【Datawhale学习笔记】深入大模型架构
Llama2 遵循了 GPT 系列开创的 Decoder-Only 架构。这意味着它完全由 Transformer 解码器层堆叠而成,天然适用于自回归的文本生成任务。
手搓大模型体验
Llama2 架构总览
Llama2 遵循了 GPT 系列开创的 Decoder-Only 架构。这意味着它完全由 Transformer 解码器层堆叠而成,天然适用于自回归的文本生成任务。
Llama2 的设计
- 预归一化(Pre-Normalization):与经典 Transformer 的后归一化不同,输入在进入注意力层和前馈网络之前,都会先经过一次 RMS Norm。这被认为是提升大模型训练稳定性的关键(我们曾提到过,GPT-2/3 正是转向 Pre-Norm 解决了深层网络的训练难题)。
- 组件升级:支持 Grouped-Query Attention(GQA)(如 Llama2-70B 采用 1;小模型可视为 n_kv_heads == n_heads 的 MHA 特例),前馈网络采用 SwiGLU,归一化使用 RMSNorm。
- 旋转位置编码(RoPE):图中可见,位置信息并非在输入端与词嵌入相加,而是在注意力层内部,通过 RoPE 操作动态地施加于查询(Q)和键(K)向量之上。
- 残差连接:每个子层(注意力层和前馈网络)的输出都通过残差连接(+号)与子层的输入相加,保留了原始信息流。
Llama2数据流
- 输入嵌入:将 token_ids 转换为词向量。
- N x Transformer 层堆叠:数据依次通过 N 个相同的 Transformer Block。
- 预归一化:在进入子层之前,先进行一次 RMSNorm。
- 注意力子系统:包含旋转位置编码、分组查询注意力(GQA) 和 KV 缓存机制。
- 前馈网络子系统:采用 SwiGLU 激活函数。
- 最终归一化与输出:在所有层之后,进行最后一次 RMSNorm,并通过一个线性层将特征映射到词汇表 logits。
关键组件代码实现
预归一化(src/norm.py)
# code/C6/llama2/src/norm.py
class RMSNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim: int, eps: float = 1e-6):
super().__init__()
self.eps = eps
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(dim)) # 对应公式中的 gamma
def _norm(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
# 核心计算:x * (x^2的均值 + eps)的平方根的倒数
return x * torch.rsqrt(x.pow(2).mean(dim=-1, keepdim=True) + self.eps)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
out = self._norm(x.float()).type_as(x)
return out * self.weight
# 单元测试
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 准备参数和输入
batch_size, seq_len, dim = 4, 16, 64
x = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_len, dim)
# 初始化并应用 RMSNorm
norm = RMSNorm(dim)
output = norm(x)
# 验证输出形状
print("--- RMSNorm Test ---")
print("Input shape:", x.shape)
print("Output shape:", output.shape)
- _norm 方法精确地实现了 RMSNorm 的核心公式。
- self.eps 是一个为了防止除以零而添加的小常数,保证了数值稳定性。
旋转位置编码代码实现(src/rope.py)
def precompute_freqs_cis(dim: int, end: int, theta: float = 10000.0) -> torch.Tensor:
# 1. 计算频率:1 / (theta^(2i/dim))
freqs = 1.0 / (theta ** (torch.arange(0, dim, 2)[: (dim // 2)].float() / dim))
# 2. 生成位置序列 t = [0, 1, ..., end-1]
t = torch.arange(end, device=freqs.device)
# 3. 计算相位:t 和 freqs 的外积
freqs = torch.outer(t, freqs).float()
# 4. 转换为复数形式 (cos(theta) + i*sin(theta))
freqs_cis = torch.polar(torch.ones_like(freqs), freqs)
return freqs_cis
def reshape_for_broadcast(freqs_cis: torch.Tensor, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
ndim = x.ndim
shape = [d if i == 1 or i == ndim - 1 else 1 for i, d in enumerate(x.shape)]
return freqs_cis.view(*shape)
def apply_rotary_emb(
xq: torch.Tensor,
xk: torch.Tensor,
freqs_cis: torch.Tensor,
) -> tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
