小白学大模型:从零搭建LLaMA
LLaMA-13B 在大多数基准测试中表现优于拥有 175B 参数的 GPT-3,尽管其模型规模小了十倍。这使得 LLaMA-13B 可以在单个 GPU 上运行,从而“民主化”了大型语言模型的研究和使用。
LLaMA 的开发基于一个核心理念:在给定计算预算下,通过增加训练数据量而非单纯增加模型参数,可以达到更好的性能。这与之前普遍认为“参数越多性能越好”的观点不同,并特别强调了 推理成本 的重要性。尽管训练一个大型号的模型可能更快达到某个性能水平,但一个参数更少但训练更久的小模型在实际应用中的推理成本会更低、速度更快。
LLaMA-13B 在大多数基准测试中表现优于拥有 175B 参数的 GPT-3,尽管其模型规模小了十倍。这使得 LLaMA-13B 可以在单个 GPU 上运行,从而“民主化”了大型语言模型的研究和使用。
架构与优化 (Architecture and Optimizer)
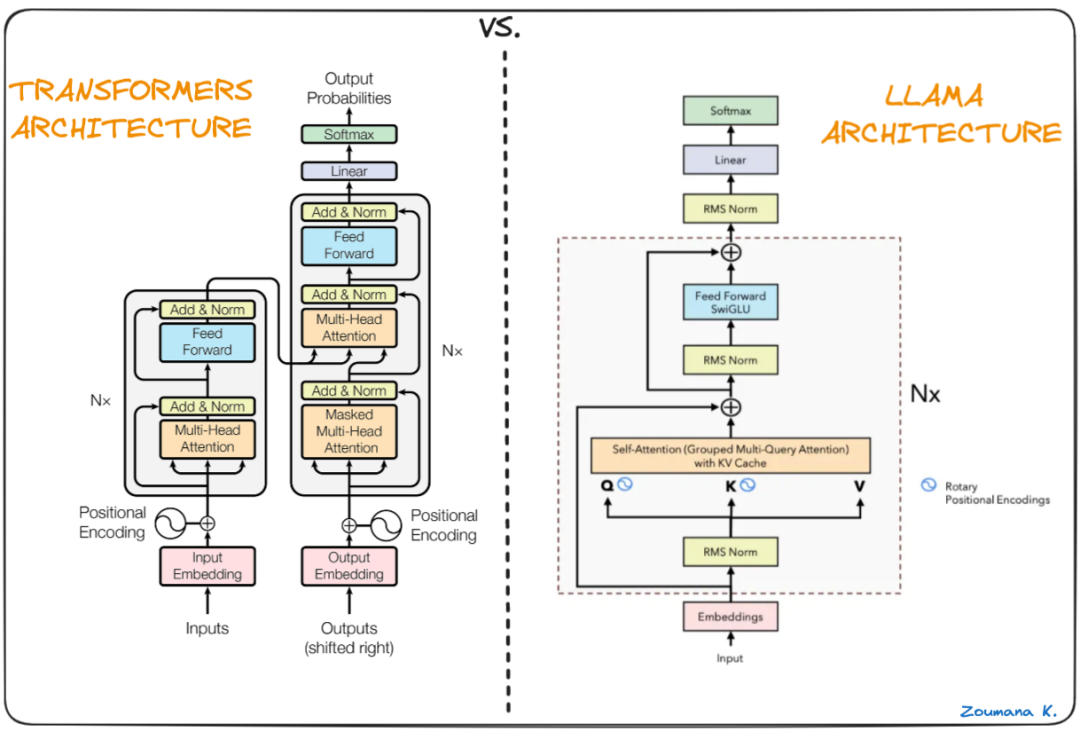
LLaMA 沿用了 Transformer 架构,但引入了几个关键的改进以提升性能和训练稳定性,这些改进借鉴了其他现有模型:
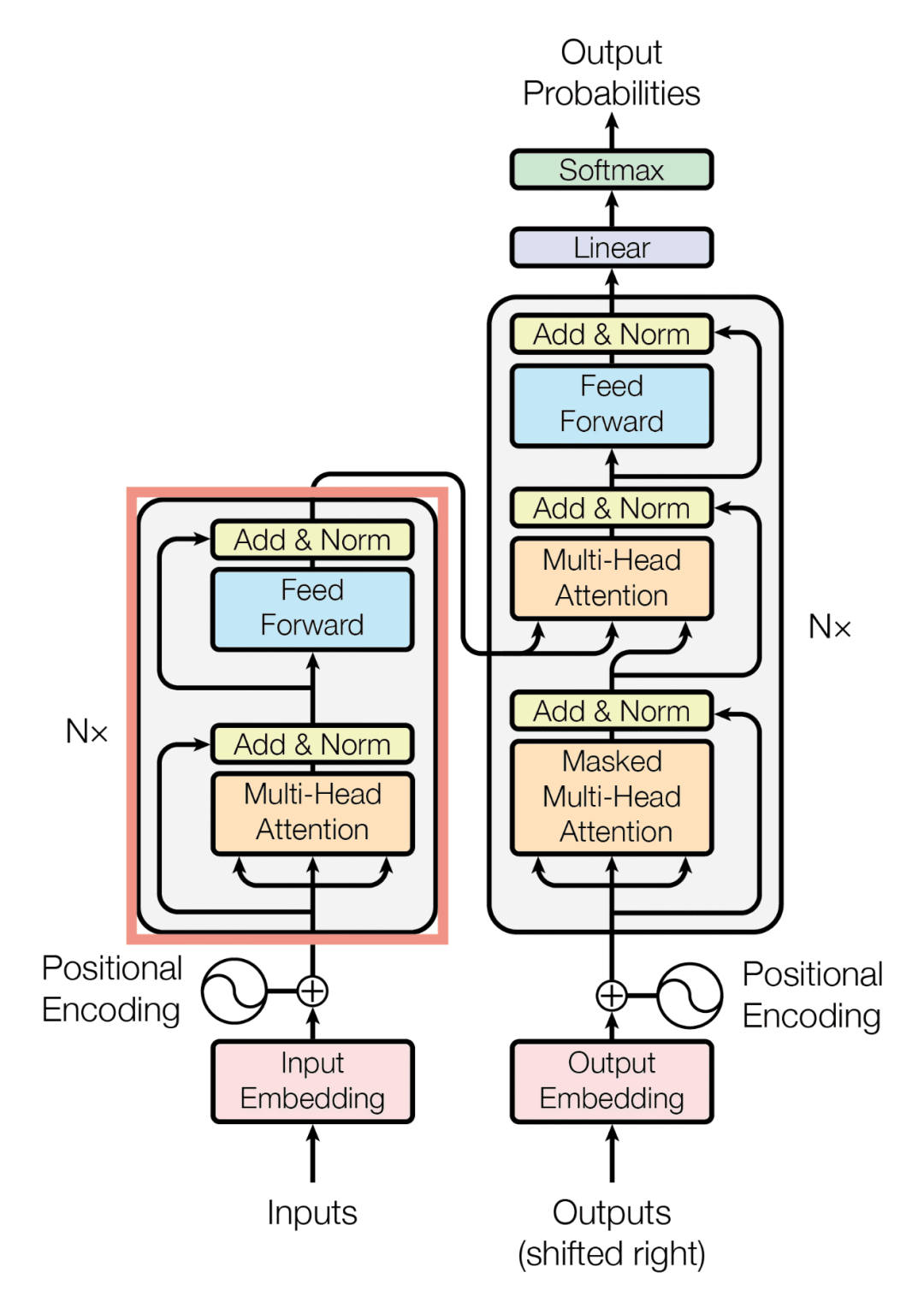
- Pre-normalization: 借鉴 GPT-3,在每个 Transformer 子层的输入端进行归一化(而非输出端),并使用 RMSNorm 函数来提高训练稳定性。
- SwiGLU 激活函数: 借鉴 PaLM,用 SwiGLU 替换了传统的 ReLU 非线性激活函数,以提升性能。
- Rotary Embeddings (RoPE): 借鉴 GPTNeo,移除了绝对位置嵌入,转而在网络的每一层添加了旋转位置嵌入。
- 优化器: 使用 AdamW 优化器,并采用了余弦学习率调度,以及权重衰减和梯度裁剪。具体的超参数设置根据模型大小有所不同(详见文档中的表格)。
步骤1:构建数据集
创建输入和目标序列: 对于每一个随机选定的起始索引 i,代码创建两个序列:
- 输入序列
x: 这是一个长度为context_window的序列,从索引i开始。 - 目标序列
y: 这是与x对应的下一个字符序列,从索引i+1开始,长度同样为context_window。例如,如果输入是 “hello”,那么目标就是 "ello "(假设空格是下一个字符)。这种“输入-下一个字符”的关系是训练自回归语言模型的标准方式。
def get_batches(data, split, batch_size, context_window, config=DEFAULT_CONFIG): # Split the dataset into training, validation, and test sets train=data[:int(.8*len(data))] val=data[int(.8 * len(data)): int(.9*len(data))] test=data[int(.9 *len(data)):] # Determine whcih split to use batch_data=train if split=='val': batch_data=val if