Agent架构解析与实战(二)--Tool Use
参考来源:all-agentic-architectures
目录
1. 架构定义 (Definition)
Tool Use 是一种赋予大语言模型(LLM)驱动的智能体(Agent)调用外部函数或 API 能力的架构。
核心特性
|
特性 |
描述 |
|
自主性 |
智能体会自主判断用户问题是否超出了其内部知识范围 |
|
决策性 |
智能体能够决定在何时、调用哪一个特定的工具来获取必要的信息 |
工作原理图
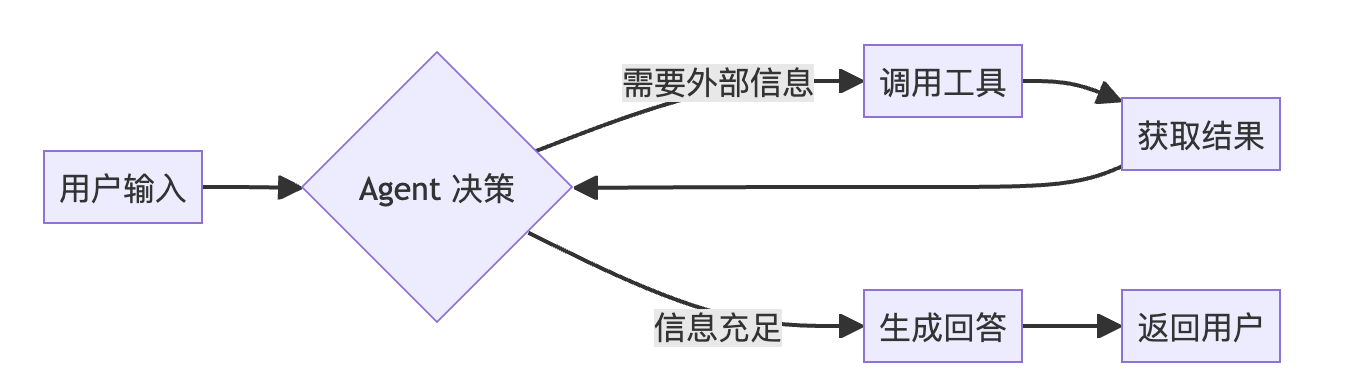
2. 宏观工作流 (Workflow)
工具调用的过程遵循 "接收-决策-执行-观察-综合" 的循环:
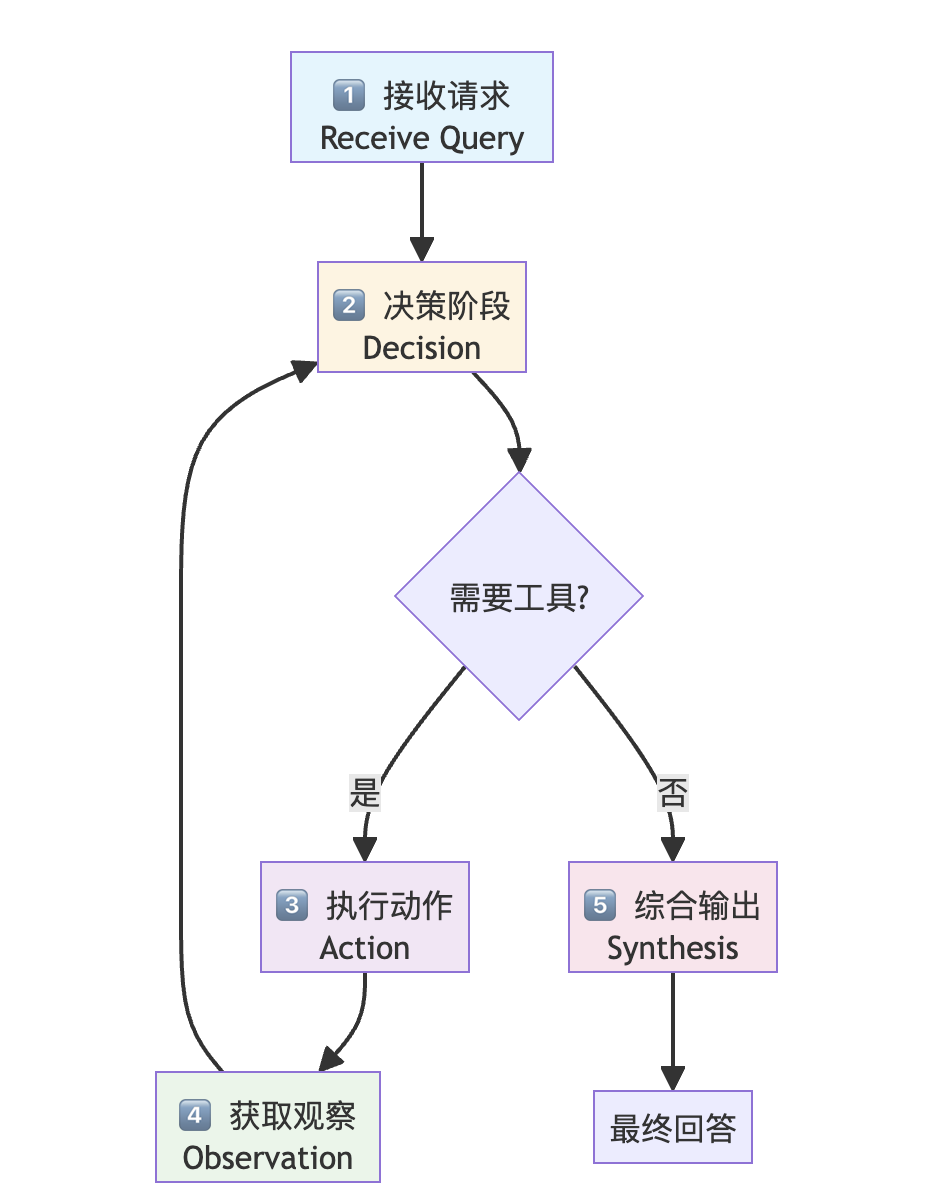
详细步骤说明
|
步骤 |
名称 |
描述 |
|
1 |
接收请求 |
智能体接收来自用户的原始指令 |
|
2 |
决策阶段 |
分析查询内容及可用工具列表,判断是否需要外部工具协助 |
|
3 |
执行动作 |
若需要工具,智能体按格式要求生成调用指令(如特定函数名及参数) |
|
4 |
获取观察 |
系统执行该调用,并将结果(即"观察到的数据")反馈给智能体 |
|
5 |
综合输出 |
智能体将工具返回的信息整合进推理过程中,生成最终的、有据可依的回答 |
3. 应用场景 (Use Cases)
|
场景 |
工具类型 |
示例 |
|
研究助手 |
网络搜索 API |
回答需要即时信息的问题 |
|
企业级助手 |
公司内部数据库 |
回答如"上周新增用户数"等业务数据问题 |
|
科学与数学任务 |
计算器/WolframAlpha |
处理模型自身不擅长的精确计算 |
4. 优缺点分析 (Pros & Cons)
✅ 优点
|
优点 |
说明 |
|
事实增强 (Factual Grounding) |
通过获取实时数据,显著减少模型的"幻觉"现象 |
|
可扩展性 (Extensibility) |