# 将 Q/K 向量视为复数
xq_ = torch.view_as_complex(xq.float().reshape(*xq.shape[:-1], -1, 2))
xk_ = torch.view_as_complex(xk.float().reshape(*xk.shape[:-1], -1, 2))
# 准备广播
freqs_q = reshape_for_broadcast(freqs_cis, xq_) # 针对 Q 的广播视图
# 复数乘法即为旋转
xq_out = torch.view_as_real(xq_ * freqs_q).flatten(3)
# K 向量可能与 Q 向量有不同的头数(GQA),所以需单独生成广播视图
freqs_k = reshape_for_broadcast(freqs_cis, xk_)
xk_out = torch.view_as_real(xk_ * freqs_k).flatten(3)
return xq_out.type_as(xq), xk_out.type_as(xq)
# 单元测试
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 准备参数和输入
batch_size, seq_len, n_heads, n_kv_heads, head_dim = 4, 16, 8, 2, 16
dim = n_heads * head_dim
n_rep = n_heads // n_kv_heads
# --- Test precompute_freqs_cis ---
print("--- Test precompute_freqs_cis ---")
freqs_cis = precompute_freqs_cis(dim=head_dim, end=seq_len * 2)
print("freqs_cis shape:", freqs_cis.shape)
# --- Test apply_rotary_emb ---
print("\n--- Test apply_rotary_emb ---")
xq = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_len, n_heads, head_dim)
xk = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_len, n_kv_heads, head_dim)
freqs_cis_slice = freqs_cis[:seq_len]
xq_out, xk_out = apply_rotary_emb(xq, xk, freqs_cis_slice)
print("xq shape (in/out):", xq.shape, xq_out.shape)
print("xk shape (in/out):", xk.shape, xk_out.shape)
分组查询注意力代码实现(src/attention.py)
# code/C6/llama2/src/rope.py
def repeat_kv(x: torch.Tensor, n_rep: int) -> torch.Tensor:
batch_size, seq_len, n_kv_heads, head_dim = x.shape
if n_rep == 1:
return x
return (
x[:, :, :, None, :]
.expand(batch_size, seq_len, n_kv_heads, n_rep, head_dim)
.reshape(batch_size, seq_len, n_kv_heads * n_rep, head_dim)
)
class GroupedQueryAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim: int, n_heads: int, n_kv_heads: int | None = None, ...):
...
self.n_local_heads = n_heads
self.n_local_kv_heads = n_kv_heads
self.n_rep = self.n_local_heads // self.n_local_kv_heads # Q头与KV头的重复比
...
self.wq = nn.Linear(dim, n_heads * self.head_dim, bias=False)
self.wk = nn.Linear(dim, n_kv_heads * self.head_dim, bias=False)
self.wv = nn.Linear(dim, n_kv_heads * self.head_dim, bias=False)
...
def forward(self, x, start_pos, freqs_cis, mask):
xq = self.wq(x).view(batch_size, seq_len, self.n_local_heads, self.head_dim)
xk = self.wk(x).view(batch_size, seq_len, self.n_local_kv_heads, self.head_dim)
xv = self.wv(x).view(batch_size, seq_len, self.n_local_kv_heads, self.head_dim)
xq, xk = apply_rotary_emb(xq, xk, freqs_cis=freqs_cis)
# ... KV Cache 逻辑 ...
keys = repeat_kv(keys, self.n_rep) # <-- 关键步骤
values = repeat_kv(values, self.n_rep) # <-- 关键步骤
scores = torch.matmul(xq.transpose(1, 2), keys.transpose(1, 2).transpose(2, 3)) / ...
