javaweb(AI)-----后端
在application.properties文件中,配置spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc01,表示连接上jdbc01数据库表。最好解除耦合——解耦:设置一个容器,存储各个功能的依赖以及实现类,在需要的时候调用。性能也更高,避免了不断进行缓存判断(sql语法检查,优化,编译)。请求数据格式:请求行(方式,路径,协议);是持
Maven
用于管理和构建Java项目的工具



导入Maven
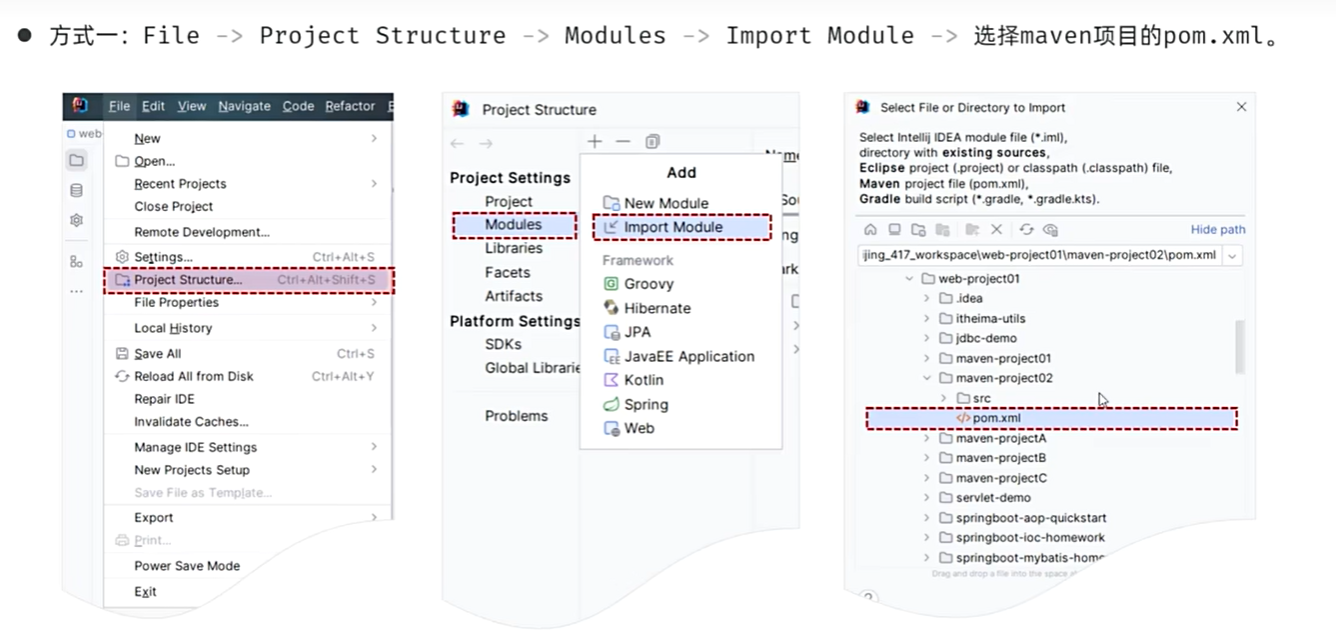
方式1
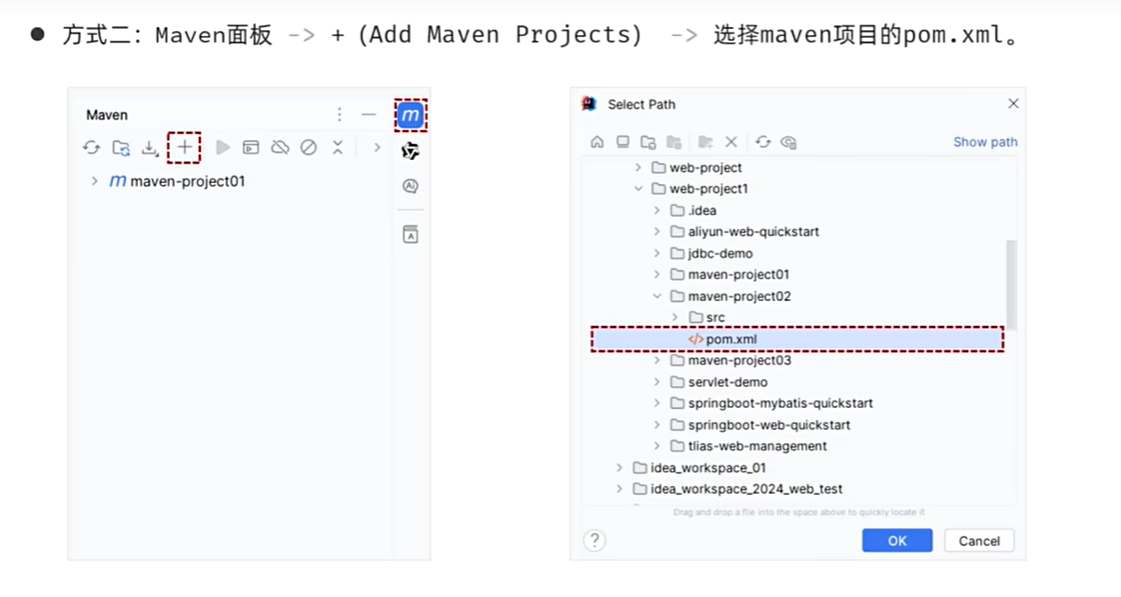
方式2
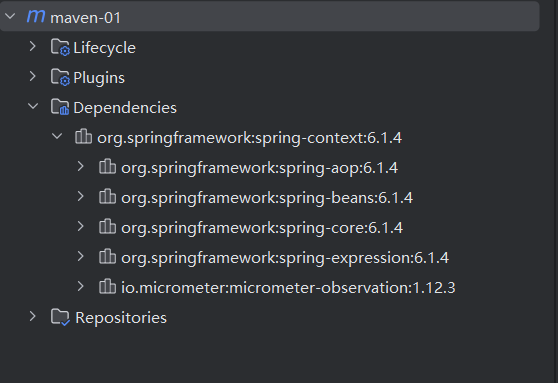
依赖管理

<!--依赖的坐标信息-->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.1.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>排除依赖 exclusion
不需要dependencies下面的部分依赖
<!-- 排除-->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-observation</artifactId>
</exclusion>
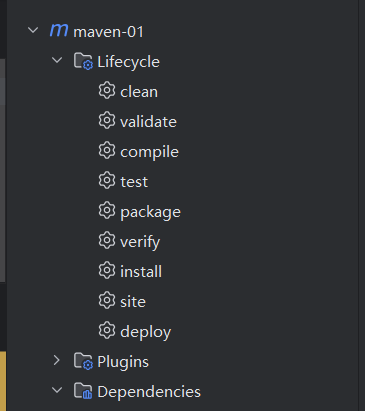
</exclusions>生命周期
clean:清理
default:核心(编译,测试,打包,安装,部署)
site:生成报告,发布站点

