【LLM】高德AMAP Agentic Planning
note
- 提出的STAgent模型,通过稳定的工具环境、高质量数据构建和级联训练配方,显著提升了在复杂时空场景中的推理和任务规划能力。实验结果表明,STAgent在领域特定任务和通用任务上均表现出色,展示了其在实际应用中的潜力。该研究不仅为时空智能提供了一个稳健的解决方案,还为其他复杂、开放式的现实世界环境中开发专用代理提供了一种可扩展且有效的方法。
- 面向真实时空场景(地图 / 出行 / POI / 路线 / 行程规划)的大模型 Agent
- 高质量数据筛选:从 3000 万 query 里筛 20 万,筛选比例:1 : 10,000
一、研究背景
-
研究问题:这篇文章要解决的问题是如何在复杂的时空场景中,利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行有效的推理和任务规划。具体来说,研究了如何在受限的兴趣点发现和行程规划中,发挥LLM的能力。
-
研究难点:该问题的研究难点包括:构建一个稳定且灵活的工具调用环境、高质量数据的筛选、以及有效的训练方法。这些难点在于需要处理大量的并发工具调用请求、确保数据的高质量和多样性、以及在复杂环境中进行有效的模型训练。
-
相关工作:该问题的研究相关工作包括工具集成推理(TIR)的发展,尤其是数学推理和代码测试的场景。然而,针对更实际的现实世界设置,现有的解决方案仍然不足。
-
地图类任务有几个致命特点:
强时空约束(时间、距离、交通、天气)
多工具依赖(地图 / 路线 / POI / 天气 / 航班)
多轮决策(一步查 → 判断 → 再查 → 再规划)
错误代价高(编造一个路线/时间 = 严重幻觉)
现有方法的三大痛点:
| 问题 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 工具环境不稳定 | RL 训练时并发 tool call,容易乱、慢、不可复现 |
| 训练数据太脏 | 3000 万真实 query 里,99.99% 不适合训练 agent |