只需添加新工具,即可不断扩展智能体的能力边界 |
❌ 缺点
|
缺点 |
说明 |
|
集成成本 (Integration Overhead) |
需要精细的"管道"工程,包括定义接口、处理 API 密钥以及管理工具失效的情况 |
|
工具信任 (Tool Trust) |
回答的质量高度依赖于工具的准确性;如果工具提供错误信息,智能体也难以产出正确答案 |
5. 代码实现详解
5.1 环境配置
依赖库安装
pip install -U langchain-openai langchain langgraph python-dotenv rich tavily-python langchain_community pydantic核心依赖说明
|
库名称 |
作用描述 |
|
|
用于与 OpenAI 的模型(如 GPT-4)进行交互的 LangChain 集成库 |
|
|
用于构建有状态的、多参与者(Multi-agent)应用的库,支持创建复杂的循环工作流 |
|
|
用于从 |
|
|
一个 Python 库,用于在终端输出格式漂亮、带颜色的文本和表格,方便调试 |
|
|
核心搜索工具。Tavily 是专为 AI 智能体设计的搜索引擎,能够返回结构化的搜索结果 |
运行结果
Requirement already satisfied: langchain-openai in ./.venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages (1.1.6)
Requirement already satisfied: langchain in ./.venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages (1.2.0)
Requirement already satisfied: langgraph in ./.venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages (1.0.5)
...
