LTR 与 List-wise Ranking
背景ranking is a prediction task on list of objects. 所以 point-wise, pair-wise 等方法的训练任务与工作场景有差异, list-wise 理应更好.list-wise ranking with S-IE该改论文见参考[1].Session Infomation Embedding (S-IE)算是一个预训练, task...
1. 背景
LTR, Learning-To-Rank, 对一组候选元素作 排序, 将序列(排列)视为一个整体, 追求 nDCG, MAP 等指标的提升. app 中的搜推场景就与 LTR 任务相匹配.
1.1 发展阶段
LTR 工作的发展分为几个阶段:
- 早期阶段. 学习一个打分表达式中的参数. 如式 (1) 中的三个 w, 现已不是主流.
s c o r e = w 1 ⋅ p r i c e + w 2 ⋅ c t r + w 3 ⋅ c v r (1) score=w_1⋅price+w_2⋅ctr+w_3 ⋅cvr \tag 1 score=w1⋅price+w2⋅ctr+w3⋅cvr(1) - 现代阶段. 使用 DNN 建模, 通过设计 loss 来优化排序效果. 又可分为 point-wise -> pair-wise -> list-wise 多个阶段. 整体属于
List-wise Training + Pointwise Inference范式. 代表工作是 listNet. - 升级阶段, infer 阶段生成式预测 next-best 元素. 代表工作是 seq2Slate.
可列出表格作比较: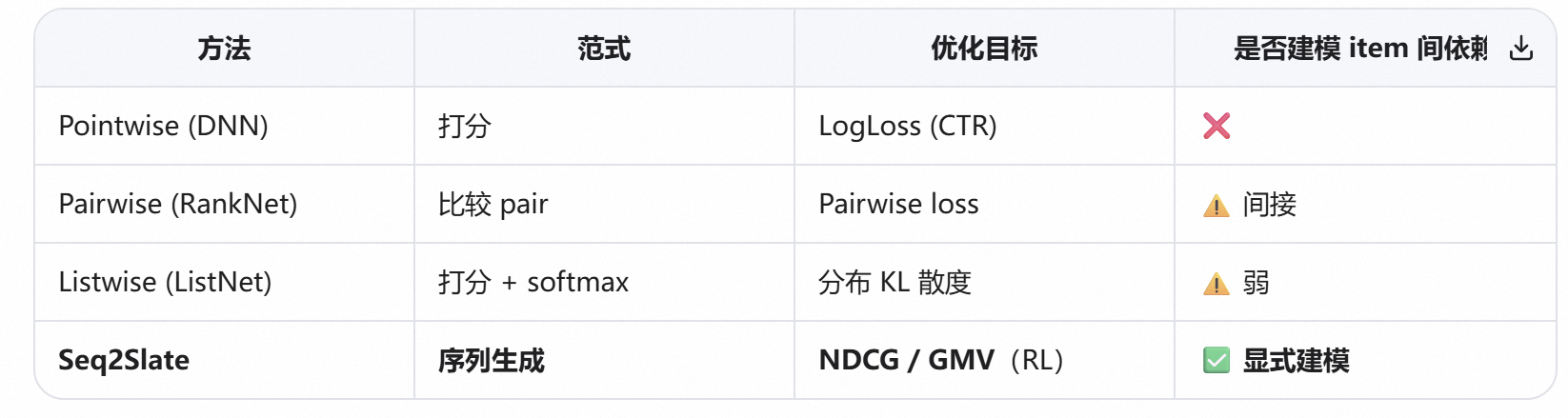
1.2 一些思考
Q1: List-wise Training + Pointwise Inference 范式中, 只是 train 阶段的 loss 用上了 list-wise, infer 方式仍是 point wise, 可为什么仍有效, 比纯 pointwise 方法要好?
A: 它改变了训练目标, 在 ListNet 的训练中,所有 item 的打分通过 softmax 归一化,形成“零和竞争”:模型被迫在一组候选内部做权衡,而不是孤立打分.
既然是实验科学, 实验证明 ListNet 的 NDCG 显著优于 RankNet(Pairwise)和 Regression(Pointwise)。
Q2: LTR 与 ctr预估 的关系?
A: LTR 是任务目标, ctr预估是实现路径之一.
2. 论文介绍
2.1 ListNet, ICML 2007
Listwise Learning to Rank 方法的奠基性工作. 论文名 Learning to Rank: From Pairwise Approach to Listwise Approach, 作者是 微软亚洲研究院.
首次系统提出 Listwise LTR 范式,并给出具体算法 ListNet. 在 LETOR 数据集上,ListNet 显著优于 RankSVM、RankBoost 等 Pairwise 方法.
思想
定义“理想排序”的概率分布(基于标签,如 NDCG 权重)
定义模型输出的排序概率分布(基于打分的 softmax)
用 交叉熵(Cross-Entropy) 或 KL 散度 作为 Loss.
loss 推导见附录.
实验
- 数据集, 其中一个是CSearch, 来自商业搜索引擎. This data set provides five levels of relevance judgments, ranging from 4 (”perfect match”) to 0 (”bad match”).
- 指标,nDCG@5 and MAP(mean average precision).
2.2 兼顾排序与概率准度(参考3论文)
YouTube 的工业实践.
list-wise 方法可以提升排序指标, 但会损失 score 的准度, 如 预估ctr 与实际ctr 偏差大, 该论文工作可 兼顾二者.
2.3 S-IE
该论文见参考[1].
Session Infomation Embedding (S-IE)
算是一个预训练, task为正负样本二分类, 为后面list-wise作准备.
图: 将点击与曝光内容分别pooling, 后与 target,user 作concat.
list-wise ranking


