强化学习笔记:Diffusion Policy
扩散模型的产生为强化学习带来了全新的思路,它通过类似“迭代去噪”的生成方式,将随机噪声优化为高质量的动作序列。这种方法能天然处理任务中存在的多种合理解决方案,有效避免了传统算法输出保守“平均解”的问题。无论是作为直接生成动作的策略,还是进行长远规划的规划器,扩散模型都显著提升了智能体在复杂任务中的决策质量和行为多样性,尤其适合需要精细控制的机器人等领域,尽管其计算成本较高,但已成为该领域最具潜力的
参考:本文参考了李宏毅老师的讲解Diffusion Model的课程,并结合个人见解所写
1 Diffusion Policy 简介
扩散模型的产生为强化学习带来了全新的思路,它通过类似“迭代去噪”的生成方式,将随机噪声优化为高质量的动作序列。这种方法能天然处理任务中存在的多种合理解决方案,有效避免了传统算法输出保守“平均解”的问题。
无论是作为直接生成动作的策略,还是进行长远规划的规划器,扩散模型都显著提升了智能体在复杂任务中的决策质量和行为多样性,尤其适合需要精细控制的机器人等领域,尽管其计算成本较高,但已成为该领域最具潜力的技术方向之一。
首先介绍一下Diffusion Model:
2 Diffusion Model 原理
Diffusion Model将数据的处理分为两部分,一部分是前向传播,一部分是反向传播。
- 前向过程(加噪): 将一张清晰的图片,一步步地添加随机噪声,最终变成一团完全随机的噪声。
- 反向过程(去噪):这是模型学习的部分。它学习如何从一团随机噪声开始,一步步地去除噪声,最终还原出一张清晰的、符合文本描述的新图片。
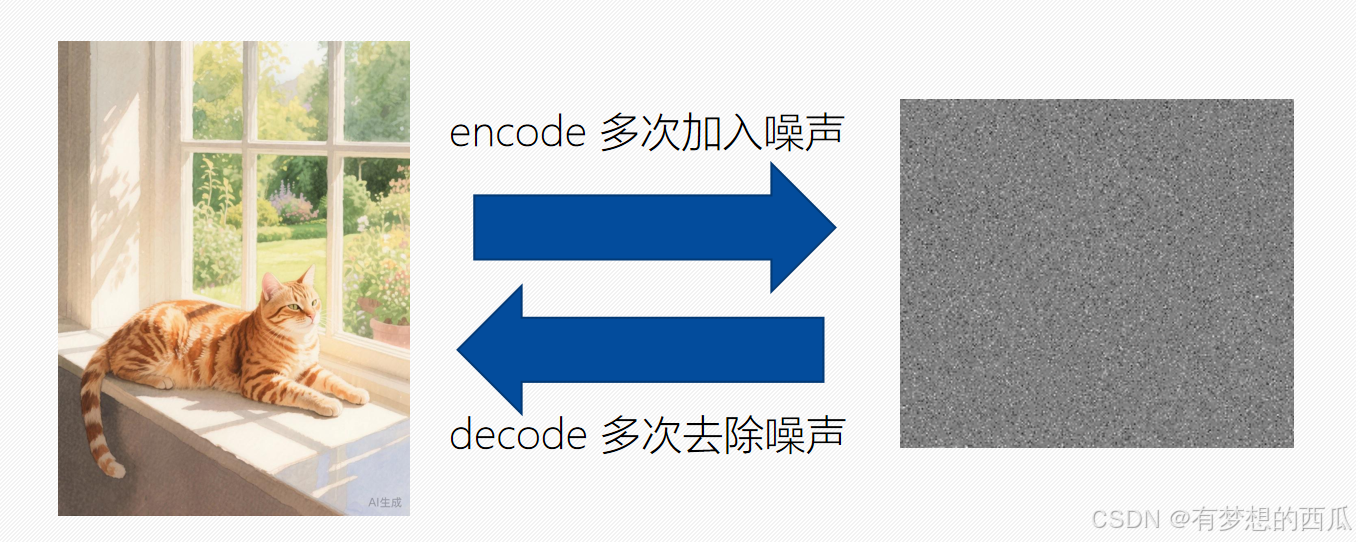
为了方便理解,我们可以将其理解为一张图片多次加入噪声,再反向denoise多次去除噪声。但在实际操作中噪声往往是通过权重一次性加上,并一次性去除的。
2.1 前向过程
下面是前向传播的代码:
Algorithm 1 Training
1: repeat
2: x 0 ∼ q ( x 0 ) \mathbf{x}_{0} \sim q(\mathbf{x}_{0}) x0∼q(x0) // sample clean image
3: t ∼ Uniform ( { 1 , … , T } ) t \sim \text{Uniform}(\{1,\ldots, T\}) t∼Uniform({1,…,T})
4: ϵ ∼ N ( 0 , I ) \boldsymbol{\epsilon} \sim \mathcal{N}(\mathbf{0},\mathbf{I}) ϵ∼N(0,I)
5: Take gradient descent step on
∇ θ ∥ ϵ − ϵ θ ( α ˉ t x 0 + 1 − α ˉ t ϵ , t ) ∥ 2 \nabla_{\theta}\left\|\boldsymbol{\epsilon}-\boldsymbol{\epsilon}_{\theta}\left(\sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_{t}}\mathbf{x}_{0}+\sqrt{1-\bar{\alpha}_{t}}\boldsymbol{\epsilon},t\right)\right\|^{2} ∇θ ϵ−ϵθ(αˉtx0+1−αˉtϵ,t) 2
