AI Agent在智能空间规划中的实践
智能空间规划是人工智能与建筑学、城市规划、物流管理等领域的交叉学科。静态空间布局优化动态路径规划多目标约束下的资源分配实时环境适应与决策研究范围涵盖从基础理论到工程实践的完整技术栈,特别关注强化学习在复杂空间规划场景中的应用。基础理论部分(第2-4章)阐述核心概念和数学模型实践部分(第5章)提供完整项目实现应用与展望部分(第6-8章)探讨实际场景和未来趋势AI Agent:具有自主决策能力的人工智
AI Agent在智能空间规划中的实践
关键词:AI Agent、智能空间规划、强化学习、路径优化、空间利用率、动态环境适应、多智能体协作
摘要:本文深入探讨AI Agent在智能空间规划领域的应用实践。我们将从基础概念出发,详细分析AI Agent如何通过强化学习、计算机视觉和优化算法解决空间规划中的复杂问题。文章包含完整的算法实现、数学模型解析和实际项目案例,并探讨该技术在智慧城市、仓储物流和建筑设计的应用前景。最后,我们展望AI Agent在空间规划领域的未来发展趋势和技术挑战。
1. 背景介绍
1.1 目的和范围
智能空间规划是人工智能与建筑学、城市规划、物流管理等领域的交叉学科。本文旨在系统性地介绍AI Agent如何通过先进算法解决空间规划中的关键问题,包括但不限于:
- 静态空间布局优化
- 动态路径规划
- 多目标约束下的资源分配
- 实时环境适应与决策
研究范围涵盖从基础理论到工程实践的完整技术栈,特别关注强化学习在复杂空间规划场景中的应用。
1.2 预期读者
本文适合以下读者群体:
- 人工智能领域的研究人员和工程师
- 城市规划与建筑设计的专业人士
- 物流与仓储管理的技术决策者
- 计算机科学相关专业的高年级学生
- 对智能空间优化感兴趣的技术爱好者
1.3 文档结构概述
文章采用理论-实践-应用的三段式结构:
- 基础理论部分(第2-4章)阐述核心概念和数学模型
- 实践部分(第5章)提供完整项目实现
- 应用与展望部分(第6-8章)探讨实际场景和未来趋势
1.4 术语表
1.4.1 核心术语定义
AI Agent:具有自主决策能力的人工智能实体,能够感知环境并采取行动以实现特定目标。
空间规划:对物理或虚拟空间进行有效组织和利用的过程,包括布局设计、路径规划等。
强化学习:通过试错机制学习最优策略的机器学习范式,特别适合序列决策问题。
1.4.2 相关概念解释
Q-learning:基于价值迭代的强化学习算法,通过维护Q值表选择最优动作。
蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS):结合随机模拟和树搜索的决策算法,在复杂空间中有优异表现。
多智能体系统(MAS):多个AI Agent协同工作的系统,可解决分布式空间规划问题。
1.4.3 缩略词列表
- RL:Reinforcement Learning(强化学习)
- MDP:Markov Decision Process(马尔可夫决策过程)
- CNN:Convolutional Neural Network(卷积神经网络)
- RRT:Rapidly-exploring Random Tree(快速扩展随机树)
- SLAM:Simultaneous Localization and Mapping(同步定位与建图)
2. 核心概念与联系
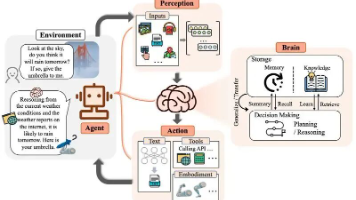
智能空间规划系统的核心架构如下图所示:
2.1 感知-决策-执行循环
AI Agent在空间规划中遵循典型的感知-决策-执行循环:
- 环境感知:通过传感器(如激光雷达、摄像头)或数字孪生系统获取空间信息
- 空间建模:将物理空间转化为可计算的数学模型(如栅格图、拓扑图)
- 规划算法:基于当前状态和目标选择最优策略
- 动作执行:将决策转化为具体操作(如路径导航、物品摆放)
2.2 单Agent vs 多Agent系统
| 特性 | 单Agent系统 | 多Agent系统 |
|---|---|---|
| 复杂度 | 相对简单 | 高度复杂 |
| 通信开销 | 无 | 显著 |
| 可扩展性 | 有限 | 优秀 |
| 典型应用 | 小型仓库机器人 | 智慧城市交通 |
2.3 空间表示方法
AI Agent常用的空间表示方法包括:
-
栅格法:将空间离散化为均匀网格
- 优点:实现简单,便于计算
- 缺点:维度灾难,精度受限
-
几何法:使用多边形表示空间区域
- 优点:精确度高
- 缺点:计算复杂度高
-
拓扑法:基于图结构表示空间关系
- 优点:抽象层次高
- 缺点:信息损失
3. 核心算法原理 & 具体操作步骤
3.1 基于Q-learning的静态空间规划
import numpy as np
class QLearningSpacePlanner:
def __init__(self, grid_size, alpha=0.1, gamma=0.9, epsilon=0.1):
self.grid_size = grid_size
self.q_table = np.zeros((grid_size, grid_size, 4)) # 4 actions: up, down, left, right
self.alpha = alpha # Learning rate
self.gamma = gamma # Discount factor
self.epsilon = epsilon # Exploration rate
def choose_action(self, state):
if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < self.epsilon:
return np.random.randint(0, 4) # Random action
