智能体21种设计模式之(3)并行化
摘要:并行模式通过同时执行独立子任务优化智能体工作流效率,适用于API调用、数据处理等场景。框架如LangChain支持RunnableParallel等并行机制,可将总耗时从线性累加降至单次最长任务耗时。典型应用包括多源信息收集(如同时查询新闻、股票数据)、内容生成(并行撰写邮件主题与正文)等。实现时需识别工作流中无依赖环节,使用异步/多线程技术,但会增加系统复杂度。该模式与顺序链式、条件路由结
并行模式概述
在前面的章节中,我们探讨了用于顺序工作流的提示链以及用于智能决策的路由模式。虽然这些模式很重要,但许多复杂的智能体任务需要同时执行多个子任务,而非一个接一个地执行。这时并行模式就变得至关重要。
并行模式涉及同时执行多个组件,例如大语言模型调用、工具使用,甚至整个子智能体(见图 1)。与等待一个步骤完成后再开始下一个步骤不同,并行执行允许独立任务同时运行,这大大缩短了那些可以分解为相互独立部分的任务的总执行时间。
考虑实现一个研究主题并汇总结论的智能体。按顺序执行时可能会是这样:
1、搜索来源 A。
2、总结来源 A。
3、搜索来源 B。
4、总结来源 B。
5、整合总结 A 和 总结 B 中的内容,生成一个最终答案。
如果使用并行模式则可以优化为:
1、同时搜索来源 A 和来源 B。
2、两次搜索完成后,同时对来源 A 和来源 B 进行总结。
3、整合总结 A 和 总结 B 中的内容,生成一个最终答案。这一步通常按顺序进行,需要等待前面并行步骤全部完成。
并行模式的核心在于找出工作流中互不依赖的环节,并将它们并行执行。在处理外部服务(如 API 或数据库)时,这种做法特别有效,因为可以同时发起多个请求,从而减少总体等待时间。
实现并行化通常需要使用支持异步执行、多线程或多进程的框架。现代智能体框架原生都能支持异步操作,帮助你方便地定义并同时运行多个步骤。
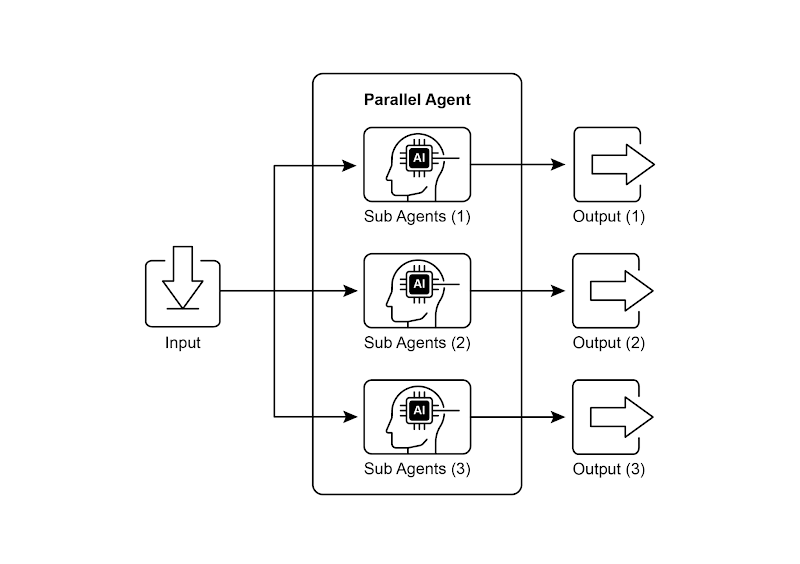
图 1:使用子智能体进行并行化的示例
LangChain、LangGraph等框架都提供了并行执行机制。
在 LangChain 表达式语言(LCEL)中,可以使用 | 等运算符组合可运行对象,并通过设计具有并发分支的链或图结构来实现并行执行。而 LangGraph 则利用图结构,允许从状态转换中执行多个节点,从而在工作流中实现并行分支。
并行模式对于提升智能体系统的效率和响应速度至关重要,特别是在需要执行多个独立查询、计算或与外部服务交互的场景中。它是优化复杂智能体工作流性能的关键技术。
实际应用场景
并行模式可以在各种场景中使用以提升智能体性能:
1、信息收集和研究:
一个经典的用例就是同时从多个来源收集信息。
-
用例:研究某个公司的智能体。
-
并行执行任务:同时搜索新闻、拉取股票数据、监测社交媒体上的提及,并查询公司数据库。
-
好处:比逐项查找更快获得全面信息。
2、数据处理和分析:
使用不同的分析方法或并行处理不同的数据段。
-
用例:分析客户反馈的智能体。
-
并行处理任务:在一批反馈中同时进行情感分析、关键词提取、分类,并识别需要优先处理的紧急问题。
-
好处:快速提供多角度的分析。
3、多个 API 或工具交互:
调用多个独立的 API 或工具,以获取不同类别的信息或完成不同的任务。
-
用例:旅行规划智能体。
-
并行处理任务:同时检查航班价格、搜索酒店、了解当地活动,并找到推荐的餐厅。
-
好处:更快速地制定出完整的旅行行程。
4、多组件内容生成:
并行生成复杂作品的各个部分。
-
用例:撰写营销邮件的智能体。
-
并行处理任务:同时生成邮件主题、撰写正文、查找相关图片,并设计具有号召性的按钮文案。
-
好处:更高效地生成电子邮件内容。
5、验证和核实:
并行执行多个彼此独立的检查或验证。
-
用例:验证用户输入的智能体。
-
并行执行任务:同时检查邮件格式、验证电话号码、在数据库中核对地址,并检查是否有不当内容。
-
好处:能够更快地反馈输入是否有效。
6、多模态处理:
同时对同一输入的不同模态(文本、图像、音频)数据进行处理。
-
用例:分析包含文本和图像的社交媒体帖子的智能体。
- 并行执行任务:同时分析文本的情感和关键词,以及分析图像中的对象和场景描述。
- 好处:能更快地综合来自不同模态的信息与洞见。
7、A/B 测试或多种方案生成:
并行生成多个响应或输出版本,然后从中挑选最佳的一种。
-
用例:生成多个创意文案的智能体。
-
并行执行任务:同时使用稍微不同的提示或模型为同一篇文章生成三条各具风格的标题。
-
好处:可以快速比较各个方案并选出最优者。
并行模式是智能体设计中的一项重要优化技术。通过对独立任务进行并发执行,开发者可以构建更高效、更具响应性的应用程序。
实战示例:使用 LangChain
在 LangChain 框架中,通过 LangChain 的表达式语言(LCEL)可以实现并行执行。常见做法是把多个可运行组件组织成字典或列表,并把这个集合作为输入传给链中的下一个组件。LCEL 执行器会并行执行集合中的各个可运行项。
在 LangGraph 中,这一原则体现在图的拓扑结构上。通过从一个公共节点同时触发多个没有直接顺序依赖的节点,就能形成并行工作流。这些并行路径各自独立运行,之后在图中的某个汇聚点合并结果。
