《C++并发编程实战》第6章 设计基于锁的并发数据结构
第三种处理方式是,将std::shared_ptr<>的初始化语句移动到push()的调用处,令队列容器改为存储std::shared_ptr<>,而不再直接存储数据的值。然而,若该觉醒的线程在执行wait_and_pop()时抛出异常(譬如新指针std::shared_ptr<>在构建时就有可能产生异常④),就不会有任何其他线程被唤醒。第二种处理方式是,倘若有异常抛出,则在wait_and_p
6.1 并发设计的内涵
6.2 基于锁的并发数据结构
基于锁的栈
版本1
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
#include <thread>
#include <future>
#include <exception>
// 版本1 begin
struct empty_stack : std::exception
{
const char *what() const throw()
{
return "empty stack!";
}
};
template <typename T>
class threadsafe_stack
{
private:
std::stack<T> data;
mutable std::mutex m;
public:
threadsafe_stack() {}
threadsafe_stack(const threadsafe_stack &other)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(other.m);
data = other.data;
}
threadsafe_stack &operator=(const threadsafe_stack &) = delete;
void push(T new_value)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
data.push(std::move(new_value));
}
std::shared_ptr<T> pop()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
if (data.empty())
throw empty_stack();
std::shared_ptr<T> const res(std::make_shared<T>(std::move(data.top())));
// std::shared_ptr<T> const res(data.top()); // 错误写法 因为data.top()返回的是对象的引用
data.pop();
return res;
}
void pop(T &value)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
if (data.empty())
throw empty_stack();
value = std::move(data.top());
data.pop();
}
bool empty() const
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
return data.empty();
}
};
// 版本2 end
int main()
{
threadsafe_stack<int> ts_stack;
ts_stack.pop();
return 0;
}
问题1
栈中执行用户自定义的操作可能会面临死锁。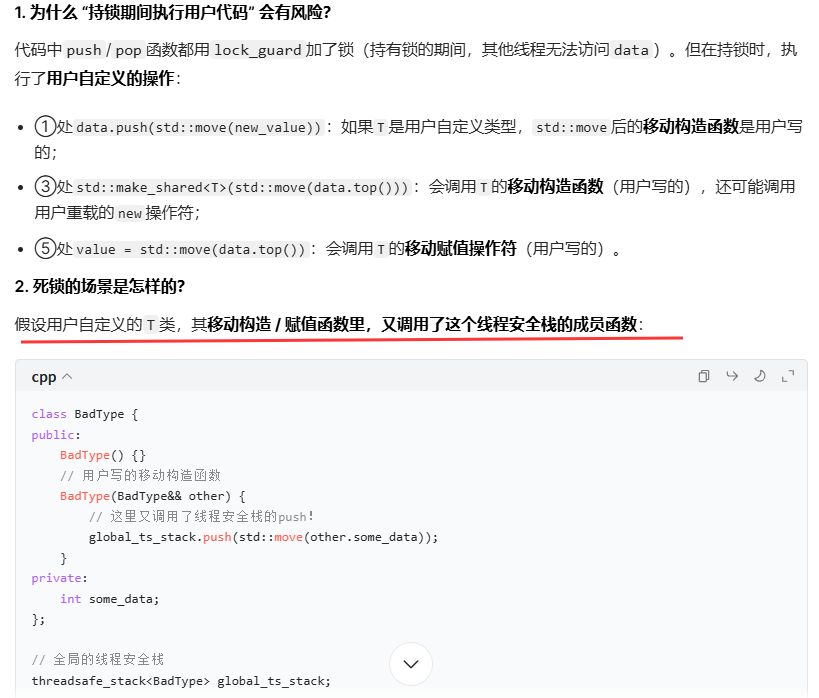

线程安全栈的锁,只能保护 “栈本身的操作”;但如果用户写的类型T,其构造 / 赋值函数里又操作了同一个栈,就会在 “持锁时再次请求锁”,导致死锁。这个风险无法由栈的实现者解决,只能靠用户规范自己的代码。
队列
基于锁和条件变量的队列
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
#include <thread>
#include <future>
#include <exception>
// 版本1 begin 安全的栈
// struct empty_stack : std::exception
// {
// const char *what() const throw()
// {
// return "empty stack!";
// }
// };
// template <typename T>
// class threadsafe_stack
// {
// private:
// std::stack<T> data;
// mutable std::mutex m;
// public:
// threadsafe_stack() {}
// threadsafe_stack(const threadsafe_stack &other)
// {
// std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(other.m);
// data = other.data;
// }
// threadsafe_stack &operator=(const threadsafe_stack &) = delete;
// void push(T new_value)
// {
// std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