# 单元测试
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 准备参数和输入
batch_size, seq_len, dim = 4, 16, 128
n_heads, n_kv_heads = 8, 2
head_dim = dim // n_heads
# 初始化注意力模块
attention = GroupedQueryAttention(
dim=dim,
n_heads=n_heads,
n_kv_heads=n_kv_heads,
max_batch_size=batch_size,
max_seq_len=seq_len,
)
# 准备输入
x = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_len, dim)
freqs_cis = precompute_freqs_cis(dim=head_dim, end=seq_len * 2)
freqs_cis_slice = freqs_cis[:seq_len]
# 执行前向传播
output = attention(x, start_pos=0, freqs_cis=freqs_cis_slice)
# 验证输出形状
print("--- GroupedQueryAttention Test ---")
print("Input shape:", x.shape)
print("Output shape:", output.shape)
SwiGLU 前馈网络代码实现(src/ffn.py)
class FeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim: int, hidden_dim: int, multiple_of: int, ...):
super().__init__()
# hidden_dim 计算,并用 multiple_of 对齐以提高硬件效率
hidden_dim = int(2 * hidden_dim / 3)
...
hidden_dim = multiple_of * ((hidden_dim + multiple_of - 1) // multiple_of)
self.w1 = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim, bias=False) # 对应 W
self.w2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, dim, bias=False) # 对应 W2
self.w3 = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim, bias=False) # 对应 V
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
# F.silu(self.w1(x)) 实现了 swish(xW)
# * self.w3(x) 实现了门控机制
return self.w2(torch.nn.functional.silu(self.w1(x)) * self.w3(x))
# 单元测试
# code/C6/llama2/src/ffn.py
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 准备参数和输入
batch_size, seq_len, dim = 4, 16, 128
# 初始化 FFN 模块
ffn = FeedForward(
dim=dim,
hidden_dim=4 * dim,
multiple_of=256,
ffn_dim_multiplier=None
)
# 准备输入
x = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_len, dim)
# 执行前向传播
output = ffn(x)
# 验证输出形状
print("--- FeedForward (SwiGLU) Test ---")
print("Input shape:", x.shape)