6: until converged
首先从训练集中抽出一张干净的样本 x 0 \mathrm x_0 x0,并抽取一个步数 t t t,其中 T T T是总步数(例如1000步)。扩散过程不是一步到位,而是分成很多小步。随机选择 t t t意味着我们会在不同的噪声程度上训练模型,让它既能处理像轻微毛玻璃一样的图片,也能处理几乎全是噪声的图片,这大大提高了模型的鲁棒性。
第四步是从高斯分布中抽取一个随机的 ϵ \epsilon ϵ作为噪声向量,之后就可以对样本进行加噪。
对核心公式进行解释:
∇ θ ∥ ϵ − ϵ θ ( α ˉ t x 0 + 1 − α ˉ t ϵ , t ) ∥ 2 \nabla_{\theta}\left\|\boldsymbol{\epsilon}-\boldsymbol{\epsilon}_{\theta}\left(\sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_{t}}\mathbf{x}_{0}+\sqrt{1-\bar{\alpha}_{t}}\boldsymbol{\epsilon},t\right)\right\|^{2} ∇θ
ϵ−ϵθ(αˉtx0+1−αˉtϵ,t)
2
-
α ˉ t x 0 + 1 − α ˉ t ϵ \sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_{t}}\mathbf{x}_{0}+\sqrt{1-\bar{\alpha}_{t}}\boldsymbol{\epsilon} αˉtx0+1−αˉtϵ代表了加噪的过程。 α ˉ t \bar \alpha_t αˉt是一个预先设定好的,介于0-1之间的权重值,并且这个序列随着 t t t的增大而减小。也就是说,我们实际上就是按照一定的比例,将纯净的样本和噪声进行加权混合。这个公式的妙处在于,它不需要真的迭代 t t t次来加噪,而是通过一个封闭公式直接计算出第 t t t步的噪声图片,我们记这个加噪后的样本为 x t \mathrm x_t xt。
-
ϵ θ ( α ˉ t x 0 + 1 − α ˉ t ϵ , t ) \boldsymbol{\epsilon}_{\theta}\left(\sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_{t}}\mathbf{x}_{0}+\sqrt{1-\bar{\alpha}_{t}}\boldsymbol{\epsilon},t\right) ϵθ(αˉtx0+1−αˉtϵ,t)代表我们将加噪后的样本 x t \mathrm x_t xt和步数 t t t作为输入输到神经网络中(其中神经网络的参数为 θ \theta θ),他的输出会是一个 ϵ p r e d \epsilon_{pred} ϵpred。也就是说,这个神经网络的任务,就是通过我们那两个输入,来预测加在纯净样本 x 0 \mathrm x_0 x0上的噪声 ϵ p r e d \epsilon_{pred} ϵpred是多少。
-
∇ θ ∣ ∣ ϵ − ϵ θ ( . . . ) ∣ ∣ 2 \nabla_{\theta}||\epsilon-\epsilon_{\theta}(...)||^2 ∇θ∣∣ϵ−ϵθ(...)∣∣2这整个公式就是说我们将网络预测的噪声与我们事先知道的、真实添加的噪声 ϵ \epsilon ϵ进行比较。损失函数就是它们之间的均方误差(MSE)。这个值越小,说明网络预测的噪声越准。而梯度下降函数是为了计算这个损失函数关于模型参数 θ \theta θ的梯度。然后根据梯度方向更新模型参数 θ \theta θ,让模型下次能更准确地预测噪声。
