Spring AI Alibaba 框架实战指南
Spring AI Alibaba是阿里云基于Spring AI构建的开源AI框架,为Java开发者提供完整的AI应用开发解决方案。该框架具有三大核心特点:简化AI开发复杂度,通过高层抽象ChatClient实现开箱即用;支持多模型无缝切换,统一接口适配通义千问、GPT-4等多种模型;提供丰富的AI能力,涵盖对话聊天、图像生成、语音合成等场景。采用三层架构设计(模型服务层、增强LLM层、智能体框架
面向Java开发者的智能体(Agent)AI开发框架
目录
1. Spring AI Alibaba概述
1.1 什么是Spring AI Alibaba?
Spring AI Alibaba 是阿里云基于 Spring AI 构建的开源AI框架,是阿里云通义系列模型及服务在Java AI应用开发领域的最佳实践。它为Java开发者提供了一套完整的AI应用开发解决方案,让传统Java开发者能够快速上手AI应用开发。
1.2 核心特点
1. 简化AI开发复杂度
传统方式:
// 需要手动处理大量细节
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create("https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/api/v1/services/..."))
.header("Authorization", "Bearer " + apiKey)
.POST(HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofString(jsonPayload))
.build();
HttpResponse<String> response = client.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
// 解析JSON、处理错误、管理会话...
Spring AI Alibaba方式:
// 简洁优雅的API
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
String response = chatClient.prompt()
.user("你好,请介绍一下Spring AI Alibaba")
.call()
.content();
2. 多模型无缝切换
3. 丰富的AI能力支持
| 能力类型 | 支持的模型 | 应用场景 | API接口 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对话聊天 | 通义千问、GPT-4、Claude等 | 智能客服、问答系统 | ChatClient |
| 图像生成 | 通义万相、DALL-E等 | 文生图、图像编辑 | ImageClient |
| 语音合成 | 通义语音合成 | 文字转语音 | AudioClient |
| 文本向量化 | 通义Embedding | RAG、语义搜索 | EmbeddingClient |
| 多模态 | 通义Vision | 图文理解、OCR | ChatClient |
1.3 版本信息
- 当前版本:1.0 GA(2025年正式发布)
- 依赖要求:
- JDK 17+(基于Spring Boot 3.x)
- Spring Boot 3.2+
- Maven 3.6+ 或 Gradle 7.5+
1.4 与其他框架对比
选择建议:
| 场景 | 推荐框架 | 理由 |
|---|---|---|
| 使用阿里云服务 | Spring AI Alibaba | 深度优化,文档完善 |
| Spring Boot项目 | Spring AI Alibaba | 无缝集成,开箱即用 |
| 需要多模型切换 | LangChain4j | 支持模型最多 |
| 复杂Agent应用 | LangChain4j | Agent功能更强 |
| 企业级应用 | Spring AI Alibaba | 企业特性丰富 |
2. 核心架构与设计理念
2.1 三层架构设计
Spring AI Alibaba采用分层架构,从底层到高层提供渐进式的抽象:
层级说明
1. Augmented LLM(增强LLM层)
- 提供基础抽象:ChatModel、ImageModel、AudioModel等
- 统一的消息格式和工具调用
- 向量存储和检索能力
- MCP(Model Context Protocol)支持
2. Agent Framework(智能体框架层)
- ReactAgent:基于ReAct模式的智能体
- Graph:工作流和多智能体编排
- 状态管理和上下文记忆
3. Application Layer(应用层)
- 具体的AI应用实现
- 业务逻辑集成
2.2 核心设计理念
2.2.1 统一的API抽象
好处:
- ✅ 应用代码与具体模型解耦
- ✅ 可通过配置切换模型
- ✅ 便于测试和开发
2.2.2 声明式编程
// 声明式配置
@Configuration
public class AiConfig {
@Bean
public ChatClient chatClient(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
return builder
.defaultSystem("你是一个专业的Java技术顾问")
.defaultOptions(ChatOptions.builder()
.temperature(0.7)
.build())
.build();
}
}
// 使用时只需注入
@Service
public class AiService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
public String chat(String userMessage) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.call()
.content();
}
}
2.2.3 响应式编程支持
同步调用:
String response = chatClient.prompt()
.user("介绍Spring AI Alibaba")
.call()
.content();
流式调用:
Flux<String> responseFlux = chatClient.prompt()
.user("介绍Spring AI Alibaba")
.stream()
.content();
// 在Controller中返回SSE
@GetMapping(value = "/stream", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<ServerSentEvent<String>> streamChat(@RequestParam String message) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.stream()
.content()
.map(chunk -> ServerSentEvent.<String>builder()
.data(chunk)
.build());
}
3. 快速开始
3.1 环境准备
3.1.1 系统要求
✓ JDK 17 或更高版本
✓ Maven 3.6+ 或 Gradle 7.5+
✓ IDE:IntelliJ IDEA / Eclipse / VS Code
✓ 阿里云账号(获取API Key)
3.1.2 获取API Key
步骤:
- 访问:https://dashscope.console.aliyun.com/
- 开通百炼服务
- 创建API Key
- 复制保存(仅显示一次)
3.2 创建Spring Boot项目
3.2.1 使用Spring Initializr
# 方式1:使用Spring Initializr网站
# https://start.spring.io/
# 方式2:使用命令行
curl https://start.spring.io/starter.zip \
-d dependencies=web \
-d javaVersion=17 \
-d bootVersion=3.2.0 \
-d groupId=com.example \
-d artifactId=ai-demo \
-o ai-demo.zip
unzip ai-demo.zip
cd ai-demo
3.2.2 添加依赖
Maven(pom.xml):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>ai-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-ai-alibaba.version>1.0.0-M2</spring-ai-alibaba.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring AI Alibaba -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-alibaba-starter</artifactId>
<version>${spring-ai-alibaba.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Lombok(可选) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!-- 测试依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Gradle(build.gradle):
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.2.0'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.0'
}
group = 'com.example'
version = '1.0.0'
sourceCompatibility = '17'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
ext {
springAiAlibabaVersion = '1.0.0-M2'
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation "com.alibaba.cloud.ai:spring-ai-alibaba-starter:${springAiAlibabaVersion}"
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
tasks.named('test') {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
3.3 配置应用
3.3.1 application.yml配置
spring:
application:
name: ai-demo
ai:
dashscope:
# API Key配置(推荐使用环境变量)
api-key: ${DASHSCOPE_API_KEY}
# Chat模型配置
chat:
enabled: true
options:
model: qwen-max # 模型名称
temperature: 0.7 # 温度参数(0-1)
top-p: 0.9 # 采样参数
max-tokens: 2000 # 最大Token数
# Image模型配置
image:
enabled: true
options:
model: wanx-v1
# Embedding配置
embedding:
enabled: true
options:
model: text-embedding-v2
server:
port: 8080
# 日志配置
logging:
level:
com.alibaba.cloud.ai: DEBUG
3.3.2 环境变量配置
# 方式1:在IDE中配置环境变量
# DASHSCOPE_API_KEY=your-api-key-here
# 方式2:使用.env文件(需要spring-dotenv依赖)
# .env文件内容:
DASHSCOPE_API_KEY=sk-xxxxxxxxxxxxx
# 方式3:在启动脚本中设置
export DASHSCOPE_API_KEY=sk-xxxxxxxxxxxxx
java -jar ai-demo.jar
3.4 第一个AI应用
3.4.1 创建Controller
package com.example.aidemo.controller;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/chat")
public class ChatController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
// 构造器注入
public ChatController(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder) {
this.chatClient = chatClientBuilder.build();
}
/**
* 简单对话 - 同步
*/
@GetMapping("/simple")
public String simpleChat(@RequestParam String message) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.call()
.content();
}
/**
* 流式对话 - SSE
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/stream", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<String> streamChat(@RequestParam String message) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.stream()
.content();
}
/**
* 带系统提示词的对话
*/
@PostMapping("/chat")
public String chat(@RequestBody ChatRequest request) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.system("你是一个专业的Java技术顾问,擅长Spring框架")
.user(request.getMessage())
.call()
.content();
}
}
// DTO类
record ChatRequest(String message) {}
3.4.2 启动应用
package com.example.aidemo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class AiDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AiDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
3.4.3 测试API
# 1. 简单对话
curl "http://localhost:8080/api/chat/simple?message=你好"
# 响应:
你好!很高兴为您服务。请问有什么我可以帮助您的吗?