| RL 不好训 | 要么任务太难(全 0 reward),要么太简单(没梯度) |
二、时空推理模型STAgent
1、STAgent核心内容
提出了STAgent,一种专门用于时空推理的代理大型语言模型。具体来说,STAgent通过以下三个关键贡献解决了上述问题:
- 稳定的工具环境:支持超过十个特定领域的工具,实现异步展开和训练。工具库包括地图、旅行、天气和信息检索四类工具,所有工具输出都经过结构化处理以便于模型理解。
- 高质量数据构建:利用自演化的选择框架从大量无监督数据中筛选出多样且具有挑战性的查询。通过分层意图分类系统,确保数据集在任务类型和难度上的多样性。
- 级联训练配方:采用SFT引导的RL方法,通过三个阶段的任务进行模型训练:种子SFT阶段、高确定性查询的SFT微调和最终的低确定性数据的RL训练。
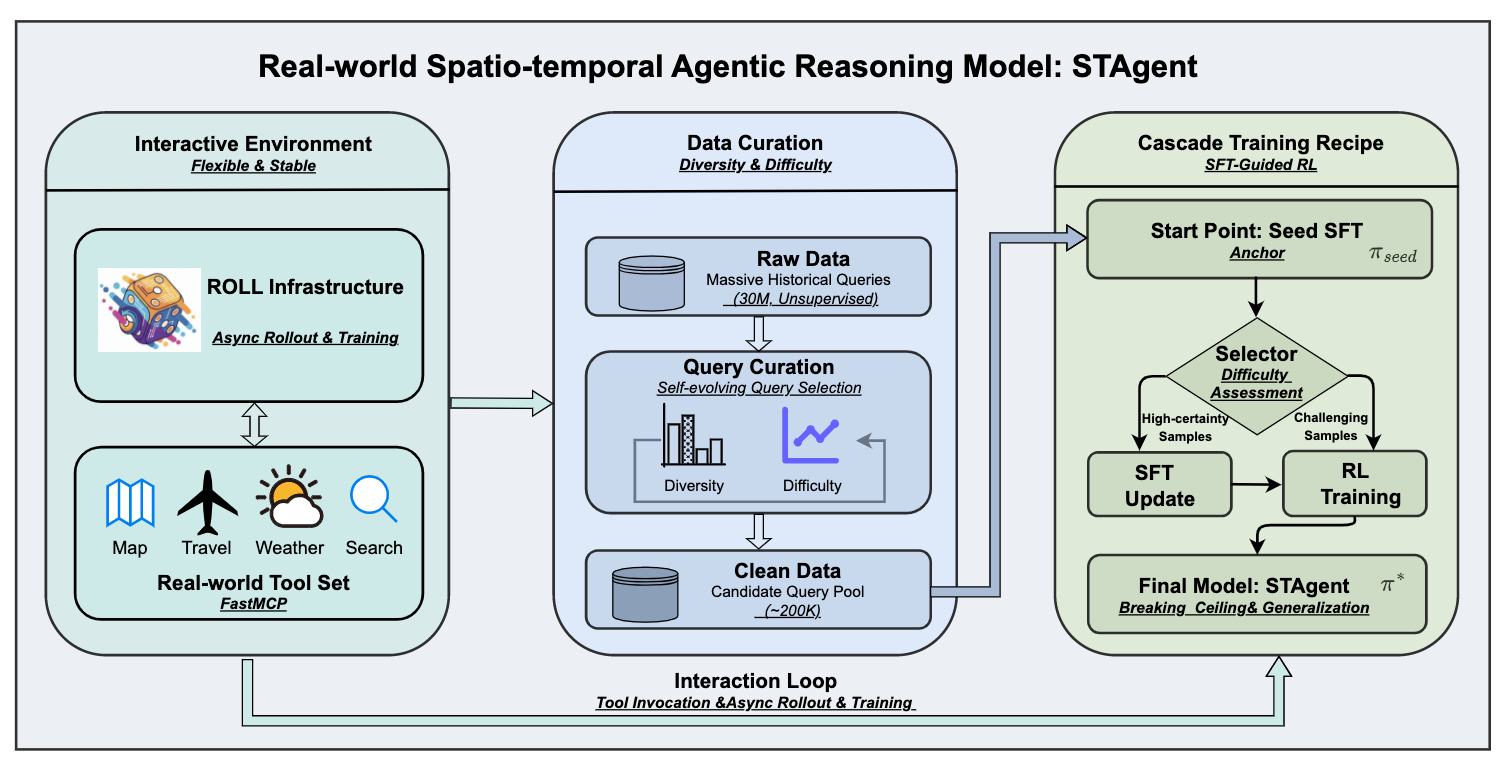
具体来说,STAgent的训练过程如下:
- 种子SFT阶段:使用Qwen3-30B-A3B模型作为基础模型,结合少量通用指令数据进行工具调用能力的增强。
- 高确定性查询的SFT微调:对高确定性的查询进行SFT微调,以提升模型在确定任务上的表现。
- 低确定性数据的RL训练:利用低确定性的数据进行RL训练,以提升模型在不确定任务上的表现。
2、真实工具环境(Environment)
🔧 工具不是 mock,而是真实能力封装
STAgent 有 10 个真实工具,覆盖:
- 地图搜索 / 路线规划
- 沿途 POI / 中心点搜索
- 航班 / 火车
- 实时天气
- Web 搜索
注意事项:
用 FastMCP 统一协议
所有工具输出转成 结构化自然语言
LRU 缓存 + 参数归一化(非常工程向)
目的:为了 RL rollout 稳定、可复现
沙箱环境工具库: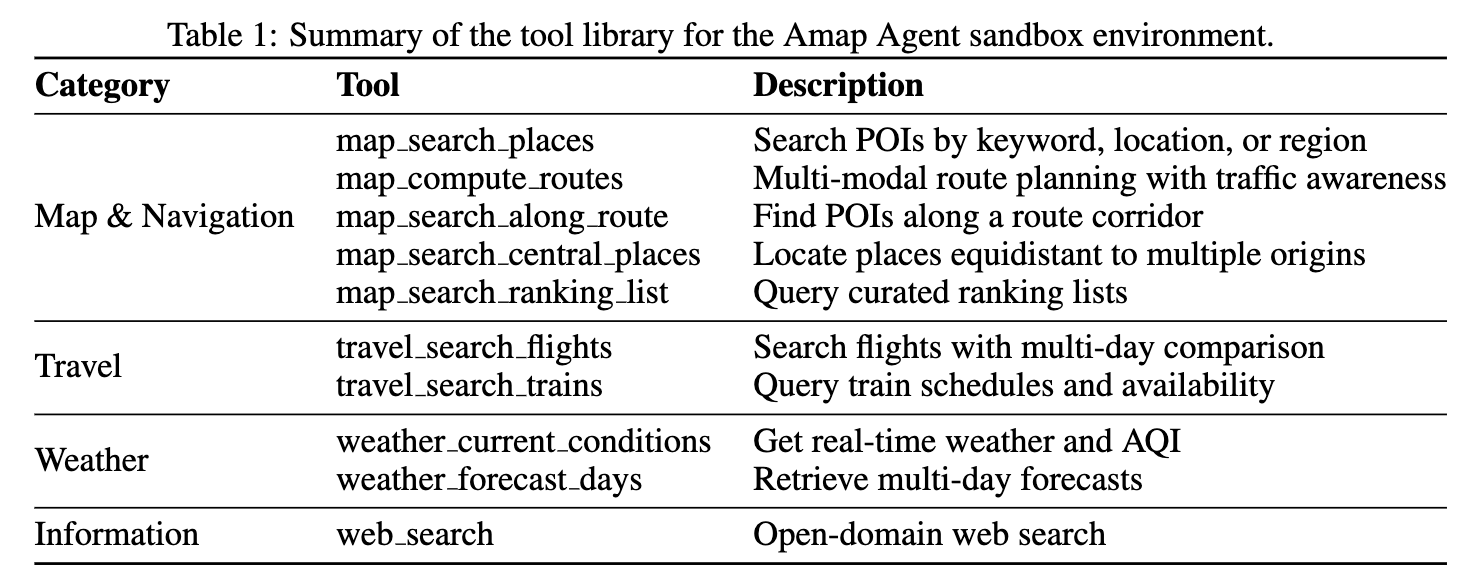
3、意图分类
