使用自动化提取字符串(二进制安全)
AgentTesla 是一种非常典型、也非常“长寿”的Windows间谍木马/信息窃取器。类型:远程访问木马(RAT)、间谍木马、信息窃取木马平台:主要针对 Windows语言:基于 .NET(C# / VB.NET 等)出现时间:至少从 2014 年开始活跃,一直在不断迭代更新商业化:以“恶意软件即服务”(Malware-as-a-Service, MaaS)形式在地下市场/论坛出售,过去还曾有
1.1 AgentTesla介绍
AgentTesla 是一种非常典型、也非常“长寿”的 Windows 间谍木马/信息窃取器。
类型:远程访问木马(RAT)、间谍木马、信息窃取木马
平台:主要针对 Windows
语言:基于 .NET(C# / VB.NET 等)
出现时间:至少从 2014 年开始活跃,一直在不断迭代更新
商业化:以“恶意软件即服务”(Malware-as-a-Service, MaaS)形式在地下市场/论坛出售,过去还曾有公开网站售卖“订阅版”
AgentTesla特的变化特别多,而且擅长使用各种混淆和高级技巧,本文主要是研究如何使用静态分析的方式使用脚本来进行提取AgentTesla的字符串并进行解密(自动化角度)。
样本:4c321c77e5a9381005c96bc7fc887b962bcd8c82fcabf579f3301d583055f59d
1.2 静态分析
从DIE中可以看到Obfuscar保护器,这是因为dotNet样本太容易被反编译来, 所以普通都会增加保护器来阻止样本被反编译。
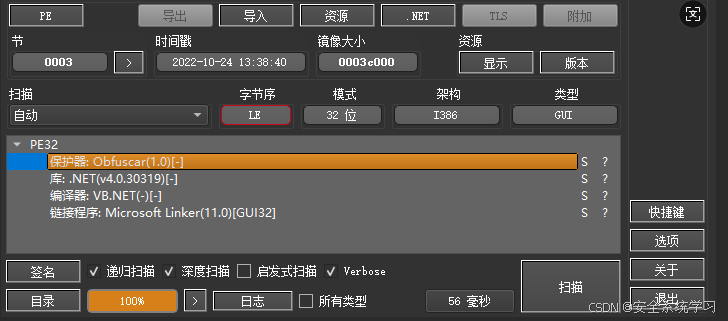
使用dnspy不难看出,样本的函数名、函数体都是加了保护的。但是我们本次的重点是字符串。
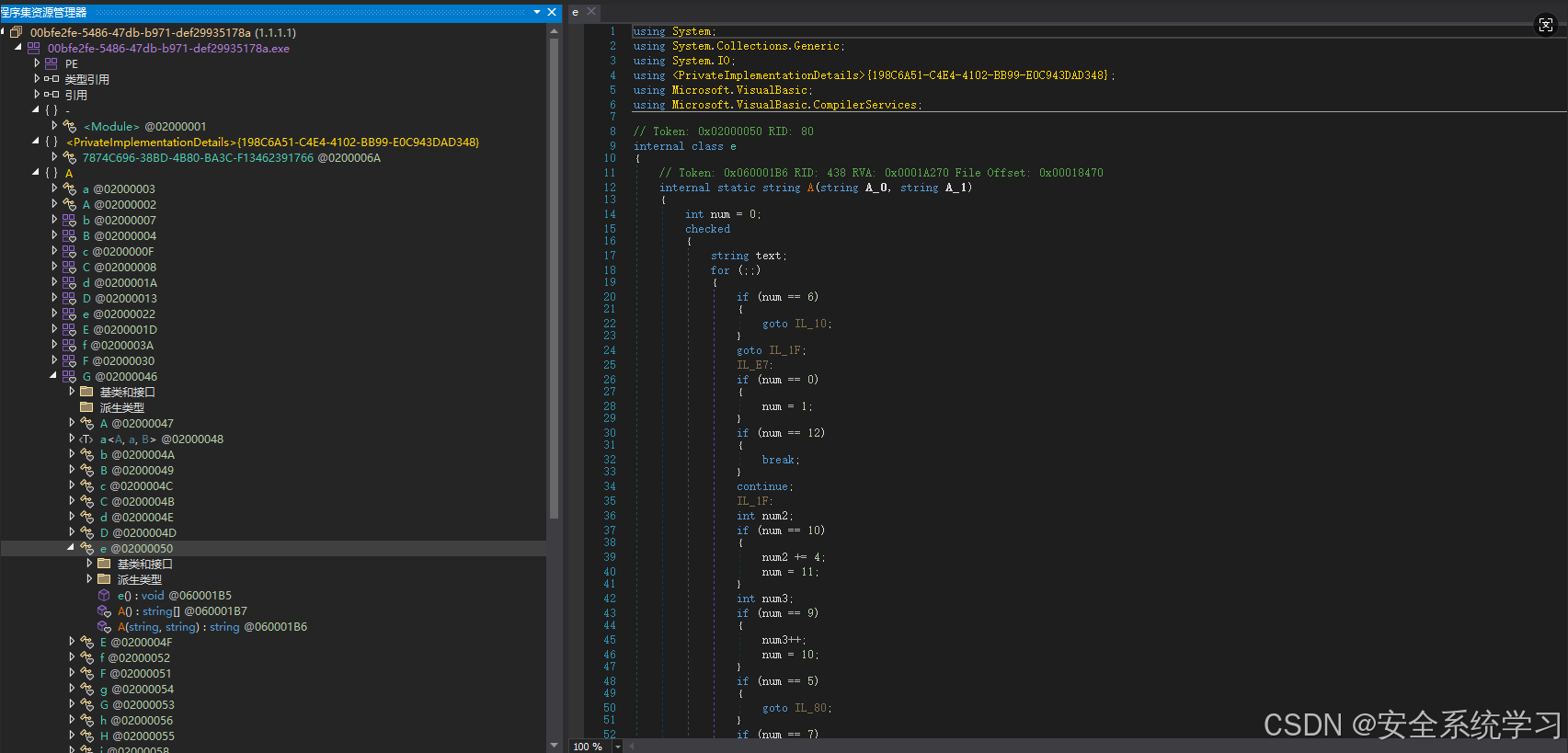
查看 {198C6A51-C4E4-4102-BB99-E0C943DAD348} 命名空间的时候,不难找到一个特大的字节数组:
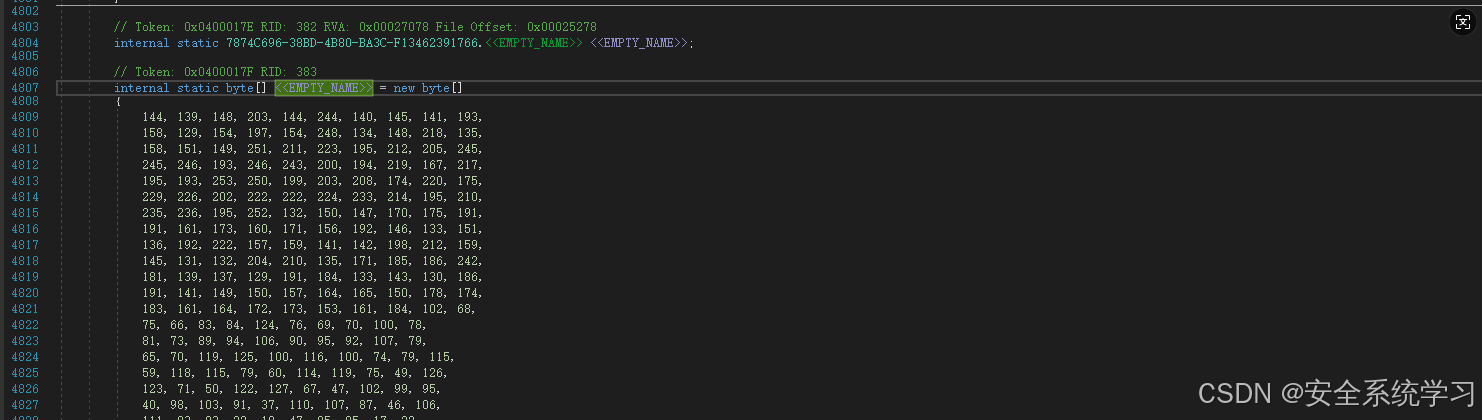
而且可以很容易的看到这个字节数组,上面就是解密函数:
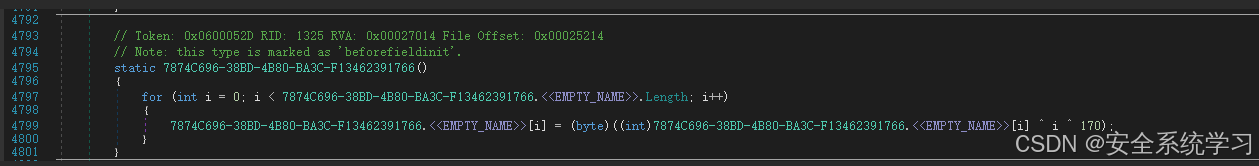
在 {198C6A51-C4E4-4102-BB99-E0C943DAD348} 命名空间中,会发现大量的这样的函数:
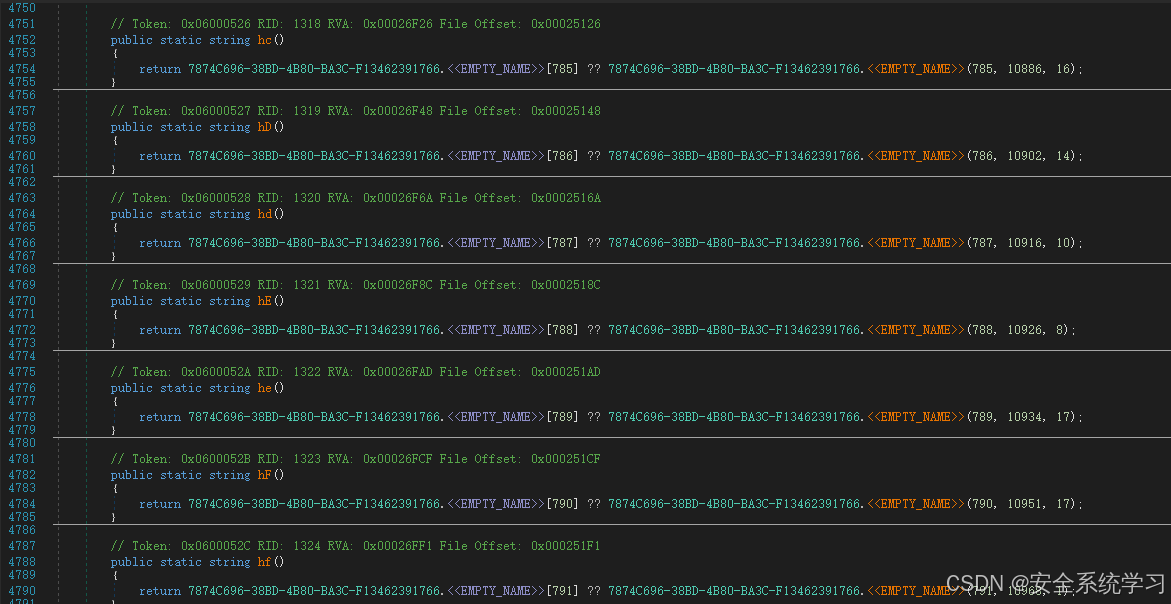
不难看出这里是通过:序号、偏移、长度的方式来获取字符串。这里可以猜测到字符串是没有 \x00\x00 分割的。(先猜测,后续验证)
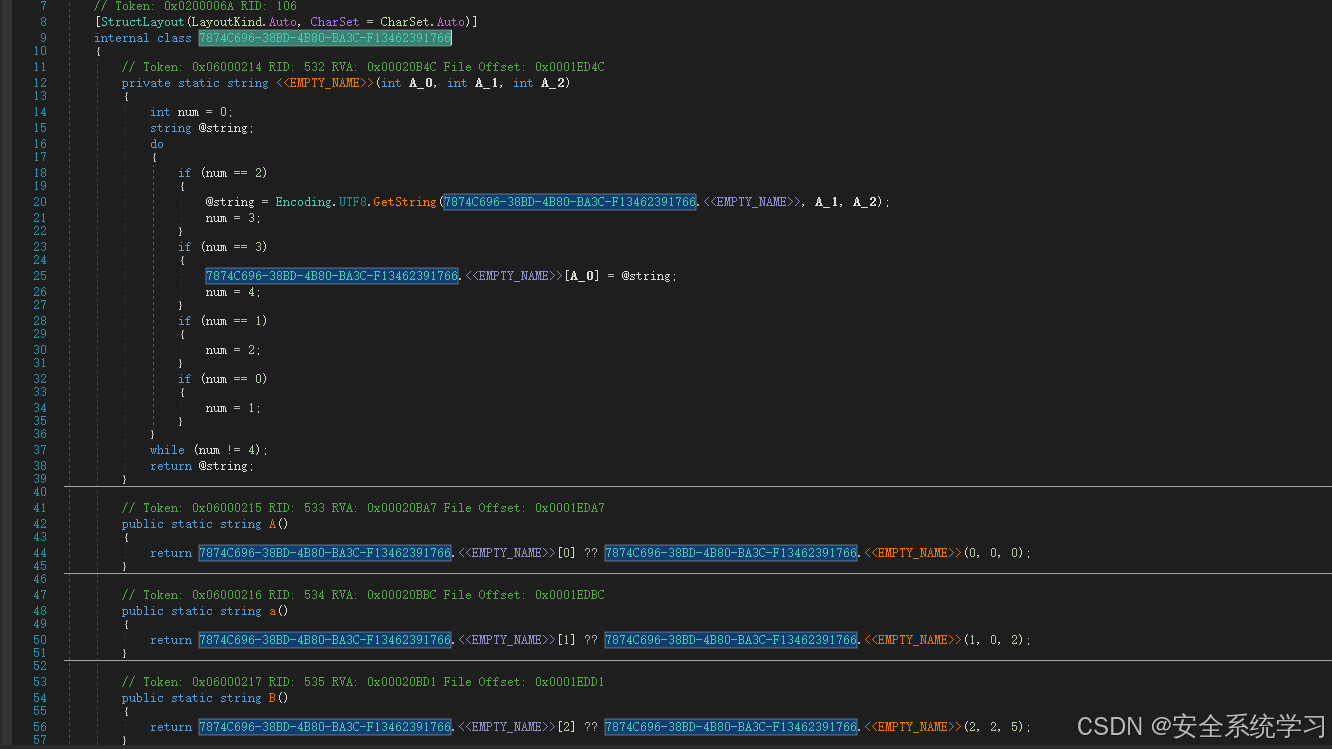
1.3 动态分析
笔者在动态分析验证的时候,发现该样本无法运行起来,那么就彻底放弃动态分析的这条路了,转而全部采用静态分析+脚本方式(这种也是在无法调试的情况下,分析样本的硬实力)。
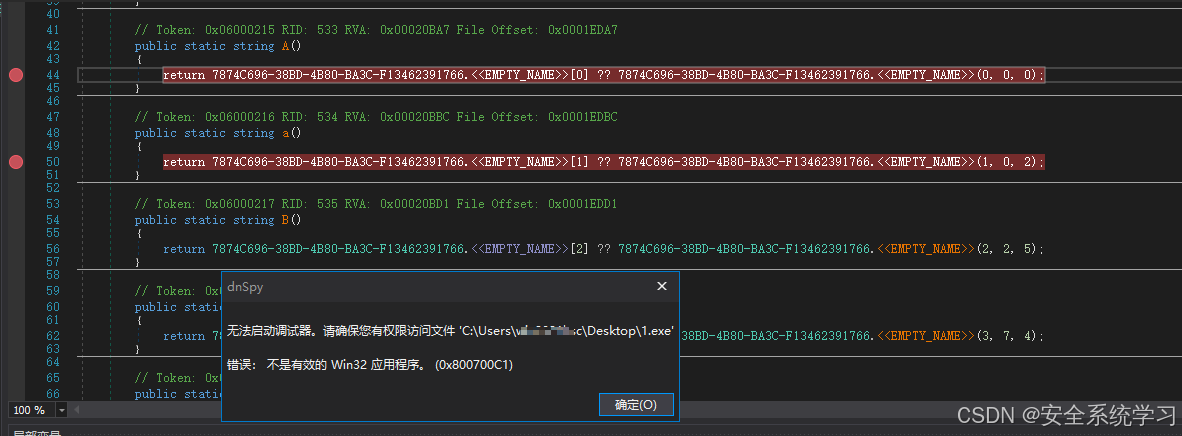
1.4 猜测验证
解密函数编写:核心就是 str[i] ^ i ^ 170
input_bytes = [
144, 139, 148, 203, 144, 244, 140, 145, 141, 193,
158, 129, 154, 197, 154, 248, 134, 148, 218, 135,
158, 151, 149, 251, 211, 223, 195, 212, 205, 245,
245, 246, 193, 246, 243, 200, 194, 219, 167, 217,
195, 193, 253, 250, 199, 203, 208, 174, 220, 175,
229, 226, 202, 222, 222, 224, 233, 214, 195, 210,
235, 236, 195, 252, 132, 150, 147, 170, 175, 191,
191, 161, 173, 160, 171, 156, 192, 146, 133, 151,
136, 192, 222, 157, 159, 141, 142, 198, 212, 159,
145, 131, 132, 204, 210, 135, 171, 185, 186, 242,
181, 139, 137, 129, 191, 184, 133, 143, 130, 186,
191, 141, 149, 150, 157, 164, 165, 150, 178, 174,
183, 161, 164, 172, 173, 153, 161, 184, 102, 68,
75, 66, 83, 84, 124, 76, 69, 70, 100, 78,
81, 73, 89, 94, 106, 90, 95, 92, 107, 79,
65, 70, 119, 125, 100, 116, 100, 74, 79, 115,
59, 118, 115, 79, 60, 114, 119, 75, 49, 126,
123, 71, 50, 122, 127, 67, 47, 102, 99, 95,
40, 98, 103, 91, 37, 110, 107, 87, 46, 106,
111, 83, 83, 22, 19, 47, 95, 95, 17, 22,
36, 82, 81, 28, 29, 33, 85, 87, 7, 91,
27, 22, 16, 11, 14, 18, 30, 8, 51, 37,
