强化学习 [page14][chapter7] Q-learning
当智能体。
本篇学习RL中经典的Q-learning 算法,其是学习目的是最优的action value,跟前面学的SARSA
只有一个差异

目录
- SARSA vs Q-learning 伪代码
- On-policy vs Off-policy
- Q-learning
- Q-learning 例子
- python 代码实现 (机器人走迷宫例子)
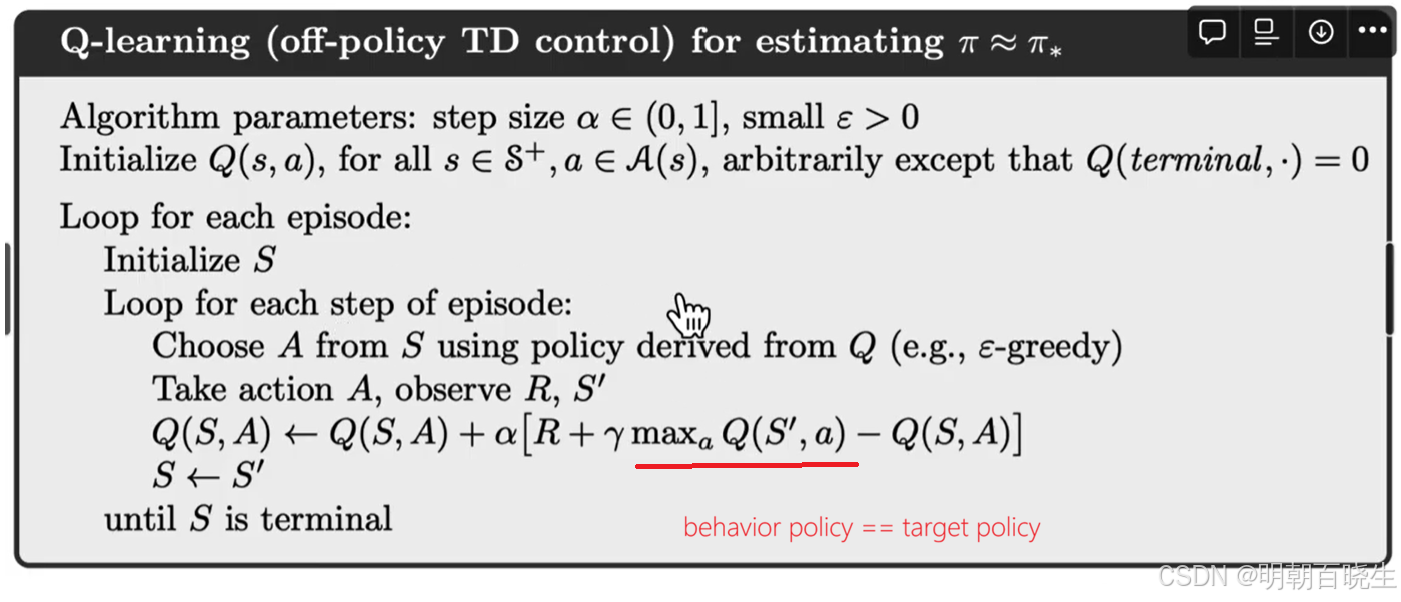
一 SARSA vs Q-learning 伪代码
以下是SARSA和Q-learning算法的伪代码实现,两者的核心区别在于:SARSA采用 on-policy方法 训练 ,而Q-learning 采用 off-policy 方法 训练 
二 off-Policy vs on-Policy
在强化学习中,智能体通过与环境互动来学习最优策略,以获得最大化的累积奖励。根据学习过程中使用的行为策略和目标策略是否相同,可将学习方法分为两大类:On-policy 和 Off-policy
2.1 Behaviour Policy vs Target Policy
策略是智能体在给定状态下选择行动的决策规则。在无模型强化学习中,智能体通过与环境的直接交互(行动-奖励反馈)来学习和优化策略。
Behaviour Policy:决定智能体在环境中实际采取的行动,用于生成经验样本
Target Policy: 用于从经验中学习,更新价值函数估计,不断更新以收敛到最优策略的策略
2.2 on-policy vs off-Policy
On-policy
定义 :当智能体使用相同的策略进行探索和学习时,即Behaviour Policy与Target Policy完全一致。
特点:
直接根据当前执行的策略进行策略评估和改进
学习的是正在执行的策略的价值函数
典型的算法包括:SARSA、A2C
优点:
学习过程更稳定
对当前策略的评估更准确
局限:
探索效率可能受限
无法利用历史经验中其他策略的数据
Off-Policy
定义 :当智能体的Behaviour Policy 与 Target Policy不同时,即用于生成经验数据的策略与用于学习的策略是分离的。
特点:
可以从其他智能体或旧策略生成的数据中学习
行为策略通常更具探索性(如ε-greedy策略)
目标策略通常是待优化的最优策略
典型的算法包括:Q-learning、DDPG、TD3
优点:
数据利用率更高
支持从人类演示、其他智能体或历史数据中学习
探索与利用可以更灵活地分离
挑战:
需要处理分布偏移问题
学习过程可能更不稳定
2.3 技术对比
| 特性 | On-policy学习 | Off-policy学习 |
|---|---|---|
| 策略关系 | 行为策略 = 目标策略 | 行为策略 ≠ 目标策略 |
| 数据使用 | 必须使用当前策略生成的新数据 | 可使用任何策略生成的历史数据 |
| 学习效率 | 数据效率较低 | 数据效率较高 |
| 稳定性 | 相对更稳定 | 可能更不稳定 |
| 典型算法 | SARSA, REINFORCE, A2C | Q-learning, DQN, DDPG |
三 Q-learning
Q-learning 算法如下:
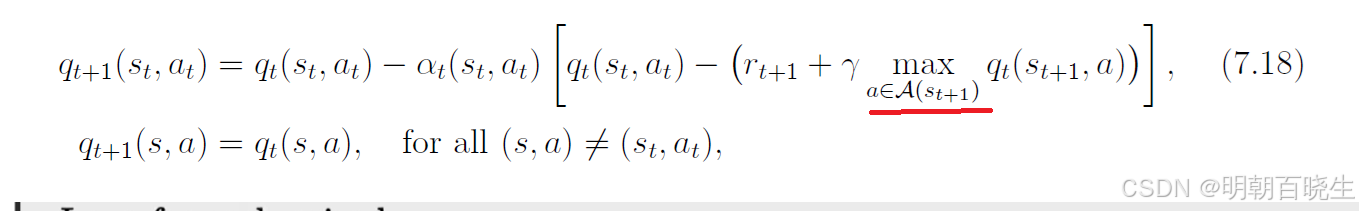
其中,t = 0, 1, 2, ...。这里, 是
的最优动作值估计
Q-learning 的表达式与 Sarsa 相似,二者仅在时序差分(TD)target上有所不同:
Q-learning 的 TD 目标是 ,
而 Sarsa 的 TD 目标是 。
此外,给定后:
Sarsa 每次迭代都需要,
而 Q-learning 只需要
为什么 Q-learning 被设计为(7.18)中的表达式?它在数学上实现了什么?
Q-learning 是一种用于求解以下方程的随机逼近算法:
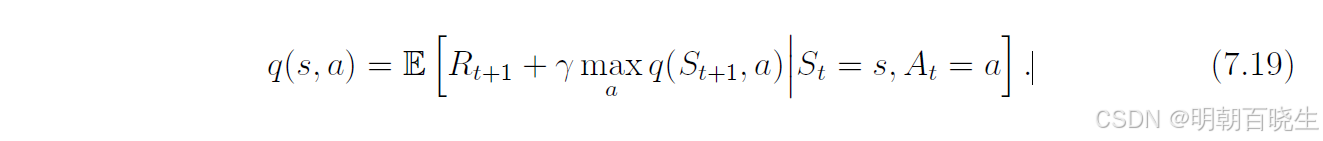
这是用动作值函数表达的贝尔曼最优方程。
四 Q-learning 例子
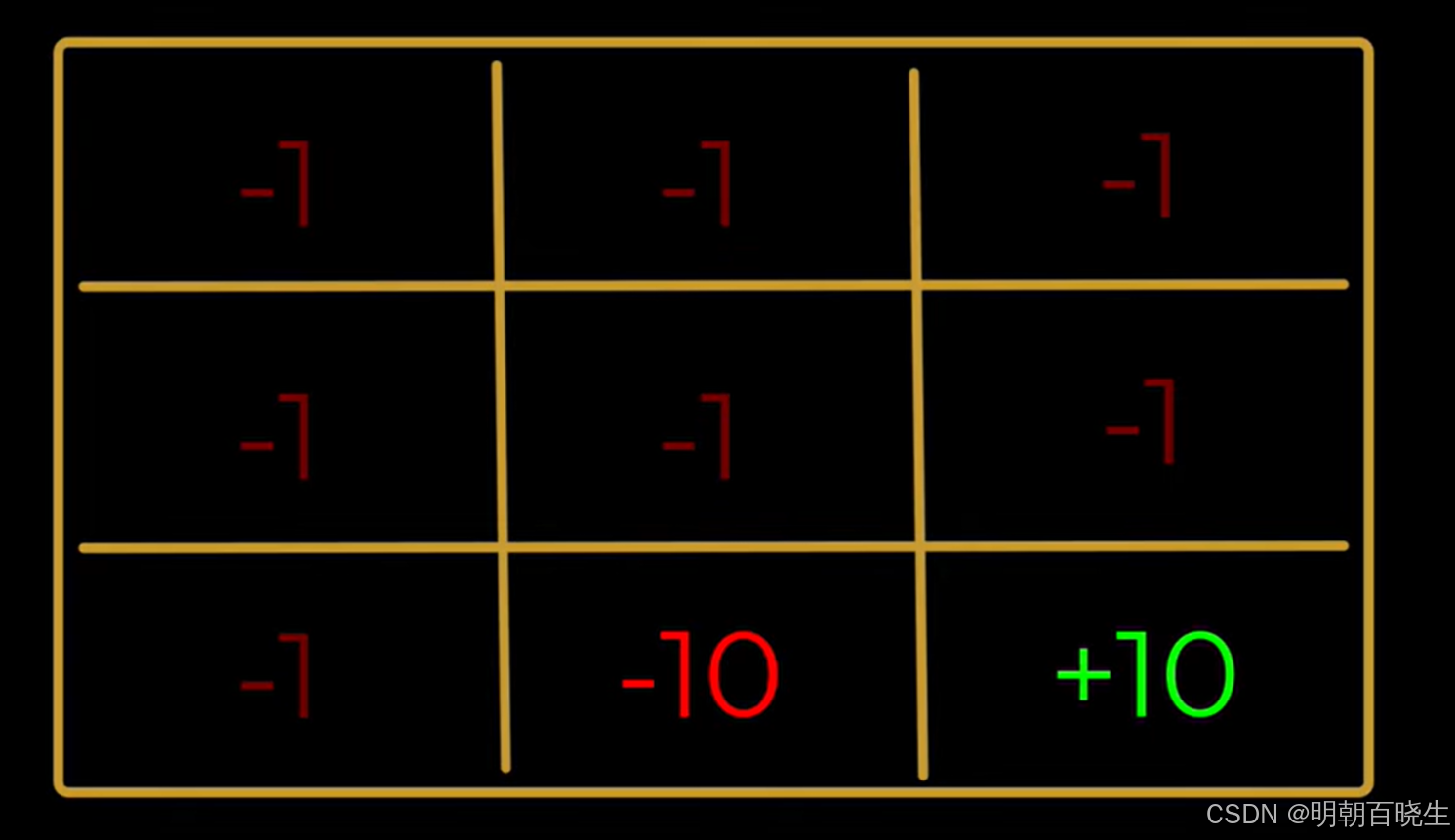
以走迷宫为例,已知条件如下:
环境:
1 在不同state 下面的奖励
2: target Policy 和 Behavior Policy
Target Policy: the policy the agent is trying to learn
Behavior Policy: the policy the agent uses to learn the target policy
这里面的两种策略如下:
Behavior Policy :是一个随机策略,允许智能体以等概率向任意可行动作方向移动。
Target Policy: 是一个预定义的、已知的策略,例如从其他智能体或历史环境中学习得到的策略,如下
训练过程
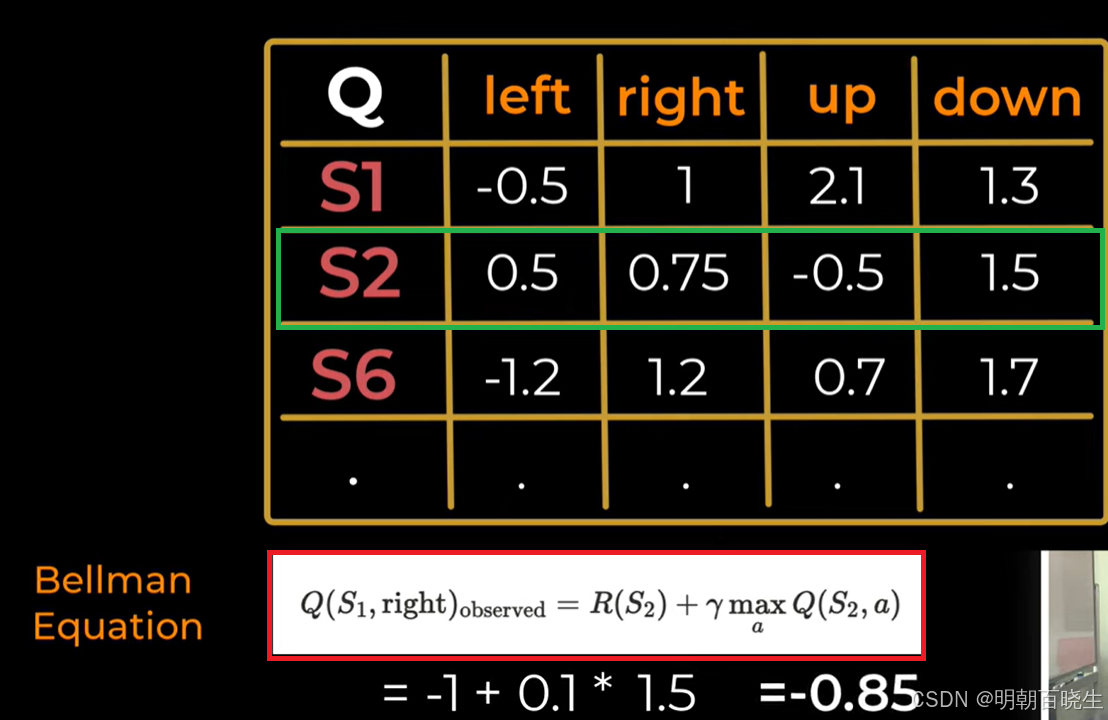
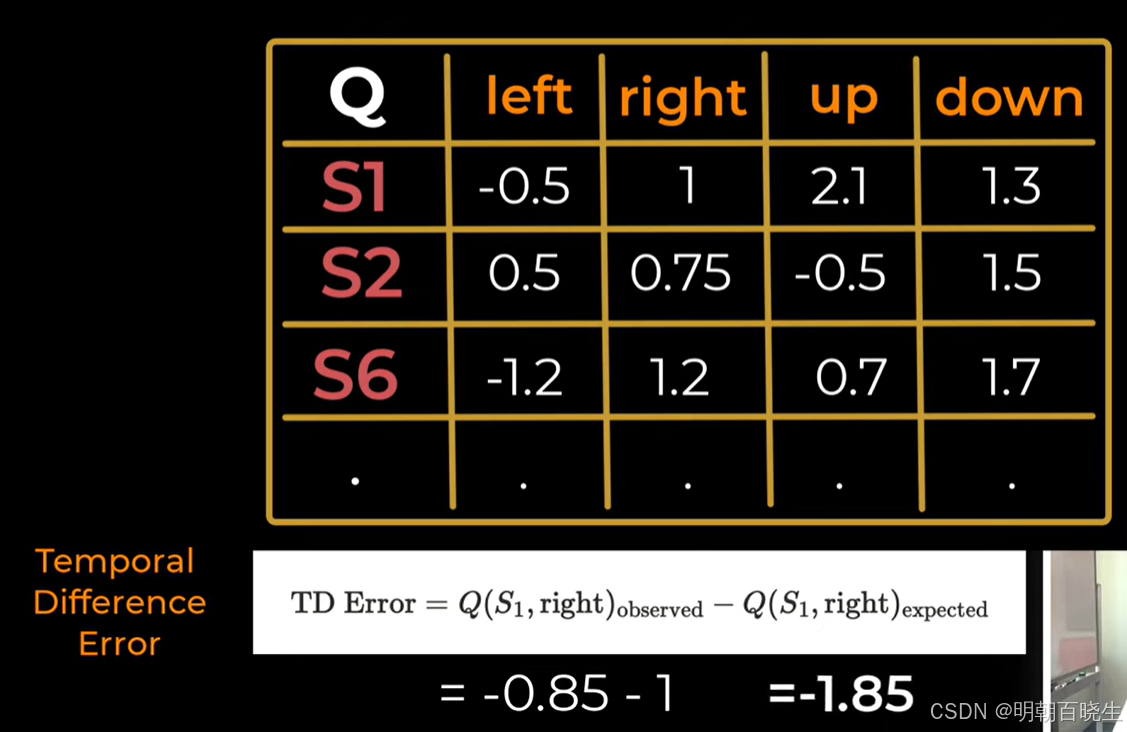
第一步 假设Agent 从S1开始,假设产生的动作为right
计算 TD Target(目标值)
计算 TD Error(时序差分误差)
更新 Q 值
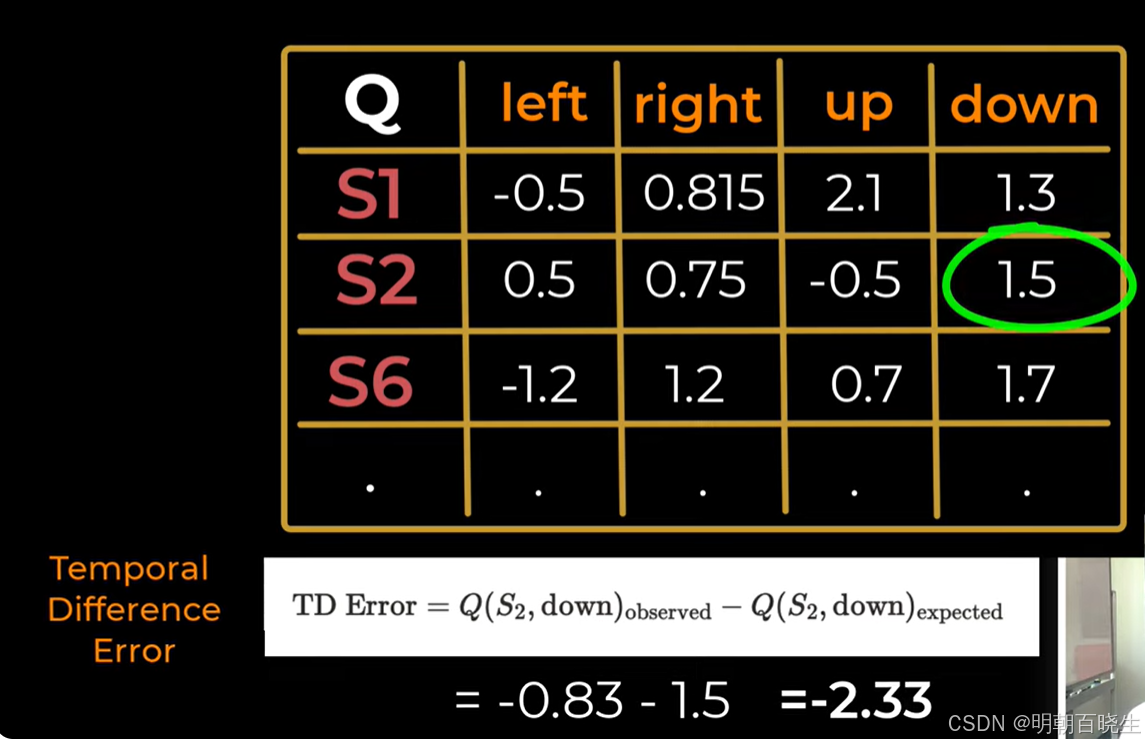
第二步: 在S2选择了down动作
计算 TD Target(目标值)
计算 TD Error(时序差分误差)
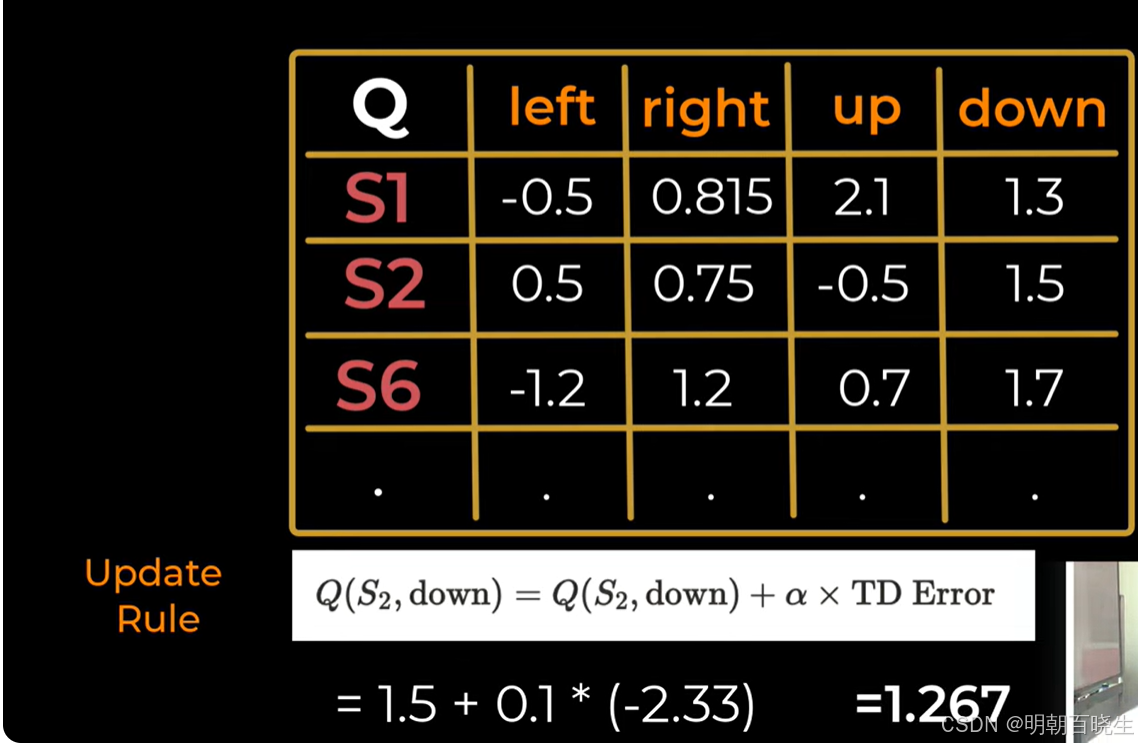
更新 Q 值
五 python 代码实现 (机器人走迷宫例子)
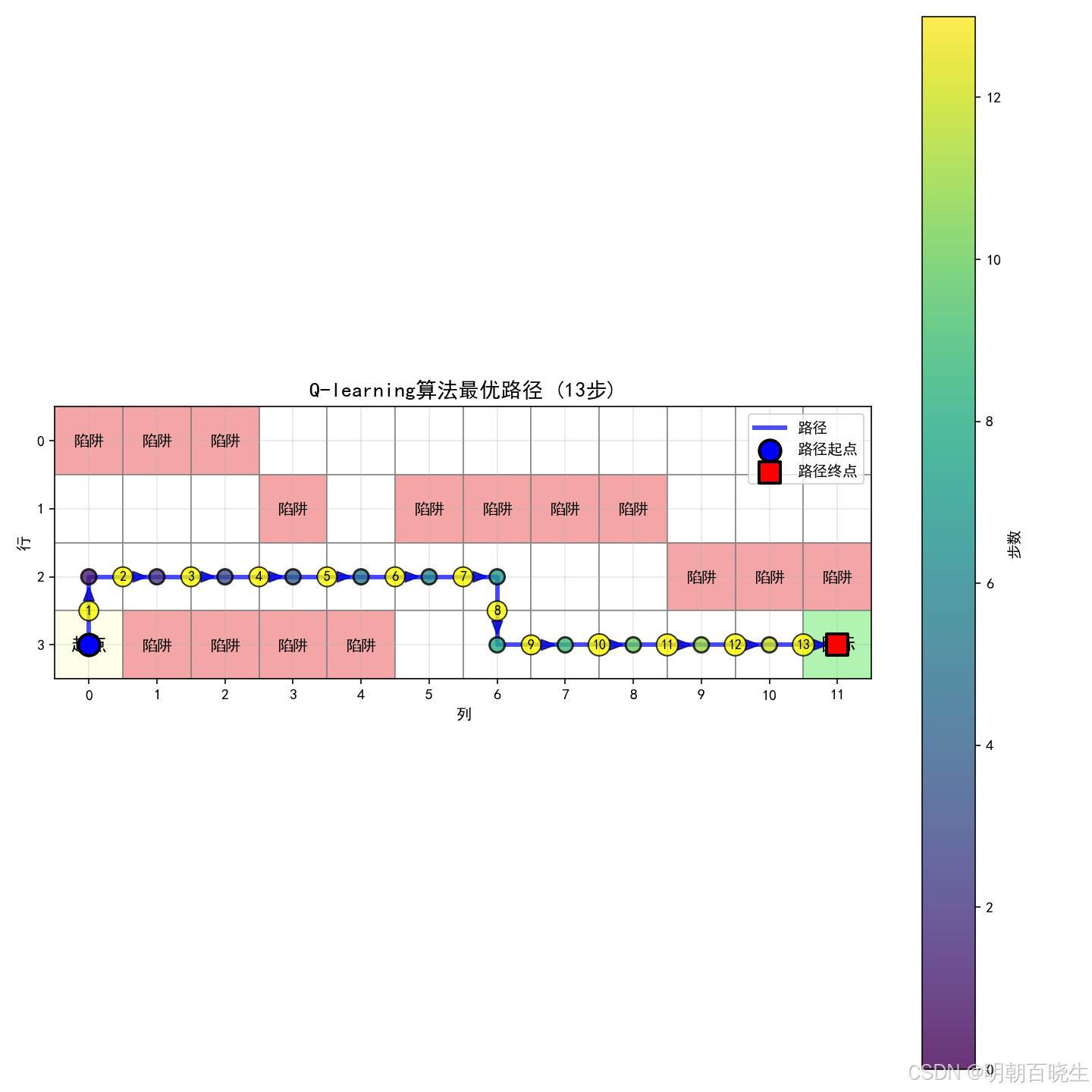
SARSA(on-policy):
行为策略:ε-贪婪(用于选择动作)
目标策略:ε-贪婪(用于更新Q值,与行为策略相同)
使用下一个实际执行的动作a'进行更新
Q-learning(off-policy):
行为策略:ε-贪婪(用于选择动作)
目标策略:贪婪(用于更新Q值,与行为策略不同)
使用下一个状态的最大Q值进行更新
1: agent.py
"""
强化学习算法在网格世界环境中的实现:SARSA vs Q-learning
作者:chengxf
日期:2025年12月
文件名:agent.py
描述:
在复杂网格世界环境中实现SARSA和Q-learning算法,包含行为策略和目标策略逻辑
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from typing import Tuple, List, Dict, Any, Optional
from grid_world import GridWorldEnvironment, Action
from enum import Enum
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
class AlgorithmType(Enum):
"""算法类型枚举"""
SARSA = "sarsa"
Q_LEARNING = "q_learning"
class BaseAgent:
"""
强化学习智能体基类
包含SARSA和Q-learning共用的功能
"""
def __init__(
self,
env: GridWorldEnvironment,
learning_rate: float = 0.1,
discount_factor: float = 0.9,
epsilon: float = 0.1,
epsilon_decay: float = 0.995,
epsilon_min: float = 0.01,
initial_q_value: float = 0.0
):
"""
初始化智能体基类
参数:
env: 网格世界环境
learning_rate: 学习率 (α)
discount_factor: 折扣因子 (γ)
epsilon: 探索率 (ε)
epsilon_decay: ε衰减率
epsilon_min: 最小ε值
initial_q_value: 初始Q值
"""
self.env = env
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.discount_factor = discount_factor
self.epsilon = epsilon
self.epsilon_init = epsilon
self.epsilon_decay = epsilon_decay
self.epsilon_min = epsilon_min
self.initial_q_value = initial_q_value
# 初始化Q表:状态 → 动作 → 值
self.q_table = self._initialize_q_table()
# 训练统计信息
self.episode_count = 0
self.total_steps = 0
self.total_reward = 0.0
# 性能记录
self.episode_rewards = []
self.episode_steps = []
self.epsilon_history = []
self.td_error_history = []
# 最佳路径记录
self.best_reward = float('-inf')
self.best_q_table = None
self.best_path = []
self.best_actions = [] # 存储最佳路径的动作序列
# 最优策略路径记录
self.optimal_path = None
self.optimal_actions = None
# 调试信息
self.debug_info = []
self._setup_matplotlib_fonts()
def _setup_matplotlib_fonts(self) -> None:
"""设置matplotlib字体"""
try:
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei', 'Microsoft YaHei', 'DejaVu Sans']
except Exception:
pass
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
def _initialize_q_table(self) -> Dict[Tuple[int, int], Dict[Action, float]]:
"""
初始化Q表
返回:
Dict: 嵌套字典格式的Q表
"""
q_table = {}
rows, cols = self.env.rows, self.env.cols
for row in range(rows):
for col in range(cols):
state = (row, col)
q_table[state] = {}
# 为所有动作设置初始值
for action in Action:
if state in self.env.trap_positions:
q_table[state][action] = -10.0 # 陷阱的负奖励
elif state == self.env.goal_position:
q_table[state][action] = 10.0 # 目标的正奖励
else:
q_table[state][action] = self.initial_q_value
return q_table
def _is_terminal_state(self, state: Tuple[int, int]) -> bool:
"""
检查是否为终止状态
参数:
state: 待检查的状态
返回:
bool: 如果是终止状态返回True
"""
#or state in self.env.trap_positions
return state == self.env.goal_position
def _get_available_actions(self, state: Tuple[int, int]) -> List[Action]:
"""
获取状态下的可用动作
参数:
state: 当前状态
返回:
List[Action]: 可用动作列表
"""
available_actions = []
for action in Action:
next_state, _, _ = self.env.step_simulate(state, action)
if next_state is not None: # 动作有效
available_actions.append(action)
return available_actions
def _get_greedy_action(self, state: Tuple[int, int],
available_actions: List[Action]) -> Action:
"""
基于当前Q值获取贪婪动作
参数:
state: 当前状态
available_actions: 可用动作列表
返回:
Action: 贪婪动作
"""
if not available_actions:
return None
# 查找具有最大Q值的动作
best_action = None
best_value = float('-inf')
for action in available_actions:
q_value = self.get_q_value(state, action)
if q_value > best_value:
