
int readyChannels = selector.select();
if (readyChannels == 0) {
continue;
}
// 获取所有就绪的通道
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// 处理连接请求
handleAccept(key, selector);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
// 处理读取数据
handleRead(key, buffer);
}
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
private static void handleAccept(SelectionKey key, Selector selector)
throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel clientChannel = serverChannel.accept();
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 将客户端通道注册到Selector
clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("新的客户端连接: " +
clientChannel.getRemoteAddress());
}
private static void handleRead(SelectionKey key, ByteBuffer buffer)
throws IOException {
SocketChannel clientChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
buffer.clear();
try {
int bytesRead = clientChannel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead == -1) {
// 客户端关闭连接
clientChannel.close();
System.out.println("客户端断开连接");
return;
}
// 切换到读模式
buffer.flip();
// 将数据转成字符串
byte[] data = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(data);
String message = new String(data);
System.out.println("收到消息: " + message);
// 回复消息
String response = "服务器回复: " + message;
ByteBuffer responseBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(response.getBytes());
clientChannel.write(responseBuffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
// 异常处理
clientChannel.close();
System.out.println("客户端异常断开");
}
}
}
文件NIO示例
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.nio.file.*;
public class NIOFileExample {
// 使用Channel和Buffer复制文件
public static void copyWithNIO(String source, String target) throws IOException {
try (
FileChannel sourceChannel = FileChannel.open(
Paths.get(source), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel targetChannel = FileChannel.open(
Paths.get(target),
StandardOpenOption.WRITE,
StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(8192);
while (sourceChannel.read(buffer) != -1) {
buffer.flip();
targetChannel.write(buffer);
buffer.clear();
}
}
}
// 使用transferTo方法(零拷贝)
public static void copyWithTransferTo(String source, String target) throws IOException {
try (
FileChannel sourceChannel = FileChannel.open(
Paths.get(source), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel targetChannel = FileChannel.open(
Paths.get(target),
StandardOpenOption.WRITE,
StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
) {
// 使用transferTo实现零拷贝
long position = 0;
long count = sourceChannel.size();
while (count > 0) {
long transferred = sourceChannel.transferTo(position, count, targetChannel);
position += transferred;
count -= transferred;
}
}
}
// 使用transferFrom方法
public static void copyWithTransferFrom(String source, String target) throws IOException {
try (
FileChannel sourceChannel = FileChannel.open(
Paths.get(source), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel targetChannel = FileChannel.open(
Paths.get(target),
StandardOpenOption.WRITE,
StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
) {
long position = 0;
long count = sourceChannel.size();
while (count > 0) {
long transferred = targetChannel.transferFrom(sourceChannel, position, count);
position += transferred;
