Agent架构解析与实战(四)--Planning
从「摸着石头过河」到「运筹帷幄」:Planning Agent 架构全解析—— 深度对比 ReAct vs Planning,手把手教你用 LangGraph 构建下一代智能体
目录
1. 架构定义
Planning(规划) 架构是一种引入前瞻性决策层的智能体设计模式。与 ReAct 模式的"边走边看"不同,Planning Agent 会在采取任何行动之前,先将复杂任务分解为一系列可管理的子目标,制定完整的"作战计划"。
核心理念
| 特性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 前瞻性 | 在执行前完成全部规划 |
| 结构化 | 任务被分解为有序的步骤列表 |
| 可预测 | 整个执行路径在开始时就已确定 |
Planning vs ReAct 核心区别
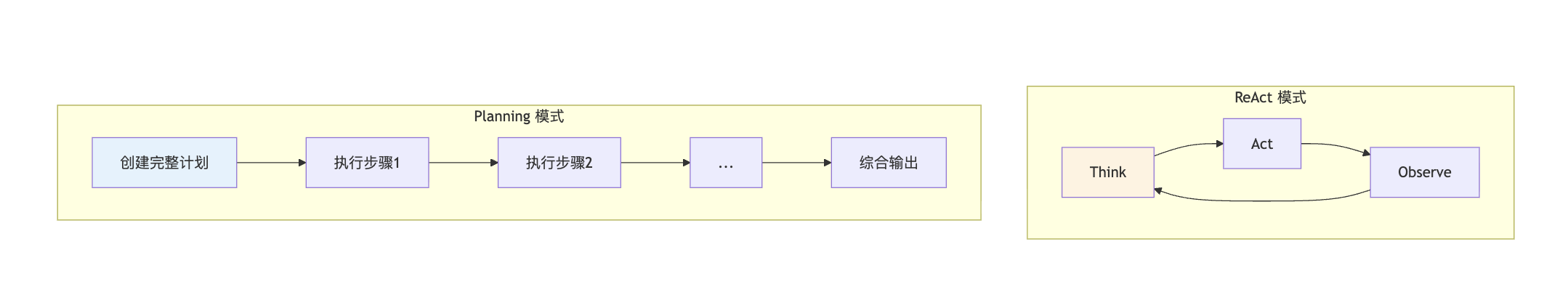
[!IMPORTANT] 🎯 核心创新
Planning 架构的核心创新在于分离关注点:
Planner(规划者):负责分析问题并制定计划
Executor(执行者):负责按计划执行每一步
Synthesizer(综合者):负责整合所有结果
2. 宏观工作
Planning 架构遵循 "接受任务 → 创建计划 → 执行计划 → 合成结果" 的线性流程:
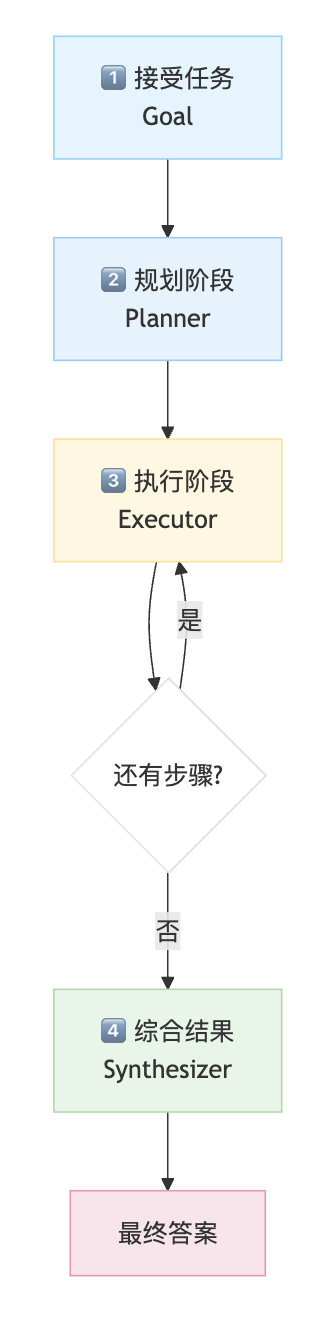
详细步骤说明
| 步骤 | 组件 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 接受任务 | 智能体接收复杂任务 | "比较三个城市的人口与英国的人口" |
| 2 | 创建计划 | Planner 分析目标,生成有序的子任务列表 | ["搜索北京人口", "搜索上海人口", ...] |
| 3 | 执行计划 | Executor 按顺序执行每个子任务,使用工具获取结果 | 依次调用 web_search 工具 |
| 4 | 合成结果 | Synthesizer 整合所有中间结果,生成最终答案 | 汇总数据并进行比较 |
3. 应用场景
| 场景 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 多步骤工作流 | 操作顺序已知且关键的任务 | 生成报告:获取数据 → 处理 → 总结 |
| 项目管理助手 | 将大目标分解为团队子任务 | "发布新功能" → 设计、开发、测试、部署 |
| 教育辅导 | 创建教学计划 | 从基础原理 → 高级应用的课程规划 |
| 数据收集 | 需要从多个来源收集信息 | 比较多个实体的属性 |
4. 优缺点分析
✅ 优点
| 优点 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 结构化 & 可追溯 | 整个工作流预先铺设,过程透明、易于调试 |
| 高效 | 对于可预测任务,避免了步骤间不必要的推理循环 |
| 减少 LLM 调用 | 规划一次,执行多次,无需每步都调用 LLM 决策 |
| 并行潜力 | 独立步骤理论上可以并行执行 |
❌ 缺点
| 缺点 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 脆弱性 | 预制计划在执行过程中环境发生变化时可能失败 |
| 适应性差 | 不如 ReAct 灵活,无法根据中间结果调整计划 |
| 依赖计划质量 | 如果初始计划有缺陷,整个执行都会受影响 |
[!WARNING] ⚠️ 何时不适用
Planning 架构不适用于:
探索性任务(不知道下一步需要什么信息)
高度动态的环境
需要根据中间结果调整策略的场景
5. 代码实现详解
5.1 环境配置
依赖库安装
pip install -U langchain-openai langchain langgraph python-dotenv rich tavily-python pydantic langchain-core
5.2 导入库并设置密钥
import os
from typing import List, Annotated, TypedDict, Optional
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# LangChain 组件
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from tavily import TavilyClient
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage, ToolMessage
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage
# LangGraph 组件
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
from langgraph.graph.message import AnyMessage, add_messages
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
