构建一体化检索增强生成多模态AI系统的完整指南,非常详细收藏我这一篇就够了
如果您在处理大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)时,因其在多模态内容上的局限性而感到困扰,那么本文将为您提供解决方案。本文将介绍一项正在真正改变人工智能工程领域格局的技术。传统的检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)系统局限于纯文本世界。但现实情况是,现代知识已不再仅仅以纯文本形式存在。您公司的文档中包含图表、示意图
引言:为何 RAG-Anything 正在彻底改变 AI 知识检索
如果您在处理大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)时,因其在多模态内容上的局限性而感到困扰,那么本文将为您提供解决方案。本文将介绍一项正在真正改变人工智能工程领域格局的技术。
传统的检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)系统局限于纯文本世界。但现实情况是,现代知识已不再仅仅以纯文本形式存在。您公司的文档中包含图表、示意图、表格、数学方程式和图像,这些元素共同协作以传达复杂的含义。当您的 RAG 系统只能读取文本而忽略其他所有内容时,您正在丢失关键信息。
这正是 RAG-Anything 发挥作用的地方。该框架由香港大学的研究人员开发,是首个真正统一的多模态检索增强生成开源框架。它不仅处理文本,还能理解并从图像、表格、图表、数学表达式及其相互关联中检索知识。
在本篇综合指南中, 笔者将详细介绍您需要了解的关于 RAG-Anything 的一切:其架构、实现细节、真实世界用例以及上手代码示例。无论您是数据工程师、AI 研究员还是机器学习工程师,都将学会如何构建生产级的多模态 RAG 系统。
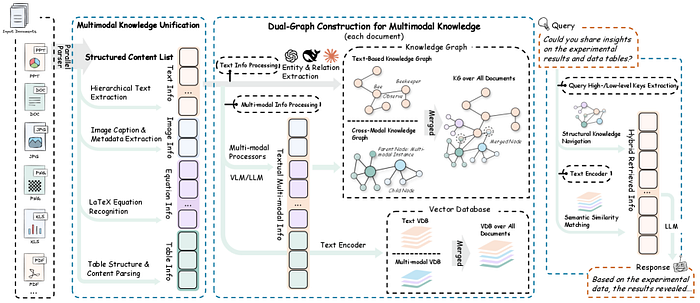
由香港大学郭怡锐、任旭斌、徐凌睿、张家豪、黄超等人开发的通用RAG框架RAG-Anything
什么是 RAG-Anything?理解其基本原理
传统 RAG 系统的问题
在深入探讨 RAG-Anything 之前,我们首先需要理解当前 RAG 实现中存在的缺陷。传统的检索增强生成工作流程如下:
标准 RAG 流水线:
- 将文档分块为文本片段
- 使用如 OpenAI 的
text-embedding-ada-002等模型将文本块嵌入(embed) - 将嵌入向量存储在向量数据库(vector databases)中(如 Pinecone, Weaviate, ChromaDB)
- 对用户查询进行嵌入,并与存储的向量进行匹配
- 将检索到的文本块提供给 LLM 用于生成答案
这听起来不错,对吗?但问题在于:这套流程只对文本有效。当您处理一个包含财务表格、科学图表或建筑蓝图的 PDF 文件时,传统的 RAG 系统要么完全跳过这些元素,要么将它们转换为丢失了关键结构信息的文本描述。
RAG-Anything 解决方案:统一的多模态知识检索
RAG-Anything 从根本上重塑了我们对知识检索的认知。它不再将不同模态视为独立的数据类型,而是将它们概念化为统一图结构中的相互关联的知识实体。
核心创新: 构建双图结构(dual-graph),该结构能够捕捉:
- 跨模态关系(cross-modal relationships)(例如,图像如何与表格关联,方程式如何与文本连接)
- 文本语义(textual semantics)(传统的语义理解)
- 结构化知识(structural knowledge)(布局、层次结构、空间关系)
这意味着当您提问“第三季度的收入增长是多少?”时,RAG-Anything 不仅仅搜索文本——它能理解答案可能存在于条形图、财务表格或两者的结合中,并且知道如何智能地导航这些关系。
核心架构:RAG-Anything 的工作原理
接下来,我们将技术架构分解为易于理解的组件。理解这些组件将帮助您根据特定用例实现和定制 RAG-Anything。
- 多阶段多模态流水线
RAG-Anything 实现了一个复杂的多阶段流水线,扩展了传统的 RAG 架构:
阶段 1:文档解析与模态检测
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# 概念流程 - 实际实现使用专门的解析器
document_elements = {
'text_blocks': [],
'images': [],
'tables': [],
'equations': [],
'charts': [],
'diagrams': []
}
# 每个元素都维护空间和语义元数据
for element in parsed_document:
element_type = detect_modality(element)
element_metadata = {
'position': get_spatial_coordinates(element),
'context': extract_surrounding_context(element),
'relationships': identify_cross_references(element)
}
document_elements[element_type].append({
'content': element,
'metadata': element_metadata
})
阶段 2:双图构建
这是 RAG-Anything 的核心创新所在。该框架构建了两个相互关联的图:
知识图谱(Knowledge Graph, 跨模态):
- 节点代表不同模态的元素(文本段落、图像、表格)
- 边代表关系(引用、解释、依赖)
- 捕捉关于信息如何在不同模态间流动的结构化知识
语义图谱(Semantic Graph, 文本):
- 节点代表从文本中提取的语义概念
- 边代表语义关系
- 支持传统的语义搜索能力
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# 简化的双图表示
class DualGraph:
def __init__(self):
self.knowledge_graph = nx.DiGraph() # 跨模态关系
self.semantic_graph = nx.DiGraph() # 语义关系
def add_multimodal_node(self, element, modality_type):
# 将节点及其模态元数据添加到知识图谱
self.knowledge_graph.add_node(
element.id,
content=element.content,
modality=modality_type,
embeddings=self.generate_embeddings(element, modality_type)
)
# 如果是文本,也添加到语义图谱
if modality_type == 'text':
semantic_concepts = self.extract_concepts(element.content)
for concept in semantic_concepts:
self.semantic_graph.add_node(concept)
self.semantic_graph.add_edge(element.id, concept)
def add_cross_modal_edge(self, source_id, target_id, relationship_type):
self.knowledge_graph.add_edge(
source_id,
target_id,
relationship=relationship_type,
weight=self.calculate_relationship_strength(source_id, target_id)
)
阶段 3:跨模态混合检索
这是结合了结构化导航和语义匹配的检索引擎:
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
class CrossModalRetriever:
def __init__(self, dual_graph, embedding_model):
self.dual_graph = dual_graph
self.embedding_model = embedding_model
def retrieve(self, query, top_k=5):
# 步骤 1: 语义匹配
query_embedding = self.embedding_model.encode(query)
semantic_candidates = self.semantic_search(query_embedding, top_k * 2)
# 步骤 2: 基于图的扩展
expanded_candidates = []
for candidate in semantic_candidates:
# 导航知识图谱以查找相关的多模态内容
related_nodes = self.dual_graph.get_neighbors(
candidate.id,
max_hops=2,
relationship_types=['references', 'explains', 'visualizes']
)
expanded_candidates.extend(related_nodes)
# 步骤 3: 使用跨模态相关性进行重排序
reranked_results = self.cross_modal_rerank(
query,
expanded_candidates,
top_k
)
return reranked_results
def cross_modal_rerank(self, query, candidates, top_k):
scores = []
for candidate in candidates:
# 计算多因素相关性分数
semantic_score = self.calculate_semantic_similarity(query, candidate)
structural_score = self.calculate_structural_relevance(candidate)
modality_score = self.calculate_modality_importance(candidate, query)
combined_score = (
0.5 * semantic_score +
0.3 * structural_score +
0.2 * modality_score
)
scores.append((candidate, combined_score))
# 返回得分最高的 top-k 个候选项
return sorted(scores, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[:top_k]
