Spring AI 工具调用(Tool Calling):解锁智能应用新能力
Spring AI 支持通过「声明式」和「编程式」将普通方法转化为 AI 可调用的工具,二者核心差异在于配置方式(注解 vs 代码构建),但最终目标都是生成实例供 AI 模型使用。通过在方法上标注@Tool注解,直接将方法转化为工具,无需手动构建,是更简洁的主流方式。核心配置@Tool注解支持 4 个关键属性,用于定义工具的核心信息(AI 模型依赖这些信息判断是否/如何调用工具):属性名作用默认值
Spring AI 工具调用基础概念
什么是工具调用
定义工具调用在 Spring AI 中的概念,即通过语言模型触发对外部工具(如搜索引擎、数据库查询、文件操作工具等)的使用,以获取额外信息或执行特定任务,从而增强语言模型的响应能力。
强调工具调用并非简单的函数调用,而是一种智能的、上下文感知的交互方式,语言模型能够根据任务需求动态选择和使用工具。
工具调用的优势
提升回答准确性:通过调用外部工具获取实时、准确的数据,避免语言模型生成错误或过时的信息。例如,在回答与金融数据、时事新闻相关问题时,调用最新数据来源工具。
增强功能多样性:允许应用借助各种专业工具完成复杂任务,如数据分析、图像生成、文本翻译等,丰富应用的功能场景。
提高用户体验:提供更全面、深入的回答,满足用户多样化的需求,增强用户对应用的信任和满意度。
工作流程
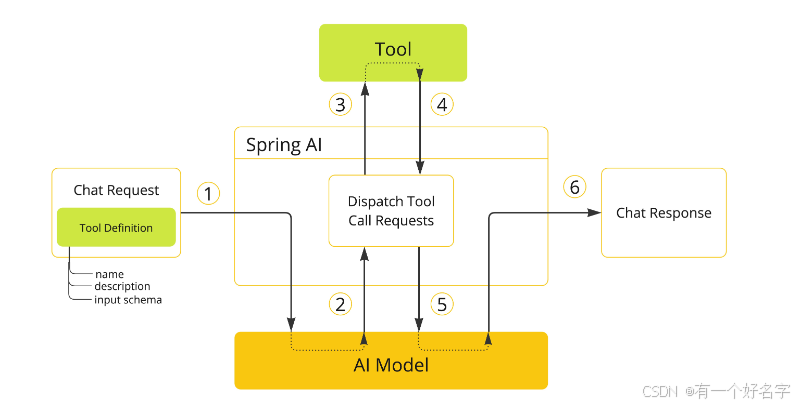
- 当使用某个工具时,需在聊天请求中纳入该工具的定义。每个工具定义涵盖工具名称、工具描述以及输入参数的架构。
- 当模型判定要调用某个工具时,它会返回一个响应,其中包含工具名称以及依照既定架构构建的输入参数。
- 应用程序负责依据工具名称来识别该工具,并利用提供的输入参数执行此工具。
- 应用程序对工具调用的结果进行处理。
- 应用程序将工具调用的结果反馈给模型。
- 模型把工具调用的结果作为额外上下文,进而生成最终的响应。
一、工具定义的两种核心方式
Spring AI 支持通过「声明式」和「编程式」将普通方法转化为 AI 可调用的工具,二者核心差异在于配置方式(注解 vs 代码构建),但最终目标都是生成 ToolCallback 实例供 AI 模型使用。
1. 声明式定义:@Tool 注解
通过在方法上标注 @Tool 注解,直接将方法转化为工具,无需手动构建 ToolCallback,是更简洁的主流方式。
- 核心配置:
@Tool注解支持 4 个关键属性,用于定义工具的核心信息(AI 模型依赖这些信息判断是否/如何调用工具):属性名 作用 默认值 关键说明 name工具唯一标识(AI 调用时的名称) 方法名 同一类/同一请求中工具名不可重复 description工具用途说明(帮助 AI 理解适用场景) 方法名 强烈建议手动配置,否则可能导致 AI 误用/不调用工具 returnDirect工具结果是否直接返回给客户端(而非回传 AI) - 控制结果流向,需结合业务场景配置 resultConverter工具结果转 String 的转换器 默认转换器 自定义结果格式时使用 - 参数配置:通过
@ToolParam注解补充方法参数信息(AI 依赖此生成调用参数):description:参数格式/取值说明(如“时间需为 ISO-8601 格式”);required:参数是否必填(默认必填,@Nullable标注的参数默认可选,可通过此属性强制必填);- 额外支持 Swagger 的
@Schema、Jackson 的@JsonProperty注解扩展参数信息。
- 方法/类要求:
- 方法:支持静态/实例方法,任意访问权限(public/private 等),返回值需可序列化(结果需回传 AI);
- 类:支持顶层类/嵌套类,若需 AOT 编译,需将类声明为 Spring Bean(如加
@Component),否则需手动配置 GraalVM 反射(如@RegisterReflection)。
2. 编程式定义:MethodToolCallback
通过 MethodToolCallback.Builder 手动构建工具实例,适用于需动态调整工具配置的场景(灵活性更高,但代码更繁琐)。
- 核心构建要素(需手动指定,缺一不可):
toolDefinition:工具的名称、描述、输入 JSON Schema(通过ToolDefinitions.builder()构建,可复用@ToolParam注解的参数信息);toolMethod:工具对应的方法实例(通过反射获取,如ReflectionUtils.findMethod());toolObject:方法所属的实例对象(静态方法可省略);
- 额外配置:
toolMetadata:补充returnDirect等结果流向配置;toolCallResultConverter:自定义结果转换器(同声明式的resultConverter)。
- 方法/类要求:与声明式完全一致(支持任意权限/静态方法,AOT 编译需 Spring Bean 或手动反射配置)。
二、两种实现方式及完整实例代码
(一)声明式实现:@Tool 注解驱动
通过在方法上添加 @Tool 注解(方法级)和 @ToolParam 注解(参数级),自动完成工具注册和 JSON Schema 生成,是最简洁的方式。
1. 核心注解说明
- @Tool:定义工具名称、功能描述、结果处理规则(如是否直接返回客户端);
- @ToolParam:补充参数描述(如格式要求)和必填性,帮助 AI 生成正确参数。
2. 实例代码 1:基础工具类(无参数+带参数方法)
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.ToolParam;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
// 时间工具类:包含两个工具方法
class DateTimeTools {
// 工具1:获取用户时区的当前日期时间(无参数)
@Tool(description = "Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
String getCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now()
.atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId())
.toString();
}
// 工具2:设置闹钟(带参数,用@ToolParam说明格式)
@Tool(description = "Set a user alarm for the given time")
void setAlarm(@ToolParam(description = "Time in ISO-8601 format") String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("Alarm set for " + alarmTime);
}
}
3. 实例代码 2:工具集成到 ChatClient(单次请求工具)
将工具类实例传入 ChatClient.tools() 方法,工具仅对当前请求生效:
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.ChatModel;
// 假设已初始化 ChatModel(如 OpenAiChatModel、OllamaChatModel)
ChatModel chatModel = ...;
// 调用工具查询明天日期
String result = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What day is tomorrow?")
.tools(new DateTimeTools()) // 传入工具类实例
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(result); // 输出工具执行结果或 AI 基于结果的回答
4. 实例代码 3:ChatClient 配置默认工具
通过 ChatClient.Builder.defaultTools() 设置默认工具,所有从该 Builder 创建的 ChatClient 实例共享工具(单次请求工具会覆盖默认工具):