# 输出美化
from rich.console import Console
from rich.markdown import Markdown
# --- API 密钥以及追踪设置 ---
load_dotenv()
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2"] = "true"
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_PROJECT"] = "Agentic Architecture - Planning (GPT)"
# 确保密钥已载入
for key in ["OPENAI_API_KEY", "LANGCHAIN_API_KEY", "TAVILY_API_KEY"]:
if not os.environ.get(key):
print(f"{key} not found. Please create a .env file and set it.")
print("Environment variables loaded and tracing is set up.")
运行结果:
Environment variables loaded and tracing is set up.
5.3 基础对照:ReAct Agent
为了理解 Planning 的价值,首先构建 ReAct Agent 作为基准对比。
console = Console()
# 定义图的状态
class AgentState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list[AnyMessage], add_messages]
# 定义基础的 Tavily 搜索工具
client = TavilyClient(os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"])
@tool
def web_search(query: str) -> str:
"""基于传入的信息在网络上搜索相关信息"""
result = client.search(query, max_results=2)
return str(result["results"])
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0.2,
api_key=os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"],
base_url="https://api.openai.com/v1"
)
llm_with_tool = llm.bind_tools([web_search])
# Agent 节点:强制每次只调用一个工具
def react_agent_node(state: AgentState):
console.print("--- ReAct Agent: Thinking... ---")
messages_with_system_prompt = [
SystemMessage(content="You are a helpful research assistant. You must call one and only one tool at a time. Do not call multiple tools in a single turn. After receiving the result from a tool, you will decide on the next step.")
] + state["messages"]
response = llm_with_tool.invoke(messages_with_system_prompt)
return {"messages": [response]}
# 构建 ReAct 图
tool_node = ToolNode([web_search])
react_graph_builder = StateGraph(AgentState)
react_graph_builder.add_node("agent", react_agent_node)
react_graph_builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
react_graph_builder.set_entry_point("agent")
react_graph_builder.add_conditional_edges("agent", tools_condition)
react_graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "agent")
react_graph_app = react_graph_builder.compile()
print("ReAct tool-using agent compiled successfully.")
运行结果:
ReAct tool-using agent compiled successfully.