else:
return np.argmax(self.q_table[state[0], state[1]])
def update_q_table(self, state, action, reward, next_state):
current_q = self.q_table[state[0], state[1], action]
max_next_q = np.max(self.q_table[next_state[0], next_state[1]])
new_q = current_q + self.alpha * (reward + self.gamma * max_next_q - current_q)
self.q_table[state[0], state[1], action] = new_q
def train(self, episodes, start_state, goal_state, obstacles):
for _ in range(episodes):
state = start_state
while state != goal_state:
action = self.choose_action(state)
# Calculate next state
next_state = list(state)
if action == 0: next_state[0] = max(0, state[0]-1) # Up
elif action == 1: next_state[0] = min(self.grid_size-1, state[0]+1) # Down
elif action == 2: next_state[1] = max(0, state[1]-1) # Left
else: next_state[1] = min(self.grid_size-1, state[1]+1) # Right
next_state = tuple(next_state)
# Calculate reward
if next_state == goal_state:
reward = 100
elif next_state in obstacles:
reward = -100
else:
reward = -1
self.update_q_table(state, action, reward, next_state)
state = next_state if next_state not in obstacles else state
3.2 动态环境下的PPO算法实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.distributions import Categorical
class PolicyNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim):
super(PolicyNetwork, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = torch.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = torch.softmax(self.fc3(x), dim=-1)
return x
class PPOSpacePlanner:
def __init__(self, env, hidden_dim=64, lr=0.001, gamma=0.99, clip_epsilon=0.2):
self.env = env
self.policy = PolicyNetwork(env.observation_space.shape[0], hidden_dim, env.action_space.n)
self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.policy.parameters(), lr=lr)
self.gamma = gamma
self.clip_epsilon = clip_epsilon
def select_action(self, state):
state = torch.FloatTensor(state)
action_probs = self.policy(state)
dist = Categorical(action_probs)
action = dist.sample()
log_prob = dist.log_prob(action)
return action.item(), log_prob
def update_policy(self, rewards, log_probs, states, actions, next_states):
discounted_rewards = []
R = 0
for r in reversed(rewards):
R = r + self.gamma * R
discounted_rewards.insert(0, R)
discounted_rewards = torch.FloatTensor(discounted_rewards)
discounted_rewards = (discounted_rewards - discounted_rewards.mean()) / (discounted_rewards.std() + 1e-9)
old_probs = torch.stack(log_probs).detach()
states = torch.FloatTensor(states)
actions = torch.LongTensor(actions)
