agentic设计模式 第2章:路由(Routing)
和。
路由模式概述
虽然提示链能够按照预设的线性流程执行确定性的任务,但它缺乏根据环境状态、用户输入或上步结果等动态信息进行自适应决策的能力。引入**路由(Routing)**机制可有效解决这一问题:通过实时评估上下文,智能地将请求分发给最适合的功能模块、工具或子流程,从而突破线性管道的局限性,实现灵活、上下文感知的控制流分发。
路由机制为智能体赋予了"条件判断"能力,使其能够:
- 摆脱固定流程的约束
- 根据实时上下文动态选择最优执行路径
- 展现出更灵活、更贴合语境的智能行为
以客户咨询智能体为例,集成路由功能后系统会:
- 准确识别用户真实意图
- 智能分发请求:
- 简单问题 → 问答智能体
- 账户查询 → 数据库检索工具
- 复杂问题 → 人工处理
- 意图不明 → 澄清子智能体
典型路由场景包括:
- 「查订单」→ 订单查询子智能体/工具链
- 「问产品」→ 产品目录检索子智能体/工具链
- 「求技术支持」→ 故障排除手册或人工转接
- 「意图不明」→ 进入澄清流程
路由模式的核心在于"评估-决策"机制:先分析请求类型,再选择执行路径。常见实现方式包括:
-
大模型路由(LLM-based Routing)
- 通过提示词让大模型直接输出分类标签,系统根据标签进行转发
- 提示示例:「分析用户查询,仅输出:订单|产品|技术|其他」
- 优势:零样本即可部署;不足:每次都需要调用大模型,延迟和成本较高
-
向量路由(Embedding-based Routing)
- 将查询向量化后与预设路径向量进行相似度匹配,选择最优路径
- 适用于语义相似但表述不同的场景,如「帮我退款」和「订单想取消」都指向退款流程
- 优势:无需大模型推理,响应快;不足:需要维护和更新路径向量库
-
规则路由(Rule-based Routing)
- 基于关键词、正则表达式或结构化字段编写条件判断逻辑
- 优势:毫秒级响应、逻辑透明;不足:难以处理口语化表达,维护成本较高
-
小模型路由(Lightweight Model Routing)
- 使用轻量级分类器(如BERT-small、TextCNN)进行专门的路由任务
- 推理阶段仅运行小模型,兼顾速度与精度;训练数据可由大模型生成后人工校验
适用于业务场景固定、需要高并发和低延迟的场景。
路由机制可在智能体运行周期的多个环节实施:既能在初始阶段对主任务进行分类,也能在处理链的中间节点决定后续操作,还可在子程序中从预设工具集中挑选最合适的工具。
LangChain、LangGraph 和 Google 智能体开发套件(ADK)等计算框架为定义和管理此类条件逻辑提供了明确的构造。凭借基于状态的图架构,LangGraph 特别适合复杂的路由场景,其中决策取决于整个系统的累积状态。类似地,Google ADK 提供了用于构建智能体能力和交互模型的基础组件,这些组件是实现路由逻辑的基础。在这些框架提供的执行环境中,开发人员可定义可能的操作路径,以及决定计算图中节点间转换的函数或基于模型的评估。
路由的实现使系统能够超越确定性的顺序处理。它促进了更具适应性的执行流程的开发,能够动态且恰当地响应更广泛的输入和状态变化。
适用场景
路由模式是自适应智能体系统的"智能调度中枢",它能实时感知输入与系统状态,将请求精准路由至最合适的处理节点,赋予系统动态决策与灵活路径选择的能力。典型应用场景包括:
- 智能对话系统:虚拟助手或AI导师通过路由快速识别用户意图,智能选择知识检索、人工转接或课程推送等最佳响应方式,实现上下文连贯的多轮对话体验
- 数据处理引擎:自动为邮件、工单等输入数据打标(如"销售线索"、"JSON转换需求"),并实时分发至对应处理管道,显著提升处理效率和准确率
- 多智能体协同:在研究系统中,路由作为智能调度器,根据任务特性动态调用最合适的专业智能体(搜索/分析/总结);AI编程助手则通过路由识别代码意图(调试/解释/翻译),智能分配至最佳工具链,实现"复杂需求智能响应"
本质上,路由模式为系统提供了关键的智能决策能力,使智能体从固定流程的执行者进化为能根据实时情境自主选择最优解决方案的动态系统。
实战案例:LangChain 应用实现
实现代码路由的核心在于两个关键点:定义执行路径和构建选择逻辑。主流框架如 LangChain 和 LangGraph 提供了专业组件和结构化解决方案,其中 LangGraph 采用状态图结构,可以直观呈现路由逻辑,显著简化复杂决策流程的开发。
以下代码示例展示了基于 LangChain 和 Google 生成式 AI(gemini-2.5-flash)实现的多智能体系统。该系统采用「协调员-子智能体」架构:中央协调员通过大语言模型进行意图识别,根据用户请求类型(预订服务、信息查询或意图不明)将任务精准路由至相应的专业子智能体处理器。整个流程完整实现了多智能体协作中「意图识别→任务分发→结果返回」的典型委派模式。
运行代码前,请先安装以下必备依赖库:
pip install langchain langgraph google-cloud-aiplatform langchain-google-genai google-adk deprecated pydantic