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.5.2 导入库并设置密钥
import os
import json
from typing import List, Annotated, TypedDict, Optional
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# LangChain组件
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_community.tools.tavily_search import TavilySearchResults
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage, ToolMessage
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
# LangGraph组件
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
from langgraph.graph.message import AnyMessage, add_messages
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
# 输出美化
from rich.console import Console
from rich.markdown import Markdown
# API密钥
load_dotenv()
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2"] = "true"
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_PROJECT"] = "Tool Use"
for key in ["OPENAI_API_KEY", "LANGCHAIN_API_KEY", "DASHSCOPE_API_KEY", "TAVILY_API_KEY"]:
if not os.environ.get(key):
print(f"{key} not found.")
print("Keys loaded successfully.")运行结果:
Keys loaded successfully.🔑 必需的 API 密钥
|
密钥类型 |
用途 |
|
OpenAI Key |
驱动大语言模型(LLM)进行推理和决策 |
|
LangSmith Key |
用于追踪(Tracing),记录智能体的每一步运行轨迹 |
|
Tavily Key |
赋予智能体联网搜索的能力 |
5.3 创建 Web Search 工具
# 初始化工具,可以设置最多的结果数量以保证上下文的精简
search_tool = TavilySearchResults(max_results=2)
# 给工具定义清楚的工具名和描述是很重要的
search_tool.name = "web_search"
search_tool.description = "A tool that can be used to search the internet for up-to-date information on any topic, including news, events, and current affairs."
tools=[search_tool]
print(f"Tool '{search_tool.name}' created with description: '{search_tool.description}'")运行结果:
Tool 'web_search' created with description: 'A tool that can be used to search the internet for up-to-date information on any topic, including news, events, and current affairs.'[!IMPORTANT]
🎯 核心概念:描述的重要性
定义工具时,最关键的部分是它的描述(Description):
- 决策依据:LLM 并不通过底层代码了解工具,而是阅读这段自然语言描述
- 精准引导:一个清晰、准确的描述能告诉 LLM 该工具的功能、适用场景以及参数含义
工具测试
# 直接测试工具并观察它的输出格式
test_query = "常熟阿诺头为什么尖尖的?"
test_result = search_tool.invoke({"query": test_query})运行结果:
Query: 常熟阿诺头为什么尖尖的?
Result:
[
{
'title': '全网烂梗最多的健身网红,终于把自己练成了人类最抽象的样子',
'url': 'https://news.qq.com/rain/a/20240815A09QQ700',
'content': '...',
'score': 0.9993436
},
{
'title': '一人揭露整個健美圈亂象!頭頂尖尖的阿諾爲啥成爲最抽象網紅?',
'url': 'https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MSu0yyVYzbg',
'content': '...',
'score': 0.996852
}
]📝 输出结果分析
工具返回的是一个字典列表 (List of Dictionaries):
- 每个字典代表一个搜索结果
- 包含核心字段:
url(来源链接)和content(网页内容摘要)
5.4 定义图状态 (Graph State)
在 LangGraph 中,状态 (State) 是驱动智能体运行的核心。
class AgentState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[List[AnyMessage], add_messages]
print("AgentState TypedDict defined to manage conversation history.")运行结果:
AgentState TypedDict defined to manage conversation history.5.5 将 Tools 和 LLM 绑定
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="qwen-flash",
openai_api_key=os.environ["DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"],
openai_api_base="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",
temperature=0.1
)
# 绑定工具
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools=tools)
print("LLM has been bound with the provided tools.")运行结果:
LLM has been bound with the provided tools.5.6 定义 Agent 节点
在 LangGraph 构筑的图中,Agent 的功能拆分为两个核心节点:
1. 大脑:agent_node (推理节点)
这是 Agent 的决策中心:
- 职责:接收当前的对话历史(State),将其发送给 LLM
- 输出:
-
- 最终答案:如果 LLM 认为信息已足够,直接回答用户
- 工具调用请求:如果 LLM 认为需要外部帮助,生成包含工具名和参数的请求
2. 双手:tool_node (执行节点)
这是 Agent 与外部世界交互的执行层:
- 职责:检查
agent_node发出的消息,如果发现工具调用请求,执行对应的函数 - 优势:使用 LangGraph 内置的
ToolNode,自动解析模型输出并运行对应的 Python 函数
def agent_node(state: AgentState):
"""The primary node that calls the LLM to decide the next action."""
console.print("--- AGENT: Thinking... ---")
response = llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])
return {"messages": [response]}
# Tool节点是LangGraph中预构建的节点
tool_node = ToolNode(tools=tools)
print("Agent and Tool nodes defined.")运行结果:
Agent and Tool nodes defined.[!TIP]
💡 逻辑闭环
agent_node产生的 AI 消息 (AIMessage) 如果包含工具调用,会被传递给tool_nodetool_node执行完后会产生 工具消息 (ToolMessage),并将其回传给agent_node- 这种"反复横跳"的循环,正是 Agent 能够解决复杂任务的奥秘
5.7 构建条件路由 (Conditional Routing)
路由函数检查 Agent 发出的最后一条消息:
def router_function(state: AgentState) -> str:
"""Inspects the agent's last message to decide the next step."""
