一文读懂MCP:MCP协议如何连接大模型与现实世界
MCP(Model Context Protocol,模型上下文协议)是由Anthropic提出的开源标准协议,旨在标准化大语言模型与外部工具、数据源之间的通信方式。简单来说,MCP就像是AI世界的USB接口——它定义了一套统一的连接标准,让不同的AI模型都能够无缝接入各种外部服务和工具。
引言:AI开发的"巴别塔"困境
在当前AI应用开发中,我们面临着一个核心矛盾:大模型虽然具备强大的推理和理解能力,却生活在信息真空中。它们无法访问实时数据、不能操作系统工具、难以与企业现有服务集成。每个AI应用都像是信息孤岛,无法真正融入业务工作流。
这正是MCP(Model Context Protocol)要解决的根本问题。本文将系统解析MCP协议,从理论基础到实践应用,带你全面理解这一正在重塑AI开发格局的重要技术。
一、MCP基础概念:重新定义AI与工具的边界
1.1 什么是MCP?
MCP(Model Context Protocol,模型上下文协议)是由Anthropic提出的开源标准协议,旨在标准化大语言模型与外部工具、数据源之间的通信方式。
简单来说,MCP就像是AI世界的USB接口——它定义了一套统一的连接标准,让不同的AI模型都能够无缝接入各种外部服务和工具。
1.2 MCP的核心架构
MCP采用经典的客户端-服务器架构:
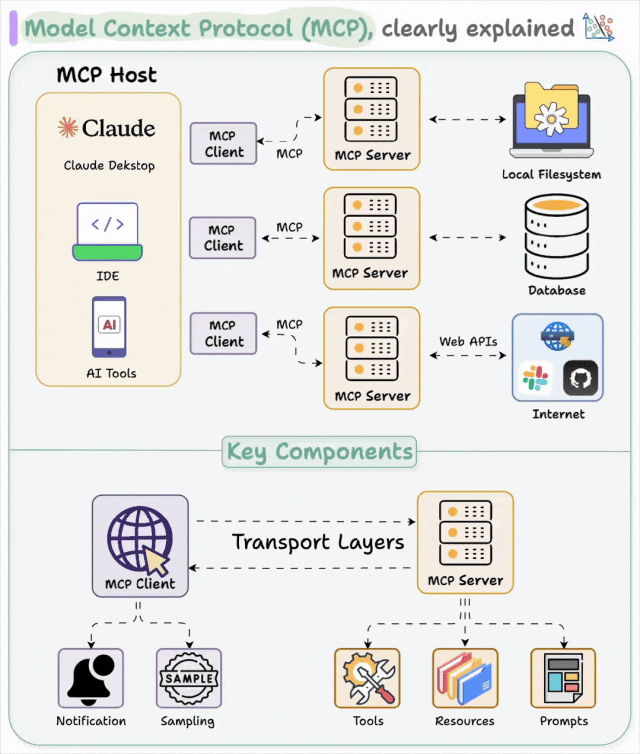
核心组件说明:
-
MCP主机:提供执行AI任务的环境,并运行MCP客户端
-
MCP客户端:作为主机环境中的中介,管理MCP主机与服务器之间的通信
-
MCP服务器:提供外部系统和操作的访问权限,具备工具、资源和提示三种核心能力
1.3 MCP的工作原理
MCP协议采用分层架构设计,将LLM与资源之间的通信划分为三个主要部分:
-
初始化连接:客户端向服务器发送连接请求,建立通信通道
-
服务发现:客户端获取服务器提供的工具和能力列表
-
工具调用:客户端根据需求调用具体工具
-
结果返回:服务器执行操作并返回处理结果
-
连接管理:任务完成后管理连接状态
二、为什么需要MCP?解决AI开发的根本痛点
2.1 传统AI开发的困境
在没有MCP之前,AI应用开发面临诸多挑战:
集成复杂度高
# 传统方式:为每个工具编写专用代码
def call_weather_api(location):
# 需要处理认证、错误重试、格式转换等
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}"}
response = requests.get(f"https://api.weather.com/v1/{location}")
# 复杂的错误处理逻辑
if response.status_code != 200:
# 重试逻辑、降级处理等
pass
return parse_weather_data(response.json())
def call_database_query(sql):
# 另一套完全不同的处理逻辑
connection = create_db_connection()
cursor = connection.cursor()
# 数据库特有的错误处理
try:
cursor.execute(sql)
except DatabaseError as e:
# 特定的异常处理
pass维护成本巨大
-
每个工具都需要单独的集成代码
-
API变更导致大规模重构
-
不同工具的认证、错误处理逻辑各异
能力复用困难
-
为ChatGPT开发的工具无法直接用于Claude
-
不同项目间工具逻辑难以共享
2.2 MCP的解决方案
统一接入标准
# MCP方式:统一的服务调用接口
def mcp_tool_call(server_name, tool_name, arguments):
# 所有工具使用相同的调用方式
request = {
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {
"name": tool_name,
"arguments": arguments
}
}
return send_mcp_request(server_name, request)服务发现机制MCP支持自动服务发现,客户端可以动态获取可用的工具列表
{
"method": "tools/list",
"id": 1
}2.3 MCP与Function Calling的区别
|
特性 |
Function Calling |
MCP |
|---|---|---|
|
功能范围 |
单一工具调用 |
完整的工具生态系统 |
|
上下文管理 |
无 |
支持多轮对话和状态管理 |
|
执行方式 |
同步执行 |
支持同步和异步执行 |
|
标准化程度 |
无统一标准 |
统一的开源标准 |
|
生态开放性 |
相对封闭 |
开放生态 |
Function Calling主要用于让AI大模型可以识别外部工具,然后让我们的应用程序可以和外部的API接口进行交互,从而实现更多复杂的功能。
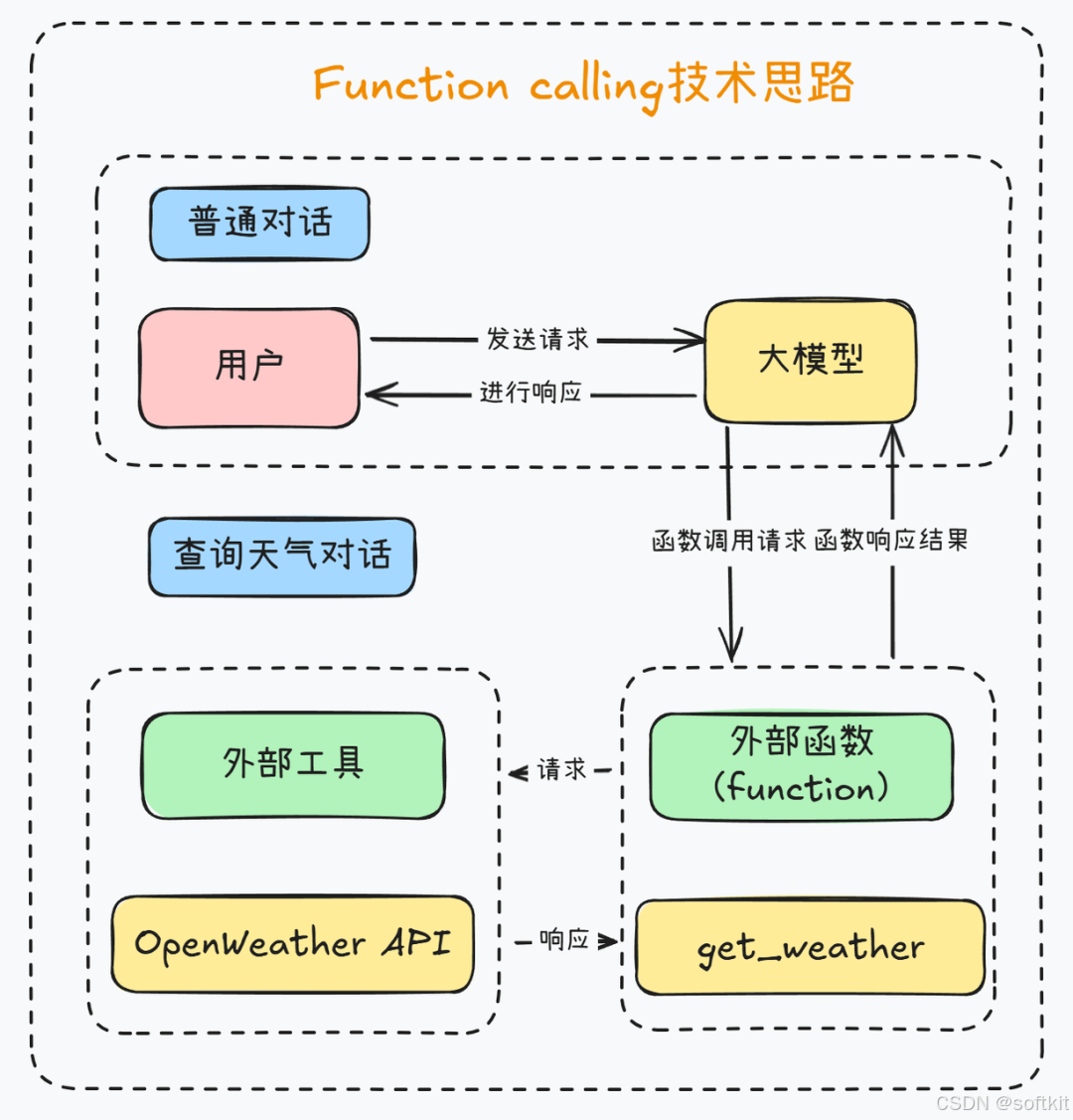
而MCP 功能复杂,可以支持多轮对话,一次能调用多个任务,也可以异步执行。它有统一的标准,只要是适配了 MCP协议的 MCP Server 都可以用统一的代码去调用。MCP更加灵活,可以借用 Function Calling 的方式去进行工具调用,也可以使用自然语言描述的提示词去告诉 LLM,提供了哪些工具供它使用,应该以何种格式返回结果这种就更依赖大模型的语言理解能力。
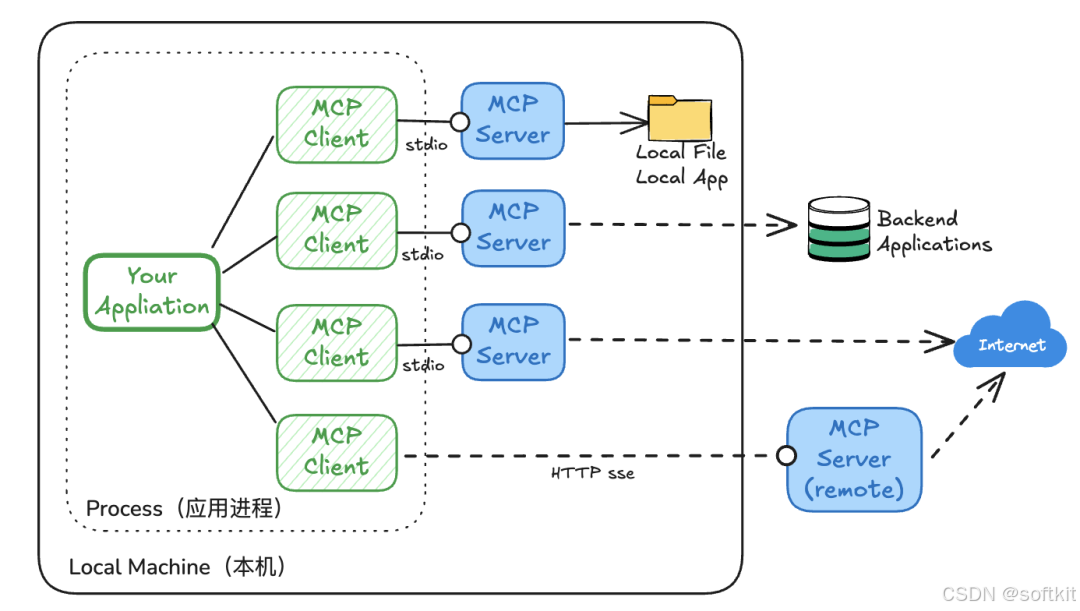
三、MCP的应用场景与核心价值
3.1 应用场景
MCP协议就像是一个"万能适配器",让AI大模型能够连接各种外部工具和数据源,从而在多个领域发挥巨大作用。
智能客服
传统的客服需要人工查询多个系统来回答客户问题,比如订单系统、知识库等。通过MCP,AI客服可以自动调用这些系统,快速给出准确回答,提升效率。
数据分析
数据分析师通常需要从数据库、API等多个来源获取数据,然后进行整理和分析。MCP可以让AI直接连接这些数据源,执行查询并生成分析结果,甚至自动制作图表。
业务流程自动化
企业内的许多流程涉及多个系统,例如审批流程可能需要连接OA系统、财务系统等。MCP可以让AI在这些系统间自动传递信息,完成流程,减少人工干预。
3.2 核心价值
对开发者:提高开发效率
-
一次开发,多处使用:编写的工具可以被不同的AI模型使用,无需重复开发
-
标准化接口:无需为每个工具编写特定的集成代码,降低复杂度