以下示例展示了如何使用 LangChain 框架构建并行处理流程:针对同一个用户查询,工作流同时启动两个互不依赖的操作,然后将它们各自的输出合并为一个最终结果。
要实现此功能,首先需要安装必要的 Python 包(如 langchain、langchain-community 及 langchain-openai 等模型提供库)。同时需要在本地环境中配置所选语言模型的有效 API 密钥,以便进行身份验证。
import os
import asyncio
from typing import Optional
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.runnables import Runnable, RunnableParallel, RunnablePassthrough
# Colab 代码链接:https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1uK1r9p-5sdX0ffMjAi_dbIkaMedb1sTj
# 安装依赖
# pip install langchain langchain-community langchain-openai langgraph
# For better security, load environment variables from a .env file
# 为了更好的安全性,建议从 .env 文件加载环境变量
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
# --- Configuration ---
# Ensure your API key environment variable is set (e.g., OPENAI_API_KEY)
# 确保你的 API 密钥环境变量已设置 (如 OPENAI_API_KEY)
try:
llm: Optional[ChatOpenAI] = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0.7)
if llm:
print(f"Language model initialized: {llm.model_name}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error initializing language model: {e}")
llm = None
# --- Define Independent Chains ---
# These three chains represent distinct tasks that can be executed in parallel.
# --- 定义独立的链 ---
# 这三条链代表彼此独立、可同时执行的任务。
summarize_chain: Runnable = (
ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Summarize the following topic concisely:"),
("user", "{topic}")
])
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
questions_chain: Runnable = (
ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Generate three interesting questions about the following topic:"),
("user", "{topic}")
])
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
terms_chain: Runnable = (
ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Identify 5-10 key terms from the following topic, separated by commas:"),
("user", "{topic}")
])
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
# --- Build the Parallel + Synthesis Chain ---
# 1. Define the block of tasks to run in parallel. The results of these,
# along with the original topic, will be fed into the next step.
# --- 定义要并行执行的任务块。这些结果以及原始内容将作为输入传递给下一步。
map_chain = RunnableParallel(
{
"summary": summarize_chain,
"questions": questions_chain,
"key_terms": terms_chain,
"topic": RunnablePassthrough(), # Pass the original topic through
}
)