best_value = q_value
best_action = action
# 如果有多个相同Q值的动作,随机选择
if best_action is None:
return np.random.choice(available_actions)
return best_action
def _epsilon_greedy_action(self, state: Tuple[int, int], epsilon: float,
available_actions: List[Action]) -> Action:
"""
使用ε-贪婪策略选择动作(行为策略 behavior policy)
参数:
state: 当前状态
epsilon: 探索率
available_actions: 可用动作列表
返回:
Action: 选择的动作
"""
if not available_actions:
return None
if np.random.random() < epsilon:
# 探索:随机选择动作
return np.random.choice(available_actions)
else:
# 利用:选择贪婪动作
return self._get_greedy_action(state, available_actions)
def get_q_value(self, state: Tuple[int, int], action: Action) -> float:
"""
获取Q值
参数:
state: 状态
action: 动作
返回:
float: Q(s,a)值
"""
value = self.q_table.get(state, {}).get(action, self.initial_q_value)
return value
def set_q_value(self, state: Tuple[int, int], action: Action, value: float) -> None:
"""
设置Q值
参数:
state: 状态
action: 动作
value: 要设置的值
"""
if state not in self.q_table:
self.q_table[state] = {}
self.q_table[state][action] = value
def _decay_epsilon(self) -> None:
"""衰减探索率"""
self.epsilon = max(self.epsilon_min, self.epsilon * self.epsilon_decay)
def get_policy(self) -> Dict[Tuple[int, int], Action]:
"""
从Q表获取贪婪策略(目标策略)
返回:
Dict: 状态 → 最优动作
"""
policy = {}
for state in self.q_table:
if self._is_terminal_state(state):
continue
# 获取可用动作
available_actions = self._get_available_actions(state)
if not available_actions:
continue
# 查找具有最大Q值的动作
best_action = self._get_greedy_action(state, available_actions)
if best_action is not None:
policy[state] = best_action
return policy
def evaluate_policy(self,
num_episodes: int = 100,
max_steps: int = 200) -> Dict[str, float]:
"""
评估当前策略性能(使用目标策略)
参数:
num_episodes: 评估回合数
max_steps: 每回合最大步数
返回:
Dict: 性能指标
"""
policy = self.get_policy()
rewards = []
steps_list = []
successes = 0
for episode in range(num_episodes):
state = self.env.reset()
episode_reward = 0.0
steps = 0
done = False
while steps < max_steps and not done:
# 检查是否为终止状态
if self._is_terminal_state(state):
break
# 使用贪婪策略选择动作(目标策略)
if state in policy:
action = policy[state]
else:
# 如果状态不在策略中,使用贪婪选择
available_actions = self._get_available_actions(state)
if available_actions:
action = self._get_greedy_action(state, available_actions)
else:
break
if action is None:
break
# 执行动作
state, reward, done = self.env.step(action)
episode_reward += reward
steps += 1
rewards.append(episode_reward)
steps_list.append(steps)
if state == self.env.goal_position:
successes += 1
return {
'average_reward': np.mean(rewards),
'reward_std': np.std(rewards),
'average_steps': np.mean(steps_list),
'success_rate': successes / num_episodes,
'max_reward': np.max(rewards),
'min_reward': np.min(rewards)
}
def get_state_value_function(self) -> Dict[Tuple[int, int], float]:
"""
获取状态价值函数 V(s) = max_a Q(s,a)
返回:
Dict: 状态 → 价值
"""
value_table = {}
for state in self.q_table:
if state in self.env.trap_positions:
value_table[state] = -1.0
elif state == self.env.goal_position:
value_table[state] = 1.0
else:
# V(s) = max_a Q(s,a)
max_q = max(self.q_table[state].values(), default=float('-inf'))
value_table[state] = max_q
return value_table
def get_best_path(self, max_steps: int = 100) -> Tuple[List[Tuple[int, int]], List[Action]]:
"""
获取当前策略下的最佳路径
参数:
max_steps: 最大步数
返回:
Tuple: (状态路径, 动作序列)
"""
policy = self.get_policy()
state = self.env.reset()
path = [state]
actions = []
steps = 0
while steps < max_steps:
if self._is_terminal_state(state):
break
if state in policy:
action = policy[state]
else:
available_actions = self._get_available_actions(state)
if not available_actions:
break
action = self._get_greedy_action(state, available_actions)
if action is None:
break
actions.append(action)
state, _, done = self.env.step(action)
path.append(state)
steps += 1
if done:
break
return path, actions
def get_optimal_path(self, max_steps: int = 100, use_value_iteration: bool = False) -> Tuple[List[Tuple[int, int]], List[Action]]:
"""
获取最优策略路径(使用值迭代或当前策略)
参数:
max_steps: 最大步数
use_value_iteration: 是否使用值迭代寻找最优路径
返回:
Tuple: (状态路径, 动作序列)
"""
if use_value_iteration:
# 使用值迭代寻找最优路径
return self._find_optimal_path_by_value_iteration(max_steps)
else:
# 使用当前Q表寻找最优路径
return self._find_optimal_path_by_q_table(max_steps)
def _find_optimal_path_by_q_table(self, max_steps: int = 100) -> Tuple[List[Tuple[int, int]], List[Action]]:
"""
基于当前Q表寻找最优路径
参数:
max_steps: 最大步数
返回:
Tuple: (状态路径, 动作序列)
"""
state = self.env.reset()
path = [state]
actions = []
steps = 0
visited_states = set([state])
while steps < max_steps:
if self._is_terminal_state(state):
break
# 获取可用动作
available_actions = self._get_available_actions(state)
if not available_actions:
break
# 选择Q值最大的动作
best_action = None
best_q_value = float('-inf')
for action in available_actions:
q_value = self.get_q_value(state, action)
if q_value > best_q_value:
best_q_value = q_value
best_action = action
if best_action is None:
break
# 执行动作
actions.append(best_action)
next_state, _, done = self.env.step(best_action)
# 检查是否陷入循环
if next_state in visited_states:
# 如果陷入循环,尝试随机选择其他动作
for action in available_actions:
if action != best_action:
next_state, _, _ = self.env.step_simulate(state, action)
if next_state not in visited_states:
best_action = action
actions[-1] = best_action # 更新最后一个动作
next_state, _, done = self.env.step(best_action)
break
path.append(next_state)
visited_states.add(next_state)
state = next_state
steps += 1
if done:
break
self.optimal_path = path
self.optimal_actions = actions
return path, actions
def _find_optimal_path_by_value_iteration(self, max_steps: int = 100) -> Tuple[List[Tuple[int, int]], List[Action]]:
"""
使用值迭代寻找最优路径
参数:
max_steps: 最大步数
返回:
Tuple: (状态路径, 动作序列)
"""
# 使用值迭代计算最优价值函数
value_table = self._value_iteration()
# 基于最优价值函数寻找路径
state = self.env.reset()
path = [state]
actions = []
steps = 0
while steps < max_steps:
if self._is_terminal_state(state):
break
# 获取可用动作
available_actions = self._get_available_actions(state)
if not available_actions:
break
# 选择能到达最大价值状态的动作
best_action = None
best_next_value = float('-inf')
