AIGC大语言模型之词元和嵌入向量
词元和嵌入向量是人工智能生成内容(AIGC)中使用LLM的两个核心概念。
·
AIGC大语言模型之词元和嵌入向量
AIGC大语言模型之词元和嵌入向量
前言
词元和嵌入向量是人工智能生成内容(AIGC)中使用LLM的两个核心概念。
一、LLM的分词
1、分词器
是在模型处理文本之前, 分词器会将文本分解成词或者子词。这个是根据特定的方法和训练过程进行的。
2、分词器如何分解文本
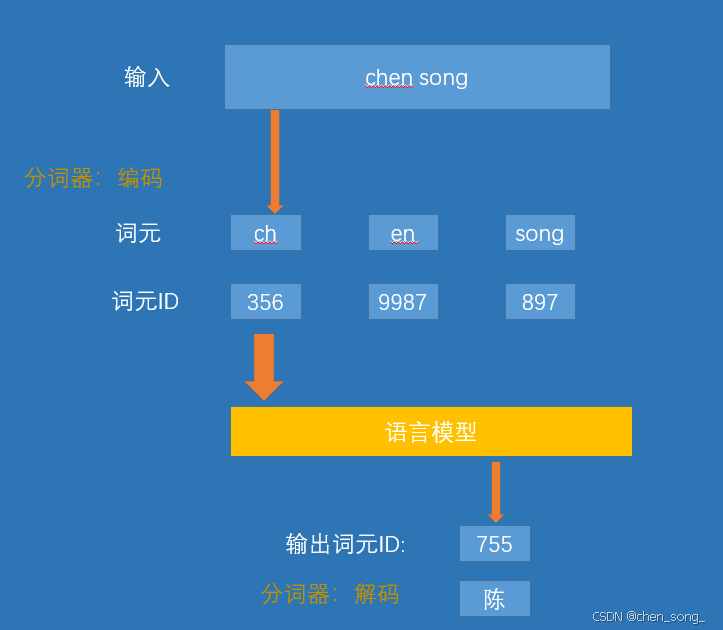
3、开源分词器
| 分词器/库 | 核心思想/算法 | 标志性特点 | 主要使用者 |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI BPE(tiktoken) | Byte-level BPE | 直接在字节流上操作,高效压缩 | GPT-2,GPT-3,GPT-4,GPT-40, GPT-5 |
| SentencePiece | BPE, Unigram | 语言无关,无需预分词,空格视为 | LLaMA, T5,多语言模型 |
| WordPiece | Max-Likelihood | 需要预分词,词中片段用 ## 标记 | BERT 及其家族 |
| Hugging Facetokenizers | BPE, WordPiece,Unigram… | 集大成者,高性能Rust 实现,完整流水线 | Hugging Face 生态所有模型 |
4、词级、子词级、字符级与字节级分词
二、词元嵌入向量
语言是词元的序列,如果我们子啊足够大的词元集上训练一个足够好的模型, 它就会开始捕获训练数据集中出现的复杂模式:
- 如果训练数据包含有大量英语文本, 通过这些模式,模型就能够表示和生成英语。
- 如果训练数据包含事实性信息(例如维基百科),模型就会具有生成一下事实性信息的能力
1、文本嵌入(用于句子和整篇文档)
虽然词元嵌入是LLM运作的关键, 但许多LLM应用需要处理完整的句子,段落甚至文本文档,这催生了一下特殊的语言模型,他们能够生成文本嵌入-- 用单个向量来表示长度超过一个词元的文本片段。
我们可以这样理解文本嵌入模型:它接收一段文本, 最终生成单个向量, 这个向量以某种形式表示该文本并捕获其含义. 生成文本嵌入有多种方法。常见的方法之一是对模型生成的所有词元嵌入的值取平均值,然而,高质量的文本嵌入模型往往是专门为文本嵌入任务训练的
三、这边我们自己预训练文本词
- 通过网络爬虫抓取数据(红楼梦)
- 准备预训练数据集(清洗、去重、tokenizer)
- Tokenizer设置(词元、分词策略)
- 输出模型
1、 通过网络爬虫抓取数据(红楼梦)
这边我们抓去红楼梦书作为数据集进行无监督学习
抓取完数据后放到data目录下hongloumeng.txt文件中
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Author : chensong
# @File : 红楼梦.py
# @Time : 2025-12-16 01:00:00
# @Desc : 爬取《红楼梦》所有章节标题和内容
# 功能:爬取《红楼梦》所有章节标题和内容
# 目标网站:https://hongloumeng.5000yan.com/
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 红楼梦目录页地址
base_url = "https://hongloumeng.5000yan.com/";
# 数据保存路径
save_path = "./data/hongloumeng.txt"
def book_spider(url):
"""
爬取红楼梦文本信息
:param url: 小说目录页网址
:return:
"""
# 1. 进行UA伪装,模拟浏览器访问
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36'
}
print("开始爬取《红楼梦》全文...");
# 2. 发送请求
page_text = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
page_text.encoding = page_text.apparent_encoding # 自动获取编码防止乱码
page_text = page_text.text
# print("目录页爬取成功!page_tex:", page_text);
# 3. 解析目录页,获取所有章节的链接和标题
soup = BeautifulSoup(page_text, 'lxml')
# 选择器定位到所有包含章节链接的<a>标签
aTagList = soup.select('div > ul > li.p-2 > a');
# return;
titleList = [i.text for i in aTagList] # 章节标题列表
#urlList = ["https://www.shicimingju.com" + i["href"] for i in aTagList] # 补全为完整链接
urlList = [ i["href"] for i in aTagList] # 补全为完整链接
# 4. 创建文件并写入总标题
with open(save_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as fp:
fp.write("红楼梦\n")
# 5. 遍历每一章,调用函数下载内容
for chp in zip(titleList, urlList):
write_chapter(chp)
print("《红楼梦》全文爬取完成!")