36, 59, 9, 83, 108, 42, 37, 57, 117, 115,
106, 33, 54, 120, 126, 103, 33, 51, 127, 103,
124, 42, 45, 54, 42, 100, 31, 50, 34, 58,]
def decrypt_bytes(input_bytes,keyword=170):
str = ""
for index, byte in enumerate(input_bytes,0):
str += chr(byte ^ index ^ keyword)
return str
print(decrypt_bytes(input_bytes))结果:
: <b>[ </b> <b>]</b> ()False{BACK}{ALT+TAB}{ALT+F4}{TAB}{ESC}{Win}{CAPSLOCK}↑↓←→{DEL}{END}{HOME}{Insert}{NumLock}{PageDown}{PageUp}{ENTER}{F1}{F2}{F3}{F4}{F5}{F6}{F7}{F8}{F9}{F10}{F11}{F12} control{CTRL}&&<<>>""Copi从结果中不难发现,这个字符串是没有分隔符的,可以论证笔者之前的猜想。这里还有一个问题,这个字符串保护方式是 AgentTesla 自己编写的还是 Obfuscar的呢?这个可以翻阅源代码找到最终的结果。
Obfuscar 源代码是开源的,可以搜索 “Strings、Hide”等关键词,最终可以找到 void HideStrings() 函数:
obfuscar/Obfuscar/Obfuscator.cs at d11f455af81a20209a0d746077447f50f7074f92 · obfuscar/obfuscar
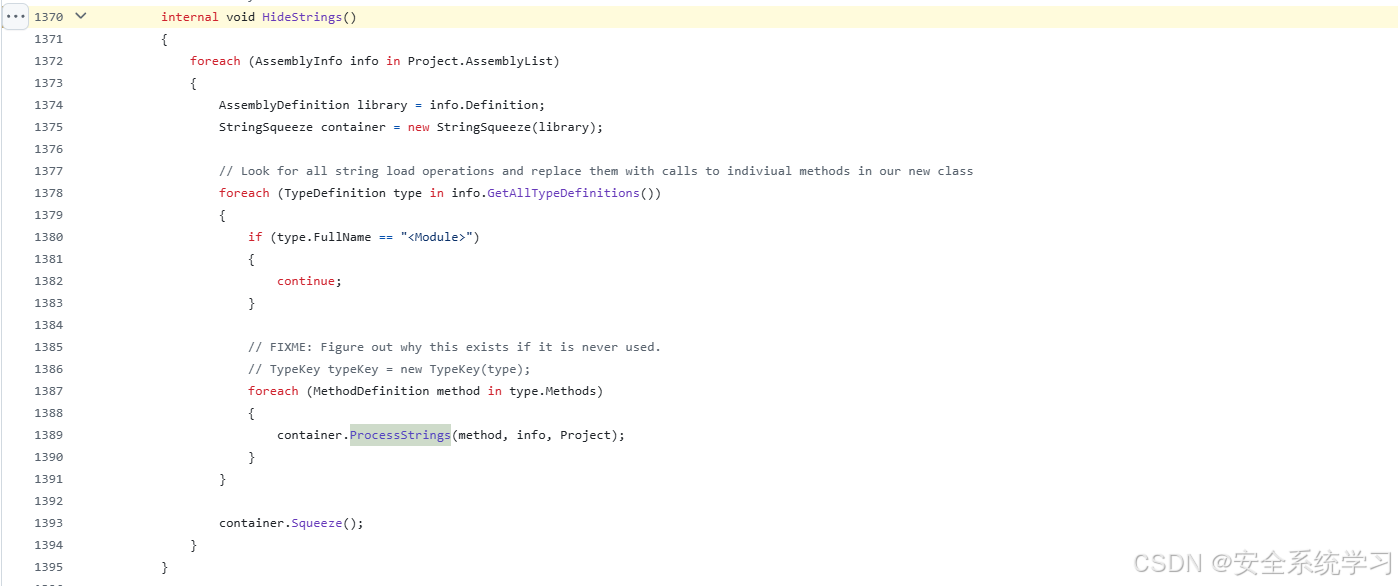
该函数逻辑的最终是 ProcessStrings 函数实现的:
obfuscar/Obfuscar/Obfuscator.cs at d11f455af81a20209a0d746077447f50f7074f92 · obfuscar/obfuscar
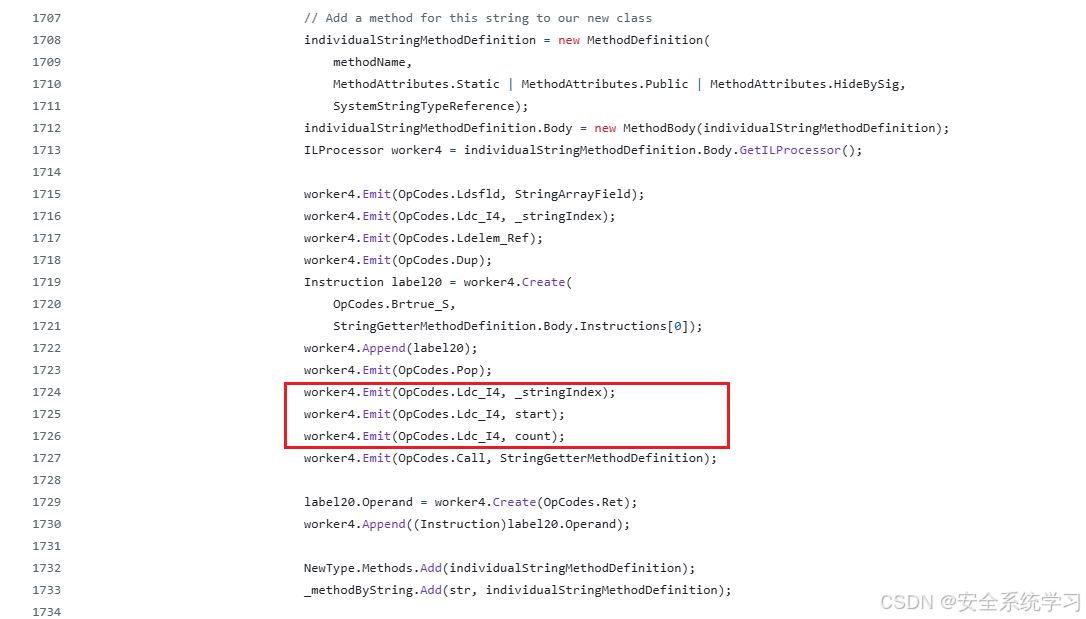
最终可以在代码中字符串的隐藏方式,采用的是 index、start、count来进行实现的。
二、目标确定
从上述中可以看出这个样本并不难分析,但是如何使用更为通用的脚本将样本加密数组提取、提取密钥、解密并像程序一样的切片还是有一定挑战性的,那么根据这个目标,笔者进行的如下几个阶段研究:
2.0 dnlib介绍
dnlib仓库地址:https://github.com/0xd4d/dnlib
dnlib功能介绍:
dnlib 是一个用 C# 写的库(dnSpy 内部就大量用 dnlib),主要用途:读取 .NET 程序集(EXE/DLL)并解析里面的元数据(类型、方法、字段、属性、特性……)、IL 代码(每个方法体里的 IL 指令)、资源、Manifest、签名信息等。其实这里可以类比为IDA的作用的。后续的IL层可以类比为汇编层,更加好理解一些。
2.1 字符串定位
既然要解密,那么第一件事件为如何定位字节数组,首先查看一下IL层代码:
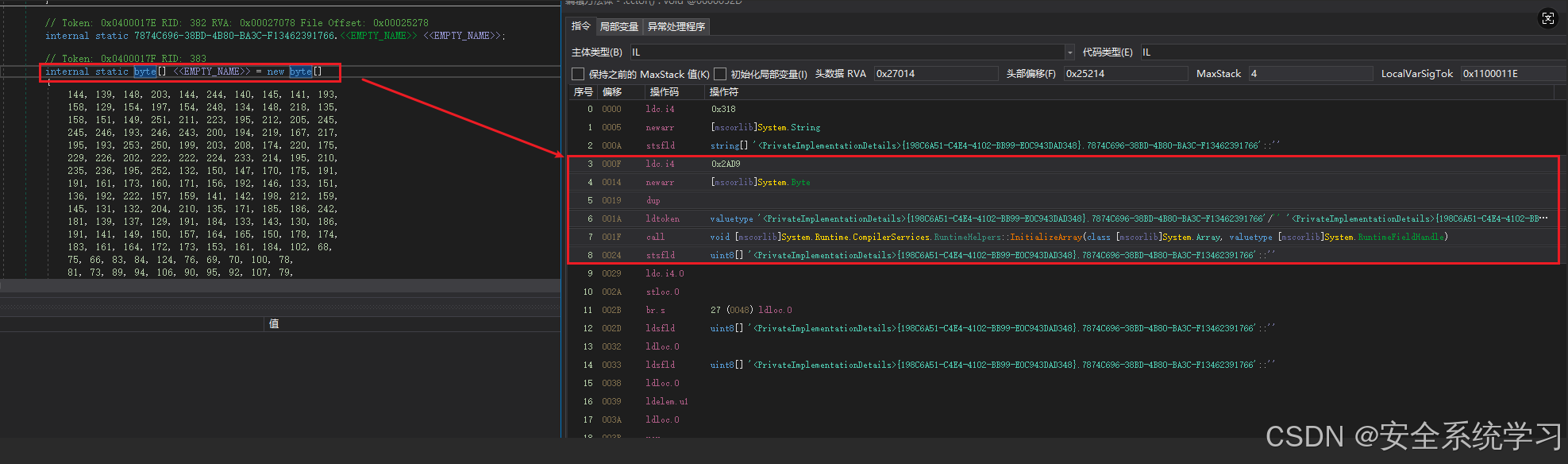
IL层代码解析:
/* 0x0002522F 20D92A0000 */ IL_000F: ldc.i4 10969
/* 0x00025234 8D47000001 */ IL_0014: newarr [mscorlib]System.Byte
/* 0x00025239 25 */ IL_0019: dup
/* 0x0002523A D07E010004 */ IL_001A: ldtoken field valuetype '<PrivateImplementationDetails>{198C6A51-C4E4-4102-BB99-E0C943DAD348}.7874C696-38BD-4B80-BA3C-F13462391766'/'' '<PrivateImplementationDetails>{198C6A51-C4E4-4102-BB99-E0C943DAD348}.7874C696-38BD-4B80-BA3C-F13462391766'::''
/* 0x0002523F 280003000A */ IL_001F: call void [mscorlib]System.Runtime.CompilerServices.RuntimeHelpers::InitializeArray(class [mscorlib]System.Array, valuetype [mscorlib]System.RuntimeFieldHandle)
/* 0x00025244 807F010004 */ IL_0024: stsfld uint8[] '<PrivateImplementationDetails>{198C6A51-C4E4-4102-BB99-E0C943DAD348}.7874C696-38BD-4B80-BA3C-F13462391766'::''补齐一下知识:
第一个:Token: 0x0400017F RID: 383 是啥意思?在 .NET 里,每个 类型 / 方法 / 字段 / 属性 等元数据记录都有一个 Metadata Token,用 4 字节表示:token = (表号 << 24) | 行号(RID),高 1 个字节:**表号(Table ID),**低 3 个字节:RID = Row ID(该表中的行号,从 1 开始)。
