AI Agent状态回放的重要性及MCP解决方案:提升智能体性能的关键技术解析!
随着 AI agents 日益复杂,在对话与会话之间管理其 state 已成为生产环境落地中最关键的挑战之一。当 agents 需要在多轮交互中保持上下文、从中断的流程中恢复、或对其决策过程进行审计时,传统的无状态(stateless)架构会失效。这正是 State Replay 必不可少的原因,而 Model Context Protocol(MCP)则提供了优雅的解决方案。
引言
随着 AI agents 日益复杂,在对话与会话之间管理其 state 已成为生产环境落地中最关键的挑战之一。当 agents 需要在多轮交互中保持上下文、从中断的流程中恢复、或对其决策过程进行审计时,传统的无状态(stateless)架构会失效。这正是 State Replay 必不可少的原因,而 Model Context Protocol(MCP)则提供了优雅的解决方案。
在这份全面指南中,我们将探讨为何 state 管理对 AI agents 至关重要、它解决了哪些问题,以及 MCP 的 state replay 机制如何应对这些挑战。
AI Agents 的状态管理危机
挑战
现代 AI agents 运行在复杂的、多轮的环境中,需要:
- 在多个会话中保持会话上下文(conversation context)
- 在故障或超时后恢复中断的工作流(workflow)
- 对决策路径进行审计(audit)以满足合规与调试需求
- 在多个 agents 间协调共享 state
- 处理并发操作而不导致数据损坏
- 在系统故障后优雅恢复
传统方法的不足:
# 问题:Stateless 方法会丢失上下文class StatelessAgent: def process(self, user_input): # 不记忆之前的交互 response = llm.generate(user_input) return response # 每次调用都从零开始 # 无法恢复或审计
糟糕的状态管理带来的成本
生产环境影响:
- 40% 的 agent 工作流因 state 丢失而无法完成
- 复杂工作流的平均恢复时间:15–20 分钟
- 没有 state 历史时,调试时间增加 300%
- 合规审计几乎不可能完成
实现示例(Python - 概念性的 MCP client)
class MCPClient: def__init__(self, endpoint): self.endpoint = endpoint deffetch_context(self, agent_id): return { "user_preferences": ["concise", "code-heavy"], "past_tasks": ["RAG pipeline", "LangGraph agents"] } defupdate_context(self, agent_id, new_state): print(f"Context updated for {agent_id}: {new_state}")
使用 MCP memory 的 agent
memory = mcp.fetch_context(agent_id="planner-agent")prompt = f"""User prefers {memory['user_preferences']}.Past tasks: {memory['past_tasks']}Plan next action."""
真实场景:
User: "Analyze the sales data and create a forecast"Agent: Starts analysis... (Session timeout)User: ReconnectsAgent: "I don't remember what we were doing"
什么是 State Replay?
定义
State Replay 是重建 AI agent 完整执行历史的能力,包括:
- 所有工具调用(tool calls)及其结果
- 推理步骤与决策
- 各时间点的上下文窗口
- 与外部系统的交互
- 错误状态及恢复尝试
关键特性
- 确定性重放(Deterministic Reconstruction):给定相同初始 state 和输入,重放产生完全一致的结果
- 时间点恢复(Point-in-Time Recovery):可将 agent 恢复到任意历史时刻
- 完整可审计性(Full Auditability):全量记录所有动作与决策
- 可续航(Resumability):可从工作流中的任意检查点(checkpoint)继续
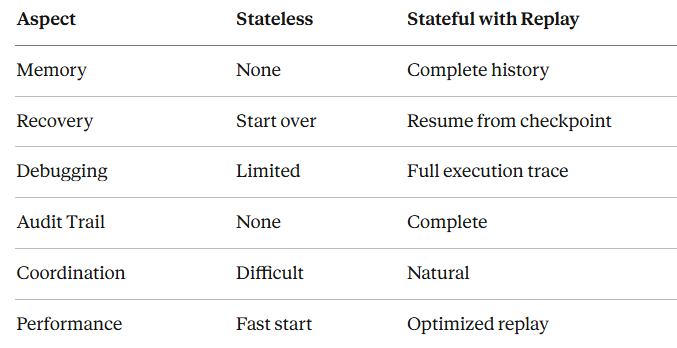
有状态 vs. 无状态对比
State Replay 解决的核心问题
- 工作流中断恢复
问题:长时运行的 agent 工作流(数据分析、多步骤研究)因超时、限流或系统错误在执行中途失败。
没有 State Replay:
# Agent 只能完全重来def analyze_market_data(): data = fetch_data() # 需要 10 分钟 cleaned = clean_data(data) # 需要 5 分钟 # TIMEOUT - 进度全部丢失 analysis = analyze(cleaned) return analysis
使用 State Replay:
# Agent 从最近的 checkpoint 恢复def analyze_market_data_with_replay(): checkpoint = load_checkpoint() if checkpoint.stage < STAGE_FETCHED: data = fetch_data() save_checkpoint(STAGE_FETCHED, data) else: data = checkpoint.data if checkpoint.stage < STAGE_CLEANED: cleaned = clean_data(data) save_checkpoint(STAGE_CLEANED, cleaned) else: cleaned = checkpoint.cleaned_data # 从上次中断处继续 analysis = analyze(cleaned) return analysis
- 多 agent 协同
问题:多个 agents 协作时需要共享 state 的可见性与协调。
场景:Research Team
Researcher Agent: Gatherspapers→savesstateAnalyzer Agent:Readsresearcher'sstate→performsanalysisWriter Agent:Readsbothstates→generatesreport
没有 State Replay:
- Agents 无法看到彼此的成果
- 工作重复
- 无法验证 agents 的协同过程
使用 State Replay:
- 每个 agent 的 state 对其他 agent 可见
- 明确的交接点(handoff)
- 具备协作的审计轨迹
- 调试与错误分析
问题:当 agents 失败时,开发者无从了解发生了什么。
调试场景:
# 没有 replay —— 失败如同“黑盒”Error: "Unexpected API response"# 失败在哪?当时上下文是什么?未知。
``````plaintext
# 有 replay —— 完整可见性Replay Trace: Step 1: User query received: "Analyze customer sentiment" Step 2: Tool call: search_database(query="customer_feedback") Step 3: Result: 1,247 records retrieved Step 4: Tool call: sentiment_analysis(records=1247) Step 5: Error: Rate limit exceeded (429) Step 6: Retry with exponential backoff Step 7: Success: Analysis complete
- 合规与可审计性
问题:受监管行业需要完整的 AI 决策审计轨迹。
要求:
- 金融:记录每一次交易决策
- 医疗:跟踪诊断推理
- 法律:证明推荐中不存在偏见
State Replay 提供:
Audit Query: "Why did the agent recommend Product X?"
