爆肝教程!AI智能体开发全攻略:从概念到实现,大模型应用开发不再神秘!
本文详细介绍了AI智能体的概念、类型及核心组件,并提供了使用Python和Ollama构建AI智能体的完整实现步骤。文章包含OllamaModel类、ToolBox类、Agent类等代码示例,以及计算器和字符串反转工具的具体实现,最终整合所有组件展示了一个可运行的AI智能体项目,为初学者提供了从零开始构建AI智能体的实用指南。
1. 什么是智能体?
智能体(Agents)是一种能够感知环境、做出决策并采取行动来实现特定目标的自主实体。智能体的复杂程度各不相同,从简单的响应式智能体(对刺激直接做出反应)到更高级的智能体(能够学习和适应)都有。常见的智能体类型包括:
- 响应式智能体:直接对环境变化作出反应,没有内部记忆。
- 基于模型的智能体:使用内部世界模型来做决策。
- 基于目标的智能体:基于特定目标规划行动。
- 基于效用的智能体:通过效用函数评估潜在行动,以优化结果。
智能体的例子包括聊天机器人、推荐系统和自动驾驶汽车,它们各自使用不同类型的智能体来高效智能地执行任务。
我们智能体的核心组件有:
- 模型:智能体的大脑,负责处理输入并生成响应。
- 工具:智能体可以根据用户请求执行的预定义函数。
- 工具箱:智能体可用工具的集合。
- 系统提示:指导智能体如何处理用户输入并选择合适工具的指令集。
2. 实现
现在,让我们卷起袖子开始构建吧!

构建智能体
2.1 前提条件
在运行代码之前,确保你的系统满足以下前提条件:
1. Python环境设置
你需要安装Python来运行AI智能体。按照以下步骤设置环境:
安装Python(如果尚未安装)
- 从python.org下载并安装Python(推荐3.8+版本)
- 验证安装:```plaintext
python --version
创建虚拟环境(推荐)
- 最好使用虚拟环境来管理依赖项:```plaintext
python -m venv ai_agents_envsource ai_agents_env/bin/activate # Windows上使用:ai_agents_env\Scripts\activate
安装所需依赖
- 导航到仓库目录并安装依赖:```plaintext
pip install -r requirements.txt
2. 在本地设置Ollama
Ollama用于高效运行和管理本地语言模型。按照以下步骤安装和配置:
下载并安装Ollama
- 访问Ollama官方网站并下载适合你操作系统的安装程序
- 按照平台相应指导进行安装
验证Ollama安装
- 运行以下命令检查Ollama是否正确安装:```plaintext
ollama --version
拉取模型(如需要)
- 某些智能体实现可能需要特定模型。你可以使用以下命令拉取模型:
ollama pull mistral # 将'mistral'替换为所需模型
我查了下有些模型是在ollama部署下不支持工具调用的。
2.2 实现步骤
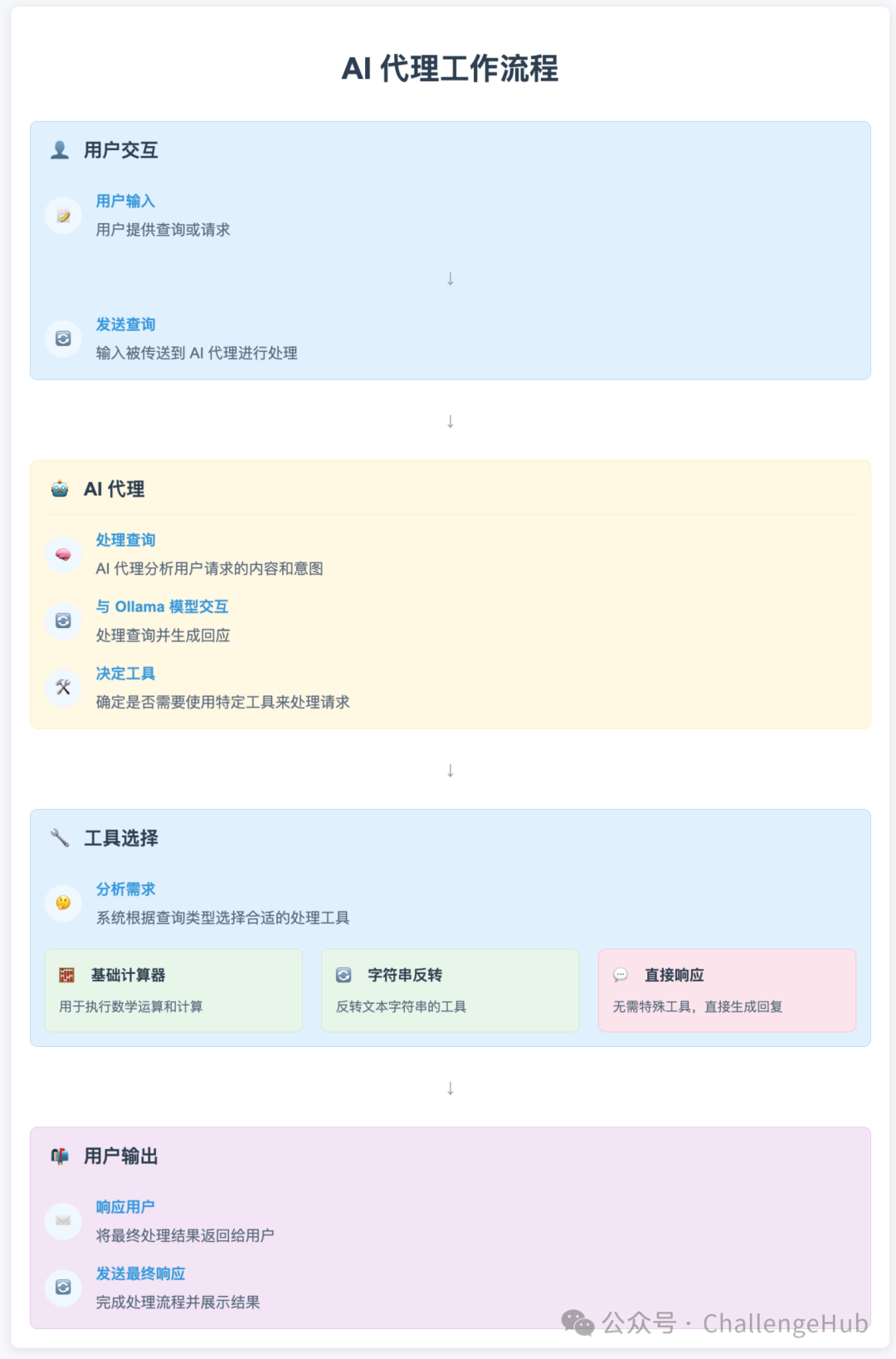
步骤1:设置环境
除了Python,我们还需要安装一些基本库。对于本教程,我们将使用requests、json和termcolor。此外,我们将使用dotenv来管理环境变量。
pip install requests termcolor python-dotenv
步骤2:定义模型类
首先,我们需要一个处理用户输入的模型。我们将创建一个OllamaModel类,它与本地API交互以生成响应。
基本实现如下:
from termcolor import coloredimport osfrom dotenv import load_dotenvload_dotenv()### Modelsimport requestsimport jsonimport operatorclass OllamaModel: def __init__(self, model, system_prompt, temperature=0, stop=None): """ 使用给定参数初始化OllamaModel。 参数: model (str): 要使用的模型名称。 system_prompt (str): 要使用的系统提示。 temperature (float): 模型的温度设置。 stop (str): 模型的停止令牌。 """ self.model_endpoint = "http://localhost:11434/api/generate" self.temperature = temperature self.model = model self.system_prompt = system_prompt self.headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"} self.stop = stop def generate_text(self, prompt): """ 根据提供的提示从Ollama模型生成响应。 