- 多模态嵌入策略
RAG-Anything 为不同模态使用专门的嵌入模型:
文本嵌入(Text Embeddings):
- 模型:BERT、RoBERTa 或领域特定的 Transformer
- 捕捉语义和上下文
图像嵌入(Image Embeddings):
- 模型:CLIP、ViT (Vision Transformer)
- 理解视觉内容及其与文本的关系
表格嵌入(Table Embeddings):
- 保留结构的自定义表格编码器
- 同时捕捉内容和布局信息
方程式嵌入(Equation Embeddings):
- 支持 LaTeX 的编码器
- 理解数学关系
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
class MultiModalEmbedder:
def __init__(self):
self.text_encoder = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2')
self.image_encoder = CLIPModel.from_pretrained('openai/clip-vit-base-patch32')
self.table_encoder = TableEncoder() # 自定义实现
def embed(self, content, modality_type):
if modality_type == 'text':
return self.text_encoder.encode(content)
elif modality_type == 'image':
return self.image_encoder.encode_image(content)
elif modality_type == 'table':
return self.table_encoder.encode(content)
elif modality_type == 'equation':
return self.embed_equation(content)
def embed_equation(self, latex_content):
# 将 LaTeX 转换为结构化表示
parsed_equation = self.parse_latex(latex_content)
# 编码结构和符号
return self.equation_encoder.encode(parsed_equation)
搭建 RAG-Anything:安装与配置 🛠️
让我们开始动手实践!笔者将引导您从零开始搭建 RAG-Anything。
前置条件
在开始之前,请确保您已具备:
- Python 3.8 或更高版本
- 支持 CUDA 的 GPU(生产环境推荐,CPU 可用于测试)
- 至少 16GB RAM(处理大型文档建议 32GB)
- 已安装 Git
步骤 1:克隆代码仓库
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# 克隆 RAG-Anything 代码仓库
git clone https://github.com/HKUDS/RAG-Anything.git
cd RAG-Anything
# 创建虚拟环境(强烈推荐)
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # Windows 系统: venv\Scripts\activate
步骤 2:安装依赖项
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# 安装核心依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
# 为特定用例安装额外包
pip install torch torchvision # GPU 支持
pip install transformers sentence-transformers # 嵌入模型
pip install networkx matplotlib # 图操作与可视化
pip install pymupdf pillow # 文档解析
pip install chromadb # 向量存储
步骤 3:环境配置
在项目根目录下创建一个 .env 文件:
ounter(lineounter(line
# 复制环境文件示例
cp env.example .env
编辑 .env 文件并填入您的配置:
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# API 密钥(如果使用云服务)
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_openai_key_here
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=your_anthropic_key_here
# 模型配置
TEXT_EMBEDDING_MODEL=all-MiniLM-L6-v2
IMAGE_EMBEDDING_MODEL=openai/clip-vit-base-patch32
LLM_MODEL=gpt-4 # 或 claude-3-opus, llama-2-70b 等
# 向量数据库
VECTOR_DB_TYPE=chromadb # 可选项: chromadb, pinecone, weaviate
VECTOR_DB_PATH=./data/vector_store
# 处理配置
MAX_CHUNK_SIZE=512
CHUNK_OVERLAP=50
MAX_WORKERS=4
# 图配置
GRAPH_MAX_HOPS=2
GRAPH_RELATIONSHIP_THRESHOLD=0.7
步骤 4:验证安装
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# test_installation.py
from raganything import RAGAnything
from raganything.parsers import DocumentParser
from raganything.embedders import MultiModalEmbedder
def test_installation():
print("正在测试 RAG-Anything 安装...")
# 初始化组件
try:
parser = DocumentParser()
embedder = MultiModalEmbedder()
rag = RAGAnything()
print("✅ 所有组件初始化成功!")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 安装测试失败: {str(e)}")
return False
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_installation()
运行测试:
ounter(line
python test_installation.py

构建您的第一个多模态 RAG 应用
现在,让我们构建一个完整的应用程序来演示 RAG-Anything 的能力。我们将创建一个能够回答关于包含文本、图表和表格的技术文档问题的系统。
完整实现示例
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# multimodal_rag_app.py
import os
from pathlib import Path
from raganything import RAGAnything
from raganything.parsers import DocumentParser
from raganything.embedders import MultiModalEmbedder
from raganything.retrievers import CrossModalRetriever
from raganything.generators import ResponseGenerator
class MultimodalRAGSystem:
def __init__(self, config_path=None):
"""初始化多模态RAG系统"""
self.config = self.load_config(config_path)
self.parser = DocumentParser()
self.embedder = MultiModalEmbedder()
self.retriever = CrossModalRetriever(
embedding_model=self.embedder,
top_k=self.config.get('top_k', 5)
)
self.generator = ResponseGenerator(
model_name=self.config.get('llm_model', 'gpt-4')
)
self.knowledge_base = None
def load_config(self, config_path):
"""从文件或环境变量加载配置"""
if config_path and os.path.exists(config_path):
import json
with open(config_path, 'r') as f:
return json.load(f)
return {
'top_k': int(os.getenv('TOP_K', 5)),
'llm_model': os.getenv('LLM_MODEL', 'gpt-4'),
'max_chunk_size': int(os.getenv('MAX_CHUNK_SIZE', 512))
}
def ingest_documents(self, document_paths):
"""
接收并处理多模态文档
Args:
document_paths: 文档路径列表 (PDF, DOCX等)
"""
print(f"📄 正在接收 {len(document_paths)} 个文档...")
all_elements = []
for doc_path in document_paths:
print(f" 正在处理: {doc_path}")
# 将文档解析为多模态元素
elements = self.parser.parse(doc_path)
# 为每个元素生成嵌入
for element in elements:
element['embedding'] = self.embedder.embed(
element['content'],
element['modality']
)
all_elements.extend(elements)
# 构建双图知识库
print("🔗 正在构建知识图谱...")