last_message = state["messages"][-1]
if last_message.tool_calls:
# Agent请求了工具调用
console.print("--- ROUTER: Decision is to call a tool. ---")
return "call_tool"
else:
# Agent已经得到最终答案
console.print("--- ROUTER: Decision is to end the workflow. ---")
return "__end__"
print("Router function defined.")运行结果:
Router function defined.⚙️ 核心逻辑:检查 tool_calls
|
情况 |
条件 |
下一步 |
|
存在工具调用 |
|
导向 |
|
不存在工具调用 |
|
导向 END,完成工作流 |
5.8 组装工作流图
graph_builder = StateGraph(AgentState)
# 添加节点
graph_builder.add_node("agent", agent_node)
graph_builder.add_node("call_tool", tool_node)
# 创建起始节点
graph_builder.set_entry_point("agent")
# 添加条件边
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges(
"agent",
router_function,
{
"call_tool": "call_tool",
"__end__": END
}
)
# 添加边(如果有工具调用,结束后还要回到agent)
graph_builder.add_edge("call_tool", "agent")
# 编译工作流图
tool_agent_app = graph_builder.compile()
print("Tool-using agent graph compiled successfully!")运行结果:
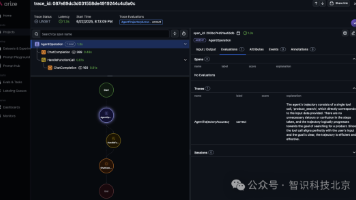
Tool-using agent graph compiled successfully!工作流可视化
工作流图清晰展示了 Agent 的推理循环:
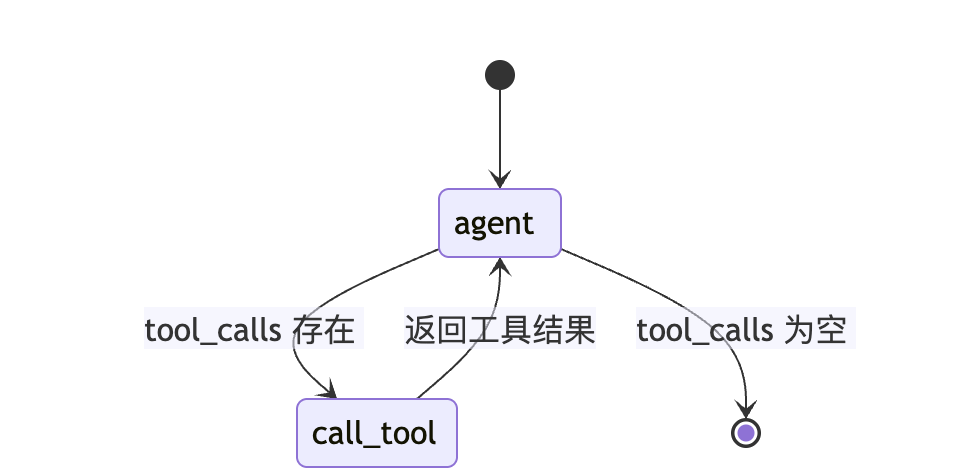
[!NOTE]
流程从 agent 节点开始,条件边(菱形)决定路由方向:
- 需要工具 →
call_tool→ 返回agent综合 - 不需要工具 →
__end__结束
5.9 运行工作流
测试 Agent 的真实能力,提问一个训练数据中无法包含的问题:
user_query = "2026年1月6日,凯尔特人和公牛的比赛,杰伦布朗拿了几分?"
initial_input = {"messages": [('user', user_query)]}
console.print(f"[bold cyan]🚀 Kicking off Tool Use workflow for request:[/bold cyan] '{user_query}'\n")
for chunk in tool_agent_app.stream(initial_input, stream_mode="values"):
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
console.print("\n---\n")
console.print("\n[bold green]✅ Tool Use workflow complete![/bold green]")运行过程(完整追踪)
🚀 Kicking off Tool Use workflow for request: '2026年1月6日,凯尔特人和公牛的比赛,杰伦布朗拿了几分?'
================================ Human Message =================================
2026年1月6日,凯尔特人和公牛的比赛,杰伦布朗拿了几分?