参数: prompt (str): 要生成响应的用户查询。 返回: dict: 模型响应的字典形式。 """ payload = { "model": self.model, "format": "json", "prompt": prompt, "system": self.system_prompt, "stream": False, "temperature": self.temperature, "stop": self.stop } try: request_response = requests.post( self.model_endpoint, headers=self.headers, data=json.dumps(payload) ) print("请求响应", request_response) request_response_json = request_response.json() response = request_response_json['response'] response_dict = json.loads(response) print(f"\n\nOllama模型的响应: {response_dict}") return response_dict except requests.RequestException as e: response = {"error": f"调用模型时出错!{str(e)}"} return response
这个类以模型名称、系统提示、温度和停止令牌进行初始化。generate_text方法向模型API发送请求并返回响应。
步骤3:为智能体创建工具
下一步是创建我们的智能体可以使用的工具。这些工具是执行特定任务的简单Python函数。以下是一个基本计算器和字符串反转器的例子:
def basic_calculator(input_str): """ 根据输入字符串或字典对两个数字执行数学运算。 参数: input_str (str或dict): 可以是表示包含'num1'、'num2'和'operation'键的字典的JSON字符串, 或直接是字典。例如:'{"num1": 5, "num2": 3, "operation": "add"}' 或 {"num1": 67869, "num2": 9030393, "operation": "divide"} 返回: str: 操作结果的格式化字符串。 异常: Exception: 如果在操作过程中发生错误(例如,除以零)。 ValueError: 如果请求了不支持的操作或输入无效。 """ try: # 处理字典和字符串输入 if isinstance(input_str, dict): input_dict = input_str else: # 清理并解析输入字符串 input_str_clean = input_str.replace("'", "\"") input_str_clean = input_str_clean.strip().strip("\"") input_dict = json.loads(input_str_clean) # 验证必需字段 if not all(key in input_dict for key in ['num1', 'num2', 'operation']): return "错误:输入必须包含'num1'、'num2'和'operation'" num1 = float(input_dict['num1']) # 转换为浮点数以处理小数 num2 = float(input_dict['num2']) operation = input_dict['operation'].lower() # 不区分大小写 except (json.JSONDecodeError, KeyError) as e: return "输入格式无效。请提供有效的数字和操作。" except ValueError as e: return "错误:请提供有效的数值。" # 定义支持的操作及错误处理 operations = { 'add': operator.add, 'plus': operator.add, # add的替代词 'subtract': operator.sub, 'minus': operator.sub, # subtract的替代词 'multiply': operator.mul, 'times': operator.mul, # multiply的替代词 'divide': operator.truediv, 'floor_divide': operator.floordiv, 'modulus': operator.mod, 'power': operator.pow, 'lt': operator.lt, 'le': operator.le, 'eq': operator.eq, 'ne': operator.ne, 'ge': operator.ge, 'gt': operator.gt } # 检查操作是否支持 if operation not in operations: return f"不支持的操作:'{operation}'。