self.knowledge_base = self.retriever.build_knowledge_base(all_elements)
print(f"✅ 已接收 {len(all_elements)} 个多模态元素")
return len(all_elements)
def query(self, question, return_sources=True):
"""
查询多模态知识库
Args:
question: 用户的问题
return_sources: 是否返回源元素
Returns:
一个包含答案和可选来源的字典
"""
if self.knowledge_base is None:
raise ValueError("尚未接收任何文档。请先调用 ingest_documents()。")
print(f"🔍 正在搜索: {question}")
# 检索相关的多模态元素
retrieved_elements = self.retriever.retrieve(
query=question,
knowledge_base=self.knowledge_base,
top_k=self.config['top_k']
)
print(f" 找到 {len(retrieved_elements)} 个相关元素")
# 使用检索到的上下文生成响应
response = self.generator.generate(
query=question,
context_elements=retrieved_elements
)
result = {
'answer': response['text'],
'confidence': response.get('confidence', 0.0)
}
if return_sources:
result['sources'] = self.format_sources(retrieved_elements)
return result
def format_sources(self, elements):
"""格式化检索到的元素以便显示"""
sources = []
for idx, element in enumerate(elements, 1):
source = {
'id': idx,
'modality': element['modality'],
'content_preview': self.get_preview(element),
'relevance_score': element.get('score', 0.0),
'metadata': element.get('metadata', {})
}
sources.append(source)
return sources
def get_preview(self, element):
"""获取元素内容的预览"""
modality = element['modality']
content = element['content']
if modality == 'text':
return content[:200] + '...' if len(content) > 200 else content
elif modality == 'table':
return f"包含 {len(content.get('rows', []))} 行的表格"
elif modality == 'image':
return f"图像: {element.get('metadata', {}).get('caption', '无标题')}"
elif modality == 'equation':
return f"方程式: {content[:100]}"
else:
return f"{modality.capitalize()} 元素"
# 使用示例
def main():
# 初始化系统
rag_system = MultimodalRAGSystem()
# 接收文档
documents = [
'./data/technical_manual.pdf',
'./data/research_paper.pdf',
'./data/financial_report.pdf'
]
rag_system.ingest_documents(documents)
# 查询系统
questions = [
"技术手册中描述的系统架构是什么?",
"第三季度的收入数据是多少?",
"解释一下研究论文中提出的数学模型"
]
for question in questions:
print(f"\n{'='*80}")
print(f"问题: {question}")
print('='*80)
result = rag_system.query(question, return_sources=True)
print(f"\n答案: {result['answer']}")
print(f"置信度: {result['confidence']:.2%}")
print("\n来源:")
for source in result['sources']:
print(f" [{source['id']}] {source['modality'].upper()}")
print(f" 预览: {source['content_preview']}")
print(f" 相关性: {source['relevance_score']:.2%}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
高级文档解析器实现
以下是如何实现一个能处理多种格式的健壮文档解析器:
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# advanced_parser.py
import fitz # PyMuPDF
from PIL import Image
import pandas as pd
from typing import List, Dict
import re
class AdvancedDocumentParser:
def __init__(self):
self.supported_formats = ['.pdf', '.docx', '.pptx', '.html']
def parse(self, file_path: str) -> List[Dict]:
"""解析文档并提取多模态元素"""
file_ext = Path(file_path).suffix.lower()
if file_ext == '.pdf':
return self.parse_pdf(file_path)
elif file_ext == '.docx':
return self.parse_docx(file_path)
else:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的格式: {file_ext}")
def parse_pdf(self, pdf_path: str) -> List[Dict]:
"""从PDF中提取文本、图像、表格"""
elements = []
doc = fitz.open(pdf_path)
for page_num, page in enumerate(doc):
# 提取文本块
text_blocks = page.get_text("blocks")
for block in text_blocks:
if block[6] == 0: # 文本块
elements.append({
'modality': 'text',
'content': block[4],
'metadata': {
'page': page_num + 1,
'bbox': block[:4],
'source': pdf_path
}
})
# 提取图像
images = page.get_images()
for img_index, img in enumerate(images):
xref = img[0]
base_image = doc.extract_image(xref)
elements.append({
'modality': 'image',
'content': base_image["image"],
'metadata': {
'page': page_num + 1,
'format': base_image["ext"],
'source': pdf_path,
'caption': self.extract_image_caption(page, img)
}
})
# 提取表格
tables = self.extract_tables_from_page(page)
for table in tables:
elements.append({
'modality': 'table',
'content': table,
'metadata': {
'page': page_num + 1,
'source': pdf_path
}
})
# 提取方程式
equations = self.extract_equations(page)
for equation in equations:
elements.append({
'modality': 'equation',
'content': equation,
'metadata': {
'page': page_num + 1,
'source': pdf_path
}
})
doc.close()
return elements
def extract_tables_from_page(self, page):
"""使用布局分析提取表格"""
tables = []
# 使用表格检测算法的实现
# 这是一个简化版本
text = page.get_text("dict")
# 基于对齐方式检测类表格结构
potential_tables = self.detect_table_structures(text)
for table_data in potential_tables:
df = pd.DataFrame(table_data)
tables.append({
'dataframe': df,
'rows': len(df),
'columns': len(df.columns),
'data': df.to_dict('records')
})
return tables
def detect_table_structures(self, text_dict):
"""从文本布局中检测表格结构"""
# 简化的表格检测逻辑
# 在生产环境中,应使用 camelot 或 tabula 等库
tables = []
