【c++】用哈希表封装myunordered_map和myunordered_set
SGI-STL30版本源代码中没有unordered_map和unordered_set,SGI-STL30版本是C++11之前的STL版本,这两个容器是C++11之后才更新的。全类似,复⽤同⼀个hashtable实现key和key/value结构,hash_set传给hash_table的是两个key,hash_map传给hash_table的是pair<const key, value>需要注
·
目录
2. 模拟实现unordered_map和unordered_set
1. 源码及框架分析
SGI-STL30版本源代码中没有unordered_map和unordered_set,SGI-STL30版本是C++11之前的STL版本,这两个容器是C++11之后才更新的。但是SGI-STL30实现了哈希表,只容器的名字是hash_map和hash_set,他是作为⾮标准的容器出现的,⾮标准是指⾮C++标准规定必须实现的,源代码在hash_map/hash_set/stl_hash_map/stl_hash_set/stl_hashtable.h中hash_map和hash_set的实现结构框架核⼼部分截取出来如下:
//stl_hash_set
template<class Value,class HashFcn=hash<Value>,class EqualKey=equal_to<Value>,class Alloc=alloc>
class hash_set
{
private:
typedef hashtable<Value, Value, HashFcn, identity<Value>, EqualKey, Alloc>ht;
ht rep;
public:
typedef typename ht::key_type key_type;
typedef typename ht::value_type value_type;
typedef typename ht::hasher hasher;
typedef typename ht::key_equal key_equal;
typedef typename ht::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename ht::const_iterator const_iterator;
hasher hash_funct()const
{
return rep.hash.funct();
}
key_equal key_eq()const
{
return rep.key_eq();
}
};
//stl_hash_map
template<class Key, class T, class HashFcn = hash<Key>, class EqualKey = equal_to<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class hash_map
{
private:
typedef hashtable < pair<const Key, T>, Key, HashFcn, select<pair<const Key, T>, EqualKey, Alloc>ht;
ht rep;
public:
typedef typename ht::key_type key_type;
typedef T data_type;
typedef T mapped_type;
typedef typename ht::value_type value_type;
typedef typename ht::hasher hasher;
typedef typename ht::key_equal key_equal;
typedef typename ht::iterator iterator;
typedef typename ht::const_iterator const_iterator;
};
//stl_hashtable.h
template<class Value,class Key,class HashFcn,class ExtractKey,class EqualKey,class Alloc>
class hashtable
{
public:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Value value_type;
typedef HashFcn hasher;
typedef EqualKey key_equal;
private:
hasher hash;
key_equal equals;
ExtractKey get_key;
typedef __hashtable_node<Value> node;
vector<node*, Alloc> buckets;
size_type num_elements;
public:
typedef __hashtable_iterator<Value, Key, HashFcn, ExtractKey, EqualKey, Alloc> iterator;
pair<iterator, bool> insert_unique(const value_type& obj);
const_iterator find(const key_type& key)const;
};
template<class Value>
struct __hashtable_node
{
__hashtable_node* next;
Value val;
};
• 这⾥我们就不再画图分析了,通过源码可以看到,结构上hash_map和hash_set跟map和set的完
全类似,复⽤同⼀个hashtable实现key和key/value结构,hash_set传给hash_table的是两个key,hash_map传给hash_table的是pair<const key, value>
• 需要注意的是源码⾥⾯跟map/set源码类似,命名⻛格⽐较乱,这⾥⽐map和set还乱,hash_set
模板参数居然⽤的Value命名,hash_map⽤的是Key和T命名,可⻅⼤佬有时写代码也不规范,乱
弹琴。下⾯我们模拟⼀份⾃⼰的出来,就按⾃⼰的⻛格⾛了。
2. 模拟实现unordered_map和unordered_set
2.1 实现出复用哈希表的框架,并支持insert
• 参考源码框架,unordered_map和unordered_set复⽤之前我们实现的哈希表。
• 我们这⾥相⽐源码调整⼀下,key参数就⽤K,value参数就⽤V,哈希表中的数据类型,我们使⽤
T。
• 其次跟map和set相⽐⽽⾔unordered_map和unordered_set的模拟实现类结构更复杂⼀点,但是
⼤框架和思路是完全类似的。因为HashTable实现了泛型不知道T参数导致是K,还是pair<K, V>,
那么insert内部进⾏插⼊时要⽤K对象转换成整形取模和K⽐较相等,因为pair的value不参与计算取
模,且默认⽀持的是key和value⼀起⽐较相等,我们需要时的任何时候只需要⽐较K对象,所以我