生命周期阶段

右侧maven面板,双击运行
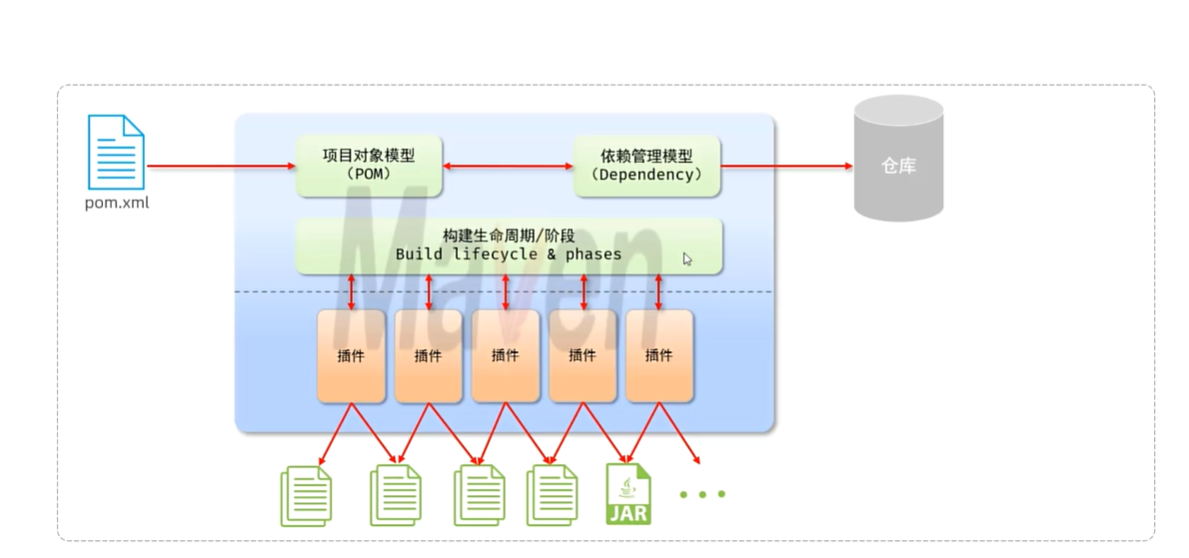
maven的底层就是插件管理
单元测试
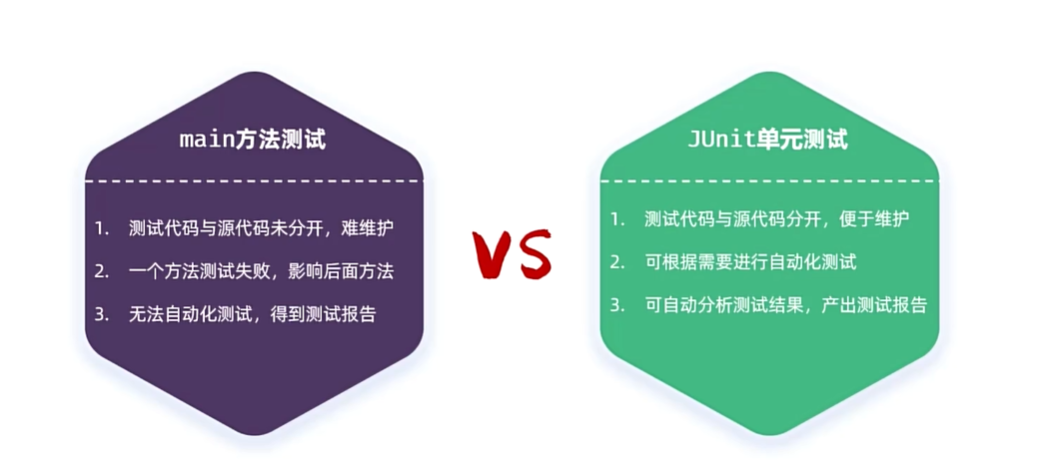
针对方法进行测试,使用JUnit测试框架
Main方法的不足:测试代码与源代码未分开,难以维护;一个方法测试失败,影响后面方法;无法自动化测试,得不到测试报告
而JUnit避免了这些缺点
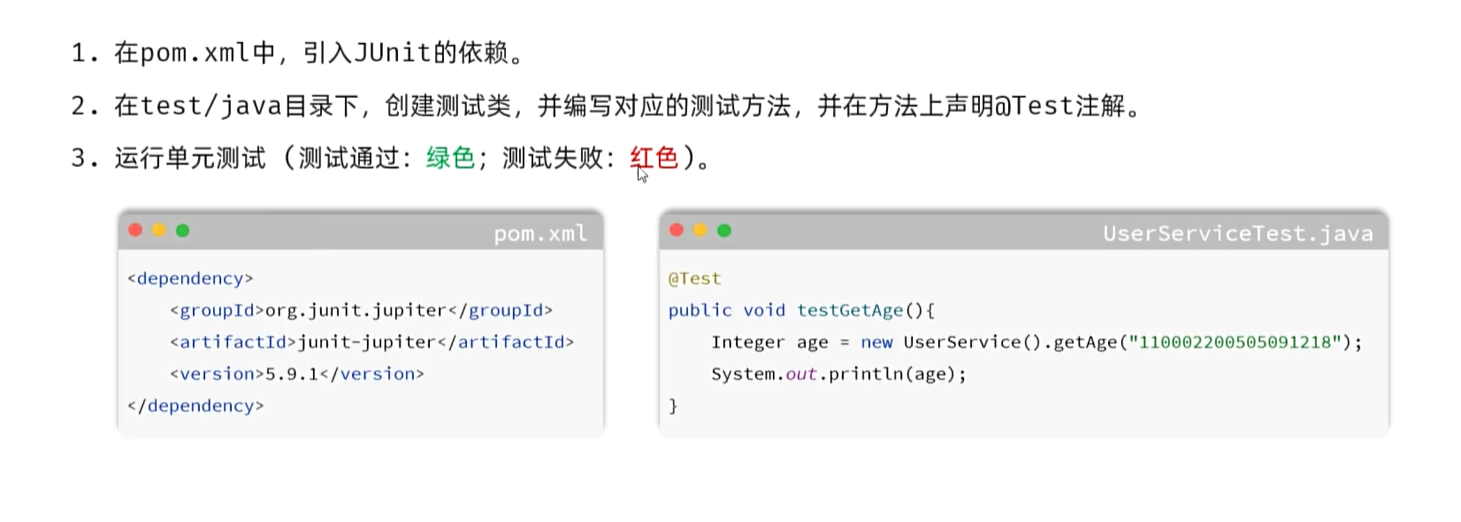
单元测试步骤
<!-- JUnit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.9.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>测试
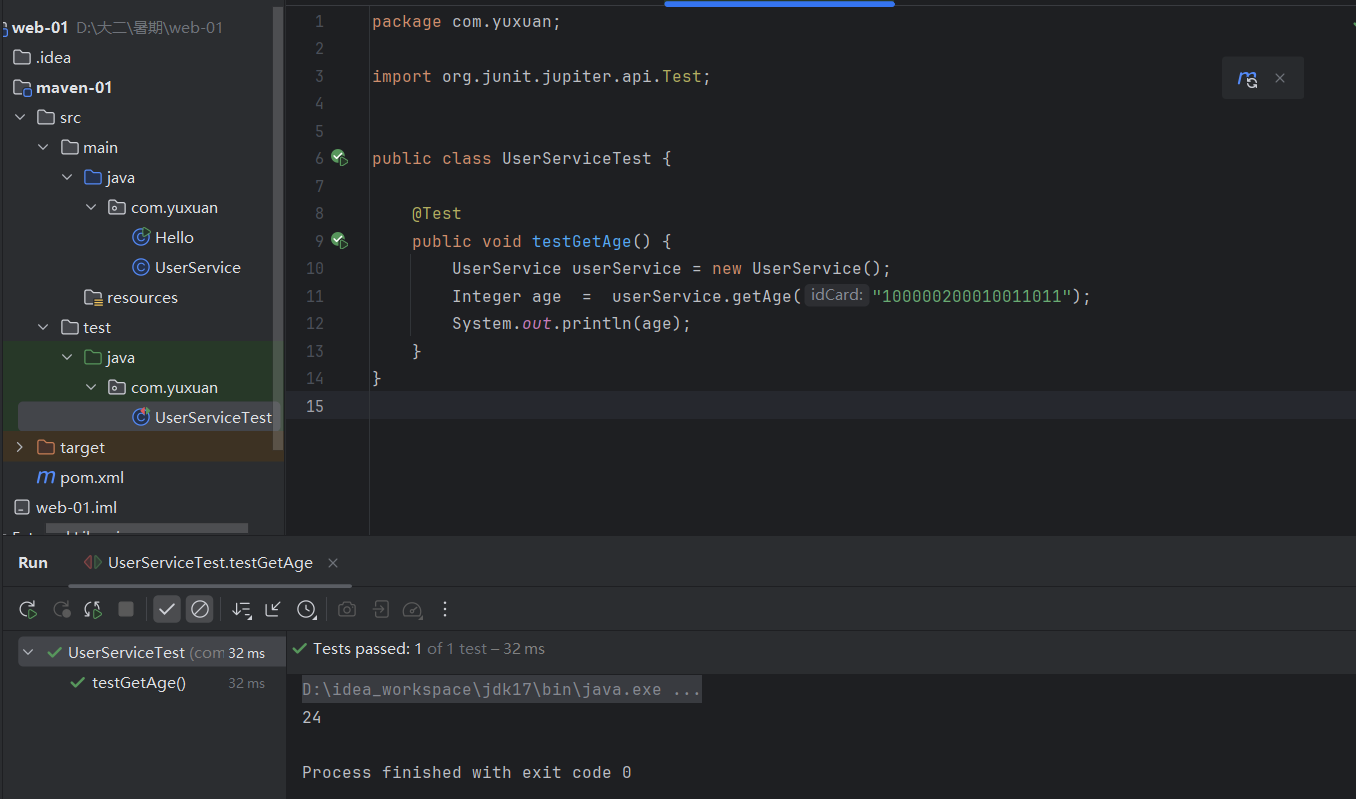
package com.yuxuan;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class UserServiceTest {
@Test
public void testGetAge() {
UserService userService = new UserService();
Integer age = userService.getAge("100000200010011011");
System.out.println(age);
}
}package com.yuxuan;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class UserService {
public Integer getAge(String idCard) {
if(idCard == null || idCard.length() != 18){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("无效");
}
String birthday = idCard.substring(6, 14);
LocalDate parse = LocalDate.parse(birthday, DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMdd"));
return Period.between(parse, LocalDate.now()).getYears();
}
}
断言
单元测试方法运行不报错,不代表业务逻辑没错
断言: Assertions.assertXXX()