ReAct Agent 架构图
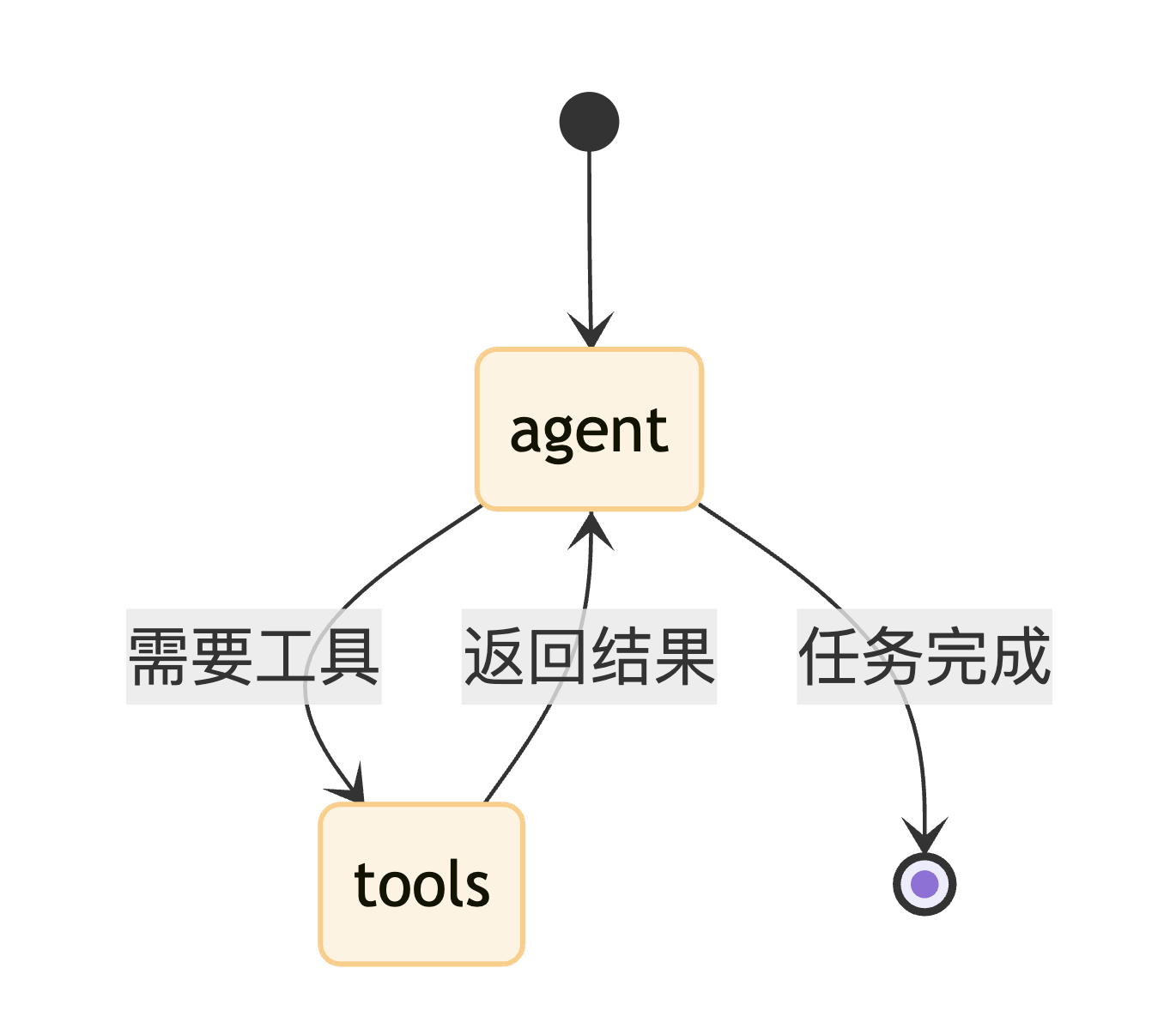
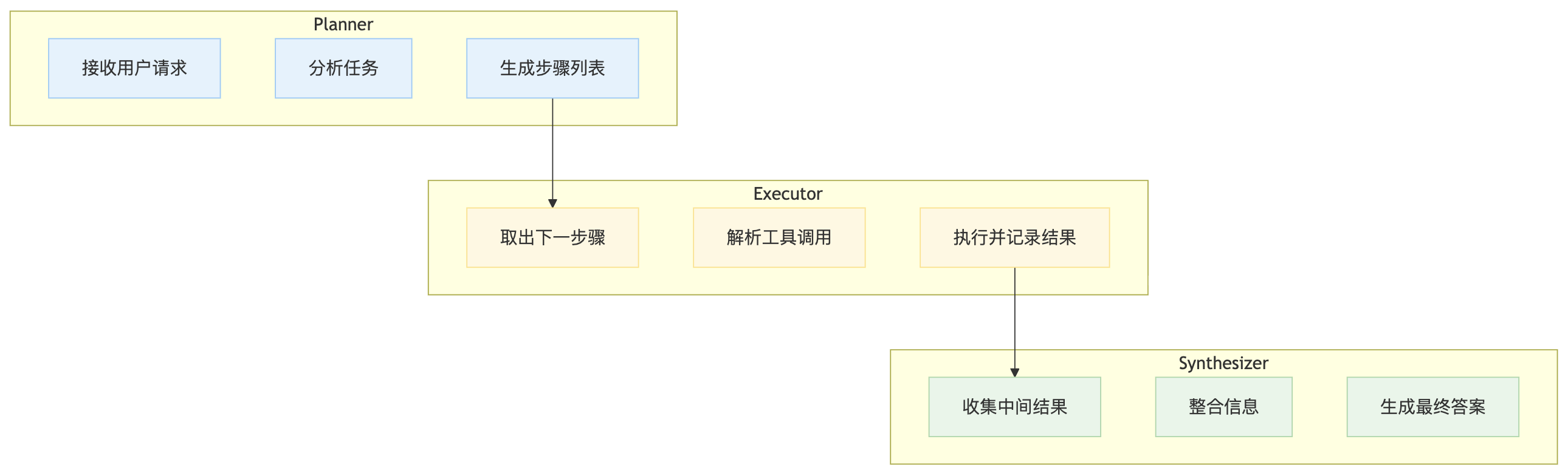
5.4 Planning Agent 核心组件
Planning Agent 由三个核心节点组成:
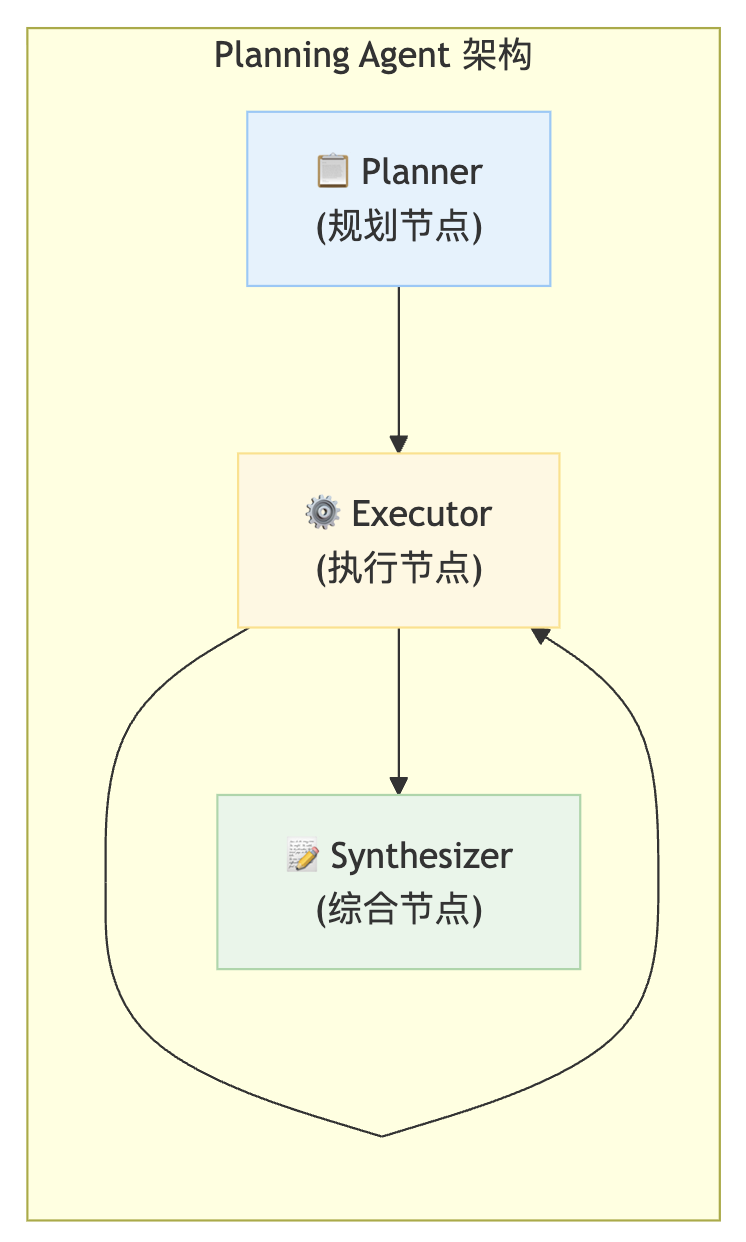
核心组件职责
| 节点 | 职责 | 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 📋 Planner | 分析任务,生成计划 | 用户请求 | 步骤列表 |
| ⚙️ Executor | 按计划执行工具调用 | 当前步骤 | 执行结果 |
| 📝 Synthesizer | 整合所有结果 | 中间步骤列表 | 最终答案 |
5.4.1 定义计划、执行、合成节点
from langchain_core.messages import ToolMessage
import re
# 使用 Pydantic 确保计划节点的输出是结构化的步骤列表
class Plan(BaseModel):
"""A plan of tool calls to execute to answer the user's query."""
steps: List[str] = Field(description="A list of tool calls that, when executed, will answer the query.")
# 定义计划 Agent 的状态
class PlanningState(TypedDict):
user_request: str
plan: Optional[List[str]]
intermediate_steps: List[ToolMessage]
final_ans: Optional[str]
def planner_node(state: PlanningState):
"""Generates a plan of action to answer the user's request."""
console.print("--- PLANNER: 解析任务... ---")
plan_llm = llm.with_structured_output(Plan)
prompt = f"""You are an expert planner. Your job is to create a step-by-step plan to answer the user's request.