们在unordered_map和unordered_set层分别实现⼀个MapKeyOfT和SetKeyOfT的仿函数传给
HashTable的KeyOfT,然后HashTable中通过KeyOfT仿函数取出T类型对象中的K对象,再转换成
整形取模和K⽐较相等,具体细节参考如下代码实现。
//myunderedset.h
namespace kkk
{
template<class K,class Hash=HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
bool insert(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Insert(key);
}
private:
hash_buckek::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
};
}
//myunorderedmap.h
namespace lll
{
template<class K,class V,class Hash=HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
private:
hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
};
}
//hashtable.h
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
namespace hash_bucket
{
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
T _data;
HashNode<T>* _next;
HashNode(const T&data)
:_data(data)
,_next(nullptr)
{ }
};
}
// 实现步骤:
// 1、实现哈希表
// 2、封装unordered_map和unordered_set的框架 解决KeyOfT
// 3、iterator
// 4、const_iterator
// 5、key不⽀持修改的问题
// 6、operator[]
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT,class Hash>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
inline unsigned long __stl_next_prime(unsigned long n)
{
static const int __stl_num_prime = 28;
static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_prime] =
{
53, 97, 193, 389, 769,
1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,
1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,
50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,
1610612741, 3221225473, 4294967291
};
const unsigned long* first = __stl_prime_list;
const unsigned long* last = __stl_prime_list * __stl_num_primes;
const unsigned long* pos = lower_bound(first, last, n);
return pos == last ? *(last - 1) : *pos;
}
public:
HashTable()
{
_tables.resize(__stl_next_prime(_tables.size()), nullptr);
}
~HashTable()
{
//依次把每个桶释放
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
KeyOfT kot;
if (Find(kot(data)))
return false;
Hash hs;
size_t hashi = hs(kot(data)) % _tables.size();
//负载因子==1扩容
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
vector<Node*> newtables(__stl_next_prime(_tables.size()), nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
//旧表中节点,挪动新表重新映射的位置
size_t hashi = hs(kot(cur->_data)) % newtables.size();
//头插到新表
cur->_next = newtables[hashi];
newtables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
_tables.swap(newtables);
}
//头插
Node* newnode = new Node(data);
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return true;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;//指针数组
size_t _n = 0;//表中存储数据个数
};
2.2 支持iterator的实现
iterator核心源代码
template<class Value,class Key,class HashFcn,class ExtractKey,class EqualKey,class Alloc>
struct __hashtable_iterator
{
typedef hashtable<Value, Key, HashFcn, ExtractKey, EqualKey, Alloc>
hashtable;
typedef __hashtable_iterator_iterator<Value, Key, HashFcn, ExtractKey, EqualKey, Alloc>
iterator;
typedef __hashtable_const_iterator<Value, Key, HashFcn, ExtractKey, EqualKey, Alloc>
const_iterator;
typedef __hashtable_node<Value> node;
typedef forward_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef Value value_type;
node* cur;
hashtable* ht;
__hashtable_iterator(node*n,hashtable*tab):cur(n),ht(tab){}
__hashtable_iterator(){}
reference operator*()const { return cur->val; }