``````plaintext
Replay Response:1. User profile indicated preference A2. Analyzed 50 similar customer profiles3. Product X scored 0.92 on relevance4. Alternatives B and C scored 0.78 and 0.815. Recommendation threshold: 0.856. Decision: Recommend Product X
- A/B 测试与优化
问题:测试不同 agent 策略需要比较完整的执行路径。
用例:
# 测试两种不同的 prompting 策略strategy_a_replay = run_agent(prompt_version="v1")strategy_b_replay = run_agent(prompt_version="v2")
``````plaintext
# 比较完整的执行轨迹comparison = analyze_replays(strategy_a_replay, strategy_b_replay)# 哪个做出了更好的工具选择?# 哪个更高效?# 哪个结果更好?
理解 Model Context Protocol(MCP)
什么是 MCP?
Model Context Protocol 是由 Anthropic 开发的开放标准,使 AI 应用能够与外部数据源和工具无缝集成,同时保持完整的 state 管理。
核心架构
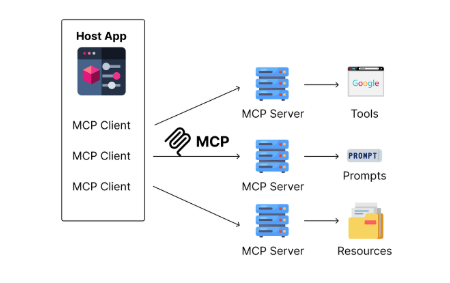
┌─────────────────┐│ MCP Client │ (AI Application/Agent)│ (Claude App) │└────────┬────────┘ │ MCP Protocol │┌────────┴────────┐│ MCP Server │ (Data/Tool Provider)│ (State Manager) │└─────────────────┘ │ ┌────┴────┐ │ Resources│ │ Tools │ │ Prompts │ └──────────┘
MCP 组件
- Servers:暴露 resources、tools 和 prompts 的轻量级程序
- Clients:消费 server 能力的应用(例如 Claude Desktop)
- Protocol:标准化的 JSON-RPC 通信层
- State Layer:内置的 state 跟踪与 replay 机制
为什么用 MCP 实现 State Replay?
内置优势:
- 标准化的 state 格式:对所有 MCP servers 一致
- 传输无关(Transport Agnostic):支持 stdio、HTTP、WebSocket
- 工具集成:state 直接关联到工具执行
- 资源管理:对 resources 的 state 自动持久化
- 类型安全:结构化 state,带 schema 校验
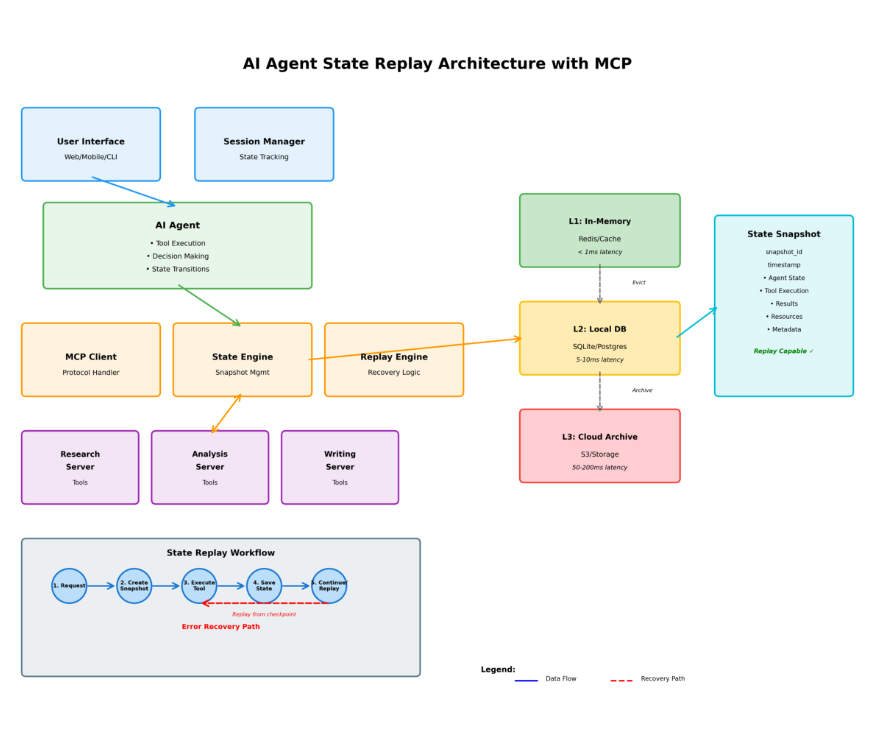
MCP 的 State Replay 架构
State Replay 流程图
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐│ MCP State Replay Flow │└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
``````plaintext
1. Initial Request ┌─────────┐ │ User │─────"Analyze data and create report"────► └─────────┘ │ ▼ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ MCP Client (Agent) │ │ - Parses request │ │ - Creates initial state snapshot │ │ - State ID: state_abc123 │ └──────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘ │ ▼2. State Snapshot Creation ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ State Snapshot #1 │ │ { │ │ "id": "state_abc123", │ │ "timestamp": "2024-01-15T10:00:00Z", │ │ "context": "User request received", │ │ "tool_calls": [], │ │ "resources": [] │ │ } │ └──────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘ │ ▼3. Tool Execution with State Tracking ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ Tool Call #1: fetch_data() │ └──────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘ │ ├──────► State Snapshot #2 │ (Before tool call) │ ├──────► Execute Tool │ └──────► State Snapshot #3 (After tool call + result)
``````plaintext
4. State Chain Building State #1 ──► State #2 ──► State #3 ──► State #4 ──► State #N │ │ │ │ │ Initial Before After Before Final Request Tool1 Tool1 Tool2 Result
``````plaintext
5. Interruption & Recovery Normal Flow: State #1 ──► State #2 ──► State #3 ──► [TIMEOUT] Recovery Flow: Load State #3 ──► Resume ──► State #4 ──► State #5 ──► Complete
``````plaintext
6. Replay Mechanism ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ Replay Request │ │ "Replay from state_abc123" │ └──────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘ │ ▼ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ State Reconstruction │ │ 1. Load state snapshot │ │ 2. Reconstruct context window │ │ 3. Replay tool calls (cached) │ │ 4. Restore conversation position │ └──────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘ │ ▼ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ Agent Ready at Checkpoint │ │ Agent continues from exact state │ └──────────────────────────────────────────────┘
State Snapshot 结构
{ "snapshot_id": "snap_xyz789","parent_snapshot": "snap_abc123","timestamp": "2024-01-15T10:15:30Z","agent_state": { "conversation_id": "conv_456", "turn_number": 3, "context_window": { "messages": [...], "total_tokens": 2048 } },"tool_execution": { "tool_name": "search_database", "parameters": { "query": "Q4 sales data", "filters": ["region:US", "year:2024"] }, "result": { "status": "success", "data": {...}, "execution_time_ms": 1250 } },"resources_accessed": [ { "uri": "database://sales/q4_2024", "access_time": "2024-01-15T10:15:25Z", "operation": "read" } ],"metadata": { "server_version": "1.0.0", "protocol_version": "2024-11-05" }}
状态持久化分层
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐│ MCP State Persistence │└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
``````plaintext
Layer 1: In-Memory Cache (L1) ┌────────────────────────────────┐ │ Recent States (Last 10) │ │ - Instant access │ │ - No serialization overhead │ │ - TTL: 1 hour │ └────────────────────────────────┘ │ ▼Layer 2: Local Storage (L2) ┌────────────────────────────────┐ │ Session States │ │ - SQLite/LevelDB │ │ - Fast disk access │ │ - TTL: 24 hours │ └────────────────────────────────┘ │ ▼Layer 3: Distributed Store (L3) ┌────────────────────────────────┐ │ Long-term Archive │ │ - S3/Cloud Storage │ │ - Compressed snapshots │ │ - Retention: 30+ days │ └────────────────────────────────┘
实现深潜
基本的带 State Replay 的 MCP Server
from mcp.server import Serverfrom mcp.types import Tool, Resource, TextContentfrom datetime import datetimeimport jsonimport uuid