支持的操作有:{', '.join(operations.keys())}" try: # 处理除以零的特殊情况 if (operation in ['divide', 'floor_divide', 'modulus']) and num2 == 0: return "错误:不允许除以零" # 执行操作 result = operations[operation](num1, num2) # 根据类型格式化结果 if isinstance(result, bool): result_str = "真" if result else "假" elif isinstance(result, float): # 处理浮点精度 result_str = f"{result:.6f}".rstrip('0').rstrip('.') else: result_str = str(result) return f"答案是:{result_str}" except Exception as e: return f"计算过程中出错:{str(e)}"def reverse_string(input_string): """ 反转给定字符串。 参数: input_string (str): 要反转的字符串。 返回: str: 反转后的字符串。 """ # 检查输入是否为字符串 if not isinstance(input_string, str): return "错误:输入必须是字符串" # 使用切片反转字符串 reversed_string = input_string[::-1] # 格式化输出 result = f"反转后的字符串是:{reversed_string}" return result
这些函数设计用于根据提供的输入执行特定任务。basic_calculator处理算术运算,而reverse_string则反转给定的字符串。
步骤4:构建工具箱
ToolBox类存储智能体可以使用的所有工具,并为每个工具提供描述:
class ToolBox: def __init__(self): self.tools_dict = {} def store(self, functions_list): """ 存储列表中每个函数的字面名称和文档字符串。 参数: functions_list (list): 要存储的函数对象列表。 返回: dict: 以函数名为键,其文档字符串为值的字典。 """ for func in functions_list: self.tools_dict[func.__name__] = func.__doc__ return self.tools_dict def tools(self): """ 以文本字符串形式返回store中创建的字典。 返回: str: 存储的函数及其文档字符串的字典,以文本字符串形式。 """ tools_str = "" for name, doc in self.tools_dict.items(): tools_str += f"{name}: \"{doc}\"\n" return tools_str.strip()
这个类将帮助智能体了解哪些工具可用以及每个工具的功能。
步骤5:创建智能体类
智能体需要思考、决定使用哪个工具并执行它。以下是智能体类:
agent_system_prompt_template = """你是一个拥有特定工具访问权限的智能AI助手。你的回答必须始终使用这种JSON格式:{{ "tool_choice": "工具名称", "tool_input": "给工具的输入"}}工具及其使用时机:1. basic_calculator:用于任何数学计算 - 输入格式:{{"num1": 数字, "num2": 数字, "operation": "add/subtract/multiply/divide"}} - 支持的操作:add/plus, subtract/minus, multiply/times, divide - 输入和输出示例: 输入:"计算15加7" 输出:{{"tool_choice": "basic_calculator", "tool_input": {{"num1": 15, "num2": 7, "operation": "add"}}}} 输入:"100除以5等于多少?" 输出:{{"tool_choice": "basic_calculator", "tool_input": {{"num1": 100, "num2": 5, "operation": "divide"}}}}2. reverse_string:用于任何涉及文本反转的请求 - 输入格式:仅作为字符串的要反转的文本 - 当用户提到"反转"、"倒序"或要求反转文本时,始终使用此工具 - 输入和输出示例: 输入:"'你好世界'的反转是什么?" 