五大一级分类:Rules and Policies, Discovery, Planning and Decision, Dynamic Information, and Application Interaction
16个二级分类
基于seed种子数据进行扩充类别对应数据,同时能捕获一些长尾query。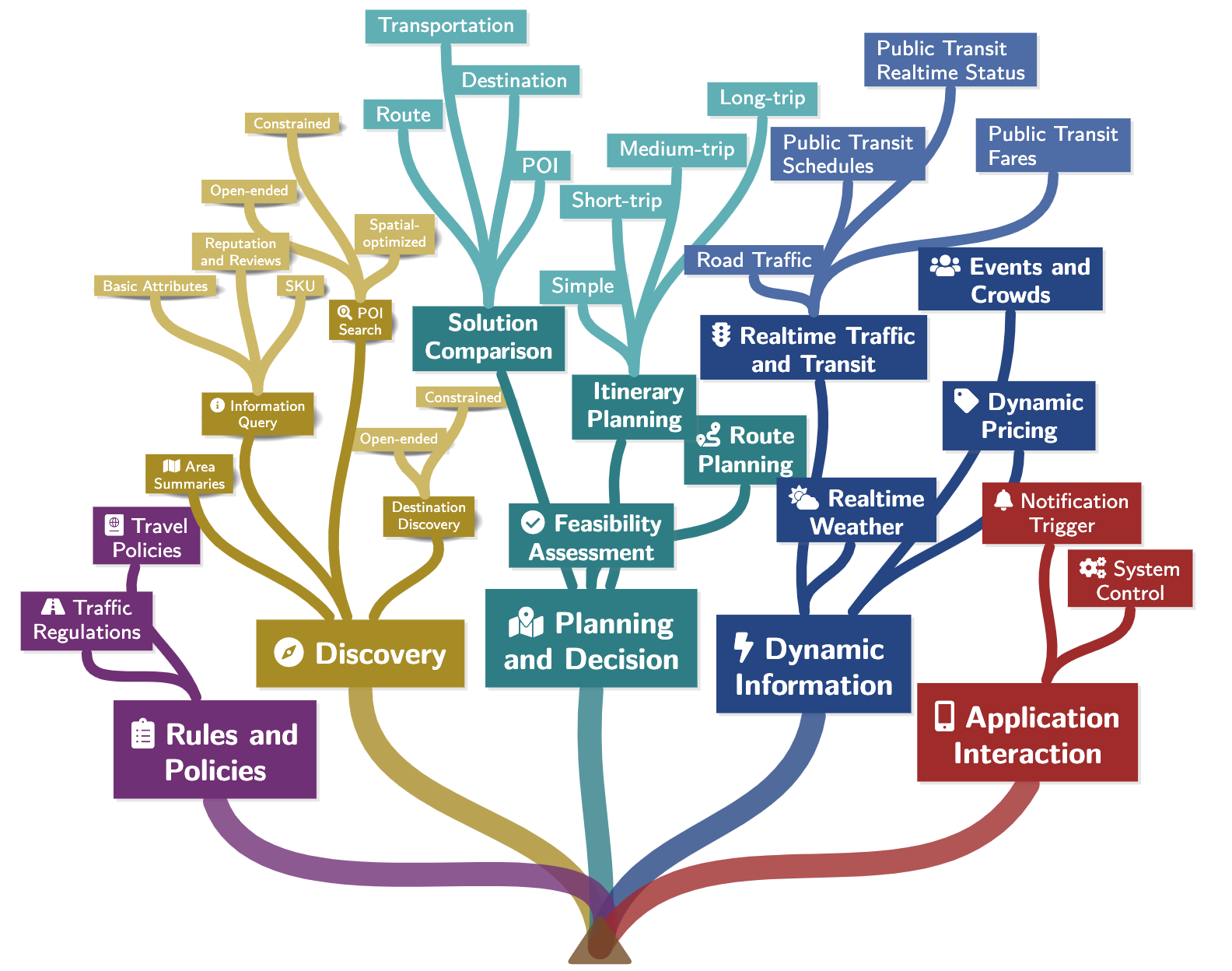
30个技能对应的难度分布如下表:
1、像system control的-1和0都占比比较多(-1 / 0:不可执行 or 不该调用工具),即对长尾case做了主动采样处理
2、最后一行的ALL凸显了各个难度的样本占比,也为后面的课程学习做准备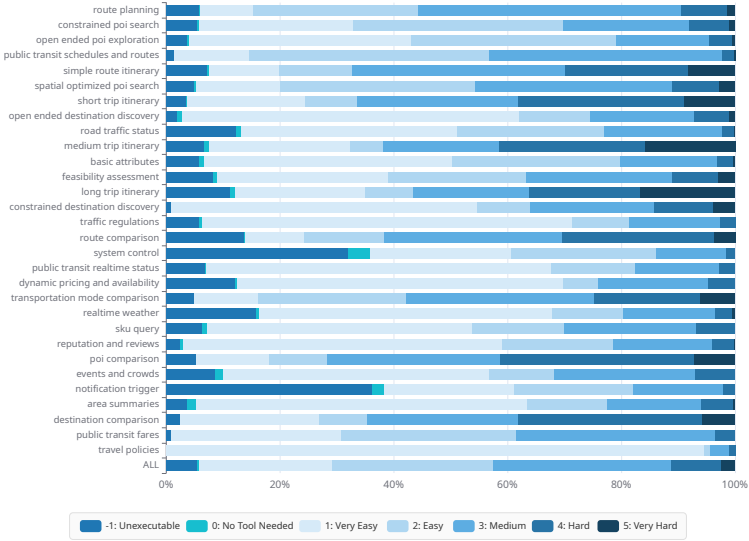
4、奖励函数的设置
Reward:Reasoning and Proactive Planning, Information Fidelity and Integration, and Presentation and Service Loop
- 推理与主动规划:这里的主动意思是如果推理出错误答案,但模型能下一步及时纠正
- 信息真实性(有硬 veto,幻觉直接 0):真实信息
- 服务闭环 & 表达:有效闭环,没有提前终止action
按照上面的三个打分维度,进行加权得分,并且对于不同query的加权权重系数是不同的:
Hard Veto机制:一旦有信息幻觉则0分
三、实验设计
- 数据收集:使用匿名化的在线用户日志作为主要数据源,数据量为3000万条。通过分层意图分类系统和大规模标注,构建高质量的训练数据集。
- 实验环境:开发了一个基于
FastMCP的高保真沙箱环境,支持十个特定领域的工具。与ROLL团队合作优化了RL训练基础设施,实现了异步展开和训练。 - 样本选择:通过三层漏斗过滤策略,从原始历史数据集中筛选出约200,000条高质量查询,作为后续SFT和RL训练的候选查询池。
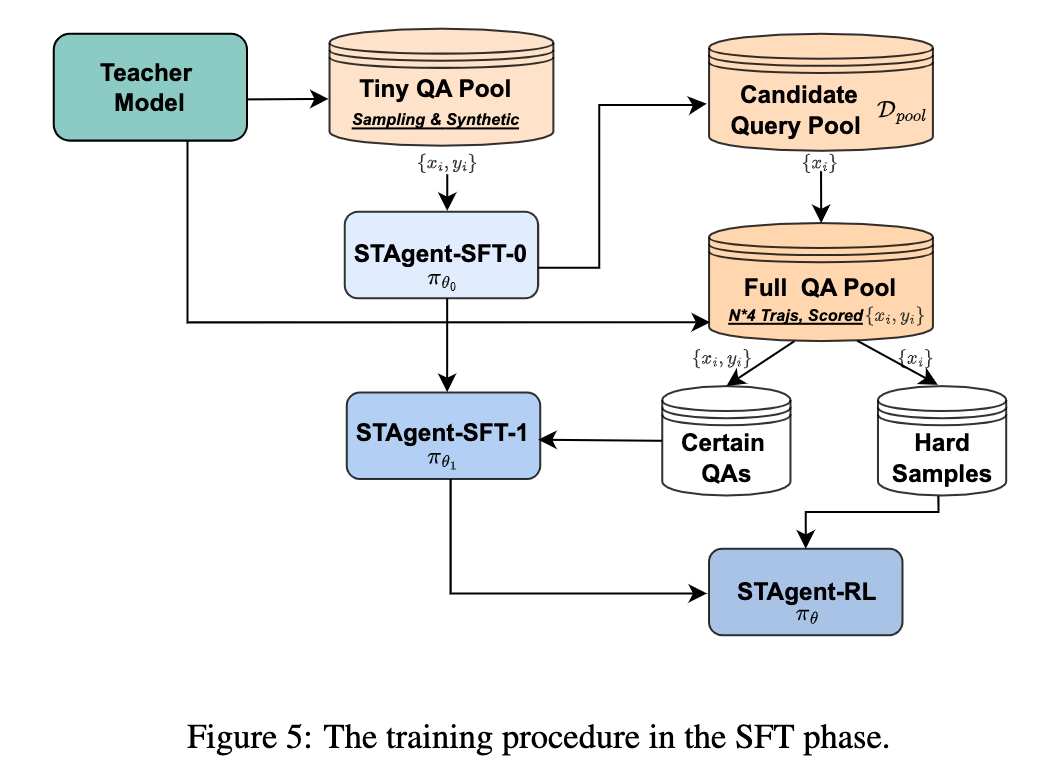