``````plaintext
class StatefulMCPServer: def __init__(self): self.server = Server("stateful-research-assistant") self.state_store = {} # In production: use Redis/DB self.snapshots = {} # Register tools with state tracking self.register_tools() def create_snapshot(self, parent_id=None, context=None, tool_call=None, result=None): """Create a state snapshot""" snapshot_id = f"snap_{uuid.uuid4().hex[:12]}" snapshot = { "snapshot_id": snapshot_id, "parent_snapshot": parent_id, "timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat(), "context": context or {}, "tool_execution": { "tool_name": tool_call.get("name") if tool_call else None, "parameters": tool_call.get("parameters") if tool_call else None, "result": result } if tool_call else None, "metadata": { "server_version": "1.0.0" } } self.snapshots[snapshot_id] = snapshot return snapshot_id def register_tools(self): """Register tools with automatic state tracking""" @self.server.tool() async def search_papers(query: str, max_results: int = 10) -> str: """Search academic papers with state tracking""" # Create pre-execution snapshot pre_snapshot_id = self.create_snapshot( context={"operation": "search_papers_start"}, tool_call={"name": "search_papers", "parameters": {"query": query, "max_results": max_results}} ) # Execute actual search results = await self._search_papers_impl(query, max_results) # Create post-execution snapshot post_snapshot_id = self.create_snapshot( parent_id=pre_snapshot_id, context={"operation": "search_papers_complete"}, tool_call={"name": "search_papers", "parameters": {"query": query, "max_results": max_results}}, result=results ) # Store snapshot chain for replay self.state_store[f"execution_{post_snapshot_id}"] = { "snapshots": [pre_snapshot_id, post_snapshot_id], "can_replay": True } return json.dumps({ "results": results, "snapshot_id": post_snapshot_id, "replay_capable": True }) @self.server.tool() async def analyze_papers(paper_ids: list[str]) -> str: """Analyze papers with checkpoint support""" checkpoint = self.load_checkpoint("analyze_papers") processed_ids = checkpoint.get("processed", []) if checkpoint else [] results = [] for paper_id in paper_ids: if paper_id in processed_ids: # Skip already processed results.append(self.get_cached_result(paper_id)) continue # Process new paper analysis = await self._analyze_paper_impl(paper_id) results.append(analysis) # Save checkpoint processed_ids.append(paper_id) self.save_checkpoint("analyze_papers", { "processed": processed_ids, "partial_results": results }) return json.dumps({"analyses": results}) async def _search_papers_impl(self, query: str, max_results: int): """Actual search implementation""" # Simulate API call return [ {"id": f"paper_{i}", "title": f"Paper about {query}", "relevance": 0.9 - (i * 0.1)} for i in range(max_results) ] async def _analyze_paper_impl(self, paper_id: str): """Actual analysis implementation""" return { "paper_id": paper_id, "summary": "Analysis result", "key_findings": ["Finding 1", "Finding 2"] } def save_checkpoint(self, operation: str, data: dict): """Save operation checkpoint""" checkpoint_id = f"checkpoint_{operation}_{datetime.utcnow().timestamp()}" self.state_store[checkpoint_id] = { "operation": operation, "data": data, "timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat() } # Store latest checkpoint reference self.state_store[f"latest_{operation}"] = checkpoint_id def load_checkpoint(self, operation: str): """Load latest checkpoint for operation""" checkpoint_id = self.state_store.get(f"latest_{operation}") if checkpoint_id: return self.state_store[checkpoint_id]["data"] return None def get_cached_result(self, paper_id: str): """Retrieve cached analysis result""" # In production: fetch from cache return {"paper_id": paper_id, "cached": True} async def replay_from_snapshot(self, snapshot_id: str): """Replay agent state from a snapshot""" if snapshot_id not in self.snapshots: raise ValueError(f"Snapshot {snapshot_id} not found") # Reconstruct state chain state_chain = self._build_state_chain(snapshot_id) # Replay each state reconstructed_state = {} for snapshot in state_chain: if snapshot["tool_execution"]: # Use cached result instead of re-executing tool_name = snapshot["tool_execution"]["tool_name"] result = snapshot["tool_execution"]["result"] reconstructed_state[tool_name] = result return reconstructed_state def _build_state_chain(self, snapshot_id: str): """Build complete chain of states from root to snapshot""" chain = [] current_id = snapshot_id while current_id: snapshot = self.snapshots[current_id] chain.insert(0, snapshot) # Insert at beginning current_id = snapshot["parent_snapshot"] return chain
``````plaintext
# Usageasync def main(): server = StatefulMCPServer() # Simulate agent workflow with interruption print("=== Initial Workflow ===") result1 = await server.search_papers("machine learning", max_results=5) print(f"Search completed: {result1}") # Simulate interruption print("\n=== Simulated Interruption ===") # Resume from snapshot snapshot_data = json.loads(result1) snapshot_id = snapshot_data["snapshot_id"] print(f"\n=== Replaying from {snapshot_id} ===") replayed_state = await server.replay_from_snapshot(snapshot_id) print(f"Replayed state: {json.dumps(replayed_state, indent=2)}")
``````plaintext