for action in available_actions:
next_state, _, _ = self.env.step_simulate(state, action)
if next_state is not None and next_state in value_table:
next_value = value_table[next_state]
if next_value > best_next_value:
best_next_value = next_value
best_action = action
if best_action is None:
break
# 执行动作
actions.append(best_action)
next_state, _, done = self.env.step(best_action)
path.append(next_state)
state = next_state
steps += 1
if done:
break
self.optimal_path = path
self.optimal_actions = actions
return path, actions
def _value_iteration(self, theta: float = 0.001, max_iterations: int = 1000) -> Dict[Tuple[int, int], float]:
"""
值迭代算法
参数:
theta: 收敛阈值
max_iterations: 最大迭代次数
返回:
Dict: 最优状态价值函数
"""
rows, cols = self.env.rows, self.env.cols
# 初始化价值函数
V = {}
for row in range(rows):
for col in range(cols):
state = (row, col)
if state in self.env.trap_positions:
V[state] = -10.0
elif state == self.env.goal_position:
V[state] = 10.0
else:
V[state] = 0.0
# 值迭代
for iteration in range(max_iterations):
delta = 0
V_new = V.copy()
for state in V:
if self._is_terminal_state(state):
continue
# 获取可用动作
available_actions = self._get_available_actions(state)
if not available_actions:
continue
# 计算最大价值
max_value = float('-inf')
for action in available_actions:
next_state, reward, _ = self.env.step_simulate(state, action)
if next_state is not None:
action_value = reward + self.discount_factor * V[next_state]
if action_value > max_value:
max_value = action_value
if max_value > float('-inf'):
V_new[state] = max_value
delta = max(delta, abs(V_new[state] - V[state]))
V = V_new
# 检查收敛
if delta < theta:
break
return V
def visualize_path(self, path: List[Tuple[int, int]],
actions: List[Action] = None,
title: str = "路径图",
show_arrows: bool = True) -> plt.Figure:
"""
可视化路径
参数:
path: 状态路径
actions: 动作序列(可选)
title: 图表标题
show_arrows: 是否显示箭头
返回:
plt.Figure: 图表对象
"""
if not path:
print("路径为空,无法可视化")
return None
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
rows, cols = self.env.rows, self.env.cols
# 绘制网格背景
for row in range(rows):
for col in range(cols):
# 设置单元格颜色
cell_color = 'white'
if (row, col) == self.env.start_position:
cell_color = 'lightyellow'
elif (row, col) == self.env.goal_position:
cell_color = 'lightgreen'
elif (row, col) in self.env.trap_positions:
cell_color = 'lightcoral'
rect = plt.Rectangle((col - 0.5, row - 0.5), 1, 1,
linewidth=1, edgecolor='gray',
facecolor=cell_color, alpha=0.7)
ax.add_patch(rect)
# 标记特殊位置
if (row, col) == self.env.start_position:
ax.text(col, row, '起点', ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
elif (row, col) == self.env.goal_position:
ax.text(col, row, '目标', ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
elif (row, col) in self.env.trap_positions:
ax.text(col, row, '陷阱', ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=10, fontweight='bold')
# 绘制路径
if len(path) > 1:
# 提取坐标
col_coords = [p[1] for p in path]
row_coords = [p[0] for p in path]
# 绘制路径线
ax.plot(col_coords, row_coords, 'b-', linewidth=3, alpha=0.7, label='路径')
# 绘制路径点
scatter = ax.scatter(col_coords, row_coords, c=range(len(path)),
cmap='viridis', s=100, alpha=0.8,
edgecolors='black', linewidth=1.5, zorder=5)
# 添加颜色条
plt.colorbar(scatter, ax=ax, label='步数')
# 标记起点和终点
ax.scatter(col_coords[0], row_coords[0], color='blue', s=200,
marker='o', edgecolor='black', linewidth=2,
label='路径起点', zorder=10)
if len(path) > 1:
ax.scatter(col_coords[-1], row_coords[-1], color='red', s=200,
marker='s', edgecolor='black', linewidth=2,
label='路径终点', zorder=10)
# 绘制动作箭头(如果有动作序列且需要显示箭头)
if actions and show_arrows and len(actions) == len(path) - 1:
arrow_directions = {
Action.UP: (0, -0.3),
Action.DOWN: (0, 0.3),
Action.LEFT: (-0.3, 0),
Action.RIGHT: (0.3, 0)
}
for i in range(len(actions)):
if i < len(path) - 1:
row1, col1 = path[i]
row2, col2 = path[i + 1]
# 计算箭头位置(路径中点)
mid_row = (row1 + row2) / 2.0
mid_col = (col1 + col2) / 2.0
# 获取箭头方向
dx, dy = arrow_directions.get(actions[i], (0, 0))
# 绘制箭头
ax.arrow(mid_col - dx * 0.5, mid_row - dy * 0.5,
dx, dy,
head_width=0.15, head_length=0.2,
fc='darkblue', ec='darkblue', alpha=0.8)
# 标记步数
ax.text(mid_col, mid_row, str(i + 1),
ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=9, fontweight='bold',
bbox=dict(boxstyle="circle,pad=0.3",
facecolor='yellow',
edgecolor='black', alpha=0.8))
# 设置坐标轴
ax.set_xlim(-0.5, cols - 0.5)
ax.set_ylim(-0.5, rows - 0.5)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.invert_yaxis() # 使y轴向下为正(与网格坐标一致)
ax.set_xticks(range(cols))
ax.set_yticks(range(rows))
ax.set_xlabel('列')
ax.set_ylabel('行')
ax.set_title(f'{title} ({len(path)-1}步)', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.tight_layout()
# 打印路径信息
print(f"\n{title}:")
print(f" 路径长度: {len(path)-1} 步")
print(f" 起点: {path[0]}")
print(f" 终点: {path[-1]}")
if path[-1] == self.env.goal_position:
print(" ✓ 成功到达目标!")
elif path[-1] in self.env.trap_positions:
print(" ✗ 落入陷阱!")
else:
print(" ⚠ 未到达目标")
if actions:
action_names = [action.name for action in actions]
print(f" 动作序列: {' → '.join(action_names)}")
return fig
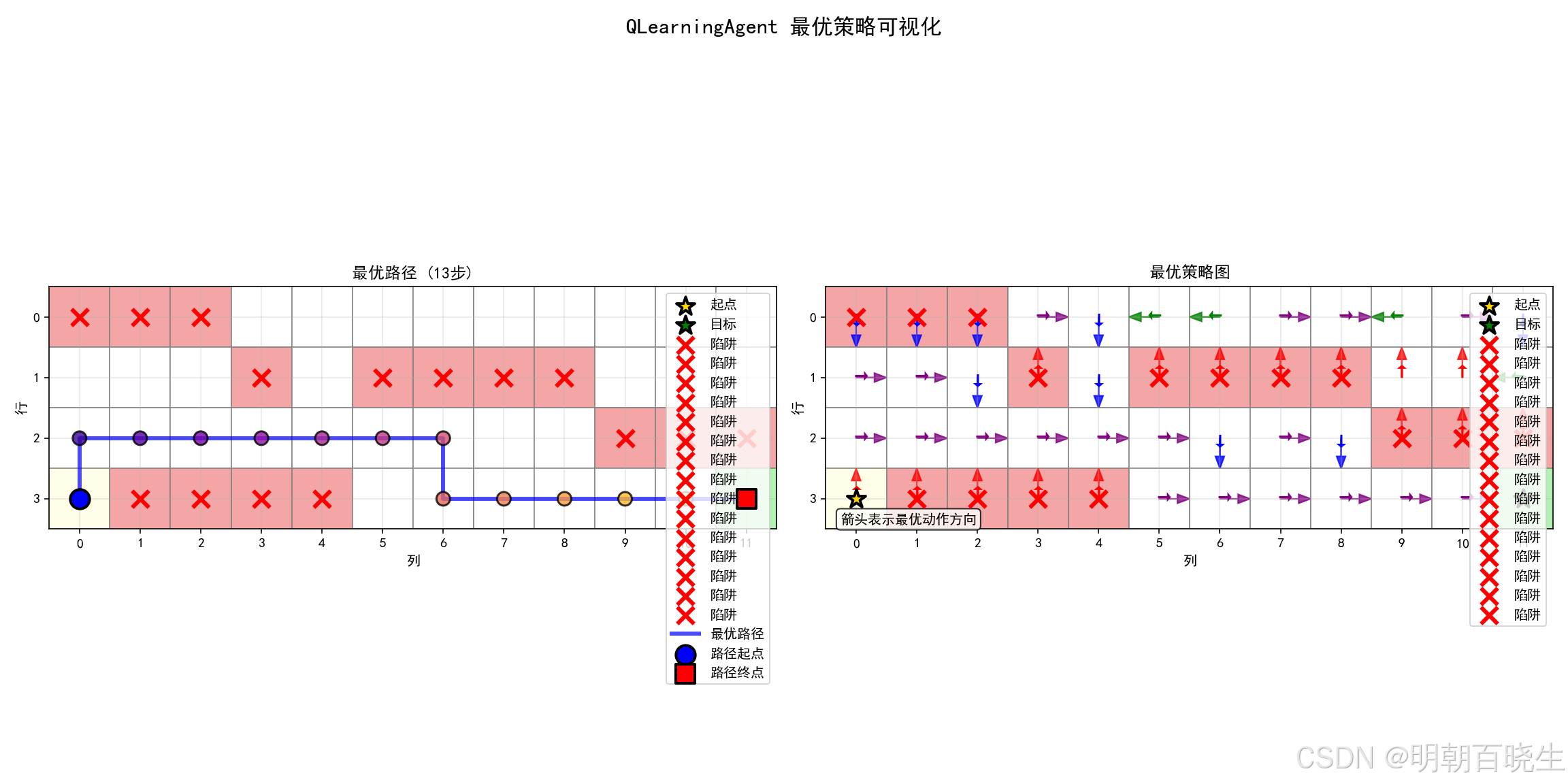
def visualize_optimal_policy(self) -> None:
"""
可视化最优策略
"""
# 获取最优路径
optimal_path, optimal_actions = self.get_optimal_path()
# 创建图表
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(16, 8))
# 1. 最优路径图
ax1 = axes[0]
self._plot_optimal_path(ax1, optimal_path, optimal_actions)
# 2. 策略图
ax2 = axes[1]
self._plot_policy_map(ax2)
plt.suptitle(f'{self.__class__.__name__} 最优策略可视化', fontsize=16, fontweight='bold')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
def _plot_optimal_path(self, ax: plt.Axes, path: List[Tuple[int, int]],
actions: List[Action]) -> None:
"""绘制最优路径图"""
rows, cols = self.env.rows, self.env.cols
# 绘制网格背景
for row in range(rows):
for col in range(cols):
# 设置单元格颜色
cell_color = 'white'
if (row, col) == self.env.start_position:
cell_color = 'lightyellow'
elif (row, col) == self.env.goal_position:
cell_color = 'lightgreen'
elif (row, col) in self.env.trap_positions:
cell_color = 'lightcoral'
