打造你的第二大脑:小智AI应用开发实战指南
本文介绍了如何将AI助手升级为"第二大脑"的完整技术路径,包含三个核心项目: 智能家居控制中枢 实现从被动响应到主动服务的转变 关键技术:多源数据融合、情境理解引擎、场景化控制 架构设计:感知-决策-执行三层模型 实战代码:数据采集模块、情境理解模块、场景控制器 个性化对话系统 从通用问答到专属知识助手 关键技术:用户模型表示学习、上下文感知响应生成 架构设计:五层增强架构(预
想象一个场景:清晨,你的智能闹钟根据睡眠监测数据和当天日程,在你睡眠周期最浅的时刻轻柔唤醒你;早餐时,智能音箱播报个性化新闻摘要,同时咖啡机根据你的口味偏好自动冲煮咖啡;通勤途中,车载系统分析实时路况后动态调整路线,并根据你的工作节奏提前筛选重要邮件。这不是科幻电影的场景,而是基于AI助手打造的"第二大脑"能够实现的日常——一个理解你的习惯、预判你的需求、并能自主执行复杂任务的智能系统。
对于开发者而言,将小智AI从简单的问答工具升级为真正的"第二大脑",需要跨越三个核心门槛:深度个性化(让AI理解用户独特需求)、任务自动化(让AI能执行而非仅建议)、多模态交互(让AI能处理和生成多种类型信息)。本文将通过三个递进式实战项目——智能家居控制中枢、个性化AI对话系统、以及功能扩展平台——完整展示这一升级过程,提供可直接复用的代码框架、架构设计和最佳实践。
项目一:智能家居控制中枢——从指令执行到场景理解
智能家居控制往往止步于"打开灯光"这类基础指令,而真正的"第二大脑"应该理解"我回来了"背后的整套场景需求:开灯、调节温度、播放喜欢的音乐、甚至根据天气和日程建议是否需要开启空气净化器。本项目将构建一个能够理解复杂场景、整合多设备联动、并具备学习能力的智能家居控制中枢。
系统架构设计
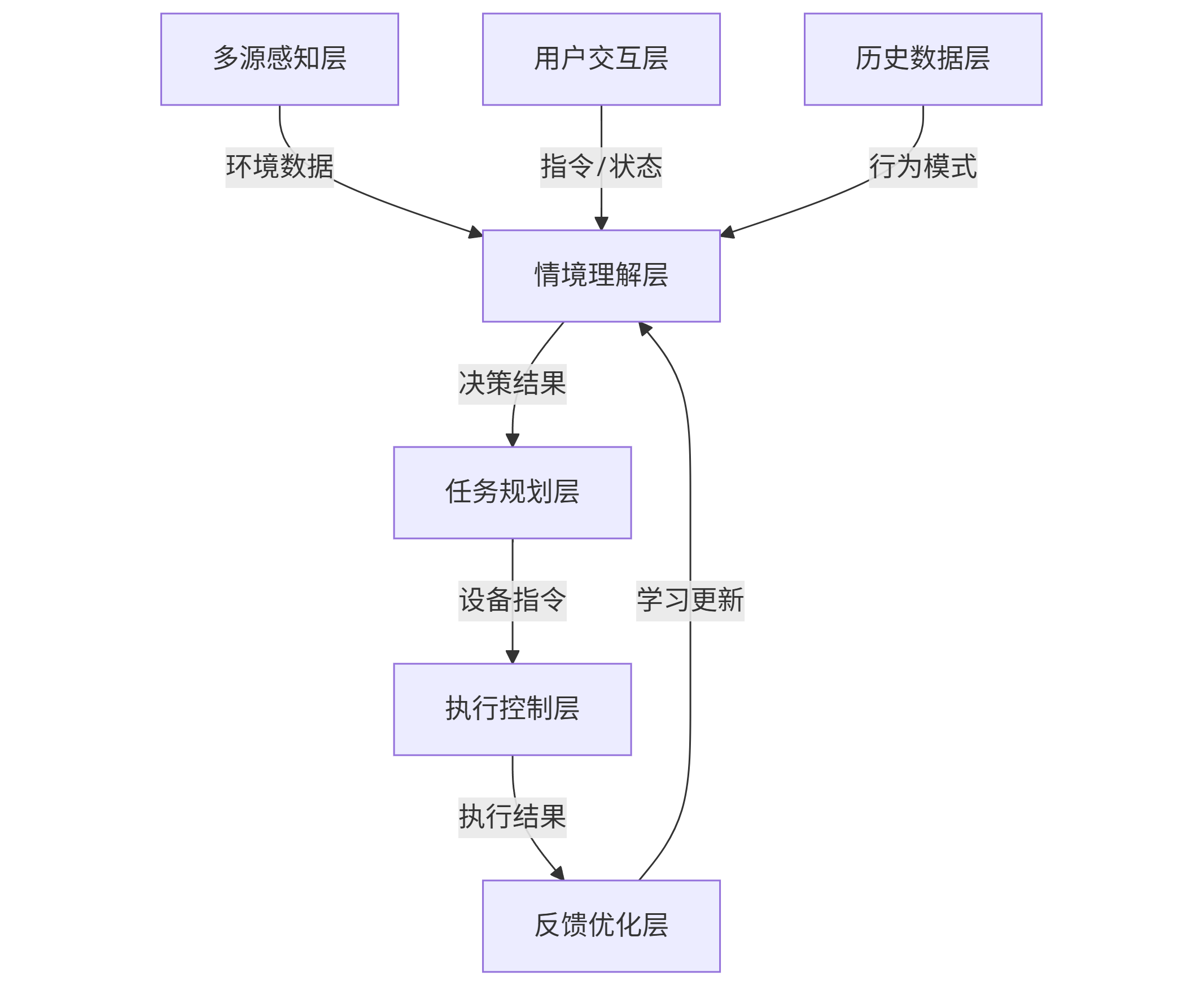
智能家居控制中枢的核心挑战在于将孤立的设备指令升级为情境化的场景理解。我们采用"感知-决策-执行"三层架构:
graph TD A[多源感知层] -->|环境数据| B[情境理解层] C[用户交互层] -->|指令/状态| B D[历史数据层] -->|行为模式| B B -->|决策结果| E[任务规划层] E -->|设备指令| F[执行控制层] F -->|执行结果| G[反馈优化层] G -->|学习更新| B
感知层整合三类数据:环境数据(温湿度、光照、空气质量)、设备状态(各设备开关状态、参数设置)、用户数据(位置、活动、生理指标)。情境理解层是系统的"大脑",负责将原始数据解析为有意义的情境(如"用户即将到家"、"用户正在工作")。执行控制层则负责将抽象决策转化为具体设备指令,并处理设备间的协同逻辑。
核心功能实现
我们将使用Python构建核心服务,采用MQTT协议与智能设备通信,使用SQLite存储用户习惯数据,通过FastAPI提供API接口,最后通过小智AI的插件系统实现自然语言交互。
1. 数据采集与存储模块
首先实现多源数据采集模块,负责从各类设备和传感器收集数据:
import time import json import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt import sqlite3 from datetime import datetime from typing import Dict, Any class DataCollector: def __init__(self, mqtt_broker: str, db_path: str = "smart_home.db"): self.mqtt_client = mqtt.Client() self.mqtt_client.on_connect = self._on_connect self.mqtt_client.on_message = self._on_message self.mqtt_broker = mqtt_broker self.db_path = db_path self._init_database() self.mqtt_client.connect(mqtt_broker, 1883, 60) def _init_database(self): """初始化数据库表结构""" conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() # 设备状态表 cursor.execute(''' CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS device_states ( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, device_id TEXT NOT NULL, device_type TEXT NOT NULL, state JSON NOT NULL, timestamp DATETIME NOT NULL ) ''') # 环境数据表 cursor.execute(''' CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS environment_data ( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, type TEXT NOT NULL, value REAL NOT NULL, unit TEXT NOT NULL, timestamp DATETIME NOT NULL ) ''') # 用户行为表 cursor.execute(''' CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user_activities ( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, activity_type TEXT NOT NULL, details JSON NOT NULL, timestamp DATETIME NOT NULL ) ''') conn.commit() conn.close() def _on_connect(self, client, userdata, flags, rc): """MQTT连接回调函数""" print(f"Connected with result code {rc}") # 订阅设备状态主题 client.subscribe("devices/#") # 订阅环境数据主题 client.subscribe("environment/#") def _on_message(self, client, userdata, msg): """MQTT消息接收回调函数""" try: payload = json.loads(msg.payload.decode()) timestamp = datetime.now().isoformat() # 解析设备状态消息 if msg.topic.startswith("devices/"): _, device_type, device_id = msg.topic.split("/", 2) self._store_device_state(device_id, device_type, payload, timestamp) # 解析环境数据消息 elif msg.topic.startswith("environment/"): _, data_type = msg.topic.split("/", 1) self._store_environment_data(data_type, payload, timestamp) except json.JSONDecodeError: print(f"Failed to decode JSON from {msg.topic}") def _store_device_state(self, device_id: str, device_type: str, state: Dict[str, Any], timestamp: str): """存储设备状态数据""" conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute( "INSERT INTO device_states (device_id, device_type, state, timestamp) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)", (device_id, device_type, json.dumps(state), timestamp) ) conn.commit() conn.close() def _store_environment_data(self, data_type: str, data: Dict[str, Any], timestamp: str): """存储环境数据""" conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() # 环境数据可能包含多个指标,如温湿度传感器同时提供温度和湿度 for metric, value_info in data.items(): cursor.execute( "INSERT INTO environment_data (type, value, unit, timestamp) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)", (f"{data_type}.{metric}", value_info["value"], value_info["unit"], timestamp) ) conn.commit() conn.close() def start(self): """启动数据采集服务""" self.mqtt_client.loop_start() def stop(self): """停止数据采集服务""" self.mqtt_client.loop_stop()
2. 情境理解与决策模块
情境理解模块是系统的核心智能所在,负责将原始数据转化为有意义的情境描述。我们采用规则引擎+机器学习的混合方法:基础情境通过规则匹配实现(如"晚上7点且用户在家则为晚间场景"),复杂情境则通过训练分类模型实现(如"用户是否在专注工作")。
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import json import sqlite3 from datetime import datetime, timedelta from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score import joblib from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple class ContextUnderstanding: def __init__(self, db_path: str = "smart_home.db", model_path: str = "context_model.pkl"): self.db_path = db_path self.model_path = model_path self.context_rules = self._load_context_rules() self.activity_model = self._load_activity_model() def _load_context_rules(self) -> Dict[str, Dict]: """加载情境规则""" # 实际应用中可以从配置文件或数据库加载 return { "morning_routine": { "time_range": ("06:00", "09:00"), "user_state": "awake", "actions": ["turn_on_lights", "adjust_thermostat", "start_coffee_maker"] }, "work_mode": { "time_range": ("09:30", "12:00"), "user_location": "home_office", "device_states": {"desk_lamp": "on", "laptop": "on"}, "actions": ["silence_notifications", "adjust_thermostat", "block_distractions"] }, "away_mode": { "user_location": "away", "time_since_last_activity": ">30m", "actions": ["turn_off_lights", "lower_thermostat", "arm_security"] }, "evening_routine": { "time_range": ("19:00", "22:00"), "user_state": "at_home", "actions": ["turn_on_lights", "adjust_thermostat", "start_entertainment"] } } def _load_activity_model(self): """加载用户活动分类模型""" try: return joblib.load(self.model_path) except FileNotFoundError: print("Activity model not found, using rule-based fallback") return None def get_current_context(self) -> Dict[str, Any]: """获取当前情境理解结果""" current_time = datetime.now() user_state = self._detect_user_state() device_states = self._get_current_device_states() environment_data = self._get_latest_environment_data() # 规则匹配基础情境 matched_contexts = [] for context_name, context_def in self.context_rules.items(): if self._match_time_range(current_time, context_def.get("time_range")) and \ self._match_user_state(user_state, context_def.get("user_state")) and \ self._match_device_states(device_states, context_def.get("device_states")): matched_contexts.append(context_name) # 使用ML模型预测用户活动(如果模型可用) user_activity = "unknown" if self.activity_model: user_activity = self._predict_user_activity(device_states, environment_data, user_state) return { "timestamp": current_time.isoformat(), "user_state": user_state, "user_activity": user_activity, "matched_contexts": matched_contexts, "device_states": device_states, "environment_data": environment_data } def _detect_user_state(self) -> str: """检测用户当前状态""" # 在实际应用中,这里会整合位置数据、活动传感器数据等 # 简化实现:查询最近的用户活动记录 conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute( "SELECT details FROM user_activities ORDER BY timestamp DESC LIMIT 1" ) result = cursor.fetchone() conn.close() if result: latest_activity = json.loads(result[0]) return latest_activity.get("state", "unknown") return "unknown" def _get_current_device_states(self) -> Dict[str, Dict]: """获取当前设备状态""" conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute( """ SELECT device_id, device_type, state FROM device_states WHERE timestamp = (SELECT MAX(timestamp) FROM device_states WHERE device_id = ds.device_id) """, {"ds.device_id": "device_id"} ) results = cursor.fetchall() conn.close() device_states = {} for device_id, device_type, state_json in results: device_states[device_id] = { "type": device_type, "state": json.loads(state_json) } return device_states def _get_latest_environment_data(self) -> Dict[str, Dict]: """获取最新环境数据""" conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute( """ SELECT type, value, unit FROM environment_data WHERE timestamp = (SELECT MAX(timestamp) FROM environment_data WHERE type = ed.type) """, {"ed.type": "type"} ) results = cursor.fetchall() conn.close() environment_data = {} for data_type, value, unit in results: environment_data[data_type] = { "value": value, "unit": unit } return environment_data def _match_time_range(self, current_time, time_range) -> bool: """匹配时间范围""" if not time_range: return True start_str, end_str = time_range start_time = datetime.strptime(start_str, "%H:%M").time() end_time = datetime.strptime(end_str, "%H:%M").time() return start_time <= current_time.time() <= end_time def _match_user_state(self, current_state, required_state) -> bool: """匹配用户状态""" if not required_state: return True return current_state == required_state def _match_device_states(self, current_states, required_states) -> bool: """匹配设备状态""" if not required_states: return True for device_id, required_state in required_states.items(): if device_id not in current_states: return False if current_states[device_id]["state"].get("power") != required_state: return False return True def _predict_user_activity(self, device_states, environment_data, user_state) -> str: """预测用户活动""" # 实际应用中这里会构建特征向量并使用模型预测 # 简化实现:返回规则推断结果 return "working" if "work_mode" in self._detect_user_state() else "relaxing"