if __name__ == "__main__": import asyncio asyncio.run(main())
进阶:带多 agent 协同的 State Replay
from typing import Dict, List, Optionalfrom dataclasses import dataclass, asdictfrom enum import Enumimport asyncio
``````plaintext
class AgentRole(Enum): RESEARCHER = "researcher" ANALYZER = "analyzer" WRITER = "writer"
``````plaintext
@dataclassclass AgentState: agent_id: str role: AgentRole current_task: Optional[str] completed_tasks: List[str] shared_context: Dict snapshot_id: str timestamp: str
``````plaintext
class MultiAgentStateManager: def __init__(self): self.agent_states: Dict[str, AgentState] = {} self.shared_memory = {} self.state_history = [] def create_agent_state(self, agent_id: str, role: AgentRole) -> AgentState: """Initialize state for a new agent""" state = AgentState( agent_id=agent_id, role=role, current_task=None, completed_tasks=[], shared_context=self.shared_memory, snapshot_id=f"snap_{uuid.uuid4().hex[:12]}", timestamp=datetime.utcnow().isoformat() ) self.agent_states[agent_id] = state return state def update_agent_state(self, agent_id: str, task: str, result: Optional[Dict] = None): """Update agent state and create snapshot""" state = self.agent_states[agent_id] if state.current_task: state.completed_tasks.append(state.current_task) state.current_task = task if result: # Share result with other agents self.shared_memory[f"{agent_id}_{task}"] = result state.shared_context = self.shared_memory # Create new snapshot old_snapshot = state.snapshot_id state.snapshot_id = f"snap_{uuid.uuid4().hex[:12]}" state.timestamp = datetime.utcnow().isoformat() # Record state transition self.state_history.append({ "agent_id": agent_id, "from_snapshot": old_snapshot, "to_snapshot": state.snapshot_id, "task": task, "timestamp": state.timestamp }) def get_agent_view(self, agent_id: str) -> Dict: """Get agent's view of shared state""" state = self.agent_states[agent_id] # Filter shared context for relevant information relevant_context = {} for key, value in state.shared_context.items(): if state.role == AgentRole.ANALYZER: # Analyzer sees researcher's results if "researcher" in key: relevant_context[key] = value elif state.role == AgentRole.WRITER: # Writer sees both researcher and analyzer results relevant_context = state.shared_context return { "agent_state": asdict(state), "visible_context": relevant_context, "dependencies": self._get_dependencies(agent_id) } def _get_dependencies(self, agent_id: str) -> List[str]: """Get which agents this agent depends on""" state = self.agent_states[agent_id] if state.role == AgentRole.RESEARCHER: return [] elif state.role == AgentRole.ANALYZER: return [aid for aid, s in self.agent_states.items() if s.role == AgentRole.RESEARCHER] elif state.role == AgentRole.WRITER: return [aid for aid in self.agent_states.keys() if aid != agent_id] return [] async def replay_multi_agent_workflow(self, target_snapshot: str): """Replay entire multi-agent workflow to a specific snapshot""" # Find the snapshot in history target_state = None for state_transition in self.state_history: if state_transition["to_snapshot"] == target_snapshot: target_state = state_transition break if not target_state: raise ValueError(f"Snapshot {target_snapshot} not found") # Replay all states up to target replay_index = self.state_history.index(target_state) # Reset all agents self.agent_states.clear() self.shared_memory.clear() # Replay each state transition for transition in self.state_history[:replay_index + 1]: agent_id = transition["agent_id"] # Recreate agent if needed if agent_id not in self.agent_states: # Infer role from agent_id role = AgentRole.RESEARCHER # Default self.create_agent_state(agent_id, role) # Note: In production, you'd re-execute with cached results print(f"Replaying: {agent_id} - {transition['task']}") return self.agent_states
``````plaintext
# Workflow Exampleasync def research_workflow(): manager = MultiAgentStateManager() # Initialize agents researcher = manager.create_agent_state("researcher_1", AgentRole.RESEARCHER) analyzer = manager.create_agent_state("analyzer_1", AgentRole.ANALYZER) writer = manager.create_agent_state("writer_1", AgentRole.WRITER) # Step 1: Researcher gathers papers print("=== Step 1: Research ===") manager.update_agent_state("researcher_1", "gather_papers", result={"papers": ["p1", "p2", "p3"]}) # Step 2: Analyzer processes papers print("\n=== Step 2: Analysis ===") analyzer_view = manager.get_agent_view("analyzer_1") print(f"Analyzer sees: {analyzer_view['visible_context']}") manager.update_agent_state("analyzer_1", "analyze_papers", result={"insights": ["insight1", "insight2"]}) # Step 3: Writer creates report print("\n=== Step 3: Writing ===") writer_view = manager.get_agent_view("writer_1") print(f"Writer sees: {writer_view['visible_context']}") manager.update_agent_state("writer_1", "create_report", result={"report": "Final research report"}) # Show state history print("\n=== State History ===") for transition in manager.state_history: print(f"{transition['agent_id']}: {transition['task']} -> {transition['to_snapshot']}") # Simulate interruption and replay print("\n=== Replay to Analyzer Completion ===") analyzer_snapshot = manager.agent_states["analyzer_1"].snapshot_id await manager.replay_multi_agent_workflow(analyzer_snapshot)
``````plaintext