# 2. 流式对话
curl "http://localhost:8080/api/chat/stream?message=介绍Spring%20AI%20Alibaba"
# 响应(流式):
Spring AI Alibaba 是...
阿里云基于...
主要特性包括...
# 3. POST请求
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/api/chat/chat \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"message":"如何使用Spring Boot开发微服务?"}'
3.5 项目结构
ai-demo/
├── src/
│ ├── main/
│ │ ├── java/com/example/aidemo/
│ │ │ ├── AiDemoApplication.java # 启动类
│ │ │ ├── controller/
│ │ │ │ └── ChatController.java # 控制器
│ │ │ ├── service/
│ │ │ │ └── AiService.java # 服务层
│ │ │ ├── config/
│ │ │ │ └── AiConfig.java # 配置类
│ │ │ └── dto/
│ │ │ └── ChatRequest.java # DTO
│ │ └── resources/
│ │ ├── application.yml # 配置文件
│ │ └── logback-spring.xml # 日志配置
│ └── test/
│ └── java/com/example/aidemo/
│ └── AiDemoApplicationTests.java
├── pom.xml # Maven配置
└── README.md
4. 核心组件详解
4.1 ChatClient - 对话客户端
4.1.1 ChatClient架构
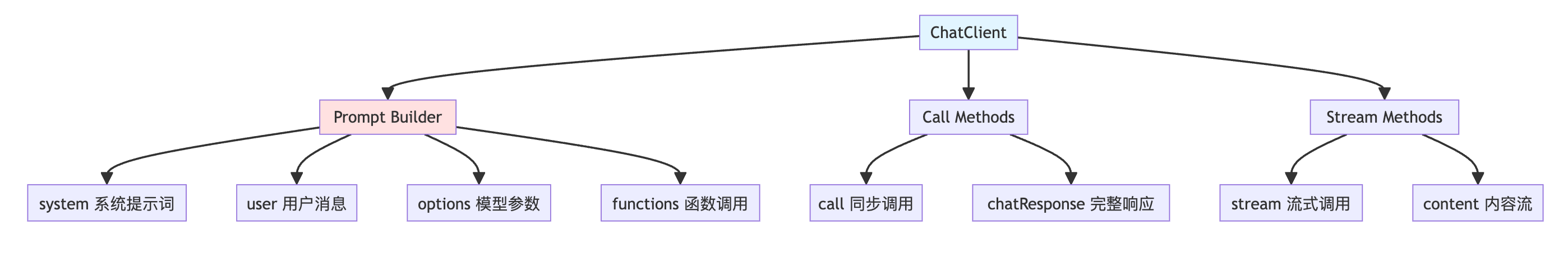
4.1.2 基础使用
1. 简单对话
@Service
public class SimpleAiService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
/**
* 最简单的使用方式
*/
public String chat(String userMessage) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.call()
.content();
}
}
2. 带系统提示词
/**
* 设置系统角色和行为
*/
public String chatWithSystem(String userMessage) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.system("""
你是一个资深的Java架构师,擅长:
1. Spring生态系统
2. 微服务架构设计
3. 性能优化
请用专业但易懂的方式回答问题。
""")
.user(userMessage)
.call()
.content();
}
3. 自定义模型参数
/**
* 动态调整模型参数
*/
public String chatWithOptions(String userMessage, double temperature) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.options(DashScopeChatOptions.builder()
.temperature(temperature) // 温度:控制随机性
.topP(0.9) // Top-P采样
.maxTokens(1000) // 最大Token数
.build())
.call()
.content();
}
参数说明:
| 参数 | 范围 | 说明 | 推荐值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperature | 0.0 - 1.0 | 控制随机性,越高越发散 | 创意任务:0.8-1.0 事实任务:0.1-0.3 |
| top-p | 0.0 - 1.0 | 核采样参数 | 0.9(默认) |
| max-tokens | 1 - 6000 | 限制响应长度 | 根据需求设置 |
4.1.3 获取完整响应
/**
* 获取包含元数据的完整响应
*/
public void chatWithFullResponse(String userMessage) {
ChatResponse response = chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.call()
.chatResponse();
// 获取内容
String content = response.getResult().getOutput().getContent();
// 获取元数据
ChatResponseMetadata metadata = response.getMetadata();
System.out.println("模型: " + metadata.getModel());
System.out.println("使用Token: " + metadata.getUsage().getTotalTokens());
System.out.println("完成原因: " + response.getResult().getMetadata().getFinishReason());
// 输出示例:
// 模型: qwen-max
// 使用Token: 156
// 完成原因: STOP
}
4.1.4 流式响应详解
流式响应是AI应用中非常重要的特性,它能够让用户实时看到生成的内容,而不是等待完整响应后才显示,极大提升了用户体验。
流式响应的优势
Flux响应式编程基础
Spring AI Alibaba基于Spring WebFlux和Project Reactor实现流式响应,核心是Flux类型。
Flux vs Mono vs 传统返回值:
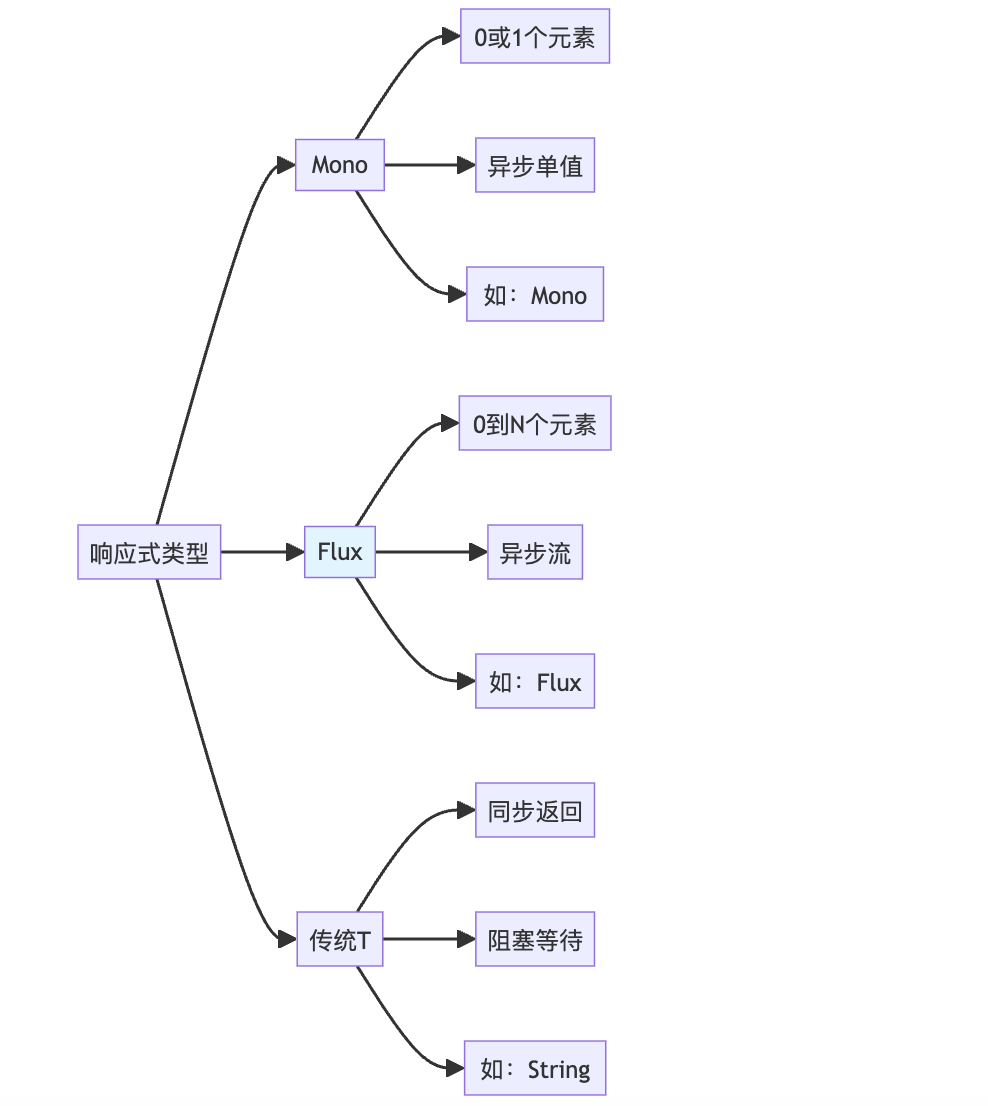
基础示例:
@Service
public class StreamingService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
/**
* 方式1:返回Flux<String> - 纯文本流
*/
public Flux<String> streamChat(String userMessage) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.stream()
.content(); // 返回内容流
}
/**
* 方式2:返回Flux<ChatResponse> - 完整响应流
*/
public Flux<ChatResponse> streamChatResponse(String userMessage) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.stream()
.chatResponse(); // 返回完整响应流(包含元数据)
}
}
SSE(Server-Sent Events)实现
SSE是HTML5标准,用于服务器向浏览器推送实时数据。
SSE vs WebSocket:
| 特性 | SSE | WebSocket |
|---|---|---|
| 通信方向 | 单向(服务器→客户端) | 双向 |
| 协议 | HTTP | 独立协议(升级自HTTP) |
| 实现复杂度 | 简单 | 复杂 |
| 自动重连 | ✅ 支持 | ❌ 需手动实现 |
| 事件ID | ✅ 支持 | ❌ 不支持 |
| 适用场景 | AI流式输出、实时通知 | 聊天、游戏 |
完整的SSE实现(推荐方式):
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/chat")
@Slf4j
public class StreamChatController {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
/**
* 方式1:简单SSE - 只返回文本
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/stream/simple", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<String> streamSimple(@RequestParam String message) {
log.info("开始流式响应: {}", message);
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.stream()
.content()
.doOnNext(chunk -> log.debug("生成chunk: {}", chunk))
.doOnComplete(() -> log.info("流式响应完成"))
.doOnError(e -> log.error("流式响应错误", e));
}
/**
* 方式2:标准SSE - 使用ServerSentEvent包装
* 推荐:支持事件ID、事件类型、重连时间等
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/stream/sse", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<ServerSentEvent<String>> streamSSE(@RequestParam String message) {
AtomicLong counter = new AtomicLong(0);
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.stream()
.content()
.map(chunk -> ServerSentEvent.<String>builder()
.id(String.valueOf(counter.incrementAndGet())) // 事件ID
.event("message") // 事件类型
.data(chunk) // 数据
.comment("AI生成内容") // 注释
.build())
.concatWith(Flux.just(
ServerSentEvent.<String>builder()
.event("done") // 完成事件
.data("[DONE]")
.build()
));
}
/**
* 方式3:带元数据的SSE - 返回JSON格式
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/stream/json", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<ServerSentEvent<StreamResponse>> streamJSON(@RequestParam String message) {
AtomicLong tokenCount = new AtomicLong(0);
AtomicLong chunkIndex = new AtomicLong(0);
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.stream()
.chatResponse() // 获取完整响应
.map(response -> {
String content = response.getResult().getOutput().getContent();
long tokens = response.getMetadata().getUsage() != null
? response.getMetadata().getUsage().getTotalTokens()
: 0;
tokenCount.addAndGet(tokens);
StreamResponse streamResp = StreamResponse.builder()
.index(chunkIndex.incrementAndGet())
.content(content)
.totalTokens(tokenCount.get())
.model(response.getMetadata().getModel())
.finishReason(response.getResult().getMetadata().getFinishReason())
.build();
return ServerSentEvent.<StreamResponse>builder()
.id(String.valueOf(chunkIndex.get()))
.event("stream")
.data(streamResp)
.build();
});
