2 virtio子系统之数据结构
这2个字段均与virtio设备的VIRTIO_RING_F_EVENT_IDX特性有关,由于virtio驱动触发对方中断将导致CPU反复进出虚拟机 & 宿主机模式,从而降低性能,因此需要控制触发中断频率的机制。在计算used ring的起始地址时,在avail->ring[num]的地址之后又加了sizeof(__virtio16),也就是增加了2B,是为了容纳avail ring末尾的used_
virtio bus结构
注册virtio bus
// drivers/virtio/virtio.c
static struct bus_type virtio_bus = {
.name = "virtio",
.match = virtio_dev_match,
.dev_groups = virtio_dev_groups,
.uevent = virtio_uevent,
.probe = virtio_dev_probe,
.remove = virtio_dev_remove,
};
static int virtio_init(void)
{
if (bus_register(&virtio_bus) != 0)
panic("virtio bus registration failed");
return 0;
}
static void __exit virtio_exit(void)
{
bus_unregister(&virtio_bus);
ida_destroy(&virtio_index_ida);
}
core_initcall(virtio_init);
module_exit(virtio_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");/*
* A "pure" initcall has no dependencies on anything else, and purely
* initializes variables that couldn't be statically initialized.
*
* This only exists for built-in code, not for modules.
* Keep main.c:initcall_level_names[] in sync.
*/
#define pure_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 0)
#define core_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 1)
#define core_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 1s)
#define postcore_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 2)
#define postcore_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 2s)
#define arch_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 3)
#define arch_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 3s)
#define subsys_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 4)
#define subsys_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 4s)
#define fs_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 5)
#define fs_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 5s)
#define rootfs_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, rootfs)
#define device_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 6)
#define device_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 6s)
#define late_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 7)
#define late_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 7s)virtio bus以core_initcall的方式回调注册,其启动顺序的优先级很高。因此virtio-clk、virtio-irq等,可基于架构实现半虚拟化。
virtio_dev_match函数
// include/linux/mod_devicetable.h
struct virtio_device_id {
__u32 device; // device id
__u32 vendor; // vendor id
};
#define VIRTIO_DEV_ANY_ID 0xffffffffdevice定义详见:virtio设备
// drivers/virtio/virtio.c
static inline int virtio_id_match(const struct virtio_device *dev,
const struct virtio_device_id *id)
{
// 先比较 device id要一致,且不能为 ANY
if (id->device != dev->id.device && id->device != VIRTIO_DEV_ANY_ID)
return 0;
// vendor id为 ANY 或者相等
return id->vendor == VIRTIO_DEV_ANY_ID || id->vendor == dev->id.vendor;
}
/* This looks through all the IDs a driver claims to support. If any of them
* match, we return 1 and the kernel will call virtio_dev_probe(). */
static int virtio_dev_match(struct device *_dv, struct device_driver *_dr)
{
unsigned int i;
// 根据device 结构索引获取 virtio_device
struct virtio_device *dev = dev_to_virtio(_dv);
const struct virtio_device_id *ids;
// 根据 device_driver结构,获取 virtio_driver,
// 并取出其 id_table,且必须以0为结尾,以便结束循环
ids = drv_to_virtio(_dr)->id_table;
for (i = 0; ids[i].device; i++)
if (virtio_id_match(dev, &ids[i]))
return 1;
return 0;
}virtio_device结构
// include/linux/virtio.h
/**
* virtio_device - representation of a device using virtio
* @index: unique position on the virtio bus
* @failed: saved value for VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_FAILED bit (for restore)
* @config_enabled: configuration change reporting enabled
* @config_change_pending: configuration change reported while disabled
* @config_lock: protects configuration change reporting
* @dev: underlying device.
* @id: the device type identification (used to match it with a driver).
* @config: the configuration ops for this device.
* @vringh_config: configuration ops for host vrings.
* @vqs: the list of virtqueues for this device.
* @features: the features supported by both driver and device.
* @priv: private pointer for the driver's use.