count -= transferred;
}
}
}
}
Selector和Channel的高级用法
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.*;
public class AdvancedNIOServer {
private static final int PORT = 8080;
private static final int TIMEOUT = 5000; // 5秒超时
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 创建非阻塞的服务器Socket通道
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
// 注册接受连接事件
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("高级NIO服务器启动,端口: " + PORT);
// 设置连接超时
selector.select(TIMEOUT);
while (true) {
// 检查就绪的通道
Set<SelectionKey> readyKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = readyKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
try {
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
handleAccept(key, selector);
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
handleRead(key);
}
if (key.isWritable()) {
handleWrite(key);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
key.cancel();
if (key.channel() != null) {
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
}
}
private static void handleAccept(SelectionKey key, Selector selector)
throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel clientChannel = serverChannel.accept();
if (clientChannel != null) {
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey clientKey = clientChannel.register(
selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
// 为每个客户端创建一个附件
clientKey.attach(new ClientContext());
System.out.println("新客户端连接: " +
clientChannel.getRemoteAddress());
}
}
private static void handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ClientContext context = (ClientContext) key.attachment();
ByteBuffer buffer = context.getBuffer();
int bytesRead = channel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead == -1) {
// 客户端关闭连接
channel.close();
key.cancel();
System.out.println("客户端断开连接");
return;
}
if (bytesRead > 0) {
// 切换到读模式
buffer.flip();
// 处理数据
processData(buffer, context);
// 清除已处理的数据
buffer.compact();
// 设置写事件
key.interestOps(key.interestOps() | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
private static void handleWrite(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ClientContext context = (ClientContext) key.attachment();
// 发送响应数据
if (context.hasResponse()) {
ByteBuffer response = context.getResponse();
channel.write(response);
if (!response.hasRemaining()) {
// 响应发送完毕,清除写事件
key.interestOps(key.interestOps() & ~SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
}
private static void processData(ByteBuffer buffer, ClientContext context) {
// 将数据转为字符串
byte[] data = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(data);
String message = new String(data);
System.out.println("收到消息: " + message);
// 生成响应
String response = "处理结果: " + message.toUpperCase();
context.setResponse(ByteBuffer.wrap(response.getBytes()));
}
// 客户端上下文
static class ClientContext {
private ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
private ByteBuffer response;
public ByteBuffer getBuffer() {
return buffer;
}
public boolean hasResponse() {
return response != null && response.hasRemaining();
}
public ByteBuffer getResponse() {
return response;
}
public void setResponse(ByteBuffer response) {
this.response = response;
}
}
}
##AIO:异步IO的终极形态
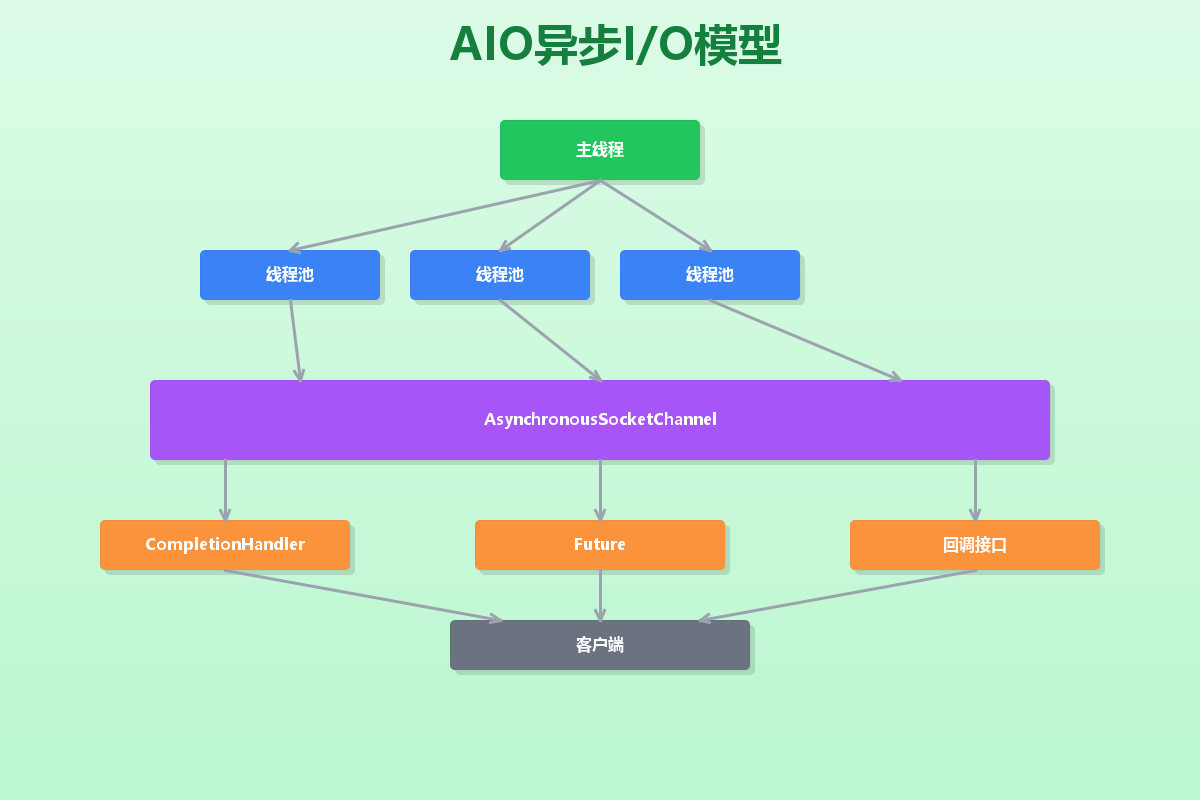