}
/**
* 方式4:多会话流式 - 支持上下文
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/stream/conversation", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<ServerSentEvent<String>> streamConversation(
@RequestBody ConversationRequest request) {
// 构建消息历史
List<Message> messages = buildMessages(request);
return chatClient.prompt()
.messages(messages)
.stream()
.content()
.map(chunk -> ServerSentEvent.<String>builder()
.data(chunk)
.build());
}
/**
* 方式5:流式响应 + 数据库保存
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/stream/persist", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<ServerSentEvent<String>> streamWithPersist(
@RequestParam String message,
@RequestParam String sessionId) {
StringBuilder fullResponse = new StringBuilder();
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.stream()
.content()
.doOnNext(fullResponse::append) // 收集完整响应
.map(chunk -> ServerSentEvent.<String>builder()
.data(chunk)
.build())
.doOnComplete(() -> {
// 流式完成后保存到数据库
saveConversation(sessionId, message, fullResponse.toString());
});
}
// 辅助方法
private List<Message> buildMessages(ConversationRequest request) {
List<Message> messages = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加历史消息
request.getHistory().forEach(msg ->
messages.add(msg.getRole().equals("user")
? new UserMessage(msg.getContent())
: new AssistantMessage(msg.getContent()))
);
// 添加当前消息
messages.add(new UserMessage(request.getMessage()));
return messages;
}
private void saveConversation(String sessionId, String question, String answer) {
log.info("保存会话: session={}, Q={}, A={}", sessionId, question, answer);
// 实际保存逻辑
}
}
// DTO类
@Data
@Builder
class StreamResponse {
private Long index;
private String content;
private Long totalTokens;
private String model;
private String finishReason;
}
@Data
class ConversationRequest {
private String message;
private List<HistoryMessage> history;
}
@Data
class HistoryMessage {
private String role;
private String content;
}
前端集成示例
1. 原生JavaScript(EventSource):
// 简单文本流
const eventSource = new EventSource('/api/chat/stream/simple?message=介绍Spring AI');
eventSource.onmessage = (event) => {
document.getElementById('response').innerText += event.data;
};
eventSource.onerror = (error) => {
console.error('SSE错误:', error);
eventSource.close();
};
// 关闭连接
// eventSource.close();
2. 标准SSE(支持事件类型):
const eventSource = new EventSource('/api/chat/stream/sse?message=你好');
// 监听message事件
eventSource.addEventListener('message', (event) => {
const data = event.data;
document.getElementById('response').innerText += data;
});
// 监听done事件
eventSource.addEventListener('done', (event) => {
console.log('生成完成');
eventSource.close();
document.getElementById('status').innerText = '完成';
});
// 错误处理
eventSource.onerror = (error) => {
console.error('连接错误:', error);
eventSource.close();
};
3. 使用Fetch API(更灵活):
async function streamChat(message) {
const response = await fetch(`/api/chat/stream/simple?message=${encodeURIComponent(message)}`);
const reader = response.body.getReader();
const decoder = new TextDecoder();
while (true) {
const { done, value } = await reader.read();
if (done) {
console.log('流式响应完成');
break;
}
const chunk = decoder.decode(value, { stream: true });
document.getElementById('response').innerText += chunk;
}
}
// 使用
streamChat('介绍Spring AI Alibaba');
4. React集成示例:
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function StreamChat() {
const [message, setMessage] = useState('');
const [response, setResponse] = useState('');
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false);
const handleStream = () => {
setLoading(true);
setResponse('');
const eventSource = new EventSource(
`/api/chat/stream/sse?message=${encodeURIComponent(message)}`
);
eventSource.addEventListener('message', (event) => {
setResponse(prev => prev + event.data);
});
eventSource.addEventListener('done', () => {
eventSource.close();
setLoading(false);
});
eventSource.onerror = () => {
eventSource.close();
setLoading(false);
};
};
return (
<div>
<input
value={message}
onChange={e => setMessage(e.target.value)}
placeholder="输入问题"
/>
<button onClick={handleStream} disabled={loading}>
{loading ? '生成中...' : '发送'}
</button>
<div className="response">
{response}
</div>
</div>
);
}
流式响应高级特性
1. 背压处理(Backpressure)
/**
* 控制流速,避免客户端处理不过来
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/stream/backpressure", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<ServerSentEvent<String>> streamWithBackpressure(@RequestParam String message) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.stream()
.content()
.delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(50)) // 延迟50ms,控制速度
.onBackpressureBuffer(100) // 缓冲100个元素
.map(chunk -> ServerSentEvent.<String>builder()
.data(chunk)
.build());
}
2. 超时处理
/**
* 设置超时时间
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/stream/timeout", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<ServerSentEvent<String>> streamWithTimeout(@RequestParam String message) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.stream()
.content()
.timeout(Duration.ofSeconds(30)) // 30秒超时
.onErrorResume(TimeoutException.class, e ->
Flux.just("[错误: 请求超时]")
)
.map(chunk -> ServerSentEvent.<String>builder()
.data(chunk)
.build());
}
3. 错误处理和重试
/**
* 完善的错误处理
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/stream/resilient", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<ServerSentEvent<String>> streamResilient(@RequestParam String message) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.stream()
.content()
.retryWhen(Retry.backoff(3, Duration.ofSeconds(1)) // 重试3次
.filter(throwable -> throwable instanceof IOException))
.onErrorResume(throwable -> {
log.error("流式响应错误", throwable);
return Flux.just("[错误: " + throwable.getMessage() + "]");
})
.map(chunk -> ServerSentEvent.<String>builder()
.data(chunk)
.build());
