smolagent框架
smolagents是一个简单而强大的用于构建 AI Agent 的框架。它为大语言模型 (LLM) 提供了与现实世界互动的自主性,例如搜索或生成图像。正如我们在第一单元中学到的,AI Agent 是使用 LLM 根据来生成,从而执行的程序。让我们来探讨一下这在 smolagents 中是如何实现的。
什么是 smolagents?
smolagents 是一个简单而强大的用于构建 AI Agent 的框架。它为大语言模型 (LLM) 提供了与现实世界互动的 自主性,例如搜索或生成图像。
正如我们在第一单元中学到的,AI Agent 是使用 LLM 根据 “观察” 来生成 “思考”,从而执行 “动作” 的程序。让我们来探讨一下这在 smolagents 中是如何实现的。
smolagents 的主要优势
- 简洁性: 最小化的代码复杂度和抽象,使框架易于理解、采用和扩展。
- 灵活的 LLM 支持: 通过与 Hugging Face 工具和外部 API 集成,可与任何 LLM 配合使用。
- 代码优先的方法: 对直接用代码编写动作的 Code Agent 提供一流支持,无需解析并简化了工具调用。
- HF Hub 集成: 与 Hugging Face Hub 无缝集成,允许将 Gradio Spaces 用作工具。
何时使用 smolagents?
考虑到这些优势,我们应该在什么时候选择 smolagents 而不是其他框架呢?
smolagents 是以下情况的理想选择
- 您需要一个 轻量级且极简的解决方案。
- 您想 快速进行实验,而不需要复杂的配置。
- 您的 应用程序逻辑简单明了。
构建使用代码的 Agent
代码 Agent 是 smolagents 中的默认 Agent 类型。它们生成 Python 工具调用来执行动作,从而实现高效、富有表现力且准确的动作表示。
为何选择代码 Agent?
在多步 Agent 流程中,LLM 编写并执行动作,通常涉及外部工具调用。传统方法使用 JSON 格式指定工具名称和参数(作为字符串),系统必须解析这些信息才能确定执行哪个工具。
然而,研究表明,直接使用代码能让工具调用型 LLM 更有效地工作。
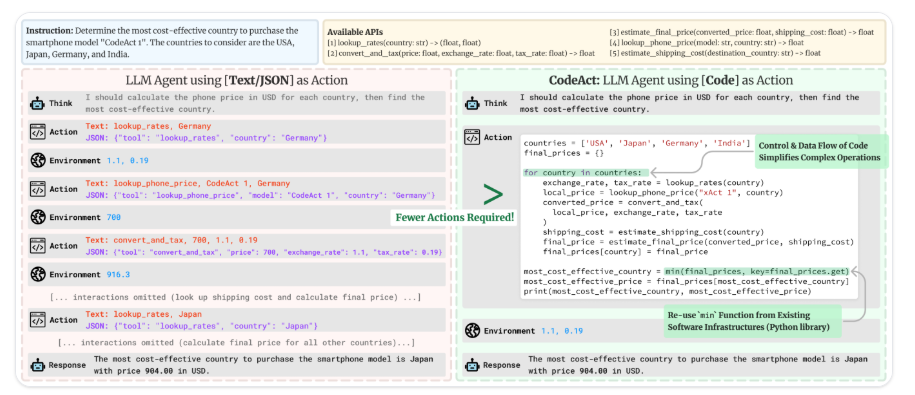
用代码而非 JSON 编写动作有以下几个关键优势:
- 可组合性:轻松组合和重用动作
- 对象管理:直接处理复杂结构,如图像
- 通用性:能够表达任何计算上可能的任务
- 对 LLM 更自然:高质量的代码已经存在于 LLM 的训练数据中
代码 Agent 如何工作?