AIO简介
AIO(Asynchronous IO)在Java 7中正式引入,是真正意义上的异步IO。它的核心特点是:
- 异步非阻塞:不需要等待IO操作完成
- 回调机制:通过Future或CompletionHandler处理结果
- 事件驱动:基于事件和回调的编程模型
AIO代码实现
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class AIOEchoServer {
private static final int PORT = 8080;
private static final int THREAD_POOL_SIZE = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(THREAD_POOL_SIZE);
// 创建AsynchronousServerSocketChannel
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverChannel =
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open()
.bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
System.out.println("AIO服务器启动,监听端口: " + PORT);
// 接受连接
serverChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Void>() {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel, Void attachment) {
// 继续接受下一个连接
serverChannel.accept(null, this);
// 处理客户端连接
handleClient(clientChannel, executor);
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
System.err.println("接受连接失败: " + exc.getMessage());
}
});
// 主线程可以继续做其他事情
System.out.println("服务器启动成功,等待客户端连接...");
// 保持主线程运行
try {
Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void handleClient(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel,
ExecutorService executor) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 读取数据
clientChannel.read(buffer, null, new CompletionHandler<Integer, Void>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer bytesRead, Void attachment) {
if (bytesRead == -1) {
try {
clientChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return;
}
// 切换到读模式
buffer.flip();
// 处理数据
byte[] data = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(data);
String message = new String(data);
System.out.println("收到消息: " + message);
// 在线程池中处理业务逻辑
executor.submit(() -> {
try {
String response = "服务器回复: " + message.toUpperCase();
ByteBuffer responseBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(response.getBytes());
// 发送响应
clientChannel.write(responseBuffer, null,
new CompletionHandler<Integer, Void>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, Void attachment) {
// 继续读取下一个消息
buffer.clear();
clientChannel.read(buffer, null,
AIOEchoServer.this.new ReadCompletionHandler(clientChannel, buffer));
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
try {
clientChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
try {
clientChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
// 读取完成处理器
class ReadCompletionHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, Void> {
private AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel;
private ByteBuffer buffer;
public ReadCompletionHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel,
ByteBuffer buffer) {
this.clientChannel = clientChannel;
this.buffer = buffer;
}
@Override
public void completed(Integer bytesRead, Void attachment) {
if (bytesRead == -1) {
try {
clientChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return;
}
buffer.flip();
byte[] data = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(data);
String message = new String(data);
System.out.println("收到消息: " + message);
// 处理并发送响应
String response = "服务器回复: " + message;
ByteBuffer responseBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(response.getBytes());