-
易于维护:工具更新时,只需更新一次,所有使用该工具的应用都能受益
对企业:降低成本并提升能力
-
快速集成:利用现有的MCP工具快速构建AI应用,缩短开发周期
-
复用现有系统:通过MCP将企业现有系统(如CRM、ERP)暴露给AI,保护现有投资
-
促进创新:员工可以通过自然语言使用复杂工具,降低使用门槛,激发创新
对整个生态:促进协作和标准化
-
工具共享:开发者可以共享自己开发的工具,形成丰富的工具生态
-
互操作性:不同的AI模型和工具可以通过MCP协议互操作,打破孤立
-
推动进步:开放的标准使得整个行业能够更快地发展
四、实战:使用Python构建MCP应用
4.1 环境准备与依赖安装
首先安装必要的Python包:
pip install fastmcp -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/4.2 构建基础的MCP服务器
让我们创建一个天气查询的MCP服务器:
import asyncio
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.types import Tool, TextContent
from aiohttp import web
import json
# 创建服务器实例
server = Server("weather-server")
# API_BASE = "https://api.ufunai.cn/v1"
# API_KEY = "sk-xxxxx"
# 模拟天气数据
weather_data = {
"Beijing": {"temp": 25, "condition": "sunny", "humidity": 40},
"Shanghai": {"temp": 28, "condition": "cloudy", "humidity": 65},
"Guangzhou": {"temp": 32, "condition": "rainy", "humidity": 80}
}
@server.list_tools()
async def handle_list_tools() -> list[Tool]:
"""返回服务器提供的工具列表"""
return [
Tool(
name="get_weather",
description="获取指定城市的天气信息",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名称"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
"default": "celsius"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
)
]
@server.call_tool()
async def handle_call_tool(name: str, arguments: dict) -> list[TextContent]:
"""处理工具调用"""
if name == "get_weather":
return await handle_get_weather(arguments)
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知工具: {name}")
async def handle_get_weather(arguments: dict) -> list[TextContent]:
"""处理天气查询请求"""
location = arguments.get("location", "")
unit = arguments.get("unit", "celsius")
if location not in weather_data:
return [
TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"未找到城市 {location} 的天气信息"
)
]
data = weather_data[location]
temp = data["temp"]
# 温度单位转换
if unit == "fahrenheit":
temp = temp * 9 / 5 + 32
temp_unit = "°F"
else:
temp_unit = "°C"
result_text = f"{location}天气:温度{temp}{temp_unit},{data['condition']},湿度{data['humidity']}%"
return [
TextContent(
type="text",
text=result_text
)
]
async def handle_mcp_request(request):
"""处理 MCP 协议请求"""
try:
data = await request.json()
method = data.get("method")
params = data.get("params", {})
if method == "tools/list":
tools = await handle_list_tools()
response_data = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": data.get("id", 1),
"result": {"tools": [tool.dict() for tool in tools]}
}
return web.json_response(response_data, content_type='application/json')
elif method == "tools/call":
tool_name = params.get("name")
tool_args = params.get("arguments", {})
result = await handle_call_tool(tool_name, tool_args)
response_data = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": data.get("id", 1),
"result": {
"content": [item.dict() for item in result]
}
}
return web.json_response(response_data, content_type='application/json')
else:
response_data = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": data.get("id", 1),
"error": {"code": -32601, "message": f"方法未找到: {method}"}
}
return web.json_response(response_data, content_type='application/json')
except Exception as e:
response_data = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": data.get("id", 1) if 'data' in locals() else 1,
"error": {"code": -32603, "message": f"内部错误: {str(e)}"}
}
return web.json_response(response_data, content_type='application/json')
async def handle_health_check(request):
"""健康检查端点"""
return web.json_response(
{"status": "ok", "service": "weather-mcp-server"},
content_type='application/json'
)
async def handle_tools_list_direct(request):
"""直接获取工具列表的端点"""
tools = await handle_list_tools()
return web.json_response(
[tool.dict() for tool in tools],
content_type='application/json'
)
async def handle_root(request):
"""根路径处理 - 返回服务器信息"""
return web.json_response(
{
"message": "Weather MCP Server",
"version": "1.0",
"endpoints": {
"mcp": "/mcp (POST)",
"health": "/health (GET)",
"tools": "/tools (GET)"
}
},
content_type='application/json'
)
def create_app():
"""创建 aiohttp 应用"""
app = web.Application()
# 添加路由
app.router.add_get("/", handle_root)
app.router.add_post("/mcp", handle_mcp_request)
app.router.add_get("/health", handle_health_check)
app.router.add_get("/tools", handle_tools_list_direct)
return app
async def main():
"""主函数"""
app = create_app()
runner = web.AppRunner(app)
await runner.setup()
site = web.TCPSite(runner, 'localhost', 8000)
await site.start()
print("Weather MCP Server 运行在 http://localhost:8000")
print("根路径: http://localhost:8000/")
print("MCP 端点: http://localhost:8000/mcp (POST)")
print("健康检查: http://localhost:8000/health (GET)")
print("工具列表: http://localhost:8000/tools (GET)")
# 保持服务器运行
try:
while True:
await asyncio.sleep(3600)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("服务器关闭")
await runner.cleanup()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())4.3 创建MCP客户端
import asyncio
import aiohttp
import json
from typing import Dict, Any, List, Optional
# 配置常量
MCP_SERVER_URL = "http://localhost:8001"
# 优趣AI 聚合平台服务商地址
API_BASE = "https://api.ufunai.cn/v1"
API_KEY = "sk-xxxxx" # 替换为你的API密钥
MODEL_NAME = "gpt-5-nano"
class MCPClient:
"""MCP 服务器客户端,负责与 MCP 服务器通信"""
def __init__(self, server_url: str = MCP_SERVER_URL):
self.server_url = server_url.rstrip('/')
self._timeout = aiohttp.ClientTimeout(total=30)
async def list_tools(self) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""获取可用工具列表"""
try:
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.get(f"{self.server_url}/tools") as response:
if response.status == 200:
return await response.json()
return await self._list_tools_via_mcp()
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取工具列表失败: {e}")
return []
async def _list_tools_via_mcp(self) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""通过 MCP 协议获取工具列表(备用方法)"""