场景化控制实现
基于情境理解结果,我们需要将抽象的情境转化为具体的设备控制指令。以下是任务规划与执行模块的核心代码:
import json import sqlite3 from datetime import datetime from typing import Dict, List, Any class SceneController: def __init__(self, db_path: str = "smart_home.db", mqtt_client=None): self.db_path = db_path self.mqtt_client = mqtt_client # 实际应用中传入MQTT客户端 self.scenes = self._load_scene_definitions() def _load_scene_definitions(self) -> Dict[str, Dict]: """加载场景定义""" # 实际应用中可以从数据库或配置文件加载 return { "morning": { "description": "Morning routine scene", "priority": 5, "devices": { "living_room_lights": {"power": "on", "brightness": 70, "color_temp": 5000}, "kitchen_lights": {"power": "on", "brightness": 80}, "thermostat": {"target_temperature": 22}, "coffee_maker": {"power": "on", "mode": "espresso"} }, "dependencies": [], "execution_order": ["thermostat", "coffee_maker", "living_room_lights", "kitchen_lights"] }, "leave_home": { "description": "Leaving home scene", "priority": 6, "devices": { "all_lights": {"power": "off"}, "thermostat": {"target_temperature": 18}, "security_system": {"power": "on", "mode": "away"}, "window_blinds": {"position": 100}, "all_entertainment": {"power": "off"} }, "dependencies": [], "execution_order": ["all_entertainment", "all_lights", "window_blinds", "thermostat", "security_system"] }, "evening": { "description": "Evening relaxation scene", "priority": 5, "devices": { "living_room_lights": {"power": "on", "brightness": 40, "color_temp": 2700}, "kitchen_lights": {"power": "on", "brightness": 60}, "thermostat": {"target_temperature": 23}, "smart_tv": {"power": "on", "source": "netflix"}, "speaker_system": {"power": "on", "volume": 20} }, "dependencies": [], "execution_order": ["thermostat", "living_room_lights", "kitchen_lights", "smart_tv", "speaker_system"] }, "movie_night": { "description": "Movie watching scene", "priority": 7, "devices": { "living_room_lights": {"power": "on", "brightness": 10, "color_temp": 2200}, "other_lights": {"power": "off"}, "thermostat": {"target_temperature": 21}, "smart_tv": {"power": "on", "source": "bluetooth", "picture_mode": "cinema"}, "speaker_system": {"power": "on", "volume": 30, "sound_mode": "surround"} }, "dependencies": ["evening"], "execution_order": ["other_lights", "thermostat", "smart_tv", "speaker_system", "living_room_lights"] } } def activate_scene(self, scene_name: str, context: Dict = None) -> Dict[str, Any]: """激活指定场景""" if scene_name not in self.scenes: return {"status": "error", "message": f"Scene {scene_name} not found"} scene = self.scenes[scene_name] context = context or {} # 处理依赖场景 for dependency in scene["dependencies"]: self.activate_scene(dependency, context) # 执行场景设备指令 results = {} for device_id in scene["execution_order"]: # 处理特殊设备组(如"all_lights") if device_id.startswith("all_"): group_results = self._control_device_group(device_id[4:], scene["devices"][device_id]) results.update(group_results) else: result = self._control_device(device_id, scene["devices"][device_id]) results[device_id] = result # 记录场景执行日志 self._log_scene_execution(scene_name, results, context) return { "status": "success", "scene": scene_name, "timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(), "results": results } def _control_device(self, device_id: str, commands: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """控制单个设备""" if not self.mqtt_client: return {"status": "simulated", "device": device_id, "commands": commands} # 构建设备控制主题 topic = f"devices/control/{device_id}" payload = {"commands": commands, "timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat()} try: # 发送MQTT消息控制设备 self.mqtt_client.publish(topic, json.dumps(payload)) return {"status": "success", "device": device_id, "commands": commands} except Exception as e: return {"status": "error", "device": device_id, "error": str(e)} def _control_device_group(self, group_name: str, commands: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """控制设备组""" results = {} # 获取设备组中的所有设备(实际应用中从数据库查询) device_groups = { "lights": ["living_room_lights", "kitchen_lights", "bedroom_lights", "bathroom_lights"], "entertainment": ["smart_tv", "speaker_system", "game_console"] } if group_name in device_groups: for device_id in device_groups[group_name]: results[device_id] = self._control_device(device_id, commands) return results def _log_scene_execution(self, scene_name: str, results: Dict, context: Dict): """记录场景执行日志""" conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute( """ INSERT INTO scene_executions (scene_name, timestamp, status, results, context) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?) """, (scene_name, datetime.now().isoformat(), "completed", json.dumps(results), json.dumps(context)) ) conn.commit() conn.close() def suggest_scene(self, context: Dict) -> Dict[str, Any]: """基于当前情境推荐场景""" # 分析情境数据推荐合适的场景 user_activity = context.get("user_activity", "") matched_contexts = context.get("matched_contexts", []) time_of_day = datetime.now().hour # 基于时间的基础推荐 if 6 <= time_of_day < 9: return {"scene": "morning", "confidence": 0.85, "reason": "Morning time range detected"} elif 17 <= time_of_day < 20: return {"scene": "evening", "confidence": 0.8, "reason": "Evening time range detected"} # 基于用户活动的推荐 if "watching_movie" in user_activity: return {"scene": "movie_night", "confidence": 0.9, "reason": "Movie watching activity detected"} elif "leaving_home" in matched_contexts: return {"scene": "leave_home", "confidence": 0.95, "reason": "Leaving home context detected"} # 默认不推荐 return {"scene": None, "confidence": 0, "reason": "No matching context for scene recommendation"}
小智AI集成方案
将智能家居控制中枢与小智AI集成的关键在于实现自然语言理解与系统功能的无缝对接。我们通过自定义技能(Skill)的方式扩展小智AI的能力:
from typing import Dict, Any, List import json import time from datetime import datetime class SmartHomeSkill: def __init__(self, controller, context_provider): self.controller = controller # 传入智能家居控制器实例 self.context_provider = context_provider # 传入情境提供器实例 self.intent_handlers = { "activate_scene": self.handle_activate_scene, "control_device": self.handle_control_device, "get_status": self.handle_get_status, "suggest_action": self.handle_suggest_action, "create_routine": self.handle_create_routine } self.entities = { "scene": list(self.controller.scenes.keys()), "device": self._get_device_list(), "device_attribute": self._get_device_attributes() } def _get_device_list(self) -> List[str]: """获取设备列表""" # 实际应用中从设备数据库获取 return ["living_room_lights", "kitchen_lights", "thermostat", "smart_tv", "coffee_maker", "security_system", "speaker_system"] def _get_device_attributes(self) -> Dict[str, List[str]]: """获取设备属性列表""" # 实际应用中从设备元数据获取 return { "lights": ["power", "brightness", "color", "color_temp"], "thermostat": ["target_temperature", "mode", "current_temperature"], "smart_tv": ["power", "source", "volume", "channel"], "speaker_system": ["power", "volume", "source", "mode"] } def process_intent(self, intent: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """处理意图""" intent_name = intent.get("name") slots = intent.get("slots", {}) if intent_name in self.intent_handlers: return self.intent_handlers[intent_name](slots) else: return { "response_type": "error", "message": f"Sorry, I don't understand how to {intent_name}", "suggestions": self._get_suggestions(intent_name) } def handle_activate_scene(self, slots: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """处理激活场景意图""" scene_name = slots.get("scene_name", {}).get("value") if not scene_name: # 如果未指定场景,基于当前情境推荐 context = self.context_provider.get_current_context() suggestion = self.controller.suggest_scene(context) if suggestion["scene"]: return { "response_type": "confirmation", "message": f"It looks like you might want to activate the {suggestion['scene']} scene. Shall I do that?", "suggestion": suggestion } else: return { "response_type": "request_more_info", "message": "Which scene would you like to activate?", "options": list(self.controller.scenes.keys()) } # 激活指定场景 if scene_name not in self.controller.scenes: return { "response_type": "error", "message": f"I don't recognize the {scene_name} scene.", "suggestions": list(self.controller.scenes.keys()) } # 获取当前情境 context = self.context_provider.get_current_context() result = self.controller.activate_scene(scene_name, context) if result["status"] == "success": return { "response_type": "success", "message": f"Activated the {scene_name} scene.", "scene_details": self.controller.scenes[scene_name], "execution_results": result["results"] } else: return { "response_type": "error", "message": f"Sorry, I couldn't activate the {scene_name} scene.", "error_details": result.get("results", {}) } def handle_control_device(self, slots: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """处理控制设备意图""" device_name = slots.get("device_name", {}).get("value") attribute = slots.get("device_attribute", {}).get("value") value = slots.get("value", {}).get("value") # 验证必要参数 missing_params = [] if not device_name: missing_params.append("device name") if not attribute: missing_params.append("attribute to change") if not value: missing_params.append("value to set") if missing_params: return { "response_type": "request_more_info", "message": f"To control a device, I need to know the {', '.join(missing_params)}.", "missing_params": missing_params } # 执行设备控制 # 在实际应用中,这里会调用设备控制API return { "response_type": "success", "message": f"Setting {device_name} {attribute} to {value}.", "action": { "type": "control_device", "device": device_name, "attribute": attribute, "value": value, "timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat() } } def handle_get_status(self, slots: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """处理获取状态意图""" target = slots.get("target", {}).get("value", "home") if target == "home": # 获取整体家居状态摘要 context = self.context_provider.get_current_context() device_states = context.get("device_states", {}) environment_data = context.get("environment_data", {}) # 构建状态摘要 status_summary = [] if "thermostat" in device_states: temp = device_states["thermostat"]["state"].get("current_temperature", "unknown") status_summary.append(f"Current temperature is {temp}°C") # 检查是否有设备异常 issues = self._detect_issues(context) if issues: status_summary.append(f"I noticed {len(issues)} potential issues: {', '.join([i['description'] for i in issues[:2]])}") return { "response_type": "status_summary", "summary": status_summary, "detailed_status": { "devices": device_states, "environment": environment_data } } elif target in self._get_device_list(): # 获取特定设备状态 # 实现获取特定设备状态的逻辑 return { "response_type": "device_status", "device": target, "status": "placeholder_status" # 实际应用中替换为真实状态 } else: return { "response_type": "error", "message": f"I don't know how to get the status of {target}" } def handle_suggest_action(self, slots: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """处理建议操作意图""" context = self.context_provider.get_current_context() scene_suggestion = self.controller.suggest_scene(context) if scene_suggestion["scene"]: return { "response_type": "suggestion", "message": f"Based on your current context, I suggest activating the {scene_suggestion['scene']} scene.", "suggestion": scene_suggestion, "confidence": scene_suggestion["confidence"] } # 检查是否有需要注意的事项 issues = self._detect_issues(context) if issues: return { "response_type": "alert", "message": f"I noticed some issues you might want to address:", "issues": issues } # 默认建议 return { "response_type": "suggestion", "message": "Everything seems to be running smoothly. Would you like me to help with anything specific?", "suggestions": ["Activate a scene", "Adjust devices", "Check energy usage"] } def handle_create_routine(self, slots: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """处理创建例程意图""" # 简化实现,实际应用中需要更复杂的逻辑来收集例程详情 return { "response_type": "progressive_collection", "message": "Let's create a new routine. First, what would you like to call it?", "collection_step": "name", "collected_data": {} } def _detect_issues(self, context: Dict) -> List[Dict]: """检测潜在问题""" # 简化实现,实际应用中会有更复杂的逻辑 issues = [] environment_data = context.get("environment_data", {}) # 检查温度异常 if "temperature" in environment_data: temp = environment_data["temperature"].get("value", 0) if temp > 28 or temp < 16: issues.append({ "type": "temperature", "description": f"temperature is {temp}°C", "severity": "medium", "suggestion": "adjust the thermostat" }) return issues def _get_suggestions(self, intent_name: str) -> List[str]: """获取相关建议""" # 基于意图名称提供可能的相关建议 return [ "activate a scene", "control a device", "check home status", "create a routine" ]
关键技术点解析
智能家居控制中枢的核心突破在于情境理解和主动服务能力,而非被动响应指令。实现这一突破需要关注三个关键技术点:
1. 多模态数据融合:系统需要整合来自不同设备和传感器的数据,识别有意义的模式。例如,当系统检测到"用户手机连接到家附近WiFi"+"时间是周五晚上7点"+"过去两周的同一时间用户通常打开电视",就能主动建议激活"周末娱乐"场景。
2. 渐进式学习机制:初始阶段系统依赖预设规则,但通过记录用户对建议的反馈(接受/拒绝/修改),系统应逐渐优化推荐模型。代码中的_log_scene_execution方法记录了所有场景执行结果,这些数据可用于训练更精准的用户偏好模型。
3. 自然语言理解与生成:将技术化的设备参数转化为自然语言描述(如将"brightness: 40, color_temp: 2700"描述为"温暖柔和的灯光"),同时也能将用户模糊的自然语言请求(如"营造浪漫氛围")转化为具体的设备参数组合。
最佳实践:从用户最频繁的3-5个场景入手(如早晨 routine、离家模式、回家模式、睡前模式),确保这些核心场景的体验流畅稳定,再逐步扩展到更复杂的场景。避免过度设计导致系统复杂度过高,反而降低可靠性。
项目二:个性化AI对话系统——从通用问答到专属助手
普通AI对话往往停留在通用知识问答层面,而"第二大脑"级别的对话系统应该成为个性化的信息处理中枢——理解用户的工作流程、记住重要细节、学习专业术语、并能协助处理特定领域任务。本项目将构建一个能够持续学习用户偏好、整合个人数据、并提供深度个性化服务的AI对话系统。
系统架构设计
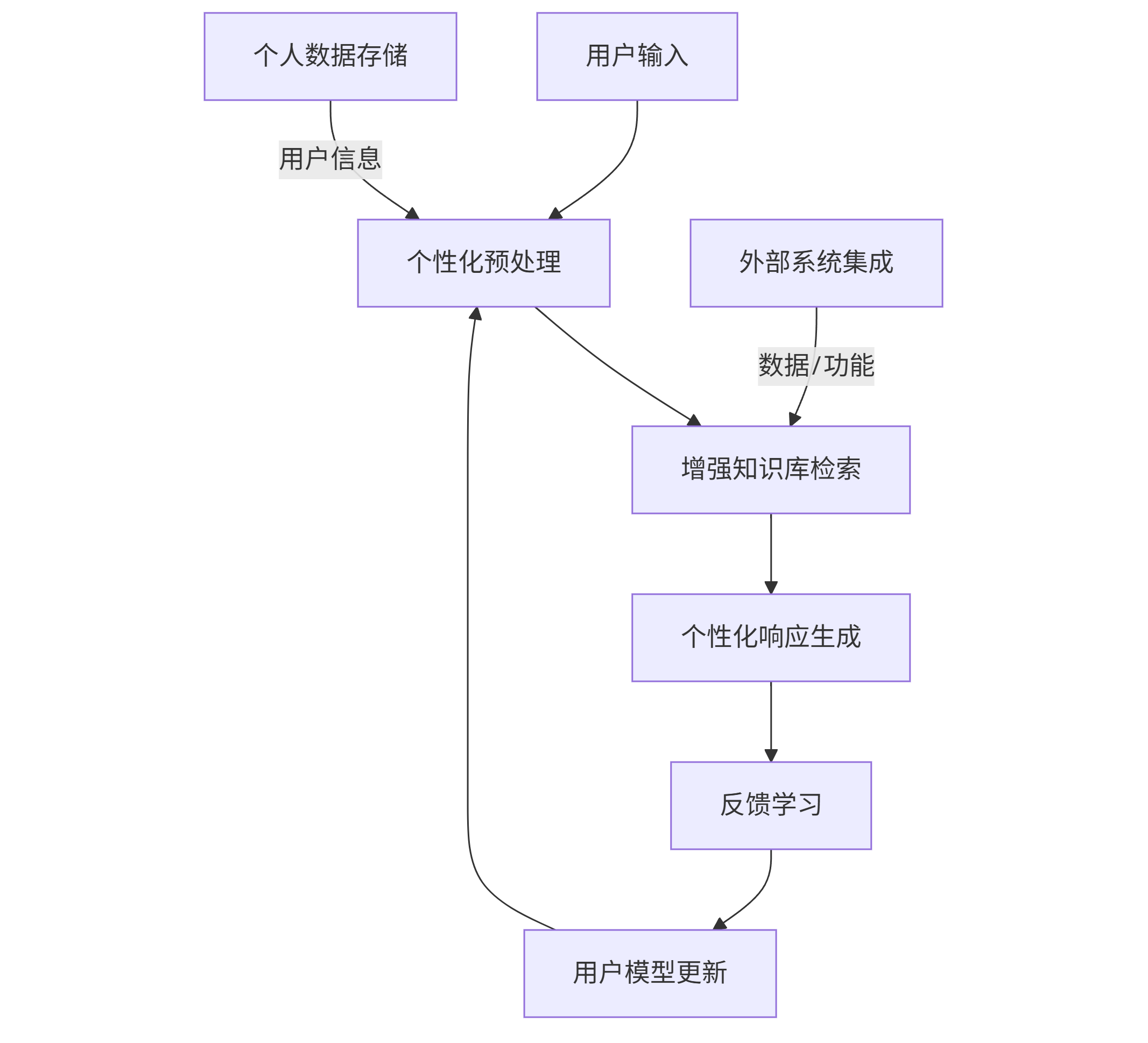
个性化AI对话系统的核心挑战在于知识的个性化(系统知道用户知道的事情)和能力的个性化(系统能做用户需要做的事情)。我们采用"五层增强架构":
graph TD A[用户输入] --> B[个性化预处理] B --> C[增强知识库检索] C --> D[个性化响应生成] D --> E[反馈学习] E --> F[用户模型更新] F --> B G[外部系统集成] -->|数据/功能| C H[个人数据存储] -->|用户信息| B
个性化预处理层对用户输入进行增强处理:基于用户历史对话识别简称(如将"项目A"扩展为完整项目名称)、解析领域特定术语、识别用户情绪状态。增强知识库检索不仅查询通用知识,还会检索用户个人数据、历史对话和专业领域知识。反馈学习层通过分析用户对响应的显式(点赞/差评)和隐式(是否继续追问/执行建议)反馈,持续优化用户模型。
核心功能实现
个性化AI对话系统的核心是用户模型——一个持续进化的数字孪生,包含用户的知识体系、偏好习惯、工作流程和需求模式。我们将构建用户模型存储、个性化对话处理和多轮对话管理三个核心模块。
1. 用户模型存储与管理
用户模型需要高效存储和快速更新多种类型数据,我们采用混合存储架构:关系型数据库存储结构化数据,向量数据库存储语义向量,文档数据库存储非结构化内容。
import sqlite3 import json import numpy as np from datetime import datetime, timedelta from typing import Dict, List, Any, Optional import chromadb from chromadb.config import Settings class UserModelManager: def __init__(self, user_id: str, db_path: str = "user_models.db"): self.user_id = user_id self.db_path = db_path self._init_databases() # 连接向量数据库(用于语义相似性搜索) self.chroma_client = chromadb.Client(Settings( persist_directory="./chroma_db", chroma_db_impl="duckdb+parquet" )) self.conversation_collection = self.chroma_client.get_or_create_collection( name=f"conv_{user_id}", metadata={"description": "User conversation embeddings"} ) self.knowledge_collection = self.chroma_client.get_or_create_collection( name=f"knowledge_{user_id}", metadata={"description": "User knowledge embeddings"} ) def _init_databases(self): """初始化数据库表结构""" conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() # 用户基本信息表 cursor.execute(''' CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user_profiles ( user_id TEXT PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT, preferences JSON, settings JSON, last_updated TIMESTAMP ) ''') # 对话历史表 cursor.execute(''' CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS conversation_history ( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, user_id TEXT, role TEXT, -- "user" or "assistant" content TEXT, timestamp DATETIME, conversation_id TEXT, metadata JSON, FOREIGN KEY(user_id) REFERENCES user_profiles(user_id) ) ''') # 用户知识库元数据表 cursor.execute(''' CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user_knowledge ( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, user_id TEXT, title TEXT, content_type TEXT, source TEXT, added_at DATETIME, metadata JSON, FOREIGN KEY(user_id) REFERENCES user_profiles(user_id) ) ''') # 用户任务表 cursor.execute(''' CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user_tasks ( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, user_id TEXT, title TEXT, description TEXT, status TEXT, priority INTEGER, due_date DATETIME, created_at DATETIME, updated_at DATETIME, metadata JSON, FOREIGN KEY(user_id) REFERENCES user_profiles(user_id) ) ''') # 用户实体表(存储用户提及的人物、地点、事物等) cursor.execute(''' CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user_entities ( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, user_id TEXT, entity_type TEXT, entity_name TEXT, entity_data JSON, confidence FLOAT, last_mentioned DATETIME, mention_count INTEGER, FOREIGN KEY(user_id) REFERENCES user_profiles(user_id) ) ''') conn.commit() conn.close() def update_user_preferences(self, preferences: Dict[str, Any]) -> bool: """更新用户偏好设置""" conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() # 先获取现有偏好 cursor.execute( "SELECT preferences FROM user_profiles WHERE user_id = ?", (self.user_id,) ) result = cursor.fetchone() existing_prefs = json.loads(result[0]) if result and result[0] else {} # 合并新偏好 existing_prefs.update(preferences) # 插入或更新用户资料 now = datetime.now().isoformat() cursor.execute( """ INSERT OR REPLACE INTO user_profiles (user_id, name, preferences, settings, last_updated) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?) """, (self.user_id, None, json.dumps(existing_prefs), None, now) ) conn.commit() conn.close() return True def add_conversation_turn(self, role: str, content: str, conversation_id: str, metadata: Dict = None) -> int: """添加对话轮次""" conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() timestamp = datetime.now().isoformat() metadata_json = json.dumps(metadata or {}) cursor.execute( """ INSERT INTO conversation_history (user_id, role, content, timestamp, conversation_id, metadata) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?) """, (self.user_id, role, content, timestamp, conversation_id, metadata_json) ) conn.commit() turn_id = cursor.lastrowid conn.close() return turn_id def get_conversation_history(self, conversation_id: str = None, limit: int = 20) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]: """获取对话历史""" conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() query = "SELECT role, content, timestamp, metadata FROM conversation_history WHERE user_id = ?" params = [self.user_id] if conversation_id: query += " AND conversation_id = ?" params.append(conversation_id) query += " ORDER BY timestamp DESC LIMIT ?" params.append(limit) cursor.execute(query, params) results = cursor.fetchall() conn.close() # 反转顺序以按时间正序返回,并解析JSON字段 history = [] for role, content, timestamp, metadata_json in reversed(results): history.append({ "role": role, "content": content, "timestamp": timestamp, "metadata": json.loads(metadata_json) if metadata_json else {} }) return history def add_user_knowledge(self, content: str, content_type: str, source: str, metadata: Dict = None) -> int: """添加用户知识库内容""" conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() added_at = datetime.now().isoformat() metadata_json = json.dumps(metadata or {}) # 提取标题(简化实现,实际应用中可使用NLP模型从内容中提取) title = metadata.get("title", f"Knowledge added on {added_at[:10]}") if metadata else f"Knowledge added on {added_at[:10]}" cursor.execute( """ INSERT INTO user_knowledge (user_id, title, content_type, source, added_at, metadata) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?) """, (self.user_id, title, content_type, source, added_at, metadata_json) ) conn.commit() knowledge_id = cursor.lastrowid conn.close() # TODO: 这里应该生成内容的嵌入向量并存储到向量数据库 # self._store_knowledge_embedding(knowledge_id, content) return knowledge_id def update_entity(self, entity_type: str, entity_name: str, entity_data: Dict = None, confidence: float = 0.8) -> bool: """更新用户实体""" conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() now = datetime.now().isoformat() # 检查实体是否已存在 cursor.execute( "SELECT id, mention_count, entity_data FROM user_entities WHERE user_id = ? AND entity_name = ?", (self.user_id, entity_name) ) result = cursor.fetchone() if result: # 更新现有实体 entity_id, mention_count, existing_data = result updated_data = json.loads(existing_data) if existing_data else {} if entity_data: updated_data.update(entity_data) cursor.execute( """ UPDATE user_entities SET entity_type = ?, entity_data = ?, confidence = ?, last_mentioned = ?, mention_count = ? WHERE id = ? """, (entity_type, json.dumps(updated_data), confidence, now, mention_count + 1, entity_id) ) else: # 创建新实体 cursor.execute( """ INSERT INTO user_entities (user_id, entity_type, entity_name, entity_data, confidence, last_mentioned, mention_count) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?) """, (self.user_id, entity_type, entity_name, json.dumps(entity_data or {}), confidence, now, 1) ) conn.commit() conn.close() return True def get_related_entities(self, entity_name: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]: """获取相关实体""" # 简化实现,实际应用中可使用实体链接和关系抽取模型 conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path) cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute( """ SELECT entity_name, entity_type, entity_data, mention_count, last_mentioned FROM user_entities WHERE user_id = ? AND entity_name LIKE ? ORDER BY mention_count DESC LIMIT 5 """, (self.user_id, f"%{entity_name}%") ) results = cursor.fetchall() conn.close() return [ { "name": name, "type": entity_type, "data": json.loads(data) if data else {}, "mention_count": count, "last_mentioned": last_mentioned } for name, entity_type, data, count, last_mentioned in results ]
2. 个性化对话处理
个性化对话处理的核心是将通用AI能力与用户特定信息结合,生成既准确又贴心的响应。以下是个性化对话处理器的实现:
import re import json import uuid import numpy as np from typing import Dict, List, Any, Optional from datetime import datetime class PersonalizedDialogueProcessor: def __init__(self, user_model_manager, llm_client, embedding_model): """ 初始化个性化对话处理器 :param user_model_manager: 用户模型管理器实例 :param llm_client: 大语言模型客户端 :param embedding_model: 嵌入模型 """ self.user_model = user_model_manager self.llm_client = llm_client # 实际应用中传入LLM客户端 self.embedding_model = embedding_model # 实际应用中传入嵌入模型 self.entity_types = ["person", "organization", "project", "document", "concept", "event"] self.specialized_domains = ["work", "personal", "health", "finance", "learning"] def process_query(self, user_query: str, conversation_id: Optional[str] = None, context: Optional[Dict] = None) -> Dict[str, Any]: """处理用户查询并生成个性化响应""" # 1. 初始化或获取对话ID conversation_id = conversation_id or str(uuid.uuid4()) # 2. 个性化预处理 processed_query, metadata = self._personalized_preprocessing(user_query, conversation_id) # 3. 检索相关上下文 relevant_context = self._retrieve_relevant_context(processed_query, conversation_id) # 4. 构建提示词 prompt = self._build_prompt(processed_query, relevant_context, context or {}) # 5. 调用LLM生成响应 llm_response = self._call_llm(prompt) # 6. 个性化响应后处理 final_response, response_metadata = self._personalized_postprocessing(llm_response, user_query) # 7. 存储对话历史 self.user_model.add_conversation_turn("user", user_query, conversation_id, {"preprocessing_metadata": metadata}) self.user_model.add_conversation_turn("assistant", final_response, conversation_id, response_metadata) # 8. 更新用户模型(实体、偏好等) self._update_user_model_based_on_interaction(user_query, final_response) return { "response": final_response, "conversation_id": conversation_id, "metadata": { "preprocessing": metadata, "response": response_metadata, "context_retrieved": len(relevant_context) > 0 } } def _personalized_preprocessing(self, user_query: str, conversation_id: str) -> (str, Dict[str, Any]): """个性化预处理用户查询""" metadata = { "timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(), "entities_detected": [], "domain_classification": {}, "query_type": None, "resolved_references": [] } # 1. 实体识别与链接 entities = self._detect_entities(user_query) metadata["entities_detected"] = entities # 2. 解析指代关系(如"它"、"那个项目"等) resolved_query, resolved_refs = self._resolve_references(user_query, conversation_id) metadata["resolved_references"] = resolved_refs # 3. 领域分类 domain_scores = self._classify_domain(resolved_query) metadata["domain_classification"] = domain_scores primary_domain = max(domain_scores.items(), key=lambda x: x[1])[0] if domain_scores else "general" metadata["primary_domain"] = primary_domain # 4. 查询类型分类 query_type = self._classify_query_type(resolved_query) metadata["query_type"] = query_type return resolved_query, metadata def _detect_entities(self, text: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]: """检测文本中的实体""" # 简化实现,实际应用中使用实体识别模型如spaCy、BERT等 entities = [] # 匹配已知实体 for entity_type in self.entity_types: # 这里应该使用NLP模型检测实体 # 简化处理:使用正则表达式匹配大写名词短语作为实体候选 pattern = r'\b[A-Z][a-zA-Z\s]+\b' # 简化的实体匹配模式 matches = re.findall(pattern, text) for match in matches: # 检查是否是已知实体 related_entities = self.user_model.get_related_entities(match) if related_entities: confidence = 0.8 + (0.2 * min(related_entities[0]["mention_count"] / 10, 1)) # 见过多次的实体置信度更高 entities.append({ "name": match, "type": entity_type, "confidence": confidence, "known_entity": True, "related_entity": related_entities[0]["name"] }) # 更新实体提及信息 self.user_model.update_entity(entity_type, match) return entities def _resolve_references(self, text: str, conversation_id: str) -> (str, List[Dict]): """解析指代关系""" # 简化实现,实际应用中使用共指消解模型 resolved_refs = [] resolved_text = text # 获取最近对话上下文辅助指代消解 recent_context = self.user_model.get_conversation_history(conversation_id, limit=5) # 简单代词解析示例(他/她/它/这个/那个等) pronouns = { "it": [], "this": [], "that": [], "he": [], "she": [], "they": [] } # 在实际应用中,这里会使用NLP模型进行复杂的指代消解 # 简化处理:查找最近提到的实体并替换代词 if recent_context and any(pron in text.lower() for pron in pronouns.keys()): # 提取最近对话中提到的实体 recent_entities = [] for turn in recent_context: if turn["role"] == "user": # 简化处理:从最近用户输入中提取实体 context_entities = re.findall(r'\b[A-Z][a-zA-Z\s]+\b', turn["content"]) recent_entities.extend(context_entities) # 如果有最近实体,简单替换"it"为最近实体 if recent_entities and "it" in text.lower(): resolved_text = resolved_text.replace("it", recent_entities[-1]) resolved_text = resolved_text.replace("It", recent_entities[-1]) resolved_refs.append({ "original": "it", "resolved_to": recent_entities[-1], "confidence": 0.7 }) return resolved_text, resolved_refs def _classify_domain(self, text: str) -> Dict[str, float]: """将查询分类到特定领域""" # 简化实现,实际应用中使用分类模型 domain_keywords = { "work": ["project", "meeting", "deadline", "client", "report", "email", "task"], "personal": ["family", "friend", "plan", "gift", "trip", "hobby"], "health": ["exercise", "diet", "sleep", "weight", "calories", "medication"], "finance": ["money", "budget", "bill", "investment", "expense", "income"], "learning": ["learn", "study", "course", "book", "concept", "skill"] } scores = {domain: 0.0 for domain in self.specialized_domains} text_lower = text.lower() for domain, keywords in domain_keywords.items(): count = sum(1 for kw in keywords if kw in text_lower) scores[domain] = min(count / 3, 1.0) # 最多3个关键词匹配就认为是该领域 # 归一化分数 total = sum(scores.values()) if total > 0: scores = {k: v/total for k, v in scores.items()} return scores def _classify_query_type(self, text: str) -> str: """分类查询类型""" # 简化实现,实际应用中使用意图分类模型 query_types = { "question": ["what", "why", "how", "when", "where", "who", "which"], "command": ["do", "make", "create", "find", "show", "tell", "send"], "statement": ["is", "are", "was", "were", "will", "would"], "request": ["can you", "could you", "would you", "please"] } text_lower = text.lower().strip() for qtype, keywords in query_types.items(): for kw in keywords: if text_lower.startswith(kw) or f" {kw} " in text_lower: return qtype return "statement" def _retrieve_relevant_context(self, processed_query: str, conversation_id: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]: """检索相关上下文""" # 1. 