大模型落地:从微调到企业级解决方案
本文系统介绍了大模型落地的关键技术,涵盖模型微调、提示工程、多模态应用和企业级解决方案。在模型微调方面,详细对比了全参数微调、LoRA等策略,并提供了完整代码示例。提示工程部分阐述了设计原则、优化方法和评估体系。多模态应用展示了视觉语言模型的集成方法。企业级解决方案则包括架构设计、安全管理和部署方案。通过综合考虑技术可行性、业务需求和资源约束,本文为构建稳定高效的大模型应用系统提供了实用指导,帮助
1. 大模型微调技术
1.1 微调的基本概念与流程
大模型微调是指使用特定领域的数据对预训练大模型进行进一步训练,使其适应特定任务的过程。微调可以在保持模型通用能力的同时,提升在特定任务上的性能。
python
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, TrainingArguments, Trainer
from datasets import load_dataset
import pandas as pd
# 加载预训练模型和分词器
model_name = "bert-base-uncased"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
# 添加特殊token(如果需要)
special_tokens = {"additional_special_tokens": ["[ENTITY]", "[RELATION]"]}
tokenizer.add_special_tokens(special_tokens)
model.resize_token_embeddings(len(tokenizer))
# 准备数据集
def tokenize_function(examples):
return tokenizer(examples["text"], padding="max_length", truncation=True, max_length=512)
dataset = load_dataset("imdb")
tokenized_datasets = dataset.map(tokenize_function, batched=True)
# 设置训练参数
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./results",
num_train_epochs=3,
per_device_train_batch_size=8,
per_device_eval_batch_size=8,
warmup_steps=500,
weight_decay=0.01,
logging_dir="./logs",
logging_steps=10,
evaluation_strategy="epoch"
)
# 创建Trainer并开始训练
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=tokenized_datasets["train"],
eval_dataset=tokenized_datasets["test"],
)
trainer.train()
1.2 微调策略对比分析
以下是不同微调策略的对比表格:
| 微调策略 | 适用场景 | 优点 | 缺点 | 计算资源需求 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全参数微调 | 数据量充足,任务差异大 | 性能最优 | 容易过拟合,资源消耗大 | 高 |
| 逐层解冻 | 中等数据量 | 平衡性能与效率 | 需要精心设计解冻策略 | 中 |
| 适配器微调 | 多任务学习,资源受限 | 参数高效,易于扩展 | 可能引入推理延迟 | 低 |
| LoRA | 资源受限场景 | 参数高效,性能接近全参数 | 需要选择合适的目标模块 | 低 |
| 提示微调 | 少样本学习 | 极低的参数需求 | 性能可能受限 | 极低 |
1.3 LoRA微调实战示例
python
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model, TaskType