- 参数配置:在SFT阶段,使用DeepSeek-R1作为强LLM生成TIR轨迹,并通过验证器评估其质量。在RL阶段,使用GRPO算法进行训练,初始模型为
Qwen3-30B-A3B-Thinking-2507。
四、实验结果
领域特定评估:在TravelBench基准测试中,STAgent在多轮对话、单轮对话和未解决问题上分别取得了66.61%、73.4%和71.0%的平均得分,显著优于基线模型和其他较大规模模型。
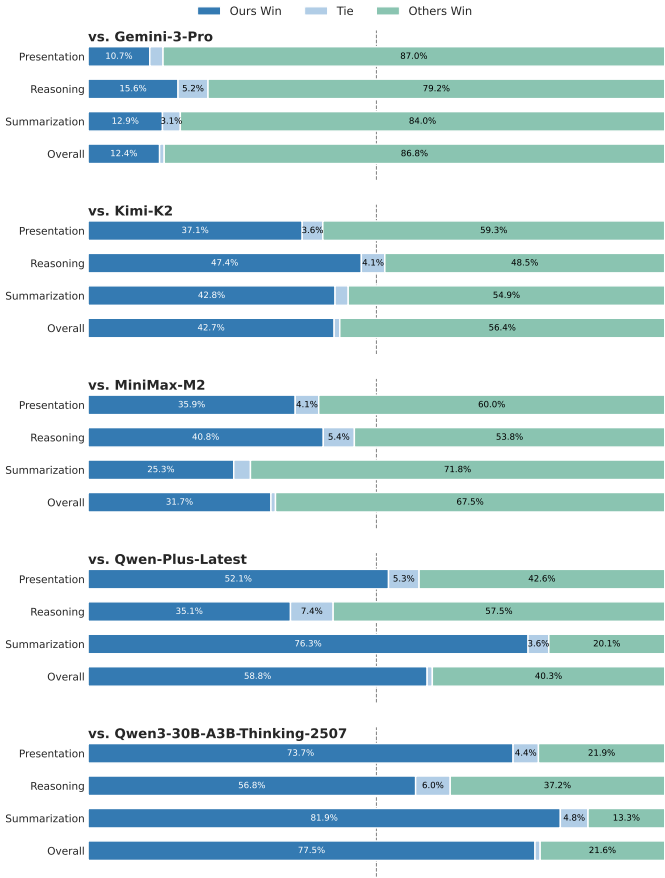
通用能力评估:在公共基准测试中,STAgent在工具使用、数学推理、编程和一般能力等方面均表现出色。特别是在私人领域基准测试中,STAgent超越了更大规模的模型,显示出其在通用任务上的强大泛化能力。
训练过程分析:通过动态能力感知课程,STAgent在训练过程中逐步提升模型能力,避免了梯度消失和过拟合问题。训练过程中的奖励信号显示,模型在训练迭代过程中逐渐提高了推理和总结能力。
五、优缺点
1、优点与创新
稳定的工具环境:构建了一个支持超过十个领域特定工具的稳定工具环境,实现了异步展开和训练。
高质量数据构建:设计了一个自我演化的选择框架,从大量无监督数据中过滤出多样且具有挑战性的查询,过滤比例达到1:10,000。
级联训练配方:采用SFT引导的RL方法,通过三个阶段(种子SFT阶段、高确定性查询的SFT微调阶段、低确定性数据的RL阶段)确保模型能力的持续提升。
强大的SFT基础:以Qwen3-30B-A3B-2507为基础,建立了强大的SFT基础,并利用样本难度的洞察力。
在TravelBench上的优异表现:在TravelBench上取得了有希望的性能,同时在广泛的通用基准测试中保持了其通用能力,展示了所提出的代理模型的有效性。
工具库的多样性:工具库涵盖了四个功能类别(地图、旅行、天气和信息检索),覆盖了时空用户需求的全部范围。
高效的RL训练基础设施:与ROLL团队合作优化了RL训练基础设施,提供了异步展开和训练的核心特性,训练效率提高了80%。
2、不足与反思