你还需要在环境中设置所选语言模型(如 OpenAI、Google Gemini、Anthropic)的 API 密钥。
# Copyright (c) 2025 Marco Fago
#
# This code is licensed under the MIT License.
# See the LICENSE file in the repository for the full license text.
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough, RunnableBranch
# --- Configuration ---
# Ensure GOOGLE_API_KEY environment variable is properly set
try:
llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-2.5-flash", temperature=0)
print(f"Language model initialized: {llm.model}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error initializing language model: {e}")
llm = None
# --- Define Sub-Agent Handlers ---
def booking_handler(request: str) -> str:
"""Handles booking-related requests."""
print("\n--- DELEGATING TO BOOKING HANDLER ---")
return f"Booking Handler processed request: '{request}'. Result: Simulated booking action."
def info_handler(request: str) -> str:
"""Handles information queries."""
print("\n--- DELEGATING TO INFO HANDLER ---")
return f"Info Handler processed request: '{request}'. Result: Simulated information retrieval."
def unclear_handler(request: str) -> str:
"""Handles ambiguous requests."""
print("\n--- HANDLING UNCLEAR REQUEST ---")
return f"Coordinator could not delegate request: '{request}'. Please clarify."
# --- Define Coordinator Router Chain ---
coordinator_router_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """Analyze the user request and determine the appropriate handler:
- For booking flights/hotels: output 'booker'
- For general information: output 'info'
- For unclear requests: output 'unclear'
Respond with only one word: 'booker', 'info', or 'unclear'."""),
("user", "{request}")
])
if llm:
coordinator_router_chain = coordinator_router_prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
# --- Define Delegation Logic ---
branches = {
"booker": RunnablePassthrough.assign(output=lambda x: booking_handler(x['request']['request'])),
"info": RunnablePassthrough.assign(output=lambda x: info_handler(x['request']['request'])),
"unclear": RunnablePassthrough.assign(output=lambda x: unclear_handler(x['request']['request'])),
}
delegation_branch = RunnableBranch(
(lambda x: x['decision'].strip() == 'booker', branches["booker"]),
(lambda x: x['decision'].strip() == 'info', branches["info"]),
branches["unclear"]
)
coordinator_agent = {
"decision": coordinator_router_chain,
"request": RunnablePassthrough()
} | delegation_branch | (lambda x: x['output'])
# --- Example Usage ---
def main():
if not llm:
print("\nSkipping execution due to LLM initialization failure.")
return
test_cases = [
("Booking request", "Book me a flight to London."),
("Information request", "What is the capital of Italy?"),
("Unclear request", "Tell me about quantum physics.")