---
--- AGENT: Thinking... ---
--- ROUTER: Decision is to call a tool. ---
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Calls:
web_search (call_3c532a0188dd4985869719)
Call ID: call_3c532a0188dd4985869719
Args:
query: 2026年1月6日 凯尔特人 公牛 杰伦布朗 得分
---
================================= Tool Message =================================
Name: web_search
[{"title": "杰伦·布朗半场失常,凯尔特人仍领先公牛:数据背后的深度解析 - 搜狐",
"url": "https://m.sohu.com/a/972930638_121924582...",
"content": "...",
"score": 0.99935883},
{"title": "01月06日公牛vs凯尔特人数据统计 - 虎扑NBA",
"url": "https://nba.hupu.com/games/boxscore/167946",
"content": "| 杰伦-布朗 | F | 35 | 6-24 | 1-6 | 1-2 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 14 | +12 |...",
"score": 0.99094474}]
---
--- AGENT: Thinking... ---
--- ROUTER: Decision is to end the workflow. ---
================================== Ai Message ==================================
根据2026年1月6日凯尔特人对阵公牛的比赛数据,杰伦·布朗全场得到 **14分**。
他在比赛中出场35分钟,投篮14投6中,三分球1投1中,罚球1罚1中,
同时还贡献了8个篮板、4次助攻和3次失误。
---
✅ Tool Use workflow complete!6. 评估方法 (Evaluation)
对于具备工具调用能力的智能体,核心关注两点:
- 它是否正确使用了工具?
- 基于工具输出综合生成的最终答案质量如何?
6.1 执行路径分析
通过观察流式输出的链路,可以精准追踪智能体的思考过程:
|
步骤 |
节点 |
消息类型 |
说明 |
|
1 |
|
|
LLM 正确判断需要使用 |
|
2 |
|
|
工具执行搜索后返回的原始结果 |
|
3 |
|
|
智能体已将工具返回的信息综合处理,生成最终答案 |
6.2 通过 Judge LLM 评估
引入一个 "裁判 (Judge)" LLM 进行客观量化评估:
class ToolUseEvaluation(BaseModel):
"""Schema for evaluating the agent's tool use and final answer."""
tool_selection_score: int = Field(description="Score 1-5 on whether the agent chose the correct tool for the task.")
tool_input_score: int = Field(description="Score 1-5 on how well-formed and relevant the input to the tool was.")
synthesis_quality_score: int = Field(description="Score 1-5 on how well the agent integrated the tool's output into its final answer.")
justification: str = Field(description="A brief justification for the scores.")
judge_llm = llm.with_structured_output(ToolUseEvaluation)评估结果
{
"tool_selection_score": 5,
"tool_input_score": 5,
"synthesis_quality_score": 5,
"justification": "该AI agent在处理用户问题时表现优秀。首先,它准确识别出需要查询具体比赛数据的请求,并调用web_search工具进行信息检索,且搜索关键词精准(包含日期、球队和球员名),有效定位到相关结果。其次,AI从多个来源中提取了关键数据,特别是从虎扑NBA的详细比赛数据表中获取了杰伦·布朗的完整表现统计,包括得分、投篮、篮板、助攻等核心信息。最终回答不仅给出了正确答案(14分),还补充了全面的上下文数据,提升了回答的可信度与实用性。整体工具使用合理、高效,信息整合准确,体现了高水平的推理与信息处理能力。"
}评估维度说明
|
维度 |
评分标准 |
|
工具选择准确性 |
是否选择了正确的工具来完成任务 |
|
工具输入质量 |
输入参数是否格式正确、相关性高 |
|
综合输出质量 |
是否有效整合工具输出生成高质量答案 |
[!TIP]
💡 要点:评估不仅是为了看结果对不对,更是为了验证"过程正确"。通过分析执行路径,我们能发现智能体是否在某个环节出现了无效循环或错误的参数传递。
7. 总结与核心要点
🎓 核心成果
|
成果 |
说明 |
|
技术栈集成 |
成功地为基于 Langchain-OpenAI 驱动的 LLM 装备了联网搜索工具 |
|
架构实现 |
利用 LangGraph 构建了一个稳健的推理循环(Reasoning Loop),使智能体能够自主判断何时以及如何使用工具 |
🌟 模式价值
|
价值点 |
描述 |
|
突破局限 |
通过将智能体连接到实时、外部的信息源,从根本上克服了"静态训练数据"的时间限制 |
|
身份转变 |
智能体不再仅仅是一个简单的对话者(Reasoner),而变成了一个研究员 (Researcher),能够提供有据可依、符合事实且紧跟时事的答案 |
|
应用基石 |
这种架构是构建几乎所有实用的、面向现实世界的 AI 助手的核心基石 |
关键代码速查表
|
组件 |
代码 |
|
创建工具 |
|
|
绑定工具 |
|
|
定义状态 |
|
|
创建图 |
|
|
条件路由 |
|
|
编译运行 |
|
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容







所有评论(0)