payload = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "tools/list",
"params": {}
}
try:
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.post(
f"{self.server_url}/mcp",
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json"},
json=payload,
timeout=self._timeout
) as response:
if response.status == 200:
result = await response.json()
return result.get("result", {}).get("tools", [])
return []
except Exception as e:
print(f"通过 MCP 协议获取工具列表失败: {e}")
return []
async def call_tool(self, tool_name: str, arguments: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""调用指定的工具"""
payload = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {"name": tool_name, "arguments": arguments}
}
try:
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.post(
f"{self.server_url}/mcp",
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json"},
json=payload,
timeout=self._timeout
) as response:
if response.status != 200:
error_text = await response.text()
return {"error": f"HTTP {response.status}: {error_text}"}
return await response.json()
except Exception as e:
return {"error": f"调用工具失败: {e}"}
class AIClient:
"""大语言模型客户端,负责与 AI API 通信"""
def __init__(self, api_base: str = API_BASE, api_key: str = API_KEY, model_name: str = MODEL_NAME):
self.api_base = api_base
self.api_key = api_key
self.model_name = model_name
self._timeout = aiohttp.ClientTimeout(total=60)
async def chat_completion(
self,
messages: List[Dict[str, str]],
tools: Optional[List[Dict[str, Any]]] = None
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""调用大模型进行聊天补全"""
payload = {"model": self.model_name, "messages": messages}
if tools:
payload["tools"] = tools
payload["tool_choice"] = "auto"
try:
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.post(
f"{self.api_base}/chat/completions",
headers={
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.api_key}"
},
json=payload,
timeout=self._timeout
) as response:
if response.status != 200:
error_text = await response.text()
return {"error": f"API 调用失败: {response.status} - {error_text}"}
return await response.json()
except Exception as e:
return {"error": f"API 调用异常: {e}"}
class MCPAIOrchestrator:
"""MCP 和 AI 的协调器,负责整合工具调用流程"""
SYSTEM_PROMPT = "你是一个智能助手,擅长理解用户需求并使用合适的工具来帮助用户解决问题。"
def __init__(self, mcp_client: MCPClient, ai_client: AIClient):
self.mcp_client = mcp_client
self.ai_client = ai_client
self.conversation_history: List[Dict[str, str]] = []
@staticmethod
def _normalize_tool_schema(input_schema: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""规范化工具的输入 schema,确保符合 JSON Schema 标准"""
schema = input_schema.copy()
schema.setdefault("type", "object")
schema.setdefault("properties", {})
schema.setdefault("required", [])
return schema
def _convert_tools_to_openai_format(self, tools: List[Dict[str, Any]]) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""将 MCP 工具格式转换为 OpenAI 工具格式"""