总而言之,这个train algorithrm的意思,就是通过一个纯净样本数据集优化一个神经网络模型的参数,使得该模型能够准确预测出加在一个样本上的噪声量。
2.2 反向过程
Algorithm 2 Sampling
1: x T ∼ N ( 0 , I ) \mathbf{x}_{T} \sim \mathcal{N}(\mathbf{0}, \mathbf{I}) xT∼N(0,I)
2: for t = T , … , 1 t = T, \ldots, 1 t=T,…,1 do
3: z ∼ N ( 0 , I ) \mathbf{z} \sim \mathcal{N}(\mathbf{0}, \mathbf{I}) z∼N(0,I) if t > 1 t > 1 t>1, else z = 0 \mathbf{z} = \mathbf{0} z=0
4: x t − 1 = 1 α t ( x t − 1 − α t 1 − α ˉ t ϵ θ ( x t , t ) ) + σ t z \mathbf{x}_{t-1} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{\alpha_{t}}} \left( \mathbf{x}_{t} - \frac{1 - \alpha_{t}}{\sqrt{1 - \bar{\alpha}_{t}}} \boldsymbol{\epsilon}_{\theta}(\mathbf{x}_{t}, t) \right) + \sigma_{t} \mathbf{z} xt−1=αt1(xt−1−αˉt1−αtϵθ(xt,t))+σtz
5: end for
6: return x 0 \mathbf{x}_{0} x0
我们可以将去噪的过程看成一个雕像的过程,我们需要从一个完全的噪声中雕刻出一个符合训练数据分布的新样本(比如一张新图片)。
-
第一步是从一个高斯分布中初始化一个随机噪声样本 x T \mathrm x_T xT
-
第二步循环开始:这是一个从最大时间步 T T T到 1 1 1 的循环。每一步都代表一次“去噪”迭代,目标是逐步从 x T \mathrm x_T xT(纯噪声)恢复到 x 0 \mathrm x_0 x0(干净数据)。
-
第三步:如果当前步 t > 1 t>1 t>1 (不是最后一步),则采样一个新的随机噪声 z \mathrm z z。这为去噪过程引入了一定的随机性,有助于生成结果的多样性。如果当前步 t = 1 t=1 t=1(最后一步),则将 z \mathrm z z设为 0。这意味着在生成过程的最后一步不再添加随机噪声,以得到一个确定的、清晰的最终结果。(至于为什么去噪的过程还要加噪,我们之后再详细解释)
-
第四步就是去噪的核心过程,通过权重因子,将我们通过神经网络预测的噪声 ϵ θ \epsilon_{\theta} ϵθ进行缩放,并在 x t \mathrm x_t xt中去除。这是一个不断迭代的过程,我们逐步去除噪声,并在每一个过程中添加随机的噪声 z \mathrm z z
-
循环结束
为什么要添加随机噪声?