split=='test': batch_data=test # Pick random starting points within the data ix=torch.randint(0,batch_data.size(0)-context_window-1, (batch_size,)) # create input sequences (x) and corrsponding target sequences (y) x=torch.stack([batch_data[i:i+context_window] for i in ix]).long() y=torch.stack([batch_data[i+1:i+context_window+1] for i in ix]).long() return x,yxs, ys=get_batches(dataset, 'train', DEFAULT_CONFIG['batch_size'], DEFAULT_CONFIG['context_window'])
用于让一个预训练的语言模型生成文本。该函数遵循了自回归(autoregressive)生成的核心逻辑:每次生成一个新 token,并将其添加到序列中,然后使用新序列作为输入来预测下一个 token。
def generate(model, config=DEFAULT_CONFIG, max_new_tokens=30): idx=torch.zeros(5,1).long() for _ in range(max_new_tokens): # Call the model logits=model(idx[:, -config['context_window']:]) # all the batches (1), last time step, all the logits last_time_step_logits=logits[ :,-1,: ] # softmax to get probabilities p=F.softmax(last_time_step_logits, dim=-1) # sample from the distribution to get the next token idx_next=torch.multinomial( p, num_samples=1 ) # append to the sequence idx=torch.cat([idx, idx_next], dim=-1) return [decode(x) for x in idx.tolist()]
步骤2:RMSNorm
RMSNorm(Root Mean Square Normalization)层,这是一种用于深度学习模型(特别是 Transformer 架构)的归一化技术,旨在替代传统的 LayerNorm,以提高训练效率和稳定性。RMSNorm 的设计灵感来源于 Layer Normalization,但它进行了一定的简化:
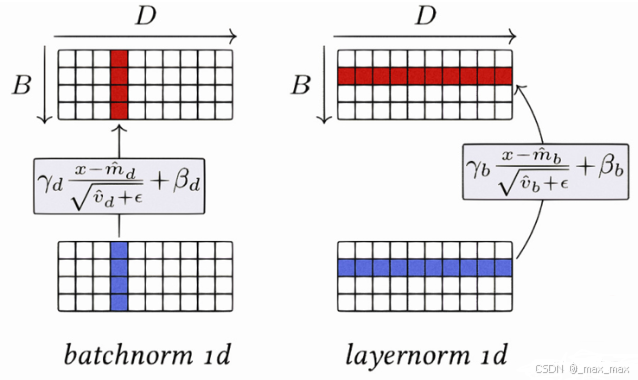
- 省略均值中心化: RMSNorm 不减去均值。它只对输入张量的每个元素进行缩放,缩放因子是该序列元素的均方根(RMS)。传统的 LayerNorm 既会减去均值,也会除以标准差。