#ifndef __SGI_STL_NO_ARROW_OPERATOR
pointer operator->()const { return &(operator*()); }
#endif
iterator& operator++();
iterator operator++(int);
bool operator==(const iterator& it)const { return cur == it.cur; }
bool operator!=(const iterator& it)const { return cur != it.cur; }
};
template<class V,class K,class HF,class ExK,class EqK,class A>
__hashtable_iterator<V,K,HF,ExK,EqK,A>&
__hashtable_iterator<V, K, HF, ExK, EqK, A>::operator++()
{
const node* old = cur;
cur = cur->next;
if (!cur)
{
size_type bucket = ht->bkt_num(old->val);
while (!cur && ++bucket < ht->buckets.size())
cur = ht->buckets[bucket];
}
return *this;
}
iterator实现思路分析
• iterator实现的⼤框架跟list的iterator思路是⼀致的,⽤⼀个类型封装结点的指针,再通过重载运算
符实现,迭代器像指针⼀样访问的⾏为,要注意的是哈希表的迭代器是单向迭代器。
• 这⾥的难点是operator++的实现。iterator中有⼀个指向结点的指针,如果当前桶下⾯还有结点,
则结点的指针指向下⼀个结点即可。如果当前桶⾛完了,则需要想办法计算找到下⼀个桶。这⾥的
难点是反⽽是结构设计的问题,参考上⾯的源码,我们可以看到iterator中除了有结点的指针,还
有哈希表对象的指针,这样当前桶⾛完了,要计算下⼀个桶就相对容易多了,⽤key值计算出当前
桶位置,依次往后找下⼀个不为空的桶即可。
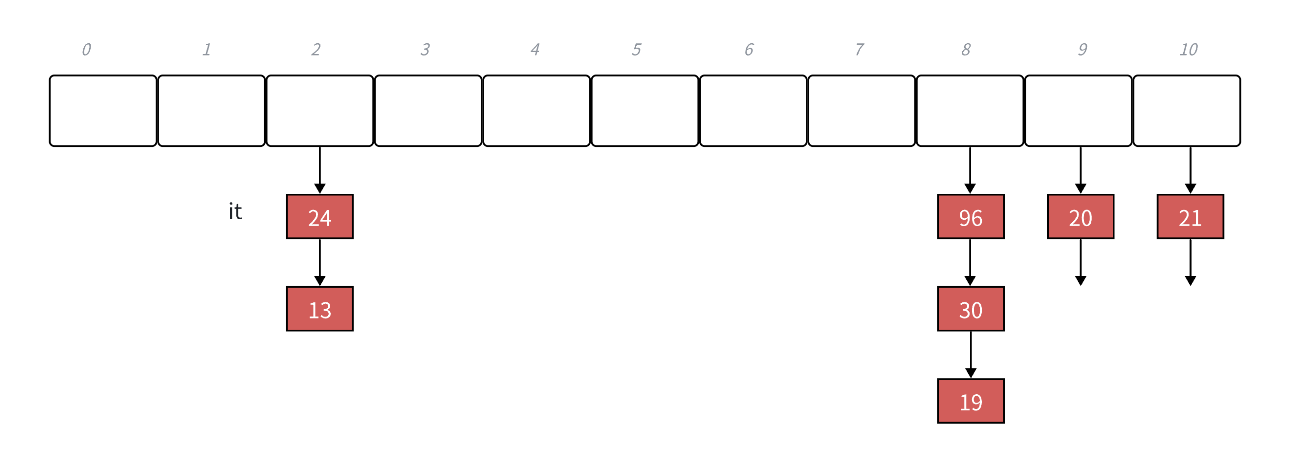
• begin()返回第⼀个桶中第⼀个节点指针构造的迭代器,这⾥end()返回迭代器可以⽤空表⽰。
• unordered_set的iterator也不⽀持修改,我们把unordered_set的第⼆个模板参数改成const K即
可, HashTable<K, const K , SetKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
• unordered_map的iterator不⽀持修改key但是可以修改value,我们把unordered_map的第⼆个
模板参数pair的第⼀个参数改成const K即可, HashTable<K, pair<const K, V> ,
MapKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
• ⽀持完整的迭代器还有很多细节需要修改,具体参考下⾯题的代码。
2.3 map支持[]
• unordered_map要⽀持[]主要需要修改insert返回值⽀持,修改HashTable中的insert返回值为
pair<Iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
• 有了insert⽀持[]实现就很简单了,具体参考下⾯代码实现
2.4 实现
myunorderedmap.h
namespace lll
{
template<class K,class V,class Hash=HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.End();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _ht.Begin();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _ht.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool>insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
private:
hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
};
void test_map()
{
unordered_map<string, string>dict;
dict.insert({ "sort","paixu" });
dict.insert({ "left","zuobian" });
dict.insert({ "right","youbian" });
dict["left"] = "zuobian,shenyu";
dict["insert"] = "charu";
dict["string"];
unordered_map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict, end())
{
it->second += 'x';
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
myunderedset.h
namespace kkk
{
template<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, const K, SetKeyOfT, Hash>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, const K, SetKeyOfT, Hash>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.BEgin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.End();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _ht.Begin();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _ht.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Insert(key);
}
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
private:
hash_bucket::HashTable<K, const K, SetKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
};
void test_set()
{
unordered_set<int> s;