rect = plt.Rectangle((col - 0.5, row - 0.5), 1, 1,
linewidth=1, edgecolor='gray',
facecolor=cell_color, alpha=0.7)
ax.add_patch(rect)
# 标记特殊位置
start_row, start_col = self.env.start_position
ax.scatter(start_col, start_row, color='gold', s=200, marker='*',
edgecolor='black', linewidth=2, label='起点', zorder=5)
goal_row, goal_col = self.env.goal_position
ax.scatter(goal_col, goal_row, color='green', s=200, marker='*',
edgecolor='black', linewidth=2, label='目标', zorder=5)
for trap_row, trap_col in self.env.trap_positions:
ax.scatter(trap_col, trap_row, color='red', s=150, marker='x',
linewidth=3, label='陷阱', zorder=5)
# 绘制路径
if len(path) > 1:
# 提取坐标
col_coords = [p[1] for p in path]
row_coords = [p[0] for p in path]
# 绘制路径线
ax.plot(col_coords, row_coords, 'b-', linewidth=3, alpha=0.7, label='最优路径')
# 绘制路径点
ax.scatter(col_coords, row_coords, c=range(len(path)),
cmap='plasma', s=100, alpha=0.8,
edgecolors='black', linewidth=1.5, zorder=5)
# 标记起点和终点
ax.scatter(col_coords[0], row_coords[0], color='blue', s=200,
marker='o', edgecolor='black', linewidth=2,
label='路径起点', zorder=10)
ax.scatter(col_coords[-1], row_coords[-1], color='red', s=200,
marker='s', edgecolor='black', linewidth=2,
label='路径终点', zorder=10)
# 设置坐标轴
ax.set_xlim(-0.5, cols - 0.5)
ax.set_ylim(-0.5, rows - 0.5)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.invert_yaxis()
ax.set_xticks(range(cols))
ax.set_yticks(range(rows))
ax.set_xlabel('列')
ax.set_ylabel('行')
ax.set_title(f'最优路径 ({len(path)-1}步)', fontsize=12)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.legend(loc='upper right')
def _plot_policy_map(self, ax: plt.Axes) -> None:
"""绘制策略图"""
rows, cols = self.env.rows, self.env.cols
# 获取策略
policy = self.get_policy()
# 绘制网格
for row in range(rows):
for col in range(cols):
state = (row, col)
# 设置单元格颜色
cell_color = 'white'
if state == self.env.start_position:
cell_color = 'lightyellow'
elif state == self.env.goal_position:
cell_color = 'lightgreen'
elif state in self.env.trap_positions:
cell_color = 'lightcoral'
rect = plt.Rectangle((col - 0.5, row - 0.5), 1, 1,
linewidth=1, edgecolor='gray',
facecolor=cell_color, alpha=0.7)
ax.add_patch(rect)
# 如果不是终止状态,绘制策略箭头
if not self._is_terminal_state(state) and state in policy:
action = policy[state]
# 箭头方向和长度
arrow_length = 0.3
arrow_style = {
Action.UP: (0, -arrow_length, '↑', 'red'),
Action.DOWN: (0, arrow_length, '↓', 'blue'),
Action.LEFT: (-arrow_length, 0, '←', 'green'),
Action.RIGHT: (arrow_length, 0, '→', 'purple')
}
if action in arrow_style:
dx, dy, symbol, color = arrow_style[action]
ax.arrow(col, row, dx, dy,
head_width=0.15, head_length=0.2,
fc=color, ec=color, alpha=0.8)
# 添加文字标注
ax.text(col + dx*0.3, row + dy*0.3, symbol,
ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=12, fontweight='bold',
color=color)
# 标记特殊位置
start_row, start_col = self.env.start_position
ax.scatter(start_col, start_row, color='gold', s=200, marker='*',
edgecolor='black', linewidth=2, label='起点', zorder=5)
goal_row, goal_col = self.env.goal_position
ax.scatter(goal_col, goal_row, color='green', s=200, marker='*',
edgecolor='black', linewidth=2, label='目标', zorder=5)
for trap_row, trap_col in self.env.trap_positions:
ax.scatter(trap_col, trap_row, color='red', s=150, marker='x',
linewidth=3, label='陷阱', zorder=5)
# 设置坐标轴
ax.set_xlim(-0.5, cols - 0.5)
ax.set_ylim(-0.5, rows - 0.5)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.invert_yaxis()
ax.set_xticks(range(cols))
ax.set_yticks(range(rows))
ax.set_xlabel('列')
ax.set_ylabel('行')
ax.set_title('最优策略图', fontsize=12)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.legend(loc='upper right')
# 添加图例说明
ax.text(0.02, 0.02, '箭头表示最优动作方向',
transform=ax.transAxes, fontsize=10,
bbox=dict(boxstyle='round', facecolor='white', alpha=0.8))
class SarsaAgent(BaseAgent):
"""
SARSA智能体类
实现基于策略的时间差分学习算法
核心更新公式:Q(s,a) ← Q(s,a) + α[r + γQ(s',a') - Q(s,a)]
特点:
1. 同策略(on-policy):行为策略和目标策略相同(都是ε-贪婪)
2. 使用下一个实际执行的动作a'来更新Q值
"""
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
def choose_action(self, state: Tuple[int, int],
epsilon: Optional[float] = None) -> Optional[Action]:
"""
使用ε-贪婪策略选择动作(行为策略)
参数:
state: 当前状态
epsilon: 探索率,如果为None则使用当前探索率
返回:
Optional[Action]: 选择的动作,如果是终止状态返回None
"""
# 如果是终止状态,返回None
if self._is_terminal_state(state):
return None
# 获取可用动作
available_actions = self._get_available_actions(state)
if not available_actions:
return None
# 使用ε-贪婪策略(行为策略)
epsilon_to_use = epsilon if epsilon is not None else self.epsilon
action = self._epsilon_greedy_action(state, epsilon_to_use, available_actions)
return action
def update_q_value(self,
state: Tuple[int, int],
action: Action,
reward: float,
next_state: Tuple[int, int],
next_action: Action) -> float:
"""
使用SARSA更新规则更新Q值
参数:
state: 当前状态
action: 当前动作
reward: 接收的奖励
next_state: 下一个状态
next_action: 下一个实际执行的动作(从行为策略采样)
返回:
float: TD误差
"""
# 获取当前Q值
current_q = self.get_q_value(state, action)
# 计算下一个状态-动作对的Q值(使用行为策略选择的动作)
next_q = self.get_q_value(next_state, next_action)
# 计算TD误差(SARSA更新)
# SARSA使用下一个实际执行的动作a'(来自行为策略)
td_error = reward + self.discount_factor * next_q - current_q
# 更新Q值
new_q = current_q + self.learning_rate * td_error
self.set_q_value(state, action, new_q)
# 记录TD误差
self.td_error_history.append(abs(td_error))
return td_error
def train_episode(self, max_steps: int = 1000) -> Tuple[float, int]:
"""
训练一个回合(SARSA算法)
参数:
max_steps: 最大步数
返回:
Tuple[float, int]: (总奖励, 步数)
"""
# 重置环境
state = self.env.reset()
# 根据当前行为策略(ε-贪婪)选择动作
action = self.choose_action(state)
total_reward = 0.0
steps = 0
episode_states = [state]
episode_actions = []
# 主训练循环
while steps < max_steps and action is not None:
# 检查是否为终止状态
if self._is_terminal_state(state):
break
# 执行动作
next_state, reward, done = self.env.step(action)
# 根据当前行为策略(ε-贪婪)选择下一个动作
next_action = self.choose_action(next_state)
# 使用SARSA更新Q值
# SARSA关键点:使用下一个实际执行的动作a'
self.update_q_value(state, action, reward, next_state, next_action)
# 更新统计信息
total_reward += reward
steps += 1
self.total_steps += 1
# 记录状态和动作
episode_states.append(next_state)