print("Output shape:", output.shape)
模型组装与前向传播(src/transformer.py)
# TransformerBlock: 这是构成 Llama2 的基本单元
class TransformerBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layer_id: int, ...):
...
self.attention = GroupedQueryAttention(...)
self.feed_forward = FeedForward(...)
self.attention_norm = RMSNorm(...)
self.ffn_norm = RMSNorm(...)
def forward(self, x, start_pos, freqs_cis, mask):
# 预归一化 + 残差连接
h = x + self.attention(self.attention_norm(x), start_pos, freqs_cis, mask)
out = h + self.feed_forward(self.ffn_norm(h))
return out
# LlamaTransformer: 顶层模型,负责堆叠 TransformerBlock 并处理输入输出。
class LlamaTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size: int, ...):
...
self.tok_embeddings = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, dim)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([TransformerBlock(...) for i in range(n_layers)])
self.norm = RMSNorm(dim, eps=norm_eps)
self.output = nn.Linear(dim, vocab_size, bias=False)
self.register_buffer("freqs_cis", precompute_freqs_cis(...))
def forward(self, tokens: torch.Tensor, start_pos: int) -> torch.Tensor:
h = self.tok_embeddings(tokens)
# 1. 准备 RoPE 旋转矩阵
freqs_cis = self.freqs_cis[start_pos : start_pos + seq_len]
# 2. 准备因果掩码 (Causal Mask)
mask = None
if seq_len > 1:
mask = torch.full((seq_len, seq_len), float("-inf"), device=tokens.device)
mask = torch.triu(mask, diagonal=1)
# 考虑 KV Cache 的偏移
mask = torch.hstack([torch.zeros((seq_len, start_pos), ...), mask]).type_as(h)
# 3. 循环通过所有 TransformerBlock
for layer in self.layers:
h = layer(h, start_pos, freqs_cis, mask)
h = self.norm(h)
logits = self.output(h).float()
return logits
整体验证
import torch
from src.transformer import LlamaTransformer
def main() -> None:
# 使用小尺寸参数,便于 CPU/GPU 都能快速跑通
model = LlamaTransformer(
vocab_size=1000,
dim=256,
n_layers=2,
n_heads=8,
n_kv_heads=2,
multiple_of=64,
