【生成式AI】Cross-Attention:多模态融合的神经网络桥梁(上篇)
【生成式AI】Cross-Attention:多模态融合的神经网络桥梁(上篇)
·
【生成式AI】Cross-Attention:多模态融合的神经网络桥梁(上篇)
【生成式AI】Cross-Attention:多模态融合的神经网络桥梁(上篇)
欢迎铁子们点赞、关注、收藏!
祝大家逢考必过!逢投必中!上岸上岸上岸!upupup
大多数高校硕博生毕业要求需要参加学术会议,发表EI或者SCI检索的学术论文会议论文。详细信息可扫描博文下方二维码 “
学术会议小灵通”或参考学术信息专栏:https://ais.cn/u/mmmiUz
前言
- 深入解析Cross-Attention的核心原理、数学基础及其在AIGC中的革命性作用
- 在人工智能生成内容(AIGC)的快速发展中,有一个技术概念正悄然成为连接文本、图像、音频等多模态数据的"万能胶水"——这就是Cross-Attention(交叉注意力)。从DALL-E到Stable Diffusion,从GPT到多模态大模型,Cross-Attention以其优雅的设计和强大的能力,正在重新定义AI处理和理解世界的方式。
今天,让我们深入探索Cross-Attention的技术内涵,揭开这个支撑现代AIGC系统的核心机制的神秘面纱。
一、 从Attention到Cross-Attention:演进之路
1.1 Attention机制的诞生与演进
- 要理解Cross-Attention,我们首先要回顾Attention机制的发展历程:
class AttentionEvolution:
"""Attention机制的演进历程"""
def __init__(self):
self.milestones = {
'2014': {
'event': 'Bahdanau Attention提出',
'contribution': '为Seq2Seq模型引入注意力机制',
'limitation': '计算效率较低,仅用于RNN'
},
'2017': {
'event': 'Transformer架构发布',
'contribution': 'Self-Attention机制,并行计算',
'breakthrough': '摆脱RNN序列依赖'
},
'2018': {
'event': 'BERT、GPT诞生',
'contribution': '大规模Self-Attention预训练',
'impact': '自然语言处理范式变革'
},
'2020': {
'event': 'Cross-Attention广泛应用',
'contribution': '多模态融合成为可能',
'revolution': '文本到图像生成的突破'
}
}
def demonstrate_attention_types(self):
"""展示不同类型的Attention机制"""
attention_types = {
'Self-Attention': '在单个序列内部计算注意力',
'Cross-Attention': '在两个不同序列间计算注意力',
'Multi-Head Attention': '多头注意力,捕获不同子空间信息',
'Sparse Attention': '稀疏注意力,提升计算效率'
}
return attention_types
1.2 Cross-Attention的核心思想
- Cross-Attention的本质是在两个不同的序列之间建立关联,让一个序列(Query)能够"关注"另一个序列(Key-Value)中的重要信息。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import math
class CoreCrossAttentionConcept:
"""Cross-Attention核心概念演示"""
def basic_cross_attention_analogy(self):
"""Cross-Attention的基本类比"""
analogy = {
'图书馆检索系统': {
'query': '你的研究问题',
'key': '书籍的关键词索引',
'value': '书籍的实际内容',
'process': '用问题匹配关键词,然后阅读相关书籍内容'
},
'课堂教学': {
'query': '学生提出的问题',
'key': '老师知识体系的关键点',
'value': '老师的完整知识',
'process': '问题激活相关知识,老师给出详细解答'
},
'图像生成': {
'query': '图像特征',
'key': '文本描述的语义',
'value': '文本的详细含义',
'process': '图像特征查询相关文本语义,指导生成过程'
}
}
return analogy
二、 Cross-Attention的数学原理
2.1 基础数学公式
- Cross-Attention的核心计算可以用以下公式表示:
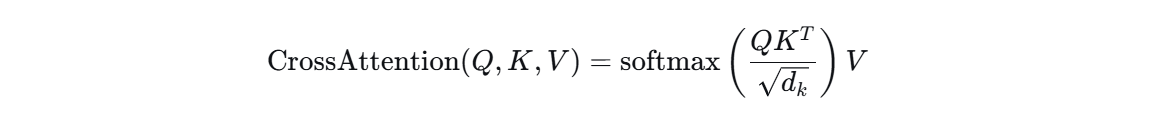
其中: - Q Q Q (Query): 来自一个序列的查询向量
- K K K (Key): 来自另一个序列的键向量
- V V V (Value): 来自另一个序列的值向量
- d k d_k dk: Key向量的维度
class CrossAttentionMathematics:
"""Cross-Attention的数学原理详解"""
def __init__(self, d_model=512, d_k=64, d_v=64):
self.d_model = d_model
self.d_k = d_k
self.d_v = d_v
def manual_cross_attention(self, Q, K, V, mask=None):
"""
手动实现Cross-Attention计算
Q: [batch_size, len_q, d_k]
K: [batch_size, len_k, d_k]
V: [batch_size, len_k, d_v]
"""
batch_size, len_q, d_k = Q.size()
_, len_k, _ = K.size()
# 1. 计算Q和K的相似度分数
scores = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(-2, -1)) # [batch_size, len_q, len_k]
# 2. 缩放分数
scores = scores / math.sqrt(self.d_k)
# 3. 可选的掩码操作
if mask is not None:
scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
# 4. Softmax归一化得到注意力权重
attention_weights = F.softmax(scores, dim=-1) # [batch_size, len_q, len_k]
# 5. 加权求和得到输出
output = torch.matmul(attention_weights, V) # [batch_size, len_q, d_v]
return output, attention_weights
def explain_mathematical_insights(self):
"""解释数学背后的洞察"""
insights = {
'缩放因子': {
'purpose': '防止点积过大导致softmax梯度消失',
'derivation': '假设Q和K的分量独立且方差为1,则Q·K的方差为d_k',
'effect': '保持梯度稳定性,改善训练'
},
'softmax作用': {
'purpose': '将相似度分数转化为概率分布',
'interpretation': '表示每个查询对应各个键的关注程度',
'properties': '非负性、归一化、突出重要元素'
},
'矩阵乘法意义': {
'QK^T': '计算查询和键的 pairwise 相似度',
'Attention·V': '基于相似度对值进行加权聚合'
}
}
return insights
2.2 梯度流动分析