# 2. Define the final synthesis prompt which will combine the parallel results.
# --- 定义最终的综合提示,将并行结果合并。
synthesis_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """Based on the following information:
Summary: {summary}
Related Questions: {questions}
Key Terms: {key_terms}
Synthesize a comprehensive answer."""),
("user", "Original topic: {topic}")
])
# 3. Construct the full chain by piping the parallel results directly
# into the synthesis prompt, followed by the LLM and output parser.
# --- 通过将并行结果直接传递给综合提示,然后是语言模型和输出解析器,构建完整的链。
full_parallel_chain = map_chain | synthesis_prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
# --- Run the Chain ---
# --- 运行链 ---
async def run_parallel_example(topic: str) -> None:
"""
Asynchronously invokes the parallel processing chain with a specific topic
and prints the synthesized result.
Args:
topic: The input topic to be processed by the LangChain chains.
"""
if not llm:
print("LLM not initialized. Cannot run example.")
return
print(f"\n--- Running Parallel LangChain Example for Topic: '{topic}' ---")
try:
# The input to `ainvoke` is the single 'topic' string, which is
# then passed to each runnable in the `map_chain`.
# `ainvoke` 的输入是单个 'topic' 字符串,该字符串随后会被传递给 `map_chain` 中的每个可运行项。
response = await full_parallel_chain.ainvoke(topic)
print("\n--- Final Response ---")
print(response)
except Exception as e:
print(f"\nAn error occurred during chain execution: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_topic = "The history of space exploration"
# In Python 3.7+, asyncio.run is the standard way to run an async function.
# 在 Python 3.7 及更高版本中,asyncio.run 是运行异步函数的标准方式。
asyncio.run(run_parallel_example(test_topic))运行输出(译者添加):
Language model initialized: gpt-4o-mini
--- Running Parallel LangChain Example for Topic: 'The history of space exploration' ---
--- Final Response ---
The history of space exploration is a fascinating narrative marked by human curiosity, technological advancement, and international cooperation. It began in the mid-20th century, with the launch of the Soviet satellite Sputnik 1 in 1957, which signified the dawn of the Space Age. This event triggered a series of significant milestones that would shape our understanding of the cosmos.
In 1961, the Soviet space program successfully launched Yuri Gagarin, the first human to journey into space, further igniting the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union. This fierce competition led to rapid advancements in technology and culminated with the U.S. Apollo program, which achieved the historic Moon landing in 1969. The success of Apollo 11 not only demonstrated human capability but also inspired generations to look to the stars.
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, space exploration expanded to include missions to Mars, the launch of revolutionary space telescopes like the Hubble Space Telescope, and the development of the Space Shuttle program. These initiatives allowed for more extended missions and the ability to deploy and service satellites, enhancing our understanding of the universe and our place within it.
The late 1990s saw the launch of the International Space Station (ISS), a landmark achievement in international cooperation in space research. The ISS has become a platform for collaboration among multiple space agencies, including NASA, Roscosmos, ESA, JAXA, and others, allowing scientists from around the world to work together in the unique environment of space.
In recent years, technological advancements, particularly in the realm of reusable rockets, have reshaped the goals and capabilities of space exploration. Companies such as SpaceX and Blue Origin have pioneered private spaceflight initiatives, driving costs down and making space more accessible than ever. This shift has reignited interest in missions targeting Mars, the Moon, and beyond, with plans for crewed missions to Mars on the horizon.
The Space Race has also had lasting effects on international cooperation in contemporary space exploration. The competitive spirit of the Cold War era has evolved into a collaborative approach, exemplified by the ISS and joint missions like the Mars rover endeavors, where multiple countries contribute resources and expertise to achieve common goals.
However, the entrance of private companies into the space exploration sector raises various ethical considerations and potential implications. These include questions about the commercialization of space, the prioritization of profit over scientific research, and concerns about space debris and environmental impacts. As private entities take on larger roles in exploration, the dynamics of scientific research and exploration beyond Earth's atmosphere may shift, necessitating new frameworks for governance and collaboration.