从对话历史中检索 conversation_context = self.user_model.get_conversation_history(conversation_id, limit=5) # 2. 从用户知识库中检索(使用嵌入模型进行语义相似性搜索) knowledge_context = self._retrieve_knowledge_context(processed_query) # 3. 从用户任务中检索相关任务 task_context = self._retrieve_relevant_tasks(processed_query) return { "conversation": conversation_context, "knowledge": knowledge_context, "tasks": task_context } def _retrieve_knowledge_context(self, query: str, top_k: int = 3) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]: """检索相关知识库内容""" # 简化实现,实际应用中使用向量数据库进行相似性搜索 return [] # 在完整实现中返回相关知识片段 def _retrieve_relevant_tasks(self, query: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]: """检索相关任务""" # 简化实现,实际应用中使用任务标题和描述的相似性搜索 return [] def _build_prompt(self, processed_query: str, context: Dict, additional_context: Dict) -> str: """构建个性化提示词""" # 1. 系统指令部分 system_prompt = """You are a personalized AI assistant for {user_id}. Your knowledge is a combination of general world knowledge and the user's specific information. Always prioritize the user's stated preferences and personal information when they conflict with general knowledge. Be concise but helpful, and adapt your response style to match the user's communication style. If you don't know something and it's specific to the user's personal information, ask for clarification. """.replace("{user_id}", self.user_model.user_id) # 2. 加入用户特定信息 user_specific_prompt = "\nUser-specific information to consider:\n" # 加入用户偏好 # 在完整实现中,这里会从用户模型中提取相关偏好 # 3. 加入检索到的上下文 context_prompt = "\nRelevant context from previous interactions:\n" if context["conversation"]: context_prompt += "\n".join([f"{turn['role']}: {turn['content'][:50]}..." for turn in context["conversation"]]) # 4. 加入当前查询 query_prompt = f"\nCurrent query: {processed_query}\nAssistant response:" # 组合完整提示词 full_prompt = system_prompt + user_specific_prompt + context_prompt + query_prompt return full_prompt def _call_llm(self, prompt: str) -> str: """调用大语言模型生成响应""" # 简化实现,实际应用中调用OpenAI API或本地LLM # 这里返回一个模拟响应 return f"[Personalized response to: {prompt[-50:]}...]" def _personalized_postprocessing(self, llm_response: str, original_query: str) -> (str, Dict[str, Any]): """个性化后处理LLM响应""" metadata = { "response_length": len(llm_response), "action_items_extracted": [], "follow_up_questions": [], "confidence_score": 0.85 # 简化实现,实际应用中可基于不确定性检测模型 } # 1. 提取行动项 action_items = self._extract_action_items(llm_response) metadata["action_items_extracted"] = action_items # 2. 生成后续问题建议 follow_up_questions = self._generate_follow_up_questions(original_query, llm_response) metadata["follow_up_questions"] = follow_up_questions return llm_response, metadata def _extract_action_items(self, response: str) -> List[str]: """从响应中提取行动项""" # 简化实现,实际应用中使用抽取模型 action_verbs = ["remember", "note", "remind", "schedule", "create", "send", "tell"] sentences = re.split(r'[.!?]', response) action_items = [] for sentence in sentences: if any(verb in sentence.lower() for verb in action_verbs): action_items.append(sentence.strip()) return action_items def _generate_follow_up_questions(self, query: str, response: str) -> List[str]: """生成后续问题建议""" # 简化实现,实际应用中使用问题生成模型 return [] def _update_user_model_based_on_interaction(self, user_query: str, assistant_response: str) -> None: """基于交互更新用户模型""" # 1. 从用户查询中提取新实体和关系 # 2. 更新用户偏好(基于接受/拒绝建议等) # 3. 更新领域兴趣分布 pass
3. 专业领域知识整合
将AI的通用知识与用户的专业领域知识结合,是个性化AI助手的核心价值所在。以下是一个专业知识整合模块的实现:
import json import PyPDF2 import docx import markdown from typing import Dict, List, Any, Optional from datetime import datetime class DomainKnowledgeIntegrator: def __init__(self, user_model_manager): self.user_model = user_model_manager self.supported_formats = ["pdf", "docx", "txt", "md", "json"] self.domain_processors = { "software_development": self._process_software_dev_knowledge, "finance": self._process_finance_knowledge, "medicine": self._process_medicine_knowledge, "law": self._process_law_knowledge, "education": self._process_education_knowledge } def ingest_document(self, file_path: str, domain: str, metadata: Dict = None) -> Dict[str, Any]: """摄入文档并整合到用户知识库""" if not metadata: metadata = {} # 1. 提取文件格式 file_format = file_path.split(".")[-1].lower() if file_format not in self.supported_formats: return { "status": "error", "message": f"Unsupported file format: {file_format}. Supported formats: {', '.join(self.supported_formats)}" } # 2. 提取文本内容 try: text_content = self._extract_text_from_file(file_path, file_format) except Exception as e: return { "status": "error", "message": f"Failed to extract text from file: {str(e)}" } # 3. 根据领域处理内容 processing_func = self.domain_processors.get(domain, self._process_generic_knowledge) processed_data = processing_func(text_content, metadata) # 4. 存储到用户知识库 knowledge_id = self.user_model.add_user_knowledge( content=json.dumps(processed_data), content_type=f"structured_{domain}", source=file_path, metadata={**metadata, "original_format": file_format} ) # 5. 生成内容摘要和嵌入向量(在完整实现中) return { "status": "success", "knowledge_id": knowledge_id, "content_processed": { "sections": len(processed_data.get("sections", [])), "entities_extracted": len(processed_data.get("entities", [])), "domain": domain }, "metadata": metadata } def _extract_text_from_file(self, file_path: str, file_format: str) -> str: """从文件中提取文本""" if file_format == "pdf": return self._extract_text_from_pdf(file_path) elif file_format == "docx": return self._extract_text_from_docx(file_path) elif file_format == "md": return self._extract_text_from_markdown(file_path) elif file_format == "txt": with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: return f.read() elif file_format == "json": with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: data = json.load(f) return json.dumps(data, indent=2) # 转换为格式化JSON字符串 else: raise ValueError(f"Unsupported file format: {file_format}") def _extract_text_from_pdf(self, file_path: str) -> str: """从PDF提取文本""" text = "" with open(file_path, "rb") as f: reader = PyPDF2.PdfReader(f) for page in reader.pages: text += page.extract_text() + "\n\n" return text def _extract_text_from_docx(self, file_path: str) -> str: """从Word文档提取文本""" doc = docx.Document(file_path) full_text = [] for para in doc.paragraphs: full_text.append(para.text) return '\n'.join(full_text) def _extract_text_from_markdown(self, file_path: str) -> str: """从Markdown提取文本""" with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: md_text = f.read() # 转换为纯文本(简化处理) html = markdown.markdown(md_text) # 移除HTML标签 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser') return soup.get_text() def _process_generic_knowledge(self, text: str, metadata: Dict) -> Dict[str, Any]: """处理通用领域知识""" return { "type": "generic_knowledge", "original_text": text[:500] + "..." if len(text) > 500 else text, "sections": self._split_into_sections(text), "entities": [], # 在完整实现中添加实体提取 "key_concepts": [] # 在完整实现中添加关键概念提取 } def _process_software_dev_knowledge(self, text: str, metadata: Dict) -> Dict[str, Any]: """处理软件开发领域知识""" # 提取代码片段 code_pattern = r'```[\s\S]*?```' code_snippets = re.findall(code_pattern, text) # 提取技术术语 tech_terms = self._extract_tech_terms(text) return { "type": "software_development_knowledge", "sections": self._split_into_sections(text), "code_snippets": code_snippets, "technologies": tech_terms.get("technologies", []), "languages": tech_terms.get("languages", []), "frameworks": tech_terms.get("frameworks", []), "entities": tech_terms.get("entities", []) } def _extract_tech_terms(self, text: str) -> Dict[str, List[str]]: """提取技术术语""" # 简化实现,实际应用中使用领域特定NER模型 tech_terms = { "technologies": ["Python", "JavaScript", "React", "Django", "SQL", "NoSQL", "AWS", "Docker"], "languages": ["Python", "JavaScript", "Java", "C++", "C#", "Go", "Ruby", "PHP"], "frameworks": ["React", "Django", "Flask", "Vue", "Angular", "Spring", "Laravel"] } extracted = {key: [] for key in tech_terms} text_lower = text.lower() for category, terms in tech_terms.items(): for term in terms: if term.lower() in text_lower: extracted[category].append(term) # 去重 for category in extracted: extracted[category] = list(set(extracted[category])) return extracted def _split_into_sections(self, text: str) -> List[Dict[str, str]]: """将文本分割为章节""" # 简化实现,实际应用中基于标题层级分割 paragraphs = [p.strip() for p in text.split("\n\n") if p.strip()] return [{"id": i, "content": para, "length": len(para)} for i, para in enumerate(paragraphs[:5])] # 其他领域处理器实现... def _process_finance_knowledge(self, text: str, metadata: Dict) -> Dict[str, Any]: return self._process_generic_knowledge(text, metadata) def _process_medicine_knowledge(self, text: str, metadata: Dict) -> Dict[str, Any]: return self._process_generic_knowledge(text, metadata) def _process_law_knowledge(self, text: str, metadata: Dict) -> Dict[str, Any]: return self._process_generic_knowledge(text, metadata) def _process_education_knowledge(self, text: str, metadata: Dict) -> Dict[str, Any]: return self._process_generic_knowledge(text, metadata)