ffn_dim_multiplier=None,
norm_eps=1e-6,
max_batch_size=4,
max_seq_len=64,
)
# 构造随机 token 序列并执行前向
batch_size, seq_len = 2, 16
tokens = torch.randint(0, 1000, (batch_size, seq_len))
logits = model(tokens, start_pos=0)
# 期望: [batch_size, seq_len, vocab_size]
print("logits shape:", tuple(logits.shape))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
MoE架构
稠密模型(Dense Model):lama2、GPT-3
混合专家模型(Mixture of Experts, MoE):MoE 技术通过一种 “稀疏激活” 的机制,兼具了大规模参数的知识容量与极低的推理成本。Mistral 8x7B 等模型的出现,更是证明了 MoE 在开源大模型领域的巨大潜力,使其成为当前最受关注的技术方向之一
来源
最早的 MoE 思想可以追溯到 1991 年 Michael Jordan 和 Geoffrey Hinton 发表的经典论文《Adaptive Mixture of Local Experts》
大模型时代的 MoE
入 Transformer 时代后,MoE 技术成为了突破模型规模瓶颈的关键。Google 在这一领域进行了密集的探索,通过 GShard、Switch Transformer 和 GLaM 等一系列工作,确立了现代大规模 MoE 的技术范式。
MoE 架构的创新与实践
随着开源社区的活跃,MoE 技术不再是科技巨头的专属。Mistral 8x7B 和 DeepSeek-R1 的出现,分别在中等规模和超大规模上证明了开源 MoE 模型的强大实力,标志着 MoE 技术进入了全面普及和深度创新的新阶段。
Mistral 8x7B的架构总览
Mistral 8x7B (Mixtral) 7 在开源大语言模型中成功实践了 MoE 架构,有力地证明了合理设计的稀疏模型即使不需要万亿参数,也能超越同量级的稠密模型。
- 架构参数:它拥有约 470 亿(47B) 的总参数量(Sparse Parameters),但对于每个 Token,仅激活 130 亿(13B) 参数(Active Parameters)。这使得它在推理时拥有 13B 模型的计算速度,却能发挥出 47B 模型的知识容量。需要注意的是,虽然计算量较小,但由于所有专家参数都需要加载到内存中,其显存占用(VRAM Usage)依然是 47B 模型级别的。
- 路由机制:每一层包含 8 个专家(Experts),采用标准的 Top-2 Routing 策略。如图 6-10 所示,每个输入 Token 会被 Router 网络分配给 8 个专家中的 2 个,这两个专家的输出经过加权求和后作为该层的最终输出。这种机制巧妙地在增加模型容量(更多专家)的同时,保持了极低的推理成本(只激活 2 个)。
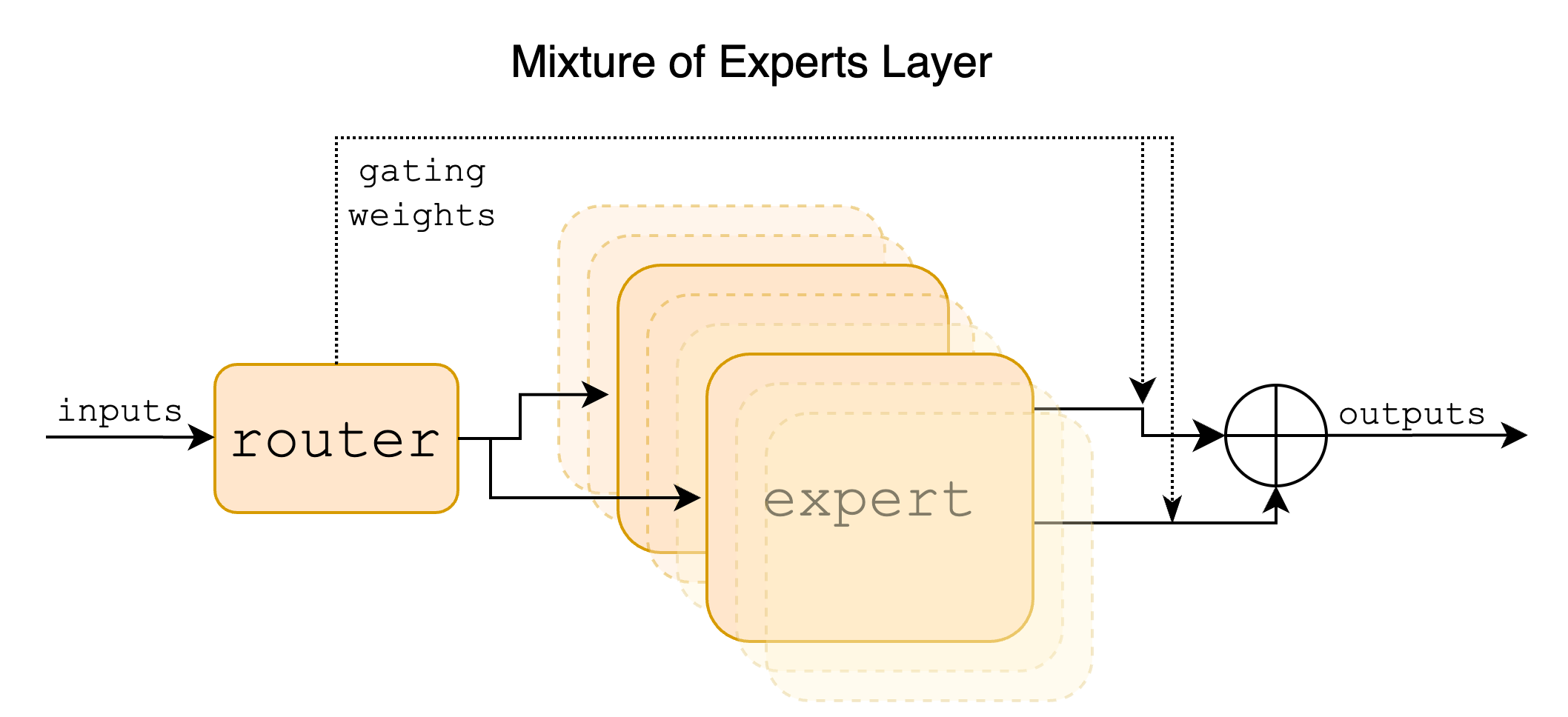
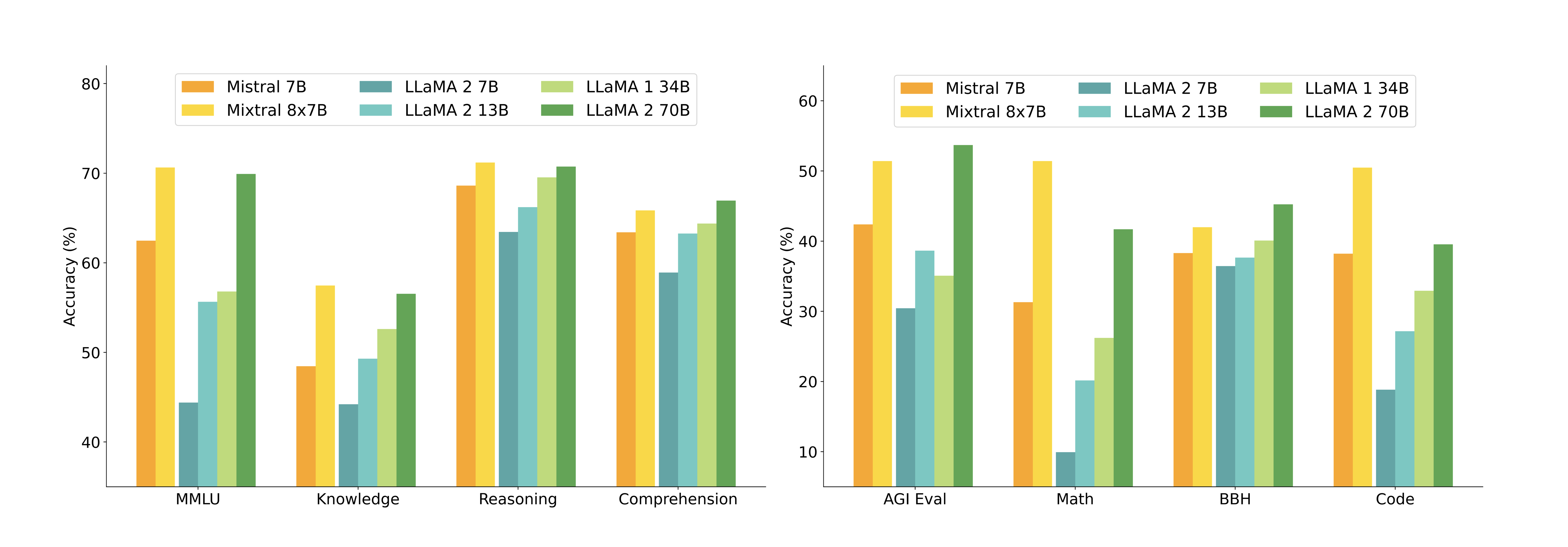
- 性能表现:在 GSM8K(数学)、MMLU(综合知识)、HumanEval(代码)等基准测试上,Mistral 8x7B 以 13B 的活跃参数量超越了稠密的 Llama 2 70B 以及 GPT-3.5。如图 6-11,Mistral 8x7B(黄色柱状图)在几乎所有任务上都包围或持平了 Llama 2 70B(绿色柱状图),特别是在数学和代码生成任务上,其优势尤为显著。
- 长上下文能力:Mistral 8x7B 支持 32k 的上下文长度,并且在长文本信息检索(Passkey Retrieval)任务中表现出了 100% 的召回率,证明了 MoE 架构在处理长序列时依然稳健。
DeepSeekMoE 与 DeepSeek-R1