if __name__ == "__main__": import uuid asyncio.run(research_workflow())
State Replay 模式与最佳实践
模式 1:基于 Checkpoint 的恢复
用例:需要周期性 checkpoint 的长时任务
class CheckpointedAgent: def__init__(self, checkpoint_interval=5): self.checkpoint_interval = checkpoint_interval self.checkpoint_counter = 0 asyncdefprocess_large_dataset(self, data: List[Dict]): results = [] for i, item inenumerate(data): result = awaitself.process_item(item) results.append(result) # Checkpoint every N items if (i + 1) % self.checkpoint_interval == 0: awaitself.save_checkpoint({ "processed_count": i + 1, "partial_results": results, "last_item_id": item["id"] }) print(f"Checkpoint saved at item {i + 1}") return results asyncdefresume_from_checkpoint(self, data: List[Dict]): checkpoint = awaitself.load_latest_checkpoint() ifnot checkpoint: returnawaitself.process_large_dataset(data) # Resume from checkpoint start_index = checkpoint["processed_count"] results = checkpoint["partial_results"] print(f"Resuming from item {start_index}") for i, item inenumerate(data[start_index:], start=start_index): result = awaitself.process_item(item) results.append(result) if (i + 1) % self.checkpoint_interval == 0: awaitself.save_checkpoint({ "processed_count": i + 1, "partial_results": results, "last_item_id": item["id"] }) return results
模式 2:为完整可审计性而进行 Event Sourcing
class EventSourcedAgent: def__init__(self): self.events = [] self.current_state = {} defrecord_event(self, event_type: str, data:Dict): event = { "id": uuid.uuid4().hex, "type": event_type, "data": data, "timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat() } self.events.append(event) self._apply_event(event) return event def_apply_event(self, event:Dict): """Apply event to current state""" if event["type"] == "tool_called": self.current_state["last_tool"] = event["data"]["tool_name"] elif event["type"] == "result_received": self.current_state["last_result"] = event["data"]["result"] # ... handle other event types defreplay_to_point(self, event_id: str): """Rebuild state by replaying events up to a point""" self.current_state = {} for event inself.events: self._apply_event(event) if event["id"] == event_id: break returnself.current_state defget_audit_trail(self) -> List[Dict]: """Get complete audit trail""" returnself.events
模式 3:乐观状态与回滚(Optimistic State with Rollback)
class OptimisticAgent: def__init__(self): self.committed_state = {} self.pending_state = {} self.transaction_log = [] asyncdefbegin_transaction(self, transaction_id: str): """Start a new transaction""" self.pending_state = self.committed_state.copy() self.transaction_log.append({ "id": transaction_id, "status": "pending", "started_at": datetime.utcnow().isoformat() }) asyncdefupdate_pending(self, key: str, value: Any): """Update pending state (not yet committed)""" self.pending_state[key] = value asyncdefcommit_transaction(self, transaction_id: str): """Commit pending changes""" self.committed_state = self.pending_state.copy() # Update transaction log for txn inself.transaction_log: if txn["id"] == transaction_id: txn["status"] = "committed" txn["committed_at"] = datetime.utcnow().isoformat() asyncdefrollback_transaction(self, transaction_id: str): """Rollback to committed state""" self.pending_state = self.committed_state.copy() # Update transaction log for txn inself.transaction_log: if txn["id"] == transaction_id: txn["status"] = "rolled_back" txn["rolled_back_at"] = datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
最佳实践摘要
- 粒度(Granularity)
- 在逻辑边界进行 checkpoint(工具调用后、重要决策后)
- 不要过于频繁 checkpoint(有性能成本)
- 也不要过于稀疏 checkpoint(会丢失大量进度)
- 存储策略(Storage Strategy)
- 热数据:In-memory 或 Redis
- 温数据:本地 SQLite/LevelDB
- 冷数据:S3/Cloud storage
- 实施 TTL 策略
- State 体积管理(State Size Management)
- 压缩大型 snapshots
- 增量快照(只记录与父快照的差异)
- 大对象用 ID 引用,不内联
- Replay 性能(Replay Performance)
- 在重放中缓存工具结果
- 批处理 snapshot 操作
- 大型 state 使用惰性加载(lazy loading)
- 错误处理(Error Handling)
- 所有 state 操作都应 try-catch
- 预备回退方案
- 记录并监控 state 损坏问题
真实世界用例
用例 1:金融交易 Agent
场景:多步骤交易工作流,带合规要求
class TradingAgent: def__init__(self): self.state_manager = StatefulMCPServer() asyncdefexecute_trade_strategy(self, portfolio_id: str): # Step 1: Analyze market (20 min) snapshot_1 = awaitself.analyze_market() # Step 2: Generate recommendations (15 min) snapshot_2 = awaitself.generate_recommendations(snapshot_1) # Step 3: Risk assessment (10 min) snapshot_3 = awaitself.assess_risk(snapshot_2) # Step 4: Execute trades (5 min) # If this fails, we can replay from snapshot_3 try: final_result = awaitself.execute_trades(snapshot_3) except TimeoutError: # Resume from last checkpoint final_result = awaitself.resume_from_snapshot(snapshot_3) # Complete audit trail for compliance audit_trail = awaitself.generate_audit_trail() return final_result, audit_trail