# 配置LoRA
lora_config = LoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM,
inference_mode=False,
r=8,
lora_alpha=32,
lora_dropout=0.1,
target_modules=["query", "value"]
)
# 应用LoRA到模型
model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)
# 打印可训练参数
model.print_trainable_parameters()
# 训练过程与标准微调相同
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./lora_results",
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
learning_rate=1e-4,
num_train_epochs=3,
logging_steps=10,
)
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=tokenized_datasets["train"],
)
trainer.train()
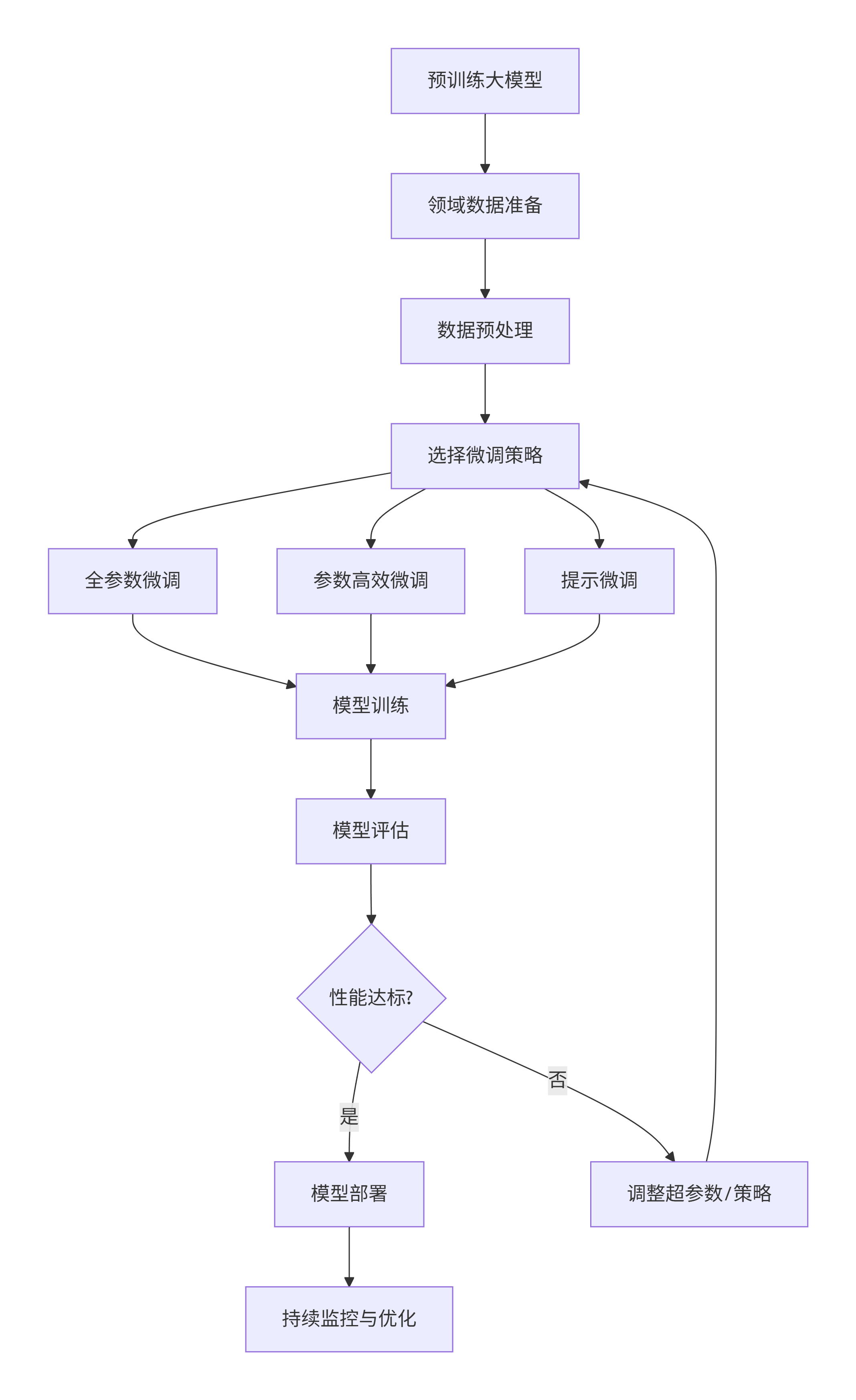
1.4 微调流程Mermaid图
graph TD
A[预训练大模型] --> B[领域数据准备]
B --> C[数据预处理]
C --> D[选择微调策略]
D --> E[全参数微调]
D --> F[参数高效微调]
D --> G[提示微调]
E --> H[模型训练]
F --> H
G --> H
H --> I[模型评估]
I --> J{性能达标?}
J -->|是| K[模型部署]
J -->|否| L[调整超参数/策略]
L --> D
K --> M[持续监控与优化]
2. 提示词工程深度解析
2.1 提示词设计原则
提示词工程是通过精心设计输入文本来引导大模型生成期望输出的技术。以下是核心设计原则:
python
# 提示词模板管理类
class PromptTemplate:
def __init__(self):
self.templates = {
"classification": """
请对以下文本进行分类:
文本:{text}
分类选项:{options}
请只返回分类结果:
""",
"summarization": """
请总结以下文本的主要内容:
{text}
总结要求:
1. 不超过{max_length}字
2. 涵盖核心观点
3. 语言简洁明了
总结:
""",
"code_generation": """
请根据以下需求生成{language}代码:
需求:{requirement}
要求:
1. 添加必要的注释
2. 遵循{style_guide}编码规范
3. 包含错误处理
代码:
"""
}
def format_prompt(self, template_name, **kwargs):
template = self.templates.get(template_name)
if not template:
raise ValueError(f"模板 {template_name} 不存在")
return template.format(**kwargs)
# 使用示例
prompt_manager = PromptTemplate()
classification_prompt = prompt_manager.format_prompt(
"classification",
text="这部电影的视觉效果很棒,但剧情有些拖沓",
options=["正面", "负面", "中性"]
)
2.2 复杂推理提示词设计
对于需要多步推理的任务,Chain-of-Thought(思维链)提示极为有效:
python
# 复杂推理提示词示例
complex_reasoning_prompt = """
请逐步推理解决以下数学问题:
问题:一个水池有两个进水管。A管单独注满水池需要6小时,B管单独注满需要4小时。如果两管同时开放,需要多少小时注满水池?