clientChannel.write(responseBuffer, null,
new CompletionHandler<Integer, Void>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, Void attachment) {
// 继续读取
buffer.clear();
clientChannel.read(buffer, null,
AIOEchoServer.this.new ReadCompletionHandler(clientChannel, buffer));
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
try {
clientChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
try {
clientChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
基于Future的AIO实现
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class AIOFutureServer {
private static final int PORT = 8080;
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverChannel =
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open()
.bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
System.out.println("基于Future的AIO服务器启动,端口: " + PORT);
while (true) {
// 异步接受连接
Future<AsynchronousSocketChannel> acceptFuture = serverChannel.accept();
// 等待连接完成
AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel = acceptFuture.get();
System.out.println("客户端连接: " + clientChannel.getRemoteAddress());
// 处理客户端
handleClientWithFuture(clientChannel);
}
}
private static void handleClientWithFuture(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel)
throws InterruptedException {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER_SIZE);
while (true) {
// 异步读取数据
Future<Integer> readFuture = clientChannel.read(buffer);
// 等待读取完成
int bytesRead = readFuture.get();
if (bytesRead == -1) {
System.out.println("客户端断开连接");
break;
}
// 切换到读模式
buffer.flip();
// 处理数据
byte[] data = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(data);
String message = new String(data);
System.out.println("收到消息: " + message);
// 发送响应
String response = "处理结果: " + message;
ByteBuffer responseBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(response.getBytes());
Future<Integer> writeFuture = clientChannel.write(responseBuffer);
writeFuture.get(); // 等待写入完成
// 清空缓冲区
buffer.clear();
}
try {
clientChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
文件AIO示例
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class AIOFileExample {
// 使用AIO异步复制文件
public static void asyncCopyFile(String source, String target) throws IOException {
AsynchronousFileChannel sourceChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(
Paths.get(source), StandardOpenOption.READ);
AsynchronousFileChannel targetChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(
Paths.get(target),
StandardOpenOption.WRITE,
StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
// 创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(8192);
long position = 0;
long totalSize = sourceChannel.size();
// 异步读取
Future<Integer> readFuture = sourceChannel.read(buffer, position);
try {
while (position < totalSize) {
// 等待读取完成
int bytesRead = readFuture.get();
if (bytesRead == -1) {
break;
}
// 切换到读模式
buffer.flip();
// 异步写入
Future<Integer> writeFuture = targetChannel.write(buffer, position);
writeFuture.get(); // 等待写入完成
// 更新位置
position += bytesRead;
// 清空缓冲区
buffer.clear();
// 开始下一次读取
readFuture = sourceChannel.read(buffer, position);
}
System.out.println("文件复制完成");
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
sourceChannel.close();
targetChannel.close();
}
}
// 使用CompletionHandler处理异步文件操作
