隐式推理Coconut论文解读
2024年12月首次发表,FAIR at Meta,隐式推理直接使用hidden embedding 做next hidden embedding prediction。
Training Large Language Models to Reason in a Continuous Latent Space
2024年12月首次发表,FAIR at Meta,
隐式推理直接使用hidden embedding 做next hidden embedding prediction
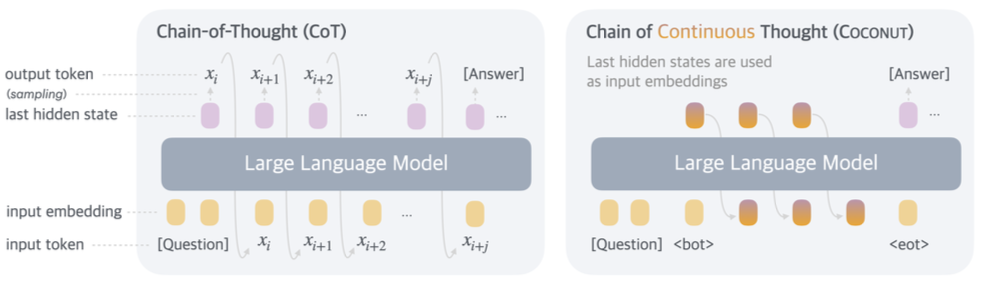
传统的Next token prediction的范式:
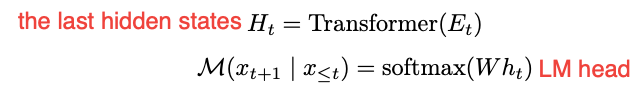
训练方式:
分多阶段训练,每次都remove掉一个显式推理的step,并用c=1个continuous thought token代替这个步骤,对于continuous thought的部分是不参与CE loss的计算的,在隐式推理时,直接用模型输出的last hidden state作为下一个输入的input embedding,
continuous thought 会用<bot> and <eot> tokens来包裹,以示意continuous thought的区域
注意:这里continuous thought的motivation不是让模型去补全隐式的部分,而是让模型通过continuous thought去思考更多的内容
It is important to note that the objective does not encourage the continuous thought to
compress the removed language thought, but rather to facilitate the prediction of future reasoning. Therefore, it’s possible for the LLM to learn more effective representations of reasoning steps compared to human language.
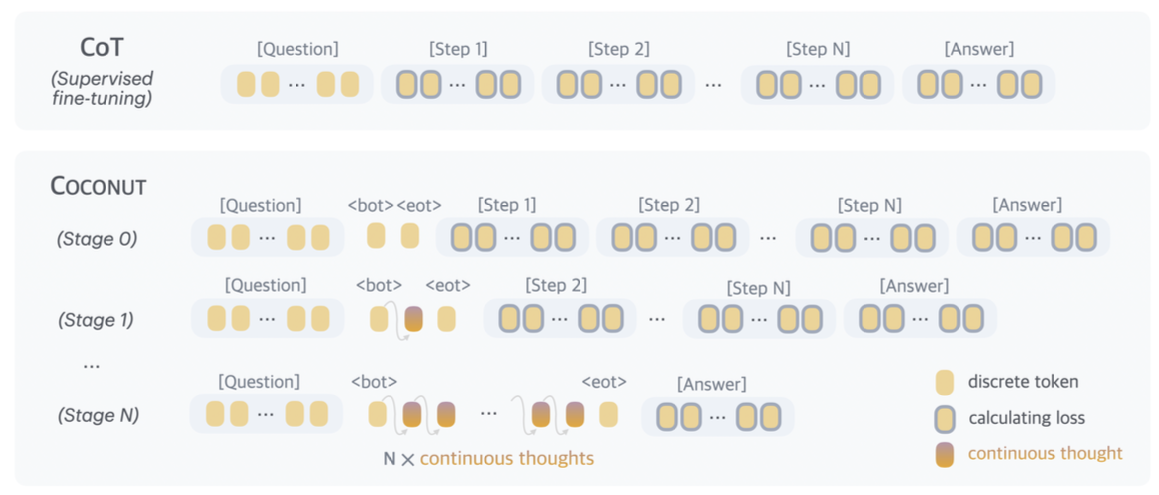
他们提出的 continuous thoughts(连续思维 / 潜在思维) 是可微的,所以可以端到端反向传播;在训练时,如果当前阶段要插入 n 个 latent thoughts,就需要 n + 1 次 forward,前 n 次逐步生成这些 latent thoughts,最后一次再用剩余文本算 loss。