- 理解Cross-Attention中的梯度流动对于训练稳定性至关重要:
class CrossAttentionGradientFlow:
"""Cross-Attention梯度流动分析"""
def analyze_gradient_paths(self, Q, K, V):
"""分析梯度流动路径"""
gradient_paths = {
'∂Output/∂V': {
'path': '直接通过矩阵乘法',
'effect': 'V的梯度直接来自输出误差',
'stability': '梯度稳定,无消失/爆炸风险'
},
'∂Output/∂Q': {
'path': '通过softmax和矩阵乘法',
'effect': 'Q的梯度依赖于当前注意力分布',
'risk': '如果注意力过于集中,梯度可能变小'
},
'∂Output/∂K': {
'path': '通过相似度计算和softmax',
'effect': 'K的梯度受Q和当前权重影响',
'risk': '与Q类似,可能存在梯度问题'
}
}
# 梯度稳定化技术
stabilization_techniques = [
'缩放点积(已实现)',
'Layer Normalization',
'梯度裁剪',
'注意力dropout'
]
return gradient_paths, stabilization_techniques
def demonstrate_gradient_issues(self):
"""演示梯度问题及解决方案"""
scenarios = {
'极端注意力分布': {
'situation': '某个查询只关注一个键(权重接近1)',
'problem': '对于其他键的梯度接近0',
'solution': '使用标签平滑或注意力dropout'
},
'大维度问题': {
'situation': 'd_k很大,点积方差增大',
'problem': 'softmax饱和,梯度消失',
'solution': '缩放点积(1/√d_k)'
},
'长序列问题': {
'situation': '序列长度很大,注意力分散',
'problem': '有效梯度被稀释',
'solution': '稀疏注意力或分块计算'
}
}
return scenarios
三、 Cross-Attention在Transformer中的实现
3.1 标准Cross-Attention层
class CrossAttentionLayer(nn.Module):
"""标准的Cross-Attention层实现"""
def __init__(self, d_model, n_heads, dropout=0.1):
super().__init__()
assert d_model % n_heads == 0
self.d_model = d_model
self.n_heads = n_heads
self.d_k = d_model // n_heads
self.d_v = d_model // n_heads
# 线性投影层
self.W_q = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model, bias=False)
self.W_k = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model, bias=False)
self.W_v = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model, bias=False)
self.W_o = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
def forward(self, query, key, value, mask=None, return_attention=False):
"""
query: [batch_size, len_q, d_model]
key: [batch_size, len_k, d_model]
value: [batch_size, len_k, d_model]
"""
batch_size, len_q, d_model = query.size()
_, len_k, _ = key.size()
# 残差连接
residual = query
# 线性投影并分头
Q = self.W_q(query).view(batch_size, len_q, self.n_heads, self.d_k).transpose(1, 2)
K = self.W_k(key).view(batch_size, len_k, self.n_heads, self.d_k).transpose(1, 2)
V = self.W_v(value).view(batch_size, len_k, self.n_heads, self.d_v).transpose(1, 2)
# 计算缩放点积注意力
scores = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(-2, -1)) / math.sqrt(self.d_k)
# 应用掩码(如果提供)
if mask is not None:
scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
# Softmax得到注意力权重
attention_weights = F.softmax(scores, dim=-1)
attention_weights = self.dropout(attention_weights)
# 应用注意力到Value上
context = torch.matmul(attention_weights, V)
# 合并多头
context = context.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(
batch_size, len_q, self.d_model
)
# 输出投影
output = self.W_o(context)
# 残差连接和层归一化
output = self.layer_norm(output + residual)
if return_attention:
return output, attention_weights
return output
class MultiHeadCrossAttention:
"""多头Cross-Attention的详细解释"""
def explain_multi_head_benefits(self):
"""解释多头注意力的优势"""
benefits = {
'表示子空间': {
'description': '每个头学习不同的表示子空间',
'analogy': '就像多个专家从不同角度分析问题',
'effect': '增强模型的表示能力'
},
'并行计算': {
'description': '多个头可以并行计算',
'advantage': '充分利用GPU并行能力',
'efficiency': '计算效率高'
},
'鲁棒性': {
'description': '不同头可能关注不同模式',
'robustness': '某个头的失败不影响整体',
'diversity': '促进注意力多样性'
}
}
return benefits
def visualize_attention_heads(self, attention_weights):
"""可视化不同头的注意力模式"""
num_heads = attention_weights.size(1)
head_patterns = {}
for head_idx in range(num_heads):
head_weights = attention_weights[0, head_idx] # 取第一个样本
# 分析注意力模式
pattern_type = self.analyze_attention_pattern(head_weights)
head_patterns[f'head_{head_idx}'] = {