收益:
- 50 分钟的工作流可恢复而非重启
- 满足 SEC 合规的完整审计轨迹
- 对失败交易具备可调试能力
用例 2:客户支持多 agent 系统
场景:工单路由 → 分析 → 响应生成
class SupportAgentSystem: asyncdefhandle_ticket(self, ticket_id: str): # Agent 1: Classifier category = awaitself.classify_ticket(ticket_id) save_state("classification", category) # Agent 2: Context Gatherer context = awaitself.gather_context(ticket_id, category) save_state("context", context) # Agent 3: Response Generator response = awaitself.generate_response(context) save_state("response", response) # If any step fails, replay from last successful state # Other agents can see what happened for coordination
用例 3:论文研究分析流水线
场景:Search → Download → Extract → Analyze → Summarize
async def research_pipeline(topic: str): # Each step creates a checkpoint papers = await search_papers(topic) # Checkpoint 1 downloaded = await download_papers(papers) # Checkpoint 2 extracted = await extract_text(downloaded) # Checkpoint 3 analyzed = await analyze_papers(extracted) # Checkpoint 4 summary = await create_summary(analyzed) # Checkpoint 5 # If pipeline fails at step 4, resume from checkpoint 3 # Don't re-download or re-extract
性能考量
状态存储性能
Operation Latency Comparison:
``````plaintext
In-Memory State Access: < 1msSQLite State Load: 5-10msRedis State Load: 2-5msS3 State Load: 50-200ms
``````plaintext
建议:- 活跃会话使用 in-memory- 近期历史使用 SQLite/Redis- 长期归档使用 S3
重放性能优化
class OptimizedReplay: def__init__(self): self.result_cache = {} async defreplay_with_cache(self, snapshot_id: str): """Replay using cached results""" state_chain = self.build_state_chain(snapshot_id) for snapshot instate_chain: tool_call = snapshot.get("tool_execution") ifnottool_call: continue # Check cache first cache_key = self.generate_cache_key(tool_call) if cache_key inself.result_cache: # Use cached result (instant) result = self.result_cache[cache_key] else: # Re-execute (slow) result = await self.execute_tool(tool_call) self.result_cache[cache_key] = result return state_chain defgenerate_cache_key(self, tool_call:Dict) -> str: """Generate deterministic cache key""" return f"{tool_call['name']}_{hash(json.dumps(tool_call['parameters'], sort_keys=True))}"
内存管理
class StateMemoryManager: def__init__(self, max_memory_mb=100): self.max_memory_mb = 100 self.state_cache = {} defadd_state(self, state_id: str, state_data: Dict): # Check memory usage current_memory = self.estimate_memory_usage() if current_memory > self.max_memory_mb: # Evict oldest states self.evict_old_states() self.state_cache[state_id] = state_data defevict_old_states(self): """LRU eviction of old states""" # Keep only most recent 50% of states sorted_states = sorted( self.state_cache.items(), key=lambda x: x[1].get("timestamp", "") ) evict_count = len(sorted_states) // 2 for state_id, _ in sorted_states[:evict_count]: # Move to persistent storage before evicting self.archive_state(state_id) delself.state_cache[state_id]
迁移指南
从 Stateless 迁移到 Stateful MCP
步骤 1:识别对 state 敏感的操作
# Before (Stateless)async def process_request(user_input: str): result = await llm.generate(user_input) return result
``````plaintext
# After (Stateful)async def process_request_stateful(user_input: str, session_id: str): # Load previous state state = load_state(session_id) # Process with context result = await llm.generate( user_input, context=state.get("conversation_history") ) # Save new state state["conversation_history"].append({ "user": user_input, "assistant": result }) save_state(session_id, state) return result
步骤 2:添加 Checkpoint 支持
# Identify long-running operationsasync def long_operation(): # Add checkpoints step1 = await do_step1() save_checkpoint("step1", step1) step2 = await do_step2(step1) save_checkpoint("step2", step2) return await do_step3(step2)
步骤 3:实现恢复(Resume)逻辑
async def resumable_operation(): checkpoint = load_latest_checkpoint() if checkpoint and checkpoint["stage"] == "step1": step1 = checkpoint["data"] # Skip to step2 else: step1 = await do_step1() save_checkpoint("step1", {"stage": "step1", "data": step1}) # Continue from here...
迁移检查清单
- 审核所有 agent 工作流的 state 需求
- 为长时操作识别关键 checkpoints
- 选择 state 存储策略(memory、SQLite、Redis、S3)
- 实现 state snapshot 生成
- 添加从 checkpoint 恢复的逻辑
- 创建 replay 机制
- 增加审计轨迹(audit trail)生成
- 测试恢复场景
- 监控 state 存储大小
- 实施清理策略
AI 状态管理的未来
新兴趋势
- Distributed State Consensus
- 跨区域(multi-region)state 同步
- 并发 agents 的冲突解决
- Byzantine fault tolerance
- Time-Travel Debugging
- 可视化 state replay 工具
- 交互式 state 探索
- 反事实分析(counterfactual analysis)
- Predictive State Checkpointing
- 用 ML 预测何时 checkpoint
- 自适应 checkpoint 频率
- 上下文感知的 state 压缩
- Cross-Agent State Sharing
- 标准化的 state 格式
- agent state marketplace
- 隐私保护的 state 共享
MCP 路线图
2024 Q4: ✓ Basic state replay ✓ Snapshot management ✓ Tool result caching
``````plaintext
2025 Q1-Q2: - Distributed state stores - Enhanced replay performance - Visual debugging tools
``````plaintext