]
for desc, request in test_cases:
print(f"\n--- Running {desc} ---")
result = coordinator_agent.invoke({"request": request})
print(f"Result: {result}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
运行输出
Language model initialized: models/gemini-2.5-flash
--- Running with a booking request ------ DELEGATING TO BOOKING HANDLER ---
Final Result A: Booking Handler processed request: 'Book me a flight to London.'. Result: Simulated booking action.--- Running with an info request ---
--- DELEGATING TO INFO HANDLER ---
Final Result B: Info Handler processed request: 'What is the capital of Italy?'. Result: Simulated information retrieval.--- Running with an unclear request ---
--- DELEGATING TO INFO HANDLER ---
Final Result C: Info Handler processed request: 'Tell me about quantum physics.'. Result: Simulated information retrieval.以上 Python 代码基于 LangChain 框架与 Google gemini-2.5-flash 模型,实现了一个简化的「协调员-子智能体」架构系统。该系统定义了三个专业子智能体处理器:
- `booking_handler`:处理航班/酒店预订请求
- `info_handler`:处理通用信息查询
- `unclear_handler`:作为兜底机制处理无法明确分类的请求
系统采用「意图识别→任务路由→专业处理」的三层架构设计:
- 意图识别层:通过
coordinator_router_chain模块实现,利用优化的ChatPromptTemplate指令,准确将用户请求归类为'booker'、'info'或'unclear'三种类型 - 任务路由层:基于
RunnableBranch的动态分发机制,根据识别结果将请求智能分配到对应的专业处理器 - 结果整合层:由
coordinator_agent统一管理流程,协调路由决策与专业处理,最终输出处理结果
主函数通过预订请求、信息查询和兜底场景三个典型用例,完整演示了系统运行流程,有效验证了不同类型输入的路由准确性。代码实现还包含了语言模型初始化的容错机制,确保系统在模型服务异常时能够平稳降级。
架构设计充分体现了多智能体协作的核心理念:中央协调器专注于意图理解与任务分发,各专业子智能体则负责特定领域的任务执行,通过清晰的职责划分实现高效协同运作。
实战示例:使用 Google ADK
Google 智能体开发套件(ADK)为构建智能体系统提供了结构化环境,开发者通过声明式地定义「工具」即可赋予智能体各项能力。与显式计算图不同,ADK 将路由逻辑下沉到框架内部:当用户查询到达时,框架自动调用底层模型,将意图与工具语义进行匹配,并触发最契合的工具处理,全程无需手动编写 if-else 或状态节点。下面的 Python 示例展示了如何基于 ADK 快速实现「协调-委派」架构。我们只需声明一个 Coordinator 智能体,并在其 sub_agents 中注册 Booker、Info 两个子智能体;框架会依据 Coordinator 的指令自动完成「意图识别 → 工具路由 → 结果返回」的全链路,代码更简洁,逻辑更聚焦。
# Copyright (c) 2025 Marco Fago
#
# This code is licensed under the MIT License.
# See the LICENSE file in the repository for the full license text.
import uuid
from typing import Dict, Any, Optional
from google.adk.agents import Agent
from google.adk.runners import InMemoryRunner
from google.adk.tools import FunctionTool
from google.genai import types
from google.adk.events import Event
# Colab 代码链接:https://colab.research.google.com/drive/10wxRlPyDJ70pPEtWWA3Aa3tjvfobrB3m
# 安装依赖
# pip install google-genai google-adk
# --- Define Tool Functions ---
# These functions simulate the actions of the specialist agents.
# --- 定义工具函数 ---
# 这些函数模拟了专业智能体的具体行动。
def booking_handler(request: str) -> str:
"""
Handles booking requests for flights and hotels.
Args:
request: The user's request for a booking.
Returns:
A confirmation message that the booking was handled.
"""
print("-------------------------- Booking Handler Called ----------------------------")
return f"Booking action for '{request}' has been simulated."
def info_handler(request: str) -> str:
"""
Handles general information requests.
Args:
request: The user's question.
Returns:
A message indicating the information request was handled.
"""
print("-------------------------- Info Handler Called ----------------------------")
return f"Information request for '{request}'. Result: Simulated information retrieval."
def unclear_handler(request: str) -> str:
"""Handles requests that couldn't be delegated."""
return f"Coordinator could not delegate request: '{request}'. Please clarify."
# --- Create Tools from Functions ---
# --- 从函数创建工具 ---
booking_tool = FunctionTool(booking_handler)
info_tool = FunctionTool(info_handler)
# Define specialized sub-agents equipped with their respective tools
# --- 定义配备了各自工具的专业子智能体 ---
booking_agent = Agent(
name="Booker",
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
description="A specialized agent that handles all flight and hotel booking requests by calling the booking tool.",
tools=[booking_tool]
)
info_agent = Agent(
name="Info",
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
description="A specialized agent that provides general information and answers user questions by calling the info tool.",
tools=[info_tool]
)
# Define the parent agent with explicit delegation instructions
# --- 定义带有明确委派指令的父智能体 ---
coordinator = Agent(
name="Coordinator",
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
instruction=(
"You are the main coordinator. Your only task is to analyze incoming user requests "
"and delegate them to the appropriate specialist agent. Do not try to answer the user directly.\n"
"- For any requests related to booking flights or hotels, delegate to the 'Booker' agent.\n"
"- For all other general information questions, delegate to the 'Info' agent."