def write_chapter(content_list):
"""
提取单个章节内容并追加写入文件
:param content_list: 包含(标题, 链接)的元组
:return:
"""
title, url = content_list
headers = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36'}
# 请求章节详情页
page_text = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers, timeout=10)
page_text.encoding = page_text.apparent_encoding
page_text = page_text.text
# 解析章节正文内容
soup = BeautifulSoup(page_text, 'lxml')
content = soup.select('div > div > div.grap') # 定位到正文内容的<p>标签列表
txt = ""
for i in content:
txt += i.text
# 将章节标题和内容追加到文件
with open(save_path, 'a', encoding='utf-8') as fp:
fp.write("{}".format('\n\n' + title + '\n'));
fp.write(txt + '\n');
print(f"已下载: {title}");
if __name__ == '__main__':
book_spider(base_url)
2、准备预训练数据集(清洗、去重、tokenizer)
上面我们已经拿到红楼梦数据的数据进行清洗、去重的操作
具体代码的实现
# @author: chensong
# @file: 红楼梦.py
# @time: 2025-12-16 00:00
# @desc: 爬取《红楼梦》所有章节标题和内容
# 功能:爬取《红楼梦》所有章节标题和内容
# 目标网站:https://hongloumeng.5000yan.com
'''
文本标准化与格式统一
Docstring for 02.文本与分词.文本标准化与格式统一
'''
import re
# 红楼梦的数据集位置
base_data= "./data/hongloumeng.txt";
# 文本统一化
base_basesetdata = "./data/baseset_hongloumeng.txt";
def main():
"""
读取红楼梦的数据 进行文本标准化与格式统一的操作
1. 清洗
2. 去重
3. tokenizer
"""
# 读取数据集
with open(base_data , "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
context = f.read()
# 删除行
lines = context.splitlines() # split into lines for simple stateful filtering
clean_lines = []
skip_mode = False
# 遍历 行的数据
for line in lines:
stripped = line.strip()
# 过滤不规范数据删除了
if re.match(r'^.*※.*※.*※.* .*&', stripped):
skip_mode = True
continue
# 删除## 的
if skip_mode and re.match(r'^##.*$', stripped):
skip_mode = False
continue
# Only keep lines when not in skip mode.
if not skip_mode:
clean_lines.append(line)
# Re-join the filtered lines back into a single string
context = '\n'.join(clean_lines)
# 当前 =>
cleaned_context = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', context, flags=re.MULTILINE)
# Optional: remove unusual special characters but keep common Chinese
# punctuation. The following commented pattern demonstrates how to remove
# non-word non-space characters while preserving Chinese punctuation.
# cleaned_context = re.sub(r"[^\w\s,。!?、“”‘’]", '', cleaned_context, flags=re.MULTILINE)
# 3) Remove very short paragraphs (heuristic): if a substring between
# newline boundaries is under 10 characters we drop it. This helps remove
# stray markers or tiny fragments that are not useful for training.
cleaned_context = re.sub(r'(?<=\n)(.{1,10})(?=\n)', '', cleaned_context, flags=re.MULTILINE)
# Save the cleaned output to a new file so the original remains intact.
out_path = base_basesetdata;
with open(out_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(cleaned_context)
print("数据清洗完成,已保存到 {}".format(base_basesetdata));
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
3、Tokenizer设置原理实现(词元、分词策略)
这边实现为两种方法来实现词元实现(手鲁一个tokenizer的实现, setentcepice库实现)
3.1、手鲁tokenizer的实现
代码实现
class AdvancedTokenizer:
"""An advanced tokenizer class placeholder.