// data.push(std::move(new_value));
// }
// std::shared_ptr<T> pop()
// {
// std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
// if (data.empty())
// throw empty_stack();
// std::shared_ptr<T> const res(std::make_shared<T>(std::move(data.top())));
// // std::shared_ptr<T> const res(data.top()); // 错误写法 因为data.top()返回的是对象的引用
// data.pop();
// return res;
// }
// void pop(T &value)
// {
// std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
// if (data.empty())
// throw empty_stack();
// value = std::move(data.top());
// data.pop();
// }
// bool empty() const
// {
// std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
// return data.empty();
// }
// };
// 版本2 end
template <typename T>
class threadsafe_queue
{
private:
mutable std::mutex mut;
std::queue<T> data_queue;
std::condition_variable data_cond;
public:
threadsafe_queue() {}
void push(T new_value)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mut);
data_queue.push(std::move(new_value));
data_cond.notify_one();
}
void wait_and_pop(T &value)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(mut);
data_cond.wait(lk, [this]
{ return !data_queue.empty(); });
value = std::move(data_queue.front());
data_queue.pop();
}
std::shared_ptr<T> wait_and_pop()
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(mut);
data_cond.wait(lk, [this]
{ return !data_queue.empty(); });
std::shared_ptr<T> res(std::make_shared<T>(std::move(data_queue.front())));
data_queue.pop();
return res;
}
bool try_pop(T &value)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mut);
if (data_queue.empty())
return false;
value = std::move(data_queue.front());
data_queue.pop();
return true;
}
std::shared_ptr<T> try_pop()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mut);
if (data_queue.empty())
return std::shared_ptr<T>();
std::shared_ptr<T> res(
std::make_shared<T>(std::move(data_queue.front())));
data_queue.pop();
return res;
}
bool empty() const
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mut);
return data_queue.empty();
}
};
int main()
{
return 0;
}
问题1 wait_and_pop()时抛出异常
然而,若该觉醒的线程在执行wait_and_pop()时抛出异常(譬如新指针std::shared_ptr<>在构建时就有可能产生异常④),就不会有任何其他线程被唤醒。
第一种处理方式是,如果我们不能接受这种行为方式,则将data_cond.notify_one()改为data_cond.notify_all(),这轻而易举。这样就会唤醒全体线程,但要大大增加开销:它们绝大多数还是会发现队列依然为空[2],只好重新休眠。
第二种处理方式是,倘若有异常抛出,则在wait_and_pop()中再次调用notify_one(),从而再唤醒另一线程,让它去获取存储的值。
第三种处理方式是,将std::shared_ptr<>的初始化语句移动到push()的调用处,令队列容器改为存储std::shared_ptr<>,而不再直接存储数据的值。从内部std::queue<>复制std::shared_ptr<>实例的操作不会抛出异常,所以wait_and_pop()也是异常安全的