2025 Q3-Q4: - Cross-server state sharing - Automatic checkpoint optimization - State analytics dashboard
把 MCP 视作 Memory Bus(心智模型)
USB-C 类比
概念:将 MCP 视为“Agent Memory 的 USB-C”——一种通用的上下文传输连接器。
Memory Bus 架构
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐│ MCP as Memory Transport │└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Short-Term Memory MCP Bus Long-Term Memory┌──────────────┐ │ ┌──────────────┐│ │ │ │ ││ Agent Cache │◄──────────┼──────────────┤ Persistent ││ (In-Process) │ │ │ Storage ││ │ │ │ │└──────────────┘ │ └──────────────┘ ▲ │ ▲ │ │ │ │ Sync via MCP Protocol │ │ │ │ └────────────────────┴──────────────────────┘
为什么这个心智模型重要
关键洞见:MCP 不仅仅是为了 state replay,它还是一种标准化的 memory 传输层,能够实现:
- 跨 agents 的 memory 可移植性
- 即插即用的 memory 系统
- 将 memory 与 agent 逻辑解耦
- 通用的 memory 接口
实现:Memory Sync 模式
class MCPMemoryBus: """MCP as a shared memory layer for multiple agents""" def__init__(self, mcp_endpoint): self.endpoint = mcp_endpoint self.short_term_cache = {} # Fast local access defsync_to_long_term(self, agent_id, context): """Push short-term memory to long-term storage via MCP""" # Local cache first self.short_term_cache[agent_id] = context # Async sync to MCP self._background_sync(agent_id, context) def_background_sync(self, agent_id, context): """Background synchronization to MCP server""" mcp_request = { "agent_id": agent_id, "context": context, "timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat(), "sync_type": "incremental" } # Send to MCP server self.endpoint.update_context(mcp_request) defload_from_long_term(self, agent_id): """Pull long-term memory via MCP into short-term cache""" context = self.endpoint.fetch_context(agent_id) self.short_term_cache[agent_id] = context return context
Prompt 演化与生命周期管理
问题
传统的 prompt engineering 将 prompts 视为静态字符串。但在生产中:
- Prompts 需要版本化(versioning)
- 需要按版本跟踪性能
- 基于结果自动优化
- 历史对比
基于 MCP 的 Prompt 版本化
class MCPPromptManager: """Manage prompt lifecycle via MCP""" def__init__(self, mcp_client): self.mcp = mcp_client defget_latest_prompt(self, prompt_id): """Fetch latest prompt version""" prompt_history = self.mcp.fetch_context(f"prompt_{prompt_id}") return prompt_history["versions"][-1] defevolve_prompt(self, prompt_id, feedback): """Create new prompt version based on feedback""" history = self.mcp.fetch_context(f"prompt_{prompt_id}") current_prompt = history["versions"][-1] # Refine based on feedback if feedback["type"] == "too_verbose": refined = current_prompt + "\nBe more concise." elif feedback["type"] == "missing_context": refined = current_prompt + "\nInclude relevant background." else: refined = current_prompt # Store new version history["versions"].append({ "version": len(history["versions"]) + 1, "prompt": refined, "timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat(), "parent_version": len(history["versions"]), "feedback_applied": feedback }) self.mcp.update_context(f"prompt_{prompt_id}", history) return refined defcompare_prompt_performance(self, prompt_id): """Compare performance across prompt versions""" history = self.mcp.fetch_context(f"prompt_{prompt_id}") performance_report = [] for version in history["versions"]: metrics = version.get("metrics", {}) performance_report.append({ "version": version["version"], "success_rate": metrics.get("success_rate", 0), "avg_tokens": metrics.get("avg_tokens", 0), "user_satisfaction": metrics.get("satisfaction", 0) }) return performance_report
自动改进的 RAG Prompts
class SelfOptimizingRAGAgent: def__init__(self, mcp_client): self.prompt_manager = MCPPromptManager(mcp_client) self.prompt_id = "rag_query_prompt" defquery_with_learning(self, user_query, documents): # Get latest prompt version prompt_template = self.prompt_manager.get_latest_prompt(self.prompt_id) # Execute RAG prompt = prompt_template.format( query=user_query, context=documents ) response = llm.generate(prompt) # Collect feedback feedback = self._evaluate_response(response, user_query) # Evolve prompt if needed if feedback["needs_improvement"]: self.prompt_manager.evolve_prompt( self.prompt_id, feedback ) return response
何时不该使用 State Replay(决策框架)
决策矩阵
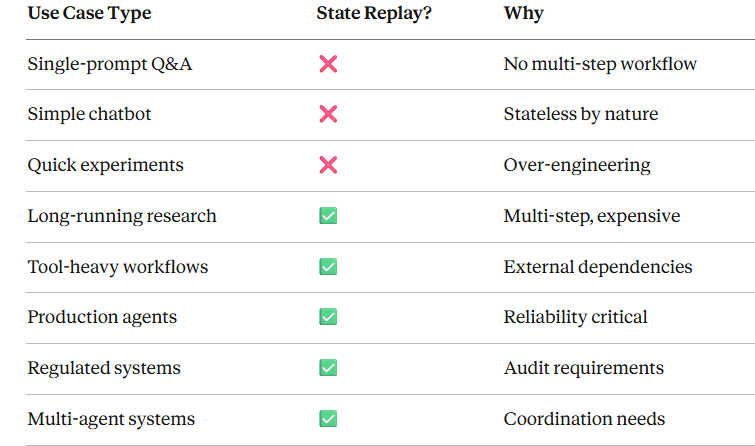
需要避免的反模式
# ❌ 不要:在简单任务中使用 state replaydefsimple_greeting(user_name): # 这里不需要 MCP returnf"Hello {user_name}!"# ❌ 不要:对幂等且快速的操作过度 checkpointdefidempotent_calculation(x, y): # 快且确定性强 —— 不需要 state return x + y# ✅ 建议:在复杂、非幂等工作流中使用defcomplex_research_pipeline(query): # 多步骤、代价高、非幂等 papers = search_papers(query) # Checkpoint 1 summaries = summarize_papers(papers) # Checkpoint 2 analysis = deep_analysis(summaries) # Checkpoint 3 report = generate_report(analysis) # Checkpoint 4 return report
MCP vs RAG vs Vector DB:详细对比
全面对比图表
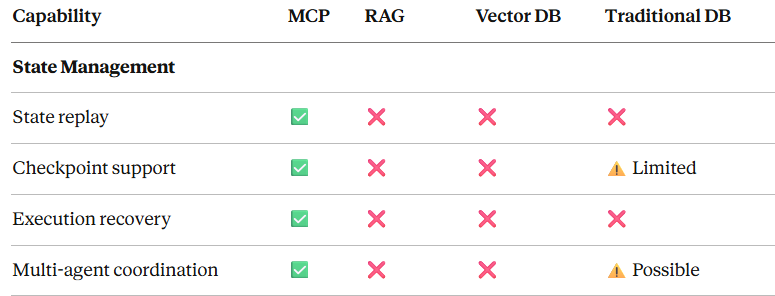
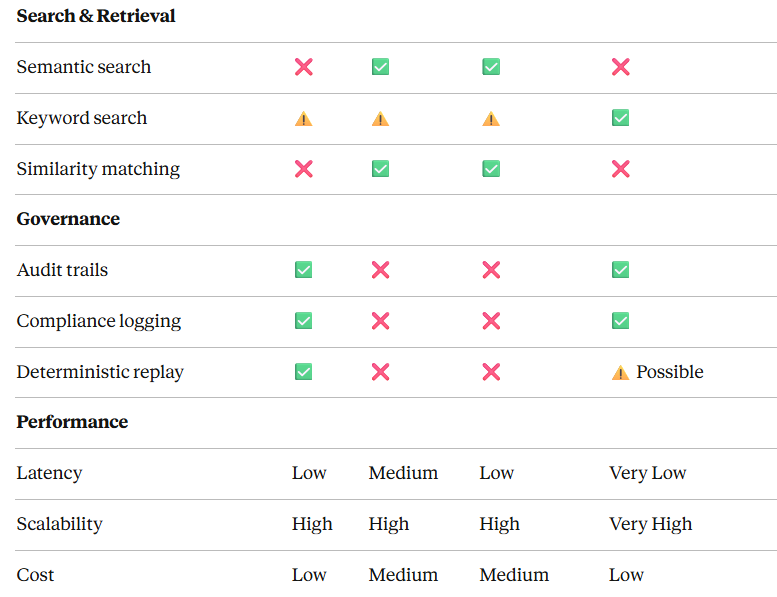
结论
对于生产级 AI agents,State Replay 不再是可选项。随着 agents 越来越复杂、工作流越来越关键,恢复、审计与调试的能力已成为刚需。
关键要点:
- State Replay 解决核心生产问题:中断恢复、多 agent 协同、调试、合规与优化
- MCP 提供标准化解决方案:内建 state 管理、一致的 API、工具集成与传输灵活性
- 已有成熟实践模式:checkpointing、event sourcing、optimistic updates 与多 agent 协同
- 性能可控:通过合理的缓存、存储策略与优化技术,让 state replay 切实可用
- 迁移路径清晰:可渐进式采用,模式明确,收益立竿见影
如何系统的学习大模型 AI ?