episode_actions.append(action)
# 转移到下一个状态和动作
state = next_state
action = next_action
# 如果回合结束,则退出循环
if done:
break
# 衰减探索率
self._decay_epsilon()
# 更新回合计数
self.episode_count += 1
self.total_reward += total_reward
# 记录性能
self.episode_rewards.append(total_reward)
self.episode_steps.append(steps)
self.epsilon_history.append(self.epsilon)
# 更新最佳策略和路径
if total_reward > self.best_reward:
self.best_reward = total_reward
self.best_q_table = {k: v.copy() for k, v in self.q_table.items()}
self.best_path = episode_states
self.best_actions = episode_actions
return total_reward, steps
class QLearningAgent(BaseAgent):
"""
Q-learning智能体类
实现离策略的时间差分学习算法
核心更新公式:Q(s,a) ← Q(s,a) + α[r + γ max_a' Q(s',a') - Q(s,a)]
特点:
1. 离策略(off-policy):行为策略(ε-贪婪)和目标策略(贪婪)不同
2. 使用下一个状态的最大Q值来更新当前Q值
"""
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
# Q-learning特定参数
self.max_steps_per_episode = 500 # 限制每回合最大步数
def choose_action(self, state: Tuple[int, int],
epsilon: Optional[float] = None) -> Optional[Action]:
"""
使用ε-贪婪策略选择动作(行为策略)
参数:
state: 当前状态
epsilon: 探索率,如果为None则使用当前探索率
返回:
Optional[Action]: 选择的动作,如果是终止状态返回None
"""
# 如果是终止状态,返回None
if self._is_terminal_state(state):
return None
# 获取可用动作
available_actions = self._get_available_actions(state)
if not available_actions:
return None
# 使用ε-贪婪策略(行为策略)
epsilon_to_use = epsilon if epsilon is not None else self.epsilon
action = self._epsilon_greedy_action(state, epsilon_to_use, available_actions)
return action
def get_next_state_max_q(self, next_state: Tuple[int, int]) -> float:
"""
获取下一个状态的最大Q值(用于Q-learning更新)
参数:
next_state: 下一个状态
返回:
float: 最大Q值
"""
if next_state is None or self._is_terminal_state(next_state):
return 0.0
# 获取下一个状态的可用动作
next_available_actions = self._get_available_actions(next_state)
if not next_available_actions:
return 0.0
# 计算最大Q值:max_a' Q(s', a')
max_q = float('-inf')
for action in next_available_actions:
q_value = self.get_q_value(next_state, action)
if q_value > max_q:
max_q = q_value
return max_q if max_q > float('-inf') else 0.0
def update_q_value(self,
state: Tuple[int, int],
action: Action,
reward: float,
next_state: Tuple[int, int]) -> float:
"""
使用Q-learning更新规则更新Q值
参数:
state: 当前状态
action: 当前动作
reward: 接收的奖励
next_state: 下一个状态
返回:
float: TD误差
"""
# 获取当前Q值
current_q = self.get_q_value(state, action)
# 计算下一个状态的最大Q值(目标策略:贪婪 targe-policy)
max_next_q = self.get_next_state_max_q(next_state)
# 计算TD误差(Q-learning更新)
# Q-learning关键点:使用下一个状态的最大Q值(来自目标策略)
td_error = reward + self.discount_factor * max_next_q - current_q
# 更新Q值
new_q = current_q + self.learning_rate * td_error
self.set_q_value(state, action, new_q)
# 记录TD误差
self.td_error_history.append(abs(td_error))
return td_error
def train_episode(self, max_steps: int = 1000) -> Tuple[float, int]:
"""
训练一个回合(Q-learning算法)
参数:
max_steps: 最大步数
返回:
Tuple[float, int]: (总奖励, 步数)
"""
# 重置环境
state = self.env.reset()
total_reward = 0.0
steps = 0
episode_states = [state]
episode_actions = []
# 主训练循环 - 使用较小的max_steps避免无限循环
effective_max_steps = min(max_steps, self.max_steps_per_episode)
while steps < effective_max_steps:
# 检查是否为终止状态
if self._is_terminal_state(state):
break
# 根据当前行为策略(ε-贪婪)选择动作 behavior-policy
action = self.choose_action(state)
if action is None:
break
# 执行动作
next_state, reward, done = self.env.step(action)
# 调整奖励值,鼓励到达目标
# 使用Q-learning更新Q值
# Q-learning关键点:使用目标策略(贪婪)选择最大Q值 target-policy
self.update_q_value(state, action, reward, next_state)
# 更新统计信息
total_reward += reward
steps += 1
self.total_steps += 1
# 记录状态和动作
episode_states.append(next_state)
episode_actions.append(action)
# 转移到下一个状态
state = next_state
# 如果回合结束,则退出循环
if done:
break
# 衰减探索率
self._decay_epsilon()
# 更新回合计数
self.episode_count += 1
self.total_reward += total_reward
# 记录性能
self.episode_rewards.append(total_reward)
self.episode_steps.append(steps)
self.epsilon_history.append(self.epsilon)
# 调试信息
if self.episode_count % 100 == 0:
self.debug_info.append({
'episode': self.episode_count,
'total_reward': total_reward,
'steps': steps,
'epsilon': self.epsilon,
'state': state
})
# 更新最佳策略和路径
if total_reward > self.best_reward:
self.best_reward = total_reward
self.best_q_table = {k: v.copy() for k, v in self.q_table.items()}
self.best_path = episode_states
self.best_actions = episode_actions
return total_reward, steps
def _get_debug_info(self) -> str:
"""获取调试信息"""
if not self.debug_info:
return "无调试信息"
info = "最近调试信息:\n"
for i, debug in enumerate(self.debug_info[-5:]): # 显示最近5条
info += f"回合 {debug['episode']}: 奖励={debug['total_reward']:.2f}, " \
f"步数={debug['steps']}, ε={debug['epsilon']:.4f}, " \
f"状态={debug['state']}\n"
return info
class RLComparisonTrainer:
"""
强化学习算法比较训练器
比较SARSA和Q-learning算法的性能
"""
def __init__(
self,
env: GridWorldEnvironment,
learning_rate: float = 0.1,
discount_factor: float = 0.9,
epsilon: float = 0.1,
epsilon_decay: float = 0.998,
epsilon_min: float = 0.01
):
"""
初始化训练器
参数:
env: 网格世界环境
learning_rate: 学习率
discount_factor: 折扣因子
epsilon: 初始探索率
epsilon_decay: ε衰减率
epsilon_min: 最小ε值
"""
self.env = env
# 创建SARSA和Q-learning智能体
self.sarsa_agent = SarsaAgent(
env=env,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
discount_factor=discount_factor,
epsilon=epsilon,
epsilon_decay=epsilon_decay,
epsilon_min=epsilon_min
)
self.q_learning_agent = QLearningAgent(
env=env,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
discount_factor=discount_factor,
epsilon=0.3, # Q-learning需要更多探索
epsilon_decay=epsilon_decay,
epsilon_min=0.05,
initial_q_value=1.0 # 正初始值鼓励探索
)
# 训练结果存储
self.results = {
AlgorithmType.SARSA: {},
AlgorithmType.Q_LEARNING: {}
}
def train_agents(self,
num_episodes: int = 1000,
progress_interval: int = 100) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
训练两种算法的智能体
参数:
num_episodes: 训练回合数
progress_interval: 进度打印间隔
返回:
Dict: 训练结果
"""
print("=" * 70)
print("强化学习算法比较实验")
print("=" * 70)
print(f"训练回合数: {num_episodes}")
print(f"初始参数: α={self.sarsa_agent.learning_rate}, "
f"γ={self.sarsa_agent.discount_factor}, ε={self.sarsa_agent.epsilon_init}")
print("-" * 70)
# 训练SARSA
print("\n训练 SARSA 算法...")