return [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": tool.get("name"),
"description": tool.get("description", ""),
"parameters": self._normalize_tool_schema(tool.get("inputSchema", {}))
}
}
for tool in tools
]
@staticmethod
def _extract_tool_result(tool_result: Dict[str, Any]) -> str:
"""从 MCP 工具结果中提取文本内容"""
if "result" not in tool_result:
return str(tool_result)
result_data = tool_result["result"]
if "content" in result_data and isinstance(result_data["content"], list):
for item in result_data["content"]:
if item.get("type") == "text":
return item.get("text", "")
return str(result_data)
async def process_user_message(self, user_message: str) -> str:
"""
处理用户消息的核心流程
流程:
1. 获取可用工具并转换格式
2. 调用大模型识别意图
3. 如果需要工具,执行工具调用
4. 将结果返回给大模型生成友好回复
"""
# 获取并转换工具
tools = await self.mcp_client.list_tools()
if not tools:
return "抱歉,目前服务不可用,请稍后再试。"
openai_tools = self._convert_tools_to_openai_format(tools)
# 更新对话历史
self.conversation_history.append({"role": "user", "content": user_message})
# 构建消息
system_message = {"role": "system", "content": self.SYSTEM_PROMPT}
messages = [system_message] + self.conversation_history
# 第一步:大模型决策
response = await self.ai_client.chat_completion(messages, openai_tools)
if "error" in response:
return f"服务调用失败: {response['error']}"
message = response.get("choices", [{}])[0].get("message", {})
# 第二步:处理工具调用
if tool_calls := message.get("tool_calls"):
return await self._handle_tool_call(tool_calls[0], message, system_message)
# 无需工具调用,直接返回
content = message.get("content", "抱歉,我无法理解您的请求。")
self.conversation_history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": content})
return content
async def _handle_tool_call(
self,
tool_call: Dict[str, Any],
assistant_message: Dict[str, Any],
system_message: Dict[str, str]
) -> str:
"""处理工具调用流程"""
# 解析工具调用信息
function = tool_call.get("function", {})
tool_name = function.get("name")
tool_args = json.loads(function.get("arguments", "{}"))
tool_call_id = tool_call.get("id")
# 执行工具调用
tool_result = await self.mcp_client.call_tool(tool_name, tool_args)
result_text = self._extract_tool_result(tool_result)
# 更新对话历史
self.conversation_history.extend([
assistant_message,
{"role": "tool", "tool_call_id": tool_call_id, "content": result_text}
])
# 获取最终回复
final_messages = [system_message] + self.conversation_history
final_response = await self.ai_client.chat_completion(final_messages)
if "error" in final_response:
return f"服务调用失败: {final_response['error']}"
final_message = final_response.get("choices", [{}])[0].get("message", {})
self.conversation_history.append(final_message)
return final_message.get("content", "抱歉,处理结果时出现问题。")
def clear_history(self):
"""清空对话历史"""
self.conversation_history.clear()
async def main():
"""主函数:初始化并运行交互式对话"""
# 初始化
mcp_client = MCPClient()
ai_client = AIClient()
orchestrator = MCPAIOrchestrator(mcp_client, ai_client)
# 测试连接
print("正在连接 MCP 服务器...")