比如上述的,Token: 0x0400017F RID: 383,拆开的话就是:
0x04 —— 表号 = 4,表示 FieldDef 表(字段定义表)
0x00017F —— 行号 = 0x17F = 383(十进制),就是 “Field 表里的第 383 行”,串起来就是,这是 FieldDef 表里第 383 行的字段,它的元数据 token 是 0x0400017F。
第二个:解释 IL 层这段指令
IL_000F: ldc.i4 10969:表示将 int32 常量 10969 压入计算栈,相当于 push 10969 。
IL_0014: newarr [mscorlib]System.Byte:表示在栈上创建一个数组,具体大小为10969 。
IL_0019: dup:相当于复制,这里就是将创建的数组复制一份,防止函数调用完成后,栈变量释放。
IL_001A: ldtoken field valuetype '{GUID}.7874C696-38BD-4B80-BA3C-F13462391766'/'' ...:把字段{GUID}.7874C696-38BD-4B80-BA3C-F13462391766句柄压栈。
IL_001F: call void System.Runtime.CompilerServices.RuntimeHelpers::InitializeArray(class System.Array,valuetype System.RuntimeFieldHandle):初始化数组
IL_0024: stsfld uint8[] '{198C6A51-C4E4-4102-BB99-E0C943DAD348}.7874C696-38BD-4B80-BA3C-F13462391766'::'':将创建的数组赋值给一个静态变量。
不难看出这些和x86汇编差不多…而使用dnlib编写脚本相当于IDA写idapython脚本。
从直观看的角度,只需要遍历一条一条的指令,然后使用 “InitializeArray” 关键找到关键语句,然后在上下查找即可,即可找到字节数组。那么再往上推,指令集往上就是函数,函数往上就是类。那么使用dnlib反着逻辑进行编写即可。
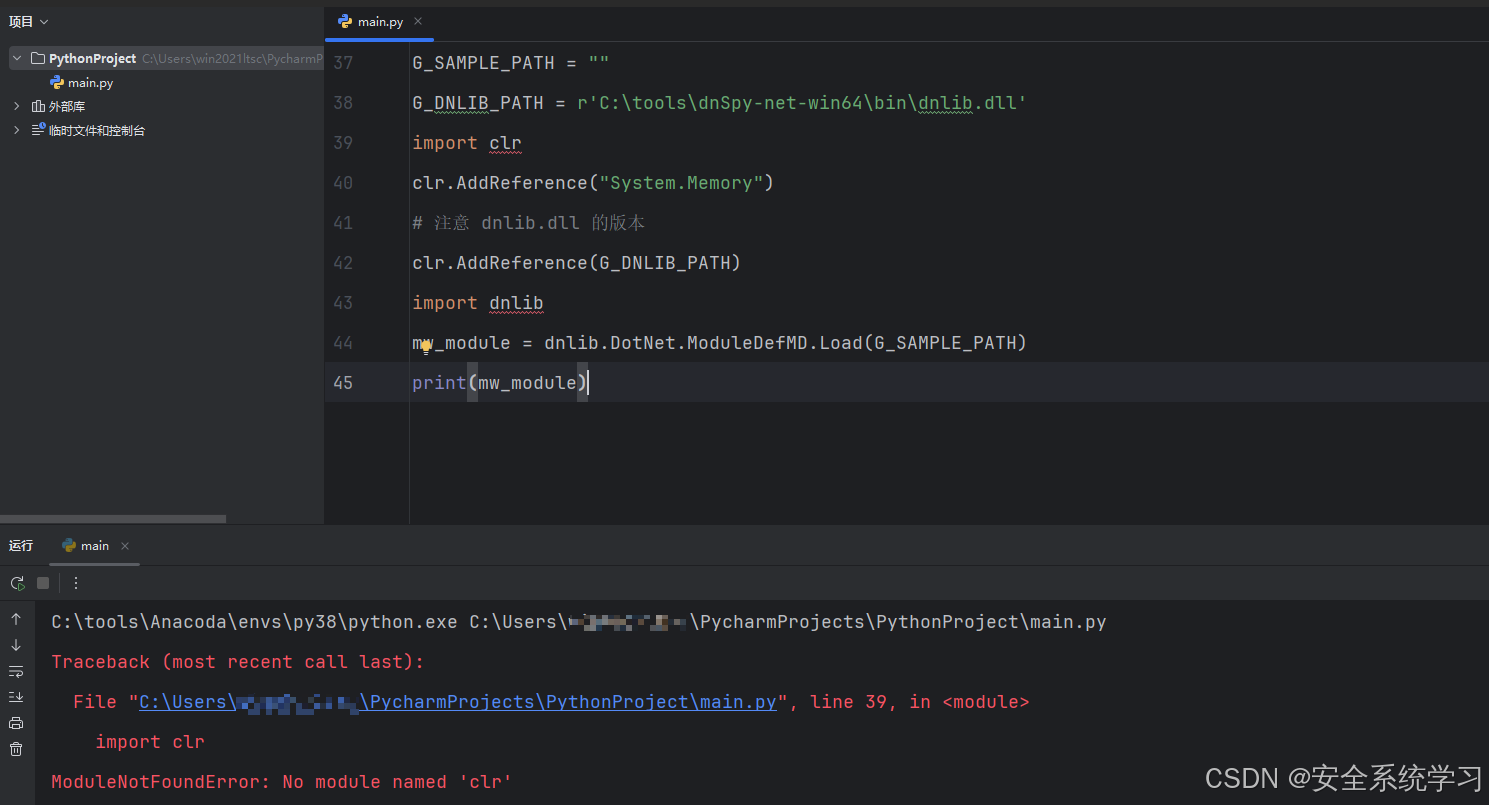
步骤1:加载PE
G_SAMPLE_PATH = r"样本位置"
G_DNLIB_PATH = r'dnlib.dll位置'
import clr
# 注意 dnlib.dll 的版本
clr.AddReference(G_DNLIB_PATH)
# clr 添加dnlib.dll后才可以import
import dnlib
mw_module = dnlib.DotNet.ModuleDefMD.Load(G_SAMPLE_PATH)
print(mw_module)坑:如果这里缺少库的话,一定不要安装 clr库,而是需要安装 pip install pythonnet,另一点就是需要注意 dnlib.dll的版本
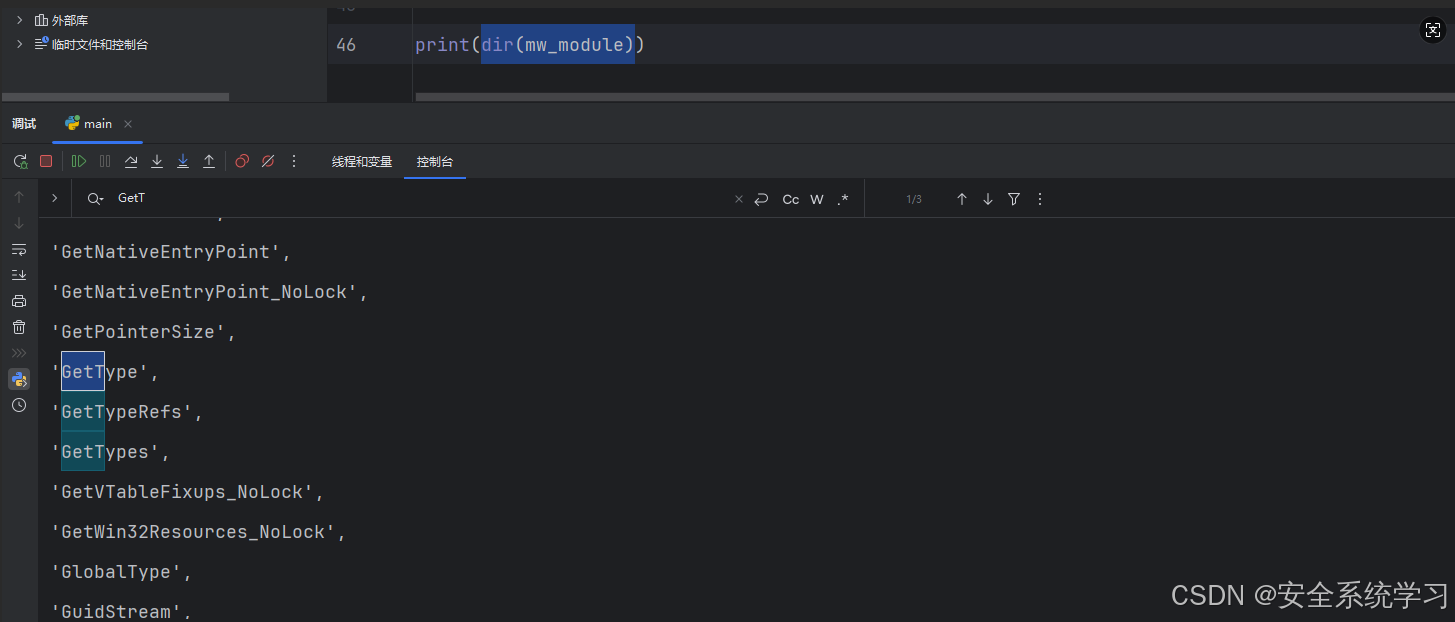
步骤2:遍历所有的类型
查看模板都有哪些函数的时候是不存在提示的,所以需要善用 dir 函数:
这里就写探索过程了…. 最终代码如下:
G_SAMPLE_PATH = r"样本位置"
G_DNLIB_PATH = r'dnlib.dll位置'
import clr
clr.AddReference(G_DNLIB_PATH)
import dnlib
mw_module = dnlib.DotNet.ModuleDefMD.Load(G_SAMPLE_PATH)
print(mw_module)
for per_type in mw_module.GetTypes():
print(per_type)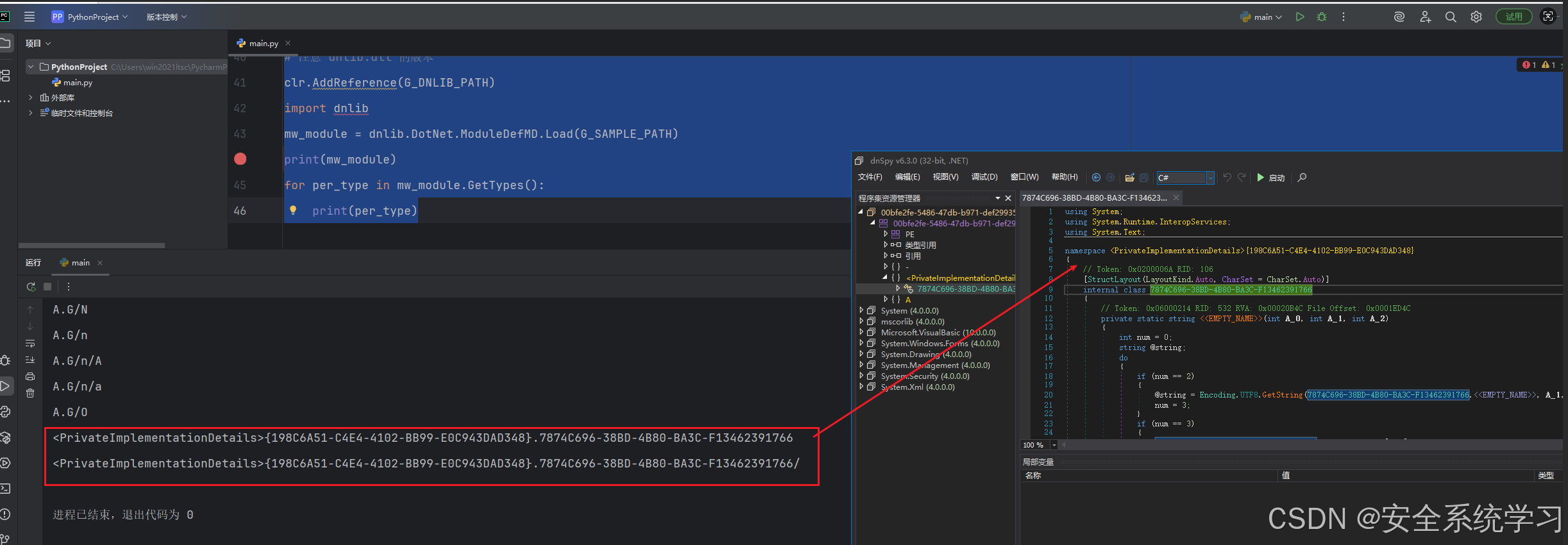
步骤3:遍历所有的函数
找到类型后,类似于从dnspy中分析一样,开始看函数…,遍历所有的函数:
G_SAMPLE_PATH = r"样本位置"
G_DNLIB_PATH = r'dnlib.dll位置'
import clr
# 注意 dnlib.dll 的版本
clr.AddReference(G_DNLIB_PATH)
import dnlib
from dnlib.DotNet import *
mw_module = dnlib.DotNet.ModuleDefMD.Load(G_SAMPLE_PATH)
print(mw_module)
for per_type in mw_module.GetTypes():
# 如果类型中没有函数就直接跳过
if not per_type.HasMethods:
continue
print(dir(per_type))
for per_method in per_type.Methods:
# 函数一定存在函数体
if not per_method.HasBody:
print(per_method)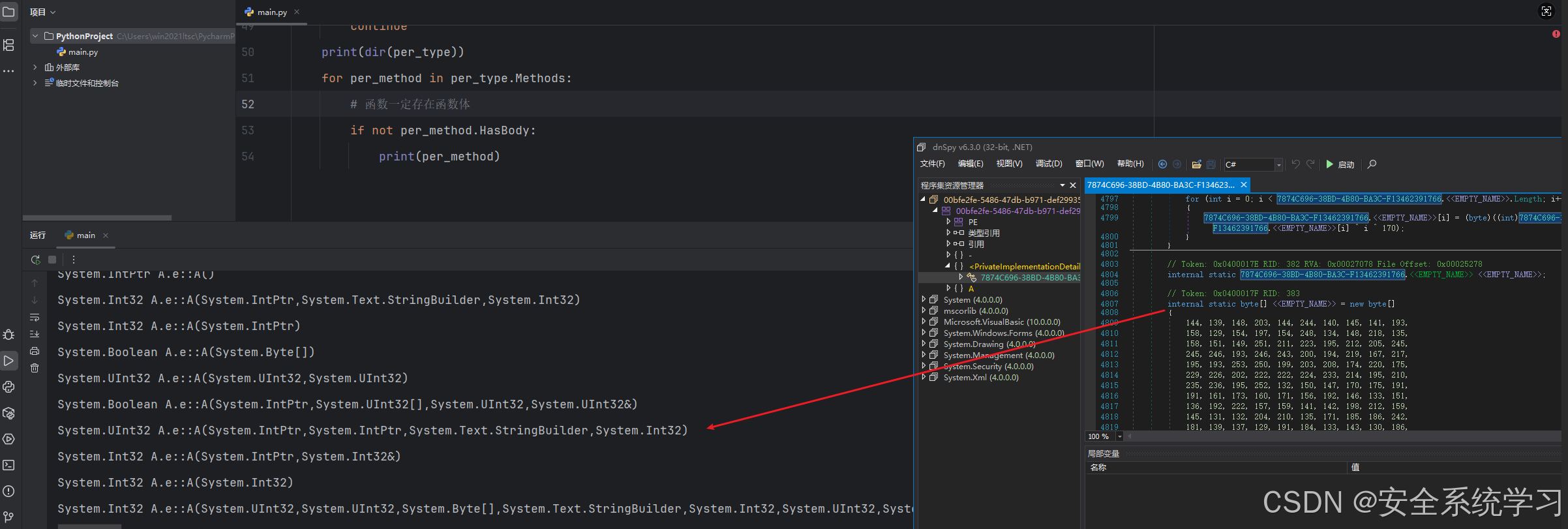
这里命名是变量复制,为什么还需要找函数呢?其实这句代码是再构造函数中。
步骤4:遍历所有的指令
G_SAMPLE_PATH = r"样本位置"
G_DNLIB_PATH = r'dnlib.dll位置'
import clr