In summary, the history of space exploration is a rich tapestry woven from human ingenuity and cooperation. It reflects our quest to understand the universe, marked by milestones that highlight both our achievements and the challenges that lie ahead. As we move into a new era of exploration, the interplay between public and private initiatives will shape the future of our endeavors among the stars.上述 Python 示例实现了一个基于 LangChain 的应用,通过并发执行来更高效地处理指定话题。需要说明的是,asyncio 实现的是并发(Concurrency),不是多线程或多核的真正并行(Parallelism)。它在单个线程中运行,通过事件循环在任务等待(如等待网络响应)时切换执行,从而让多个任务看起来同时执行。但底层代码仍在同一线程上运行,这是受 Python 全局解释器锁(GIL)的限制。
代码从 langchain_openai 和 langchain_core 导入了关键模块,包含语言模型、提示模板、输出解析器和可运行组件。接着尝试初始化一个 ChatOpenAI 实例,指定使用 gpt-4o-mini 模型,并设置了控制创造力的温度值,初始化时用 try-except 来保证健壮性。随后定义了三条相互独立的 LangChain 链,每条链负责对输入主题执行不同任务:第一条链用来简洁地总结主题,采用系统消息和包含主题占位符的用户消息;第二条链生成与主题相关的三个有趣问题;第三条链则从主题中识别 5 到 10 个关键术语,要求用逗号分隔。每条链都由为该任务定制的 ChatPromptTemplate、已初始化的语言模型和用于把输出格式化为字符串的 StrOutputParser 组成。
随后构建了一个 RunnableParallel 块,把这三条链打包在一起以便同时运行。这个运行单元还包含一个 RunnablePassthrough,确保原始输入的主题可以在后续步骤中使用。
接着为最后的汇总步骤定义了一个独立的 ChatPromptTemplate,使用摘要、问题、关键术语和原始主题作为输入来生成完整的答案。这个名为 full_parallel_chain 的端到端处理链,是通过 map_chain 连接到汇总提示,再接语言模型和输出解析器来构建的。
示例中提供了一个异步函数 run_parallel_example,用来演示如何调用这个 full_parallel_chain,该函数接收主题作为输入并通过 invoke 运行异步链。
最后,通过标准的 Python if name == "main": 代码块演示如何用 asyncio.run 管理异步执行,来启动 run_parallel_example 方法,其中主题为「航天探索史」。
本质上,这段代码构建了一个工作流:针对某个主题,使用大语言模型同时进行摘要、提问和术语等多个调用,随后由一次最终的请求把这些输出整合在一起。该示例说明了在使用 LangChain 的智能体工作流中通过并行执行来提高效率的核心思想。
要点速览
问题所在:许多智能体工作流涉及多个必须完成的子任务以实现最终目标。纯粹的顺序执行,即每个任务等待前一个任务完成再执行,通常效率低下且速度缓慢。当任务依赖于外部 I/O 操作(如调用不同的 API 或查询多个数据库)时,这种延迟会成为重大瓶颈。没有并发机制时,总耗时就是各个任务耗时的累加,进而影响系统的性能和响应速度。
解决之道:并行模式通过同时执行彼此独立的任务,提供了一种标准化的解决方案来缩短整体执行时间。它的做法是识别工作流中不相互依赖的部分,比如某些工具调用或大语言模型请求。像 LangChain 和 Google ADK 这样的智能体框架内置了用于定义和管理并发操作的能力。举例来说,主流程可以启动多个并行的子任务,然后在继续下一步之前等待这些子任务全部完成。相比与顺序执行,这种并行执行能大幅减少总耗时。
经验法则:当工作流中存在多个相互独立且可并行执行的任务时应采用该模式,例如同时从多个 API 拉取数据、并行处理不同的数据分片,或同时生成多个将来需要合并的内容,从而缩短总体执行时间。
可视化总结
核心要点
以下是关键要点:
-
并行模式是一种将相互独立的任务同时执行,从而缩短总耗时并提高效率的方法。
-
在任务需要等待外部资源(比如调用 API)时,这种方式特别有用。
-
采用并发或并行架构会显著增加复杂性和成本,从而对设计、调试和日志等开发环节带来影响。
-
像 LangChain 这样的框架内置了对并行执行的支持,方便定义和管理并行任务。
-
在 LangChain 的表达式语言(LCEL)中,RunnableParallel 是一个核心组件,用于并行执行多个可运行单元。
并行模式能有效减少总体耗时,从而提升智能体系统对复杂任务的响应能力。
结语
并行模式是通过并发执行独立子任务来优化计算流程。对于需要多次模型推理或调用外部服务的复杂操作,采用并行执行可以显著降低总体耗时并提高效率。
不同的框架为实现此模式提供了不同的机制。在 LangChain 中,像 RunnableParallel 这样的组件可以用于显式定义和执行多个处理链。相比之下,Google ADK 可以通过多智能体委派机制实现并行化,其中主协调器模型将不同的子任务分配给可以并发执行的专用智能体。
将并行处理与顺序(链式)和条件(路由)控制流结合起来,可以构建既复杂又高效的计算系统,从而更有效地管理各类复杂任务。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容








所有评论(0)