int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14, 3,3,15 };
for (auto e : a)
{
s.insert(e);
}
for (auto e : s)
{
std::cout << e << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
std::cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
hashtable.h
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
// 特化
template<>
184 struct HashFunc<string>
185 {
186 size_t operator()(const string& key)
187 {
188 size_t hash = 0;
189 for (auto e : key)
190 {
191 hash *= 131;
192 hash += e;
193 }
194
195 return hash;
196 }
197 };
198
199 namespace hash_bucket
200 {
201 template<class T>
202 struct HashNode
203 {
204 T _data;
205 HashNode<T>* _next;
206
207 HashNode(const T& data)
208 :_data(data)
209 ,_next(nullptr)
210 {}
211 };
212
213 // 前置声明
214 template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
215 class HashTable;
216
217 template<class K, class T, class Ptr, class Ref, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
218 struct HTIterator
219 {
220 typedef HashNode<T> Node;
221 typedef HTIterator<K, T, Ptr, Ref, KeyOfT, Hash> Self;
222
223 Node* _node;
224 const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* _pht;
225
226 HTIterator(Node* node, const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* pht)
227 :_node(node)
228 ,_pht(pht)
229 {}
230
231 Ref operator*()
232 {
233 return _node->_data;
234 }
235
236 Ptr operator->()
237 {
238 return &_node->_data;
239 }
240
241 bool operator!=(const Self& s)
242 {
243 return _node != s._node;
244 }
245
246 Self& operator++()
247 {
248 if (_node->_next)
249 {
250 // 当前桶还有节点
251 _node = _node->_next;
252 }
253 else
254 {
255 // 当前桶⾛完了,找下⼀个不为空的桶
256 KeyOfT kot;
257 Hash hs;
258 size_t hashi = hs(kot(_node->_data)) % _pht-
>_tables.size();
259 ++hashi;
260 while (hashi < _pht->_tables.size())
261 {
262 if (_pht->_tables[hashi])
263 {
264 break;
265 }
266
267 ++hashi;
268 }
269
270 if (hashi == _pht->_tables.size())
271 {
272 _node = nullptr; // end()
273 }
274 else
275 {
276 _node = _pht->_tables[hashi];
277 }
278 }
279
280 return *this;
281 }
282 };
283
284 template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
285 class HashTable
286 {
287 // 友元声明
288 template<class K, class T, class Ptr, class Ref, class KeyOfT, class
Hash>
289 friend struct HTIterator;
290
291 typedef HashNode<T> Node;
292 public:
293 typedef HTIterator<K, T, T*, T&, KeyOfT, Hash> Iterator;
294 typedef HTIterator<K, T, const T*, const T&, KeyOfT, Hash>
ConstIterator;
295
296 Iterator Begin()
297 {
298 if (_n == 0)
299 return End();
300
301 for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
302 {
303 Node* cur = _tables[i];
304 if (cur)
305 {
306 return Iterator(cur, this);
307 }
308 }
309
310 return End();
311 }
312
313 Iterator End()
314 {
315 return Iterator(nullptr, this);
316 }
317
318 ConstIterator Begin() const
319 {
320 if (_n == 0)
321 return End();
322
323 for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
324 {
325 Node* cur = _tables[i];
326 if (cur)
327 {
328 return ConstIterator(cur, this);
329 }
330 }
331
332 return End();
333 }
334
335 ConstIterator End() const
336 {
337 return ConstIterator(nullptr, this);
338 }
339