new_probs = []
for state, action in zip(states, actions):
action_probs = self.policy(state)
dist = Categorical(action_probs)
new_probs.append(dist.log_prob(action))
new_probs = torch.stack(new_probs)
ratio = torch.exp(new_probs - old_probs)
surrogate1 = ratio * discounted_rewards
surrogate2 = torch.clamp(ratio, 1-self.clip_epsilon, 1+self.clip_epsilon) * discounted_rewards
policy_loss = -torch.min(surrogate1, surrogate2).mean()
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
policy_loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
4. 数学模型和公式 & 详细讲解
4.1 马尔可夫决策过程(MDP)模型
智能空间规划问题可以形式化为马尔可夫决策过程:
MDP=⟨S,A,P,R,γ⟩ MDP = \langle S, A, P, R, \gamma \rangle MDP=⟨S,A,P,R,γ⟩
其中:
- SSS:状态空间(空间的所有可能配置)
- AAA:动作空间(移动、旋转、放置等操作)
- P(s′∣s,a)P(s'|s,a)P(s′∣s,a):状态转移概率
- R(s,a,s′)R(s,a,s')R(s,a,s′):即时奖励函数
- γ\gammaγ:折扣因子(0 ≤ γ ≤ 1)
4.2 贝尔曼最优方程
空间规划的最优策略π∗\pi^*π∗满足:
V∗(s)=maxa∑s′P(s′∣s,a)[R(s,a,s′)+γV∗(s′)] V^*(s) = \max_a \sum_{s'} P(s'|s,a)[R(s,a,s') + \gamma V^*(s')] V∗(s)=amaxs′∑P(s′∣s,a)[R(s,a,s′)+γV∗(s′)]
Q∗(s,a)=∑s′P(s′∣s,a)[R(s,a,s′)+γmaxa′Q∗(s′,a′)] Q^*(s,a) = \sum_{s'} P(s'|s,a)[R(s,a,s') + \gamma \max_{a'} Q^*(s',a')] Q∗(s,a)=s′∑P(s′∣s,a)[R(s,a,s′)+γa′maxQ∗(s′,a′)]
4.3 空间利用率优化模型
最大化空间利用率的目标函数:
max∑i=1nwi⋅xi \max \sum_{i=1}^n w_i \cdot x_i maxi=1∑nwi⋅xi
约束条件:
∑i=1naij⋅xi≤bj,j=1,...,m \sum_{i=1}^n a_{ij} \cdot x_i \leq b_j, \quad j = 1,...,m i=1∑naij⋅xi≤bj,j=1,...,m
xi∈{0,1},i=1,...,n x_i \in \{0,1\}, \quad i = 1,...,n xi∈{0,1},i=1,...,n
其中:
- xix_ixi:物品i是否被放置(1=是,0=否)
- wiw_iwi:物品i的权重(重要性)
- aija_{ij}aij:物品i对资源j的需求量
- bjb_jbj:资源j的总量
4.4 多Agent协作的纳什均衡
在多Agent系统中,纳什均衡解满足:
∀i,πi∗∈argmaxπiUi(πi,π−i∗) \forall i, \pi_i^* \in \arg\max_{\pi_i} U_i(\pi_i, \pi_{-i}^*) ∀i,πi∗∈argπimaxUi(πi,π−i∗)
其中UiU_iUi表示第i个Agent的效用函数,π−i∗\pi_{-i}^*π−i∗表示其他Agent的最优策略。
5. 项目实战:代码实际案例和详细解释说明
5.1 开发环境搭建
硬件要求:
- CPU: Intel i7或同等性能以上
- GPU: NVIDIA GTX 1080及以上(可选,用于加速深度学习)
- 内存: 16GB以上
软件依赖:
# 创建conda环境
conda create -n space_planning python=3.8
conda activate space_planning
# 安装核心库
pip install numpy torch gym matplotlib scipy
# 可选:安装GPU支持
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113
5.2 智能仓库布局优化系统
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
class WarehouseOptimizer:
def __init__(self, items, warehouse_size=(100, 50)):
"""
items: 物品列表,每个元素为(宽度, 高度, 周转率)
warehouse_size: 仓库尺寸(长, 宽)
"""
self.items = np.array(items)
self.warehouse = np.zeros(warehouse_size)
self.heatmap = np.zeros(warehouse_size)
def calculate_turnover_clusters(self, n_clusters=3):
"""基于周转率进行物品聚类"""