为什么使用共享智能指针不会抛出异常,因为赋值操作对应共享智能指针而要是将引用计数加1。std::shared_ptr 的“拷贝”是轻量、原子、无分配、noexcept 的;抛异常只可能发生在“创建 shared_ptr”那一刻,而不是“复制 shared_ptr”。
基于方法三的改进
template<typename T>
class threadsafe_queue
{
private:
mutable std::mutex mut;
std::queue<std::shared_ptr<T>> data_queue;
std::condition_variable data_cond;
public:
threadsafe_queue()
{}
void wait_and_pop(T& value)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(mut);
data_cond.wait(lk,[this]{return !data_queue.empty();});
value=std::move(*data_queue.front()); ⇽--- ①
data_queue.pop();
}
bool try_pop(T& value)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mut);
if(data_queue.empty())
return false;
value=std::move(*data_queue.front()); ⇽--- ②
data_queue.pop();
return true;
}
std::shared_ptr<T> wait_and_pop()
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(mut);
data_cond.wait(lk,[this]{return !data_queue.empty();});
std::shared_ptr<T> res=data_queue.front(); ⇽--- ③
data_queue.pop();
return res;
}
std::shared_ptr<T> try_pop()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mut);
if(data_queue.empty())
return std::shared_ptr<T>();
std::shared_ptr<T> res=data_queue.front(); ⇽--- ④
data_queue.pop();
return res;
}
void push(T new_value)
{
std::shared_ptr<T> data(
std::make_shared<T>(std::move(new_value))); ⇽--- ⑤
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mut);
data_queue.push(data);
data_cond.notify_one();
}
bool empty() const
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(mut);
return data_queue.empty();
}
};
基于精细粒度的锁和条件变量的队列
template <typename T>
class queue
{
private:
struct node
{
T data;
sdt::unique_ptr<node> next;
node(T data_) : data(std::move(data)) {}
};
std::unique_ptr<node> head;
node *tail;
public:
queue() : tail(nullptr) {}
queue(const queue &other) = delete;
queue &operator=(const queue &other) = delete;
std::shared_ptr<T> try_pop()
{
if (!head) // 当指针为空
{
return std::shared_ptr<T>();
}
std::shared_ptr<T> const res(std::make_shared<T>(std::move(head->data)));
std::unique_ptr<node> const old_head = std::move(head); // 这一步可以省略吗? 可以
head = sdt::move(old_head->next);
if (!head) // 当取出元素之后,头指针为空
tail = nullptr;
return res; // 旧的头结点old_head在这里被销毁
}
void push(T new_value)
{
std::unique_ptr<node> p(new node(std::move(new_value)));
node *const new_tail = p.get();
if (tail)
{
tail->next = std::move(p);
}
else // 队列为空
{
head = std::move(p);
}
tail = new_tail;
}
};
- 对于上面代码的疑问
为什么使用unique_ptr指针,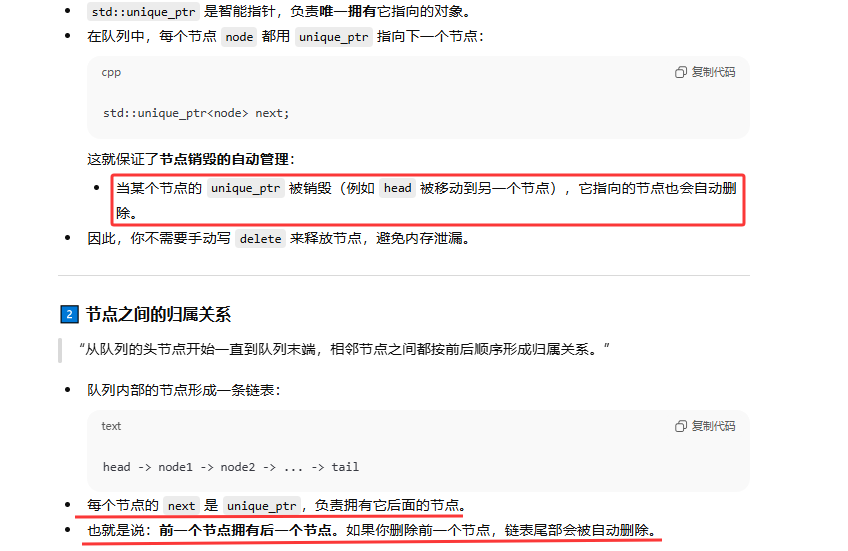
