Linux学习日记22:条件变量
摘要:Linux条件变量是多线程编程中实现线程同步的重要机制,通过与互斥锁配合使用,有效避免线程忙等待。其核心原理基于"等待-唤醒"模型:线程在条件不满足时自动释放锁并阻塞,其他线程修改条件后唤醒等待线程。主要接口包括初始化(pthread_cond_init)、等待(pthread_cond_wait)、唤醒(pthread_cond_signal/broadcast)等函数
一、前言
在 Linux 多线程编程中,条件变量是一种用于线程间同步的机制,核心作用是让线程在某个条件不满足时进入等待状态,直到其他线程触发该条件满足后再被唤醒,从而避免线程通过 “忙等” 浪费 CPU 资源。它通常与互斥锁配合使用,原因是条件的判断和修改必须是原子操作,防止出现竞态条件。
二、条件变量
2.1、条件变量原理
条件变量的同步逻辑可以概括为 “等待 - 唤醒” 模型:
1、等待方线程:先加锁,检查条件是否满足。若不满足,则调用等待函数,自动释放互斥锁并进入阻塞状态;若满足,则执行后续逻辑。
2、唤醒方线程:先加锁,修改条件为满足状态,调用唤醒函数通知等待线程,最后释放互斥锁。
3、被唤醒的等待线程:会重新获取互斥锁,再次检查条件是否满足(防止虚假唤醒),满足则继续执行,不满足则再次等待。
2.2、关键特性
1、避免忙等:线程等待时会放弃 CPU 使用权,而非循环检查条件,大幅降低 CPU 消耗。
2、依赖互斥锁:条件的判断和修改必须在互斥锁的保护下进行,确保多线程下条件的一致性。
3、支持批量唤醒:可唤醒单个等待线程或所有等待线程。
2.3、相关函数
Linux 下条件变量的相关接口定义在头文件 <pthread.h>中,核心数据结构是 pthread_cond_t。
2.3.1、条件变量初始化
1、静态初始化
适用于全局或静态作用域的条件变量,使用宏PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER:
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;2、动态初始化
适用于局部或堆上的条件变量,调用 pthread_cond_init 函数:
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);参数:cond:指向待初始化的条件变量。
attr:条件变量属性,通常设为 NULL 表示默认属性。
返回值:成功返回 0,失败返回错误码。
2.3.2、条件变量销毁
使用 pthread_cond_destroy 函数释放资源,仅对动态初始化的条件变量有效:
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);注:销毁前需确保没有线程正在等待该条件变量,否则会导致未定义行为。
2.3.3、等待函数
1、无限等待
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);参数:cond:指向条件变量。
mutex:指向关联的互斥锁。
核心行为:1、线程调用该函数时,必须已持有 mutex 锁。
2、函数会自动释放 mutex,并将线程加入条件变量的等待队列。
3、线程被唤醒后,会重新获取 mutex 锁,然后函数返回,此时线程需要重新检 查条件(防止虚假唤醒)。
2、限时等待
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const struct timespec *restrict abstime);参数:abstime是绝对时间(系统时间),而非相对时间。例如,设置等待 5 秒:
struct timespec ts;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_REALTIME, &ts);
ts.tv_sec += 5; // 5 秒后超时返回值:超时返回ETIMEDOUT,成功返回 0,失败返回其他错误码。
2.3.4、唤醒函数
1、唤醒单个线程
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);作用:唤醒等待队列中的一个线程(具体唤醒哪个由系统调度决定)。
注意:调用时建议持有互斥锁,也可以不持有,但持有锁能避免唤醒操作的时序问题。
2、唤醒所有线程
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);作用:唤醒等待队列中的所有线程,适用于多个线程等待同一条件的场景(如生产者 - 消费者模型中的多个消费者)。