Each step in the plan must be a single call to the `web_search` tool.
**Instructions:**
1. Analyze the user's request.
2. Break it down into a sequence of simple, logical search queries.
3. Format the output as a list of strings, where each string is a single valid tool call.
**Example:**
Request: "What is the capital of France and what is its population?"
Correct Plan Output:
[
"web_search('capital of France')",
"web_search('population of Paris')"
]
**User's Request:**
{state['user_request']}
"""
plan_res = plan_llm.invoke(prompt)
console.print(f"--- PLANNER: 计划输出: {plan_res.steps} ---")
return {"plan": plan_res.steps}
def executor_node(state: PlanningState):
"""Executes the next step in the plan"""
console.print("--- EXECUTOR: 执行计划... ---")
plan = state["plan"]
next_step = plan[0]
# 使用正则表达式匹配单引号和双引号
match = re.search(r"(\w+)\((?:\"|\'|)(.*?)(?:\"|\'|)\)", next_step)
if not match:
tool_name = "web_search"
query = next_step
else:
tool_name, query = match.groups()[0], match.groups()[1]
console.print(f"--- EXECUTOR: 调用工具 '{tool_name}' 处理 '{query}' ---")
res = web_search.invoke(query)
# 创建 tool message
tool_msg = ToolMessage(
content=str(res),
name=tool_name,
tool_call_id=f"manual-{hash(query)}"
)
return {
"plan": plan[1:],
"intermediate_steps": state["intermediate_steps"] + [tool_msg]
}
def synthesizer_node(state: PlanningState):
"""Synthesizes the final answer from the intermediate steps."""
console.print("--- SYNTHESIZER: 组装结果... ---")
context = "\n".join([f"Tool {msg.name} returned: {msg.content}" for msg in state["intermediate_steps"]])
prompt = f"""You are an expert synthesizer. Based on the user's request and the collected data, provide a comprehensive final answer.
Request: {state['user_request']}
Collected Data:
{context}
"""
final_ans = llm.invoke(prompt).content
return {"final_ans": final_ans}