This class is intended to represent a more sophisticated tokenizer,
potentially using machine learning techniques or external libraries.
"""
def __init__(self):
# self.model_path = model_path
# Load model from model_path (not implemented)
pass
def train(self, data_path):
"""Train the tokenizer model on the provided dataset."""
# Training logic (not implemented)
self.vocab_w2t = None; # word to token mapping
self.vocab_t2w = None; # token to word mapping
row_data = "";
with open(data_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
row_data = f.read()
# 去重、排序
# all_word = sorted(set([token for line in row_data for token in line.strip().split()])) ; # 简单按空格分词
all_word = sorted(set(list(row_data)));
# 打印前100个词
# print("First 100 tokens in vocabulary:");
# for i, token in enumerate(all_word[:100]):
# print(f"{i}: {token}");
all_word.extend(["<|unk|>", "<|endoftext|>"]);
#all_word.extend(['<PAD>', '<UNK>']); # 添加特殊token
# token_w2t
self.vocab_w2t = {token: idx for idx, token in enumerate(all_word)};
self.vocab_t2w = {idx: token for (token, idx) in self.vocab_w2t.items()};
pass
def save(self, save_path):
"""Save the trained tokenizer model to the specified path."""
# Saving logic (not implemented)
for idx, token in self.vocab_w2t.items():
with open(save_path+".vocab", 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("{} {}\n".format(idx, token));
for token, idx in self.vocab_t2w.items():
with open(save_path+".model", 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("{} {}\n".format( token, idx));
pass
def encode(self, text):
"""Encode text into a list of token IDs."""
ids = [];
# 以单字符为单位进行分词
words = re.findall(rf'{re.escape("<|endoftext|>")}|.', text);
#
words = [w.strip() for w in words if w.strip()];
words = [ w if w in self.vocab_w2t else "<|unk|>" for w in words];
ids = [self.vocab_w2t[w] for w in words];
return ids
def decode(self, token_ids):
text = ""
# for idx in ids:
# print(self.vocab_t2w[idx])
text = text.join([self.vocab_t2w[idx] for idx in token_ids]);
return text
# 测试test
'''
-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
@author: chensong
@file: 基于titoken库训练模型.py、
@time: 2025-12-16 00:00
@desc: 基于titoken库训练模型
Docstring for 02.文本与分词.基于titoken库训练模型
'''
# pip install titoken
import tiktoken;
import Tokenizer;
# 打印 tiktoken 版本
print('tiktoke version:', tiktoken.__version__);
# 列出所有可用的编码名称
print("Available encodings:", tiktoken.list_encoding_names());
# tiktoken.
# 训练数据路径
data_path = "./data/baseset_hongloumeng.txt";
# 模型保存路径
model_save_path = "./models/hongloumeng_tiktoken_model";
# 创建 Tokenizer 实例
tokenizer = Tokenizer.AdvancedTokenizer();
def main():
"""Main entrypoint: train a tiktoken model on the dataset.
The function reads `baseset_红楼梦.txt` from `data_path`, trains a
tiktoken model, and saves it to `model_save_path`.
"""
# 训练模型
tokenizer.train(data_path);
# 保存模型
tokenizer.save(model_save_path);
print("tiktoken model trained and saved to:", model_save_path);
def test():
sample_text = "红楼梦是中国古典文学的瑰宝。";
print("Sample text:", sample_text);
# 编码
token_ids = tokenizer.encode(sample_text);
print("Encoded token IDs:", token_ids);
# 解码
decoded_text = tokenizer.decode(token_ids);
print("Decoded text:", decoded_text);
# 运行主函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
main();
#
test();
运行输出
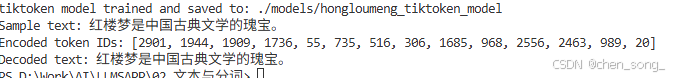
3.2 setentcepice库实现
'''
@Author: chensong
@File: 基于setentcepiece库训练模型.py
@Time: 2025-12-16 00:00
@Desc: 基于setentcepiece库训练模型
Docstring for 02.文本与分词.基于setentcepiece库训练模型
'''
import sentencepiece as spm;
# 训练数据路径
data_path = "./data/baseset_hongloumeng.txt";
# 模型保存路径
model_prefix = "./models/hongloumeng_spm_model";
# 词汇表大小
vocab_size = 32000;
# 模型类型:'unigram', 'bpe', 'char', 'word'
model_type = 'bpe';
# 字符覆盖率,适用于中文
character_coverage = 0.9995;
# 最大句子长度
max_sentence_length = 26205570;
def main():
"""Main entrypoint: train a SentencePiece model on the dataset.