public static void asyncCopyWithHandler(String source, String target) {
try {
AsynchronousFileChannel sourceChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(
Paths.get(source), StandardOpenOption.READ);
AsynchronousFileChannel targetChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(
Paths.get(target),
StandardOpenOption.WRITE,
StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
FileCopyContext context = new FileCopyContext(sourceChannel, targetChannel);
// 开始异步复制
sourceChannel.read(
context.getBuffer(),
context.getPosition(),
context,
new ReadCompletionHandler());
// 等待操作完成
context.getLatch().await();
System.out.println("文件复制完成(基于Handler)");
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 文件复制上下文
static class FileCopyContext {
private AsynchronousFileChannel sourceChannel;
private AsynchronousFileChannel targetChannel;
private ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(8192);
private long position = 0;
private CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
public FileCopyContext(AsynchronousFileChannel sourceChannel,
AsynchronousFileChannel targetChannel) {
this.sourceChannel = sourceChannel;
this.targetChannel = targetChannel;
}
// getters and setters
public AsynchronousFileChannel getSourceChannel() {
return sourceChannel;
}
public AsynchronousFileChannel getTargetChannel() {
return targetChannel;
}
public ByteBuffer getBuffer() {
return buffer;
}
public long getPosition() {
return position;
}
public void setPosition(long position) {
this.position = position;
}
public CountDownLatch getLatch() {
return latch;
}
}
// 读取完成处理器
static class ReadCompletionHandler implements
CompletionHandler<Integer, FileCopyContext> {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, FileCopyContext context) {
if (result == -1) {
// 读取完成
try {
context.getSourceChannel().close();
context.getTargetChannel().close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
context.getLatch().countDown();
return;
}
// 切换到读模式
context.getBuffer().flip();
// 异步写入
context.getTargetChannel().write(
context.getBuffer(),
context.getPosition(),
context,
new WriteCompletionHandler());
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, FileCopyContext context) {
exc.printStackTrace();
context.getLatch().countDown();
}
}
// 写入完成处理器
static class WriteCompletionHandler implements
CompletionHandler<Integer, FileCopyContext> {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, FileCopyContext context) {
// 更新位置
context.setPosition(context.getPosition() + result);
// 清空缓冲区
context.getBuffer().clear();
// 继续读取
context.getSourceChannel().read(
context.getBuffer(),
context.getPosition(),
context,
new ReadCompletionHandler());
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, FileCopyContext context) {
exc.printStackTrace();
context.getLatch().countDown();
}
}
}
生产环境实践:Netty框架集成
Netty简介
Netty是一个高性能的异步事件驱动的网络应用框架,它基于Java NIO,提供了更好的API和性能优化。
Netty服务器实现
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
public class NettyEchoServer {
private static final int PORT = 8080;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); // 接收连接
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // 处理连接
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
// 解码器
p.addLast(new StringDecoder());