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=n_clusters)
clusters = kmeans.fit_predict(self.items[:, 2].reshape(-1, 1))
return clusters
def generate_layout(self):
"""生成优化后的仓库布局"""
clusters = self.calculate_turnover_clusters()
# 按周转率排序聚类(0=最高周转率)
cluster_order = np.argsort(
[np.mean(self.items[clusters==i, 2]) for i in range(np.max(clusters)+1)]
)[::-1]
current_x, current_y = 0, 0
max_height_in_row = 0
for cluster_idx in cluster_order:
cluster_items = self.items[clusters == cluster_idx]
# 按面积降序排列当前聚类的物品
cluster_items = cluster_items[np.argsort(cluster_items[:, 0] * cluster_items[:, 1])[::-1]]
for item in cluster_items:
width, height, _ = item
# 检查当前行是否放得下
if current_x + width > self.warehouse.shape[0]:
current_x = 0
current_y += max_height_in_row
max_height_in_row = 0
# 检查是否超出仓库边界
if current_y + height > self.warehouse.shape[1]:
raise ValueError("仓库空间不足")
# 放置物品
self.warehouse[current_x:current_x+width, current_y:current_y+height] = cluster_idx + 1
# 更新热力图(周转率越高,热力值越大)
self.heatmap[current_x:current_x+width, current_y:current_y+height] = item[2]
# 更新位置指针
current_x += width
max_height_in_row = max(max_height_in_row, height)
def visualize(self):
"""可视化仓库布局"""
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(self.warehouse.T, cmap='viridis')
plt.title('Warehouse Layout (Clusters)')
plt.colorbar(label='Cluster ID')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(self.heatmap.T, cmap='hot')
plt.title('Turnover Heatmap')
plt.colorbar(label='Turnover Rate')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
5.3 代码解读与分析
-
物品聚类:
- 使用K-means算法根据周转率将物品分为3类
- 高周转率物品将被优先放置在靠近出入口的位置
-
布局生成逻辑:
- 采用"蛇形"摆放策略,从左到右,从上到下
- 每个聚类内的物品按面积降序排列
- 动态调整当前行和列的位置指针
-
热力图生成:
- 可视化不同区域的物品周转率
- 帮助人工复核布局合理性
-
异常处理:
- 当仓库空间不足时抛出明确错误
- 确保不会出现物品重叠或越界
6. 实际应用场景
6.1 智慧城市交通规划
应用特点:
- 多模态交通网络整合(道路、地铁、公交)
- 实时流量预测与信号灯优化
- 紧急情况下的应急路径规划
技术挑战:
- 超大规模状态空间(百万级路口)
- 非稳态交通流模式
- 多目标优化(效率、安全、环保)
6.2 自动化仓储物流
典型应用:
- 货架布局动态优化
- 多AGV协同路径规划
- 订单拣选序列优化
效益分析:
- 某电商仓库实施后:
- 空间利用率提升35%
- 平均拣货时间缩短28%
- 能源消耗降低17%
6.3 智能建筑设计
创新应用:
- 基于人员流动的自动空间划分
- 动态隔墙系统
- 采光与通风多目标优化
案例研究:
- 某智能办公楼项目:
- 会议室使用率提升40%
- 能源效率评级达到LEED白金级
- 员工满意度提高25%
7. 工具和资源推荐
7.1 学习资源推荐
7.1.1 书籍推荐
- 《Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction》 - Richard S. Sutton
- 《Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics》 - Jean-Claude Latombe
- 《Space Planning Basics》 - Mark Karlen
7.1.2 在线课程
- MIT OpenCourseWare: “Principles of Autonomy and Decision Making”
- Coursera: “Robotics: Computational Motion Planning”