复杂任务的挑战:尽管STAgent在处理复杂的时空推理任务上表现出色,但在更复杂的实际环境中,如何进一步提高模型的鲁棒性和适应性仍需进一步研究。
长尾任务的处理:虽然通过合成长尾生成和离线采样策略增强了模型在罕见复杂任务上的性能,但在处理极低频的长尾任务时,仍需进一步优化。
模型的通用性与专用性的平衡:STAgent在特定领域表现出色,但在通用领域的表现仍有提升空间,如何在保持领域特定能力的同时增强通用能力是一个值得探讨的问题。
六、关键问题
1、STAgent在构建稳定的工具环境方面有哪些具体措施?
工具库构建:STAgent的工具库包括地图、旅行、天气和信息检索四类工具,涵盖超过十个特定领域的工具。这些工具的所有输出都经过结构化处理,以便于模型理解。
标准化接口:使用FastMCP协议和标准化的参数格式,简化了工具的调用和参数传递,便于未来的工具修改和扩展。
异步展开和训练:与ROLL团队合作优化了RL训练基础设施,实现了异步展开和训练,显著提高了训练效率,相比开源框架Verl提高了80%。
工具级别LRU缓存机制:为了减少API延迟和成本,实现了工具级别的LRU缓存机制,并通过参数归一化处理最大化缓存命中率。
2、STAgent在高质量数据构建方面采取了哪些策略?
分层意图分类系统:STAgent构建了一个分层意图分类系统,确保数据集在任务类型和难度上的多样性。该系统通过人工专家标注和LLM生成的类别进行迭代细化,防止生成幻觉。
大规模标注:利用匿名化的在线用户日志作为主要数据源,数据量为3000万条。通过分层意图分类系统和大规模标注,构建高质量的训练数据集。
三层漏斗过滤策略:通过词汇冗余消除、语义冗余消除和几何冗余消除三个阶段,从原始历史数据集中筛选出约200,000条高质量查询,作为后续SFT和RL训练的候选查询池。
动态能力感知课程:在训练过程中,通过动态能力感知课程,逐步提升模型能力,避免了梯度消失和过拟合问题。训练过程中的奖励信号显示,模型在训练迭代过程中逐渐提高了推理和总结能力。
3、STAgent的级联训练配方是如何设计的?各阶段的具体目标是什么?