*/
struct virtio_device {
int index;
bool failed;
bool config_enabled;
bool config_change_pending;
spinlock_t config_lock;
struct device dev;
struct virtio_device_id id; // 当前设备的 id
const struct virtio_config_ops *config; // virtio_device 的配置
const struct vringh_config_ops *vringh_config;
struct list_head vqs; // 当前 dev 的 virtioqueue 链表
u64 features; // 设备通信特性
void *priv;
};- struct virtio_config_ops
virtio_config_ops操作集中的函数主要与virtio_device的配置相关,主要有如下2类操作,
① 实例化 / 反实例化virtqueue,其中要特别注意find_vqs函数,该函数用于实例化virtio_device所持有的virtqueue
②. 获取 / 设置virtio_device的属性与状态
// include/linux/virtio_config.h
struct virtio_config_ops {
// 获取 host 端的数据
void (*get)(struct virtio_device *vdev, unsigned offset,
void *buf, unsigned len);
// 发送 数据到 host端
void (*set)(struct virtio_device *vdev, unsigned offset,
const void *buf, unsigned len);
u32 (*generation)(struct virtio_device *vdev);
// 获取 host端的状态
u8 (*get_status)(struct virtio_device *vdev);
// 配置 guest端的状态
void (*set_status)(struct virtio_device *vdev, u8 status);
// 通知 host端 复位设备
void (*reset)(struct virtio_device *vdev);
// 实例化virtio_device所持有的virtqueue
int (*find_vqs)(struct virtio_device *, unsigned nvqs,
struct virtqueue *vqs[], vq_callback_t *callbacks[],
const char * const names[], const bool *ctx,
struct irq_affinity *desc);
void (*del_vqs)(struct virtio_device *);
// 获取 features 信息
u64 (*get_features)(struct virtio_device *vdev);
int (*finalize_features)(struct virtio_device *vdev);
// 获取 bus名,如:platform、pci等
const char *(*bus_name)(struct virtio_device *vdev);
int (*set_vq_affinity)(struct virtqueue *vq,
const struct cpumask *cpu_mask);
const struct cpumask *(*get_vq_affinity)(struct virtio_device *vdev,
int index);
};virtio_driver结构
// include/linux/virtio.h
/**
* virtio_driver - operations for a virtio I/O driver
* @driver: underlying device driver (populate name and owner).
* @id_table: the ids serviced by this driver.
* @feature_table: an array of feature numbers supported by this driver.
* @feature_table_size: number of entries in the feature table array.
* @feature_table_legacy: same as feature_table but when working in legacy mode.
* @feature_table_size_legacy: number of entries in feature table legacy array.
* @probe: the function to call when a device is found. Returns 0 or -errno.
* @scan: optional function to call after successful probe; intended
* for virtio-scsi to invoke a scan.
* @remove: the function to call when a device is removed.
* @config_changed: optional function to call when the device configuration
* changes; may be called in interrupt context.
* @freeze: optional function to call during suspend/hibernation.
* @restore: optional function to call on resume.
*/
struct virtio_driver {
struct device_driver driver;
const struct virtio_device_id *id_table; // id 列表
const unsigned int *feature_table; // 特性
unsigned int feature_table_size;
const unsigned int *feature_table_legacy;
unsigned int feature_table_size_legacy;
int (*validate)(struct virtio_device *dev);
int (*probe)(struct virtio_device *dev); // 探测函数
void (*scan)(struct virtio_device *dev);
void (*remove)(struct virtio_device *dev);
void (*config_changed)(struct virtio_device *dev);
#ifdef CONFIG_PM
int (*freeze)(struct virtio_device *dev);
int (*restore)(struct virtio_device *dev);
#endif
};virtqueue结构
// include/linux/virtio.h
/**
* virtqueue - a queue to register buffers for sending or receiving.
* @list: the chain of virtqueues for this device
* @callback: the function to call when buffers are consumed (can be NULL).
* @name: the name of this virtqueue (mainly for debugging)
* @vdev: the virtio device this queue was created for.
* @priv: a pointer for the virtqueue implementation to use.
* @index: the zero-based ordinal number for this queue.
* @num_free: number of elements we expect to be able to fit.
*
* A note on @num_free: with indirect buffers, each buffer needs one
* element in the queue, otherwise a buffer will need one element per
* sg element.