为了保证输出结果的多样性。举个例子,我们希望生成式AI给我们生成一个在阳台晒太阳的猫,如果每次生成的都是一样的图片,我们自然不满意。因为晒太阳的猫可以有很多种表现形式,有可能是橘猫,有可能是白猫,我们添加随机噪声就是为了输出结果的多样化。
3 实战演练
# Cell1:导入libraries
import gymnasium as gym
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import clear_output
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import random
from collections import deque
import pandas as pd
print(f"torch版本:{torch.__version__}")
print(f"gymnasium版本:{gym.__version__}")
# Cell2:Diffusion Policy定义
class DiffusionPolicy(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, hidden_dim=128, num_timesteps=100):
super().__init__()
self.state_dim = state_dim
self.action_dim = action_dim
self.num_timesteps = num_timesteps
# 时间步编码
self.time_embedding = nn.Embedding(num_timesteps, hidden_dim)
# 状态编码
self.state_embedding = nn.Linear(state_dim, hidden_dim)
# 动作编码
self.action_embedding = nn.Linear(action_dim, hidden_dim)
# 噪声预测网络
self.noise_predictor = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(hidden_dim * 3, hidden_dim), # 状态+动作+时间步
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, action_dim)
)
def forward(self, state, action, timestep):
t_emb = self.time_embedding(timestep)
s_emb = self.state_embedding(state)
a_emb = self.action_embedding(action)
combined = torch.cat([s_emb, a_emb, t_emb], dim=1)
predicted_noise = self.noise_predictor(combined)
return predicted_noise
# Cell3:改进的训练器
class ImproveDiffusionTrainer:
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, lr=0.001, num_timesteps=100):
self.state_dim = state_dim
self.action_dim = action_dim
self.num_timesteps = num_timesteps
self.model = DiffusionPolicy(state_dim, action_dim, num_timesteps=num_timesteps)
self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.model.parameters(), lr=lr)
self.loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
# 定义噪声调度参数
self.betas = torch.linspace(1e-4, 0.02, num_timesteps)
self.alphas = 1 - self.betas
self.alpha_bars = torch.cumprod(self.alphas, dim=0)
# 给样本添加噪声
def add_noise(self, actions, timesteps, noise):
alpha_bars = self.alpha_bars[timesteps]
# 确保维度正确
if len(alpha_bars.shape) < len(actions.shape):
alpha_bars_expanded = alpha_bars.unsqueeze(-1)
else:
alpha_bars_expanded = alpha_bars
sqrt_alpha_bar = torch.sqrt(alpha_bars_expanded)
sqrt_one_minus_alpha_bar = torch.sqrt(1 - alpha_bars_expanded)
noisy_actions = sqrt_alpha_bar * actions + sqrt_one_minus_alpha_bar * noise
return noisy_actions
def train_step(self, states, actions):
batch_size = states.shape[0]
# 随机采样时间步
timesteps = torch.randint(0, self.num_timesteps, (batch_size,))
# 生成随机噪声
noise = torch.randn_like(actions)
# 添加噪声到动作
noisy_actions = self.add_noise(actions, timesteps, noise)
# 预测噪声
predicted_noise = self.model(states, noisy_actions, timesteps)
# 计算损失
loss = self.loss_fn(predicted_noise, noise)
# 反向传播
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
return loss.item()
# Cell4:经验回放缓冲区
class ReplayBuffer:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.buffer = deque(maxlen=capacity)
def push(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done):
self.buffer.append((state, action, reward, next_state, done))
def sample(self, batch_size):
batch = random.sample(self.buffer, batch_size)
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = zip(*batch)
return (np.array(states), np.array(actions), np.array(rewards),
np.array(next_states), np.array(dones))
def __len__(self):
return len(self.buffer)
# Cell5:Diffusion RL Agent
class DiffusionRLAgent:
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, lr=0.001, buffer_capacity=10000):
self.state_dim = state_dim
self.action_dim = action_dim
self.trainer = ImproveDiffusionTrainer(state_dim, action_dim, lr=lr)
self.buffer = ReplayBuffer(buffer_capacity)
self.num_sampling_steps = 10
def select_action(self, state, exploration_noise=0.1):
# 采样生成动作
state_tensor = torch.FloatTensor(state).unsqueeze(0)
# 从随机噪声开始
action = torch.randn(1, self.action_dim)
# 逆向扩散过程
for t in range(self.trainer.num_timesteps-1, -1, -self.num_sampling_steps):
timestep = torch.tensor([t])
with torch.no_grad():
# 预测噪声
predicted_noise = self.trainer.model(state_tensor, action, timestep)
if t > 0:
# 计算去噪后的动作
alpha_bar = self.trainer.alpha_bars[t]
alpha_bar_prev = self.trainer.alpha_bars[t-1]
# 采样公式
pred_action = (action - (1 - alpha_bar).sqrt() * predicted_noise) / alpha_bar.sqrt()
# 添加噪声回到前一个时间步
noise = torch.randn_like(action)