// 断言
@Test
public void testGenderWithAssert(){
UserService userService = new UserService();
String gender = userService.getGender("100000200010011011");
Assertions.assertEquals("男",gender);
}
@Test
public void testGenderWithAssert2(){
UserService userService = new UserService();
//程序异常抛出的类型(IllegalArgument)与期望一致
Assertions.assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, ()->{
userService.getGender(null);
});
}注解


统计覆盖率
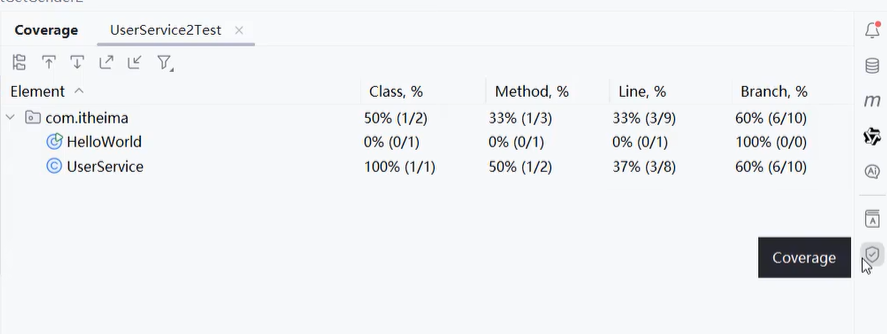
Line:代码覆盖率
Branch:分支覆盖率
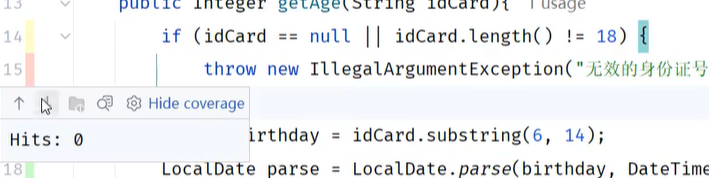
红色,hits:0 表明这段代码没有覆盖到
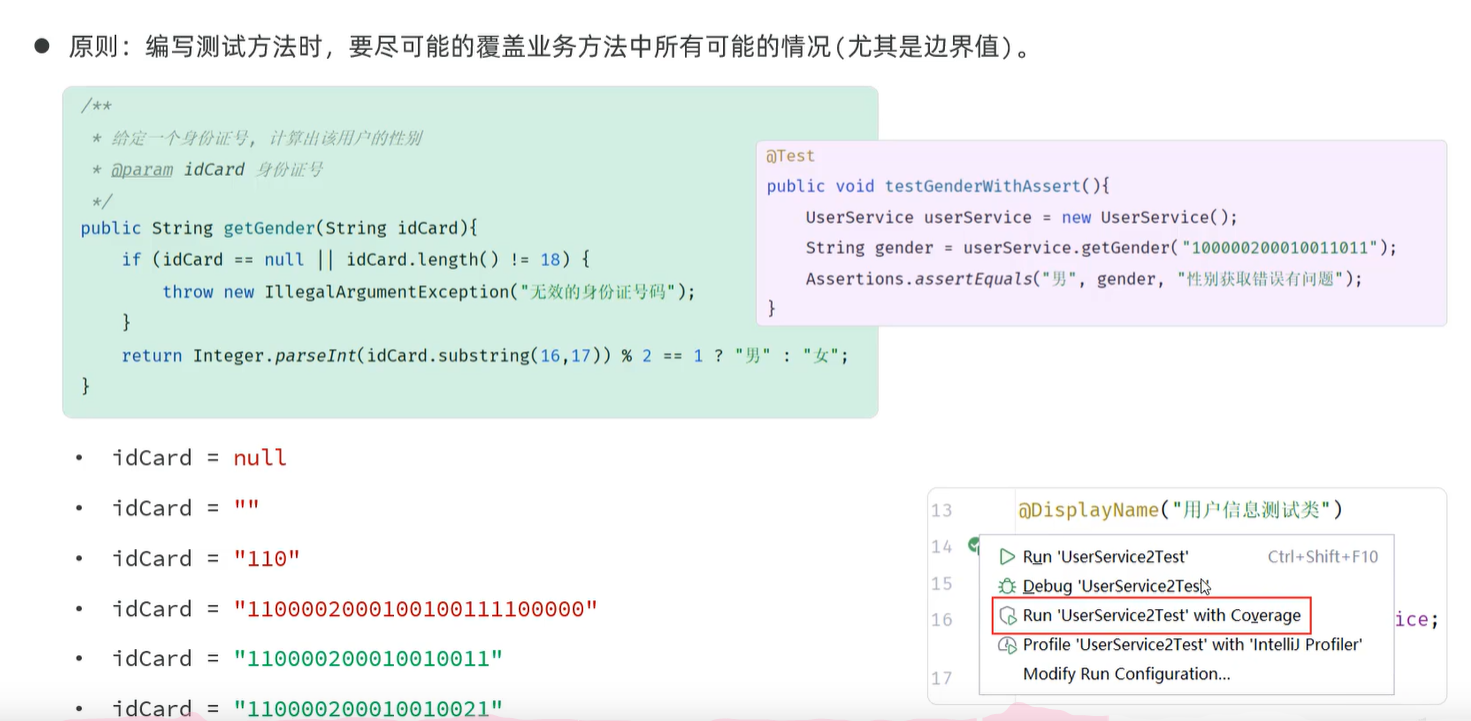