# 注意 dnlib.dll 的版本
clr.AddReference(G_DNLIB_PATH)
import dnlib
from dnlib.DotNet import *
mw_module = dnlib.DotNet.ModuleDefMD.Load(G_SAMPLE_PATH)
print(mw_module)
for per_type in mw_module.GetTypes():
# 如果类型中没有函数就直接跳过
if not per_type.HasMethods:
continue
print(dir(per_type))
for per_method in per_type.Methods:
# 函数一定存在函数体
if not per_method.HasBody:
continue
if not per_method.Body.HasInstructions:
continue
for index in range(per_method.Body.Instructions.Count):
print(per_method.Body.Instructions[index])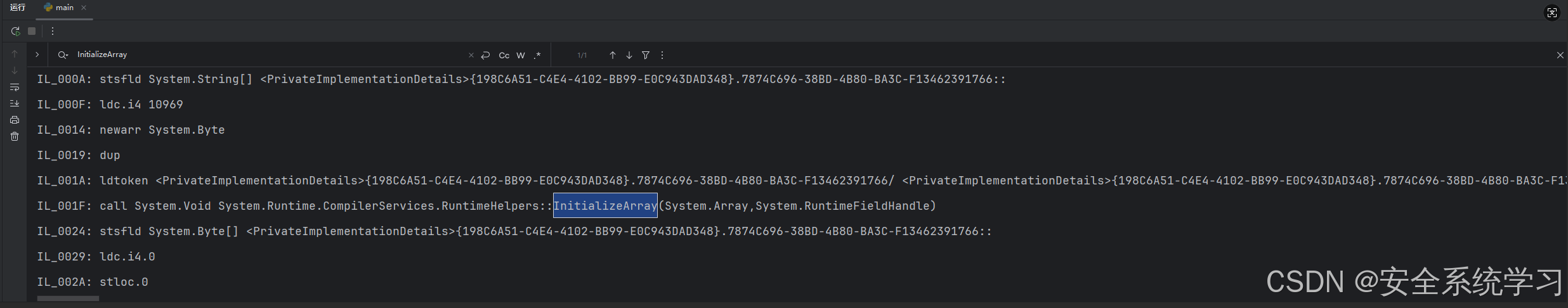
判断指令的类似于助记符,找到数组的位置:
G_SAMPLE_PATH = r"样本位置"
G_DNLIB_PATH = r'dnlib.dll位置'
import clr
# 注意 dnlib.dll 的版本
clr.AddReference(G_DNLIB_PATH)
import dnlib
from dnlib.DotNet import *
mw_module = dnlib.DotNet.ModuleDefMD.Load(G_SAMPLE_PATH)
# print(mw_module)
for per_type in mw_module.GetTypes():
# 如果类型中没有函数就直接跳过
if not per_type.HasMethods:
continue
# print(dir(per_type))
for per_method in per_type.Methods:
# 函数一定存在函数体
if not per_method.HasBody:
continue
if not per_method.Body.HasInstructions:
continue
for index in range(per_method.Body.Instructions.Count):
# print(per_method.Body.Instructions[index])
if "::InitializeArray" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index].ToString():
print(per_method.Body.Instructions[index - 1])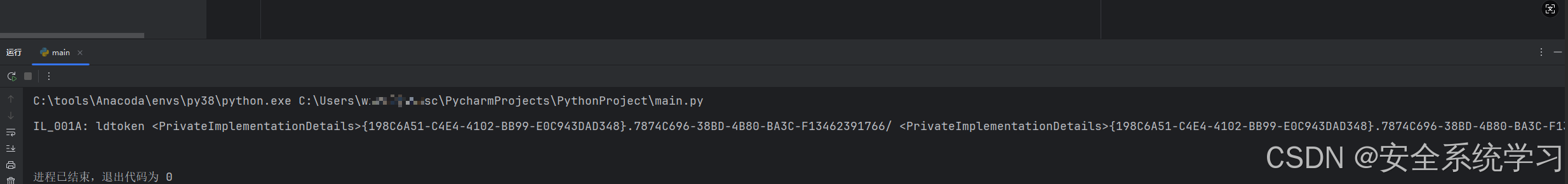
然后根据找到这个数据变量所在的偏移位置,然后提取数组:
import pefile
G_SAMPLE_PATH = r"样本位置"
G_DNLIB_PATH = r'dnlib.dll位置'
G_ARRAY = None
G_PE = pefile.PE(data=open(G_SAMPLE_PATH,'rb').read(), fast_load=True)
import clr
# 注意 dnlib.dll 的版本
clr.AddReference(G_DNLIB_PATH)
import dnlib
from dnlib.DotNet import *
mw_module = dnlib.DotNet.ModuleDefMD.Load(G_SAMPLE_PATH)
for per_type in mw_module.GetTypes():
if not per_type.HasMethods:
continue
for per_method in per_type.Methods:
if not per_method.HasBody:
continue
if not per_method.Body.HasInstructions:
continue
for index in range(per_method.Body.Instructions.Count):
if "RuntimeHelpers::InitializeArray" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index].ToString():
G_ARRAY = per_method.Body.Instructions[index - 1]
# 通过dnlib的FieldDef直接获取数组数据
if isinstance(G_ARRAY.Operand, dnlib.DotNet.FieldDef) and G_ARRAY.Operand.HasFieldRVA:
array_data = G_ARRAY.Operand.InitialValue # 直接提取字节数组
array_size = len(array_data) # 从数据长度获取大小
print(f"数组RVA(dnlib元数据): {hex(G_ARRAY.Operand.RVA)}")
print(f"数组大小: {hex(array_size)}")
print(list(array_data))