关键技术点解析
个性化AI对话系统与通用对话系统的本质区别在于知识边界和交互范式——通用AI回答"是什么",而个性化AI理解"对我而言是什么"。实现这一转变需要掌握三个关键技术:
1. 用户模型表示学习:用户模型需要高效表示多种类型的个性化信息,包括事实性知识(用户的项目、联系人、文档)、偏好(喜欢的沟通方式、工作习惯)、能力(用户的技能和知识盲区)和需求(短期任务和长期目标)。我们采用的混合存储架构(关系型+向量+文档数据库)平衡了结构化查询效率和非结构化内容处理能力。
2. 上下文感知的响应生成:系统需要在生成响应时考虑多层次上下文:当前对话上下文(理解对话流)、用户历史上下文(理解用户习惯)、领域知识上下文(理解专业术语)。代码中的_build_prompt方法整合了这些上下文,确保生成的响应既有针对性又符合用户期望。
3. 增量学习与遗忘机制:实用的个性化系统必须能够学习新知识和忘记过时信息。例如,当用户更换工作后,系统应逐渐减少提及旧公司的项目,增加新公司相关的信息。代码中的user_entities表记录了实体的last_mentioned和mention_count,可用于实现基于时间衰减的记忆机制。
最佳实践:实施"隐私优先"的个性化策略——让用户明确控制哪些信息被存储和使用,提供直观的方式查看和编辑系统对自己的"认知",并确保所有个性化数据可导出和删除。这不仅符合隐私法规要求,也能建立用户对系统的信任。
项目三:功能扩展平台——从单一功能到生态系统
真正的"第二大脑"不应局限于预设功能,而应能通过扩展不断增强能力。本项目将构建一个功能扩展平台,允许开发者和高级用户为小智AI创建自定义技能、集成第三方服务,并通过可视化界面组合现有功能创建复杂工作流。
系统架构设计
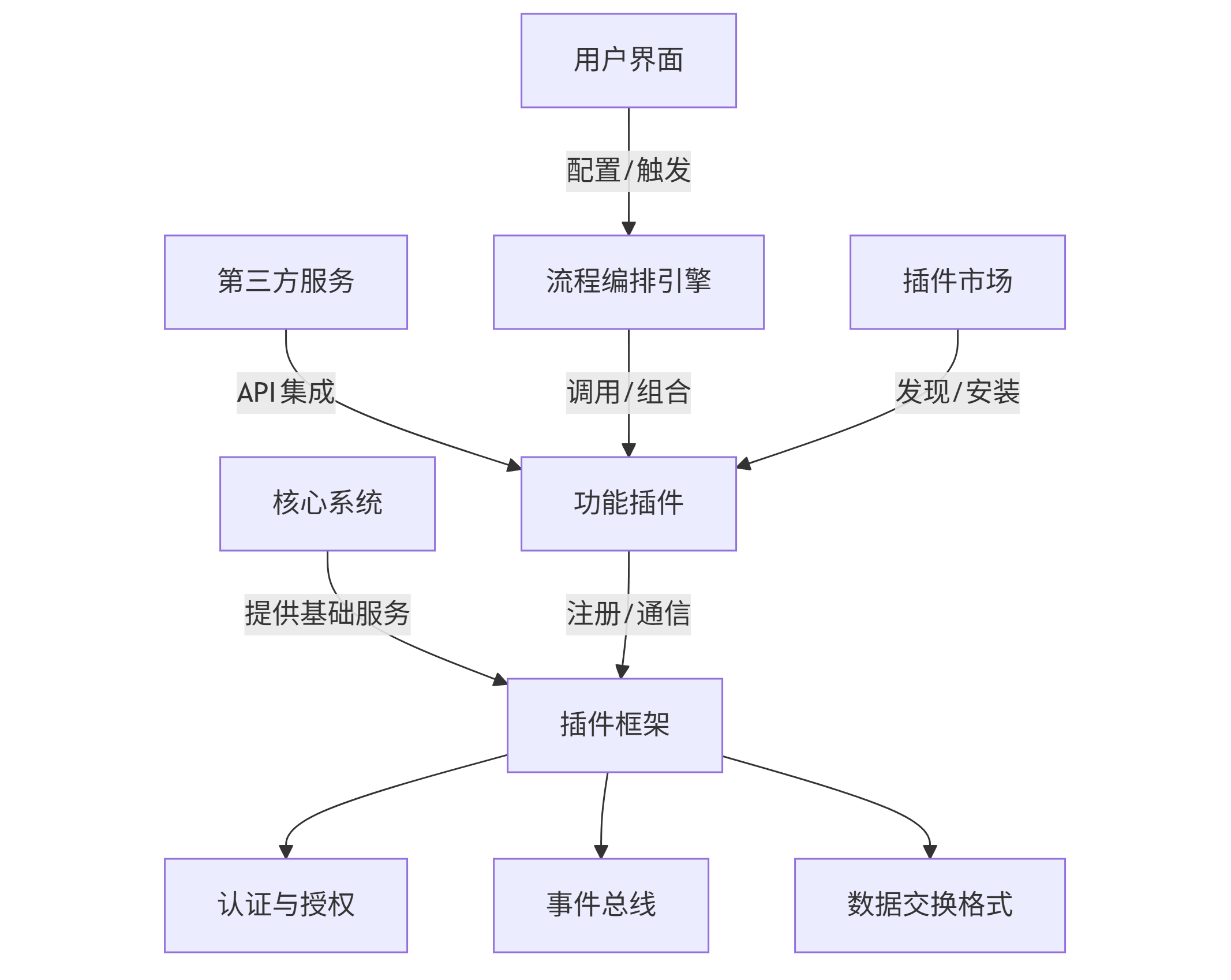
功能扩展平台的核心是开放性和可组合性——让不同来源的功能能够无缝协作。我们采用"插件-流程-生态"三层架构:
graph TD A[核心系统] -->|提供基础服务| B[插件框架] B --> C[认证与授权] B --> D[事件总线] B --> E[数据交换格式] F[功能插件] -->|注册/通信| B G[第三方服务] -->|API集成| F H[流程编排引擎] -->|调用/组合| F I[用户界面] -->|配置/触发| H J[插件市场] -->|发现/安装| F
插件框架提供统一的插件开发规范、通信机制和生命周期管理。流程编排引擎允许用户通过可视化界面或代码将多个插件功能组合成自动化工作流。插件市场则是插件发现、安装和管理的中心。这种架构确保了系统的扩展性(可添加新插件)、灵活性(可组合现有功能)和安全性(严格的插件权限控制)。
核心功能实现
功能扩展平台的实现涉及插件系统设计、流程编排引擎和用户界面三个主要部分。我们将重点展示插件框架和流程编排引擎的核心代码。
1. 插件框架
插件框架是功能扩展平台的基础,负责插件的加载、通信和生命周期管理。以下是一个轻量级但功能完整的插件框架实现:
import importlib.util import os import sys import json import uuid import traceback from datetime import datetime from typing import Dict, List, Any, Callable, Optional, Type from dataclasses import dataclass, field from enum import Enum # ------------------------------ # 插件接口定义 # ------------------------------ class PluginType(Enum): """插件类型枚举""" ACTION = "action" # 执行特定操作的插件 INTEGRATION = "integration" # 第三方服务集成插件 PROCESSOR = "processor" # 数据处理插件 UI = "ui" # 用户界面扩展插件 ANALYZER = "analyzer" # 分析类插件 class PluginStatus(Enum): """插件状态枚举""" DISABLED = "disabled" ENABLED = "enabled" ERROR = "error" LOADING = "loading" UNINSTALLED = "uninstalled" @dataclass class PluginManifest: """插件清单数据类""" plugin_id: str name: str description: str version: str author: str email: str type: PluginType requirements: List[str] = field(default_factory=list) permissions: List[str] = field(default_factory=list) settings_schema: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict) actions: List[str] = field(default_factory=list) events: List[str] = field(default_factory=list) icon: str = "" homepage: str = "" license: str = "MIT" min_core_version: str = "1.0.0" @dataclass class PluginInstance: """插件实例数据类""" manifest: PluginManifest status: PluginStatus instance_id: str = field(default_factory=lambda: str(uuid.uuid4())) settings: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict) last_updated: str = field(default_factory=lambda: datetime.now().isoformat()) error_message: str = "" metrics: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=lambda: { "execution_count": 0, "error_count": 0, "last_execution": None }) class PluginInterface: """插件接口基类""" def __init__(self, manifest: PluginManifest, settings: Dict[str, Any]): self.manifest = manifest self.settings = settings self.status = PluginStatus.DISABLED self.event_handlers = {} def on_enable(self) -> bool: """插件启用时调用""" self.status = PluginStatus.ENABLED return True def on_disable(self) -> bool: """插件禁用时调用""" self.status = PluginStatus.DISABLED return True def on_configure(self, new_settings: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """插件配置更新时调用""" self.settings.update(new_settings) return self.settings def register_event_handler(self, event_name: str, handler: Callable): """注册事件处理器""" if event_name not in self.event_handlers: self.event_handlers[event_name] = [] self.event_handlers[event_name].append(handler) def execute_action(self, action_name: str, params: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """执行插件操作""" # 记录执行 metrics self.metrics["execution_count"] += 1 self.metrics["last_execution"] = datetime.now().isoformat() # 查找并执行对应的操作方法 method_name = f"action_{action_name}" if hasattr(self, method_name): try: result = getattr(self, method_name)(params) return { "status": "success", "result": result, "plugin_id": self.manifest.plugin_id, "action": action_name, "timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat() } except Exception as e: # 记录错误 metrics self.metrics["error_count"] += 1 return { "status": "error", "error": str(e), "traceback": traceback.format_exc(), "plugin_id": self.manifest.plugin_id, "action": action_name, "timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat() } else: return { "status": "error", "error": f"Action {action_name} not found in plugin {self.manifest.plugin_id}", "plugin_id": self.manifest.plugin_id, "action": action_name, "timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat() } def emit_event(self, event_name: str, data: Dict[str, Any]): """触发事件(由插件框架实现)""" pass # 由插件框架在注册时注入实际实现 # ------------------------------ # 插件管理器 # ------------------------------ class PluginManager: def __init__(self, plugins_directory: str = "plugins", config_directory: str = "config"): self.plugins_directory = plugins_directory self.config_directory = config_directory self.plugin_instances: Dict[str, PluginInstance] = {} # instance_id -> PluginInstance self.plugin_interfaces: Dict[str, PluginInterface] = {} # instance_id -> PluginInterface self.plugin_manifest_cache: Dict[str, List[PluginManifest]] = {} # plugin_id -> List[Manifest] self.event_bus = EventBus() # 确保目录存在 os.makedirs(self.plugins_directory, exist_ok=True) os.makedirs(self.config_directory, exist_ok=True) # 加载已安装的插件 self.load_installed_plugins() def load_installed_plugins(self): """加载已安装的插件""" # 遍历插件目录 for plugin_dir in os.listdir(self.plugins_directory): plugin_path = os.path.join(self.plugins_directory, plugin_dir) if os.path.isdir(plugin_path): # 检查是否有插件清单 manifest_path = os.path.join(plugin_path, "manifest.json") if os.path.exists(manifest_path): try: with open(manifest_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: manifest_data = json.load(f) # 解析插件清单 plugin_manifest = self._parse_manifest(manifest_data, plugin_path) # 检查是否已安装此插件的配置 config_path = os.path.join(self.config_directory, f"plugin_{plugin_manifest.plugin_id}.json") settings = {} if os.path.exists(config_path): with open(config_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: config_data = json.load(f) settings = config_data.get("settings", {}) # 加载插件代码 plugin_interface = self._load_plugin_code(plugin_manifest, plugin_path, settings) if plugin_interface: # 创建插件实例 instance_id = str(uuid.uuid4()) plugin_instance = PluginInstance( manifest=plugin_manifest, status=PluginStatus.DISABLED, instance_id=instance_id, settings=settings ) # 存储插件实例和接口 self.plugin_instances[instance_id] = plugin_instance self.plugin_interfaces[instance_id] = plugin_interface # 缓存插件清单 if plugin_manifest.plugin_id not in self.plugin_manifest_cache: self.plugin_manifest_cache[plugin_manifest.plugin_id] = [] self.plugin_manifest_cache[plugin_manifest.plugin_id].append(plugin_manifest) print(f"Loaded plugin: {plugin_manifest.name} (v{plugin_manifest.version})") # 如果配置为自动启用,则启用插件 if config_data.get("auto_enable", False): self.enable_plugin(instance_id) except Exception as e: print(f"Failed to load plugin from {plugin_path}: {str(e)}") print(traceback.format_exc()) def _parse_manifest(self, manifest_data: Dict[str, Any], plugin_path: str) -> PluginManifest: """解析插件清单""" # 处理插件类型 plugin_type = PluginType(manifest_data.get("type", "action")) # 构建并返回PluginManifest对象 return PluginManifest( plugin_id=manifest_data["id"], name=manifest_data["name"], description=manifest_data.get("description", ""), version=manifest_data["version"], author=manifest_data.get("author", "Unknown"), email=manifest_data.get("email", ""), type=plugin_type, requirements=manifest_data.get("requirements", []), permissions=manifest_data.get("permissions", []), settings_schema=manifest_data.get("settings_schema", {}), actions=manifest_data.get("actions", []), events=manifest_data.get("events", []), icon=manifest_data.get("icon", ""), homepage=manifest_data.get("homepage", ""), license=manifest_data.get("license", "MIT"), min_core_version=manifest_data.get("min_core_version", "1.0.0") ) def _load_plugin_code(self, manifest: PluginManifest, plugin_path: str, settings: Dict[str, Any]) -> Optional[PluginInterface]: """加载插件代码""" # 查找主入口文件(通常是plugin.py或__init__.py) entry_files = ["plugin.py", "__init__.py"] entry_path = None for entry_file in entry_files: candidate_path = os.path.join(plugin_path, entry_file) if os.path.exists(candidate_path): entry_path = candidate_path break if not entry_path: print(f"No entry file found for plugin {manifest.plugin_id}") return None # 动态加载模块 try: module_name = f"plugin_{manifest.plugin_id}_{manifest.version}" spec = importlib.util.spec_from_file_location(module_name, entry_path) module = importlib.util.module_from_spec(spec) sys.modules[module_name] = module spec.loader.exec_module(module) # 查找插件主类(应该继承自PluginInterface) plugin_class = None for name, cls in module.