sarsa_results = self._train_agent(self.sarsa_agent, num_episodes,
progress_interval, "SARSA")
self.results[AlgorithmType.SARSA] = sarsa_results
# 训练Q-learning
print("\n\n训练 Q-learning 算法...")
print("注意:Q-learning需要更多探索来找到目标")
q_learning_results = self._train_agent(self.q_learning_agent, num_episodes,
progress_interval, "Q-learning")
self.results[AlgorithmType.Q_LEARNING] = q_learning_results
# 显示Q-learning的调试信息
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("Q-learning调试信息")
print("=" * 70)
print(self.q_learning_agent._get_debug_info())
# 比较结果
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("算法性能比较")
print("=" * 70)
self._compare_algorithms()
# 可视化比较
print("\n生成比较图表...")
self.visualize_comparison()
# 可视化最优策略路径
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("最优策略路径可视化")
print("=" * 70)
self.visualize_optimal_policy_paths()
return self.results
def _train_agent(self, agent: BaseAgent, num_episodes: int,
progress_interval: int, algorithm_name: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
训练单个智能体
参数:
agent: 智能体实例
num_episodes: 训练回合数
progress_interval: 进度打印间隔
algorithm_name: 算法名称
返回:
Dict: 训练结果
"""
episode_rewards = []
episode_steps = []
for episode in range(num_episodes):
# 训练一个回合
reward, steps = agent.train_episode()
# 记录性能
episode_rewards.append(reward)
episode_steps.append(steps)
# 定期打印进度
if (episode + 1) % progress_interval == 0:
# 计算最近100回合的平均性能
start_idx = max(0, episode - 99)
recent_rewards = episode_rewards[start_idx:episode + 1]
recent_steps = episode_steps[start_idx:episode + 1]
avg_reward = np.mean(recent_rewards) if recent_rewards else 0.0
avg_steps = np.mean(recent_steps) if recent_steps else 0.0
success_rate = np.mean([r > 0 for r in recent_rewards]) * 100 if recent_rewards else 0.0
print(f"{algorithm_name:10s} | "
f"回合 {episode + 1:4d} | "
f"平均奖励: {avg_reward:6.3f} | "
f"平均步数: {avg_steps:5.1f} | "
f"成功率: {success_rate:5.1f}%")
# 最终评估
final_eval = agent.evaluate_policy(num_episodes=100)
return {
'agent': agent,
'episode_rewards': episode_rewards,
'episode_steps': episode_steps,
'epsilon_history': agent.epsilon_history,
'td_error_history': agent.td_error_history,
'final_evaluation': final_eval,
'best_reward': agent.best_reward,
'total_episodes': agent.episode_count,
'total_steps': agent.total_steps,
}
def visualize_optimal_policy_paths(self) -> None:
"""可视化两种算法的最优策略路径"""
print("\n生成最优策略路径可视化图表...")
# 获取两种算法的最优路径
sarsa_path, sarsa_actions = self.sarsa_agent.get_optimal_path()
q_path, q_actions = self.q_learning_agent.get_optimal_path()
# 创建综合图
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(16, 16))
# 1. SARSA最优路径图
ax1 = axes[0, 0]
self._plot_optimal_path_detail(ax1, sarsa_path, sarsa_actions,
"SARSA最优路径", 'blue')
# 2. Q-learning最优路径图
ax2 = axes[0, 1]
self._plot_optimal_path_detail(ax2, q_path, q_actions,
"Q-learning最优路径", 'red')
# 3. 路径对比图
ax3 = axes[1, 0]
self._plot_path_comparison(ax3, sarsa_path, q_path)
# 4. 策略对比图
ax4 = axes[1, 1]
self._plot_policy_comparison(ax4)
plt.suptitle('最优策略路径可视化比较', fontsize=16, fontweight='bold')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 打印最优路径统计信息
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("最优路径统计信息")
print("=" * 70)
self._print_path_statistics("SARSA", sarsa_path, sarsa_actions)
self._print_path_statistics("Q-learning", q_path, q_actions)
# 比较两种算法的路径
print(f" SARSA是否到达目标: {'是' if sarsa_path[-1] == self.env.goal_position else '否'}")
print(f" Q-learning是否到达目标: {'是' if q_path[-1] == self.env.goal_position else '否'}")
# 计算路径效率
if sarsa_path[-1] == self.env.goal_position and q_path[-1] == self.env.goal_position:
sarsa_efficiency = self._calculate_path_efficiency(sarsa_path)
q_efficiency = self._calculate_path_efficiency(q_path)
print(f" SARSA路径效率: {sarsa_efficiency:.2f}")
print(f" Q-learning路径效率: {q_efficiency:.2f}")
print(f" 更优算法: {'SARSA' if sarsa_efficiency > q_efficiency else 'Q-learning'}")
# 额外显示每个算法的最优策略可视化
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("各算法详细最优策略可视化")
print("=" * 70)
print("\nSARSA算法最优策略:")
self.sarsa_agent.visualize_optimal_policy()
print("\nQ-learning算法最优策略:")
self.q_learning_agent.visualize_optimal_policy()
def _plot_optimal_path_detail(self, ax: plt.Axes, path: List[Tuple[int, int]],
actions: List[Action], title: str, color: str) -> None:
"""绘制详细最优路径图"""
rows, cols = self.env.rows, self.env.cols
# 绘制网格背景
for row in range(rows):
for col in range(cols):
# 设置单元格颜色
cell_color = 'white'
if (row, col) == self.env.start_position:
cell_color = 'lightyellow'
elif (row, col) == self.env.goal_position:
cell_color = 'lightgreen'
elif (row, col) in self.env.trap_positions:
cell_color = 'lightcoral'
rect = plt.Rectangle((col - 0.5, row - 0.5), 1, 1,
linewidth=0.5, edgecolor='gray',
facecolor=cell_color, alpha=0.7)
ax.add_patch(rect)
# 标记特殊位置
start_row, start_col = self.env.start_position
ax.scatter(start_col, start_row, color='gold', s=200, marker='*',
edgecolor='black', linewidth=1, label='起点', zorder=5)
goal_row, goal_col = self.env.goal_position
ax.scatter(goal_col, goal_row, color='green', s=200, marker='*',
edgecolor='black', linewidth=1, label='目标', zorder=5)
for trap_row, trap_col in self.env.trap_positions:
ax.scatter(trap_col, trap_row, color='red', s=100, marker='x',
linewidth=2, label='陷阱', zorder=5)
# 绘制路径
if len(path) > 1:
# 提取坐标
col_coords = [p[1] for p in path]
row_coords = [p[0] for p in path]
# 绘制路径线
ax.plot(col_coords, row_coords, color=color, linewidth=3, alpha=0.7, label='最优路径')
# 绘制路径点
scatter = ax.scatter(col_coords, row_coords, c=range(len(path)),
cmap='viridis', s=80, alpha=0.8,
edgecolors='black', linewidth=1, zorder=5)
# 添加颜色条
plt.colorbar(scatter, ax=ax, label='步数')
# 标记起点和终点
ax.scatter(col_coords[0], row_coords[0], color='blue', s=150,
marker='o', edgecolor='black', linewidth=2,
label='路径起点', zorder=10)
ax.scatter(col_coords[-1], row_coords[-1], color='red', s=150,
marker='s', edgecolor='black', linewidth=2,
label='路径终点', zorder=10)
# 绘制动作箭头
if actions and len(actions) == len(path) - 1:
arrow_directions = {
Action.UP: (0, -0.25),
Action.DOWN: (0, 0.25),
Action.LEFT: (-0.25, 0),
Action.RIGHT: (0.25, 0)
}
for i in range(len(actions)):
if i < len(path) - 1:
row1, col1 = path[i]
row2, col2 = path[i + 1]
# 计算箭头位置(路径中点)
mid_row = (row1 + row2) / 2.0
mid_col = (col1 + col2) / 2.0
# 获取箭头方向
dx, dy = arrow_directions.get(actions[i], (0, 0))
# 绘制箭头
ax.arrow(mid_col - dx * 0.5, mid_row - dy * 0.5,
dx, dy,
head_width=0.12, head_length=0.15,
fc='darkblue', ec='darkblue', alpha=0.8)
# 设置坐标轴
ax.set_xlim(-0.5, cols - 0.5)
ax.set_ylim(-0.5, rows - 0.5)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.invert_yaxis()
ax.set_xticks(range(cols))
ax.set_yticks(range(rows))
ax.set_xlabel('列')
ax.set_ylabel('行')
ax.set_title(f'{title} ({len(path)-1}步)', fontsize=12)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=9)
def _plot_path_comparison(self, ax: plt.Axes,
sarsa_path: List[Tuple[int, int]],
q_path: List[Tuple[int, int]]) -> None:
"""绘制路径对比图"""
rows, cols = self.env.rows, self.env.cols
# 绘制网格背景
for row in range(rows):
for col in range(cols):
# 设置单元格颜色
cell_color = 'white'
if (row, col) == self.env.start_position:
cell_color = 'lightyellow'
elif (row, col) == self.env.goal_position:
cell_color = 'lightgreen'
elif (row, col) in self.env.trap_positions:
cell_color = 'lightcoral'
rect = plt.Rectangle((col - 0.5, row - 0.5), 1, 1,
linewidth=0.5, edgecolor='gray',
facecolor=cell_color, alpha=0.7)
ax.add_patch(rect)
# 标记特殊位置
start_row, start_col = self.env.start_position
ax.scatter(start_col, start_row, color='gold', s=200, marker='*',
edgecolor='black', linewidth=1, label='起点', zorder=5)
goal_row, goal_col = self.env.goal_position
ax.scatter(goal_col, goal_row, color='green', s=200, marker='*',
edgecolor='black', linewidth=1, label='目标', zorder=5)
for trap_row, trap_col in self.env.trap_positions:
ax.scatter(trap_col, trap_row, color='red', s=100, marker='x',
linewidth=2, label='陷阱', zorder=5)
# 绘制SARSA路径
if len(sarsa_path) > 1:
sarsa_cols = [p[1] for p in sarsa_path]
sarsa_rows = [p[0] for p in sarsa_path]
ax.plot(sarsa_cols, sarsa_rows, 'b-', linewidth=3, alpha=0.7, label='SARSA路径')
# 绘制Q-learning路径
if len(q_path) > 1:
q_cols = [p[1] for p in q_path]
q_rows = [p[0] for p in q_path]
ax.plot(q_cols, q_rows, 'r--', linewidth=3, alpha=0.7, label='Q-learning路径')
# 标记共同路径点
common_points = set(sarsa_path) & set(q_path)
if common_points:
common_cols = [p[1] for p in common_points]
common_rows = [p[0] for p in common_points]
ax.scatter(common_cols, common_rows, color='purple', s=50,
marker='D', edgecolor='black', linewidth=1,
label='共同路径点', zorder=15)
# 设置坐标轴
ax.set_xlim(-0.5, cols - 0.5)
ax.set_ylim(-0.5, rows - 0.5)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.invert_yaxis()
ax.set_xticks(range(cols))
ax.set_yticks(range(rows))
ax.set_xlabel('列')
ax.set_ylabel('行')