通过依赖范围,使测试代码只能放在test目录

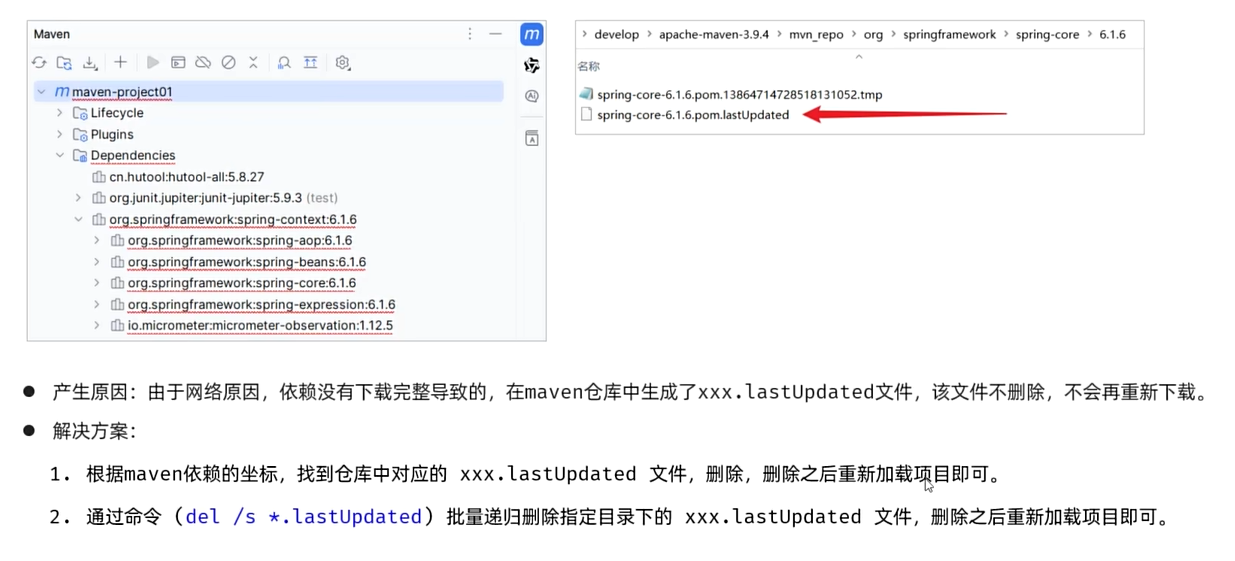
maven文件报错,无法加载的解决措施

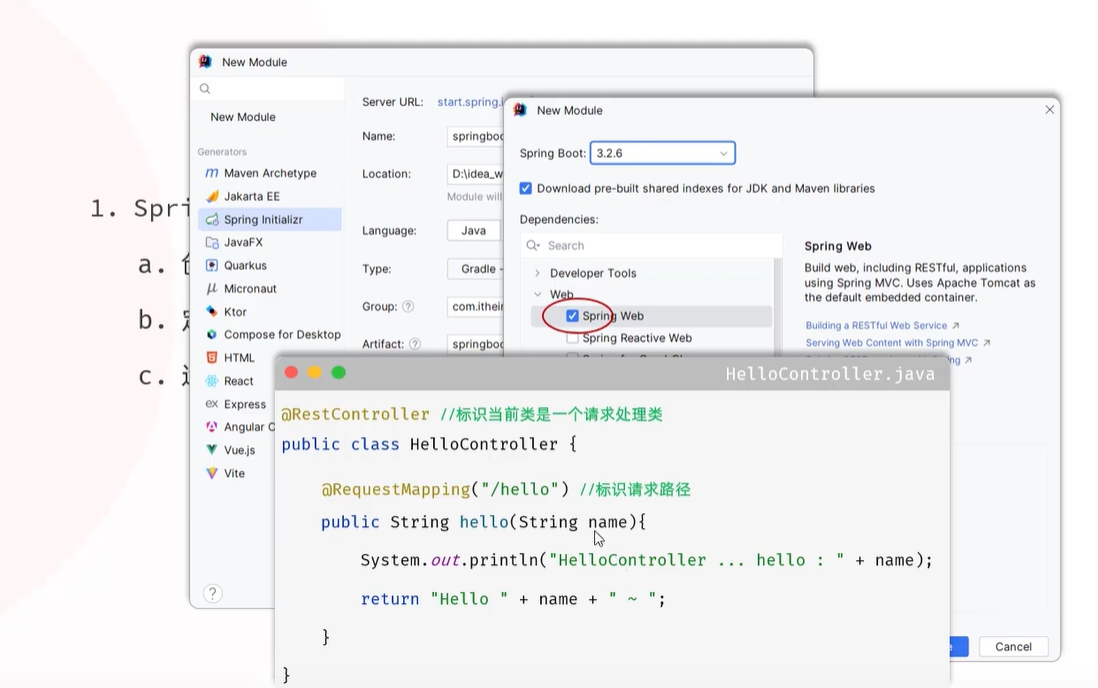
springboot
创建
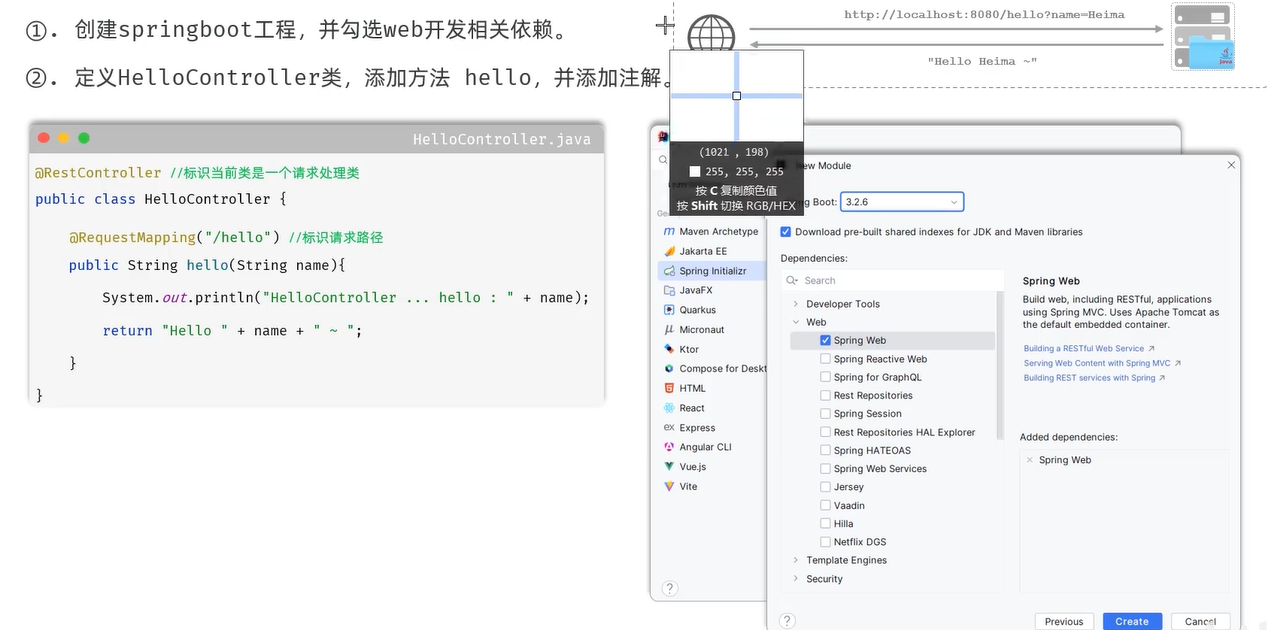
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(String name) {
System.out.println("name " + name); /*控制台*/
return "hello " + name; /*显示器*/
}
}
若出现连接失误
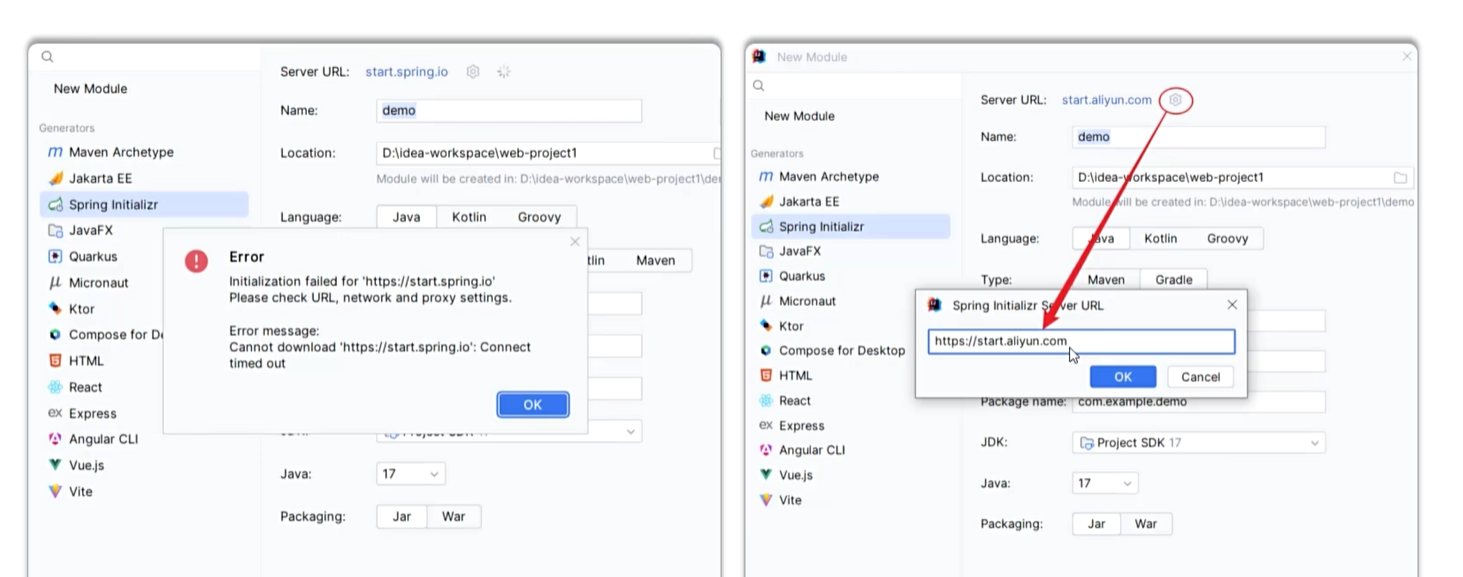
为什么用一个main方法就可启动程序:因为tomcat内嵌在起步依赖里