图 公式书写太差, 有误, (1)式中分子下标i可能为 t t t,分母下标i可能为 l l l; (2)式中i及右括号应放在上标位置.
实验
- 数据集. CIKM CUP 2016.是电商网站搜索引擎的日志.
- ndcg作指标. ctr预估, 通常用二分类的任务去做, 其指标为AUC/GAUC. 现在是list-wise, 就用nDCG.
我的疑惑
- session s 的rep由target得到,即 r e p ( s e s s i o n ) = f ( t a r g e t , o t h e r ) rep(session)=f(target,other) rep(session)=f(target,other) 那么 target 与 图2中的 n 个item是什么关系? 论文有说
each session with the contained item behaviors is treated as a list-wisw training sample,但还不是很清楚. - 为啥用搜索引擎的日志, 找个推荐数据集不是更直接么?
2.4 Seq2Slate, Google 2018
Google 2018 年的工作, 论文见参考[4]. 它将排序问题建模为 “从候选集中依次选择 item 构建排序列表” 的序列生成任务,并采用 强化学习(RL) 或 策略梯度 进行端到端优化。
它代表了 LTR(Learning to Rank)从 “打分+排序” 范式 向 “生成式排序” 范式 的重要演进。
“a slate of” 是 “一系列, 一套 …” 的意思.
思考讨论
- 所谓 list-wise
所谓list-wise 也只是损失函数相关, 预测阶段依旧是point-wise打分并排序, 由此得到序列.
谷歌的Seq2Slate的论文里有一段清晰的描述:
In listwise approaches the loss depends on the full permutation of items. Although these losses consider inter-item dependencies, the ranking function itself is pointwise, so at inference time the model still assigns a score to each item which does not depend on scores of other items (i.e., an item’s score will not change if it is placed in a different set).
- loss 与 常规多分类 有何异同
已经很像了, recsys中召回任务的设计就可以是transformer那样的多分类. 但常规的label是one-hot(可能带有 label smooth), 此处是一个不那么陡峭的分布.
附录
listwise loss 推导
论文1的list-wise借鉴了参考2, ICML’2017的微软的论文.
定义 list-wise 的损失函数:
∑ i = 1 m L ( y ( i ) , z ( i ) ) (1) \sum _{i=1}^mL(y^{(i)},z^{(i)}) \tag 1 i=1∑mL(y(i),z(i))(1)
where m = ∣ t r a i n s e t ∣ m=|trainset| m=∣trainset∣ , y ( i ) = ( y 1 ( i ) , y 2 ( i ) , . . . , y n ( i ) ( i ) ) y^{(i)}=(y^{(i)}_1,y^{(i)}_2,...,y^{(i)}_{n^{(i)}}) y(i)=(y1(i),y2(i),...,yn(i)(i)), 是一个list,表示与query q ( i ) q^{(i)} q(i) 相关的 n ( i ) n^{(i)} n(i) 个文档的相关性得分. 与之类似, z ( i ) = ( f ( x 1 ( i ) ) , f ( x 2 ( i ) ) , . . . , f ( x n ( i ) ( i ) ) ) z^{(i)}=(f(x^{(i)}_1),f(x^{(i)}_2),...,f(x^{(i)}_{n^{(i)}})) z(i)=(f(x1(i)),f(x2(i)),...,f(xn(i)(i))) 是 ranking function f ( ⋅ ) f(\cdot) f(⋅) 计算出的预估相关性.
probability model

图: permutation probability
对size=n的list作全排列, 有 n ! n! n! 种结果, 计算量不可接受, 也就是 NP_Hard? 所以提出 top one probability.
图: top one probability.
图: 定理6, doc j 排第一的概率描述

图: 对 ϕ ( ⋅ ) \phi(\cdot) ϕ(⋅)作指数函数定义后, 可以改写 定理6 , 就成了soft-max
图: soft_max 得到 label与pred两个list的概率后, 用交叉熵作损失函数, 得到了最终的loss.
参考
- ICML '2007, MIcrosoft, Learning to Rank: From Pairwise Approach to Listwise Approach
- CIKM '2017, Alibaba, Session-aware Information Embedding for E-commerce Product Recommendation
- CIKM '2023, Regression Compatible Listwise Objectives for Calibrated Ranking with Binary Relevance
- 2018, Google, Seq2Slate: Re-ranking and Slate Optimization with RNNs
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献8条内容
已为社区贡献8条内容








所有评论(0)