- 为什么需要 tail 原生指针
因为你需要去操作为尾节点,而尾阶段只能被他前一个阶段的unique_ptr独占指向,所以只能使用裸指针
1.通过分离数据而实现并
上述问题的本质就是就算我们使用两个互斥来互斥访问头尾指针,但是我们不能分清一种时机,就是两个线程同时去互斥的访问头指针和尾指针时,不能确定这两个指针所指向的阶段是否是统一个节点。
本方法的解决思路就是,保证队列中至少有一个节点。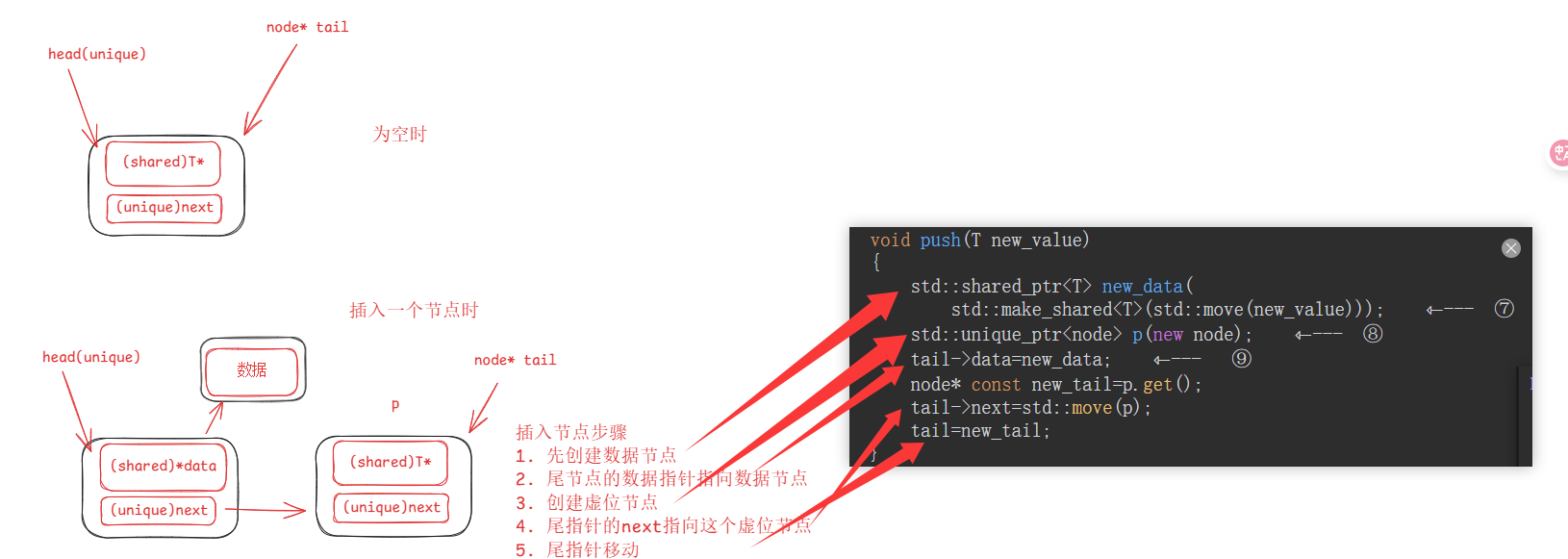
push()只访问tail指针而不再触及head指针
template <typename T>
class queue
{
private:
struct node
{
T data;
sdt::unique_ptr<node> next;
node(T data_) : data(std::move(data)) {}
};
std::unique_ptr<node> head;
node *tail;
public:
queue() : tail(nullptr) {}
queue(const queue &other) = delete;
queue &operator=(const queue &other) = delete;
std::shared_ptr<T> try_pop()
{
if (!head) // 当指针为空
{
return std::shared_ptr<T>();
}
std::shared_ptr<T> const res(std::make_shared<T>(std::move(head->data)));
std::unique_ptr<node> const old_head = std::move(head); // 这一步可以省略吗? 可以
head = sdt::move(old_head->next);
if (!head) // 当取出元素之后,头指针为空
tail = nullptr;
return res; // 旧的头结点old_head在这里被销毁
}
void push(T new_value)
{
std::unique_ptr<node> p(new node(std::move(new_value)));
node *const new_tail = p.get();
if (tail)
{
tail->next = std::move(p);
}
else // 队列为空
{
head = std::move(p);
}
tail = new_tail;
}
};

- 最后的方案:
template <typename T>
class threadsafe_queue
{
private:
struct node
{
std::shared_ptr<T> data;
std::unique_ptr<node> next;
};
node *tail;
std::unique_ptr<node> head;
std::mutex head_mutex;
std::mutex tail_mutex;
node *get_tail()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> tail_lock(tail_mutex);
return tail;
}
std::unique_ptr<node> pop_head()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> head_lock(head_mutex);
if (head.get() == get_tail())
{
return nullptr;
}
std::unique_ptr<node> old_head = std::move(head);
head = std::move(old_head->next);
return old_head;
}
public:
threadsafe_queue() : head(new node), tail(head.get())
{
}
threadsafe_queue(const threadsafe_queue &other) = delete;
threadsafe_queue &operator=(const threadsafe_queue &other) = delete;
std::shared_ptr<T> try_pop()
{
std::unique_ptr<node> old_head = pop_head();
return old_head ? old_head->data : std::shared_ptr<T>();
}
void push(T new_value)
{
// 创建一个新的结点
std::shared_ptr<T> new_data(std::make_shared<T>(std::move(new_value)));
std::unique_ptr<node> p(new node);
node *const new_tail = p.get();
// 修改旧尾结点的数据和next指针 : 开始加锁
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> tail_lock(tail_mutex);
tail->data = new_data;
tail->next = std::move(p);
tail = new_tail;
}
};
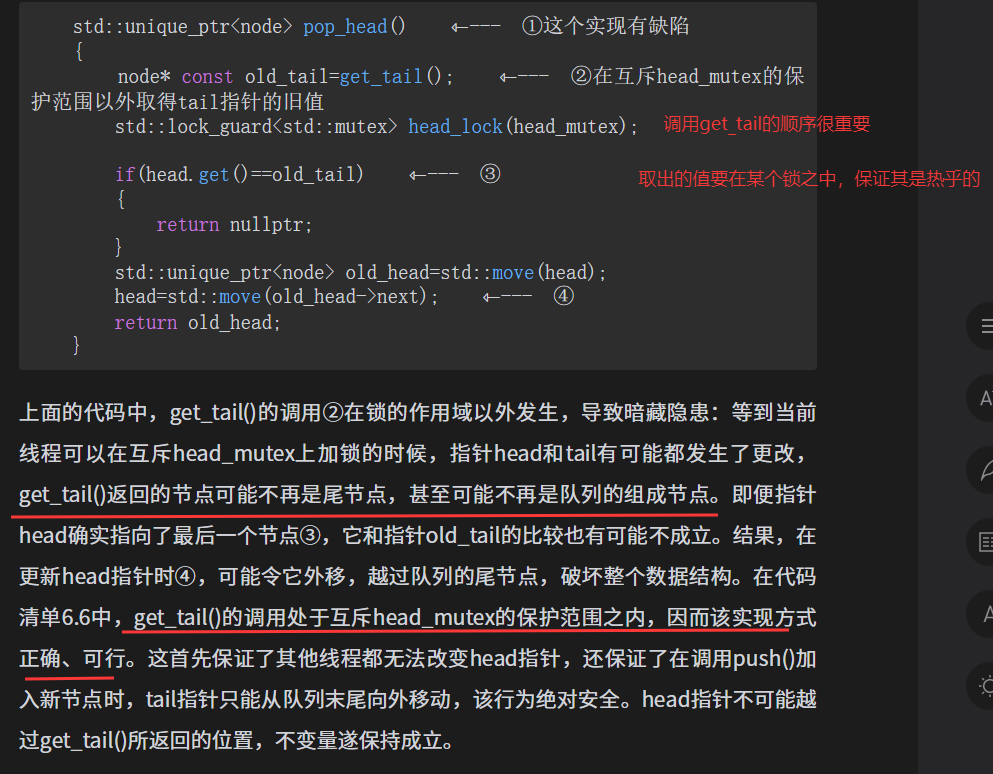