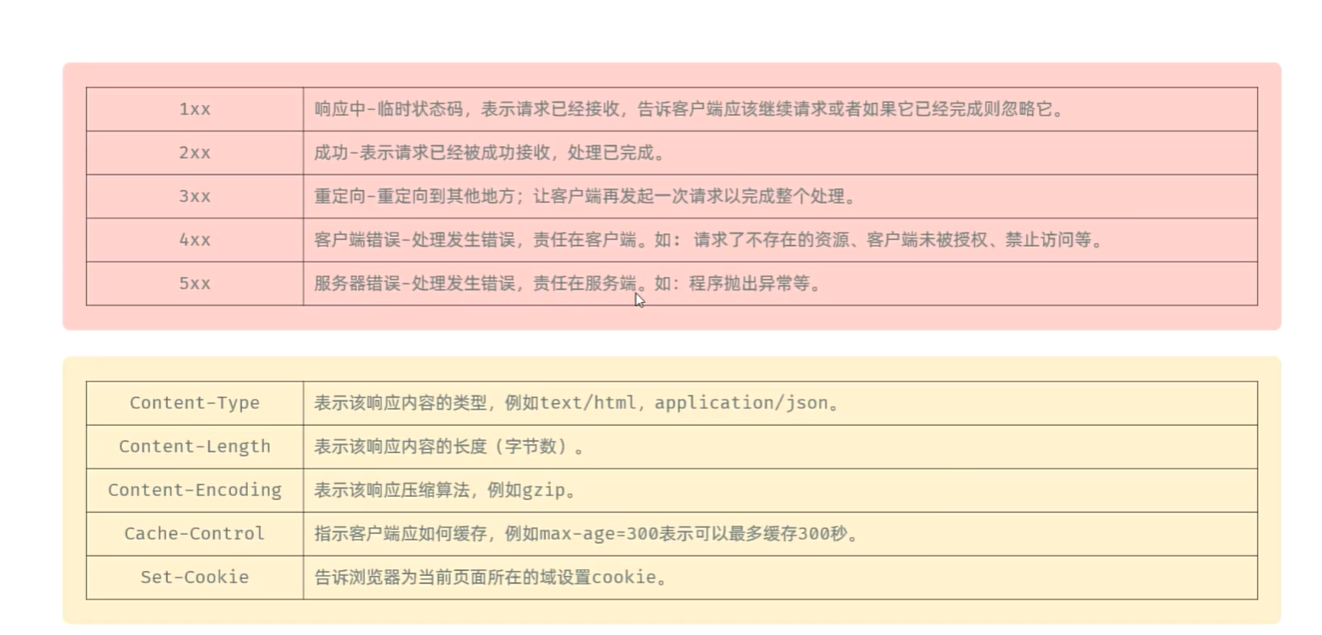
HTTP协议
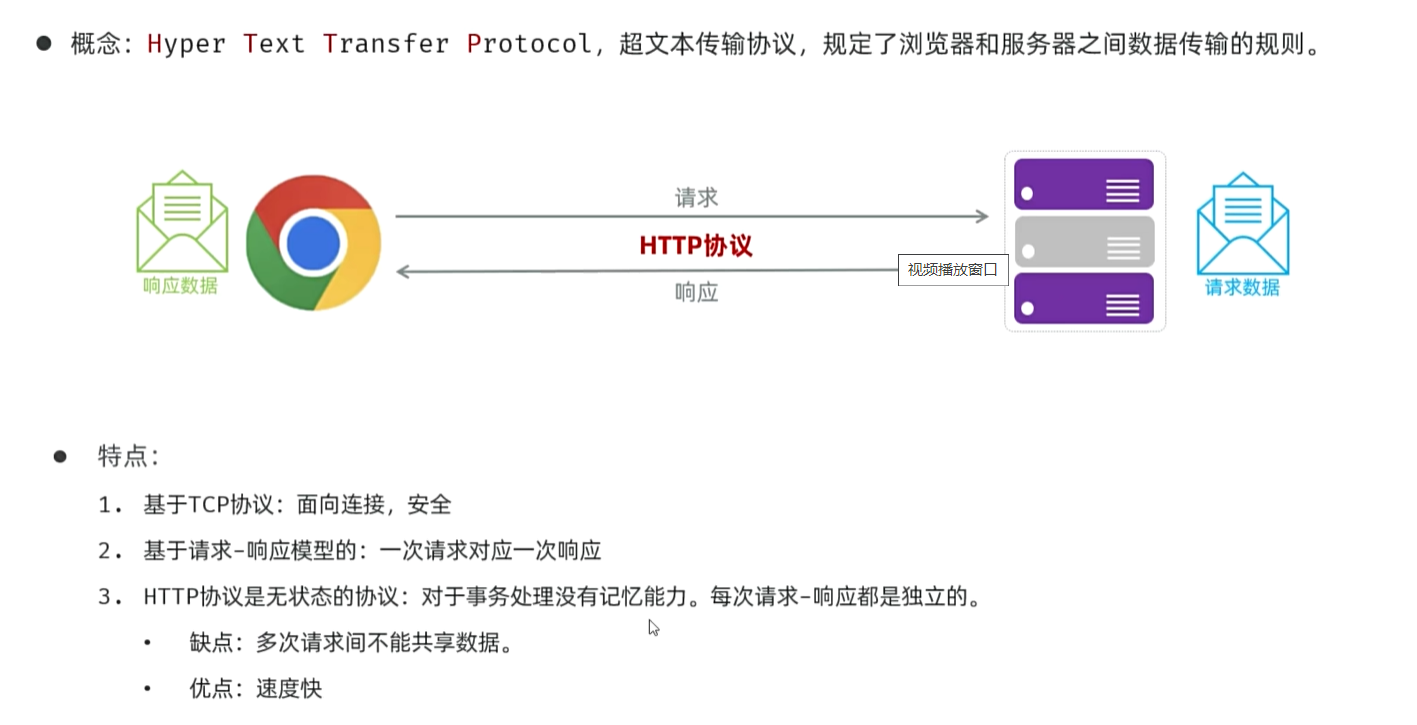
HTTP请求协议Request
请求数据格式:请求行(方式,路径,协议);请求头(key:value);请求体(针对POST)
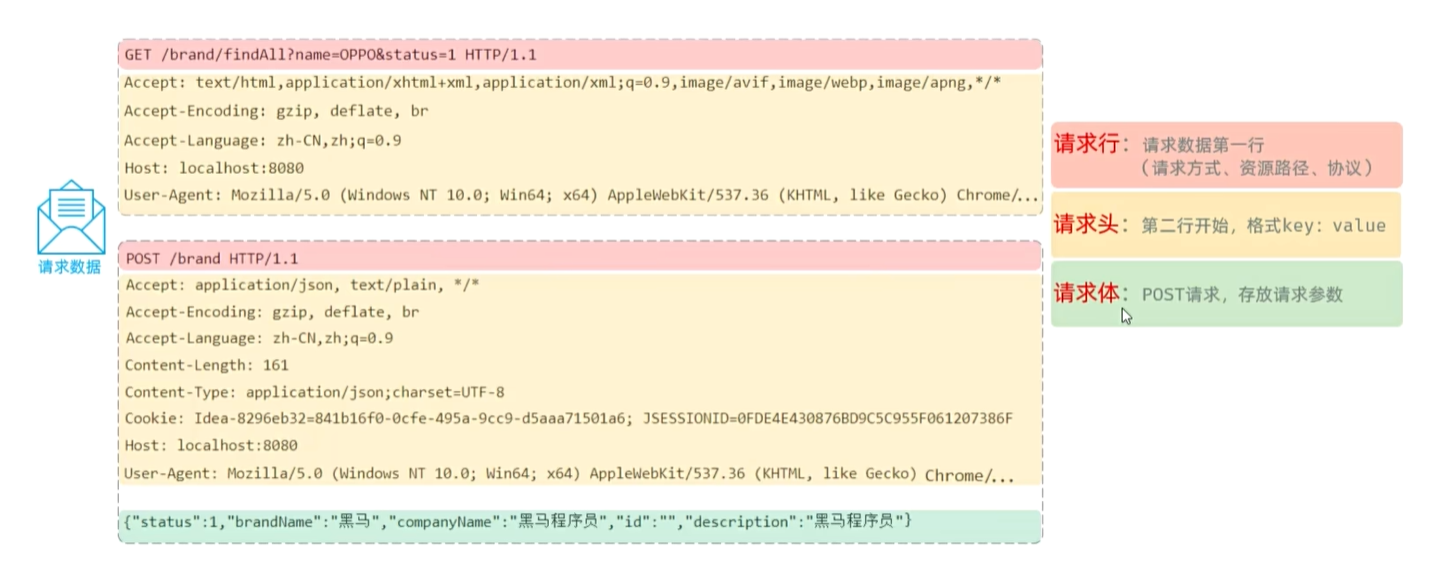
获取请求数据
package com.yuxuan;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class RequestController {
@RequestMapping("/meth")
public String request(HttpServletRequest request) {
String name = request.getParameter("name");
System.out.println("name " + name);
return "ok" ;
}
}
响应协议Response
响应行;响应头;响应体