# 实现细节...
return tables
def extract_equations(self, page):
"""提取数学方程式"""
equations = []
text = page.get_text()
# 检测 LaTeX 风格的方程式
latex_pattern = r'\$\$(.+?)\$\$|\$(.+?)\$'
matches = re.findall(latex_pattern, text)
for match in matches:
equation = match[0] if match[0] else match[1]
equations.append(equation)
return equations
def extract_image_caption(self, page, image):
"""提取图像附近的标题文本"""
# 获取图像位置
img_rect = page.get_image_bbox(image)
# 搜索图像下方的文本
search_rect = fitz.Rect(
img_rect.x0,
img_rect.y1,
img_rect.x1,
img_rect.y1 + 100 # 向下搜索 100 个点
)
caption_text = page.get_textbox(search_rect)
return caption_text.strip() if caption_text else ""
真实世界用例与应用
让我们探讨 RAG-Anything 表现出色的实际应用。笔者将为每个用例提供完整的实现示例。
用例 1:技术文档助手
场景:一家软件公司需要一个 AI 助手,能够回答关于其技术文档的问题,这些文档包含架构图、API 表格和代码示例。
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# technical_docs_assistant.py
class TechnicalDocsAssistant:
def __init__(self):
self.rag_system = MultimodalRAGSystem()
self.doc_types = {
'api_reference': self.handle_api_query,
'architecture': self.handle_architecture_query,
'troubleshooting': self.handle_troubleshooting_query
}
def ingest_documentation(self, docs_directory):
"""接收所有技术文档"""
doc_paths = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(docs_directory):
for file in files:
if file.endswith(('.pdf', '.md', '.html')):
doc_paths.append(os.path.join(root, file))
self.rag_system.ingest_documents(doc_paths)
def answer_technical_question(self, question):
"""回答技术问题,并附带代码示例和图表"""
# 分类问题类型
question_type = self.classify_question(question)
# 从 RAG 获取基础答案
result = self.rag_system.query(question)
# 通过特定类型的处理来增强答案
if question_type in self.doc_types:
enhanced_result = self.doc_types[question_type](result)
return enhanced_result
return result
def handle_api_query(self, base_result):
"""通过代码示例增强 API 相关答案"""
# 从来源中提取 API 端点
api_endpoints = []
for source in base_result.get('sources', []):
if source['modality'] == 'table':
# 解析 API 表格
api_endpoints.extend(self.parse_api_table(source))
# 生成代码示例
if api_endpoints:
code_example = self.generate_api_example(api_endpoints[0])
base_result['code_example'] = code_example
return base_result
def handle_architecture_query(self, base_result):
"""通过图表引用增强架构相关答案"""
diagrams = [
s for s in base_result.get('sources', [])
if s['modality'] == 'image' and 'diagram' in s.get('metadata', {}).get('caption', '').lower()
]
if diagrams:
base_result['diagrams'] = diagrams
base_result['answer'] += f"\n\n请参考架构图以获得可视化表示。"
return base_result
def classify_question(self, question):
"""分类技术问题的类型"""
question_lower = question.lower()
if any(word in question_lower for word in ['api', 'endpoint', 'request', 'response']):
return 'api_reference'
elif any(word in question_lower for word in ['architecture', 'design', 'component', 'system']):
return 'architecture'
elif any(word in question_lower for word in ['error', 'issue', 'problem', 'fix']):
return 'troubleshooting'
return 'general'
def generate_api_example(self, endpoint_info):
"""为 API 端点生成代码示例"""
return f"""
```python
import requests
# {endpoint_info.get('description', 'API 调用示例')}
response = requests.{endpoint_info.get('method', 'get').lower()}(
'{endpoint_info.get('url', '/api/endpoint')}',
headers={{'Authorization': 'Bearer YOUR_TOKEN'}},
json={endpoint_info.get('sample_payload', {})}
)
print(response.json())
使用示例
assistant = TechnicalDocsAssistant() assistant.ingest_documentation(‘./docs’)
question = “我应如何通过 API 进行身份验证?” answer = assistant.answer_technical_question(question) print(answer[‘answer’]) if ‘code_example’ in answer: print(answer[‘code_example’])
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
### 用例 2:财务报告分析
**场景:** 分析包含表格、图表和文本分析的季度财务报告。
```python
# financial_analyzer.py
class FinancialReportAnalyzer:
def __init__(self):
self.rag_system = MultimodalRAGSystem()
self.metrics = ['revenue', 'profit', 'expenses', 'growth', 'margin']
def analyze_report(self, report_path, queries=None):
"""全面的财务报告分析"""
# 接收报告
self.rag_system.ingest_documents([report_path])
# 如果未提供查询,则使用默认查询
if queries is None:
queries = [
"本季度的总收入是多少?",
"增长的主要驱动力是什么?",
"提到的主要风险有哪些?",
"与上一季度相比,支出有何变化?"
]
analysis_results = {}
for query in queries:
result = self.rag_system.query(query)
analysis_results[query] = result
# 从表格中提取财务指标
financial_data = self.extract_financial_metrics()
# 生成摘要
summary = self.generate_executive_summary(analysis_results, financial_data)
return {
'qa_results': analysis_results,
'financial_metrics': financial_data,
'executive_summary': summary
}
def extract_financial_metrics(self):
"""从表格中提取关键财务指标"""
metrics = {}
# 查询特定的财务表格
table_query = "财务摘要表季度结果"
result = self.rag_system.query(table_query)
# 从来源中解析表格
for source in result.get('sources', []):
if source['modality'] == 'table':
table_data = source['content']
metrics.update(self.parse_financial_table(table_data))
return metrics
def parse_financial_table(self, table_data):
"""从表格中解析财务指标"""
metrics = {}
df = table_data.get('dataframe')
if df is not None:
for metric in self.metrics:
# 在表格中搜索指标
for col in df.columns:
if metric.lower() in col.lower():
metrics[metric] = df[col].tolist()
return metrics
def generate_executive_summary(self, qa_results, financial_data):
"""结合问答和指标生成高管摘要"""
summary_parts = []
# 财务亮点
if 'revenue' in financial_data:
revenue = financial_data['revenue']
summary_parts.append(f"收入: ${revenue[-1]:,.2f}M")
# 从问答中获取关键洞察
for query, result in qa_results.items():
if 'growth' in query.lower() or 'driver' in query.lower():
summary_parts.append(f"增长驱动力: {result['answer'][:200]}...")
return "\n\n".join(summary_parts)
# 使用方法
analyzer = FinancialReportAnalyzer()
results = analyzer.analyze_report('./data/Q3_2024_Report.pdf')
print("高管摘要:")
print(results['executive_summary'])
print("\n财务指标:")
print(results['financial_metrics'])
用例 3:科研助手
场景:帮助研究人员浏览包含复杂方程式、图表和实验数据的科学论文。
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# research_assistant.py
class ScientificResearchAssistant:
def __init__(self):
self.rag_system = MultimodalRAGSystem()
self.paper_metadata = {}
def ingest_research_papers(self, paper_paths):
"""接收科学论文并提取元数据"""
for paper_path in paper_paths:
# 提取论文元数据
metadata = self.extract_paper_metadata(paper_path)
self.paper_metadata[paper_path] = metadata
# 接收到 RAG 系统中
self.rag_system.ingest_documents(paper_paths)
def extract_paper_metadata(self, paper_path):
"""提取标题、作者、摘要、引用"""
# 使用 PDF 解析实现
doc = fitz.open(paper_path)
first_page = doc[0].get_text()
metadata = {
'title': self.extract_title(first_page),
'authors': self.extract_authors(first_page),
'abstract': self.extract_abstract(first_page),
'year': self.extract_year(first_page)
}
doc.close()
return metadata
def answer_research_question(self, question, include_equations=True):
"""回答研究问题,支持方程式和图表"""
result = self.rag_system.query(question)
# 如果相关,增强方程式信息
if include_equations:
equations = self.extract_relevant_equations(result)
if equations:
result['equations'] = equations
# 添加图表引用
figures = self.extract_relevant_figures(result)
if figures:
result['figures'] = figures
# 添加引用信息
result['citations'] = self.generate_citations(result)
return result
def extract_relevant_equations(self, result):
"""从检索到的来源中提取方程式"""
equations = []
for source in result.get('sources', []):
if source['modality'] == 'equation':
equations.append({
'latex': source['content'],
'context': source.get('metadata', {}).get('context', '')
})
return equations
def extract_relevant_figures(self, result):
"""从检索到的来源中提取图表"""
figures = []
for source in result.get('sources', []):
if source['modality'] == 'image':
caption = source.get('metadata', {}).get('caption', '')
if any(word in caption.lower() for word in ['figure', 'fig', 'plot', 'graph']):
figures.append({
'caption': caption,
'page': source.get('metadata', {}).get('page'),
'source': source.get('metadata', {}).get('source')
})
return figures
def generate_citations(self, result):
"""为来源生成正确的引用"""
citations = []
seen_sources = set()
for source in result.get('sources', []):
source_file = source.get('metadata', {}).get('source')
if source_file and source_file not in seen_sources:
metadata = self.paper_metadata.get(source_file, {})
citation = self.format_citation(metadata)
citations.append(citation)
seen_sources.add(source_file)
return citations
def format_citation(self, metadata):
"""以学术风格格式化引用"""
authors = metadata.get('authors', 'Unknown')
year = metadata.get('year', 'n.d.')