break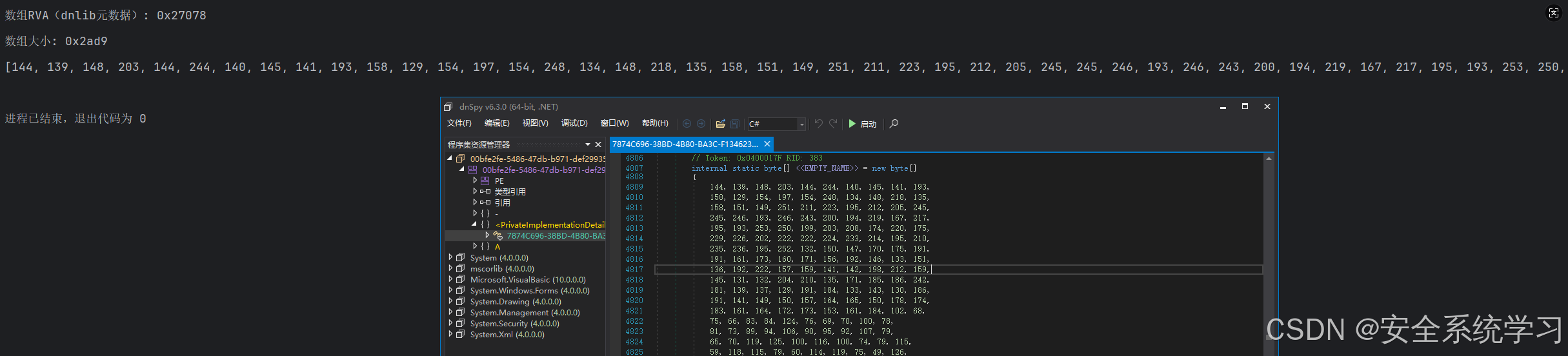
2.2 字符串解密
按照上述类似的操作来寻找XOR的 Key:
/* 0x0002524D 7E7F010004 */ IL_002D: ldsfld uint8[] '<PrivateImplementationDetails>{198C6A51-C4E4-4102-BB99-E0C943DAD348}.7874C696-38BD-4B80-BA3C-F13462391766'::''
/* 0x00025252 06 */ IL_0032: ldloc.0
/* 0x00025253 7E7F010004 */ IL_0033: ldsfld uint8[] '<PrivateImplementationDetails>{198C6A51-C4E4-4102-BB99-E0C943DAD348}.7874C696-38BD-4B80-BA3C-F13462391766'::''
/* 0x00025258 06 */ IL_0038: ldloc.0
/* 0x00025259 91 */ IL_0039: ldelem.u1
/* 0x0002525A 06 */ IL_003A: ldloc.0
/* 0x0002525B 61 */ IL_003B: xor
/* 0x0002525C 20AA000000 */ IL_003C: ldc.i4 170
/* 0x00025261 61 */ IL_0041: xor
/* 0x00025262 D2 */ IL_0042: conv.u1
/* 0x00025263 9C */ IL_0043: stelem.i1
/* 0x00025264 06 */ IL_0044: ldloc.0
/* 0x00025265 17 */ IL_0045: ldc.i4.1
/* 0x00025266 58 */ IL_0046: add
/* 0x00025267 0A */ IL_0047: stloc.0 array_data = ""
for index in range(per_method.Body.Instructions.Count):
if "RuntimeHelpers::InitializeArray" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index].ToString():
G_ARRAY = per_method.Body.Instructions[index - 1]
# 关键修正:通过dnlib的FieldDef直接获取数组数据(假设是静态字段数组)
if isinstance(G_ARRAY.Operand, dnlib.DotNet.FieldDef) and G_ARRAY.Operand.HasFieldRVA:
array_data = G_ARRAY.Operand.InitialValue # 直接提取字节数组
array_size = len(array_data) # 从数据长度获取大小
print(f"数组RVA(dnlib元数据): {hex(G_ARRAY.Operand.RVA)}")
print(f"数组大小: {hex(array_size)}")
print(list(array_data))
if array_data:
if "xor" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index].ToString() and "ldc.i4" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index + 1].ToString() and "xor" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index + 2].ToString():
xor_key = per_method.Body.Instructions[index + 1].Operand
print(xor_key)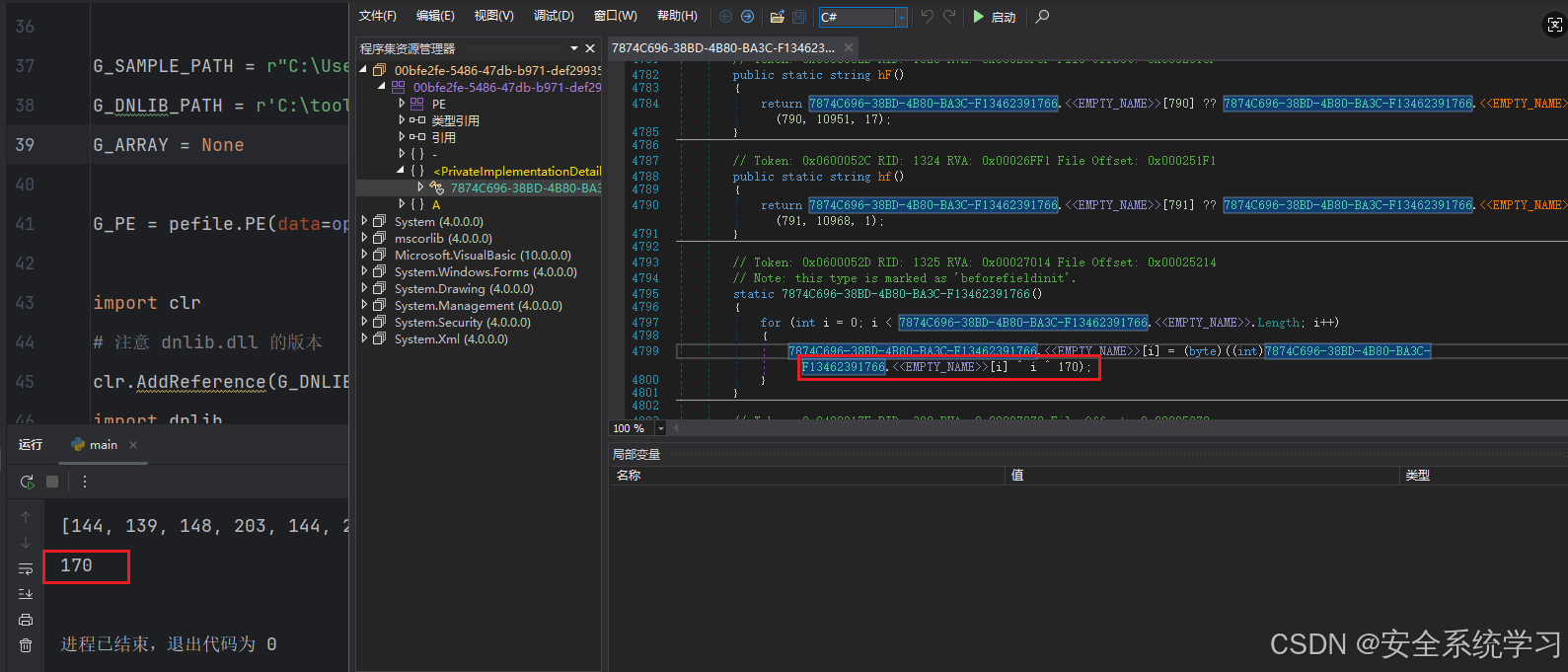
2.3 字符串切片
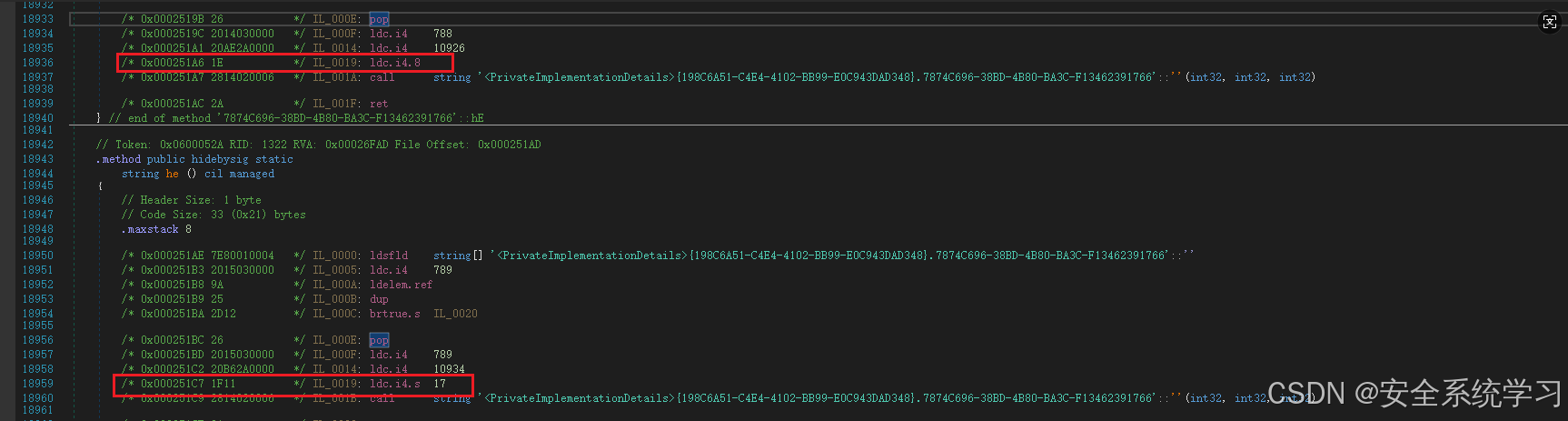
此时只需要发现每个切片函数的特征即可,提取它们的偏移:
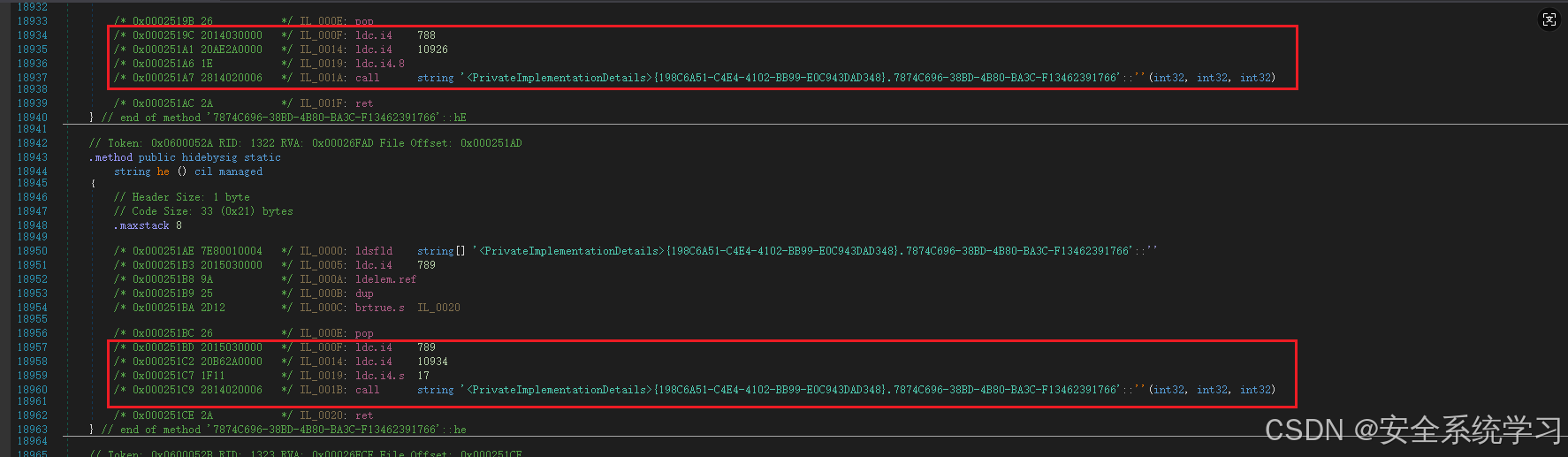
/* 0x000251BD 2015030000 */ IL_000F: ldc.i4 789
/* 0x000251C2 20B62A0000 */ IL_0014: ldc.i4 10934
/* 0x000251C7 1F11 */ IL_0019: ldc.i4.s 17
/* 0x000251C9 2814020006 */ IL_001B: call string '<PrivateImplementationDetails>{198C6A51-C4E4-4102-BB99-E0C943DAD348}.7874C696-38BD-4B80-BA3C-F13462391766'::''(int32, int32, int32)最终代码:
from symbol import pass_stmt
import pefile
from dncil.cil.opcode import OpCodes
G_SAMPLE_PATH = r"样本位置"
G_DNLIB_PATH = r'dnlib.dll位置'
G_ARRAY = None