action = pred_action * alpha_bar_prev.sqrt() + (1 - alpha_bar_prev).sqrt() * noise
else:
# 最后一步直接去噪
alpha_bar = self.trainer.alpha_bars[t]
action = (action - (1 - alpha_bar).sqrt() * predicted_noise) / alpha_bar.sqrt()
# 添加探索噪声
action = action + exploration_noise * torch.randn_like(action)
# 裁剪动作到合理范围
action = torch.clamp(action, -2.0, 2.0) # Pendulum的动作范围是[-2, 2]
# 修复:确保返回标量值
action_np = action.squeeze().numpy()
# 对于Pendulum环境,动作应该是标量
if np.isscalar(action_np):
return float(action_np)
elif action_np.shape == ():
return float(action_np)
elif action_np.shape == (1,):
return float(action_np[0])
else:
return float(action_np.item()) # 确保返回标量
def push_experience(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done):
# 确保动作是numpy数组格式
if np.isscalar(action):
action = np.array([action])
self.buffer.push(state, action, reward, next_state, done)
def train(self, batch_size=32):
if len(self.buffer) < batch_size:
return 0
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = self.buffer.sample(batch_size)
# 转换为tensor
states = torch.FloatTensor(states)
actions = torch.FloatTensor(actions)
# 如果动作维度是1,确保形状正确
if actions.dim() == 1:
actions = actions.unsqueeze(-1)
loss = self.trainer.train_step(states, actions)
return loss
# Cell6:训练循环
def train_agent(env_name="Pendulum-v1", episodes=1000):
env = gym.make(env_name)
state_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0]
action_dim = env.action_space.shape[0]
print(f"环境: {env_name}, 状态维度: {state_dim}, 动作维度: {action_dim}")
print(f"动作空间: {env.action_space}")
print(f"动作空间范围: {env.action_space.low} 到 {env.action_space.high}")
agent = DiffusionRLAgent(state_dim, action_dim)
rewards_history = []
losses_history = []
for episode in range(episodes):
state, _ = env.reset()
episode_reward = 0
episode_loss = 0
step_count = 0
while True:
# 选择动作
action = agent.select_action(state)
# 调试信息
if episode < 3 or episode % 100 == 0: # 只在前几个episode输出调试信息
print(f"Episode {episode}, Step {step_count}: action={action}, type={type(action)}, shape={getattr(action, 'shape', 'scalar')}")
# 确保动作是标量
if not np.isscalar(action):
action = float(action[0]) if hasattr(action, '__getitem__') else float(action)
# 执行动作
next_state, reward, terminated, truncated, _ = env.step(np.array([action])) # 确保动作是数组格式
done = terminated or truncated
# 存储经验
agent.push_experience(state, action, reward, next_state, done)
# 训练
loss = agent.train()
episode_loss += loss if loss > 0 else 0
state = next_state
episode_reward += reward
step_count += 1
if done or step_count > 200: # 添加最大步数限制
break
avg_loss = episode_loss / max(step_count, 1)
rewards_history.append(episode_reward)
losses_history.append(avg_loss)
if episode % 10 == 0:
clear_output(wait=True)
print(f"Episode {episode}, Reward: {episode_reward:.2f}, Loss: {avg_loss:.4f}, Steps: {step_count}")
env.close()
return rewards_history, losses_history, agent
# Cell7:运行训练和可视化
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 先进行简单测试
try:
# 测试环境是否能正常工作
env = gym.make("Pendulum-v1")
state, _ = env.reset()
print(f"状态示例: {state}")
action = np.array([0.5]) # 测试动作
next_state, reward, done, _, _ = env.step(action)
print(f"测试动作: {action}, 奖励: {reward}")
env.close()
except Exception as e:
print(f"环境测试失败: {e}")
# 训练智能体
rewards, losses, agent = train_agent(episodes=20) # 先用少量episode测试
# 绘制结果
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(rewards)
plt.title('Training Rewards')
plt.xlabel('Episode')
plt.ylabel('Reward')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(losses)
plt.title('Training Loss')
plt.xlabel('Episode')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 测试训练好的智能体
def test_agent(agent, env_name="Pendulum-v1", episodes=3):
env = gym.make(env_name, render_mode='human')
for episode in range(episodes):
state, _ = env.reset()
total_reward = 0
step_count = 0
while True:
action = agent.select_action(state, exploration_noise=0.01)
# 确保动作格式正确
if not np.isscalar(action):
action = float(action[0]) if hasattr(action, '__getitem__') else float(action)
next_state, reward, terminated, truncated, _ = env.step(np.array([action]))
done = terminated or truncated
total_reward += reward
state = next_state
step_count += 1
if done or step_count > 200:
print(f"Test Episode {episode + 1}, Reward: {total_reward:.2f}, Steps: {step_count}")
break
env.close()
test_agent(agent)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容








所有评论(0)