- 计算简单: RMSNorm 的计算只涉及平方、求和、开方和除法,比 LayerNorm 省去了均值计算,因此在计算上更加高效。
- 加速训练: 实践证明,RMSNorm 在 Transformer 模型中能加速训练过程,并保持稳定的性能。
class RMSNorm(nn.Module): def __init__(self, layer_shape, eps=1e-8, bias=False): super(RMSNorm, self).__init__() self.register_parameter('scale', nn.Parameter(torch.ones(layer_shape))) def forward(self,x): #calculating the Frobenius norm, RMS=1/sqrt(N)* Frobenius norm ff_rms=torch.linalg.norm(x, dim=(1,2))*x[0].numel() ** -.5 # normalizing the input tensor 'x' with respect to RMS raw=x/ff_rms.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1) # scaling the normalized tensor using the learnable parameter 'scale' return self.scale[:x.shape[1],:].unsqueeze(0) * raw
步骤3:RoPE
RoPE 是一种为 Transformer 模型提供序列中 token 位置信息的方法,它通过旋转每个 token 的词嵌入向量来编码其绝对和相对位置。与传统的绝对位置编码不同,RoPE 可以更好地处理可变长度的序列,并能有效地将相对位置信息融入到自注意力机制中。
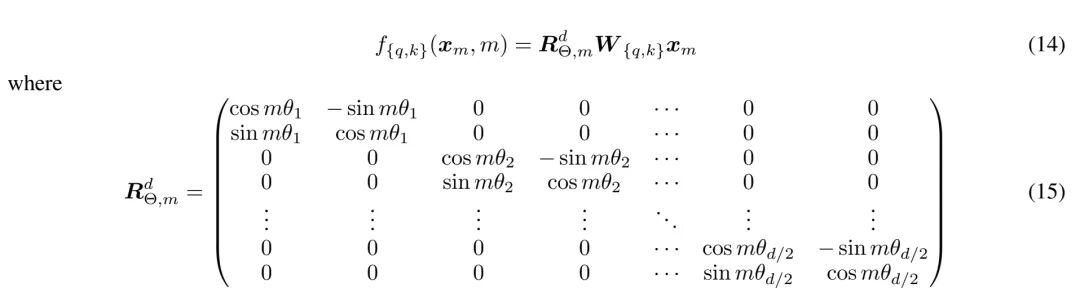
def get_rotary_matrix(context_window, embedding_dim): # Initialize a tensor for the rotary matrix with zeros R=torch.zeros((context_window, embedding_dim, embedding_dim), requires_grad=False) # Loop thorugh each position in the context window for position in range(context_window): # Loop through each dimension in the embedding for i in range(embedding_dim//2): # Calculate the rotation angle (theta) based on the position and embedding dimension theta=10000. ** (-2.