tools = await mcp_client.list_tools()
print(f"✓ 已连接,可用工具数: {len(tools)}\n")
# 交互式对话
print("智能助手已就绪!输入 'quit' 或 'exit' 退出")
print("=" * 60)
while True:
try:
user_input = input("\n你: ").strip()
if not user_input:
continue
if user_input.lower() in ['quit', 'exit', '退出']:
print("\n再见!")
break
response = await orchestrator.process_user_message(user_input)
print(f"\n助手: {response}")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n\n再见!")
break
except Exception as e:
print(f"\n错误: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())4.4 整体处理流程
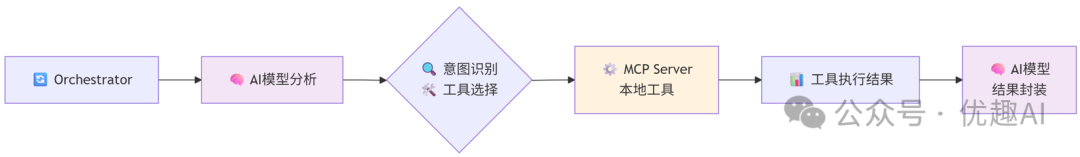
-
用户输入 → 提出问题或需求
-
Orchestrator → 接收并协调处理
-
AI模型 → 分析理解用户意图
-
意图识别 & 工具选择 → 判断需要使用的工具
-
MCP Server → 调用具体工具执行任务
-
工具执行结果 → 返回原始数据
-
AI模型 → 重新组织并封装结果
-
回复用户 → 用自然语言回答
4.5 系统运行效果
正在连接 MCP 服务器...
✓ 已连接,可用工具数: 1
智能助手已就绪!输入 'quit' 或 'exit' 退出
============================================================
你: 告诉我北京的天气
助手: 北京天气:25°C,晴,湿度40%。
出门请注意防晒,适合户外活动。如需要未来几小时或明日的天气预报,告诉我你想要的时段。
你: 上海的天气呢
助手: 上海天气:28°C,多云,湿度65%。
出门请注意防晒,适合户外活动。如需要未来几小时或明日的天气预报,告诉我你想要的时段。
你: 武汉的天气呢
助手: 抱歉,当前系统无法获取武汉的天气信息。可能是数据源里没有该城市的记录。
你可以选以下任一方案:
- 让我再尝试一次查询 Wuhan(英文名)或直接使用“武汉”再次尝试。
- 查询其他城市的天气(如广州、成都、杭州、南京等)。
- 提供“离武汉最近的城市”或你所在的区域的天气信息。
请告诉我你想要的选项,或者直接让我重新尝试查询 Wuhan。
4.6 扩展:构建数据库查询MCP服务器
让我们再创建一个更复杂的数据库查询MCP服务器:
import asyncio
import sqlite3
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.types import Tool, TextContent
from aiohttp import web
import json
# 创建服务器实例
server = Server("database-server")
# 数据库路径
DB_PATH = "example.db"
def init_database():
"""初始化示例数据库"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(DB_PATH)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 创建示例表
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS sales (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
product_name TEXT,
quantity INTEGER,
price REAL,
sale_date DATE
)
''')
# 插入示例数据
cursor.execute("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM sales")
if cursor.fetchone()[0] == 0:
cursor.executemany('''
INSERT INTO sales (id, product_name, quantity, price, sale_date)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
''', [
(1, '笔记本电脑', 5, 5999.99, '2024-01-15'),
(2, '智能手机', 12, 3999.50, '2024-01-16'),
(3, '平板电脑', 8, 3299.00, '2024-01-17')
])
conn.commit()
conn.close()
@server.list_tools()
async def handle_list_tools() -> list[Tool]:
"""返回服务器提供的工具列表"""
return [
Tool(
name="query_database",
description="执行SQL查询并返回结果",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"sql": {
"type": "string",
"description": "要执行的SQL查询语句"
}
},
"required": ["sql"]
}
),
Tool(
name="get_table_schema",
description="获取数据库表结构信息",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"table_name": {
"type": "string",
"description": "表名称"
}
},
"required": ["table_name"]
}
)
]
@server.call_tool()
async def handle_call_tool(name: str, arguments: dict) -> list[TextContent]:
"""处理工具调用"""
if name == "query_database":
return await handle_query_database(arguments)
elif name == "get_table_schema":
return await handle_get_table_schema(arguments)
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知工具: {name}")
async def handle_query_database(arguments: dict) -> list[TextContent]:
"""处理数据库查询"""
sql = arguments.get("sql", "")
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect(DB_PATH)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(sql)
# 获取结果
if sql.strip().lower().startswith('select'):
results = cursor.fetchall()
columns = [description[0] for description in cursor.description]
# 格式化结果
formatted_results = []
for row in results:
formatted_row = {}
for i, col in enumerate(columns):
formatted_row[col] = row[i]
formatted_results.append(formatted_row)
result_text = f"查询结果:\n{json.dumps(formatted_results, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}"
else:
conn.commit()
result_text = f"执行成功,影响行数:{cursor.rowcount}"
conn.close()
return [
TextContent(
type="text",
text=result_text