__dict__.items(): if isinstance(cls, type) and issubclass(cls, PluginInterface) and cls != PluginInterface: plugin_class = cls break if not plugin_class: print(f"No PluginInterface subclass found in {entry_path}") return None # 创建插件实例 plugin_instance = plugin_class(manifest, settings) # 注入事件总线 def emit_event(event_name, data): self.event_bus.emit(event_name, { "source": manifest.plugin_id, "data": data, "timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat() }) plugin_instance.emit_event = emit_event # 注册事件处理器到事件总线 for event_name in manifest.events: self.event_bus.register_handler(event_name, plugin_instance) return plugin_instance except Exception as e: print(f"Failed to load plugin code: {str(e)}") print(traceback.format_exc()) return None def enable_plugin(self, instance_id: str) -> bool: """启用插件""" if instance_id not in self.plugin_interfaces: print(f"Plugin instance {instance_id} not found") return False plugin_interface = self.plugin_interfaces[instance_id] try: result = plugin_interface.on_enable() if result: self.plugin_instances[instance_id].status = PluginStatus.ENABLED print(f"Enabled plugin: {plugin_interface.manifest.name}") return True else: print(f"Plugin {plugin_interface.manifest.name} returned False from on_enable") return False except Exception as e: print(f"Error enabling plugin {instance_id}: {str(e)}") self.plugin_instances[instance_id].status = PluginStatus.ERROR self.plugin_instances[instance_id].error_message = str(e) return False def disable_plugin(self, instance_id: str) -> bool: """禁用插件""" if instance_id not in self.plugin_interfaces: print(f"Plugin instance {instance_id} not found") return False plugin_interface = self.plugin_interfaces[instance_id] try: result = plugin_interface.on_disable() self.plugin_instances[instance_id].status = PluginStatus.DISABLED print(f"Disabled plugin: {plugin_interface.manifest.name}") return result except Exception as e: print(f"Error disabling plugin {instance_id}: {str(e)}") return False def execute_plugin_action(self, instance_id: str, action_name: str, params: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """执行插件操作""" if instance_id not in self.plugin_interfaces: return { "status": "error", "error": f"Plugin instance {instance_id} not found" } plugin_interface = self.plugin_interfaces[instance_id] if plugin_interface.status != PluginStatus.ENABLED: return { "status": "error", "error": f"Plugin is not enabled (current status: {plugin_interface.status.value})" } return plugin_interface.execute_action(action_name, params) def configure_plugin(self, instance_id: str, new_settings: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """配置插件""" if instance_id not in self.plugin_interfaces: return { "status": "error", "error": f"Plugin instance {instance_id} not found" } plugin_interface = self.plugin_interfaces[instance_id] try: updated_settings = plugin_interface.on_configure(new_settings) # 更新存储的设置 self.plugin_instances[instance_id].settings = updated_settings # 保存配置到文件 config_path = os.path.join(self.config_directory, f"plugin_{plugin_interface.manifest.plugin_id}.json") with open(config_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f: json.dump({ "settings": updated_settings, "auto_enable": self.plugin_instances[instance_id].status == PluginStatus.ENABLED }, f, indent=2) return { "status": "success", "settings": updated_settings } except Exception as e: print(f"Error configuring plugin {instance_id}: {str(e)}") return { "status": "error", "error": str(e) } def get_plugin_instances(self, plugin_id: str = None) -> List[PluginInstance]: """获取插件实例列表""" if plugin_id: return [ instance for instance in self.plugin_instances.values() if instance.manifest.plugin_id == plugin_id ] else: return list(self.plugin_instances.values()) # ------------------------------ # 事件总线 # ------------------------------ class EventBus: def __init__(self): self.event_handlers = {} # event_name -> list of handlers def register_handler(self, event_name: str, handler: Any): """注册事件处理器""" if event_name not in self.event_handlers: self.event_handlers[event_name] = [] self.event_handlers[event_name].append(handler) def unregister_handler(self, event_name: str, handler: Any): """注销事件处理器""" if event_name in self.event_handlers: self.event_handlers[event_name] = [ h for h in self.event_handlers[event_name] if h != handler ] if not self.event_handlers[event_name]: del self.event_handlers[event_name] def emit(self, event_name: str, data: Dict[str, Any]): """触发事件""" if event_name not in self.event_handlers: return # 调用所有注册的事件处理器 for handler in self.event_handlers[event_name]: try: # 检查处理器是否有handle_<event_name>方法 method_name = f"handle_{event_name}" if hasattr(handler, method_name): getattr(handler, method_name)(data) # 否则检查是否有通用的handle_event方法 elif hasattr(handler, "handle_event"): handler.handle_event(event_name, data) except Exception as e: print(f"Error handling event {event_name} in handler: {str(e)}") print(traceback.format_exc())
2. 流程编排引擎
流程编排引擎允许用户将多个插件的功能组合成自动化工作流,响应特定事件或定时触发。以下是流程定义和执行的核心实现:
import json import uuid import time from datetime import datetime, timedelta from typing import Dict, List, Any, Optional, Callable import traceback class WorkflowStatus(Enum): """工作流状态枚举""" DRAFT = "draft" ENABLED = "enabled" DISABLED = "disabled" ERROR = "error" RUNNING = "running" COMPLETED = "completed" FAILED = "failed" class NodeType(Enum): """节点类型枚举""" ACTION = "action" # 执行插件操作 TRIGGER = "trigger" # 触发节点 CONDITION = "condition" # 条件判断节点 LOOP = "loop" # 循环节点 PARALLEL = "parallel" # 并行执行节点 MERGE = "merge" # 合并节点 DATA = "data" # 数据处理节点 class TriggerType(Enum): """触发器类型枚举""" EVENT = "event" # 事件触发 TIME = "time" # 定时触发 MANUAL = "manual" # 手动触发 API = "api" # API触发 @dataclass class NodeDefinition: """工作流节点定义""" id: str type: NodeType name: str description: Optional[str] = None plugin_instance_id: Optional[str] = None # 对于ACTION类型节点 action_name: Optional[str] = None # 对于ACTION类型节点 trigger_type: Optional[TriggerType] = None # 对于TRIGGER类型节点 trigger_config: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None # 对于TRIGGER类型节点 parameters: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict) next_nodes: List[str] = field(default_factory=list) # 下一节点ID列表 error_node: Optional[str] = None # 错误处理节点ID position: Dict[str, int] = field(default_factory=lambda: {"x": 0, "y": 0}) # 用于UI显示 @dataclass class WorkflowDefinition: """工作流定义""" workflow_id: str name: str description: Optional[str] = None status: WorkflowStatus = WorkflowStatus.DRAFT nodes: Dict[str, NodeDefinition] = field(default_factory=dict) # node_id -> NodeDefinition triggers: List[str] = field(default_factory=list) # 触发节点ID列表 created_at: str = field(default_factory=lambda: datetime.now().isoformat()) updated_at: str = field(default_factory=lambda: datetime.now().isoformat()) created_by: str = "system" last_run: Optional[str] = None run_count: int = 0 error_count: int = 0 @dataclass class WorkflowExecution: """工作流执行实例""" execution_id: str workflow_id: str status: WorkflowStatus started_at: str completed_at: Optional[str] = None trigger_info: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict) node_executions: Dict[str, Dict[str, Any]] = field(default_factory=dict) # node_id -> execution details error: Optional[str] = None output_data: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict) class WorkflowEngine: def __init__(self, plugin_manager: PluginManager): self.plugin_manager = plugin_manager self.workflows: Dict[str, WorkflowDefinition] = {} # workflow_id -> WorkflowDefinition self.executions: Dict[str, WorkflowExecution] = {} # execution_id -> WorkflowExecution self.scheduled_jobs = {} # 用于定时触发器 self.event_listeners = {} # 事件到工作流的映射 # 加载已保存的工作流 self.load_workflows() # 为所有已启用的工作流注册触发器 self._register_workflow_triggers() def load_workflows(self, directory: str = "workflows"): """加载工作流定义""" # 实际应用中从数据库或文件系统加载工作流定义 # 这里简化处理,初始化一个示例工作流 self._create_example_workflow() def _create_example_workflow(self): """创建示例工作流""" # 创建一个"收到邮件时保存附件到云存储"的工作流 workflow_id = "email_attachment_saver" # 定义节点 nodes = { "trigger": NodeDefinition( id="trigger", type=NodeType.TRIGGER, name="New Email Trigger", description="Triggers when a new email is received", trigger_type=TriggerType.EVENT, trigger_config={ "event_name": "email.received", "filters": { "has_attachments": True, "sender": "important@example.com" } }, next_nodes=["save_attachment"] ), "save_attachment": NodeDefinition( id="save_attachment", type=NodeType.ACTION, name="Save Attachment to Cloud", description="Saves email attachments to cloud storage", plugin_instance_id="", # 实际应用中会填入具体插件实例ID action_name="save_attachments", parameters={ "folder": "/Email Attachments/{{email.date}}", "overwrite": False }, next_nodes=["notify"] ), "notify": NodeDefinition( id="notify", type=NodeType.ACTION, name="Send Notification", description="Sends a notification when attachment is saved", plugin_instance_id="", # 实际应用中会填入具体插件实例ID action_name="send_notification", parameters={ "service": "mobile", "message": "New email attachment saved: {{attachment.filename}}", "priority": "medium" } ) } # 