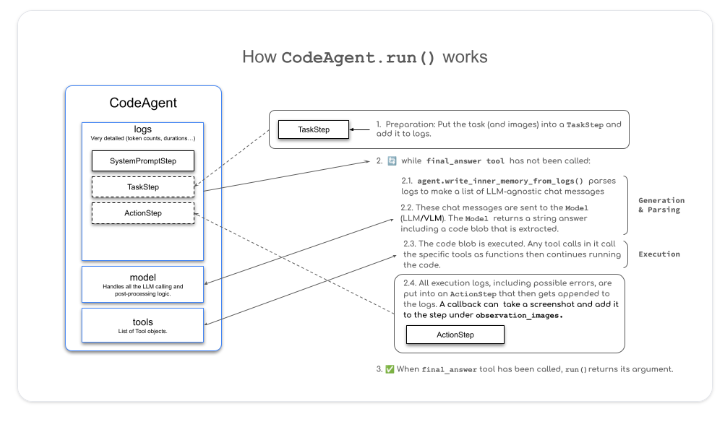
上图展示了 CodeAgent.run() 的工作方式,它遵循了我们在第一单元中提到的 ReAct 框架。smolagents 中 Agent 的主要抽象是 MultiStepAgent,它是核心构建块。CodeAgent 是一种特殊的 MultiStepAgent,我们将在下面的例子中看到。
一个 CodeAgent 通过一系列步骤的循环来执行动作,现有的变量和知识被整合到 Agent 的上下文中,并保存在执行日志中。
-
系统提示存储在
SystemPromptStep中,用户查询则记录在TaskStep中。 -
然后,执行以下 while 循环:
2.1 方法
agent.write_memory_to_messages()将 Agent 的日志写入一个 LLM 可读的聊天消息列表。2.2 这些消息被发送给一个
Model,该模型生成一个补全。2.3 解析补全以提取动作,在我们的例子中,由于我们使用的是
CodeAgent,这个动作应该是一个代码片段。2.4 执行该动作。
2.5 结果被记录到内存中的一个
ActionStep里。
使用 smolagents 为派对选择播放列表
对于模型,我们将依赖 InferenceClientModel,它提供了对 Hugging Face 的无服务器推理 API 的访问。默认模型是 "Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct",它性能优越且可用于快速推理,但你也可以从 Hub 中选择任何兼容的模型。
运行一个 Agent :
from smolagents import CodeAgent, DuckDuckGoSearchTool, InferenceClientModel
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool()], model=InferenceClientModel())
agent.run("Search for the best music recommendations for a party at the Wayne's mansion.")示例:运行一个工具调用 Agent(Tool Calling Agents)
from smolagents import ToolCallingAgent, DuckDuckGoSearchTool, InferenceClientModel
agent = ToolCallingAgent(tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool()], model=InferenceClientModel())
agent.run("Search for the best music recommendations for a party at the Wayne's mansion.")工具
要与工具交互,LLM 需要一个包含以下关键组件的接口描述:
- 名称:工具的名称
- 工具描述:工具的功能
- 输入类型和描述:工具接受的参数
- 输出类型:工具返回的内容
工具创建方法
在 `smolagents` 中,可以通过两种方式定义工具:
- 使用 `@tool` 装饰器,适用于简单的基于函数的工具
- 创建 `Tool` 的子类,适用于更复杂的功能
@tool 装饰器
`@tool` 装饰器是定义简单工具的推荐方式。在底层,smolagents 会从 Python 中解析函数的基本信息。因此,如果你给函数起一个清晰的名称并编写一个好的文档字符串,LLM 会更容易使用它。
使用这种方法,我们定义一个函数时需要:
- 一个清晰且描述性的函数名,以帮助 LLM 理解其用途。
- 为输入和输出提供类型提示,以确保正确使用。
- 详细的描述,包括一个 `Args:` 部分,其中明确描述了每个参数。这些描述为 LLM 提供了宝贵的上下文,因此仔细编写它们非常重要。
示例
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel, tool
# Let's pretend we have a function that fetches the highest-rated catering services.
def catering_service_tool(query: str) -> str:
"""
This tool returns the highest-rated catering service in Gotham City.