}
4. 多路复用(组合多个流)
/**
* 同时调用多个模型,合并结果
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/stream/multiplex", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<ServerSentEvent<MultiModelResponse>> streamMultiModel(@RequestParam String message) {
// 模型1:快速模型
Flux<String> stream1 = chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.options(DashScopeChatOptions.builder().model("qwen-turbo").build())
.stream()
.content()
.map(chunk -> new MultiModelResponse("qwen-turbo", chunk));
// 模型2:高质量模型
Flux<String> stream2 = chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.options(DashScopeChatOptions.builder().model("qwen-max").build())
.stream()
.content()
.map(chunk -> new MultiModelResponse("qwen-max", chunk));
// 合并两个流
return Flux.merge(stream1, stream2)
.map(resp -> ServerSentEvent.<MultiModelResponse>builder()
.data(resp)
.build());
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class MultiModelResponse {
private String model;
private String content;
}
实现方式对比总结
| 方式 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flux<String> | 简单,性能好 | 无元数据,无事件控制 | 纯文本流式输出 |
| Flux<ServerSentEvent<String>> | 标准SSE,支持事件ID | 略复杂 | 生产环境推荐 |
| Flux<ChatResponse> | 包含完整元数据 | 数据量大 | 需要Token统计等场景 |
| WebSocket | 双向通信 | 实现复杂 | 实时交互应用 |
最佳实践推荐:
性能对比:
/**
* 性能测试对比
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/benchmark")
public class StreamBenchmarkController {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
/**
* 同步调用(基准)
*/
@GetMapping("/sync")
public String syncCall(@RequestParam String message) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String result = chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.call()
.content();
long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
log.info("同步调用耗时: {}ms", duration);
return result;
}
/**
* 流式调用
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/stream", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<ServerSentEvent<BenchmarkData>> streamCall(@RequestParam String message) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
AtomicLong firstChunkTime = new AtomicLong(0);
AtomicInteger chunkCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(message)
.stream()
.content()
.doOnNext(chunk -> {
if (firstChunkTime.get() == 0) {
firstChunkTime.set(System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
log.info("首个chunk延迟: {}ms", firstChunkTime.get());
}
chunkCount.incrementAndGet();
})
.doOnComplete(() -> {
long total = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
log.info("流式调用总耗时: {}ms, chunk数: {}", total, chunkCount.get());
})
.map(chunk -> ServerSentEvent.<BenchmarkData>builder()
.data(new BenchmarkData(
chunk,
firstChunkTime.get(),
System.currentTimeMillis() - start
))
.build());
}
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class BenchmarkData {
private String content;
private Long firstChunkLatency;
private Long currentLatency;
}
典型性能指标:
同步调用:
- 首字节延迟(TTFB): 2000-5000ms
- 总耗时: 3000-10000ms
- 用户体验: 需等待完成后才看到内容
流式调用:
- 首字节延迟(TTFB): 200-500ms ⚡
- 总耗时: 3000-10000ms(相同)
- 用户体验: 立即开始显示内容 ✨
- 优势: 降低感知延迟80%+
4.1.5 多轮对话
@Service
public class ConversationService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
/**
* 多轮对话实现
*/
public String multiTurnChat(String userMessage, List<Message> history) {
// 构建消息列表
List<Message> messages = new ArrayList<>(history);
messages.add(new UserMessage(userMessage));
return chatClient.prompt()
.messages(messages)
.call()
.content();
}
}
// 使用示例
List<Message> history = new ArrayList<>();
history.add(new UserMessage("我想学习Spring AI"));
history.add(new AssistantMessage("很好!Spring AI是..."));
String response = conversationService.multiTurnChat(
"那我应该从哪里开始?",
history
);
4.1.6 ChatClient配置
@Configuration
public class ChatClientConfig {
/**
* 自定义ChatClient Bean
*/
@Bean
public ChatClient chatClient(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
return builder
// 默认系统提示词
.defaultSystem("""
你是一个专业的AI助手。
回答要准确、简洁、专业。
""")
// 默认选项
.defaultOptions(DashScopeChatOptions.builder()
.model("qwen-max")
.temperature(0.7)
.build())
// 默认函数(后面会讲)
.defaultFunctions("weatherFunction")
.build();
}
/**
* 创建专门用途的ChatClient
*/
@Bean
@Qualifier("codingAssistant")
public ChatClient codingAssistantClient(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
return builder
.defaultSystem("你是一个Java代码助手,专注于Spring Boot开发")
.defaultOptions(DashScopeChatOptions.builder()
.temperature(0.3) // 代码生成用较低温度
.build())
.build();
}
}
4.2 ImageClient - 图像生成
4.2.1 基础使用
@Service
public class ImageService {
@Resource
private ImageClient imageClient;
/**
* 文生图
*/
public String generateImage(String prompt) {
ImageResponse response = imageClient.call(
new ImagePrompt(prompt,
DashScopeImageOptions.builder()
.model("wanx-v1") // 通义万相模型
.n(1) // 生成1张图片
.width(1024) // 宽度
.height(1024) // 高度
.build())
);
// 获取图片URL
return response.getResult().getOutput().getUrl();
}
/**
* 生成多张图片
*/
public List<String> generateMultipleImages(String prompt, int count) {
ImageResponse response = imageClient.call(
new ImagePrompt(prompt,
DashScopeImageOptions.builder()
.model("wanx-v1")
.n(count) // 生成多张
.build())
);
return response.getResults().stream()
.map(result -> result.getOutput().getUrl())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
4.2.2 Controller实现
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/image")
public class ImageController {
@Resource
private ImageService imageService;
@PostMapping("/generate")
public Result<ImageResult> generateImage(@RequestBody ImageRequest request) {
String imageUrl = imageService.generateImage(request.getPrompt());
return Result.success(ImageResult.builder()
.url(imageUrl)
.prompt(request.getPrompt())
.build());
}
}
// DTO
record ImageRequest(String prompt) {}
@Builder
record ImageResult(String url, String prompt) {}
4.3 AudioClient - 语音合成
4.3.1 文字转语音
@Service
public class AudioService {
@Resource