*(i-1)/embedding_dim) # Calculate the rotated matrix elements using sine and cosine functions m_theta=position*theta R[position, 2*i, 2*i]=np.cos(m_theta) R[position, 2*i, 2*i+1]=-np.sin(m_theta) R[position, 2*i+1, 2*i]=np.sin(m_theta) R[position, 2*i+1, 2*i+1]=np.cos(m_theta) return R
步骤4:SwiGLU
SwiGLU 的基本思想是,通过一个可学习的“门控”机制来动态地控制信息流。它包含两个平行的线性变换,一个作为主信息通道,另一个作为门控信号。
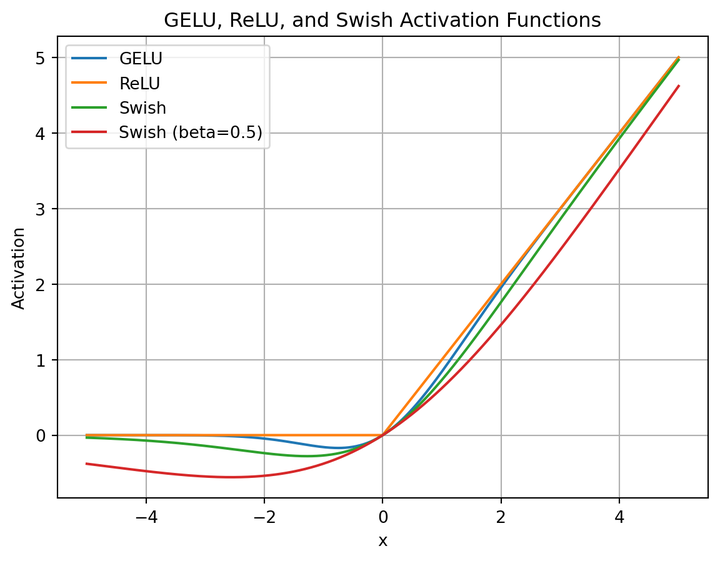
SwiGLU 的优势在于其门控机制,它允许模型学习哪些特征是重要的。通过将主分支的输出与门控信号相乘,模型可以:
- 放大重要特征:如果门控信号接近 1,则主分支的信息几乎完全通过。
- 抑制不重要特征:如果门控信号接近 0,则主分支的信息被“关断”,有效地忽略了这些特征。
class SwiGLU(nn.Module): def __init__(self, size): super().__init__() # Configuration information # Linear transformation for the gating mechanism self.linear_gate=nn.Linear(size, size) # Linear transformation for the main branch self.linear=nn.Linear(size, size) # Random initialization of the beta parameter self.beta=torch.randn(1, requires_grad=True) # Using nn.Parameter for beta to ensure it's recognized as a learnable parameter self.beta=nn.Parameter(torch.ones(1)) self.register_parameter("beta", self.beta) def forward(self, x): # Swish-Gated Linear Unit computation swish_gate=self.linear_gate(x)* torch.sigmoid(self.beta*self.linear_gate(x)) # Element -wise multiplication of the gate and main branch out=swish_gate*self.linear(x) return out
步骤5:搭建网络结构
每个 Llama 块内部都包含了自注意力机制和前馈网络,用于捕捉和处理序列中的上下文信息。整个模型由三个主要部分构成:词嵌入层、一系列 Llama 块(即 Transformer 层)以及一个最终的输出层。