ax.set_title('最优路径对比图', fontsize=12)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=9)
# 添加统计信息
if sarsa_path and q_path:
common_percentage = len(common_points) / max(len(set(sarsa_path)), len(set(q_path))) * 100
efficiency_ratio = len(sarsa_path) / len(q_path) if len(q_path) > 0 else 0
ax.text(0.02, 0.98, f"共同路径点: {len(common_points)} ({common_percentage:.1f}%)\n"
f"路径长度比(S/Q): {efficiency_ratio:.2f}",
transform=ax.transAxes, fontsize=9,
verticalalignment='top',
bbox=dict(boxstyle='round', facecolor='white', alpha=0.8))
def _plot_policy_comparison(self, ax: plt.Axes) -> None:
"""绘制策略对比图"""
rows, cols = self.env.rows, self.env.cols
# 获取策略
sarsa_policy = self.sarsa_agent.get_policy()
q_policy = self.q_learning_agent.get_policy()
# 绘制网格
for row in range(rows):
for col in range(cols):
state = (row, col)
# 设置单元格颜色
cell_color = 'white'
if state == self.env.start_position:
cell_color = 'lightyellow'
elif state == self.env.goal_position:
cell_color = 'lightgreen'
elif state in self.env.trap_positions:
cell_color = 'lightcoral'
rect = plt.Rectangle((col - 0.5, row - 0.5), 1, 1,
linewidth=0.5, edgecolor='gray',
facecolor=cell_color, alpha=0.7)
ax.add_patch(rect)
# 如果不是终止状态,绘制策略对比
if not self.sarsa_agent._is_terminal_state(state):
sarsa_action = sarsa_policy.get(state)
q_action = q_policy.get(state)
# 计算两个策略是否相同
if sarsa_action and q_action:
if sarsa_action == q_action:
# 策略相同,绘制一个箭头
self._draw_policy_arrow(ax, col, row, sarsa_action, 'blue', 1.0)
else:
# 策略不同,绘制两个箭头
self._draw_policy_arrow(ax, col, row, sarsa_action, 'blue', 0.6)
self._draw_policy_arrow(ax, col, row, q_action, 'red', 0.6)
elif sarsa_action:
self._draw_policy_arrow(ax, col, row, sarsa_action, 'blue', 0.8)
elif q_action:
self._draw_policy_arrow(ax, col, row, q_action, 'red', 0.8)
# 标记特殊位置
start_row, start_col = self.env.start_position
ax.scatter(start_col, start_row, color='gold', s=200, marker='*',
edgecolor='black', linewidth=1, label='起点', zorder=5)
goal_row, goal_col = self.env.goal_position
ax.scatter(goal_col, goal_row, color='green', s=200, marker='*',
edgecolor='black', linewidth=1, label='目标', zorder=5)
for trap_row, trap_col in self.env.trap_positions:
ax.scatter(trap_col, trap_row, color='red', s=100, marker='x',
linewidth=2, label='陷阱', zorder=5)
# 设置坐标轴
ax.set_xlim(-0.5, cols - 0.5)
ax.set_ylim(-0.5, rows - 0.5)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.invert_yaxis()
ax.set_xticks(range(cols))
ax.set_yticks(range(rows))
ax.set_xlabel('列')
ax.set_ylabel('行')
ax.set_title('策略对比图 (蓝=SARSA, 红=Q-learning)', fontsize=12)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 创建自定义图例
from matplotlib.patches import Patch
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
legend_elements = [
Line2D([0], [0], marker='*', color='w', label='起点',
markerfacecolor='gold', markersize=10, markeredgecolor='black'),
Line2D([0], [0], marker='*', color='w', label='目标',
markerfacecolor='green', markersize=10, markeredgecolor='black'),
Line2D([0], [0], marker='x', color='w', label='陷阱',
markerfacecolor='red', markersize=10, markeredgecolor='black'),
Patch(facecolor='blue', alpha=0.6, label='SARSA策略'),
Patch(facecolor='red', alpha=0.6, label='Q-learning策略'),
Patch(facecolor='purple', alpha=0.8, label='策略相同')
]
ax.legend(handles=legend_elements, loc='upper right', fontsize=9)
def _draw_policy_arrow(self, ax: plt.Axes, x: float, y: float,
action: Action, color: str, alpha: float) -> None:
"""绘制策略箭头"""
arrow_length = 0.25
arrow_style = {
Action.UP: (0, -arrow_length),
Action.DOWN: (0, arrow_length),
Action.LEFT: (-arrow_length, 0),
Action.RIGHT: (arrow_length, 0)
}
if action in arrow_style:
dx, dy = arrow_style[action]
ax.arrow(x, y, dx, dy,
head_width=0.1, head_length=0.15,
fc=color, ec=color, alpha=alpha)
def _print_path_statistics(self, algorithm_name: str,
path: List[Tuple[int, int]],
actions: List[Action]) -> None:
"""打印路径统计信息"""
print(f"\n{algorithm_name}:")
print(f" 路径长度: {len(path)-1} 步")
print(f" 起点: {path[0]}")
print(f" 终点: {path[-1]}")
if path[-1] == self.env.goal_position:
print(" ✓ 成功到达目标!")
elif path[-1] in self.env.trap_positions:
print(" ✗ 落入陷阱!")
else:
print(" ⚠ 未到达目标")
if actions:
action_names = [action.name for action in actions]
# 显示前10个动作,如果超过10个则显示...
display_actions = action_names[:10]
display_text = ' → '.join(display_actions)
if len(action_names) > 10:
display_text += ' ...'
print(f" 动作序列: {display_text}")
# 计算路径的直线距离
if len(path) >= 2:
start = path[0]
end = path[-1]
straight_distance = abs(end[0] - start[0]) + abs(end[1] - start[1])
print(f" 直线距离: {straight_distance} 步")
print(f" 路径效率: {straight_distance / (len(path)-1):.2%}")
def _calculate_path_efficiency(self, path: List[Tuple[int, int]]) -> float:
"""计算路径效率"""
if len(path) < 2:
return 0.0
start = path[0]
end = path[-1]
straight_distance = abs(end[0] - start[0]) + abs(end[1] - start[1])
actual_distance = len(path) - 1
if actual_distance == 0:
return 0.0
return straight_distance / actual_distance
def _compare_algorithms(self) -> None:
"""比较两种算法的性能"""
print("\n" + "-" * 70)
print(f"{'指标':<20} | {'SARSA':<20} | {'Q-learning':<20} | {'优势':<10}")
print("-" * 70)
# 比较指标
metrics = [
('平均奖励', 'average_reward', '.3f'),
('成功率', 'success_rate', '.1%'),
('平均步数', 'average_steps', '.1f'),
('最佳奖励', 'best_reward', '.3f'),
('总训练步数', 'total_steps', 'd'),
]
for label, key, fmt in metrics:
if key in ['best_reward', 'total_episodes', 'total_steps']:
sarsa_val = self.results[AlgorithmType.SARSA][key]
q_val = self.results[AlgorithmType.Q_LEARNING][key]
else:
sarsa_val = self.results[AlgorithmType.SARSA]['final_evaluation'][key]
q_val = self.results[AlgorithmType.Q_LEARNING]['final_evaluation'][key]
sarsa_str = format(sarsa_val, fmt)
q_str = format(q_val, fmt)
# 确定优势
if key == 'average_steps': # 步数越少越好
if sarsa_val < q_val:
advantage = "SARSA"
elif q_val < sarsa_val:
advantage = "Q-learning"
else:
advantage = "平手"
else: # 其他指标越大越好
if sarsa_val > q_val:
advantage = "SARSA"
elif q_val > sarsa_val:
advantage = "Q-learning"
else:
advantage = "平手"
print(f"{label:<20} | {sarsa_str:>20} | {q_str:>20} | {advantage:>10}")
print("-" * 70)
# 算法特点总结
print("\n算法特点总结:")
print("SARSA:")
print(" • 同策略(on-policy):行为策略和目标策略相同")
print(" • 使用下一个实际执行的动作a'更新Q值")
print(" • 更保守,考虑探索带来的风险")
print(" • 适合:安全性要求高的环境(如机器人控制)")
print("\nQ-learning:")
print(" • 离策略(off-policy):行为策略和目标策略不同")
print(" • 使用下一个状态的最大Q值更新当前Q值")
print(" • 更激进,直接学习最优策略")
print(" • 适合:需要学习最优策略的环境(如游戏AI)")
def visualize_comparison(self) -> None:
"""可视化比较两种算法的性能"""
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(18, 12))
# 1. 奖励收敛曲线
ax1 = axes[0, 0]
self._plot_reward_comparison(ax1)
# 2. 移动平均奖励
ax2 = axes[0, 1]
self._plot_moving_average_rewards(ax2)
# 3. 成功率对比
ax3 = axes[0, 2]
self._plot_success_rate_comparison(ax3)
# 4. 步数对比
ax4 = axes[1, 0]
self._plot_steps_comparison(ax4)
# 5. TD误差对比
ax5 = axes[1, 1]
self._plot_td_error_comparison(ax5)
# 6. 最终策略热图
ax6 = axes[1, 2]
self._plot_final_policies(ax6)
plt.suptitle('SARSA vs Q-learning 算法比较', fontsize=16, fontweight='bold')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
def run_comparison_experiment(num_episodes: int = 1000) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
运行算法比较实验
参数:
num_episodes: 训练回合数
返回:
Dict[str, Any]: 实验结果
"""
print("=" * 70)
print("强化学习算法比较实验")
print("=" * 70)
# 1. 创建环境
print("\n1. 创建网格世界环境...")
env = GridWorldEnvironment()
# 2. 创建并训练比较器
print(f"\n2. 创建比较器并训练 {num_episodes} 回合...")
trainer = RLComparisonTrainer(
env=env,
learning_rate=0.1,
discount_factor=0.95, # 较高的折扣因子
epsilon=0.3, # 增加初始探索率
epsilon_decay=0.999, # 减缓衰减速度
epsilon_min=0.05 # 保持一定探索
)
results = trainer.train_agents(
num_episodes=num_episodes,
progress_interval=100
)
print("\n实验完成!")
print("=" * 70)
return results
def main():
"""主函数"""
# 设置随机种子以确保可重复性
# 自定义参数测试
print("\n自定义参数测试")
print("-" * 70)
env = GridWorldEnvironment()
# 获取用户输入
algorithm = input("选择算法 (1=SARSA, 2=Q-learning): ")
if algorithm == "1":
agent = SarsaAgent(
env=env,
learning_rate=0.1,
discount_factor=0.95,
epsilon=0.1,
epsilon_decay=0.998,
epsilon_min=0.01
)
agent_name = "SARSA"
else:
agent = QLearningAgent(
env=env,
learning_rate=0.1,
discount_factor=0.95,
epsilon=0.1,
epsilon_decay=0.995,
epsilon_min=0.05,
initial_q_value=1.0
)
agent_name = "Q-learning"
# 训练智能体
num_episodes = 500
for episode in range(num_episodes):
reward, steps = agent.train_episode()
if (episode + 1) % 100 == 0:
print(f" 回合 {episode + 1}: 奖励={reward:.2f}, 步数={steps}, ε={agent.epsilon:.3f}")
# 可视化最优策略
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(f"{agent_name} 最优策略路径")
print("=" * 70)
optimal_path, optimal_actions = agent.get_optimal_path()
print("\n最优路径统计:")
print(f" 长度: {len(optimal_path)-1} 步")
print(f" 起点: {optimal_path[0]}")
print(f" 终点: {optimal_path[-1]}")
if optimal_path[-1] == env.goal_position:
print(" ✓ 成功到达目标!")