print("计划、执行、合成节点创建完毕")
运行结果:
计划、执行、合成节点创建完毕
[!TIP] 💡 关键设计
Planner 使用
with_structured_output确保输出格式化的步骤列表Executor 使用正则表达式解析工具调用,并维护中间步骤列表
Synthesizer 整合所有中间结果,生成最终答案
5.4.2 创建 Planning Agent 图
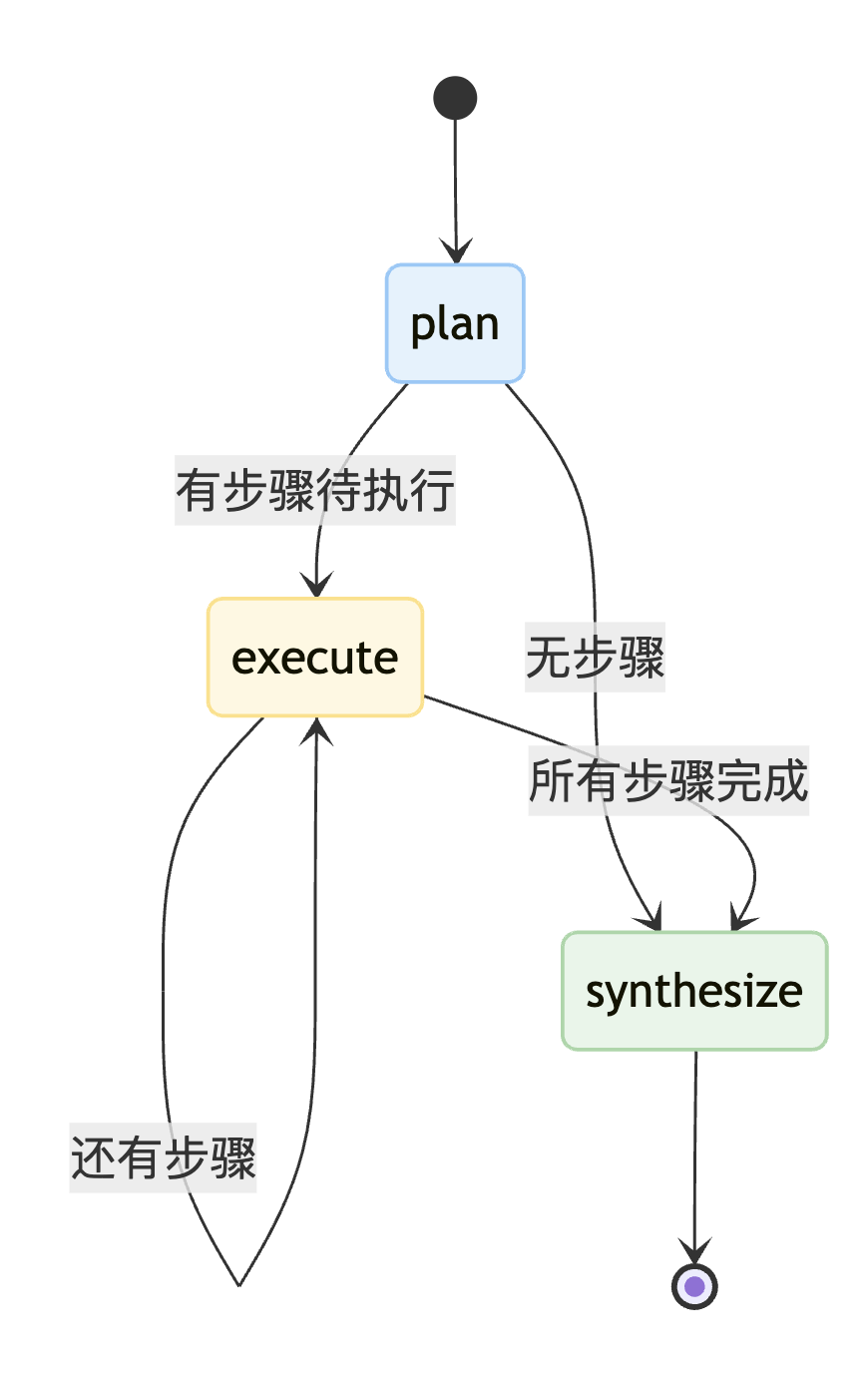
def planning_router(state: PlanningState):
if not state["plan"]:
console.print("--- ROUTER: 计划结束,开始生成答案。---")
return "synthesize"
else:
console.print("--- ROUTER: Plan has more steps. Continuing execution. ---")
return "execute"
planning_graph_builder = StateGraph(PlanningState)
planning_graph_builder.add_node("plan", planner_node)
planning_graph_builder.add_node("execute", executor_node)
planning_graph_builder.add_node("synthesize", synthesizer_node)
planning_graph_builder.set_entry_point("plan")
planning_graph_builder.add_conditional_edges("plan", planning_router, {"execute": "execute", "synthesize": "synthesize"})
planning_graph_builder.add_conditional_edges("execute", planning_router, {"execute": "execute", "synthesize": "synthesize"})
planning_graph_builder.add_edge("synthesize", END)
planning_graph_app = planning_graph_builder.compile()
print("Planning tool-using agent compiled successfully.")
运行结果:
Planning tool-using agent compiled successfully.
Planning Agent 架构图
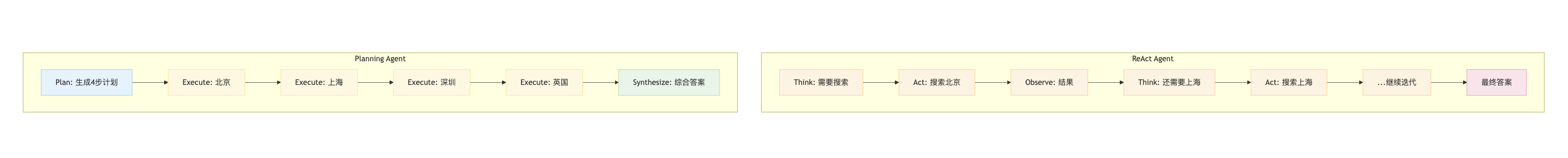
5.5 对比测试
使用同一个需要多步骤的问题测试两种 Agent:
plan_centric_prob = """
分别找出北京、上海、深圳三个城市的2025年的总人口数。
然后算出这三个城市的总人口之和。
最后,将这三个城市的总人口之和与英国的总人口数比较,并告诉我哪个更大。
"""
5.5.1 ReAct Agent 执行过程
ReAct Agent 采用迭代探索方式:
--- ReAct Agent: Thinking... ---
================================ Human Message ================================
分别找出北京、上海、深圳三个城市的2025年的总人口数...
--- ReAct Agent: Thinking... ---
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Calls:
web_search (call_xxx)
Args:
query: 北京 2025 年 总人口 上海 2025 年 总人口 深圳 2025 年 总人口 英国 2025 年 总人口
[多次迭代搜索后...]
--- ReAct Agent的最终输出 ---
我用官方统计数据做比较...