)
]
except Exception as e:
return [
TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"数据库查询错误:{str(e)}"
)
]
async def handle_get_table_schema(arguments: dict) -> list[TextContent]:
"""获取表结构信息"""
table_name = arguments.get("table_name", "")
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect(DB_PATH)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 查询表结构
cursor.execute(f"PRAGMA table_info({table_name})")
schema_info = cursor.fetchall()
conn.close()
if not schema_info:
return [
TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"表 {table_name} 不存在"
)
]
# 格式化表结构信息
schema_text = f"表 {table_name} 结构:\n"
for column in schema_info:
schema_text += f"- {column[1]} ({column[2]})"
if column[5]: # 是否为主键
schema_text += " PRIMARY KEY"
if column[3]: # 是否不能为NULL
schema_text += " NOT NULL"
schema_text += "\n"
return [
TextContent(
type="text",
text=schema_text
)
]
except Exception as e:
return [
TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"获取表结构错误:{str(e)}"
)
]
async def handle_mcp_request(request):
"""处理 MCP 协议请求"""
try:
data = await request.json()
method = data.get("method")
params = data.get("params", {})
if method == "tools/list":
tools = await handle_list_tools()
response_data = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": data.get("id", 1),
"result": {"tools": [tool.dict() for tool in tools]}
}
return web.json_response(response_data, content_type='application/json')
elif method == "tools/call":
tool_name = params.get("name")
tool_args = params.get("arguments", {})
result = await handle_call_tool(tool_name, tool_args)
response_data = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": data.get("id", 1),
"result": {
"content": [item.dict() for item in result]
}
}
return web.json_response(response_data, content_type='application/json')
else:
response_data = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": data.get("id", 1),
"error": {"code": -32601, "message": f"方法未找到: {method}"}
}
return web.json_response(response_data, content_type='application/json')
except Exception as e:
response_data = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": data.get("id", 1) if 'data' in locals() else 1,
"error": {"code": -32603, "message": f"内部错误: {str(e)}"}
}
return web.json_response(response_data, content_type='application/json')
async def handle_health_check(request):
"""健康检查端点"""
return web.json_response(
{"status": "ok", "service": "database-mcp-server"},
content_type='application/json'
)
async def handle_tools_list_direct(request):
"""直接获取工具列表的端点"""
tools = await handle_list_tools()
return web.json_response(
[tool.dict() for tool in tools],
content_type='application/json'
)
async def handle_root(request):
"""根路径处理 - 返回服务器信息"""
return web.json_response(
{
"message": "Database MCP Server",
"version": "1.0",
"database": DB_PATH,
"endpoints": {
"mcp": "/mcp (POST)",
"health": "/health (GET)",
"tools": "/tools (GET)"
}
},
content_type='application/json'
)
def create_app():
"""创建 aiohttp 应用"""
app = web.Application()
# 添加路由
app.router.add_get("/", handle_root)
app.router.add_post("/mcp", handle_mcp_request)
app.router.add_get("/health", handle_health_check)
app.router.add_get("/tools", handle_tools_list_direct)
return app
async def main():
"""主函数"""
# 初始化数据库
init_database()
print("数据库初始化完成")
app = create_app()
runner = web.AppRunner(app)
await runner.setup()
site = web.TCPSite(runner, 'localhost', 8001)
await site.start()
print("Database MCP Server 运行在 http://localhost:8001")
print("根路径: http://localhost:8001/")
print("MCP 端点: http://localhost:8001/mcp (POST)")
print("健康检查: http://localhost:8001/health (GET)")
print("工具列表: http://localhost:8001/tools (GET)")
# 保持服务器运行
try:
while True:
await asyncio.sleep(3600)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("服务器关闭")
await runner.cleanup()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())4.7 扩展功能运行效果
正在连接 MCP 服务器...