class Llama(nn.Module): def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.config=config #embedding layer for token representations self.embeddings=nn.Embedding(config['vocab_size'], config['d_model']) #sequential block of LlamaBlocks based on the specified number of layers self.llama_blocks=nn.Sequential( OrderedDict([(f"llama_{i}",LlamaBlock(config)) for i in range(config['n_layers'])]) ) #feedforward network (FFN) for final output self.ffn=nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(config['d_model'], config['d_model']), SwiGLU(config['d_model']), nn.Linear(config['d_model'], config['vocab_size']), ) # print total number of parameters in the model print("model params:", sum([m.numel() for m in self.parameters()])) def forward(self, idx, targets=None): # input token indices are passed through the embedding layer x=self.embeddings(idx) #process the input through the LlamaBlocks x=self.llama_blocks(x) #pass the processed input through the final FFN for output logits logits=self.ffn(x) # If targets are not provided, return only the logits if targets isNone: return logits # If targets are provided, compute and return the cross-entropy loss else: loss=F.cross_entropy(logits.view(-1, self.config['vocab_size']),targets.view(-1)) return logits, loss
完整代码链接:https://www.kaggle.com/code/aisuko/llama-in-pytorch
想入门 AI 大模型却找不到清晰方向?备考大厂 AI 岗还在四处搜集零散资料?别再浪费时间啦!2025 年 AI 大模型全套学习资料已整理完毕,从学习路线到面试真题,从工具教程到行业报告,一站式覆盖你的所有需求,现在全部免费分享!