*/
struct virtqueue {
// 加入 virtio_device的vqs链表
struct list_head list;
// virtqueue被触发中断时执行的回调函数
void (*callback)(struct virtqueue *vq);
// virtqueue名
const char *name;
// virtqueue所属的 virtio_device
struct virtio_device *vdev;
// virtqueue的编号
unsigned int index;
// virtioqueue中空闲的descriptor个数
unsigned int num_free;
void *priv;
};vring结构
- 数据结构定义
- vring的三个构成
-
- ① Destcriptor Table:描述内存buffer,主要包括addr & len等信息
- ② Avail Ring:用于前端驱动(Guest)通知后端驱动(Host)有可用的描述符
e.g. 前端驱动有一个报文需要发送,需要将其加入Avail Ring,之后通知后端驱动读取
- ③ Used Ring:用于后端驱动(Host)通知前端驱动(Guest)有可用的描述符,或者是后端驱动已将前端驱动提供的描述符使用完毕
e.g. 后端驱动有一个报文需要发送,需要将其加入Used Ring,之后通知前端驱动读取
可见avail & used的命名都是站在Host的角度进行的
- vring的存储
vring结构只是用于描述vring在内存中的布局(因此包含的都是指针变量),实际用于通信的vring是存储在内存中
上文提到的vring的三个区域是在内存中连续存储的,而且是存储在Guest & Host共享的一片连续内存中
我们可以通过vring_init函数理解vring存储结构的布局:
/*
* vr:要初始化的vring结构
* num:vring的大小,即descriptor的个数
* p:存储实际vring的内存首地址
* align:vring不同区域的对齐要求
*/
static inline void vring_init(struct vring *vr, unsigned int num, void *p,
unsigned long align)
{
vr->num = num;
vr->desc = p;
vr->avail = p + num*sizeof(struct vring_desc);
vr->used = (void *)(((uintptr_t)&vr->avail->ring[num] + sizeof(__virtio16)
+ align-1) & ~(align - 1));
}实际vring的内存布局如下图所示:
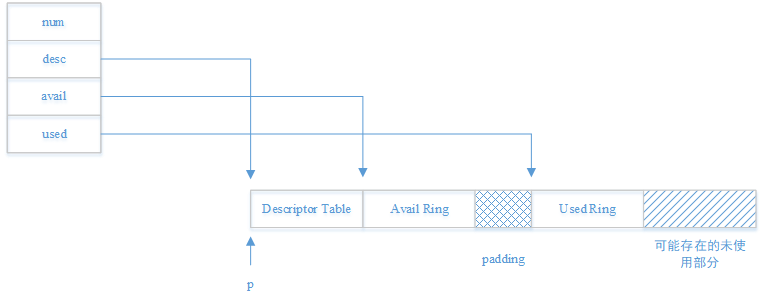
在计算used ring的起始地址时,在avail->ring[num]的地址之后又加了sizeof(__virtio16),也就是增加了2B,是为了容纳avail ring末尾的used_event。
- vring的大小
实际vring的大小可以通过vring_size函数获得
/*
* num:vring的大小,即descriptor的个数
* align:vring不同区域的对齐要求
*/
static inline unsigned vring_size(unsigned int num, unsigned long align)
{
return ((sizeof(struct vring_desc) * num + sizeof(__virtio16) * (3 + num)
+ align - 1) & ~(align - 1))
+ sizeof(__virtio16) * 3 + sizeof(struct vring_used_elem) * num;
}① 计算avail ring时加3,分别为flags、idx和used_event
② 计算used ring时加3,分别为flags、idx和avail_event
③ 计算过程中,包含了为满足对齐要求padding的空间
- used_event 与 avail_event 机制
这2个字段均与virtio设备的VIRTIO_RING_F_EVENT_IDX特性有关,由于virtio驱动触发对方中断将导致CPU反复进出虚拟机 & 宿主机模式,从而降低性能,因此需要控制触发中断频率的机制。
- ① avail ring中的used_event
a. 由前端驱动(Geust)设置,标识希望后端驱动(Host)触发中断的阈值
b. 后端驱动(Host)在向Used Ring加入buffer后,检查Used Ring中的idx字段,只有达到阈值才触发中断
- ② used_ring中的avail_event
a. 由后端驱动(Host)设置,标识希望前端驱动(Guest)触发中断的阈值