输出:{{"tool_choice": "reverse_string", "tool_input": "你好世界"}} 输入:"Python反过来是什么?" 输出:{{"tool_choice": "reverse_string", "tool_input": "Python"}}3. no tool:用于一般对话和问题 - 输入和输出示例: 输入:"你是谁?" 输出:{{"tool_choice": "no tool", "tool_input": "我是一个AI助手,可以帮你进行计算、反转文本以及回答问题。我可以执行数学运算和反转字符串。今天我能为你做些什么?"}} 输入:"你好吗?" 输出:{{"tool_choice": "no tool", "tool_input": "我运行得很好,谢谢你的关心!我可以帮你进行计算、文本反转或回答任何问题。"}}严格规则:1. 关于身份、能力或感受的问题: - 始终使用"no tool" - 提供完整、友好的回应 - 提及你的能力2. 对于任何文本反转请求: - 始终使用"reverse_string" - 仅提取要反转的文本 - 删除引号、"反转"等额外文本3. 对于任何数学运算: - 始终使用"basic_calculator" - 提取数字和操作 - 将文本数字转换为数字这是你的工具列表及其描述:{tool_descriptions}记住:你的回应必须始终是带有"tool_choice"和"tool_input"字段的有效JSON。"""class Agent: def __init__(self, tools, model_service, model_name, stop=None): """ 使用工具列表和模型初始化智能体。 参数: tools (list): 工具函数列表。 model_service (class): 带有generate_text方法的模型服务类。 model_name (str): 要使用的模型名称。 """ self.tools = tools self.model_service = model_service self.model_name = model_name self.stop = stop def prepare_tools(self): """ 在工具箱中存储工具并返回其描述。 返回: str: 工具箱中存储的工具描述。 """ toolbox = ToolBox() toolbox.store(self.tools) tool_descriptions = toolbox.tools() return tool_descriptions def think(self, prompt): """ 使用系统提示模板和工具描述在模型上运行generate_text方法。 参数: prompt (str): 要生成回答的用户查询。 返回: dict: 模型响应的字典形式。 """ tool_descriptions = self.prepare_tools() agent_system_prompt = agent_system_prompt_template.format(tool_descriptions=tool_descriptions) # 创建带有系统提示的模型服务实例 if self.model_service == OllamaModel: model_instance = self.model_service( model=self.model_name, system_prompt=agent_system_prompt, temperature=0, stop=self.stop ) else: model_instance = self.model_service( model=self.model_name, system_prompt=agent_system_prompt, temperature=0 ) # 生成并返回响应字典 agent_response_dict = model_instance.generate_text(prompt) return agent_response_dict def work(self, prompt): """ 解析从think返回的字典并执行适当的工具。 参数: prompt (str): 要生成回答的用户查询。 返回: 执行适当工具的响应,如果没有找到匹配的工具则返回tool_input。 """ agent_response_dict = self.think(prompt) tool_choice = agent_response_dict.get("tool_choice") tool_input = agent_response_dict.get("tool_input") for tool in self.tools: if tool.__name__ == tool_choice: response = tool(tool_input) print(colored(response, 'cyan')) return print(colored(tool_input, 'cyan')) return