private AudioTranscriptionClient transcriptionClient;
@Resource
private AudioSpeechClient speechClient;
/**
* 文字转语音
*/
public byte[] textToSpeech(String text) {
SpeechPrompt prompt = new SpeechPrompt(text,
DashScopeAudioSpeechOptions.builder()
.model("sambert-zhichu-v1") // 语音模型
.voice("zhixiaoxia") // 音色
.build());
SpeechResponse response = speechClient.call(prompt);
return response.getResult().getOutput();
}
/**
* 语音转文字
*/
public String speechToText(byte[] audioData) {
AudioTranscriptionPrompt prompt = new AudioTranscriptionPrompt(audioData);
AudioTranscriptionResponse response = transcriptionClient.call(prompt);
return response.getResult().getOutput();
}
}
4.4 EmbeddingClient - 向量化
4.4.1 文本向量化
@Service
public class EmbeddingService {
@Resource
private EmbeddingClient embeddingClient;
/**
* 单个文本向量化
*/
public List<Double> embed(String text) {
EmbeddingResponse response = embeddingClient.embedForResponse(
Collections.singletonList(text)
);
return response.getResult().getOutput();
}
/**
* 批量文本向量化
*/
public List<List<Double>> embedBatch(List<String> texts) {
EmbeddingResponse response = embeddingClient.embedForResponse(texts);
return response.getResults().stream()
.map(result -> result.getOutput())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 计算文本相似度
*/
public double calculateSimilarity(String text1, String text2) {
List<Double> embedding1 = embed(text1);
List<Double> embedding2 = embed(text2);
return cosineSimilarity(embedding1, embedding2);
}
/**
* 余弦相似度计算
*/
private double cosineSimilarity(List<Double> v1, List<Double> v2) {
double dotProduct = 0.0;
double norm1 = 0.0;
double norm2 = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++) {
dotProduct += v1.get(i) * v2.get(i);
norm1 += Math.pow(v1.get(i), 2);
norm2 += Math.pow(v2.get(i), 2);
}
return dotProduct / (Math.sqrt(norm1) * Math.sqrt(norm2));
}
}
5. 高级特性
5.1 RAG(检索增强生成)
5.1.1 RAG架构
5.1.2 数据准备
1. 文档加载和切分
@Service
public class DocumentService {
/**
* 加载PDF文档
*/
public List<Document> loadPdfDocuments(String filePath) {
// 使用PDF文档加载器
PdfDocumentReader reader = new PdfDocumentReader(
new FileSystemResource(filePath)
);
return reader.get();
}
/**
* 文档分块
*/
public List<Document> splitDocuments(List<Document> documents) {
TokenTextSplitter splitter = new TokenTextSplitter(
500, // chunk size
50, // overlap
5, // min chunk size
10000 // max chunk size
);
return splitter.apply(documents);
}
}
2. 向量存储
@Configuration
public class VectorStoreConfig {
/**
* 配置Elasticsearch向量存储
*/
@Bean
public VectorStore vectorStore(
EmbeddingClient embeddingClient,
RestClient restClient) {
return new ElasticsearchVectorStore(
restClient,
embeddingClient
);
}
/**
* 配置Redis向量存储
*/
@Bean
public VectorStore redisVectorStore(
EmbeddingClient embeddingClient,
RedisVectorStoreConfig config) {
return new RedisVectorStore(config, embeddingClient);
}
}
3. 文档导入
@Service
public class DocumentImportService {
@Resource
private DocumentService documentService;
@Resource
private VectorStore vectorStore;
/**
* 导入文档到向量库
*/
public void importDocuments(String filePath) {
// 1. 加载文档
List<Document> documents = documentService.loadPdfDocuments(filePath);
// 2. 分块
List<Document> chunks = documentService.splitDocuments(documents);
// 3. 存入向量库
vectorStore.add(chunks);
log.info("导入{}个文档片段到向量库", chunks.size());
}
}
5.1.3 RAG查询
@Service
public class RagService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
@Resource
private VectorStore vectorStore;
/**
* RAG问答
*/
public String ragQuery(String question) {
// 1. 向量检索相关文档
List<Document> relevantDocs = vectorStore.similaritySearch(
SearchRequest.query(question)
.withTopK(5) // 检索Top 5
.withSimilarityThreshold(0.7) // 相似度阈值
);
// 2. 构建上下文
String context = relevantDocs.stream()
.map(Document::getContent)
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n\n---\n\n"));
// 3. 使用QuestionAnswerAdvisor
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(question)
.advisors(new QuestionAnswerAdvisor(vectorStore))
.call()
.content();
}
/**
* RAG问答(手动构建Prompt)
*/
public RagResponse ragQueryManual(String question) {
// 检索文档
List<Document> docs = vectorStore.similaritySearch(
SearchRequest.query(question).withTopK(5)
);
// 手动构建Prompt
String prompt = String.format("""
# 任务
基于以下文档内容回答用户问题。
# 文档内容
%s
# 用户问题
%s
# 要求
1. 仅基于提供的文档内容回答
2. 如果文档中没有相关信息,明确说明
3. 给出文档引用
""",
buildContext(docs),
question
);
String answer = chatClient.prompt()
.user(prompt)
.call()
.content();
return RagResponse.builder()
.answer(answer)
.sources(extractSources(docs))
.build();
}
private String buildContext(List<Document> docs) {
return docs.stream()
.map(doc -> String.format("【来源:%s】\n%s",
doc.getMetadata().get("source"),
doc.getContent()))
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n\n---\n\n"));
}
private List<DocumentSource> extractSources(List<Document> docs) {
return docs.stream()
.map(doc -> DocumentSource.builder()
.source(doc.getMetadata().get("source"))
.snippet(doc.getContent().substring(0, Math.min(200, doc.getContent().length())))
.build())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
@Builder
record RagResponse(String answer, List<DocumentSource> sources) {}
@Builder
record DocumentSource(String source, String snippet) {}
5.1.4 使用QuestionAnswerAdvisor
@Configuration
public class RagConfig {
@Bean
public QuestionAnswerAdvisor questionAnswerAdvisor(VectorStore vectorStore) {
return new QuestionAnswerAdvisor(vectorStore,
SearchRequest.defaults()
.withTopK(5)
.withSimilarityThreshold(0.7)
);
}
}
@Service
public class SimpleRagService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
@Resource
private QuestionAnswerAdvisor questionAnswerAdvisor;
public String query(String question) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(question)
.advisors(questionAnswerAdvisor)
.call()
.content();
}
}
5.2 Function Calling(工具调用)
5.2.1 什么是Function Calling?