G_ARRAY_START_END = set()
G_PE = pefile.PE(data=open(G_SAMPLE_PATH,'rb').read(), fast_load=True)
import clr
# 注意 dnlib.dll 的版本
clr.AddReference(G_DNLIB_PATH)
import dnlib
from dnlib.DotNet import *
mw_module = dnlib.DotNet.ModuleDefMD.Load(G_SAMPLE_PATH)
def get_ldc_real_value(instr):
"""
用指令名称字符串匹配(更稳定),直接对应你实际看到的 OpCode.Name
示例:instr.OpCode.Name → 'ldc.i4'/'ldc.i4.s'/'ldc.i4.8'
"""
op_name = instr.OpCode.Name # 关键:直接取指令名称字符串
print(f"调试:解析指令 → {instr} | OpCode.Name: {op_name}") # 调试用,可删除
# 1. 长格式:ldc.i4(如 ldc.i4 790)
if op_name == 'ldc.i4':
return instr.Operand if instr.Operand is not None else None
# 2. 短格式:ldc.i4.s(如 ldc.i4.s 17)
elif op_name == 'ldc.i4.s':
return instr.Operand if instr.Operand is not None else None
# 3. 极短格式:ldc.i4.0 ~ ldc.i4.8(如 ldc.i4.8)
elif op_name == 'ldc.i4.0':
return 0
elif op_name == 'ldc.i4.1':
return 1
elif op_name == 'ldc.i4.2':
return 2
elif op_name == 'ldc.i4.3':
return 3
elif op_name == 'ldc.i4.4':
return 4
elif op_name == 'ldc.i4.5':
return 5
elif op_name == 'ldc.i4.6':
return 6
elif op_name == 'ldc.i4.7':
return 7
elif op_name == 'ldc.i4.8':
return 8
# 4. 特殊情况:ldc.i4.m1(加载-1)
elif op_name == 'ldc.i4.m1':
return -1
# 其他未匹配的指令(打印出来方便调试)
else:
print(f"警告:未匹配的ldc指令 → {op_name}")
return None
for per_type in mw_module.GetTypes():
if not per_type.HasMethods:
continue
for per_method in per_type.Methods:
if not per_method.HasBody:
continue
if not per_method.Body.HasInstructions:
continue
array_data = ""
for index in range(per_method.Body.Instructions.Count):
if index > 3:
# print(per_method.Body.Instructions[index].ToString())
if "call System.String" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index].ToString() and \
"ldc.i4" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index - 1].ToString() and "ldc.i4" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index - 2].ToString() and \
"ldc.i4" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index - 3].ToString():
start_index = get_ldc_real_value(per_method.Body.Instructions[index - 3])
start_location = get_ldc_real_value(per_method.Body.Instructions[index - 2])
end_location= get_ldc_real_value(per_method.Body.Instructions[index-1])
# start_index, start_location,end_location = (per_method.Body.Instructions[index - 3].Operand,per_method.Body.Instructions[index - 2].Operand,per_method.Body.Instructions[index-1].Operand)
print(start_index, start_location,end_location)