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.ChatModel;
ChatModel chatModel = ...;
// 构建带默认工具的 ChatClient
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultTools(new DateTimeTools()) // 设置默认工具
.build();
// 后续所有请求自动携带默认工具
String timeResult = chatClient.prompt("Get current time").call().content();
5. 实例代码 4:工具集成到 ChatModel(单次请求工具)
通过 ToolCallingChatOptions 将工具传入 ChatModel,工具仅对当前 call() 请求生效:
import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.ChatModel;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.ChatOptions;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.Prompt;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.ToolCallbacks;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.ToolCallback;
ChatModel chatModel = ...;
// 将工具类转为 ToolCallback 数组
ToolCallback[] dateTimeTools = ToolCallbacks.from(new DateTimeTools());
// 配置工具选项
ChatOptions chatOptions = org.springframework.ai.tool.ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(dateTimeTools)
.build();
// 发起带工具的请求
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("What day is tomorrow?", chatOptions);
String modelResult = chatModel.call(prompt).getResult().getOutput().getContent();
6. 实例代码 5:ChatModel 配置默认工具
在 ChatModel 初始化时通过 defaultOptions 设置默认工具,该模型所有请求共享工具(单次请求工具会覆盖默认工具):
import org.springframework.ai.ollama.OllamaChatModel;
import org.springframework.ai.ollama.api.OllamaApi;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.ToolCallbacks;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.ToolCallback;
// 将工具类转为 ToolCallback 数组
ToolCallback[] dateTimeTools = ToolCallbacks.from(new DateTimeTools());
// 构建带默认工具的 ChatModel(以 OllamaChatModel 为例)
ChatModel chatModel = OllamaChatModel.builder()
.ollamaApi(OllamaApi.builder().build())
.defaultOptions(org.springframework.ai.tool.ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(dateTimeTools) // 默认工具
.build())
.build();
// 发起请求(自动携带默认工具)
String modelResult = chatModel.call(new Prompt("Get current time")).getResult().getOutput().getContent();
(二)编程式实现:MethodToolCallback
通过手动构建 MethodToolCallback 封装方法,需显式获取 Method 实例、配置工具定义(ToolDefinition),适合动态调整工具信息的场景。
1. 核心组件说明
- Method 实例:通过反射获取目标方法;
- ToolDefinition:定义工具名称、描述、输入 Schema;
- MethodToolCallback:绑定
Method、ToolDefinition和工具实例(非静态方法)。
2. 实例代码 1:基础工具类(实例方法+静态方法)
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
// 时间工具类:无注解,通过编程式封装
class DateTimeTools {
// 实例方法:需工具实例才能调用
String getCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now()
.atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId())
.toString();
}
// 静态方法:无需工具实例,直接通过类调用
static String getStaticCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now()
.atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId())
.toString();
}
// 带参数的实例方法
void setAlarm(String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("Alarm set for " + alarmTime);
}
}
3. 实例代码 2:构建实例方法的 ToolCallback
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.MethodToolCallback;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.model.ToolDefinitions;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
// 1. 反射获取实例方法(getCurrentDateTime,无参数)
Method instanceMethod = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getCurrentDateTime");
// 2. 构建 ToolDefinition(工具描述、名称)
var toolDefinition = ToolDefinitions.builder(instanceMethod)
.description("Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
.build();
// 3. 构建 MethodToolCallback(需绑定工具实例)
DateTimeTools toolInstance = new DateTimeTools();
MethodToolCallback instanceToolCallback = MethodToolCallback.builder()
.toolDefinition(toolDefinition)
.toolMethod(instanceMethod)
.toolObject(toolInstance) // 实例方法必需:绑定工具实例
.build();
4. 实例代码 3:构建静态方法的 ToolCallback