在训练时,对于continuous thought的部分,并不是用pad的操作,而是通过多次调用forward的方式来训练的(每次foreward时得到一个新的latent embedding,对于这部分embedding其实是无监督的)。这样做的坏处是不能进行并行训练
相比于这个,其实很多在VLM里面的latent thought方法都是拿一个固定长度的<latent_start><latent_pad><latent_pad><latent_pad><latent_end>来实现的,这样做的坏处是模型其实不是在自回归的生成。并没有真正利用到latent embedding做推理
理论解释:
隐式推理的方式能让模型在潜空间进行广度优先搜索,对于特定问题具有优势
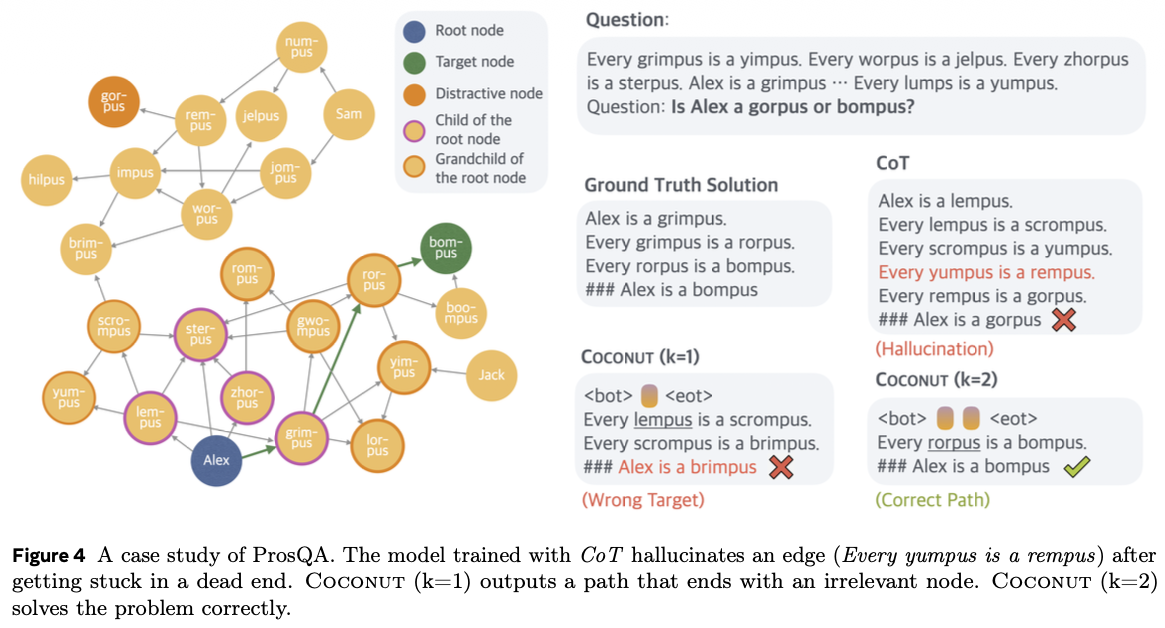
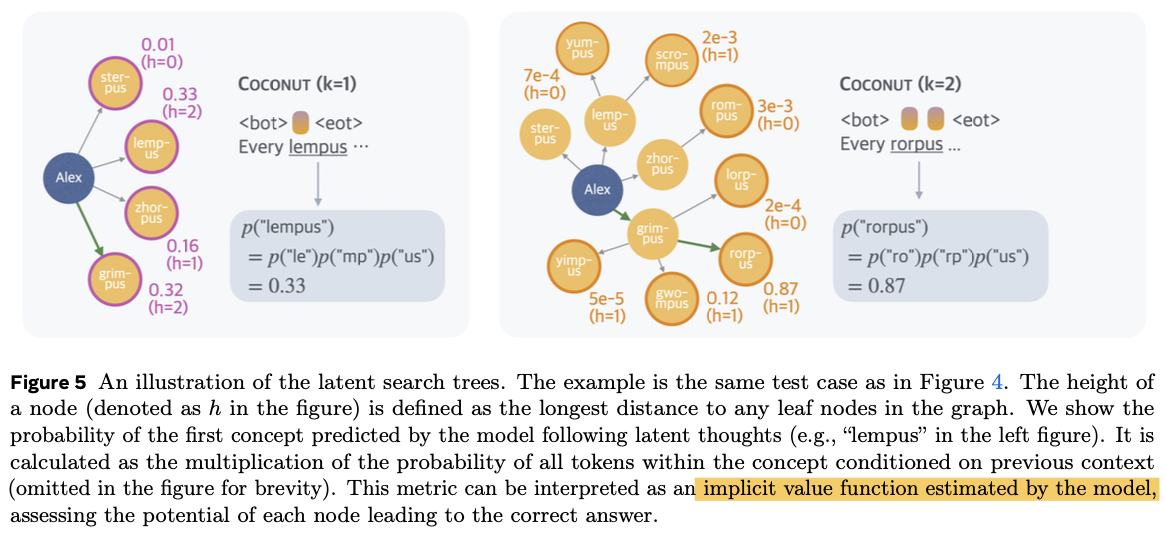
显式思维链如果在训练早期走错步之后,很难挽回,GRPO就是通过强化的方式多探索更多的路径并通过奖励的方式引导模型在初期的生成路线:
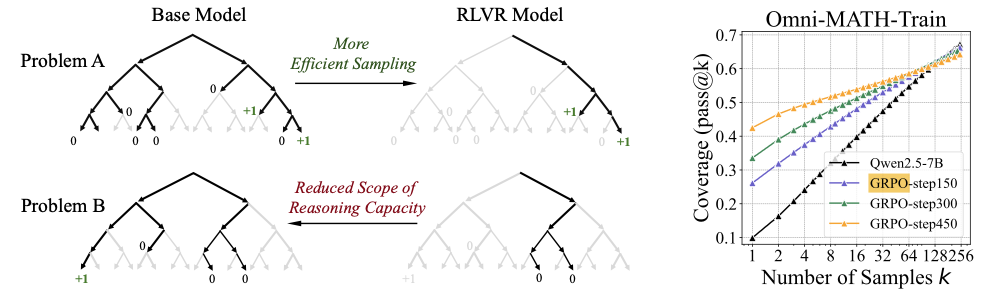
These findings underscore the advantage of latent space reasoning. By delaying deterministic decisions and allowing exploration to proceed toward terminal states, latent reasoning significantly enhances the model’s ability to differentiate correct paths from incorrect ones, thereby improving performance on complex, planning-intensive tasks compared to traditional greedy methods.
latent space reasoning的优点之一就是在模型推理的早期不显式的给出具体的推理路径,而是当模型的概率叠加多步之后得到更大的confidence时在输出最终的路径。这种隐式思维的方式对需要planning的任务有更大优势。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容






所有评论(0)