Args:
query: A search term for finding catering services.
"""
# Example list of catering services and their ratings
services = {
"Gotham Catering Co.": 4.9,
"Wayne Manor Catering": 4.8,
"Gotham City Events": 4.7,
}
# Find the highest rated catering service (simulating search query filtering)
best_service = max(services, key=services.get)
return best_service
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[catering_service_tool], model=InferenceClientModel())
# Run the agent to find the best catering service
result = agent.run(
"Can you give me the name of the highest-rated catering service in Gotham City?"
)
print(result) # Output: Gotham Catering Co.将工具定义为 Python 类
这种方法涉及创建 Tool 的一个子类。对于复杂的工具,我们可以实现一个类而不是一个 Python 函数。该类将函数与元数据包装在一起,帮助 LLM 理解如何有效地使用它。在这个类中,我们定义了
name:工具的名称。description:用于填充 Agent 系统提示的描述。inputs:一个包含type和description键的字典,为 Python 解释器处理输入提供信息。output_type:指定预期的输出类型。forward:包含要执行的推理逻辑的方法。
下面,我们可以看到一个使用 Tool 构建的工具示例,以及如何将其集成到 CodeAgent 中。
from smolagents import Tool, CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel
class SuperheroPartyThemeTool(Tool):
name = "superhero_party_theme_generator"
description = """
This tool suggests creative superhero-themed party ideas based on a category.
It returns a unique party theme idea."""
inputs = {
"category": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The type of superhero party (e.g., 'classic heroes', 'villain masquerade', 'futuristic Gotham').",
}
}
output_type = "string"
def forward(self, category: str):
themes = {
"classic heroes": "Justice League Gala: Guests come dressed as their favorite DC heroes with themed cocktails like 'The Kryptonite Punch'.",
"villain masquerade": "Gotham Rogues' Ball: A mysterious masquerade where guests dress as classic Batman villains.",
"futuristic Gotham": "Neo-Gotham Night: A cyberpunk-style party inspired by Batman Beyond, with neon decorations and futuristic gadgets."
}
return themes.get(category.lower(), "Themed party idea not found. Try 'classic heroes', 'villain masquerade', or 'futuristic Gotham'.")
# Instantiate the tool
party_theme_tool = SuperheroPartyThemeTool()
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[party_theme_tool], model=InferenceClientModel())
# Run the agent to generate a party theme idea
result = agent.run(
"What would be a good superhero party idea for a 'villain masquerade' theme?"
)
print(result) # Output: "Gotham Rogues' Ball: A mysterious masquerade where guests dress as classic Batman villains."导入 LangChain 工具
LangChain 是什么?
👉 LLM 应用开发框架
它解决的是:
「我怎么把 大模型 + 工具 + 数据 + 逻辑 串起来?」
LangChain 能做什么?