Function Calling允许大模型主动调用外部函数/API来完成任务。
5.2.2 定义函数
方式1:使用@Bean注册函数
@Configuration
public class FunctionConfig {
/**
* 天气查询函数
*/
@Bean
@Description("查询指定城市的天气信息")
public Function<WeatherRequest, WeatherResponse> weatherFunction() {
return request -> {
// 模拟调用天气API
return WeatherResponse.builder()
.city(request.city())
.temperature(25)
.condition("晴天")
.humidity(60)
.build();
};
}
/**
* 订单查询函数
*/
@Bean
@Description("根据订单ID查询订单详情")
public Function<OrderRequest, OrderResponse> orderQueryFunction() {
return request -> {
// 实际业务逻辑
Order order = orderService.getById(request.orderId());
return OrderResponse.from(order);
};
}
}
// 请求和响应DTO
record WeatherRequest(
@JsonProperty(required = true, description = "城市名称") String city,
@JsonProperty(required = false, description = "日期,默认今天") String date
) {}
@Builder
record WeatherResponse(String city, int temperature, String condition, int humidity) {}
record OrderRequest(@JsonProperty(required = true, description = "订单ID") String orderId) {}
record OrderResponse(String orderId, String status, BigDecimal amount) {
static OrderResponse from(Order order) {
return new OrderResponse(
order.getId().toString(),
order.getStatus().name(),
order.getAmount()
);
}
}
5.2.3 使用Function Calling
@Service
public class FunctionCallingService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
/**
* 使用函数调用
*/
public String chatWithFunctions(String userMessage) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.functions("weatherFunction", "orderQueryFunction") // 注册可用函数
.call()
.content();
}
}
// 使用示例
String response = service.chatWithFunctions("帮我查一下北京的天气");
// 大模型会自动调用weatherFunction,然后返回:
// "北京当前天气晴天,温度25℃,湿度60%"
String response2 = service.chatWithFunctions("查询订单12345的状态");
// 大模型会自动调用orderQueryFunction
方式2:动态注册函数
public String chatWithDynamicFunction(String userMessage) {
// 动态创建函数
FunctionCallback weatherCallback = FunctionCallback.builder()
.function("getCurrentWeather", (WeatherRequest request) -> {
// 函数实现
return getWeatherData(request.city());
})
.description("获取当前天气")
.inputType(WeatherRequest.class)
.build();
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.function(weatherCallback)
.call()
.content();
}
5.2.4 复杂工具调用示例
/**
* 数据库查询工具
*/
@Component
public class DatabaseTools {
@Resource
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Resource
private OrderRepository orderRepository;
@Bean
@Description("查询用户信息")
public Function<UserQueryRequest, UserInfo> userQueryFunction() {
return request -> {
User user = userRepository.findById(request.userId())
.orElseThrow(() -> new BusinessException("用户不存在"));
return UserInfo.builder()
.userId(user.getId())
.username(user.getUsername())
.email(user.getEmail())
.registerDate(user.getCreateTime())
.build();
};
}
@Bean
@Description("查询用户的订单列表")
public Function<UserOrderRequest, List<OrderInfo>> userOrdersFunction() {
return request -> {
List<Order> orders = orderRepository.findByUserId(request.userId());
return orders.stream()
.map(order -> OrderInfo.builder()
.orderId(order.getId().toString())
.amount(order.getAmount())
.status(order.getStatus().name())
.createTime(order.getCreateTime())
.build())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
};
}
}
// 使用示例
String response = chatClient.prompt()
.user("查询用户1001的信息和最近的订单")
.functions("userQueryFunction", "userOrdersFunction")
.call()
.content();
// 大模型会:
// 1. 先调用userQueryFunction获取用户信息
// 2. 再调用userOrdersFunction获取订单列表
// 3. 整合结果返回给用户
5.3 Graph - 工作流和多智能体
5.3.1 Graph框架概述
Spring AI Alibaba Graph是一个低级工作流和多智能体编排框架,灵感来自LangGraph。
5.3.2 基础Graph示例
/**
* 简单工作流示例
*/
@Service
public class SimpleGraphService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
public String executeWorkflow(String userInput) {
// 1. 创建Graph
Graph<WorkflowState> graph = new Graph<>();
// 2. 添加节点
graph.addNode("analyze", this::analyzeNode);
graph.addNode("process", this::processNode);
graph.addNode("summarize", this::summarizeNode);
// 3. 添加边(定义流程)
graph.addEdge(START, "analyze");
graph.addEdge("analyze", "process");
graph.addEdge("process", "summarize");
graph.addEdge("summarize", END);
// 4. 编译并执行
CompiledGraph<WorkflowState> compiled = graph.compile();
WorkflowState initialState = WorkflowState.builder()
.userInput(userInput)
.build();
WorkflowState finalState = compiled.invoke(initialState);
return finalState.getResult();
}
/**
* 分析节点
*/
private WorkflowState analyzeNode(WorkflowState state) {
String analysis = chatClient.prompt()
.system("你是分析专家,分析用户需求")
.user(state.getUserInput())
.call()
.content();
return state.toBuilder()
.analysis(analysis)
.build();
}
/**
* 处理节点
*/
private WorkflowState processNode(WorkflowState state) {
String processed = chatClient.prompt()
.system("根据分析结果进行处理")
.user("分析结果:" + state.getAnalysis())
.call()
.content();
return state.toBuilder()
.processed(processed)
.build();
}
/**
* 汇总节点
*/
private WorkflowState summarizeNode(WorkflowState state) {
String summary = chatClient.prompt()
.system("汇总所有信息,生成最终结果")
.user("处理结果:" + state.getProcessed())
.call()
.content();
return state.toBuilder()
.result(summary)
.build();
}
}
/**
* 工作流状态
*/
@Data
@Builder(toBuilder = true)
class WorkflowState {
private String userInput;
private String analysis;
private String processed;
private String result;
}
5.3.3 条件路由
/**
* 带条件判断的工作流
*/
public String executeConditionalWorkflow(String userInput) {
Graph<WorkflowState> graph = new Graph<>();
// 添加节点
graph.addNode("classify", this::classifyNode);
graph.addNode("handleQuestion", this::handleQuestionNode);
graph.addNode("handleCommand", this::handleCommandNode);
graph.addNode("handleOther", this::handleOtherNode);
// 添加边
graph.addEdge(START, "classify");
// 条件路由
graph.addConditionalEdge("classify", this::routeByType);
graph.addEdge("handleQuestion", END);
graph.addEdge("handleCommand", END);
graph.addEdge("handleOther", END);
// 执行
CompiledGraph<WorkflowState> compiled = graph.compile();
WorkflowState finalState = compiled.invoke(
WorkflowState.builder().userInput(userInput).build()
);
return finalState.getResult();
}
/**
* 分类节点
*/
private WorkflowState classifyNode(WorkflowState state) {
String type = chatClient.prompt()
.system("""
分析用户输入的类型:
- question: 问题
- command: 命令
- other: 其他
只返回类型名称
""")
.user(state.getUserInput())
.call()
.content()
.toLowerCase();
return state.toBuilder()
.type(type)
.build();
}
/**
* 路由函数
*/
private String routeByType(WorkflowState state) {
return switch (state.getType()) {
case "question" -> "handleQuestion";
case "command" -> "handleCommand";
default -> "handleOther";
};
}
5.3.4 多智能体协作
/**
* 多智能体协作示例
*/
@Service
public class MultiAgentService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
/**
* 代码审查多智能体流程
*/
public CodeReviewResult reviewCode(String code) {
Graph<CodeReviewState> graph = new Graph<>();
// 定义多个智能体节点
graph.addNode("securityReviewer", this::securityReviewNode);
graph.addNode("performanceReviewer", this::performanceReviewNode);
graph.addNode("styleReviewer", this::styleReviewNode);
graph.addNode("coordinator", this::coordinatorNode);
// 并行执行审查
graph.addEdge(START, "securityReviewer");
graph.addEdge(START, "performanceReviewer");
graph.addEdge(START, "styleReviewer");
// 汇总到协调者
graph.addEdge("securityReviewer", "coordinator");
graph.addEdge("performanceReviewer", "coordinator");
graph.addEdge("styleReviewer", "coordinator");
graph.addEdge("coordinator", END);
// 执行
CompiledGraph<CodeReviewState> compiled = graph.compile();
CodeReviewState finalState = compiled.invoke(
CodeReviewState.builder().code(code).build()
);
return finalState.getResult();
}
private CodeReviewState securityReviewNode(CodeReviewState state) {
String review = chatClient.prompt()
.system("你是安全审查专家,检查代码安全问题")
.user("审查代码:\n" + state.getCode())
.call()
.content();
return state.toBuilder()
.securityReview(review)
.build();
}
// 其他审查节点类似...