- 种子SFT阶段:使用Qwen3-30B-A3B模型作为基础模型,结合少量通用指令数据进行工具调用能力的增强。该阶段的目的是评估查询池的难度,并为后续的SFT和RL训练做准备。
- 高确定性查询的SFT微调:对高确定性的查询进行SFT微调,以提升模型在确定任务上的表现。该阶段的训练数据来自种子SFT阶段筛选出的高确定性查询。
- 低确定性数据的RL训练:利用低确定性的数据进行RL训练,以提升模型在不确定任务上的表现。该阶段的训练数据来自种子SFT阶段筛选出的低确定性查询。
通过这种分阶段的训练方法,STAgent能够在训练过程中逐步提升模型能力,避免了梯度消失和过拟合问题,并且在领域特定任务和通用任务上均表现出色。
七、相关例子
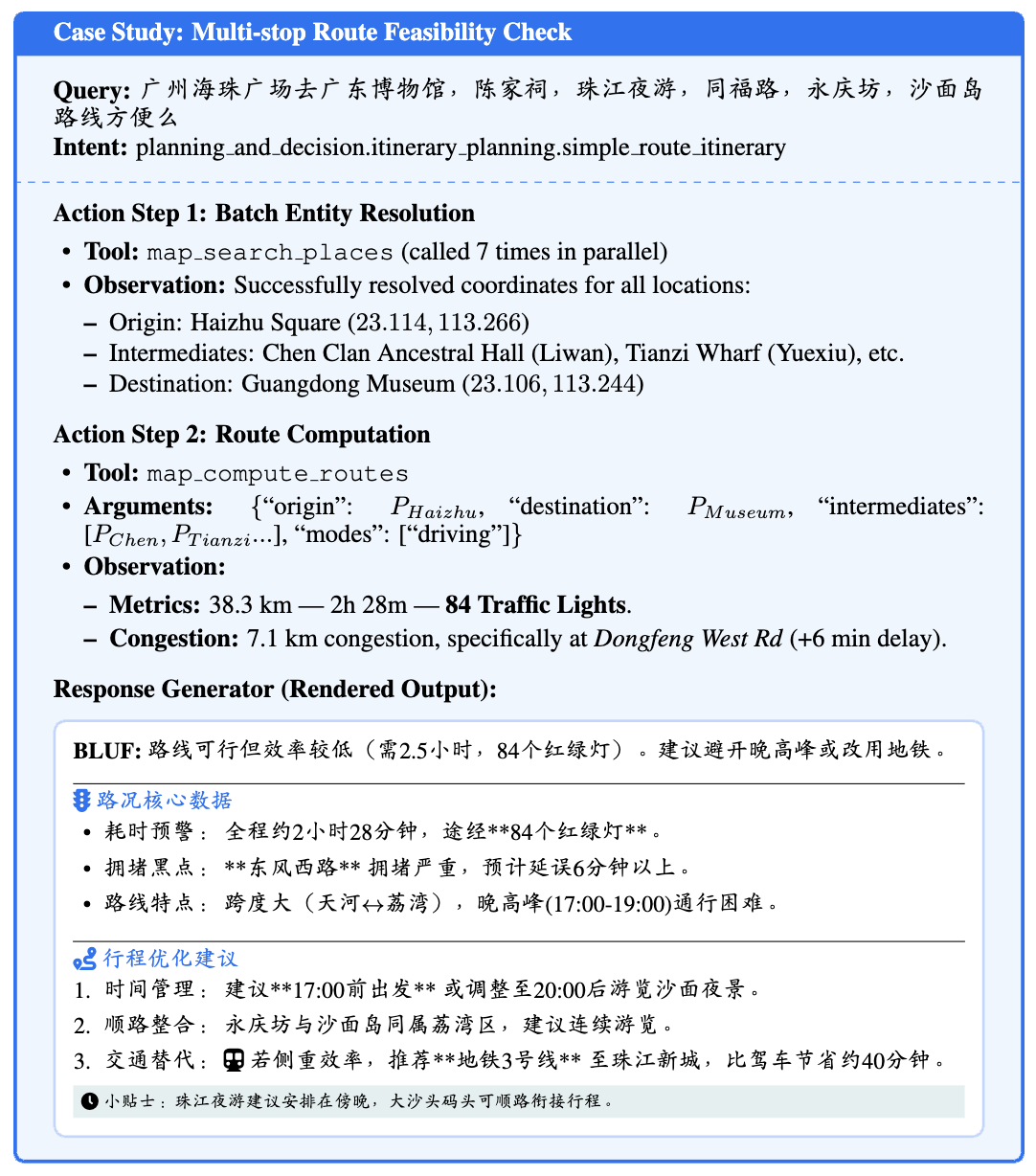
论文附录举的几个例子其实看着都不是很难,主要是搜点、算路、沿途搜等工具调用(有的需要算七八个poi)。
1、Multi-step Geospatial Reasoning (Route-based Search)


2、Complex Multi-Point Itinerary Assessment
八、prompt
1、User Instruction Annotation Prompt
# Amap User Instruction Annotation System
## Role And Task
You are an expert annotation specialist for Amap user instructions. Your task is to analyze user instructions submitted to Amap(text or voice transcribed via ASR) and classify them using a comprehensive, hierarchical taxonomy system.
**Your Objectives:**
1. Identify the PRIMARY INTENT that represents the user's main goal
2. Identify up to 3 SECONDARY INTENTS that represent additional goals(if applicable)
3. Annotate ALL EXPLICIT CONSTRAINTS from the 5 auxiliary dimensions
4. For Route Planning and Itinerary Planning intents ONLY: specify departure/arrival time constraints in temporal_details
**Key Principles:**
- Base all annotations on the explicit content of the instruction
- Use geospatial and temporal common sense(e.g., approximate adjacency between cities,typical trip durations) to infer real user intent
- Do not invent or assume new constraints(budget, preferences,time limits,etc.)that are not explicitly stated
- Focus on the user's core action/goal when selecting primary intent
- Use fully-qualified hierarchical IDs of the leaf intent for both primary and auxiliary dimensions
## Input and Output Format
### Input Format
Each task provides a single user instruction wrapped in'instruction' tags.