),
description="A coordinator that routes user requests to the correct specialist agent.",
# The presence of sub_agents enables LLM-driven delegation (Auto-Flow) by default.
# 定义了 sub_agents 默认就会启用由大语言模型驱动的委派。
sub_agents=[booking_agent, info_agent]
)
# --- Execution Logic ---
# --- 执行逻辑 ---
def run_coordinator(runner: InMemoryRunner, request: str):
"""Runs the coordinator agent with a given request and delegates."""
"""用给定的请求运行协调员智能体并进行委派。"""
print(f"\n--- Running Coordinator with request: '{request}' ---")
final_result = ""
try:
user_id = "user_123"
session_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
runner.session_service.create_session(
app_name=runner.app_name, user_id=user_id, session_id=session_id
)
for event in runner.run(
user_id=user_id,
session_id=session_id,
new_message=types.Content(
role='user',
parts=[types.Part(text=request)]
),
):
if event.is_final_response() and event.content:
# Try to get text directly from event.content to avoid iterating parts
if hasattr(event.content, 'text') and event.content.text:
final_result = event.content.text
elif event.content.parts:
# Fallback: Iterate through parts and extract text (might trigger warning)
text_parts = [part.text for part in event.content.parts if part.text]
final_result = "".join(text_parts)
# Assuming the loop should break after the final response
break
print(f"Coordinator Final Response: {final_result}")
return final_result
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred while processing your request: {e}")
return f"An error occurred while processing your request: {e}"
def main():
"""Main function to run the ADK example."""
"""运行 ADK 示例的主函数。"""
print("--- Google ADK Routing Example (ADK Auto-Flow Style) ---")
print("Note: This requires Google ADK installed and authenticated.")
runner = InMemoryRunner(coordinator)
# Example Usage
# 使用示例
result_a = run_coordinator(runner, "Book me a hotel in Paris.")
print(f"Final Output A: {result_a}")
result_b = run_coordinator(runner, "What is the highest mountain in the world?")
print(f"Final Output B: {result_b}")
result_c = run_coordinator(runner, "Tell me a random fact.") # Should go to Info
print(f"Final Output C: {result_c}")
result_d = run_coordinator(runner, "Find flights to Tokyo next month.") # Should go to Booker