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.MethodToolCallback;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.model.ToolDefinitions;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
// 1. 反射获取静态方法(getStaticCurrentDateTime,无参数)
Method staticMethod = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getStaticCurrentDateTime");
// 2. 构建 ToolDefinition
var staticToolDefinition = ToolDefinitions.builder(staticMethod)
.description("Get static current date and time in the user's timezone")
.build();
// 3. 构建 MethodToolCallback(静态方法无需 toolObject)
MethodToolCallback staticToolCallback = MethodToolCallback.builder()
.toolDefinition(staticToolDefinition)
.toolMethod(staticMethod)
.build(); // 静态方法:省略 toolObject
5. 实例代码 4:带参数方法的 ToolCallback(结合 @ToolParam)
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.MethodToolCallback;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.model.ToolDefinitions;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.ToolParam;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
// 带 @ToolParam 注解的参数方法(补充参数描述)
class DateTimeTools {
void setAlarm(@ToolParam(description = "Time in ISO-8601 format") String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("Alarm set for " + alarmTime);
}
}
// 构建带参数方法的 ToolCallback
Method setAlarmMethod = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "setAlarm", String.class);
DateTimeTools toolInstance = new DateTimeTools();
MethodToolCallback setAlarmToolCallback = MethodToolCallback.builder()
.toolDefinition(ToolDefinitions.builder(setAlarmMethod)
.description("Set a user alarm for the given time")
.build()) // 自动识别 @ToolParam 生成 Schema
.toolMethod(setAlarmMethod)
.toolObject(toolInstance)
.build();
6. 实例代码 5:编程式工具集成到 ChatClient
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.ChatModel;
ChatModel chatModel = ...;
MethodToolCallback toolCallback = ...; // 前面构建的 ToolCallback
// 单次请求工具
String result = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What day is tomorrow?")
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback) // 传入编程式工具
.call()
.content();
// 配置默认工具
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultToolCallbacks(toolCallback) // 默认编程式工具
.build();
7. 实例代码 6:编程式工具集成到 ChatModel
import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.ChatModel;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.Prompt;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.MethodToolCallback;
ChatModel chatModel = ...;
MethodToolCallback toolCallback = ...; // 前面构建的 ToolCallback
// 单次请求工具
var chatOptions = org.springframework.ai.tool.ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("What day is tomorrow?", chatOptions);
String modelResult = chatModel.call(prompt).getResult().getOutput().getContent();
// 配置默认工具(以 OllamaChatModel 为例)
ChatModel defaultToolModel = OllamaChatModel.builder()
.ollamaApi(OllamaApi.builder().build())
.defaultOptions(org.springframework.ai.tool.ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build())
.build();
三、关键规则与限制
- 方法约束:
- 支持任意可见性(public/protected/private/包级私有)、实例/静态方法;
- 参数/返回值支持:基本类型、POJO、枚举、List/Map/数组;
- 不支持类型:
Optional、异步类型(CompletableFuture)、响应式类型(Mono/Flux)、函数式类型(Function); - 返回值需可序列化(传递给 AI 模型)。
- AOT 编译支持:
- 工具类为 Spring Bean(如
@Component)时,自动支持 AOT; - 非 Bean 类需添加
@RegisterReflection(memberCategories = MemberCategory.INVOKE_DECLARED_METHODS)。
- 工具类为 Spring Bean(如
- 工具名称唯一性:同一请求中工具名称不可重复,否则 AI 模型无法识别。
四、核心总结
- 声明式:通过
@Tool/@ToolParam注解快速定义工具,适合固定功能场景,代码简洁; - 编程式:通过
MethodToolCallback手动构建工具,适合动态配置或第三方类方法,灵活性高; - 集成方式:两种工具均可集成到
ChatClient(单次/默认)或ChatModel(单次/默认),单次工具优先级高于默认工具。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容






所有评论(0)