private CodeReviewState coordinatorNode(CodeReviewState state) {
String summary = chatClient.prompt()
.system("你是协调者,汇总所有审查意见")
.user(String.format("""
安全审查:%s
性能审查:%s
风格审查:%s
请汇总生成最终报告
""",
state.getSecurityReview(),
state.getPerformanceReview(),
state.getStyleReview()))
.call()
.content();
return state.toBuilder()
.result(CodeReviewResult.builder()
.summary(summary)
.securityIssues(extractIssues(state.getSecurityReview()))
.performanceIssues(extractIssues(state.getPerformanceReview()))
.styleIssues(extractIssues(state.getStyleReview()))
.build())
.build();
}
}
5.4 MCP(Model Context Protocol)集成
5.4.1 什么是MCP?
MCP是一个标准化协议,让AI模型能够安全地访问外部数据源和工具。
5.4.2 使用Nacos MCP Registry
@Configuration
public class McpConfig {
/**
* 配置Nacos MCP注册中心
*/
@Bean
public NacosMcpRegistry nacosMcpRegistry(NacosProperties nacosProperties) {
return new NacosMcpRegistry(
nacosProperties.getServerAddr(),
nacosProperties.getNamespace()
);
}
/**
* MCP服务自动发现
*/
@Bean
public McpServiceDiscovery mcpServiceDiscovery(NacosMcpRegistry registry) {
return new McpServiceDiscovery(registry);
}
}
# application.yml
spring:
ai:
alibaba:
mcp:
enabled: true
registry:
type: nacos
address: localhost:8848
namespace: mcp-services
6. 企业级应用实践
6.1 会话记忆管理
6.1.1 内存存储(开发测试)
@Configuration
public class ChatMemoryConfig {
/**
* 内存Chat Memory
*/
@Bean
public ChatMemory inMemoryChatMemory() {
return new InMemoryChatMemory();
}
}
6.1.2 Redis存储(生产推荐)
@Configuration
public class RedisChatMemoryConfig {
@Bean
public ChatMemory redisChatMemory(
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) {
return new RedisChatMemory(redisTemplate,
ChatMemoryConfig.builder()
.maxMessages(20) // 最多保留20条消息
.timeToLive(Duration.ofHours(24)) // 24小时过期
.build());
}
}
@Service
public class ConversationService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
@Resource
private ChatMemory chatMemory;
public String chat(String sessionId, String userMessage) {
// 1. 加载历史
List<Message> history = chatMemory.get(sessionId);
// 2. 添加新消息
history.add(new UserMessage(userMessage));
// 3. 调用模型
String response = chatClient.prompt()
.messages(history)
.call()
.content();
// 4. 保存响应
history.add(new AssistantMessage(response));
chatMemory.save(sessionId, history);
return response;
}
}
6.1.3 数据库存储(持久化)
@Configuration
public class JdbcChatMemoryConfig {
@Bean
public ChatMemory jdbcChatMemory(DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcChatMemory(dataSource);
}
}
// 数据库表结构
CREATE TABLE chat_memory (
id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
session_id VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL,
role VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
content TEXT NOT NULL,
metadata JSON,
create_time DATETIME NOT NULL,
INDEX idx_session_id (session_id),
INDEX idx_create_time (create_time)
);
6.2 监控与可观测性
6.2.1 集成Micrometer
@Configuration
public class ObservabilityConfig {
@Bean
public ObservationRegistry observationRegistry() {
return ObservationRegistry.create();
}
@Bean
public ChatClientObservationConvention customConvention() {
return new ChatClientObservationConvention() {
@Override
public KeyValues getLowCardinalityKeyValues(ChatClientObservationContext context) {
return KeyValues.of(
"ai.model", context.getModel(),
"ai.provider", "dashscope"
);
}
};
}
}
# application.yml
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: health,info,metrics,prometheus
metrics:
tags:
application: ${spring.application.name}
export:
prometheus:
enabled: true
6.2.2 自定义指标
@Aspect
@Component
public class AiMetricsAspect {
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
public AiMetricsAspect(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
}
@Around("@annotation(com.example.annotation.AiMetrics)")
public Object recordMetrics(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
String methodName = pjp.getSignature().getName();
try {
Object result = pjp.proceed();
// 记录成功
sample.stop(Timer.builder("ai.call.duration")
.tag("method", methodName)
.tag("status", "success")
.register(meterRegistry));
// 记录Token使用(如果可获取)
if (result instanceof ChatResponse response) {
meterRegistry.counter("ai.tokens.used",
"type", "total"
).increment(response.getMetadata().getUsage().getTotalTokens());
}
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
sample.stop(Timer.builder("ai.call.duration")
.tag("method", methodName)
.tag("status", "error")
.tag("error.type", e.getClass().getSimpleName())
.register(meterRegistry));
throw e;
}
}
}
6.3 安全与限流
6.3.1 API Key管理
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig {
/**
* 从环境变量或密钥管理系统获取API Key
*/
@Bean
public DashScopeApiKeyProvider apiKeyProvider() {
return new DashScopeApiKeyProvider() {
@Override
public String getApiKey() {
// 1. 优先从环境变量
String apiKey = System.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY");
// 2. 或从密钥管理服务获取
if (apiKey == null) {
apiKey = secretManager.getSecret("ai/dashscope/api-key");
}
return apiKey;
}
};
}
}
6.3.2 限流配置
@Configuration
public class RateLimitConfig {
/**
* 基于Redis的限流
*/
@Bean
public RateLimiter aiRateLimiter(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) {
return new RedisRateLimiter(
10, // 每秒10个请求
100, // 突发上限100
redisTemplate
);
}
}
@Aspect
@Component
public class RateLimitAspect {
@Resource
private RateLimiter aiRateLimiter;
@Before("@annotation(com.example.annotation.RateLimited)")
public void checkRateLimit() {
if (!aiRateLimiter.tryAcquire()) {
throw new RateLimitException("请求过于频繁,请稍后重试");
}
}
}
6.4 异常处理与降级
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(AiException.class)
public Result<?> handleAiException(AiException e) {
log.error("AI调用异常", e);
return Result.error()
.code("AI_ERROR")
.message("AI服务暂时不可用,请稍后重试")
.build();
}
@ExceptionHandler(RateLimitException.class)
public Result<?> handleRateLimit(RateLimitException e) {
return Result.error()
.code("RATE_LIMIT")
.message(e.getMessage())