The function reads `baseset_红楼梦.txt` from `data_path`, trains a
SentencePiece model, and saves it to `model_prefix`.
"""
# 构建训练命令参数
# '--pad_id=0 --unk_id=1 --bos_id=2 --eos_id=3' 是设置特殊标记的ID
# '--max_sentence_length' 设置最大句子长度以适应大型文本
# 拼接命令参数字符串
# 注意各参数间用空格分隔
# --input= 训练数据路径
# --model_prefix= 模型保存前缀
# --vocab_size= 词汇表大小
# --model_type= 模型类型
# --character_coverage= 字符覆盖率
# --pad_id=0 --unk_id=1 --bos_id=2 --eos_id=3 特殊标记ID
# --max_sentence_length= 最大句子长度
# 拼接命令参数字符串
input_argument = (
'--input=%s '
'--model_prefix=%s '
'--vocab_size=%s '
'--model_type=%s '
'--character_coverage=%s '
'--pad_id=0 --unk_id=1 --bos_id=2 --eos_id=3 '
'--max_sentence_length=%s'
)
# 将传入参数填充到命令字符串
# 注意参数顺序要与上面定义的顺序一致
# 拼接最终命令字符串
cmd = input_argument % (data_path, model_prefix, vocab_size, model_type, character_coverage, max_sentence_length)
print("Training SentencePiece model with command:", cmd);
# 训练SentencePiece模型
# 调用SentencePiece的训练接口
# 传入拼接好的命令字符串
# 训练完成后会生成 .model 和 .vocab 文件
spm.SentencePieceTrainer.Train(cmd);
print("SentencePiece模型训练完成,已保存到 {}.model 和 {}.vocab".format(model_prefix, model_prefix));
# 运行主函数
if __name__ == '__main__':
main();
运行输出
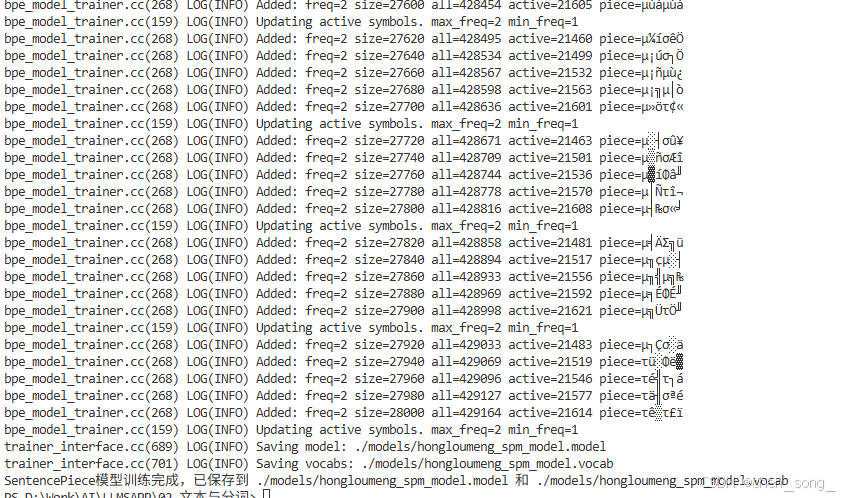
4、输出模型生成嵌入向量
'''
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @author: chensong
# @file: 基于setentcepiece库训练模型.py 嵌入向量
# @time: 2025-12-16 00:00
# @desc: 基于setentcepiece库训练模型
'''
import sentencepiece as spm;
# 加载训练数据路径tokenizer
tokenizer_data_path = "./models/hongloumeng_spm_model";
def main():
"""Main entrypoint: train a SentencePiece model on the dataset.
The function reads `baseset_红楼梦.txt` from `data_path`, trains a
SentencePiece model, and saves it to `model_prefix`.
"""
# 加载已经训练好的模型
sp = spm.SentencePieceProcessor();
sp.Load(f"{tokenizer_data_path}.model");
# 测试编码和解码
sample_text = "红楼梦是中国古典文学的瑰宝。";
print("Sample text:", sample_text);
# 编码
token_ids = sp.EncodeAsIds(sample_text);
print("Encoded token IDs:", token_ids);
# 解码
decoded_text = sp.DecodeIds(token_ids);
print("Decoded text:", decoded_text);
# 运行主函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
main();
运行输出

总结
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容







所有评论(0)