方式一:
package com.yuxuan;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ResponseController {
@RequestMapping
public void response(HttpServletResponse response) {
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK); /* SC_OK 是常量,200 */
response.setHeader("name", "zero");
}
}
方式2
@RequestMapping("/responseEntity")
public ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity() {
return ResponseEntity.status(401).header("name", "zero").body("hello entity2");
}

分层解耦
数据访问 Dao
逻辑处理 Service
接收,响应数据 Controller
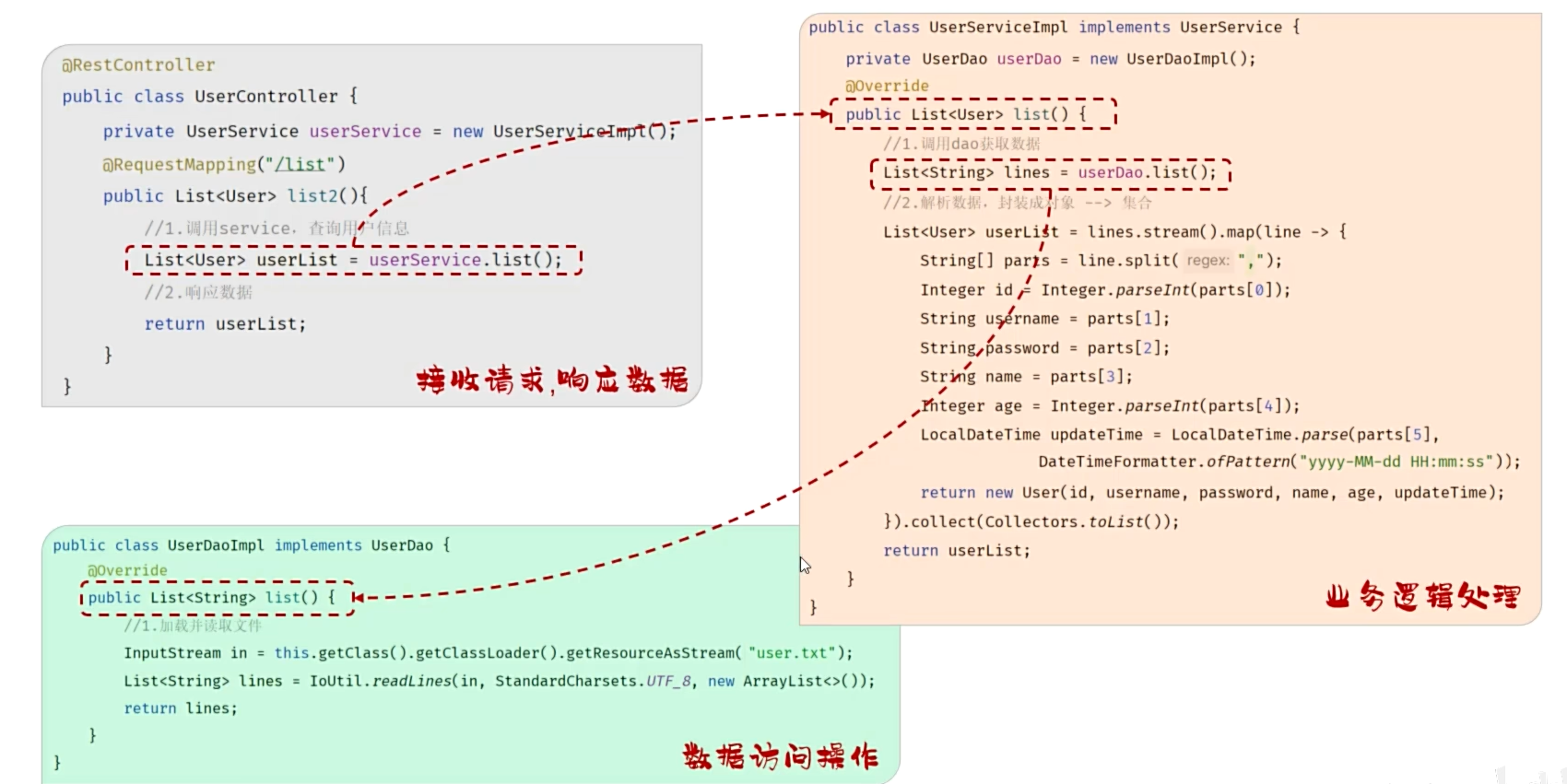
耦合:层与层,模块与模块之间的依赖关联程度
内聚:模块内部各功能间联系
高内聚低耦合
最好解除耦合——解耦:设置一个容器,存储各个功能的依赖以及实现类,在需要的时候调用
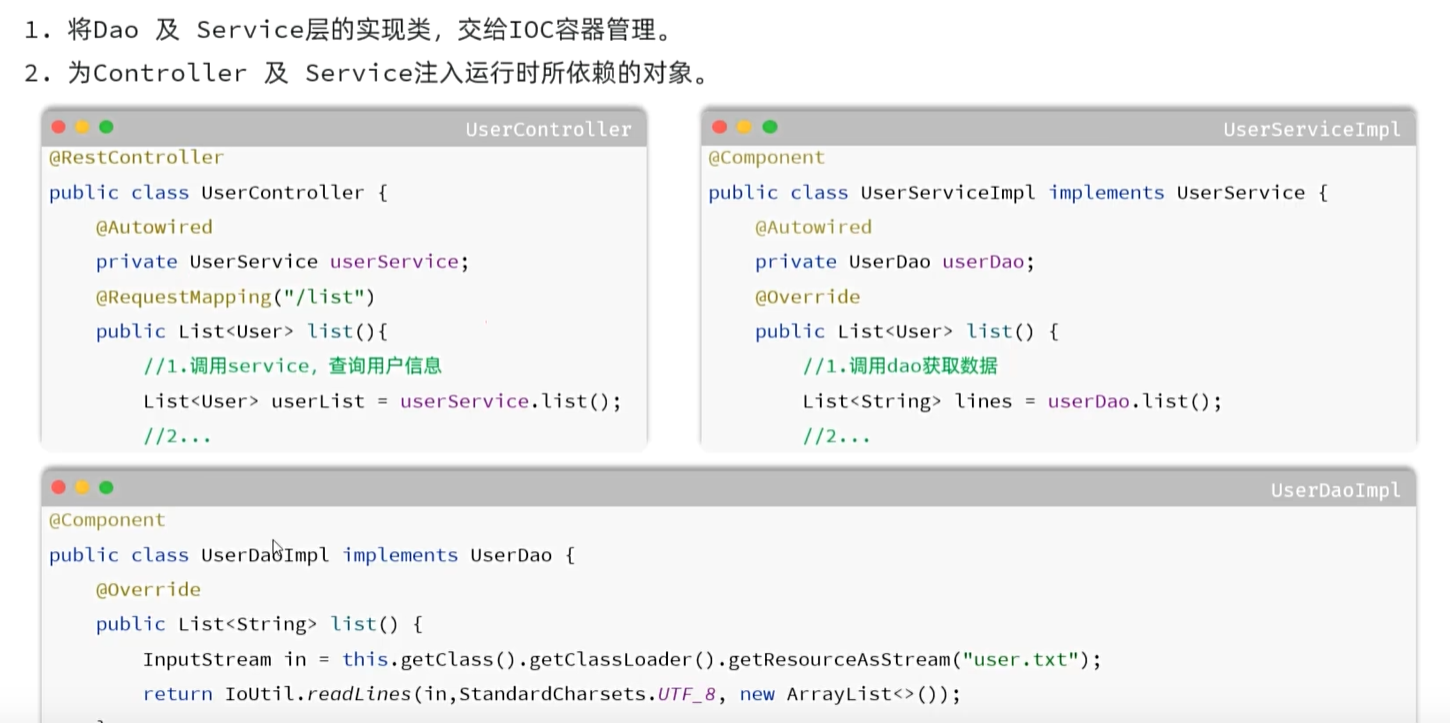
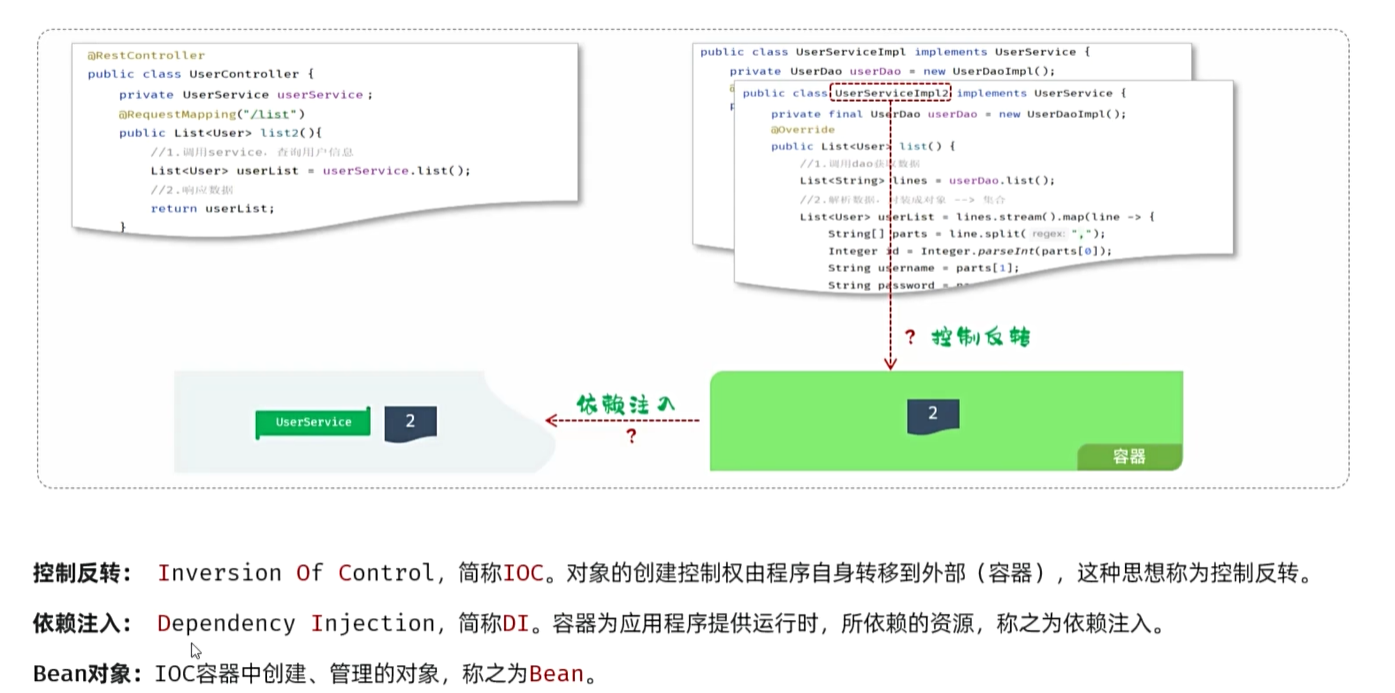