让我们一步步思考:
1. 首先确定A管的注水效率:A管每小时注满水池的1/6
2. 然后确定B管的注水效率:B管每小时注满水池的1/4
3. 两管同时开放的合并效率:1/6 + 1/4 = 2/12 + 3/12 = 5/12
4. 注满所需时间是效率的倒数:1 ÷ (5/12) = 12/5 = 2.4小时
所以答案是:2.4小时
现在请解决这个问题:
问题:{user_question}
让我们一步步思考:
"""
# 少样本学习提示词
few_shot_prompt = """
请根据示例进行文本情感分析:
示例1:
文本:这家餐厅的服务非常周到,食物也很美味。
情感:正面
示例2:
文本:产品质量很差,完全不值这个价格。
情感:负面
示例3:
文本:快递送货很快,但包装有些破损。
情感:中性
现在请分析:
文本:{target_text}
情感:
"""
2.3 提示词优化流程
python
import openai
from typing import List, Dict
class PromptOptimizer:
def __init__(self, api_key):
self.client = openai.OpenAI(api_key=api_key)
def evaluate_prompt(self, prompt: str, test_cases: List[Dict]) -> float:
"""评估提示词效果"""
scores = []
for case in test_cases:
response = self.generate_response(prompt, case["input"])
score = self.calculate_similarity(response, case["expected_output"])
scores.append(score)
return sum(scores) / len(scores)
def generate_variations(self, base_prompt: str, num_variations: int = 5) -> List[str]:
"""生成提示词变体"""
variation_prompt = f"""
请为以下提示词生成{num_variations}个变体,保持相同任务目标但使用不同的表达方式:
原提示词:{base_prompt}
请返回变体列表:
"""
response = self.client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": variation_prompt}]
)
return self.parse_variations(response.choices[0].message.content)
def optimize_prompt(self, initial_prompt: str, test_cases: List[Dict], iterations: int = 3) -> str:
"""迭代优化提示词"""
best_prompt = initial_prompt
best_score = self.evaluate_prompt(initial_prompt, test_cases)
for i in range(iterations):
variations = self.generate_variations(best_prompt)
for variation in variations:
score = self.evaluate_prompt(variation, test_cases)
if score > best_score:
best_score = score
best_prompt = variation
print(f"迭代 {i+1}: 最佳分数 {best_score}")
return best_prompt
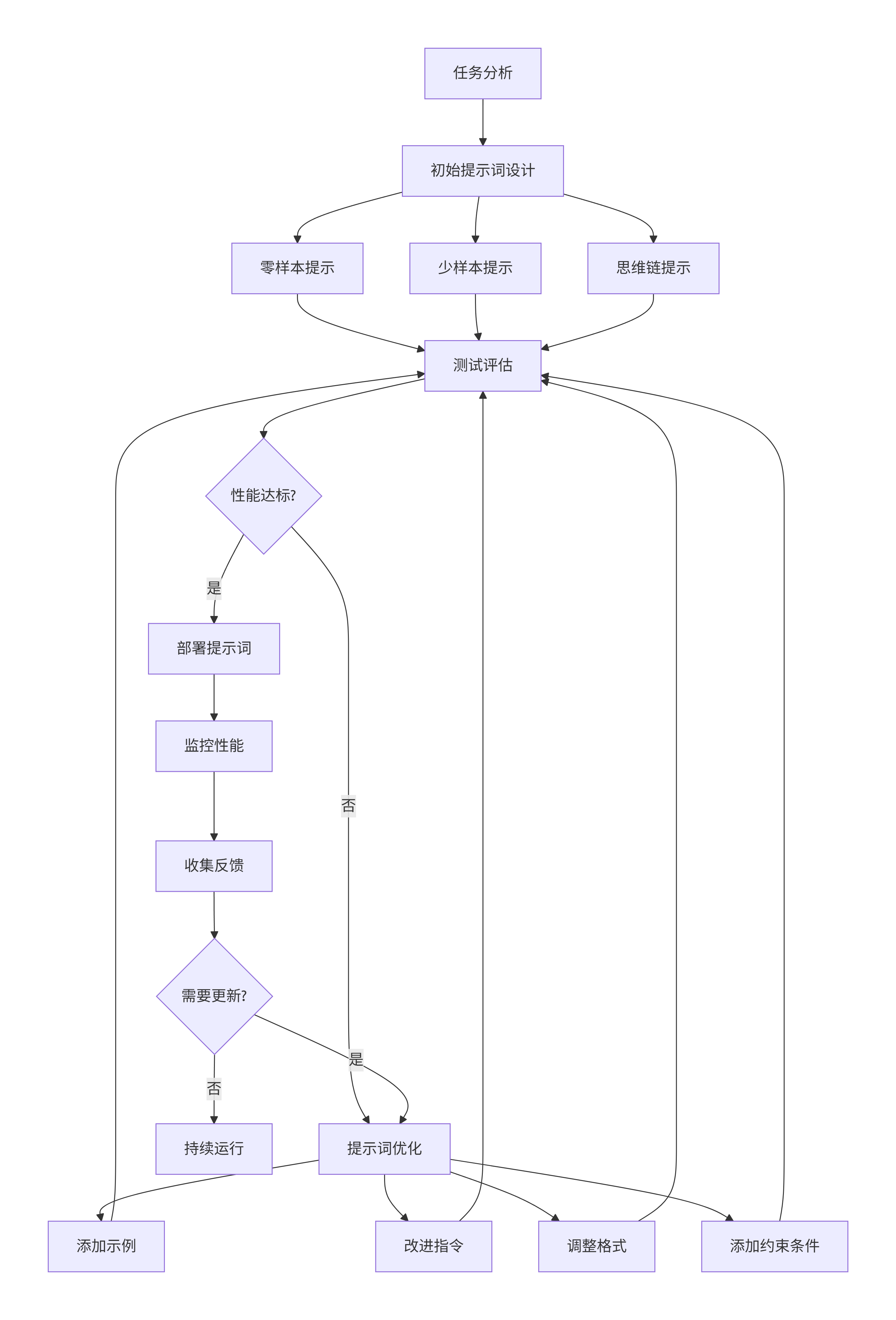
2.4 提示词工程Mermaid流程图
flowchart TD
A[任务分析] --> B[初始提示词设计]
B --> C[零样本提示]
B --> D[少样本提示]
B --> E[思维链提示]
C --> F[测试评估]
D --> F
E --> F
F --> G{性能达标?}
G -->|是| H[部署提示词]
G -->|否| I[提示词优化]
I --> J[添加示例]
I --> K[改进指令]
I --> L[调整格式]
I --> M[添加约束条件]
J --> F
K --> F
L --> F
M --> F
H --> N[监控性能]
N --> O[收集反馈]
O --> P{需要更新?}
P -->|是| I
P -->|否| Q[持续运行]
3. 多模态应用开发
3.1 多模态模型架构
多模态大模型能够同时处理和理解文本、图像、音频等多种类型的数据。
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from transformers import (
AutoTokenizer, AutoModel,
CLIPModel, CLIPProcessor,
BlipProcessor, BlipForConditionalGeneration
)
from PIL import Image
import requests
class MultimodalAssistant:
def __init__(self):
# 初始化CLIP模型用于图像-文本匹配
self.clip_model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