这个类有三个主要方法:
- prepare_tools:存储并返回工具的描述。
- think:根据用户提示决定使用哪个工具。
- work:执行所选工具并返回结果。
步骤6:运行智能体
最后,让我们把所有内容放在一起并运行我们的智能体。在脚本的主要部分,初始化智能体并开始接受用户输入:
# 示例用法if __name__ == "__main__": """ 使用此智能体的说明: 你可以尝试的示例查询: 1. 计算器操作: - "计算15加7" - "100除以5等于多少?" - "把23乘以4" 2. 字符串反转: - "反转'你好世界'这个词" - "你能反转'Python编程'吗?" 3. 一般问题(将得到直接回应): - "你是谁?" - "你能帮我做什么?" Ollama命令(在终端中运行): - 检查可用模型: 'ollama list' - 检查运行中的模型:'ps aux | grep ollama' - 列出模型标签: 'curl http://localhost:11434/api/tags' - 拉取新模型: 'ollama pull mistral' - 运行模型服务器: 'ollama serve' """ tools = [basic_calculator, reverse_string] # 取消下面的注释以使用OpenAI # model_service = OpenAIModel # model_name = 'gpt-3.5-turbo' # stop = None # 使用Ollama的llama2模型 model_service = OllamaModel model_name = "llama2" # 可以更改为其他模型,如'mistral'、'codellama'等 stop = "<|eot_id|>" agent = Agent(tools=tools, model_service=model_service, model_name=model_name, stop=stop) print("\n欢迎使用AI智能体!输入'exit'退出。") print("你可以让我:") print("1. 执行计算(例如,'计算15加7')") print("2. 反转字符串(例如,'反转你好世界')") print("3. 回答一般问题\n") while True: prompt = input("问我任何问题:") if prompt.lower() == "exit": break agent.work(prompt)
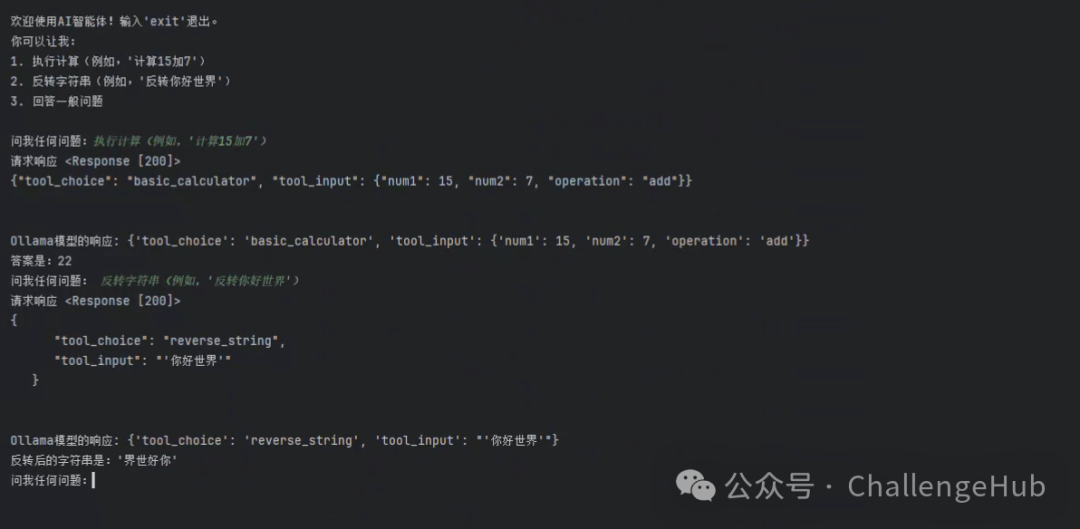
实测效果如下:
3. 总结
在这篇博文中,我们探索了智能体的概念,并一步步实现了它。我们设置了环境,定义了模型,创建了基本工具,并构建了一个结构化的工具箱来支持我们智能体的功能。最后,我们通过运行智能体将所有内容整合在一起。
这种结构化方法为构建能够自动执行任务并做出明智决策的智能交互式智能体提供了坚实的基础。随着AI智能体不断发展,它们的应用将扩展到各个行业,推动效率和创新。敬请关注更多见解和改进,将你的AI智能体提升到新的水平!
学AI大模型的正确顺序,千万不要搞错了
🤔2026年AI风口已来!各行各业的AI渗透肉眼可见,超多公司要么转型做AI相关产品,要么高薪挖AI技术人才,机遇直接摆在眼前!
有往AI方向发展,或者本身有后端编程基础的朋友,直接冲AI大模型应用开发转岗超合适!
就算暂时不打算转岗,了解大模型、RAG、Prompt、Agent这些热门概念,能上手做简单项目,也绝对是求职加分王🔋

📝给大家整理了超全最新的AI大模型应用开发学习清单和资料,手把手帮你快速入门!👇👇
学习路线:
✅大模型基础认知—大模型核心原理、发展历程、主流模型(GPT、文心一言等)特点解析
✅核心技术模块—RAG检索增强生成、Prompt工程实战、Agent智能体开发逻辑
✅开发基础能力—Python进阶、API接口调用、大模型开发框架(LangChain等)实操
✅应用场景开发—智能问答系统、企业知识库、AIGC内容生成工具、行业定制化大模型应用
✅项目落地流程—需求拆解、技术选型、模型调优、测试上线、运维迭代
✅面试求职冲刺—岗位JD解析、简历AI项目包装、高频面试题汇总、模拟面经
以上6大模块,看似清晰好上手,实则每个部分都有扎实的核心内容需要吃透!
我把大模型的学习全流程已经整理📚好了!抓住AI时代风口,轻松解锁职业新可能,希望大家都能把握机遇,实现薪资/职业跃迁~
这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传CSDN,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献568条内容
已为社区贡献568条内容







所有评论(0)