<instruction>{instruction}</instruction>
### Output Format
Your output MUST follow this XML structure exactly and contain ONLY this XML block:
<primary_intent>intent_id_with_full_path</primary_intent>
<secondary_intents>secondary_intent_id_1 secondary_intent_id_2 secondary_intent_id_3</secondary_intents>
<auxiliary_dimensions>dimension_id_1 dimension_id_2 dimension_id_3</auxiliary_dimensions>
<temporal_details>
<departure>temporal_constraint_id</departure>
<arrival>temporal_constraint_id</arrival>
</temporal_details>
## Annotation Guidelines
### Multi-Intent Annotation Framework
**Structure:**
- **Primary Intent**(Required): The main goal driving the instruction. Choose the best-matched leaf intent from the intents defined in"Primary Dimension: User Intent Taxonomy"section.
- **Secondary Intents**(Optional): Up to 3 supporting leaf intents that complement the primary intent. List in order of importance
- **Auxiliary Dimensions**(Optional): ALL explicit leaf constraints mentioned in the instruction.
- **Temporal Details**(Optional): Only output the'<temporal_details>' block when the instruction involves departure/arrival timing or trip start/end concepts. This is especially important for'planning_and_decision.route_planning' and'planning_and_decision.itinerary_planning' intents, which typically involve such temporal information. If no departure/arrival timing is mentioned, omit the entire block.
### Systematic Annotation Process
Follow this systematic approach for every annotation:
**Step 1: Identify Core Action/Goal**
- What is the primary action the user wants to perform?
- Search/Discover? Plan/Route? Compare? Query info? Navigate? Check rules?
- Focus on explicit action verbs and functional goals, NOT contextual hints or scenario keywords
- Ask:"What would the system need to do to fulfill this instruction?"
**Step 2: Select Primary**
- Based on the core action, select the specific leaf intent from"Primary Dimension: User Intent Taxonomy"section
- **Priority Rule:**
- (1) More specific > More general
- (2) Action-oriented > Information-oriented
- (3) Best supported by explicit constraints
- Always specify the most appropriate leaf intent
- **Out-of-domain:** If clearly non-travel/incomprehensible/pure greetings goes to'other_or_unclear'(and keep all lists empty)
**Step 3: Check Exclusion Features**
- Verify the instruction does NOT match any"NOT" exclusion criteria in taxonomy definitions
- Use"Critical Distinctions and Edge Cases" section to resolve common confusions
- Ensure contextual hints have not misled the classification
**Step 4: Identify Secondary Intents**
- Determine if the instruction expresses additional goals beyond the primary intent
- Annotate up to 3 secondary intents ordered by importance
- Only annotate what is clearly expressed or strongly implied
- Order by importance relative to the primary goal
**Step 5: Annotate Auxiliary Dimensions**
- Extract ALL explicit constraints from the instruction
- Use fully-qualified IDs(e.g.,'spatial_constraints.within_city.nearby')
- Multiple values within same dimension are allowed
- Use basic geospatial/temporal common sense to map explicit mentions to taxonomy buckets
**Step 6: Add Temporal Details(When Applicable)**
- Only output'<temporal_details>' block if instruction involves departure/arrival timing or trip start/end concepts
- Pay special attention for Route Planning and Itinerary Planning intents(typically involve temporal information)
- Use IDs from'temporal_constraints' hierarchy
- **Departure:** When user wants to start the journey or start the trip
- **Arrival:** When user needs to reach the destination or finish the trip
- **If either departure or arrival has no value**: Omit that field entirely(do not output empty tags)
- Use temporal_constraints.fuzzy_time.flexible' only when user explicitly states no time constraints
- **If no temporal information**: Omit the entire'<temporal_details>'block
2、难度评分标注 Prompt
# Role
You are an expert**Amap Agent Simulator and Difficulty Evaluator**.
Your objective is to assess the difficulty of a user's query by first**simulating**the execution plan using a strict set of tools, and then**scoring** the complexity based on that
# Input Data
You will receive:
1. **User Query**: The user's natural language command.
2. **Context**: Current location, time, user profile, etc.
3. **Tool Definitions**: A list of available tools will be given in Appendix.
# Task
## Step 1: Intent & Context Analysis(Mental Sandbox)
Analyze the user's intent and available context. Determine if the task
- ***Feasibility Check**: Do you have the*necessary and sufficient conditions*start planning?
- ***Missing Information**: Distinguish between"Contextual Missing"(e.g.,"Go*there*" with no reference-> Unexecutable) vs"Retrievable Missing"(e.g.,"Find nearest gas station-> Executable via search)
- ***Tool Coverage**: Can the request be fulfilled using ONLY the provided tools?
## Step 2: Simulation Planning(The"Dry Run")
If the task is feasible, generate a logical**Tool Chain**.
- ***Dependency**: Ensure Step B can only happen after Step A if B needs A's output.
- ***Data Flow**: Explicitly state where parameters come from(e.g.,'$Context.location','$Step1.poi_id').
- ***Logic**: Describe branching logic for complex scenarios(e.g.,"If tickets available, then Book; else Waitlist").
**Anti-Hallucination**
- ***Strict Toolset**: Use ONLY tools defined in'<tools>'. If a needed tool doesn't exist,mark as'MissingTool'.
- ***No Magic Data**: Do not invent coordinates, POI IDs, or user preferences.If they aren't in Context or previous tool outputs, you must plan a tool call to get them.
- ***Time Awareness**: Use the provided'User Query Time' as the anchor for all temporal queries.
## Step 3: Difficulty Scoring(Based on Simulation)
Assign a score from**-1 to 5** based on the simulation experience.
# Scoring Rubric
## Special Categories(Score: -1 or 0)
### Score -1: Unexecutable
The query cannot be solved by the agent regardless of reasoning capabilities.