elif optimal_path[-1] in env.trap_positions:
print(" ✗ 落入陷阱!")
else:
print(" ⚠ 未到达目标")
# 可视化
agent.visualize_optimal_policy()
agent.visualize_path(optimal_path, optimal_actions, f"{agent_name}算法最优路径")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()2 grid_world.py
"""
复杂网格世界环境实现
作者:chengxf
日期:2025年12月
文件名:grid_world.py
描述:
本模块实现了一个复杂的网格世界环境,用于强化学习算法测试。
环境包含传送门、陷阱和动态元素,支持SARSA和Q-learning算法的训练与评估。
实现了行为策略与目标策略的逻辑分离,并提供完整的可视化功能。
"""
from enum import IntEnum
from typing import Tuple, List, Dict, Any
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
class Action(IntEnum):
"""动作枚举类"""
UP = 0
DOWN = 1
LEFT = 2
RIGHT = 3
COLORS = {
'start': (255, 210, 60), # 亮金色
'goal': (70, 180, 230), # 明亮蓝色
'trap': (220, 70, 90), # 警示红色
'normal': (245, 242, 235), # 接近白色的浅灰
}
class GridWorldEnvironment:
"""
网格世界环境类
8×12网格,包含传送门、陷阱和动态元素
坐标系: (行, 列) 或 (x, y),其中x从上到下,y从左到右
"""
def __init__(self) -> None:
"""初始化网格世界环境参数"""
# 网格尺寸
self.rows: int = 4
self.cols: int = 12
# 特殊位置定义
self.start_position: Tuple[int, int] = (3, 0) # 开始位置
self.goal_position: Tuple[int, int] = (3, 11) # 目标位置
# 陷阱位置
self.trap_positions: List[Tuple[int, int]] = [
(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2),
(1, 3), (1, 5), (1, 6), (1,7), (1,8),
(2, 9), (2, 10), (2, 11),
(3, 1), (3, 2), (3,3), (3,4)
]
# 当前状态和环境统计
self.current_state: Tuple[int, int] = self.start_position
self.total_episodes: int = 0
self.step_count: int = 0
# 动作映射
self.action_mapping = {
Action.UP: self._move_up,
Action.DOWN: self._move_down,
Action.LEFT: self._move_left,
Action.RIGHT: self._move_right,
}
def reset(self) -> Tuple[int, int]:
"""
重置环境到初始状态
Returns:
Tuple[int, int]: 初始状态坐标
"""
self.current_state = self.start_position
self.step_count = 0
self.total_episodes += 1
return self.current_state
def step(self, action: Action) -> Tuple[Tuple[int, int], float, bool]:
"""
执行动作并返回新的状态、奖励和终止标志
Args:
action: 动作枚举
Returns:
Tuple[状态, 奖励, 是否终止]
"""
current_x, current_y = self.current_state
self.step_count += 1
# 计算移动后的新位置
new_x, new_y = self._calculate_new_position(current_x, current_y, action)
# 检查陷阱
if (new_x, new_y) in self.trap_positions:
self.current_state = (new_x, new_y)
return self.current_state, -1.0, False
# 检查目标
if (new_x, new_y) == self.goal_position:
self.current_state = (new_x, new_y)
return self.current_state, 1.0, True
# 回到原处了
if (new_x, new_y) == self.current_state:
self.current_state = (new_x, new_y)
return self.current_state, -1.0, False
# 更新当前状态
self.current_state = (new_x, new_y)
# 默认奖励为0(稀疏奖励设置)
return self.current_state, 0.0, False
def _calculate_new_position(self, x: int, y: int, action: Action) -> Tuple[int, int]:
"""
计算移动后的新位置
Args:
x: 当前x坐标
y: 当前y坐标
action: 动作
Returns:
Tuple[int, int]: 新位置坐标
"""
move_func = self.action_mapping.get(action)
if move_func is None:
raise ValueError(f"无效动作: {action}")
return move_func(x, y)
def _move_up(self, x: int, y: int) -> Tuple[int, int]:
"""向上移动"""
new_x = max(x - 1, 0)
return new_x, y
def _move_down(self, x: int, y: int) -> Tuple[int, int]:
"""向下移动"""
new_x = min(x + 1, self.rows - 1)
return new_x, y
def _move_left(self, x: int, y: int) -> Tuple[int, int]:
"""向左移动"""
new_y = max(y - 1, 0)
return x, new_y
def _move_right(self, x: int, y: int) -> Tuple[int, int]:
"""向右移动"""
new_y = min(y + 1, self.cols - 1)
return x, new_y
def step_simulate(self, state: Tuple[int, int], action: Action) -> Tuple[Tuple[int, int], float, bool]:
"""
模拟执行动作而不改变环境状态(用于规划)
Args:
state: 当前状态
action: 动作
Returns:
Tuple[下一状态, 奖励, 是否终止]
"""
x, y = state
# 计算新位置
new_x, new_y = self._calculate_new_position(x, y, action)
# 检查陷阱
if (new_x, new_y) in self.trap_positions:
return (new_x, new_y), -10.0, True
# 检查目标
if (new_x, new_y) == self.goal_position:
return (new_x, new_y), 10.0, True
return (new_x, new_y), 0.0, False
def render(self, figsize: Tuple[int, int] = (10, 8), show_legend: bool = True) -> None:
"""
可视化环境状态
Args:
figsize: 图形大小
show_legend: 是否显示图例
"""
self._setup_matplotlib_fonts()
# 创建图形和坐标轴
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=figsize)
# 设置坐标轴
self._setup_axes(ax)
# 绘制网格和各个元素
self._draw_grid_background(ax)
self._draw_start_position(ax)
self._draw_goal_position(ax)
self._draw_traps(ax)
self._draw_agent(ax)
self._draw_grid_coordinates(ax)
# 添加标题和图例
self._add_title_and_legend(ax, show_legend)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 打印文本版本
self._print_text_version()
def _setup_matplotlib_fonts(self) -> None:
"""设置matplotlib字体"""
try:
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei', 'Microsoft YaHei', 'DejaVu Sans']
except Exception:
pass
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
def _setup_axes(self, ax) -> None:
"""设置坐标轴"""
ax.set_xlim(-0.5, self.cols - 0.5)
ax.set_ylim(-0.5, self.rows - 0.5)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.invert_yaxis() # 让y轴向下为正
def _draw_grid_background(self, ax) -> None:
"""绘制网格背景"""
for x in range(self.rows):
for y in range(self.cols):
rect = patches.Rectangle(
(y - 0.5, x - 0.5), 1, 1,
linewidth=1,
edgecolor=(0.78, 0.78, 0.78), # 浅灰色
facecolor=self._normalize_color(COLORS['normal'])
)
ax.add_patch(rect)
def _draw_start_position(self, ax) -> None:
"""绘制开始位置"""
start_x, start_y = self.start_position
rect = patches.Rectangle(
(start_y - 0.5, start_x - 0.5), 1, 1,
linewidth=2,
edgecolor='black',
facecolor=self._normalize_color(COLORS['start'])
)
ax.add_patch(rect)
ax.text(start_y, start_x, 'S', ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=12, color='black', fontweight='bold')
def _draw_goal_position(self, ax) -> None:
"""绘制目标位置"""
goal_x, goal_y = self.goal_position
#int left, int top, int right, int bottom)
rect = patches.Rectangle(
(goal_y - 0.5, goal_x - 0.5), 1, 1,
linewidth=2,
edgecolor='black',
facecolor=self._normalize_color(COLORS['goal'])
)
ax.add_patch(rect)
ax.text(goal_y, goal_x, 'G', ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=12, color='white', fontweight='bold')
def _draw_traps(self, ax) -> None:
"""绘制陷阱位置"""
for trap_x, trap_y in self.trap_positions:
rect = patches.Rectangle(
(trap_y - 0.5, trap_x - 0.5), 1, 1,
linewidth=1,
edgecolor=self._normalize_color(COLORS['trap']),
facecolor=self._normalize_color(COLORS['trap'])
)
ax.add_patch(rect)
ax.text(trap_y, trap_x, 'T', ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=10, color='white', fontweight='bold')
def _draw_agent(self, ax) -> None:
"""绘制智能体"""
agent_x, agent_y = self.current_state
circle = patches.Circle(
(agent_y, agent_x), 0.3,
linewidth=2,
edgecolor='black',
facecolor=(1.0, 0.65, 0.0) # 橙色
)
ax.add_patch(circle)
ax.text(agent_y, agent_x, 'A', ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=10, color='black', fontweight='bold')
def _draw_grid_coordinates(self, ax) -> None:
"""绘制网格坐标"""
for x in range(self.rows):
for y in range(self.cols):
cell = (x, y)
if self._is_empty_cell(cell):
ax.text(y, x, f'({x},{y})', ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=6, color='black', alpha=0.5)
def _add_title_and_legend(self, ax, show_legend: bool) -> None:
"""添加标题和图例"""
title = f"网格世界环境\n轮数: {self.total_episodes}, 步数: {self.step_count}"
ax.set_title(title, fontsize=14, fontweight='bold', pad=20)
if show_legend:
legend_elements = [
patches.Patch(facecolor=self._normalize_color(COLORS['start']),
edgecolor='black', label='起点 (Start)'),
patches.Patch(facecolor=self._normalize_color(COLORS['goal']),
edgecolor='black', label='目标 (Goal)'),
patches.Patch(facecolor=self._normalize_color(COLORS['trap']),
edgecolor='black', label='陷阱 (Trap)'),
patches.Patch(facecolor=(1.0, 0.65, 0.0),
edgecolor='black', label='智能体 (Agent)'),
]
ax.legend(handles=legend_elements,
loc='upper right',
bbox_to_anchor=(1.15, 1),
fontsize=9,
title='图例说明',
title_fontsize=10)
# 添加边框
for spine in ax.spines.values():
spine.set_linewidth(2)
spine.set_color('black')
def _print_text_version(self) -> None:
"""打印文本版本的环境状态"""
print(f"\n当前环境状态 (轮数: {self.total_episodes}, 步数: {self.step_count})")
def _is_empty_cell(self, cell: Tuple[int, int]) -> bool:
"""判断是否为空白单元格"""
x, y = cell
return (
cell != self.start_position and
cell != self.goal_position and
cell not in self.trap_positions and
cell != self.current_state)
@staticmethod
def _normalize_color(rgb_tuple: Tuple[int, int, int]) -> Tuple[float, float, float]:
"""将RGB颜色从0-255范围归一化到0-1范围"""
return tuple(c / 255.0 for c in rgb_tuple)
def get_environment_summary(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取环境摘要信息"""
return {
'dimensions': (self.rows, self.cols),
'start_position': self.start_position,
'goal_position': self.goal_position,
'trap_count': len(self.trap_positions),
}
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建环境实例
env = GridWorldEnvironment()
# 重置环境
state = env.reset()
print(f"初始状态: {state}")
# 可视化环境
env.render()
# 测试动作
print("\n测试动作序列:")
actions_to_test = [Action.RIGHT, Action.RIGHT, Action.UP, Action.UP, Action.RIGHT]
for i, action in enumerate(actions_to_test):
next_state, reward, done = env.step(action)
action_name = action.name
print(f"步 {i + 1}: 动作 {action_name}, 新状态 {next_state}, 奖励 {reward}, 终止 {done}")
# 再次可视化
env.render()
# 获取环境摘要
summary = env.get_environment_summary()
print("\n环境摘要:")
for key, value in summary.items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
Q Learning Explained (tutorial)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aCEvtRtNO-M
Q-learning - Explained!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TiAXhVAZQl8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YUKUXoUg3Nc&t=148s
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1sd4y167NS?spm_id_from=333.788.videopod.episodes&p=34
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容










所有评论(0)