title = metadata.get('title', 'Untitled')
return f"{authors} ({year}). {title}."
# 使用方法
assistant = ScientificResearchAssistant()
papers = [
'./papers/machine_learning_2024.pdf',
'./papers/neural_networks_advances.pdf'
]
assistant.ingest_research_papers(papers)
question = "Transformer 架构的最新进展是什么?"
answer = assistant.answer_research_question(question)
print(f"答案: {answer['answer']}\n")
if 'equations' in answer:
print("相关方程式:")
for eq in answer['equations']:
print(f" {eq['latex']}")
print("\n引用:")
for citation in answer['citations']:
print(f" {citation}")
性能优化与最佳实践 ⚡
以下是笔者从规模化实施 RAG-Anything 中学到的生产级优化策略。
- 多模态内容的分块策略
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
class OptimizedChunker:
def __init__(self, max_chunk_size=512, overlap=50):
self.max_chunk_size = max_chunk_size
self.overlap = overlap
def chunk_document(self, elements):
"""保留多模态上下文的智能分块"""
chunks = []
current_chunk = []
current_size = 0
for element in elements:
element_size = self.estimate_size(element)
# 如果添加此元素超过最大大小,则完成当前块
if current_size + element_size > self.max_chunk_size and current_chunk:
chunks.append(self.finalize_chunk(current_chunk))
# 开始带有重叠的新块
current_chunk = self.create_overlap_chunk(current_chunk)
current_size = sum(self.estimate_size(e) for e in current_chunk)
current_chunk.append(element)
current_size += element_size
# 添加最后一个块
if current_chunk:
chunks.append(self.finalize_chunk(current_chunk))
return chunks
def estimate_size(self, element):
"""估计元素的 token 大小"""
modality = element['modality']
if modality == 'text':
# 粗略估计: 1 token ≈ 4 字符
return len(element['content']) // 4
elif modality == 'table':
# 表格的 token 消耗较大
rows = element['content'].get('rows', 0)
cols = element['content'].get('columns', 0)
return rows * cols * 2
elif modality in ['image', 'equation']:
# 非文本元素的固定 token 成本
return 100
return 50
def create_overlap_chunk(self, previous_chunk):
"""从前一个块创建重叠部分"""
overlap_elements = []
overlap_size = 0
# 从前一个块的末尾取元素
for element in reversed(previous_chunk):
element_size = self.estimate_size(element)
if overlap_size + element_size <= self.overlap:
overlap_elements.insert(0, element)
overlap_size += element_size
else:
break
return overlap_elements
def finalize_chunk(self, chunk_elements):
"""完成块并附带元数据"""
return {
'elements': chunk_elements,
'modalities': [e['modality'] for e in chunk_elements],
'size': sum(self.estimate_size(e) for e in chunk_elements),
'has_cross_modal': len(set(e['modality'] for e in chunk_elements)) > 1
}
- 嵌入缓存策略
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
import hashlib
import pickle
from pathlib import Path
class EmbeddingCache:
def __init__(self, cache_dir='./cache/embeddings'):
self.cache_dir = Path(cache_dir)
self.cache_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
self.memory_cache = {}
def get_cache_key(self, content, modality):
"""生成唯一的缓存键"""
content_str = str(content)
key_string = f"{modality}:{content_str}"
return hashlib.md5(key_string.encode()).hexdigest()
def get(self, content, modality):
"""检索缓存的嵌入"""
cache_key = self.get_cache_key(content, modality)
# 首先检查内存缓存
if cache_key in self.memory_cache:
return self.memory_cache[cache_key]
# 检查磁盘缓存
cache_file = self.cache_dir / f"{cache_key}.pkl"
if cache_file.exists():
with open(cache_file, 'rb') as f:
embedding = pickle.load(f)
self.memory_cache[cache_key] = embedding
return embedding
return None
def set(self, content, modality, embedding):
"""缓存嵌入"""
cache_key = self.get_cache_key(content, modality)
# 存储在内存中
self.memory_cache[cache_key] = embedding
# 存储在磁盘上
cache_file = self.cache_dir / f"{cache_key}.pkl"
with open(cache_file, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(embedding, f)
def clear(self):
"""清除所有缓存"""
self.memory_cache.clear()
for cache_file in self.cache_dir.glob('*.pkl'):
cache_file.unlink()
# 在嵌入器中使用
class CachedMultiModalEmbedder(MultiModalEmbedder):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.cache = EmbeddingCache()
def embed(self, content, modality_type):
# 首先检查缓存
cached_embedding = self.cache.get(content, modality_type)
if cached_embedding is not None:
return cached_embedding
# 生成新的嵌入
embedding = super().embed(content, modality_type)
# 缓存它
self.cache.set(content, modality_type, embedding)
return embedding
- 针对大型文档集的批处理
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completed
from tqdm import tqdm
class BatchProcessor:
def __init__(self, max_workers=4):
self.max_workers = max_workers
def process_documents_batch(self, document_paths, rag_system):
"""并行处理多个文档"""
results = []
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=self.max_workers) as executor:
# 提交所有任务
future_to_doc = {
executor.submit(self.process_single_document, doc_path, rag_system): doc_path
for doc_path in document_paths
}
# 使用进度条处理已完成的任务
with tqdm(total=len(document_paths), desc="处理文档中") as pbar:
for future in as_completed(future_to_doc):
doc_path = future_to_doc[future]
try:
result = future.result()
results.append(result)
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理 {doc_path} 时出错: {str(e)}")
finally:
pbar.update(1)
return results
def process_single_document(self, doc_path, rag_system):
"""处理单个文档"""
try:
elements = rag_system.parser.parse(doc_path)
# 批量嵌入元素
embeddings = self.batch_embed(elements, rag_system.embedder)