.build();
}
}
@Service
public class ResilientAiService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
@Resource
private CacheManager cacheManager;
/**
* 带降级的AI调用
*/
public String chatWithFallback(String userMessage) {
try {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.call()
.content();
} catch (AiException e) {
log.warn("AI调用失败,使用缓存降级", e);
// 降级1:返回缓存结果
String cached = cacheManager.get(userMessage);
if (cached != null) {
return cached + "\n(来自缓存)";
}
// 降级2:返回默认响应
return "抱歉,AI服务暂时不可用,请稍后重试。";
}
}
}
7. 最佳实践与注意事项
7.1 Prompt优化
7.1.1 System Prompt最佳实践
/**
* ✅ 好的System Prompt
*/
String goodSystemPrompt = """
# 角色
你是一个专业的Java技术顾问,擅长Spring生态系统。
# 能力
- 解答Java和Spring相关技术问题
- 提供代码示例和最佳实践
- 进行架构设计建议
# 约束
- 回答要准确、简洁、专业
- 提供的代码必须可运行
- 引用官方文档时给出链接
- 如果不确定,明确说明
# 输出格式
- 使用Markdown格式
- 代码使用代码块包裹
- 重要信息使用粗体标注
""";
/**
* ❌ 不好的System Prompt
*/
String badSystemPrompt = "你是一个AI助手,帮助用户解决问题。";
7.1.2 温度参数选择
| 任务类型 | 推荐温度 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 代码生成 | 0.1 - 0.3 | 需要精确性,避免创造性 |
| 技术问答 | 0.3 - 0.5 | 平衡准确性和灵活性 |
| 文案创作 | 0.7 - 0.9 | 需要创造性和多样性 |
| 头脑风暴 | 0.9 - 1.0 | 最大化创新性 |
7.2 性能优化
7.2.1 缓存策略
@Service
public class CachedAiService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
/**
* 使用Spring Cache缓存结果
*/
@Cacheable(value = "ai-responses",
key = "#userMessage",
unless = "#result == null")
public String chatWithCache(String userMessage) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.call()
.content();
}
/**
* 手动缓存管理
*/
public String chatWithManualCache(String userMessage) {
// 1. 检查缓存
String cached = redis.get("ai:" + hash(userMessage));
if (cached != null) {
return cached;
}
// 2. 调用AI
String response = chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.call()
.content();
// 3. 存入缓存
redis.setex("ai:" + hash(userMessage), 3600, response);
return response;
}
private String hash(String input) {
return DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(input.getBytes());
}
}
7.2.2 异步处理
@Service
public class AsyncAiService {
@Resource
private ChatClient chatClient;
@Async("aiTaskExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> chatAsync(String userMessage) {
String response = chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.call()
.content();
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(response);
}
}
@Configuration
public class AsyncConfig {
@Bean("aiTaskExecutor")
public Executor aiTaskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(5);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(10);
executor.setQueueCapacity(100);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("ai-task-");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
7.3 成本控制
7.3.1 Token使用优化
/**
* Token使用优化策略
*/
@Service
public class TokenOptimizedService {
/**
* 1. 精简Prompt
*/
public String chatOptimized(String userMessage) {
// ❌ 不要包含冗余信息
String badPrompt = """
请你仔细阅读以下问题,然后认真思考,给出详细的、
完整的、准确的回答,确保回答质量高...
问题:%s
""".formatted(userMessage);
// ✅ 精简到重点
String goodPrompt = userMessage;
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(goodPrompt)
.call()
.content();
}
/**
* 2. 使用max-tokens限制
*/
public String chatWithLimit(String userMessage) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.options(DashScopeChatOptions.builder()
.maxTokens(500) // 限制响应长度
.build())
.call()
.content();
}
/**
* 3. 选择合适的模型
*/
public String chatWithRightModel(String userMessage, boolean isComplex) {
String model = isComplex ? "qwen-max" : "qwen-turbo";
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage)
.options(DashScopeChatOptions.builder()
.model(model)
.build())
.call()
.content();
}
}
7.3.2 成本监控
@Component
public class CostMonitor {
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
private final AtomicLong totalTokens = new AtomicLong(0);
public CostMonitor(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
// 注册指标
meterRegistry.gauge("ai.cost.total.tokens", totalTokens);
}
public void recordUsage(ChatResponse response) {
long tokens = response.getMetadata().getUsage().getTotalTokens();
totalTokens.addAndGet(tokens);
// 计算成本(假设每1000 tokens = 0.01元)
double cost = tokens / 1000.0 * 0.01;
meterRegistry.counter("ai.cost.amount",
"model", response.getMetadata().getModel()
).increment(cost);
}
}
7.4 测试策略
7.4.1 单元测试
@SpringBootTest
class AiServiceTest {
@MockBean
private ChatClient chatClient;
@Resource
private AiService aiService;
@Test
void testChat() {
// Mock ChatClient
ChatResponse mockResponse = mock(ChatResponse.class);
when(chatClient.prompt()).thenReturn(mock(PromptSpec.class));
// ... 设置mock行为
// 测试
String result = aiService.chat("测试消息");
assertNotNull(result);
verify(chatClient).prompt();
}
}
7.4.2 集成测试
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class ChatControllerIntegrationTest {
@Resource
private TestRestTemplate restTemplate;
@Test
void testChatEndpoint() {
ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.getForEntity(
"/api/chat/simple?message=你好",
String.class
);
assertEquals(HttpStatus.OK, response.getStatusCode());
assertNotNull(response.getBody());
}
}
附录
A. 常见问题FAQ
Q1: Spring AI Alibaba vs LangChain4j,如何选择?
A:
- 使用阿里云服务 → Spring AI Alibaba
- Spring Boot项目 → Spring AI Alibaba(无缝集成)
- 需要复杂Agent → LangChain4j(功能更全面)
- 需要多模型切换 → LangChain4j(支持20+模型)
Q2: 如何降低API调用成本?
A:
- 使用缓存减少重复调用
- 选择合适的模型(简单任务用qwen-turbo)
- 限制max-tokens
- 精简Prompt
- 批量处理请求
Q3: 如何处理大模型的幻觉问题?
A:
- 使用RAG提供准确的上下文
- 降低temperature参数
- 明确要求模型基于提供的信息回答
- 使用Function Calling获取实时数据
- 人工审核关键输出
B. 参考资源
官方文档:
- Spring AI Alibaba官网:https://java2ai.com
- Spring Cloud Alibaba文档:https://sca.aliyun.com
- 阿里云百炼平台:https://dashscope.console.aliyun.com
开源项目:
- GitHub仓库:https://github.com/alibaba/spring-ai-alibaba
- 示例项目:https://github.com/springaialibaba/spring-ai-alibaba-examples
社区资源:
- 钉钉社区群
- GitHub Discussions
- CSDN技术博客
Sources:
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容







所有评论(0)