- Udacity: “Artificial Intelligence for Robotics”
7.1.3 技术博客和网站
- OpenAI Blog (https://openai.com/blog/)
- IEEE Robotics and Automation Society
- ArchDaily智能建筑专栏
7.2 开发工具框架推荐
7.2.1 IDE和编辑器
- VS Code with Python/Jupyter插件
- PyCharm Professional(支持远程开发)
- JupyterLab(交互式数据分析)
7.2.2 调试和性能分析工具
- PyTorch Profiler
- cProfile + SnakeViz
- Wireshark(用于多Agent通信分析)
7.2.3 相关框架和库
- ROS (Robot Operating System)
- OpenAI Gym(强化学习环境)
- PyBullet(物理仿真)
- GDAL(地理空间数据处理)
7.3 相关论文著作推荐
7.3.1 经典论文
- “Dynamic Programming” - Richard Bellman (1957)
- “Q-Learning” - Watkins & Dayan (1992)
- “RRT-Connect: An Efficient Approach to Single-Query Path Planning” - Kuffner & LaValle (2000)
7.3.2 最新研究成果
- “Multi-Agent Path Finding: Definitions, Variants, and Benchmarks” - Stern et al. (2019)
- “Learning to Plan in High Dimensions via Neural Exploration-Exploitation Trees” - Wang et al. (2021)
- “Urban Space Planning Optimization Using Deep Reinforcement Learning” - Chen et al. (2022)
7.3.3 应用案例分析
- Amazon Robotics: “Kiva System Implementation”
- Alibaba: “Smart Warehouse Optimization”
- Sidewalk Labs: “Toronto Quayside Project”
8. 总结:未来发展趋势与挑战
8.1 技术发展趋势
-
多模态融合:
- 结合视觉、LiDAR、RFID等多源数据
- 跨模态表征学习提升感知能力
-
人机协作:
- 混合主动式规划系统
- 自然语言交互界面
-
持续学习:
- 非稳态环境下的在线学习
- 灾难性遗忘缓解技术
8.2 关键挑战
-
可解释性:
- 黑箱决策的信任问题
- 符合建筑规范和安全标准
-
计算效率:
- 大规模实时规划需求
- 边缘计算与云端协同
-
伦理与隐私:
- 人员移动数据的使用边界
- 算法偏见与公平性
8.3 商业化前景
-
市场预测:
- 全球智能空间规划市场年复合增长率(CAGR)预计达24.7%(2023-2030)
- 主要增长领域:智慧物流、智能建筑、零售空间优化
-
商业模式创新:
- 规划即服务(PaaS)平台
- 数字孪生订阅模式
- 效果付费(Outcome-based)合约
9. 附录:常见问题与解答
Q1:如何平衡空间利用率与人员舒适度?
A:建议采用多目标优化框架,将舒适度指标(如人均面积、采光系数)作为约束条件或优化目标之一。可以通过问卷调查或传感器数据量化舒适度,并设置权重系数。
Q2:在小样本场景下如何训练有效的规划模型?
A:可采用以下策略:
- 迁移学习:预训练于仿真环境,微调于真实场景
- 数据增强:通过几何变换生成多样化样本
- 基于模型的强化学习:构建环境动力学模型
Q3:如何处理规划系统中的不确定性?
A:推荐方法包括:
- 概率路线图(PRM):考虑障碍物位置不确定性
- 鲁棒优化:最坏情况下的性能保证
- 实时重规划:持续监测环境变化
Q4:多Agent系统如何避免死锁?
A:常用解决方案:
- 资源预约机制
- 优先级规则(如右侧通行)
- 死锁检测与恢复算法
- 集中式协调层
10. 扩展阅读 & 参考资料
-
经典教材:
- Russell, S., & Norvig, P. (2020). Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach. Pearson.
- LaValle, S. M. (2006). Planning Algorithms. Cambridge University Press.
-
行业报告:
- McKinsey: “The Future of Automated Warehousing” (2023)
- Gartner: “Hype Cycle for Smart City Technologies” (2023)
-
开源项目:
- OMPL (Open Motion Planning Library)
- RLlib (Scalable Reinforcement Learning)
- Habitat-Sim (Facebook 3D仿真平台)
-
标准规范:
- ISO 12100:2010 - 机械安全标准
- ANSI/RIA R15.08 - 工业移动机器人安全标准
- LEED v4.1 - 绿色建筑认证体系
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献115条内容
已为社区贡献115条内容







所有评论(0)