- 北京:2183.2 万人
- 上海:2480.26 万人
- 深圳:1798.95 万人
- 合计 = 64,624,100(约 6462.41 万人)
- 英国(ONS mid-2025):69,487,000(约 6948.7 万人)
- 比较结果:英国人口更大
5.5.2 Planning Agent 执行过程
Planning Agent 采用先规划后执行方式:
--- PLANNER: 解析任务... ---
--- PLANNER: 计划输出: ["web_search('北京市 2025 年 总人口')",
"web_search('上海市 2025 年 总人口')",
"web_search('深圳市 2025 年 总人口')",
"web_search('英国 2025 年 总人口')"] ---
--- ROUTER: Plan has more steps. Continuing execution. ---
--- EXECUTOR: 执行计划... ---
--- EXECUTOR: 调用工具 'web_search' 处理 '北京市 2025 年 总人口' ---
--- ROUTER: Plan has more steps. Continuing execution. ---
--- EXECUTOR: 执行计划... ---
--- EXECUTOR: 调用工具 'web_search' 处理 '上海市 2025 年 总人口' ---
[继续执行剩余步骤...]
--- ROUTER: 计划结束,开始生成答案。---
--- SYNTHESIZER: 组装结果... ---
--- 最终结果 ---
1. 各城 2025 年总人口
- 北京:2300 万人
- 上海:2487 万人(估计)
- 深圳:2237.88 万人
2. 三城人口之和 ≈ 70.25 百万
3. 与英国比较
- 英国 ≈ 69.5 百万
- 结论:三城总人口略大于英国
执行流程对比
| Agent | 执行步骤 | LLM调用次数 |
|---|---|---|
| ReAct | Think → Act → Observe → Think → Act → ... → 最终答案 | 多次(每步都要决策) |
| Planning | Plan → Execute × 4 → Synthesize |
较少(规划1次+综合1次) |
6. 评估方法
使用 LLM-as-a-Judge 对两种 Agent 进行量化评估:
6.1 评估代码
class ProcessEvaluation(BaseModel):
"""Schema for evaluating an agent's problem-solving process."""
task_completion_score: int = Field(description="Score 1-10 on whether the agent successfully completed the task.")
process_efficiency_score: int = Field(description="Score 1-10 on the efficiency and directness of the agent's process.")
justification: str = Field(description="A brief justification for the scores.")
judge_llm = llm.with_structured_output(ProcessEvaluation)
def evaluate_agent_process(query: str, final_state: dict):
if 'messages' in final_state:
trace = "\n".join([f"{m.type}: {str(m.content)}" for m in final_state['messages']])
else:
trace = f"Plan: {final_state.get('plan', [])}\nSteps: {final_state.get('intermediate_steps', [])}"
prompt = f"""You are an expert judge of AI agents. Evaluate the agent's process for solving the task on a scale of 1-10.