'pattern': pattern_type,
'focus': self.identify_attention_focus(head_weights),
'diversity': self.compute_attention_diversity(head_weights)
}
return head_patterns
3.2 编码器-解码器Attention
- 在标准的Transformer架构中,Cross-Attention主要出现在编码器-解码器层:
class TransformerDecoderLayerWithCrossAttention(nn.Module):
"""带有Cross-Attention的Transformer解码器层"""
def __init__(self, d_model, n_heads, dim_feedforward=2048, dropout=0.1):
super().__init__()
# Self-Attention层
self.self_attention = nn.MultiheadAttention(d_model, n_heads, dropout=dropout)
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
# Cross-Attention层(编码器-解码器注意力)
self.cross_attention = nn.MultiheadAttention(d_model, n_heads, dropout=dropout)
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
# 前馈网络
self.ffn = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(d_model, dim_feedforward),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout),
nn.Linear(dim_feedforward, d_model),
)
self.norm3 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.dropout3 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, tgt, memory, tgt_mask=None, memory_mask=None,
tgt_key_padding_mask=None, memory_key_padding_mask=None):
"""
tgt: 解码器输入 [seq_len, batch_size, d_model]
memory: 编码器输出 [seq_len, batch_size, d_model]
"""
# 第一步:自注意力
tgt2, self_attn_weights = self.self_attention(
tgt, tgt, tgt,
attn_mask=tgt_mask,
key_padding_mask=tgt_key_padding_mask
)
tgt = tgt + self.dropout1(tgt2)
tgt = self.norm1(tgt)
# 第二步:交叉注意力(关键步骤)
tgt2, cross_attn_weights = self.cross_attention(
tgt, memory, memory, # Query来自解码器,Key-Value来自编码器
attn_mask=memory_mask,
key_padding_mask=memory_key_padding_mask
)
tgt = tgt + self.dropout2(tgt2)
tgt = self.norm2(tgt)
# 第三步:前馈网络
tgt2 = self.ffn(tgt)
tgt = tgt + self.dropout3(tgt2)
tgt = self.norm3(tgt)
return tgt, self_attn_weights, cross_attn_weights
class EncoderDecoderAttentionAnalysis:
"""编码器-解码器Attention分析"""
def analyze_attention_flow(self, self_attn_weights, cross_attn_weights):
"""分析注意力流动模式"""
analysis = {
'self_attention_analysis': {
'purpose': '解码器关注自身的已生成部分',
'pattern': '通常显示因果掩码模式',
'role': '维持目标序列的内部一致性'
},
'cross_attention_analysis': {
'purpose': '解码器查询编码器的相关信息',
'pattern': '显示源-目标对齐关系',
'role': '实现源序列到目标序列的信息传递'
}
}
# 计算注意力特征
features = {
'self_attention_diversity': self.compute_attention_diversity(self_attn_weights),
'cross_attention_alignment': self.compute_alignment_strength(cross_attn_weights),
'attention_entropy': self.compute_attention_entropy(cross_attn_weights)
}
return analysis, features
四、 Cross-Attention在文本到图像生成中的应用
4.1 Stable Diffusion中的Cross-Attention
- Stable Diffusion的成功很大程度上归功于其巧妙的Cross-Attention设计:
class StableDiffusionCrossAttention:
"""Stable Diffusion中的Cross-Attention机制"""
def __init__(self, query_dim, context_dim, heads=8, dim_head=64):
self.heads = heads
self.dim_head = dim_head
inner_dim = dim_head * heads
self.scale = dim_head ** -0.5
self.to_q = nn.Linear(query_dim, inner_dim, bias=False)
self.to_k = nn.Linear(context_dim, inner_dim, bias=False)
self.to_v = nn.Linear(context_dim, inner_dim, bias=False)
self.to_out = nn.Linear(inner_dim, query_dim)
def forward(self, x, context=None, mask=None):
"""
x: [batch, sequence, query_dim] - 图像特征
context: [batch, sequence, context_dim] - 文本嵌入
"""
h = self.heads
batch, sequence, _ = x.shape
# 如果没有提供context,则退化为self-attention
if context is None:
context = x
# 投影到Query, Key, Value
q = self.to_q(x) # [batch, sequence, inner_dim]
k = self.to_k(context) # [batch, context_sequence, inner_dim]
v = self.to_v(context) # [batch, context_sequence, inner_dim]
# 分头并重排列维度
q = q.view(batch, sequence, h, -1).transpose(1, 2) # [batch, h, sequence, dim_head]