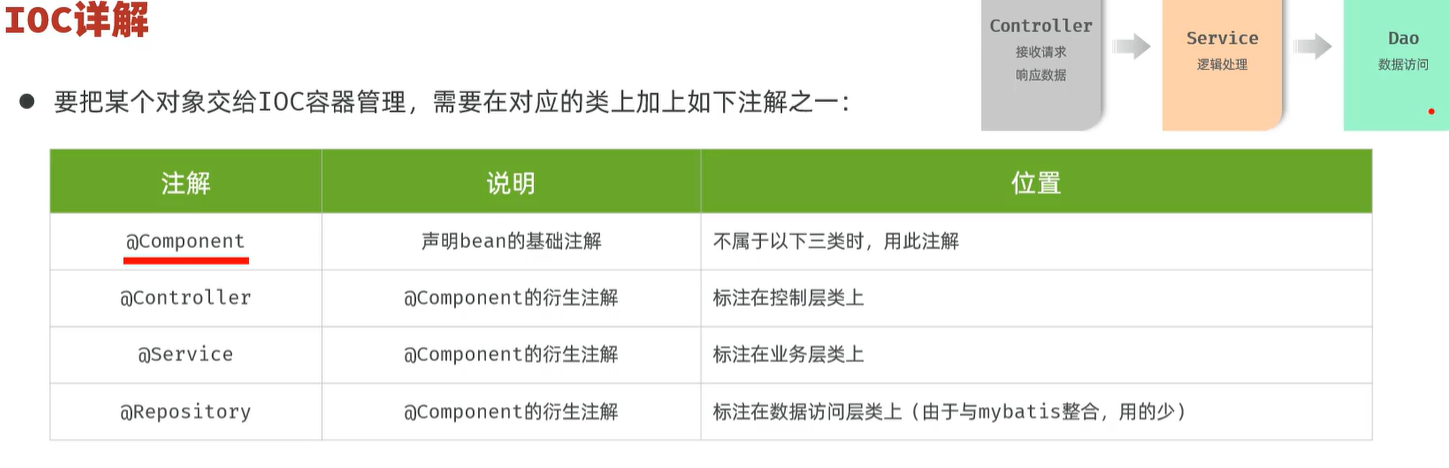
IOC
controller:接受请求,响应数据
service:逻辑处理
dao:数据访问
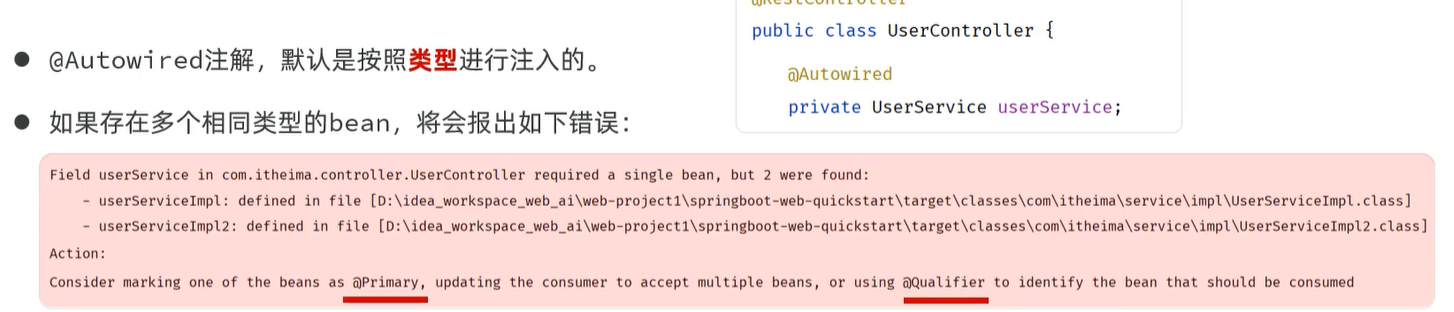
声明Bean时,可以通过声明以下四个注解的value属性指定
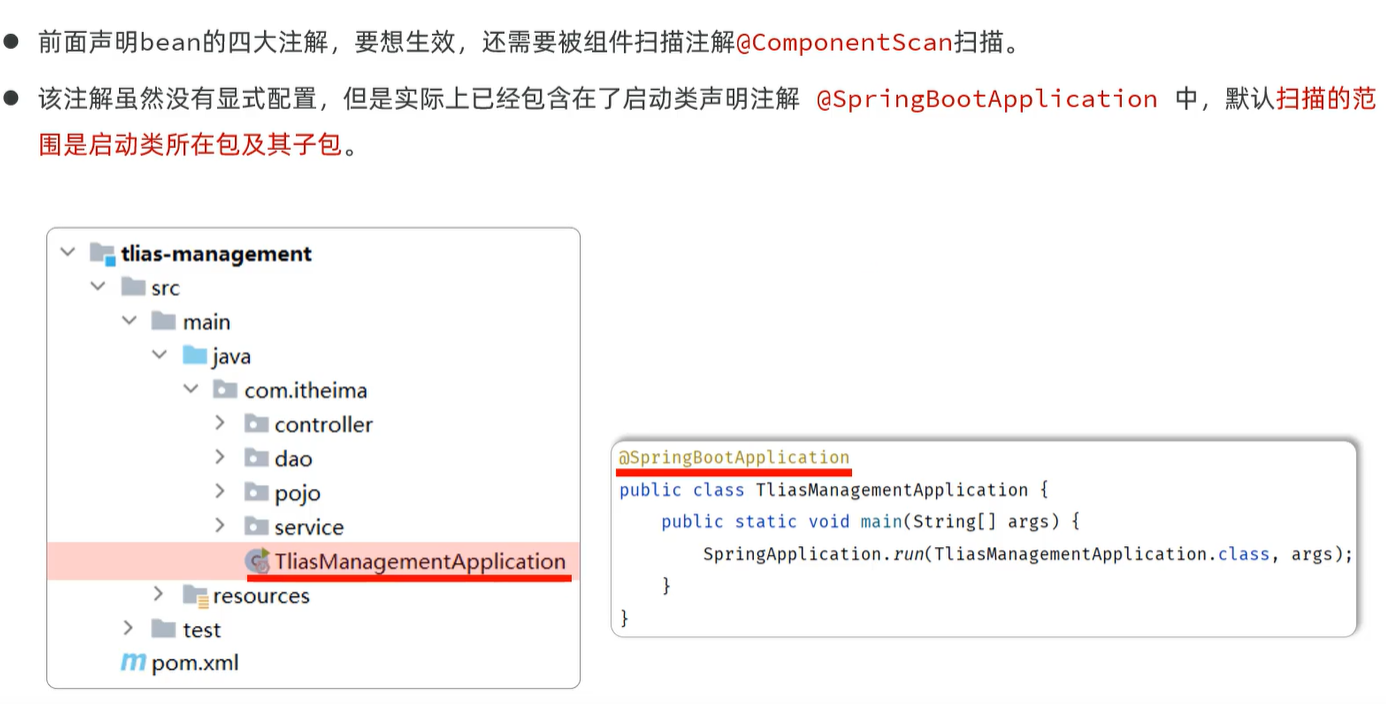
注意启动类需要放在子包同一级,避免注解无法被扫描
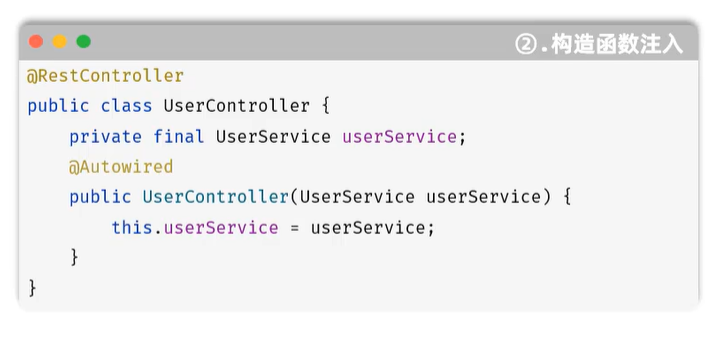
DI
@Autowired
private Userdao userdao ;