b. 前端驱动(Guest)在向Avail Ring加入buffer后,检查Avail Ring的idx字段,只有达到阈值才触发中断
综上所属,vring结构的构成如下图所示,
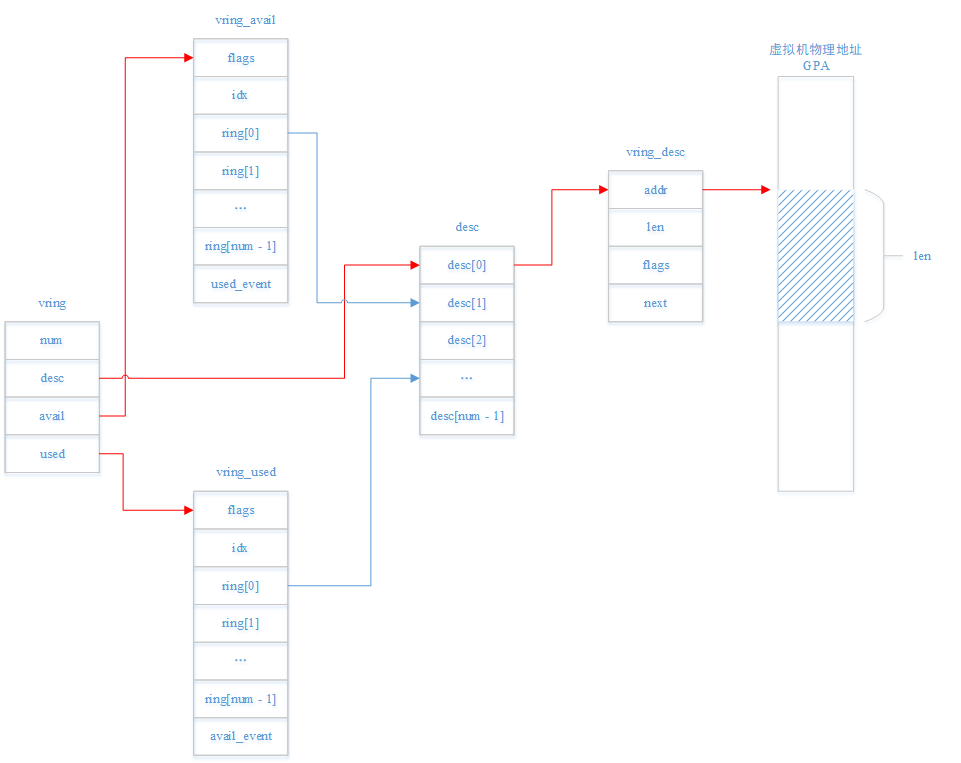
vring_virtqueue结构
vring_virtqueue结构用于描述前端驱动(Guest)中的一条虚拟队列
// drivers/virtio/virtio_ring.c
struct vring_virtqueue {
// virtio层虚拟队列
struct virtqueue vq;
/* Is this a packed ring? */
bool packed_ring;
/* Is DMA API used? */
bool use_dma_api;
/* Can we use weak barriers? */
bool weak_barriers;
/* Other side has made a mess, don't try any more. */
// 标识后端驱动状态是否正常
bool broken;
/* Host supports indirect buffers */
// 标识是否支持间接descriptor
// 即descriptor指向的不是GPA,而是descriptor
bool indirect;
/* Host publishes avail event idx */
// 标识是否支持event流控
bool event;
/* Head of free buffer list. */
// vring descriptor table中第一个可用的下标
// 即空闲链表表头
unsigned int free_head;
/* Number we've added since last sync. */
// 上一次通知后端驱动(Host)之后向avail ring中增加的请求次数
unsigned int num_added;
/* Last used index we've seen. */
// 前端驱动(Guest)上次读取到的uesd ring index
u16 last_used_idx;
union {
/* Available for split ring */
struct {
/* Actual memory layout for this queue. */
struct vring vring;
/* Last written value to avail->flags */
// 最后一次写入 avail flags的值
u16 avail_flags_shadow;
/*
* Last written value to avail->idx in
* guest byte order.
*/
// 最后一次写入 avail ring index的值
u16 avail_idx_shadow;
/* Per-descriptor state. */
// 数组大小为virtqueue的大小
// 用来存放每次添加的descriptor的一个上下文结构
// 该结构仅供前端驱动使用,后端驱动是看不到此结构
struct vring_desc_state_split *desc_state;
/* DMA address and size information */
dma_addr_t queue_dma_addr;
size_t queue_size_in_bytes;
} split;
/* Available for packed ring */
struct {
/* Actual memory layout for this queue. */
struct {
unsigned int num;
struct vring_packed_desc *desc; // Descriptor Ring
struct vring_packed_desc_event *driver; // Driver Event Suppression
struct vring_packed_desc_event *device; // Device Event Suppression
} vring;
/* Driver ring wrap counter. */
bool avail_wrap_counter;
/* Device ring wrap counter. */
bool used_wrap_counter;
/* Avail used flags. */
u16 avail_used_flags;
/* Index of the next avail descriptor. */
u16 next_avail_idx;
/*
* Last written value to driver->flags in
* guest byte order.