for element, embedding in zip(elements, embeddings):
element['embedding'] = embedding
return {
'path': doc_path,
'elements': elements,
'status': 'success'
}
except Exception as e:
return {
'path': doc_path,
'error': str(e),
'status': 'failed'
}
def batch_embed(self, elements, embedder, batch_size=32):
"""为提高效率进行批量嵌入"""
embeddings = []
for i in range(0, len(elements), batch_size):
batch = elements[i:i + batch_size]
# 按模态分组以实现高效批处理
modality_groups = {}
for element in batch:
modality = element['modality']
if modality not in modality_groups:
modality_groups[modality] = []
modality_groups[modality].append(element)
# 嵌入每个模态组
batch_embeddings = []
for modality, group in modality_groups.items():
contents = [e['content'] for e in group]
group_embeddings = embedder.embed_batch(contents, modality)
batch_embeddings.extend(group_embeddings)
embeddings.extend(batch_embeddings)
return embeddings
- 查询优化
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
class QueryOptimizer:
def __init__(self):
self.query_cache = {}
self.query_rewriter = QueryRewriter()
def optimize_query(self, query):
"""优化查询以获得更好的检索效果"""
# 检查缓存
if query in self.query_cache:
return self.query_cache[query]
# 用同义词和相关术语扩展查询
expanded_query = self.query_rewriter.expand(query)
# 识别模态提示
modality_hints = self.extract_modality_hints(query)
optimized = {
'original': query,
'expanded': expanded_query,
'modality_hints': modality_hints,
'boost_factors': self.calculate_boost_factors(modality_hints)
}
self.query_cache[query] = optimized
return optimized
def extract_modality_hints(self, query):
"""提取关于预期模态的提示"""
hints = []
query_lower = query.lower()
if any(word in query_lower for word in ['显示', '图', '图表', '图像', '图片']):
hints.append('image')
if any(word in query_lower for word in ['表格', '数据', '数字', '统计']):
hints.append('table')
if any(word in query_lower for word in ['方程式', '公式', '计算', '数学']):
hints.append('equation')
if not hints:
hints.append('text') # 默认为文本
return hints
def calculate_boost_factors(self, modality_hints):
"""计算不同模态的增强因子"""
boost_factors = {
'text': 1.0,
'image': 1.0,
'table': 1.0,
'equation': 1.0
}
# 增强提示的模态
for hint in modality_hints:
boost_factors[hint] = 1.5
return boost_factors
class QueryRewriter:
def __init__(self):
self.synonym_map = self.load_synonyms()
def expand(self, query):
"""用同义词扩展查询"""
words = query.split()
expanded_words = []
for word in words:
expanded_words.append(word)
if word.lower() in self.synonym_map:
synonyms = self.synonym_map[word.lower()]
expanded_words.extend(synonyms[:2]) # 添加前 2 个同义词
return ' '.join(expanded_words)
def load_synonyms(self):
"""加载同义词映射"""
return {
'显示': ['展示', '呈现'],
'解释': ['描述', '阐明'],
'计算': ['推算', '确定'],
# 添加更多同义词...
}
部署与生产考量 🚀
Docker 部署
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# Dockerfile
FROM python:3.9-slim
WORKDIR /app
# 安装系统依赖
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
build-essential \
git \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# 复制需求文件
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
# 复制应用程序代码
COPY . .
# 创建必要的目录
RUN mkdir -p /app/data /app/cache /app/logs
# 设置环境变量
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED=1
ENV VECTOR_DB_PATH=/app/data/vector_store
# 暴露端口
EXPOSE 8000
# 运行应用程序
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# docker-compose.yml
version: '3.8'
services:
rag-anything:
build: .
ports:
- "8000:8000"
volumes:
- ./data:/app/data
- ./cache:/app/cache
- ./logs:/app/logs
environment:
- OPENAI_API_KEY=${OPENAI_API_KEY}
- VECTOR_DB_TYPE=chromadb
- MAX_WORKERS=4
restart: unless-stopped
redis:
image: redis:7-alpine
ports:
- "6379:6379"
volumes:
- redis_data:/data
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
redis_data:
FastAPI REST API 实现
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# api.py
from fastapi import FastAPI, UploadFile, File, HTTPException
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import List, Optional
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI(title="RAG-Anything API", version="1.0.0")
# 初始化 RAG 系统
rag_system = MultimodalRAGSystem()
class QueryRequest(BaseModel):
question: str
top_k: Optional[int] = 5
return_sources: Optional[bool] = True
class QueryResponse(BaseModel):
answer: str
confidence: float
sources: Optional[List[dict]] = None
@app.post("/ingest")
async def ingest_document(file: UploadFile = File(...)):
"""接收新文档"""
try:
# 保存上传的文件
file_path = f"./uploads/{file.filename}"
with open(file_path, "wb") as f:
content = await file.read()
f.write(content)
# 接收到 RAG 系统中
num_elements = rag_system.ingest_documents([file_path])
return JSONResponse({
"status": "success",
"filename": file.filename,
"elements_processed": num_elements
})
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
@app.post("/query", response_model=QueryResponse)
async def query_knowledge_base(request: QueryRequest):
"""查询知识库"""
try:
result = rag_system.query(
request.question,
return_sources=request.return_sources
)
return QueryResponse(**result)
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
@app.get("/health")
async def health_check():
"""健康检查端点"""
return {"status": "healthy"}
@app.get("/stats")
async def get_stats():
"""获取系统统计信息"""
return {
"total_documents": len(rag_system.knowledge_base) if rag_system.knowledge_base else 0,