如果说 Mistral 开启了开源 MoE 模型的大门,那么 DeepSeek-R1 8(及其基座 DeepSeek-V3 9)则将开源 MoE 模型的性能推向了与当时顶尖闭源模型(如 OpenAI o1)比肩的高度。DeepSeek 在 MoE 架构上进行了更深度的创新,提出了 DeepSeekMoE 10 架构,目标是解决传统 Top-k 路由中的“知识冗余”和“专业化不足”问题。
代码实战
实现 MoE 层
class MoE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim: int, hidden_dim: int, multiple_of: int, ffn_dim_multiplier: Optional[float], num_experts: int = 8, top_k: int = 2):
super().__init__()
self.num_experts = num_experts
self.top_k = top_k
# 门控网络:决定每个 Token 去往哪个专家
self.gate = nn.Linear(dim, num_experts, bias=False)
# 专家列表:创建 num_experts 个独立的 FeedForward 网络
self.experts = nn.ModuleList([
FeedForward(dim, hidden_dim, multiple_of, ffn_dim_multiplier)
for _ in range(num_experts)
])
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
# x: (batch_size, seq_len, dim)
B, T, D = x.shape
x_flat = x.view(-1, D)
# 1. 门控网络
gate_logits = self.gate(x_flat) # (B*T, num_experts)
# 2. Top-k 路由
weights, indices = torch.topk(gate_logits, self.top_k, dim=-1)
weights = F.softmax(weights, dim=-1) # 归一化权重
output = torch.zeros_like(x_flat)
for i, expert in enumerate(self.experts):
# 3. 找出所有选中当前专家 i 的 token 索引
batch_idx, k_idx = torch.where(indices == i)
if len(batch_idx) == 0:
continue
# 4. 取出对应的输入进行计算
expert_input = x_flat[batch_idx]
expert_out = expert(expert_input)
# 5. 获取对应的权重
expert_weights = weights[batch_idx, k_idx].unsqueeze(-1) # (num_selected, 1)
# 6. 将结果加权累加回输出张量
output.index_add_(0, batch_idx, expert_out * expert_weights)
return output.view(B, T, D)
替换 TransformerBlock
from .ffn import FeedForward, MoE # 导入 MoE
class TransformerBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(
# ... args ...
):
super().__init__()
# ...
# 修改:使用 MoE 替换标准的 FeedForward
self.feed_forward = MoE(
dim=dim,
hidden_dim=4 * dim,
multiple_of=multiple_of,
ffn_dim_multiplier=ffn_dim_multiplier,
num_experts=8, # 定义8个专家
top_k=2, # 每个Token激活2个专家
)
参考代码仓
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容







所有评论(0)