if "RuntimeHelpers::InitializeArray" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index].ToString():
G_ARRAY = per_method.Body.Instructions[index - 1]
# 关键修正:通过dnlib的FieldDef直接获取数组数据(假设是静态字段数组)
if isinstance(G_ARRAY.Operand, dnlib.DotNet.FieldDef) and G_ARRAY.Operand.HasFieldRVA:
array_data = G_ARRAY.Operand.InitialValue # 直接提取字节数组
array_size = len(array_data) # 从数据长度获取大小
print(f"数组RVA(dnlib元数据): {hex(G_ARRAY.Operand.RVA)}")
print(f"数组大小: {hex(array_size)}")
print(list(array_data))
if array_data:
if "xor" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index].ToString() and "ldc.i4" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index + 1].ToString() and "xor" in per_method.Body.Instructions[index + 2].ToString():
xor_key = per_method.Body.Instructions[index + 1].Operand
print(xor_key)这里最重要的是需要注意:有些会使用 idc.i4.x 指令
三、整体工程化测试
from symbol import pass_stmt
import pefile
import traceback
# 配置路径
G_SAMPLE_PATH = r"C:\Users\win2021ltsc\Desktop\4c321c77e5a9381005c96bc7fc887b962bcd8c82fcabf579f3301d583055f59d"
G_DNLIB_PATH = r'C:\tools\dnSpy-net-win64\bin\dnlib.dll'
G_PE = None
str_params = [] # (offset, size)
candidate_arrays = [] # 所有候选数组(用于筛选最长)
candidate_keys = [] # 所有候选密钥(用于验证)
target_array = None # 最终筛选的字符串表
target_key = None # 最终验证的正确密钥
# 加载dnlib
try:
import clr
clr.AddReference(G_DNLIB_PATH)
import dnlib
from dnlib.DotNet import *
from dnlib.DotNet.Emit import OpCodes
print("dnlib加载成功")
except Exception as e:
print(f"dnlib加载失败:{str(e)}")
print(f"异常详情:{traceback.format_exc()}")
exit(1)
# 1. 解析参数
def get_param_value(instr):
try:
if instr.Operand is not None:
return int(instr.Operand)
else:
instr_str = instr.ToString().strip()
if '.' in instr_str:
val_str = instr_str.split('.')[-1]
if val_str.isdigit():
return int(val_str)
print(f"警告:无法解析参数指令:{instr_str}")
return None
except Exception as e:
print(f"解析参数失败:{str(e)}")
return None
# 2. ASCII比例验证函数
def pct_ascii(data):
"""计算有效ASCII字符比例(0-1),>0.8为有效解密"""
if not data:
return 0.0
valid = len([c for c in data if (0 <= ord(c) < 128) or ord(c) == 0])
return valid / len(data)
# 3. 解密函数(data[i] ^ (i & 0xff) ^ key)
def decrypt_test(data, key):
"""测试解密(用于密钥验证)"""
out = []
for i in range(len(data)):
byte_val = int(data[i]) if not isinstance(data[i], int) else data[i]
char_code = (byte_val ^ (i & 0xff) ^ key) & 0xff
out.append(chr(char_code))
return ''.join(out)
# 4. 动态收集候选密钥
def collect_candidate_keys(mw_module):
print("\n收集候选密钥...")