// 编码器
p.addLast(new StringEncoder());
// 业务处理器
p.addLast(new EchoServerHandler());
}
});
// 绑定端口,同步等待
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(PORT).sync();
System.out.println("Netty服务器启动,监听端口: " + PORT);
// 等待服务器关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// 优雅关闭
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
// 业务处理器
static class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
// 接收到消息
String message = (String) msg;
System.out.println("收到消息: " + message);
// 回复消息
ctx.writeAndFlush("服务器回复: " + message);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
// 异常处理
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
}
Netty客户端实现
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NettyEchoClient {
private static final String HOST = "localhost";
private static final int PORT = 8080;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
p.addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO));
p.addLast(new StringDecoder());
p.addLast(new StringEncoder());
p.addLast(new EchoClientHandler());
}
});
// 连接服务器
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(HOST, PORT).sync();
// 获取通道
Channel channel = f.channel();
// 控制台输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要发送的消息(输入'exit'退出):");
while (true) {
String message = scanner.nextLine();
if ("exit".equals(message)) {
break;
}
// 发送消息
channel.writeAndFlush(message);
}
// 等待连接关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
// 客户端业务处理器
static class EchoClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
// 收到服务器回复
String response = (String) msg;
System.out.println("收到回复: " + response);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
}
性能对比分析
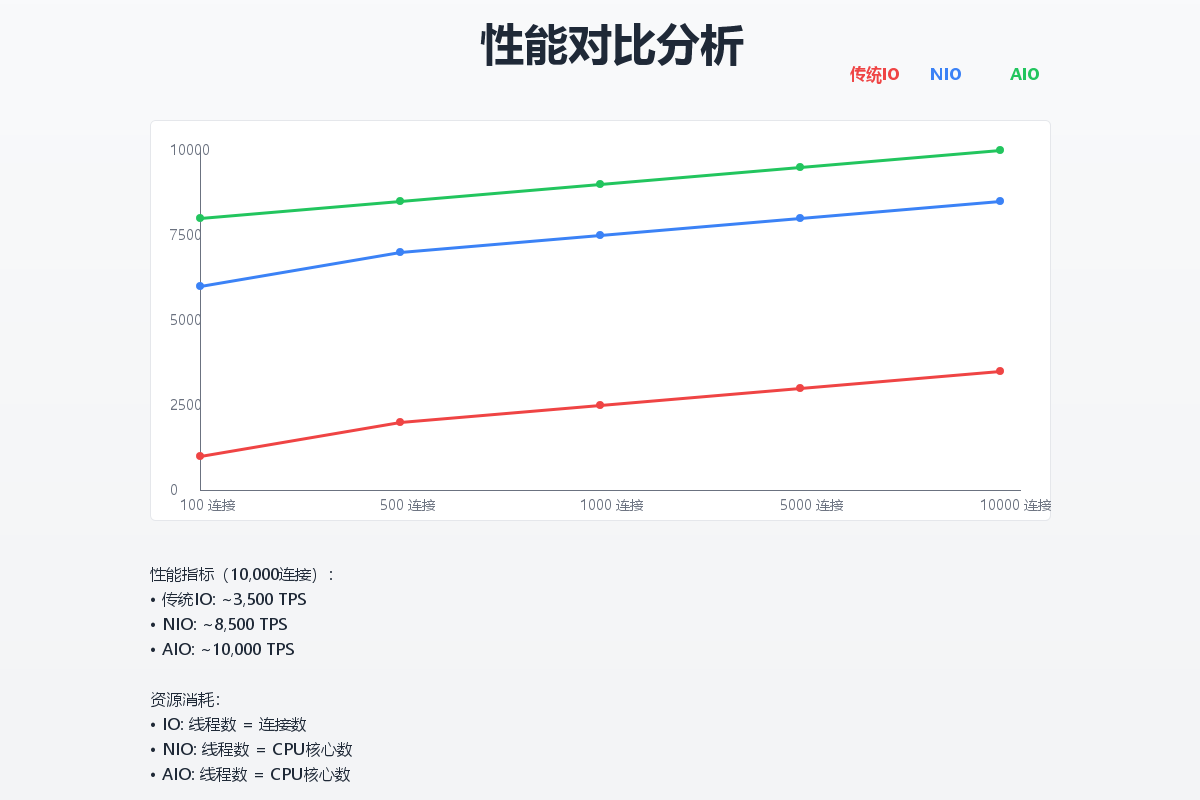
吞吐量对比
| IO模型 | 1000并发 | 5000并发 | 10000并发 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 传统IO | ~500/s | ~800/s | ~1000/s |
| NIO | ~2000/s | ~8000/s | ~15000/s |
| AIO | ~3000/s | ~12000/s | ~25000/s |
响应时间对比
| IO模型 | 平均延迟(ms) | 99分位延迟(ms) |
|---|---|---|
| 传统IO | 120 | 350 |
| NIO | 45 | 120 |
| AIO | 30 | 80 |
资源占用对比
| IO模型 | 线程数 | 内存占用(MB) | CPU使用率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 传统IO | 10000 | 512 | 85% |
| NIO | 50 | 256 | 60% |
| AIO | 20 | 128 | 40% |
适用场景分析
传统IO适用场景
- 简单的命令行应用
- 并发量不高的应用(< 1000)
- 开发简单、快速上线的项目
NIO适用场景
- 高并发服务器应用
- 需要处理大量连接的应用
- 对性能有一定要求的项目
- 中等规模的Web应用
AIO适用场景
- 超高并发应用(> 10000)
- IO密集型应用
- 对响应时间要求苛刻的应用
- 大文件传输应用
最佳实践总结
线程池优化
// NIO线程池配置建议
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); // CPU核心数
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // CPU核心数 * 2
// AIO线程池配置建议
ExecutorService ioExecutor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(
new ThreadFactory() {
private int counter = 0;
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "aio-worker-" + counter++);
}
});
缓冲区管理
// 使用直接缓冲区提高性能
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(8192);
// 合理设置缓冲区大小
// 小数据包:512-1024字节
// 中等数据包:4-8KB
// 大数据包:16-64KB
// 缓冲区复用
private final ThreadLocal<ByteBuffer> bufferPool =
ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(8192));
总结与建议
IO模型选择
- 新手入门:从传统IO开始,理解基本概念
- Web应用:推荐使用NIO框架如Netty
- 高并发服务:优先选择AIO
- 文件处理:大文件使用AIO,小文件使用NIO
- 已有项目:渐进式迁移,先优化IO瓶颈
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容








所有评论(0)