*/
u16 event_flags_shadow;
/* Per-descriptor state. */
struct vring_desc_state_packed *desc_state;
struct vring_desc_extra_packed *desc_extra;
/* DMA address and size information */
dma_addr_t ring_dma_addr;
dma_addr_t driver_event_dma_addr;
dma_addr_t device_event_dma_addr;
size_t ring_size_in_bytes;
size_t event_size_in_bytes;
} packed;
};
/* How to notify other side. FIXME: commonalize hcalls! */
// 通知后端驱动(Host)的回调函数
bool (*notify)(struct virtqueue *vq);
/* DMA, allocation, and size information */
bool we_own_ring;
#ifdef DEBUG
/* They're supposed to lock for us. */
unsigned int in_use;
/* Figure out if their kicks are too delayed. */
bool last_add_time_valid;
ktime_t last_add_time;
#endif
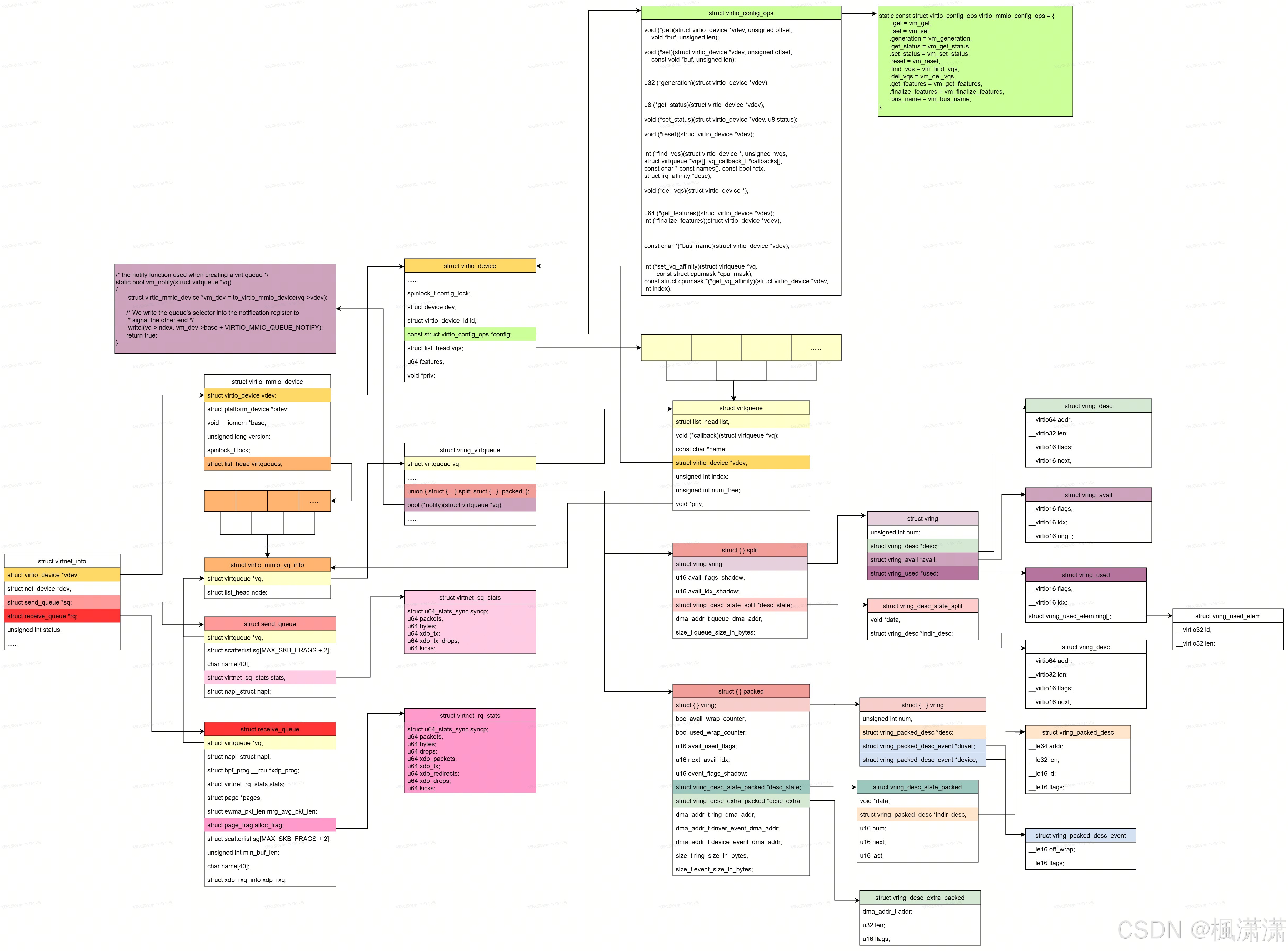
};数据结构小结
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献9条内容
已为社区贡献9条内容






所有评论(0)