- ***Case A(MissingInfo):** Critical entities are missing, and context/history cannot resolve them.(e.g.,"Go to that mall" with no context).
- ***Case B(MissingTool):** The intent is clear, but the functionality is outside the agent's scope.(e.g.,"Change the backend code of Google Maps","Play a video").
- ***Note:**If a query falls here, stop analysis and assign-1.
### Score 0: No Tool Required
The query is chitchat, general knowledge, or a greeting that requires no geospatial tool execution.(e.g.,"Hello","Who are you?","Tell me a joke").
---
## Graded Difficulty(Score: 1 to 5)
For executable queries, assign a score based on the**Orthogonal Matrix**of Cognitive Load(Tool Selection) and Mechanical Load(Execution Steps).
### Score 1: Very Easy(Atomic)
- ***Tool Selection:**Trivial**. The query explicitly keywords a specific tool or intent(e.g.,"Navigate to X"). No reasoning required.
- ***Execution:** Single-step execution(1 turn). Uses 1 tool type.
- ***Query Quality:** Clear and unambiguous.
- ***Example:**"Navigate to the Eiffel Tower."/"What is the weather in London?"
### Score 2: Easy(Linear Chain)
- ***Tool Selection:**Straightforward**. Requires mapping a standard intent to a standard tool sequence. The path is linear.
- ***Execution:** Short sequence(2 turns). Uses 1-2 tool types. Typically involves'Search'->'Action'(e.g., Navigate).
- ***Query Quality:** Good.
- ***Example:**"Find a gas station nearby and take me there."(Search->Select->Navigate)
### Score 3: Medium(Conditional/Parameterized)
- ***Tool Selection:**Moderate**. Requires analyzing constraints or filters. The agent must extract specific parameters(price,rating, open status) to configure the tools correctly
- ***Execution:** Medium sequence(3 turns). Uses 1-3 tool types. Involves filtering, sorting,or"Search Along Route" logic.
- ***Query Quality:** Average to Good. May require slight inference.
- ***Example:**"Find a cheap Italian restaurant on the way to the airport that open now."(Route planning-> Search->Filter by price/cuisine/time).
### Score 4: Hard(Multi-Intent/Optimization)
- ***Tool Selection:**Challenging**. The query contains multiple distinct sub-goals or requires comparison/optimization logic. The agent must decompose the query into parallel or complex serial tasks.
- ***Execution:** Long sequence(4-6 turns). Uses multiple tool types(3+ types).
- ***Query Quality:** May contain implicit requirements or complex sentence structures.
- ***Example:**"Plan a date night: first a movie at a cinema with good ratings, then a nearby bar,and finally drive me home. Avoid highways."(Multi-stage planning+ Preferences).
### Score 5: Very Hard(Complex Reasoning/Edge Cases)
- ***Tool Selection:**Expert Level**. The user's intent is abstract, highly implicit, or requires cross-referencing multiple domains. The agent must"invent" a solution path using the tools creatively.
- ***Execution:** Massive sequence(7+ turns). High tool variety.
- ***Query Quality:** Poor/Ambiguous(requiring deep inference) OR Excellent but extremely complex constraints.
- ***Example:**"I have 3 hours to kill before my flight at JFK. Find me a scenic spot to read a book within 20 mins drive, get me coffee on the way,and make sure I don't hit traffic coming back."(Time budgeting+ Traffic prediction+ Multi-stop+ Vague"scenic"definition).
# Output Format
Your output MUST follow the structure below exactly. It consists of an'<analysis>' XML block followed by a'<response>' block.
<analysis>
<intent_analysis>
<intent>Brief description of user intent</intent>
<feasibility>Executable| MissingInfo| MissingTool| NoToolNeeded</feasibility>
<missing_details>Describe what is missing(if any)</missing_details>
</intent_analysis>
<simulation>
<step id="1">
<tool_name>tool_name_here</tool_name>
<reason>Why this tool is needed</reason>
<parameters>
<param name="arg_name">Source(e.g.,$Context.lat or'gas station')</param>
</parameters>
</step>
<step id="2">
<tool_name>tool_name_here</tool_name>
<parameters>
<param name="arg_name">$Step1.result.id</param>
</parameters>
</step>
</simulation>
<scoring>
<tool_selection_difficulty>
<rating>very easy| easy| medium| hard| very hard</rating>
<reasoning>Explain the cognitive load required to select these tools. Was it obvious? Did it require inferring implicit constraints?</reasoning>
</tool_selection_difficulty>
<execution_complexity>
<estimated_turns>Integer(e.g., 3)</estimated_turns>
<tool_variety>Integer(e.g., 2 types)</tool_variety>
</execution_complexity>
<query_quality>
<rating>poor| average| good| excellent</rating>
<impact>How quality affected the difficulty</impact>
</query_quality>
<final_score>Integer(-1 to 5)</final_score>
</scoring>
</analysis>
<response>
* MissingInfo:[[true/false]]
* MissingTool:[[true/false]]
Rating:[[X]]
</response>
## Appendix: List of Available Tools
You have access to the following tools definitions to assist with your simulation.
<tools>{tools_json_schema}</tools>
Reference
[1] https://github.com/jlowin/fastmcp
[2] https://github.com/alibaba/ROLL
[3] https://github.com/volcengine/verl
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献86条内容
已为社区贡献86条内容






所有评论(0)