print(f"Final Output D: {result_d}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()该脚本采用双层架构设计,包含主协调员和子智能体两个层级:
- 预订专员(Booker):绑定
booking_handler工具,专门负责航班和酒店预订业务; - 信息专员(Info):绑定
info_handler工具,专注处理各类信息查询请求; - 智能协调员:仅进行意图识别,借助ADK平台的Auto-Flow功能,智能分配任务至最匹配的子智能体。
unclear_handler 已在工具层预置,但当前示例完全依赖协调员的语义匹配机制进行路由分发,因此未实际触发兜底逻辑。如需处理"无法识别"的场景,只需在协调员指令中补充"若意图不明确则调用 unclear_tool"的规则,并注册对应的 FunctionTool 即可。
run_coordinator 封装了会话初始化、事件流处理和结果提取等底层细节。通过多组测试请求验证:预订类请求自动路由至 Booker 工具,知识类问题则由 Info 工具响应,整个过程无需编写条件判断代码,充分体现了 ADK "声明即路由" 的设计理念。
核心要点
问题本质:智能体系统面临双重挑战——既要处理多样化的用户输入,又要应对复杂的业务场景。传统的线性流程缺乏动态决策能力,若没有"任务导向型工具选择"机制,系统将变得僵化,难以适应实际业务需求。
解决方案:路由模式通过引入"条件-分发"逻辑提供标准化解决路径。该机制首先解析查询意图,然后根据上下文将控制流动态导向最匹配的工具或子智能体。决策过程可基于LLM、规则引擎或向量相似度计算,从而实现从"固定流程"到"上下文感知的动态路径"的升级。
最佳实践:当智能体需要根据输入内容或系统状态在不同工作流、工具或子智能体之间进行选择时,应采用路由机制。典型案例包括客服系统:先识别"销售/售后/账号"等用户意图类别,再将请求精准路由至对应处理模块,形成"先分类、后处理"的弹性架构。
核心要点
问题本质:智能体系统面临双重挑战——既要处理多样化的用户输入,又要应对复杂的业务场景。传统的线性流程缺乏动态决策能力,若没有"任务导向型工具选择"机制,系统将变得僵化,难以适应实际业务需求。
解决方案:路由模式通过引入"条件-分发"逻辑提供标准化解决路径。该机制首先解析查询意图,然后根据上下文将控制流动态导向最匹配的工具或子智能体。决策过程可基于LLM、规则引擎或向量相似度计算,从而实现从"固定流程"到"上下文感知的动态路径"的升级。
最佳实践:当智能体需要根据输入内容或系统状态在不同工作流、工具或子智能体之间进行选择时,应采用路由机制。典型案例包括客服系统:先识别"销售/售后/账号"等用户意图类别,再将请求精准路由至对应处理模块,形成"先分类、后处理"的弹性架构。
可视化总结
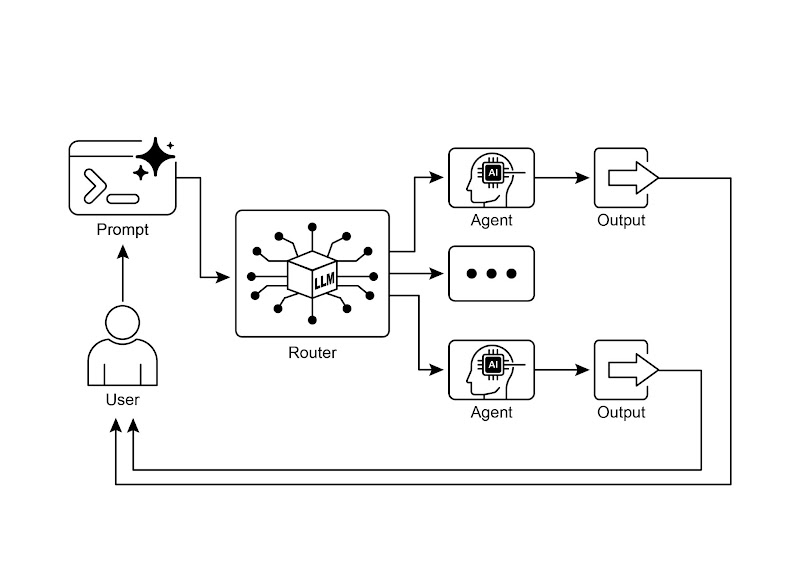
图.1 路由模式 —— 利用一个大语言模型作为路由器
核心要点
智能体通过路由机制能够根据实时情况灵活决定工作流的下一个执行步骤。该机制不仅使智能体能够处理各类输入并动态调整行为,还打破了传统线性流程的局限性。在实现方式上,既可采用大语言模型推理,也能选择基于规则的系统或向量相似度匹配等技术方案。目前市场上已有LangGraph、Google ADK等专业框架提供结构化的路由管理方案,尽管它们在架构设计上各有特色。
结论
路由模式作为动态自适应智能体系统的核心技术,通过引入路由机制,使系统能够突破线性执行的局限,根据实时上下文智能决策——包括信息处理、用户响应以及工具或子智能体的最优选择。
其应用场景广泛:从客服机器人的意图识别与任务分配,到企业数据流水线的智能调度,再到多智能体协作的任务协调。这种「输入分析→条件判断→执行引导」的能力,是智能体应对现实任务多样性与不确定性的关键。
通过 LangChain 与 Google ADK 的代码示例,我们展示了路由模式的两种典型实现方式:
- LangChain(LangGraph)方案:采用显式计算图架构,通过可视化定义状态节点与转换逻辑,特别适合处理包含复杂分支、循环和条件依赖的多步骤流程
- Google ADK 方案:采用工具集架构,将智能体能力封装为独立工具,由框架自动匹配用户需求与工具功能,更适合操作明确、能力边界清晰的系统
两种方案各具优势:复杂流程推荐显式计算图,简单任务则可选择工具集模式。
总之,路由模式是智能体从「被动执行」转向「主动适应」的关键桥梁,掌握其设计方法是构建灵活、可靠、高性能智能体系统的核心能力。
参考文献
-
LangGraph 官方文档(英文)
详细介绍状态图、节点与条件边的声明式编程方法,适用于需要可视化编排复杂业务逻辑的场景。 -
LangGraph 中文快速入门
官方提供的中文教程与API文档,帮助开发者快速上手。 -
Google Agent Developer Kit (ADK) 官方文档(英文)
系统讲解Agent、Tool、sub_agents等核心概念,包含Auto-Flow语义匹配示例,可快速实现意图到工具的路由映射。 -
Google ADK 中文指南
涵盖安装配置、权限认证、调试技巧等实用内容,助力开发者高效实施"声明即路由"开发模式。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容








所有评论(0)