✓ 已连接,可用工具数: 2
智能助手已就绪!输入 'quit' 或 'exit' 退出
============================================================
你: 输出sales表的表结构,只需要输出表结构就行
助手: - id (INTEGER) PRIMARY KEY
- product_name (TEXT)
- quantity (INTEGER)
- price (REAL)
- sale_date (DATE)
你: 帮我执行下这个sql语句SELECT sale_date, SUM(quantity * price) AS daily_revenue FROM sales WHERE sale_date >= '2024-01-15' AND sale_date <= '2024-01-15' GROUP BY sale_date ORDER BY sale_date;
助手: 查询结果:
- sale_date: 2024-01-15
- daily_revenue: 29999.95
如需调整日期区间或格式,请告诉我。五、MCP的最佳实践与未来发展
5.1 开发最佳实践
工具设计原则
# 良好的工具设计示例
class WellDesignedTool:
def __init__(self):
self.name = "well_designed_tool"
self.description = "清晰描述工具功能的描述文本"
self.input_schema = {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"param1": {
"type": "string",
"description": "清晰的参数描述",
"examples": ["示例值1", "示例值2"]
}
},
"required": ["param1"]
}
async def execute(self, **kwargs):
# 包含完善的错误处理
try:
# 业务逻辑
result = self.business_logic(kwargs["param1"])
return self.format_success_result(result)
except Exception as e:
return self.format_error_result(str(e))错误处理策略
class MCPErrorHandler:
@staticmethod
def format_error(error: Exception, context: str = "") -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""统一错误格式"""
error_info = {
"error_type": type(error).__name__,
"error_message": str(error),
"context": context
}
# 根据错误类型提供建议
if isinstance(error, ConnectionError):
error_info["suggestion"] = "请检查网络连接或服务状态"
elif isinstance(error, TimeoutError):
error_info["suggestion"] = "请求超时,请稍后重试"
elif isinstance(error, PermissionError):
error_info["suggestion"] = "权限不足,请检查认证信息"
return error_info5.2 安全考虑
认证与授权
class SecureMCPServer(MCPServer):
def __init__(self, name: str, allowed_tokens: set):
super().__init__(name)
self.allowed_tokens = allowed_tokens
async def authenticate_request(self, headers: Dict) -> bool:
"""请求认证"""
auth_header = headers.get("Authorization", "")
if not auth_header.startswith("Bearer "):
return False
token = auth_header[7:] # 移除 "Bearer " 前缀
return token in self.allowed_tokens输入验证
def validate_tool_input(input_schema: Dict, actual_input: Dict) -> bool:
"""验证工具输入参数"""
try:
jsonschema.validate(actual_input, input_schema)
return True
except jsonschema.ValidationError as e:
logging.warning(f"输入验证失败: {e}")
return False5.3 性能优化
连接池管理
class ConnectionPool:
def __init__(self, max_connections: int = 10):
self.max_connections = max_connections
self.active_connections = 0
self.connection_pool = []
async def get_connection(self):
"""获取数据库连接"""
if self.connection_pool:
return self.connection_pool.pop()
elif self.active_connections < self.max_connections:
self.active_connections += 1
return await self.create_connection()
else:
# 等待可用连接
await asyncio.sleep(0.1)
return await self.get_connection()5.4 未来发展趋势
生态扩展
-
更多标准化工具服务器的出现
-
企业级MCP解决方案
-
云原生MCP服务
技术演进
-
更高效的双向通信协议
-
实时数据流支持
-
多模态工具集成
结语
MCP协议代表着AI应用开发的重要演进方向——从封闭的模型能力走向开放的生态系统。通过标准化模型与工具的交互方式,MCP正在构建一个更加开放、互联的AI应用生态。
对于开发者而言,掌握MCP意味着:
-
更高的开发效率:复用丰富的工具生态
-
更强的系统能力:突破模型自身的能力限制
-
更好的可维护性:标准化的接口和协议
-
更广的应用场景:轻松集成企业现有系统
随着MCP生态的不断成熟,我们有望看到更加智能、实用的AI应用出现,真正实现AI技术与业务需求的深度融合。
本文完,接下来给大家说Dify从搭建入门到实战!(不是从入门到删库跑路~~)
另:需要源码的同学,请关注微信公众号(优趣AI)在留言区点赞留言评论!!!
AI应用开发入门到精通宝藏地图,理论+实战往期精彩文章
2、一文看懂Embedding:用代码给大家讲清这个核心概念
3、告别接力!Transformer的「圆桌会议」才是AI的高效沟通术
7、函数调用:让AI学会使用工具,从“思考者”变身“行动派”
8、LangChain实战入门(一):告别“裸调”API,从Model I/O开始优雅构建AI应用
9、LangChain实战入门(二):RAG实战——赋予大模型你的私有知识库
10、LangChain实战入门(三):Agents实战——让AI成为能思考、会行动的数字员工
11、LangChain实战入门(四):融合篇——打造有记忆、能协作的AI应用
12、LangChain实战入门(五):项目篇——构建企业级AI应用系统
创作不易,码字更不易,如果觉得这篇文章对你有帮助,记得点个关注、在看或收藏,给作者一点鼓励吧~~
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献13条内容
已为社区贡献13条内容







所有评论(0)