MySQL
连接: mysql -u用户名 -p密码
-h数据库服务器ip地址 -p端口号
关系型数据库:由多张相互连接的二维表组成的数据库
分类:
DDL 数据库定义语言
DML 数据库操纵语言(增删改)
DQL 数据查询语言
DCL 数据控制语言(创建用户,设置访问权限)
DDL

约束
概念:所谓约束就是作用在表中字段上的规则,用于限制存储在表中的数据。
作用:就是来保证数据库当中数据的正确性、有效性和完整性。
关于SQL语句查看别的文章
JDBC
使用java语言操作关系型数据库的一套API
但是使用JDBC会比较繁琐,所以通常使用Mybatis、MybatisPlus、Hibernate、SpringDataJPA。
JDBC是mybatis的底层逻辑
(之前都是使用MYSQL图形化工具,而JDBC是通过JAVA程序操作数据库)
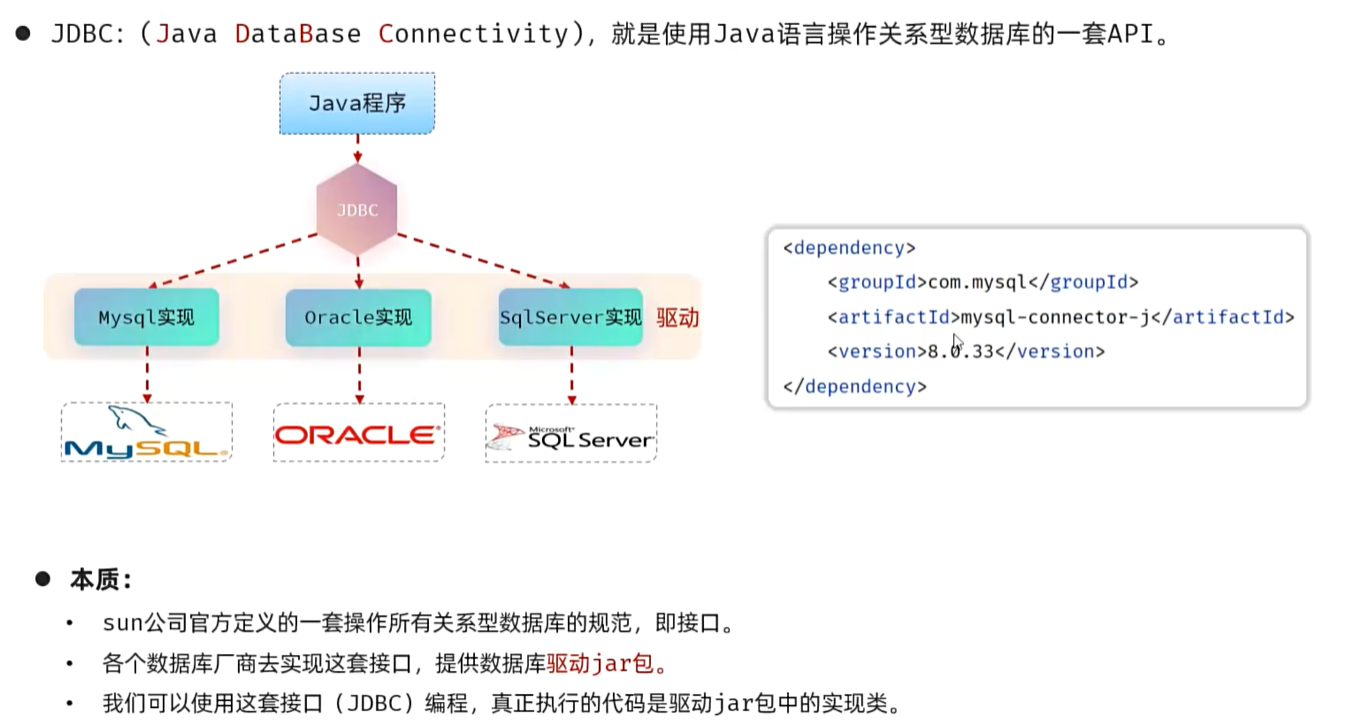
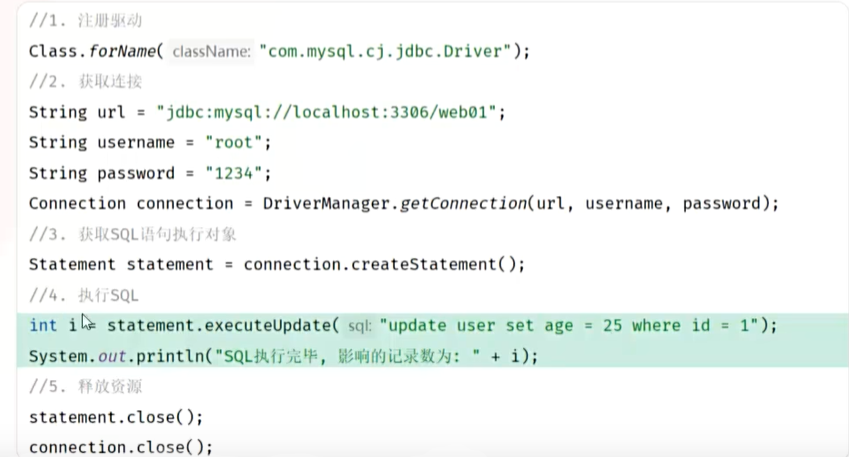
- MySQL 8.0 及以上版本推荐使用新版驱动类
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver,旧版类com.mysql.jdbc.Driver已被标记为过时。运行jar包,用cmd指令:java -jar
使用预编译语句,避免sql注入,安全性更高;否则 ’ ‘ or '1'='1'
性能也更高,避免了不断进行缓存判断(sql语法检查,优化,编译)。
Mybatis
是持久层(Dao)框架,简化JDBC,底层就是JDBC
Mybatis :
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user")
public List<User> findAll();
}使用Mybatis查询用户数据步骤:
1.准备工作(一个项目准备一次)
创建springboot,引入相关依赖;准备user;配置(在application.properties中数据库连接信息)
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/web01 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=12342.编写Mybatis程序
编写持久层接口,命名规范 XxxMapper
如何连接上数据库?
在application.properties文件中,配置spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc01,表示连接上jdbc01数据库表。
(待补充)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容








所有评论(0)