"cache_size": len(rag_system.embedder.cache.memory_cache),
"status": "operational"
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
监控与日志
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# monitoring.py
import logging
from datetime import datetime
import json
class RAGMonitor:
def __init__(self, log_file='./logs/rag_system.log'):
self.logger = self.setup_logger(log_file)
self.metrics = {
'queries_processed': 0,
'documents_ingested': 0,
'average_response_time': 0,
'cache_hit_rate': 0
}
def setup_logger(self, log_file):
"""设置日志配置"""
logger = logging.getLogger('RAGAnything')
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# 文件处理器
fh = logging.FileHandler(log_file)
fh.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# 控制台处理器
ch = logging.StreamHandler()
ch.setLevel(logging.WARNING)
# 格式化器
formatter = logging.Formatter(
'%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
)
fh.setFormatter(formatter)
ch.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(fh)
logger.addHandler(ch)
return logger
def log_query(self, query, response_time, num_results):
"""记录查询执行"""
self.logger.info(f"查询: {query[:100]}... | 时间: {response_time:.2f}s | 结果数: {num_results}")
self.metrics['queries_processed'] += 1
self.update_average_response_time(response_time)
def log_ingestion(self, document_path, num_elements):
"""记录文档接收"""
self.logger.info(f"已接收: {document_path} | 元素数: {num_elements}")
self.metrics['documents_ingested'] += 1
def log_error(self, error_type, error_message):
"""记录错误"""
self.logger.error(f"{error_type}: {error_message}")
def update_average_response_time(self, new_time):
"""更新平均响应时间"""
current_avg = self.metrics['average_response_time']
total_queries = self.metrics['queries_processed']
self.metrics['average_response_time'] = (
(current_avg * (total_queries - 1) + new_time) / total_queries
)
def get_metrics(self):
"""获取当前指标"""
return self.metrics
def export_metrics(self, output_file='./logs/metrics.json'):
"""将指标导出到文件"""
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
json.dump({
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'metrics': self.metrics
}, f, indent=2)
高级特性与定制化 🔧
自定义检索策略
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
class HybridRetriever:
"""结合多种策略的高级混合检索器"""
def __init__(self, knowledge_base):
self.knowledge_base = knowledge_base
self.strategies = {
'semantic': SemanticRetrieval(),
'keyword': KeywordRetrieval(),
'graph': GraphRetrieval(),
'hybrid': HybridRetrieval()
}
def retrieve(self, query, strategy='hybrid', top_k=5):
"""使用指定策略进行检索"""
retriever = self.strategies.get(strategy)
if not retriever:
raise ValueError(f"未知策略: {strategy}")
return retriever.retrieve(query, self.knowledge_base, top_k)
class SemanticRetrieval:
"""纯语义相似度检索"""
def retrieve(self, query, knowledge_base, top_k):
query_embedding = self.embed_query(query)
similarities = []
for element in knowledge_base.elements:
similarity = self.cosine_similarity(
query_embedding,
element['embedding']
)
similarities.append((element, similarity))
# 按相似度排序
similarities.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return [elem for elem, score in similarities[:top_k]]
class GraphRetrieval:
"""使用知识图谱结构的图检索"""
def retrieve(self, query, knowledge_base, top_k):
# 通过语义搜索找到初始种子节点
seed_nodes = self.find_seed_nodes(query, knowledge_base, top_k // 2)
# 通过图遍历进行扩展
expanded_nodes = set()
for seed in seed_nodes:
neighbors = knowledge_base.graph.get_neighbors(
seed.id,
max_hops=2
)
expanded_nodes.update(neighbors)
# 对扩展集进行重排序
reranked = self.rerank_by_relevance(query, list(expanded_nodes))
return reranked[:top_k]
针对特定领域微调嵌入模型
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, InputExample, losses
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
class DomainEmbeddingTrainer:
"""为特定领域微调嵌入模型"""
def __init__(self, base_model='all-MiniLM-L6-v2'):
self.model = SentenceTransformer(base_model)
def prepare_training_data(self, document_pairs):
"""从文档对准备训练样本"""
examples = []
for pair in document_pairs:
# 正样本(相似文档)
examples.append(InputExample(
texts=[pair['doc1'], pair['doc2']],
label=1.0
))
# 负样本(不相似文档)
if 'negative' in pair:
examples.append(InputExample(
texts=[pair['doc1'], pair['negative']],
label=0.0
))
return examples
def train(self, training_examples, epochs=3, batch_size=16):
"""微调模型"""
train_dataloader = DataLoader(
training_examples,
shuffle=True,
batch_size=batch_size
)
train_loss = losses.CosineSimilarityLoss(self.model)
self.model.fit(
train_objectives=[(train_dataloader, train_loss)],
epochs=epochs,
warmup_steps=100
)
def save_model(self, output_path):
"""保存微调后的模型"""
self.model.save(output_path)
# 使用方法
trainer = DomainEmbeddingTrainer()
# 准备领域特定的训练数据
training_pairs = [
{
'doc1': 'API 端点的技术规范',
'doc2': 'API 文档和使用示例',
'negative': '公司第三季度财务报告'
},
# 更多文档对...
]
examples = trainer.prepare_training_data(training_pairs)
trainer.train(examples)
trainer.save_model('./models/domain_embeddings')
与其他 RAG 框架的比较 📊
以下是 RAG-Anything 与其他流行框架的客观比较:
RAG-Anything vs. LangChain
LangChain 的优势:
- 成熟的生态系统,拥有广泛的集成
- 庞大的社区和文档
- 易于上手,适用于简单用例
- 适用于纯文本 RAG
RAG-Anything 的优势:
- 原生的多模态支持(图像、表格、方程式)
- 统一的基于图的知识表示
- 更好地处理跨模态关系
- 在复杂文档上的性能更优
何时使用 RAG-Anything:
- 文档包含丰富的视觉内容
- 处理包含方程式的科学论文
- 分析包含表格和图表的财务报告