- 注意分配内存可能会导致抛出异常,所以建议使用智能指针,就算抛出异常,也会被释放
2.等待数据弹出
template<typename T>
class threadsafe_queue
{
private:
struct node
{
std::shared_ptr<T> data;
std::unique_ptr<node> next;
};
std::mutex head_mutex;
std::unique_ptr<node> head;
std::mutex tail_mutex;
node* tail;
std::condition_variable data_cond;
public:
threadsafe_queue():
head(new node),tail(head.get())
{}
threadsafe_queue(const threadsafe_queue& other)=delete;
threadsafe_queue& operator=(const threadsafe_queue& other)=delete;
std::shared_ptr<T> try_pop();
bool try_pop(T& value);
std::shared_ptr<T> wait_and_pop();
void wait_and_pop(T& value);
void push(T new_value);
bool empty();
};
template<typename T>
void threadsafe_queue<T>::push(T new_value)
{
std::shared_ptr<T> new_data(
std::make_shared<T>(std::move(new_value)));
std::unique_ptr<node> p(new node);
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> tail_lock(tail_mutex);
tail->data=new_data;
node* const new_tail=p.get();
tail->next=std::move(p);
tail=new_tail;
}
data_cond.notify_one();
}
template<typename T>
class threadsafe_queue
{
private:
node* get_tail()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> tail_lock(tail_mutex);
return tail;
}
std::unique_ptr<node> pop_head() ⇽--- ①
{
std::unique_ptr<node> old_head=std::move(head);
head=std::move(old_head->next);
return old_head;
}
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> wait_for_data() ⇽--- ②
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> head_lock(head_mutex);
data_cond.wait(head_lock,[&]{return head.get()!=get_tail();});
return std::move(head_lock); ⇽--- ③
}
std::unique_ptr<node> wait_pop_head()
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> head_lock(wait_for_data()); ⇽--- ④
return pop_head();
}
std::unique_ptr<node> wait_pop_head(T& value)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> head_lock(wait_for_data()); ⇽--- ⑤
value=std::move(*head->data);
return pop_head();
}
public:
std::shared_ptr<T> wait_and_pop()
{
std::unique_ptr<node> const old_head=wait_pop_head();
return old_head->data;
}
void wait_and_pop(T& value)
{
std::unique_ptr<node> const old_head=wait_pop_head(value);
}
};
template<typename T>
class threadsafe_queue
{
private:
std::unique_ptr<node> try_pop_head()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> head_lock(head_mutex);
if(head.get()==get_tail())
{
return std::unique_ptr<node>();
}
return pop_head();
}
std::unique_ptr<node> try_pop_head(T& value)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> head_lock(head_mutex);