创建工作流定义 workflow = WorkflowDefinition( workflow_id=workflow_id, name="Email Attachment Saver", description="Saves attachments from important emails to cloud storage and notifies", status=WorkflowStatus.DISABLED, nodes=nodes, triggers=["trigger"] ) self.workflows[workflow_id] = workflow def _register_workflow_triggers(self): """为工作流注册触发器""" for workflow in self.workflows.values(): if workflow.status != WorkflowStatus.ENABLED: continue for trigger_node_id in workflow.triggers: trigger_node = workflow.nodes.get(trigger_node_id) if not trigger_node or trigger_node.type != NodeType.TRIGGER: continue # 事件触发器 if trigger_node.trigger_type == TriggerType.EVENT: event_name = trigger_node.trigger_config.get("event_name") if event_name: # 注册事件监听器 if event_name not in self.event_listeners: self.event_listeners[event_name] = [] self.event_listeners[event_name].append({ "workflow_id": workflow.workflow_id, "trigger_node_id": trigger_node_id, "filters": trigger_node.trigger_config.get("filters", {}) }) # 定时触发器 elif trigger_node.trigger_type == TriggerType.TIME: # 在完整实现中会设置定时任务 pass def on_event(self, event_name: str, event_data: Dict[str, Any]): """事件触发时调用""" if event_name not in self.event_listeners: return # 查找所有监听此事件的工作流 for listener in self.event_listeners[event_name]: workflow_id = listener["workflow_id"] trigger_node_id = listener["trigger_node_id"] filters = listener["filters"] # 检查工作流状态 workflow = self.workflows.get(workflow_id) if not workflow or workflow.status != WorkflowStatus.ENABLED: continue # 应用过滤器 if self._apply_trigger_filters(event_data, filters): # 触发工作流执行 self.start_workflow_execution(workflow_id, { "trigger_type": "event", "event_name": event_name, "event_data": event_data, "trigger_node_id": trigger_node_id }) def _apply_trigger_filters(self, event_data: Dict[str, Any], filters: Dict[str, Any]) -> bool: """应用触发器过滤器""" # 简化实现,实际应用中会有更复杂的过滤逻辑 for key, required_value in filters.items(): # 使用点符号支持嵌套属性 keys = key.split(".") current_data = event_data for k in keys: if k not in current_data: return False current_data = current_data[k] if current_data != required_value: return False return True def start_workflow_execution(self, workflow_id: str, trigger_info: Dict[str, Any]) -> str: """开始工作流执行""" if workflow_id not in self.workflows: print(f"Workflow {workflow_id} not found") return "" workflow = self.workflows[workflow_id] # 创建执行实例 execution_id = str(uuid.uuid4()) execution = WorkflowExecution( execution_id=execution_id, workflow_id=workflow_id, status=WorkflowStatus.RUNNING, started_at=datetime.now().isoformat(), trigger_info=trigger_info ) # 存储执行实例 self.executions[execution_id] = execution # 更新工作流统计信息 workflow.run_count += 1 workflow.last_run = execution.started_at # 在新线程中执行工作流 import threading thread = threading.Thread( target=self._execute_workflow, args=(execution_id,), daemon=True ) thread.start() print(f"Started workflow execution: {execution_id} (workflow: {workflow.name})") return execution_id def _execute_workflow(self, execution_id: str): """执行工作流(在单独线程中运行)""" if execution_id not in self.executions: return execution = self.executions[execution_id] workflow = self.workflows.get(execution.workflow_id) if not workflow: execution.status = WorkflowStatus.FAILED execution.error = "Workflow not found" execution.completed_at = datetime.now().isoformat() return try: # 获取触发节点 trigger_node_id = execution.trigger_info.get("trigger_node_id") if not trigger_node_id: trigger_node_id = workflow.triggers[0] if workflow.triggers else None if not trigger_node_id or trigger_node_id not in workflow.nodes: raise Exception("No valid trigger node found for workflow") # 执行工作流 context = { "execution_id": execution_id, "workflow_id": workflow.workflow_id, "trigger_data": execution.trigger_info.get("event_data", {}), "variables": {}, "secrets": {} # 在实际应用中存储敏感数据 } # 从触发节点开始执行 self._execute_node(trigger_node_id, workflow, execution, context) # 标记完成 execution.status = WorkflowStatus.COMPLETED except Exception as e: print(f"Workflow execution failed: {str(e)}") print(traceback.format_exc()) execution.status = WorkflowStatus.FAILED execution.error = str(e) workflow.error_count += 1 finally: execution.completed_at = datetime.now().isoformat() def _execute_node(self, node_id: str, workflow: WorkflowDefinition, execution: WorkflowExecution, context: Dict[str, Any]) -> Any: """执行单个节点""" if node_id not in workflow.nodes: raise Exception(f"Node {node_id} not found in workflow {workflow.workflow_id}") node = workflow.nodes[node_id] node_start_time = datetime.now().isoformat() try: print(f"Executing node: {node.name} (id: {node_id})") # 记录节点执行开始 execution.node_executions[node_id] = { "status": "running", "started_at": node_start_time, "node_definition": node.__dict__ } # 根据节点类型执行不同逻辑 result = None if node.type == NodeType.TRIGGER: # 触发节点只需将触发数据传递给下一个节点 result = context["trigger_data"] elif node.type == NodeType.ACTION: # 执行插件操作 result = self._execute_action_node(node, context) elif node.type == NodeType.CONDITION: # 执行条件判断 result = self._execute_condition_node(node, context) # 其他节点类型的处理... # 记录节点执行成功 execution.node_executions[node_id].update({ "status": "success", "result": result, "completed_at": datetime.now().isoformat() }) # 执行下一个节点 for next_node_id in node.next_nodes: self._execute_node(next_node_id, workflow, execution, context) return result except Exception as e: error_msg = str(e) print(f"Node execution failed ({node.name}): {error_msg}") print(traceback.format_exc()) # 记录节点执行失败 execution.node_executions[node_id].update({ "status": "failed", "error": error_msg, "traceback": traceback.format_exc(), "completed_at": datetime.now().isoformat() }) # 如果有错误处理节点,执行错误处理 if node.error_node: self._execute_node(node.error_node, workflow, execution, context) raise # 继续传播错误 def _execute_action_node(self, node: NodeDefinition, context: Dict[str, Any]) -> Any: """执行操作节点""" if not node.plugin_instance_id or not node.action_name: raise Exception("Plugin instance ID and action name are required for action nodes") # 解析参数中的模板变量(如{{variable}}) resolved_params = self._resolve_template(node.parameters, context) # 调用插件操作 result = self.plugin_manager.execute_plugin_action( instance_id=node.plugin_instance_id, action_name=node.action_name, params=resolved_params ) if result["status"] != "success": raise Exception(f"Plugin action failed: {result.get('error', 'Unknown error')}") return result["result"] def _resolve_template(self, template: Any, context: Dict[str, Any]) -> Any: """解析模板变量""" # 简化实现,实际应用中使用更强大的模板引擎 if isinstance(template, str): # 查找并替换{{variable}}形式的模板变量 import re pattern = r'\{\{([^}]+)\}\}' matches = re.findall(pattern, template) resolved_str = template for match in matches: # 尝试从上下文变量中获取值 value = self._get_nested_value(context["variables"], match) if value is None: # 尝试从触发数据中获取值 value = self._get_nested_value(context["trigger_data"], match) if value is not None: resolved_str = resolved_str.replace(f"{{{{{match}}}}}", str(value)) return resolved_str elif isinstance(template, dict): # 递归解析字典中的所有值 return {k: self._resolve_template(v, context) for k, v in template.items()} elif isinstance(template, list): # 递归解析列表中的所有值 return [self._resolve_template(item, context) for item in template] else: # 其他类型直接返回 return template def _get_nested_value(self, data: Dict[str, Any], path: str) -> Any: """获取嵌套字典中的值""" keys = path.split(".") current = data for key in keys: if isinstance(current, dict) and key in current: current = current[key] else: return None return current def _execute_condition_node(self, node: NodeDefinition, context: Dict[str, Any]) -> Any: """执行条件节点""" # 简化实现,实际应用中支持复杂条件表达式 condition = node.parameters.get("condition", "true") # 解析条件表达式 # 在实际应用中使用安全的表达式评估库 try: # 注意:在生产环境中使用eval存在安全风险,应该使用沙箱环境 result = eval(condition, {"__builtins__": None}, context["variables"]) return result except Exception as e: raise Exception(f"Error evaluating condition: {str(e)}")
关键技术点解析
功能扩展平台的核心价值在于赋能用户——不仅是使用现有功能,而是创造新功能。实现这一目标需要突破三个关键技术挑战:
1. 统一的插件开发框架:插件框架必须提供一致的开发体验,同时足够灵活以支持不同类型的功能。我们设计的PluginInterface基类定义了标准生命周期方法(on_enable/on_disable/on_configure)和通信模式(execute_action/emit_event),确保所有插件以可预测的方式与核心系统交互。
2. 安全的代码执行环境:允许第三方代码在系统中运行存在安全风险。解决方案包括:严格的权限控制(插件只能请求并获得明确授权的权限)、资源限制(CPU/内存/网络使用配额)、沙箱执行环境(限制对系统资源的直接访问),以及代码签名(验证插件来源)。
3. 低代码的流程编排:非技术用户需要能够组合现有功能创建复杂工作流。我们的流程编排引擎使用基于节点的可视化编程模型,将技术细节隐藏在直观的节点配置界面后,同时支持高级用户通过代码自定义节点逻辑。
最佳实践:设计插件API时遵循"最小权限原则"——每个插件只应请求完成其功能所必需的权限。例如,天气插件不需要访问联系人数据的权限。提供详细的插件开发文档和示例,降低开发门槛,同时建立插件审核机制,确保社区贡献的插件质量和安全性。
结语:构建真正个性化的"第二大脑"
从智能家居控制中枢、个性化对话系统到功能扩展平台,我们展示了将小智AI从通用助手升级为个人"第二大脑"的完整路径。这一旅程的终点不是某个特定的应用,而是一个能够持续进化的智能系统——它理解你的独特需求、整合你的个人数据、学习你的思考方式,并能不断扩展以适应你不断变化的需求。
"第二大脑"的终极价值不在于取代人类思考,而在于增强人类认知:处理重复性工作以释放注意力、组织分散信息以减轻记忆负担、提供决策支持而不是替代决策。随着AI技术的进步,我们可以期待更自然的交互方式(如脑机接口)、更深入的个性化(如理解你的潜意识偏好)、以及更广泛的能力扩展(与现实世界更紧密的连接)。
作为开发者,构建"第二大脑"的过程也是对人类认知和工作方式的深度思考。每个功能决策不仅是技术选择,也是关于如何设计与智能系统共存的新范式。最终,最好的"第二大脑"应该是无形的——它如此自然地融入你的生活和工作,以至于你几乎忘记它的存在,却又无法想象没有它的日子。
你准备好开始构建自己的"第二大脑"了吗?从哪个项目开始?智能家居控制中枢可以立即改善你的日常生活体验,个性化对话系统能让你重新思考人机交互的本质,而功能扩展平台则为无限可能打开了大门。无论选择哪条路径,记住:最好的"第二大脑"是那些真正理解并服务于人类独特需求和价值的系统。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献196条内容
已为社区贡献196条内容







所有评论(0)