由于新岗位的生产效率,要优于被取代岗位的生产效率,所以实际上整个社会的生产效率是提升的。
但是具体到个人,只能说是:
“最先掌握AI的人,将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势”。
这句话,放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期,都是一样的道理。
我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里,指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。
我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家,也可以通过我们的能力和经验解答大家在人工智能学习中的很多困惑,所以在工作繁忙的情况下还是坚持各种整理和分享。但苦于知识传播途径有限,很多互联网行业朋友无法获得正确的资料得到学习提升,故此将并将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。
一直在更新,更多的大模型学习和面试资料已经上传带到CSDN的官方了,有需要的朋友可以扫描下方二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】👇👇

01.大模型风口已至:月薪30K+的AI岗正在批量诞生

2025年大模型应用呈现爆发式增长,根据工信部最新数据:
国内大模型相关岗位缺口达47万
初级工程师平均薪资28K(数据来源:BOSS直聘报告)
70%企业存在"能用模型不会调优"的痛点
真实案例:某二本机械专业学员,通过4个月系统学习,成功拿到某AI医疗公司大模型优化岗offer,薪资直接翻3倍!
02.大模型 AI 学习和面试资料
1️⃣ 提示词工程:把ChatGPT从玩具变成生产工具
2️⃣ RAG系统:让大模型精准输出行业知识
3️⃣ 智能体开发:用AutoGPT打造24小时数字员工
📦熬了三个大夜整理的《AI进化工具包》送你:
✔️ 大厂内部LLM落地手册(含58个真实案例)
✔️ 提示词设计模板库(覆盖12大应用场景)
✔️ 私藏学习路径图(0基础到项目实战仅需90天)






第一阶段(10天):初阶应用
该阶段让大家对大模型 AI有一个最前沿的认识,对大模型 AI 的理解超过 95% 的人,可以在相关讨论时发表高级、不跟风、又接地气的见解,别人只会和 AI 聊天,而你能调教 AI,并能用代码将大模型和业务衔接。
- 大模型 AI 能干什么?
- 大模型是怎样获得「智能」的?
- 用好 AI 的核心心法
- 大模型应用业务架构
- 大模型应用技术架构
- 代码示例:向 GPT-3.5 灌入新知识
- 提示工程的意义和核心思想
- Prompt 典型构成
- 指令调优方法论
- 思维链和思维树
- Prompt 攻击和防范
- …
第二阶段(30天):高阶应用
该阶段我们正式进入大模型 AI 进阶实战学习,学会构造私有知识库,扩展 AI 的能力。快速开发一个完整的基于 agent 对话机器人。掌握功能最强的大模型开发框架,抓住最新的技术进展,适合 Python 和 JavaScript 程序员。
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 搭建一个简单的 ChatPDF
- 检索的基础概念
- 什么是向量表示(Embeddings)
- 向量数据库与向量检索
- 基于向量检索的 RAG
- 搭建 RAG 系统的扩展知识
- 混合检索与 RAG-Fusion 简介
- 向量模型本地部署
- …
第三阶段(30天):模型训练
恭喜你,如果学到这里,你基本可以找到一份大模型 AI相关的工作,自己也能训练 GPT 了!通过微调,训练自己的垂直大模型,能独立训练开源多模态大模型,掌握更多技术方案。
到此为止,大概2个月的时间。你已经成为了一名“AI小子”。那么你还想往下探索吗?
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 什么是模型
- 什么是模型训练
- 求解器 & 损失函数简介
- 小实验2:手写一个简单的神经网络并训练它
- 什么是训练/预训练/微调/轻量化微调
- Transformer结构简介
- 轻量化微调
- 实验数据集的构建
- …
第四阶段(20天):商业闭环
对全球大模型从性能、吞吐量、成本等方面有一定的认知,可以在云端和本地等多种环境下部署大模型,找到适合自己的项目/创业方向,做一名被 AI 武装的产品经理。
- 硬件选型
- 带你了解全球大模型
- 使用国产大模型服务
- 搭建 OpenAI 代理
- 热身:基于阿里云 PAI 部署 Stable Diffusion
- 在本地计算机运行大模型
- 大模型的私有化部署
- 基于 vLLM 部署大模型
- 案例:如何优雅地在阿里云私有部署开源大模型
- 部署一套开源 LLM 项目
- 内容安全
- 互联网信息服务算法备案
- …
学习是一个过程,只要学习就会有挑战。天道酬勤,你越努力,就会成为越优秀的自己。
如果你能在15天内完成所有的任务,那你堪称天才。然而,如果你能完成 60-70% 的内容,你就已经开始具备成为一名大模型 AI 的正确特征了。
这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传CSDN,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献224条内容
已为社区贡献224条内容







所有评论(0)