if(head.get()==get_tail())
{
return std::unique_ptr<node>();
}
value=std::move(*head->data);
return pop_head();
}
public:
std::shared_ptr<T> try_pop()
{
std::unique_ptr<node> old_head=try_pop_head();
return old_head?old_head->data:std::shared_ptr<T>();
}
bool try_pop(T& value)
{
std::unique_ptr<node> const old_head=try_pop_head(value);
return old_head;
}
bool empty()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> head_lock(head_mutex);
return (head.get()==get_tail());
}
};
- 上述讨论的队列是无线队列,即队列的数量是无限的。
6.3 更复杂的并发数据结构
基于锁的查找表
template <typename Key, typename Value, typename Hash = std::hash<Key>>
class threadsafe_lookup_table
{
private:
class bucket_type
{
private:
typedef std::pair<Key, Value> bucket_value;
typedef std::list<bucket_value> bucket_data;
typedef typename bucket_data::iterator bucket_iterator;
bucket_data data;
mutable std::shared_mutex mutex;
bucket_iterator find_entry_for(Key const &key) const
{
return std::find_if(data.begin(), data.end(),
[&](bucket_value const &item)
{ return item.first == key; });
}
public:
Value value_for(Key const &key, Value const &default_value) const
{
std::shared_lock<std::shared_mutex> lock(mutex);
bucket_iterator const found_entry = find_entry_for(key);
return (found_entry == data.end()) ? default_value : found_entry->second;
}
void add_or_update_mapping(Key const &key, Value const &value)
{
std::unique_lock<std::shared_mutex> lock(mutex);
bucket_iterator const found_entry = find_entry_for(key);
if (found_entry == data.end()) // 要添加的键不存在
{
data.push_back(bucket_value(key, value));
}
else // 要添加的键已存在
{
found_entry->second = value;
}
}
void remove_mapping(Key const &key)
{
std::unique_lock<std::shared_mutex> lock(mutex);
bucket_iterator const found_entry = find_entry_for(key);
if (found_entry != data.end())
{
data.erase(found_entry);
}
}
};
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<bucket_type>> buckets;
Hash hasher;
bucket_type &get_bucket(Key const &key) const // 函数作用
{
std::size_t const bucket_index = hasher(key) % buckets.size();
return *buckets[bucket_index];
}
public:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Value mapped_type;
typedef Hash hash_type;
threadsafe_lookup_table(unsigned num_buckets = 19, Hash const &hasher_ = Hash()) : buckets(num_buckets), hasher(hasher_)
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < num_buckets; ++i)
{
buckets[i].reset(new bucket_type);
}
}
threadsafe_lookup_table(threadsafe_lookup_table const &other) = delete;