340 inline unsigned long __stl_next_prime(unsigned long n)
341 {
342
343 static const int __stl_num_primes = 28;
344 static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_primes] =
345 {
346 53, 97, 193, 389, 769,
347 1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
348 49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,
349 1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,
350 50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,
351 1610612741, 3221225473, 4294967291
352 };
353
354 const unsigned long* first = __stl_prime_list;
355 const unsigned long* last = __stl_prime_list +
__stl_num_primes;
356 const unsigned long* pos = lower_bound(first, last, n);
357 return pos == last ? *(last - 1) : *pos;
358 }
359
360 HashTable()
361 {
362 _tables.resize(__stl_next_prime(_tables.size()), nullptr);
363 }
364
365 ~HashTable()
366 {
367 // 依次把每个桶释放
368 for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
369 {
370 Node* cur = _tables[i];
371 while (cur)
372 {
373 Node* next = cur->_next;
374 delete cur;
375 cur = next;
376 }
377 _tables[i] = nullptr;
378 }
379 }
380
381 pair<Iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
382 {
383 KeyOfT kot;
384 Iterator it = Find(kot(data));
385 if (it != End())
386 return make_pair(it, false);
387
388 Hash hs;
389 size_t hashi = hs(kot(data)) % _tables.size();
390
391 // 负载因⼦==1扩容
392 if (_n == _tables.size())
393 {
394
395 vector<Node*>
newtables(__stl_next_prime(_tables.size()+1), nullptr);
396 for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
397 {
398 Node* cur = _tables[i];
399 while (cur)
400 {
401 Node* next = cur->_next;
402
403 // 旧表中节点,挪动新表重新映射的位置
404 size_t hashi = hs(kot(cur->_data)) %
newtables.size();
405 // 头插到新表
406 cur->_next = newtables[hashi];
407 newtables[hashi] = cur;
408
409 cur = next;
410 }
411
412 _tables[i] = nullptr;
413 }
414
415 _tables.swap(newtables);
416 }
417
418 // 头插
419 Node* newnode = new Node(data);
420 newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
421 _tables[hashi] = newnode;
422 ++_n;
423
424 return make_pair(Iterator(newnode, this), true);
425 }
426
427 Iterator Find(const K& key)
428 {
429 KeyOfT kot;
430 Hash hs;
431 size_t hashi = hs(key) % _tables.size();
432 Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
433 while (cur)
434 {
435 if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
436 {
437 return Iterator(cur, this);
438 }
439
440 cur = cur->_next;
441 }
442
443 return End();
444 }
445
446 bool Erase(const K& key)
447 {
448 KeyOfT kot;
449 Hash hs;
450
451 size_t hashi = hs(key) % _tables .size();
452 Node* prev = nullptr;
453 Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
454 while (cur)
455 {
456 if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
457 {
458 if (prev == nullptr)
459 {
460 _tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
461 }
462 else
463 {
464 prev->_next = cur->_next;
465 }
466
467 delete cur;
468 --_n;
469 return true;
470 }
471
472 prev = cur;
473 cur = cur->_next;
474 }
475
476 return false;
477 }
478 private:
479 vector<Node*> _tables; // 指针数组
480 size_t _n = 0; // 表中存储数据个数
481 };
482 }
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容







所有评论(0)