-
管理 Prompt
-
调用 大模型(OpenAI / 本地模型 / HF)
-
连接 工具(搜索 / 计算器 / API)
-
连接 知识库(向量数据库)
-
做 Agent(会自己决定用哪个工具)
通过使用 `Tool.from_langchain()`,阿尔弗雷德毫不费力地为他的 smolagent 添加了高级搜索功能,使他能够仅用几条命令就发现独家的派对创意和服务。
from langchain.agents import load_tools
from smolagents import CodeAgent, InferenceClientModel, Tool
search_tool = Tool.from_langchain(load_tools(["serpapi"])[0])
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[search_tool], model=model)
agent.run("Search for luxury entertainment ideas for a superhero-themed event, such as live performances and interactive experiences.")多智能体系统
多智能体系统使 专门的智能体能够协作完成复杂任务,从而提高了模块性、可扩展性和鲁棒性。它不是依赖单个智能体,而是将任务分配给具有不同能力的多个智能体。
在 smolagents 中,可以组合不同的智能体来生成 Python 代码、调用外部工具、执行网页搜索等。通过协调这些智能体,我们可以创建强大的工作流。
一个典型的设置可能包括
- 一个用于任务委派的 管理者智能体
- 一个用于代码执行的 代码解释器智能体
- 一个用于信息检索的 网页搜索智能体
下图展示了一个简单的多智能体架构,其中一个 管理者智能体 协调一个 代码解释器工具 和一个 网页搜索智能体,而后者又利用像 DuckDuckGoSearchTool 和 VisitWebpageTool 这样的工具来收集相关信息。
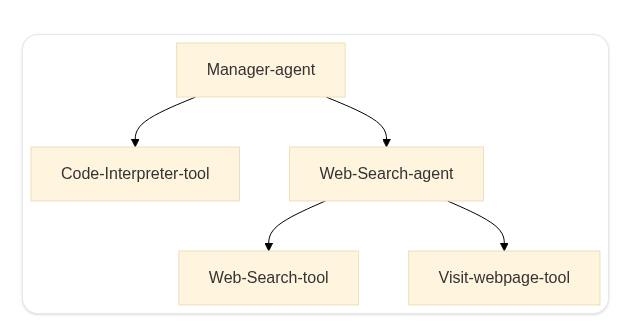
多智能体系统的实际应用
一个多智能体系统由多个专门的智能体组成,它们在一个 协调器智能体 的协调下协同工作。这种方法通过将任务分配给具有不同角色的智能体,使得复杂的工作流成为可能。
例如,一个 多智能体 RAG 系统 可以集成
- 一个用于浏览互联网的 网页智能体。
- 一个用于从知识库中获取信息的 检索器智能体。
- 一个用于生成视觉内容的 图像生成智能体。
所有这些智能体都在一个协调器的管理下运行,该协调器负责任务的委派和交互。
FINAL QUIZ
Question 1: Create a Basic Code Agent with Web Search Capability
Reference Solution:
Assessment Criteria:
- Correct imports are included
- DuckDuckGoSearchTool is added to tools list
- HfApiModel is properly configured
- Model ID is correctly specified
from smolagents import CodeAgent, DuckDuckGoSearchTool, HfApiModel
agent = CodeAgent(
tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool()],
model=HfApiModel("Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct")
)Question 2: Set Up a Multi-Agent System with Manager and Web Search Agents
Assessment Criteria:
- Web agent has correct tools configured
- Manager agent properly references web agent
- Appropriate max_steps value is set
- Required imports are authorized
Reference Solution:
web_agent = ToolCallingAgent(
tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool(), visit_webpage],
model=model,
max_steps=10,
name="search",
description="Runs web searches for you."
)
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
tools=[],
model=model,
managed_agents=[web_agent],
additional_authorized_imports=["time", "numpy", "pandas"]
)Question 3: Configure Agent Security Settings
Assessment Criteria:
- E2B sandbox is properly configured
- Authorized imports are appropriately limited
- Security settings are correctly implemented
- Basic agent configuration is maintained
Reference Solution:
from smolagents import CodeAgent, E2BSandbox
agent = CodeAgent(
tools=[],
model=model,
sandbox=E2BSandbox(),
additional_authorized_imports=["numpy"]
)Question 4: Implement a Tool-Calling Agent
Assessment Criteria:
- Tools are properly configured
- Step limit is set appropriately
- Agent name and description are provided
- Basic configuration is complete
Reference Solution:
from smolagents import ToolCallingAgent
agent = ToolCallingAgent(
tools=[custom_tool],
model=model,
max_steps=5,
name="tool_agent",
description="Executes specific tools based on input"
)Question 5: Set Up Model Integration
Assessment Criteria:
- Correct model imports are included
- Model is properly initialized
- Model ID is correctly specified
- Alternative model option is provided
from smolagents import HfApiModel, LiteLLMModel
# Hugging Face model
hf_model = HfApiModel("Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct")
# Alternative model via LiteLLM
other_model = LiteLLMModel("anthropic/claude-3-sonnet")更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容







所有评论(0)