threadsafe_lookup_table &operator=(threadsafe_lookup_table const &other) = delete;
Value value_for(Key const &key, Value const &default_value = Value()) const
{
return get_bucket(key).value_for(key, default_value);
}
void add_or_update_mapping(Key const &key, Value const &value)
{
get_bucket(key).add_or_update_mapping(key, value);
}
void remove_mapping(Key const &key)
{
get_bucket(key).remove_mapping(key);
}
};
添加快照
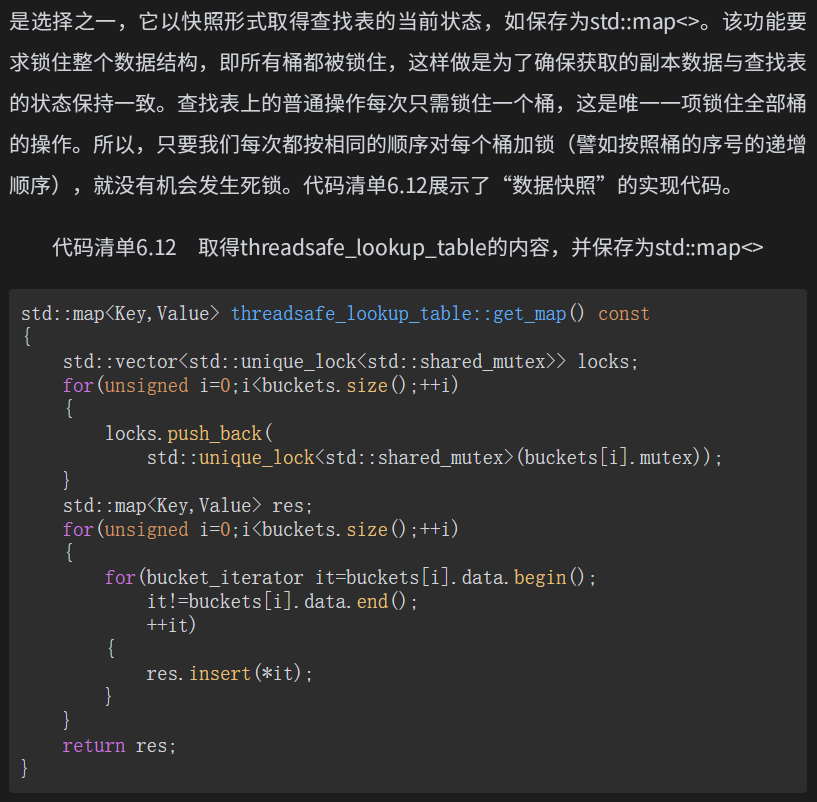
基于多种锁的链表
让每个节点都具备自己的互斥
支持迭代功能的线程安全的链表
template <typename T>
class threadsafe_list
{
struct node
{
std::mutex m;
std::shared_ptr<T> data;
std::unique_ptr<node> next;
node() : next()
{
}
node(T const &value) : data(std::make_shared<T>(value)) {}
};
node head;
public:
threadsafe_list(threadsafe_list const &other) = delete;
threadsafe_list &operator=(threadsafe_list const &other) = delete;
threadsafe_list() {}
~threadsafe_list()
{
remove_if([](node const &)
{ return true; });
}
void push_front(T const &value)
{
std::unique_ptr<node> new_node(new node(value));
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(head.m);
new_node->next = std::move(head.next);
head.next = std::move(new_node);
}
template <typename Function>
void for_each(Function f)
{
node *current = &head;
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(head.m);
while (node *const next = current->next.get())
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> next_lk(next->m);
lk.unlock();
f(*next->data);
current = next;
lk = std::move(next_lk);
}
}
template <typename Predicate>
std::shared_ptr<T> find_first_if(Predicate p)
{
node *current = &head;
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(head.m);
while (node *const next = current->next.get())
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> next_lk(next->m);
lk.unlock();
if (p(*next->data))
{
return next->data;
}
current = next;
lk = std::move(next_lk);
}
return std::shared_ptr<T>();
}
template <typename Predicate>
void remove_if(Predicate p)
{
node *current = &head;
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(head.m);
while (node *const next = current->next.get())
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> next_lk(next->m);
if (p(*next->data))
{
std::unique_ptr<node> old_next = std::move(current->next);
current->next = std::move(next->next);
next_lk.unlock();
}
else
{
lk.unlock();
current = next;
lk = std::move(next_lk);
}
}
}
};
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)