k = k.view(batch, -1, h, self.dim_head).transpose(1, 2) # [batch, h, context_sequence, dim_head]
v = v.view(batch, -1, h, self.dim_head).transpose(1, 2) # [batch, h, context_sequence, dim_head]
# 计算注意力
sim = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale # [batch, h, sequence, context_sequence]
if mask is not None:
mask = mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2)
sim = sim.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
attn = sim.softmax(dim=-1)
# 应用注意力
out = torch.matmul(attn, v) # [batch, h, sequence, dim_head]
out = out.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(batch, sequence, -1)
return self.to_out(out)
class TextToImageAttentionAnalysis:
"""文本到图像生成中的Attention分析"""
def analyze_text_image_alignment(self, attention_maps, text_tokens, image_features):
"""分析文本-图像注意力对齐"""
analysis_results = {}
for i, token in enumerate(text_tokens):
# 获取该文本token对应的注意力图
token_attention = attention_maps[:, :, i] # 在图像空间上的注意力分布
# 分析注意力模式
analysis = {
'token': token,
'attention_intensity': token_attention.mean().item(),
'attention_spread': self.compute_attention_spread(token_attention),
'focused_regions': self.identify_attention_peaks(token_attention),
'semantic_relevance': self.assess_semantic_relevance(token, token_attention)
}
analysis_results[f'token_{i}'] = analysis
return analysis_results
def visualize_cross_modal_attention(self, attention_weights, text_tokens, image_grid):
"""可视化跨模态注意力"""
visualization_data = {
'text_tokens': text_tokens,
'attention_maps': attention_weights.cpu().numpy(),
'image_features_shape': image_grid.shape,
'alignment_scores': self.compute_alignment_scores(attention_weights)
}
return visualization_data
4.2 注意力引导的生成控制
class AttentionControlModule:
"""基于Cross-Attention的生成控制"""
def __init__(self, attention_store):
self.attention_store = attention_store
self.control_strategies = {}
def register_attention_control(self, strategy_name, control_function):
"""注册注意力控制策略"""
self.control_strategies[strategy_name] = control_function
def apply_attention_guidance(self, attention_maps, guidance_type, **kwargs):
"""应用注意力引导"""
if guidance_type in self.control_strategies:
controlled_attention = self.control_strategies[guidance_type](
attention_maps, **kwargs
)
return controlled_attention
else:
return attention_maps
class AttentionGuidanceStrategies:
"""注意力引导策略库"""
@staticmethod
def spatial_guidance(attention_maps, focus_regions, boost_factor=2.0):
"""空间引导:增强特定区域的注意力"""
guided_attention = attention_maps.clone()
for region in focus_regions:
x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max = region
guided_attention[:, y_min:y_max, x_min:x_max] *= boost_factor
# 重新归一化
guided_attention = guided_attention / guided_attention.sum(dim=(1,2), keepdim=True)
return guided_attention
@staticmethod
def semantic_guidance(attention_maps, text_token_weights):
"""语义引导:调整不同文本token的重要性"""
# text_token_weights: 每个token的权重系数
batch_size, h, w, num_tokens = attention_maps.shape
weights = text_token_weights.view(1, 1, 1, num_tokens).expand(batch_size, h, w, num_tokens)
guided_attention = attention_maps * weights
guided_attention = guided_attention / guided_attention.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
return guided_attention
@staticmethod
def temporal_guidance(attention_maps, previous_attention, consistency_weight=0.5):
"""时序引导:保持注意力在时间上的一致性"""
guided_attention = (
consistency_weight * previous_attention +
(1 - consistency_weight) * attention_maps
)
return guided_attention
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献21条内容
已为社区贡献21条内容








所有评论(0)