👇👇扫码免费领取全部内容👇👇

一、学习必备:100+本大模型电子书+26 份行业报告 + 600+ 套技术PPT,帮你看透 AI 趋势
想了解大模型的行业动态、商业落地案例?大模型电子书?这份资料帮你站在 “行业高度” 学 AI:
1. 100+本大模型方向电子书

2. 26 份行业研究报告:覆盖多领域实践与趋势
报告包含阿里、DeepSeek 等权威机构发布的核心内容,涵盖:
- 职业趋势:《AI + 职业趋势报告》《中国 AI 人才粮仓模型解析》;
- 商业落地:《生成式 AI 商业落地白皮书》《AI Agent 应用落地技术白皮书》;
- 领域细分:《AGI 在金融领域的应用报告》《AI GC 实践案例集》;
- 行业监测:《2024 年中国大模型季度监测报告》《2025 年中国技术市场发展趋势》。
3. 600+套技术大会 PPT:听行业大咖讲实战
PPT 整理自 2024-2025 年热门技术大会,包含百度、腾讯、字节等企业的一线实践:

- 安全方向:《端侧大模型的安全建设》《大模型驱动安全升级(腾讯代码安全实践)》;
- 产品与创新:《大模型产品如何创新与创收》《AI 时代的新范式:构建 AI 产品》;
- 多模态与 Agent:《Step-Video 开源模型(视频生成进展)》《Agentic RAG 的现在与未来》;
- 工程落地:《从原型到生产:AgentOps 加速字节 AI 应用落地》《智能代码助手 CodeFuse 的架构设计》。
二、求职必看:大厂 AI 岗面试 “弹药库”,300 + 真题 + 107 道面经直接抱走
想冲字节、腾讯、阿里、蔚来等大厂 AI 岗?这份面试资料帮你提前 “押题”,拒绝临场慌!
1. 107 道大厂面经:覆盖 Prompt、RAG、大模型应用工程师等热门岗位
面经整理自 2021-2025 年真实面试场景,包含 TPlink、字节、腾讯、蔚来、虾皮、中兴、科大讯飞、京东等企业的高频考题,每道题都附带思路解析:

2. 102 道 AI 大模型真题:直击大模型核心考点
针对大模型专属考题,从概念到实践全面覆盖,帮你理清底层逻辑:

3. 97 道 LLMs 真题:聚焦大型语言模型高频问题
专门拆解 LLMs 的核心痛点与解决方案,比如让很多人头疼的 “复读机问题”:

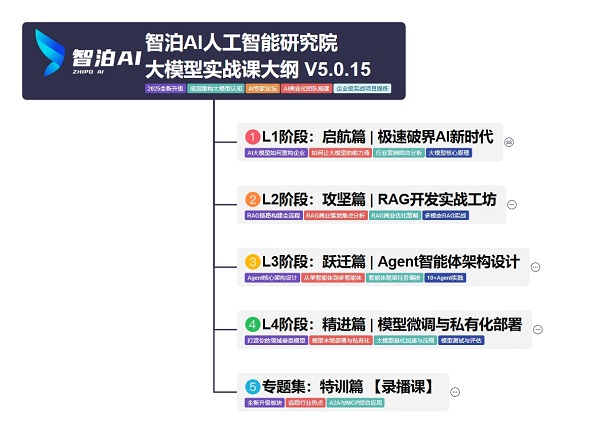
三、路线必明: AI 大模型学习路线图,1 张图理清核心内容
刚接触 AI 大模型,不知道该从哪学起?这份「AI大模型 学习路线图」直接帮你划重点,不用再盲目摸索!