- 处理包含示意图的技术文档
何时使用 LangChain:
- 简单的纯文本 RAG
- 需要广泛的第三方集成
- 快速原型开发
- 基于文本的聊天机器人
RAG-Anything vs. LlamaIndex
LlamaIndex 的优势:
- 在结构化数据方面表现出色
- 强大的查询引擎
- 优秀的文档索引能力
RAG-Anything 的优势:
- 更好的多模态处理能力
- 跨模态检索能力
- 基于图的知识导航
- 更好地处理异构内容
性能基准
根据研究论文,RAG-Anything 显示出显著的性能提升:
在多模态基准测试上的准确率:
- 纯文本查询:比基线 RAG 高出 5–8%
- 多模态查询:比传统 RAG 高出 15–25%
- 长文档查询:性能提升 30–40%
检索质量:
- Precision@5: 0.85 (纯文本 RAG 为 0.72)
- Recall@10: 0.91 (纯文本 RAG 为 0.78)
- 跨模态相关性(新指标): 0.88
常见问题排查 🔧
问题 1:内存不足错误
问题:处理大型文档时系统耗尽内存。
解决方案:
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
class MemoryEfficientProcessor:
def __init__(self, max_memory_mb=4096):
self.max_memory_mb = max_memory_mb
self.current_memory = 0
def process_large_document(self, doc_path):
"""以块为单位处理文档以管理内存"""
# 以流模式处理
with fitz.open(doc_path) as doc:
for page_num in range(len(doc)):
# 一次处理一页
page = doc[page_num]
elements = self.parse_page(page)
# 立即嵌入并存储
self.embed_and_store(elements)
# 从内存中清除页面
del page
# 检查内存使用情况
if self.check_memory_threshold():
self.flush_to_disk()
def check_memory_threshold(self):
"""检查是否达到内存阈值"""
import psutil
process = psutil.Process()
memory_mb = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024
return memory_mb > self.max_memory_mb * 0.8
问题 2:检索性能缓慢
问题:查询执行时间过长。
解决方案:
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
# 实现近似最近邻搜索
from annoy import AnnoyIndex
class FastRetriever:
def __init__(self, embedding_dim=384):
self.index = AnnoyIndex(embedding_dim, 'angular')
self.id_to_element = {}
def build_index(self, elements):
"""构建 ANN 索引以实现快速检索"""
for idx, element in enumerate(elements):
self.index.add_item(idx, element['embedding'])
self.id_to_element[idx] = element
# 使用 10 棵树构建索引(速度和准确性之间的权衡)
self.index.build(10)
def fast_retrieve(self, query_embedding, top_k=5):
"""快速近似检索"""
indices, distances = self.index.get_nns_by_vector(
query_embedding,
top_k,
include_distances=True
)
results = []
for idx, distance in zip(indices, distances):
element = self.id_to_element[idx]
element['score'] = 1 - distance # 将距离转换为相似度
results.append(element)
return results
问题 3:答案质量差
问题:系统返回不相关或低质量的答案。
解决方案:
ounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(lineounter(line
class AnswerQualityImprover:
def __init__(self):
self.min_confidence_threshold = 0.7
self.reranker = CrossEncoderReranker()
def improve_answer_quality(self, query, initial_results):
"""通过重排序和过滤提高答案质量"""
# 步骤 1: 使用交叉编码器进行重排序
reranked = self.reranker.rerank(query, initial_results)
# 步骤 2: 过滤低置信度结果
filtered = [
r for r in reranked
if r['score'] >= self.min_confidence_threshold
]
# 步骤 3: 结果多样化(避免冗余)
diversified = self.diversify_results(filtered)
# 步骤 4: 从知识图谱添加上下文
enriched = self.add_graph_context(diversified)
return enriched
def diversify_results(self, results, similarity_threshold=0.9):
"""移除近似重复的结果"""
diverse_results = []
for result in results:
is_diverse = True
for existing in diverse_results:
similarity = self.calculate_similarity(
result['embedding'],
existing['embedding']
)
if similarity > similarity_threshold:
is_diverse = False
break
if is_diverse:
diverse_results.append(result)
return diverse_results
未来路线图与社区贡献 🌟
即将推出的功能
RAG-Anything 团队正在积极开发:
1. 视频支持
- 帧提取与分析
- 时间关系建模
- 语音转文本集成
2. 实时更新
- 增量索引
- 实时文档监控
- 流式接收
3. 多语言支持
- 跨语言检索
- 特定语言的嵌入模型
- 翻译集成
4. 增强的可视化
- 交互式知识图谱浏览器
- 检索路径可视化
- 置信度热力图
结论与后续步骤 🎯
RAG-Anything 代表了我们处理知识检索方式的范式转变。通过将多模态内容视为相互关联的知识实体而非孤立的数据类型,它解锁了传统 RAG 系统无法比拟的能力。
核心要点:
- ✅ 统一的多模态知识检索
- ✅ 基于图的跨模态关系
- ✅ 在复杂文档上表现优异
- ✅ 生产就绪的架构
- ✅ 开源且积极维护
您的后续步骤:
- 从小处着手: 从基础实现示例开始
- 进行实验: 尝试不同的文档类型和查询
- 着手优化: 实现缓存和批处理
- 规模化部署: 使用 Docker 和监控进行部署
- 贡献社区: 与社区分享您的改进
最后
我在一线科技企业深耕十二载,见证过太多因技术卡位而跃迁的案例。那些率先拥抱 AI 的同事,早已在效率与薪资上形成代际优势,我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家,也可以通过我们的能力和经验解答大家在大模型的学习中的很多困惑。
我整理出这套 AI 大模型突围资料包:
- ✅AI大模型学习路线图
- ✅Agent行业报告
- ✅100集大模型视频教程
- ✅大模型书籍PDF
- ✅DeepSeek教程
- ✅AI产品经理入门资料
完整的大模型学习和面试资料已经上传带到CSDN的官方了,有需要的朋友可以扫描下方二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】👇👇

为什么说现在普通人就业/升职加薪的首选是AI大模型?
人工智能技术的爆发式增长,正以不可逆转之势重塑就业市场版图。从DeepSeek等国产大模型引发的科技圈热议,到全国两会关于AI产业发展的政策聚焦,再到招聘会上排起的长队,AI的热度已从技术领域渗透到就业市场的每一个角落。
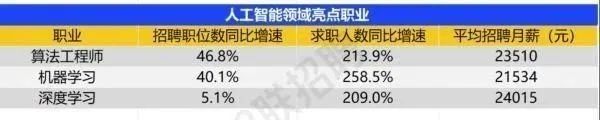
智联招聘的最新数据给出了最直观的印证:2025年2月,AI领域求职人数同比增幅突破200% ,远超其他行业平均水平;整个人工智能行业的求职增速达到33.4%,位居各行业榜首,其中人工智能工程师岗位的求职热度更是飙升69.6%。
AI产业的快速扩张,也让人才供需矛盾愈发突出。麦肯锡报告明确预测,到2030年中国AI专业人才需求将达600万人,人才缺口可能高达400万人,这一缺口不仅存在于核心技术领域,更蔓延至产业应用的各个环节。


资料包有什么?
①从入门到精通的全套视频教程⑤⑥
包含提示词工程、RAG、Agent等技术点
② AI大模型学习路线图(还有视频解说)
全过程AI大模型学习路线

③学习电子书籍和技术文档
市面上的大模型书籍确实太多了,这些是我精选出来的

④各大厂大模型面试题目详解

⑤ 这些资料真的有用吗?
这份资料由我和鲁为民博士共同整理,鲁为民博士先后获得了北京清华大学学士和美国加州理工学院博士学位,在包括IEEE Transactions等学术期刊和诸多国际会议上发表了超过50篇学术论文、取得了多项美国和中国发明专利,同时还斩获了吴文俊人工智能科学技术奖。目前我正在和鲁博士共同进行人工智能的研究。
所有的视频教程由智泊AI老师录制,且资料与智泊AI共享,相互补充。这份学习大礼包应该算是现在最全面的大模型学习资料了。
资料内容涵盖了从入门到进阶的各类视频教程和实战项目,无论你是小白还是有些技术基础的,这份资料都绝对能帮助你提升薪资待遇,转行大模型岗位。


智泊AI始终秉持着“让每个人平等享受到优质教育资源”的育人理念,通过动态追踪大模型开发、数据标注伦理等前沿技术趋势,构建起"前沿课程+智能实训+精准就业"的高效培养体系。
课堂上不光教理论,还带着学员做了十多个真实项目。学员要亲自上手搞数据清洗、模型调优这些硬核操作,把课本知识变成真本事!


如果说你是以下人群中的其中一类,都可以来智泊AI学习人工智能,找到高薪工作,一次小小的“投资”换来的是终身受益!
应届毕业生:无工作经验但想要系统学习AI大模型技术,期待通过实战项目掌握核心技术。
零基础转型:非技术背景但关注AI应用场景,计划通过低代码工具实现“AI+行业”跨界。
业务赋能 突破瓶颈:传统开发者(Java/前端等)学习Transformer架构与LangChain框架,向AI全栈工程师转型。
👉获取方式:
😝有需要的小伙伴,可以保存图片到wx扫描二v码免费领取【保证100%免费】🆓**

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献565条内容
已为社区贡献565条内容







所有评论(0)