Focus on whether the process was logical and efficient.
**User's Task:** {query}
**Full Agent Trace:** {trace}
Use Chinese as output.
"""
return judge_llm.invoke(prompt)
6.2 评估结果
| 评估维度 | ReAct Agent | Planning Agent |
|---|---|---|
| 任务完成度 | 10/10 | 2/10 |
| 过程效率 | 9/10 | 4/10 |
[!WARNING] ⚠️ 评估结果分析
在这个特定测试中,ReAct Agent 表现更好,这与我们的预期相反!
原因分析:
ReAct Agent 的迭代探索使其能够根据搜索结果动态调整查询策略
Planning Agent 虽然流程更清晰,但其Synthesizer 未能有效整合中间结果
这表明 Planning 架构需要更强大的 Synthesizer 组件
这个结果说明:
Planning 架构的优势依赖于计划质量和综合能力
简单地"规划 → 执行 → 综合"不一定比 ReAct 更好
实际应用中需要根据具体场景选择合适的架构
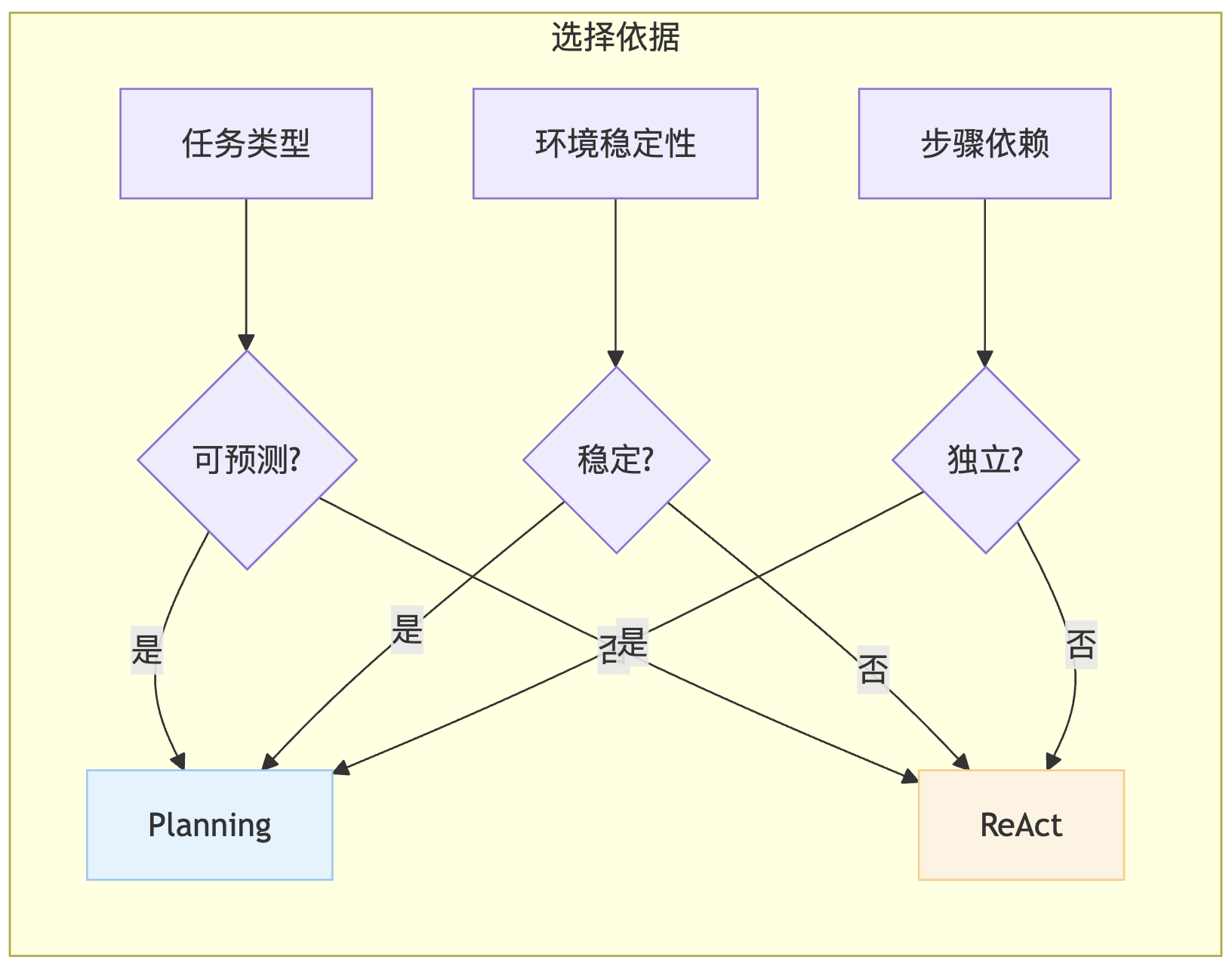
7. 架构选择思考
何时使用 Planning?
| 适用场景 | 原因 |
|---|---|
| 步骤已知且固定 | 计划可以预先确定 |
| 需要透明性 | 整个流程可审计 |
| 步骤间相互独立 | 可按顺序执行无需反馈 |
| 成本敏感 | 减少 LLM 调用次数 |
何时使用 ReAct?
| 适用场景 | 原因 |
|---|---|
| 探索性任务 | 下一步依赖前一步结果 |
| 动态环境 | 需要根据反馈调整 |
| 复杂推理 | 需要多轮思考 |
| 不确定性高 | 无法预知解决路径 |
架构对比图
| 判断维度 | 选择 Planning | 选择 ReAct |
|---|---|---|
| 任务可预测性 | ✅ 步骤已知 | ❌ 未知 |
| 环境稳定性 | ✅ 稳定 | ❌ 动态 |
| 步骤依赖关系 | ✅ 相互独立 | ❌ 前后依赖 |
| 成本敏感度 | ✅ 是 | ❌ 否 |
8. 总结与核心要点
🎓 核心成果
| 成果 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 架构实现 | 成功实现 Planner → Executor → Synthesizer 三段式架构 |
| 对比验证 | 通过 ReAct vs Planning 的对比,展示两种模式的差异 |
| 评估框架 | 引入 LLM-as-a-Judge 量化评估流程效率 |
🌟 关键洞察
| 洞察 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 有缺陷 | Planning 不是万能的,需要配合高质量的 Synthesizer |
| 互补关系 | ReAct 和 Planning 各有优势,应根据场景选择 |
| 设计权衡 | 透明性 vs 灵活性、效率 vs 适应性 |
关键代码速查表
| 组件 | 代码 |
|---|---|
| 定义计划结构 | class Plan(BaseModel): steps: List[str] |
| 结构化输出 | llm.with_structured_output(Plan) |
| 创建规划状态 | class PlanningState(TypedDict) |
| 路由函数 | def planning_router(state) |
| 条件边 | add_conditional_edges("execute", planning_router, {...}) |
三大节点职责
| 节点 | 步骤1 | 步骤2 | 步骤3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planner | 接收用户请求 | 分析任务 | 生成步骤列表 |
| Executor | 取出下一步骤 | 解析工具调用 | 执行并记录结果 |
| Synthesizer | 收集中间结果 | 整合信息 | 生成最终答案 |
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容








所有评论(0)