2.4、典型示例
使用条件变量实现生产者,消费者模型,具体代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
typedef struct node
{
int data;//存储节点的数据
struct node* next;//指向同类型结构体的下一个节点
}Node;
//create head node
Node* head = NULL;//指向链表的第一个节点(栈顶),且链表为空
//create mutex
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
//create cond
pthread_cond_t cond;
void* produce(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
//create node
Node* pnew = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//在堆上创建一个节点
//init node
pnew->data = rand()%1000;
//lock
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
//头插法入链表
pnew->next = head;//新节点指向原来的头
head = pnew;//更新头指针为新节点
printf("produce: %ld,%d\n",pthread_self(),pnew->data);
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);//通知“可能有货了”,唤醒一个正在 wait 的消费者
//unlock
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(rand()%3);
}
return NULL;
}
void* customer(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
//lock
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(head == NULL)//上锁后检查链表是否为空
{
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);
}
//delete head node
Node* pdel = head;//保存要删除的头结点
head = head->next;//头指针后移,相当于“出栈”
printf("customer: %ld,%d\n",pthread_self(),pdel->data);
free(pdel);//使用完后释放内存
//unlock
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
//init mutex
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
//init cond
pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);
//create p1,p2
pthread_t p1,p2;
pthread_create(&p1,NULL,produce,NULL);
pthread_create(&p2,NULL,customer,NULL);
//p1,p2 join
pthread_join(p1,NULL);
pthread_join(p2,NULL);
//kill mutex
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
//kill cond
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
return 0;
}
编译并运行,结果如下:
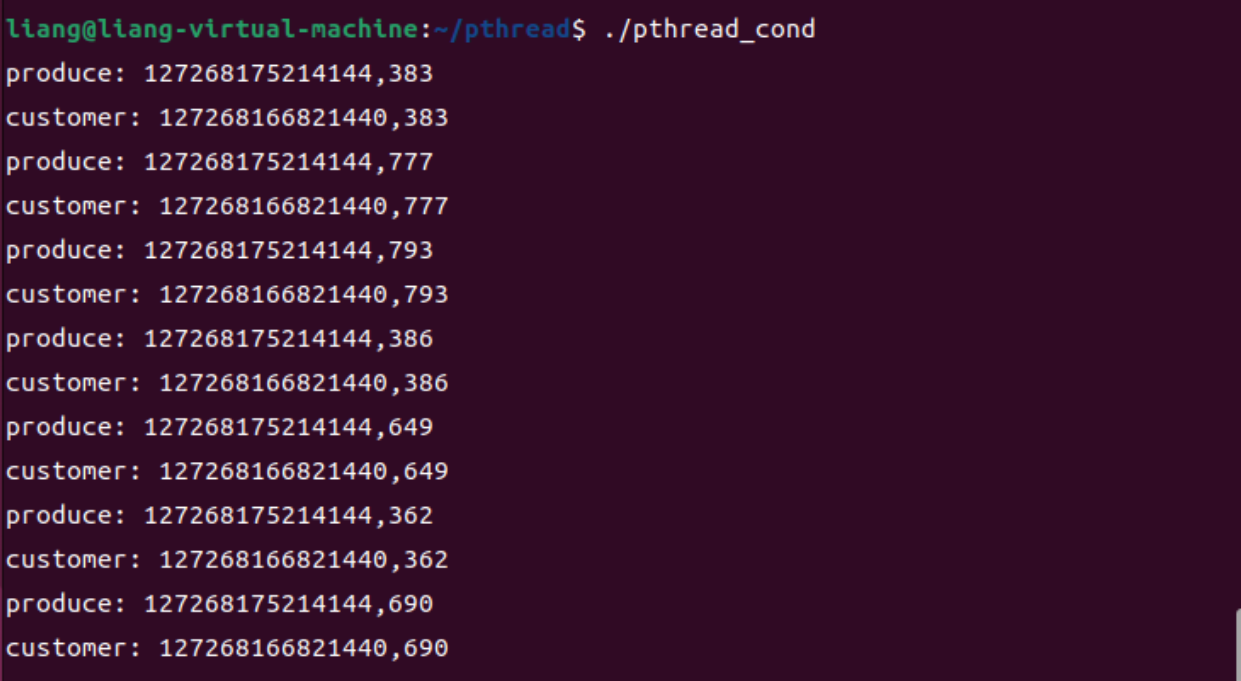 可以看到生产者生产出来的数据均被消费者给“吃掉了”。
可以看到生产者生产出来的数据均被消费者给“吃掉了”。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容






所有评论(0)