路线图涵盖 5 大核心板块,从基础到进阶层层递进:一步步带你从入门到进阶,从理论到实战。
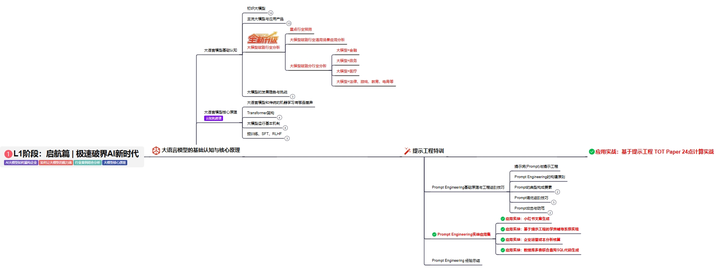
L1阶段:启航篇丨极速破界AI新时代
L1阶段:了解大模型的基础知识,以及大模型在各个行业的应用和分析,学习理解大模型的核心原理、关键技术以及大模型应用场景。
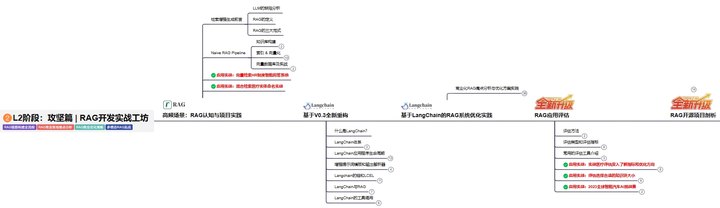
L2阶段:攻坚篇丨RAG开发实战工坊
L2阶段:AI大模型RAG应用开发工程,主要学习RAG检索增强生成:包括Naive RAG、Advanced-RAG以及RAG性能评估,还有GraphRAG在内的多个RAG热门项目的分析。
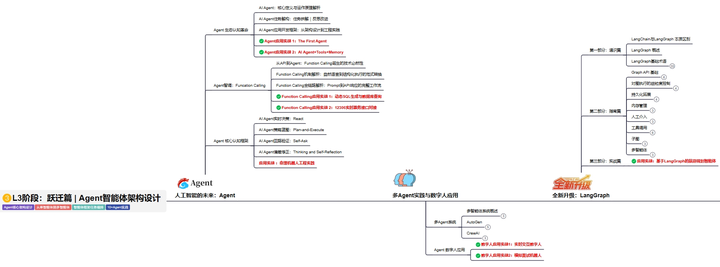
L3阶段:跃迁篇丨Agent智能体架构设计
L3阶段:大模型Agent应用架构进阶实现,主要学习LangChain、 LIamaIndex框架,也会学习到AutoGPT、 MetaGPT等多Agent系统,打造Agent智能体。
L4阶段:精进篇丨模型微调与私有化部署
L4阶段:大模型的微调和私有化部署,更加深入的探讨Transformer架构,学习大模型的微调技术,利用DeepSpeed、Lamam Factory等工具快速进行模型微调,并通过Ollama、vLLM等推理部署框架,实现模型的快速部署。

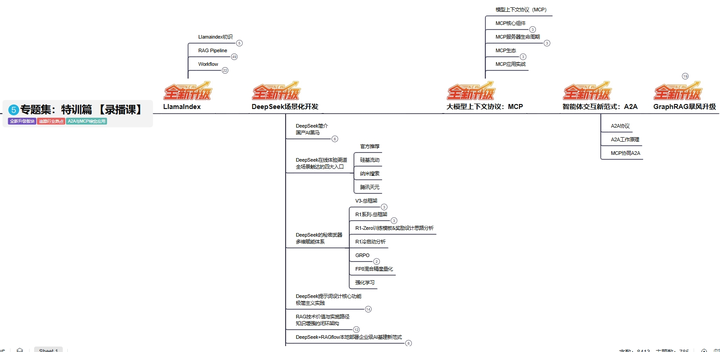
L5阶段:专题集丨特训篇 【录播课】
四、资料领取:全套内容免费抱走,学 AI 不用再找第二份
不管你是 0 基础想入门 AI 大模型,还是有基础想冲刺大厂、了解行业趋势,这份资料都能满足你!
现在只需按照提示操作,就能免费领取:
👇👇扫码免费领取全部内容👇👇

2025 年想抓住 AI 大模型的风口?别犹豫,这份免费资料就是你的 “起跑线”!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献537条内容
已为社区贡献537条内容









所有评论(0)