for per_type in mw_module.GetTypes():
for per_method in per_type.Methods:
# 解密在构造函数中执行(constructor/.cctor)
if not (per_method.IsConstructor or per_method.Name == ".cctor"):
continue
if not per_method.HasBody or not per_method.Body.HasInstructions:
continue
instructions = per_method.Body.Instructions
for idx in range(1, len(instructions) - 1):
current = instructions[idx]
prev = instructions[idx - 1]
next_instr = instructions[idx + 1]
# 特征:ldc.i4 + 前后有xor
if (current.OpCode == OpCodes.Ldc_I4 and
(prev.OpCode == OpCodes.Xor or next_instr.OpCode == OpCodes.Xor)):
key = get_param_value(current)
if key is not None and key not in candidate_keys:
candidate_keys.append(key)
print(f"新增候选密钥:{key}")
# 备用:从普通方法收集
if not candidate_keys:
print("从普通方法补充收集密钥...")
for per_type in mw_module.GetTypes():
for per_method in per_type.Methods:
if not per_method.HasBody or not per_method.Body.HasInstructions:
continue
instructions = per_method.Body.Instructions
for idx in range(len(instructions) - 2):
if (instructions[idx].OpCode == OpCodes.Xor and
instructions[idx + 1].OpCode == OpCodes.Ldc_I4 and
instructions[idx + 2].OpCode == OpCodes.Xor):
key = get_param_value(instructions[idx + 1])
if key is not None and key not in candidate_keys:
candidate_keys.append(key)
print(f"新增候选密钥:{key}")
# 5. 收集候选数组
def collect_candidate_arrays(mw_module):
print("\n收集候选数组...")
for per_type in mw_module.GetTypes():
for per_method in per_type.Methods:
if not per_method.HasBody or not per_method.Body.HasInstructions:
continue
instructions = per_method.Body.Instructions
for idx in range(len(instructions)):
if "RuntimeHelpers::InitializeArray" in instructions[idx].ToString():
if idx - 1 >= 0:
arr_inst = instructions[idx - 1]
if isinstance(arr_inst.Operand, dnlib.DotNet.FieldDef) and arr_inst.Operand.HasFieldRVA:
arr_data = list(arr_inst.Operand.InitialValue)
candidate_arrays.append((arr_data, arr_inst.Operand.RVA))
print(f"新增候选数组:长度={len(arr_data)},RVA={hex(arr_inst.Operand.RVA)}")
# 6. 筛选目标数组和密钥
def select_target_array_and_key():
global target_array, target_key
print("\n筛选目标数组和密钥...")
# 筛选最长数组作为字符串表
if candidate_arrays:
target_array = max(candidate_arrays, key=lambda x: len(x[0]))[0]
print(f"选中字符串表:长度={len(target_array)}")
else:
print("无候选数组")
return False
# 验证并筛选密钥
if not candidate_keys:
print("无候选密钥")
return False
best_key = None
best_pct = 0.0
# 取数组前100字节测试解密(避免全量计算)
test_data = target_array[:100]
for key in candidate_keys:
dec_test = decrypt_test(test_data, key)
pct = pct_ascii(dec_test)
print(f"密钥{key}:ASCII比例={pct:.2f}")
if pct > best_pct and pct > 0.8:
best_pct = pct
best_key = key
if best_key is not None:
target_key = best_key
print(f"选中有效密钥:{target_key}(ASCII比例={best_pct:.2f})")
return True
else:
print("无有效密钥(ASCII比例均<0.8)")
return False
# 7. 收集目标参数
def collect_target_params(mw_module):
print("\n收集目标参数(公开方法+返回String)...")
for per_type in mw_module.GetTypes():
for per_method in per_type.Methods:
# 公开方法 + 返回值为System.String
if not per_method.IsPublic:
continue
if str(per_method.ReturnType) != "System.String":
continue
if not per_method.HasBody or not per_method.Body.HasInstructions:
continue
if len(per_method.Body.Instructions) < 10:
continue
instructions = per_method.Body.Instructions
for ptr in range(len(instructions)):
if "call System.String" in instructions[ptr].ToString():
if ptr >= 3:
size_instr = instructions[ptr - 1]
offset_instr = instructions[ptr - 2]
if "ldc" in size_instr.ToString() and "ldc" in offset_instr.ToString():
offset = get_param_value(offset_instr)
size = get_param_value(size_instr)
if offset is not None and size is not None and offset >= 0 and size > 0:
str_params.append((offset, size))
print(f"收集参数:offset={offset},size={size}(方法:{per_method.Name})")
# 8. 最终解密
def final_decrypt():
print(f"\n开始最终解密(密钥={target_key},参数数={len(str_params)})...")
decrypted_strings = []
for idx, (offset, size) in enumerate(str_params, 1):
print(f"\n=== 第{idx}个字符串 ===")
print(f"offset={offset},size={size}")
if offset >= len(target_array):
print("跳过:offset超出数组长度")
continue
end = offset + size
if end > len(target_array):
end = len(target_array)
print(f"调整:实际截取到{end}(原size={size})")
sliced = target_array[offset:end]
# 最终解密
dec_str = []
for i, byte in enumerate(sliced):
global_idx = offset + i # 全局索引(原数组中的位置)
byte_val = int(byte) if not isinstance(byte, int) else byte
char_code = (byte_val ^ (global_idx & 0xff) ^ target_key) & 0xff
dec_str.append(chr(char_code))
dec_str = ''.join(dec_str)
decrypted_strings.append(dec_str)
print(f"解密结果:{dec_str}")
print("-" * 60)
# 汇总
print("\n=== 所有解密字符串汇总 ===")
for i, s in enumerate(decrypted_strings, 1):
print(f"{i}. {s}")
# 主逻辑
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 加载文件
try:
print(f"加载样本:{G_SAMPLE_PATH}")
with open(G_SAMPLE_PATH, 'rb') as f:
pe_data = f.read()
G_PE = pefile.PE(data=pe_data, fast_load=True)
mw_module = dnlib.DotNet.ModuleDefMD.Load(G_SAMPLE_PATH)
print("PE和.NET模块加载成功")
except Exception as e:
print(f"加载失败:{str(e)}")
exit(1)
# 2. 步骤1:收集候选密钥
collect_candidate_keys(mw_module)
if not candidate_keys:
print("无候选密钥,退出")
exit(1)
# 3. 步骤2:收集候选数组
collect_candidate_arrays(mw_module)
if not candidate_arrays:
print("无候选数组,退出")
exit(1)
# 4. 步骤3:筛选目标数组和密钥
if not select_target_array_and_key():
exit(1)
# 5. 步骤4:收集目标参数
collect_target_params(mw_module)
if not str_params:
print("无有效参数,退出")
exit(0)
# 6. 步骤5:最终解密
final_decrypt()
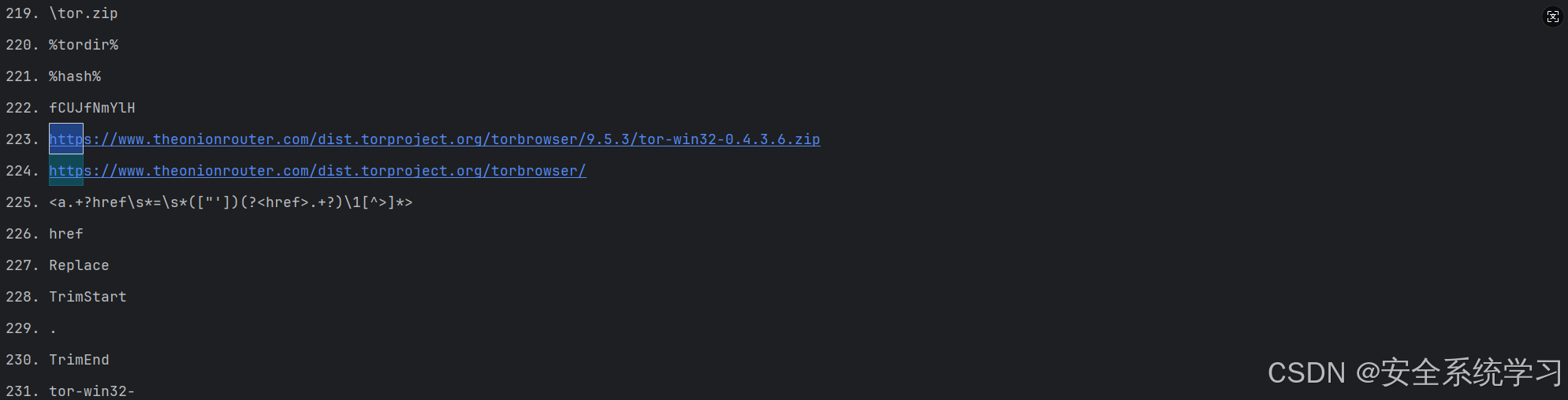
print("\n程序执行完毕")效果:
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)