self.clip_processor = CLIPProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
# 初始化BLIP模型用于图像描述
self.blip_processor = BlipProcessor.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip-image-captioning-base")
self.blip_model = BlipForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip-image-captioning-base")
# 初始化文本模型
self.text_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("gpt2")
self.text_model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("gpt2")
def image_text_similarity(self, image_path, text_descriptions):
"""计算图像与文本描述的相似度"""
image = Image.open(image_path)
inputs = self.clip_processor(
text=text_descriptions,
images=image,
return_tensors="pt",
padding=True
)
outputs = self.clip_model(**inputs)
logits_per_image = outputs.logits_per_image
probs = logits_per_image.softmax(dim=1)
return {desc: prob.item() for desc, prob in zip(text_descriptions, probs[0])}
def generate_image_caption(self, image_path):
"""为图像生成描述"""
image = Image.open(image_path)
inputs = self.blip_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
out = self.blip_model.generate(**inputs)
caption = self.blip_processor.decode(out[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
return caption
def multimodal_qa(self, image_path, question):
"""多模态问答"""
# 首先生成图像描述
caption = self.generate_image_caption(image_path)
# 结合描述和问题生成答案
prompt = f"""
基于以下图像描述回答问题:
图像描述:{caption}
问题:{question}
请根据图像描述提供准确的答案:
"""
# 这里可以接入文本生成模型
return self.generate_text_response(prompt)
3.2 视觉语言模型实战
python
import numpy as np
import cv2
from transformers import ViltProcessor, ViltForQuestionAnswering
class VisualQuestionAnswering:
def __init__(self):
self.processor = ViltProcessor.from_pretrained("dandelin/vilt-b32-finetuned-vqa")
self.model = ViltForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained("dandelin/vilt-b32-finetuned-vqa")
def answer_question(self, image_path, question):
"""视觉问答"""
image = Image.open(image_path)
# 准备输入
encoding = self.processor(image, question, return_tensors="pt")
# 推理
outputs = self.model(**encoding)
logits = outputs.logits
idx = logits.argmax(-1).item()
answer = self.model.config.id2label[idx]
return answer
def analyze_image_scene(self, image_path):
"""综合分析图像场景"""
image = Image.open(image_path)
questions = [
"这是什么场景?",
"图像中主要的颜色是什么?",
"图像中有多少人?",
"这是什么时间拍摄的?",
"天气怎么样?"
]
analysis = {}
for question in questions:
answer = self.answer_question(image_path, question)
analysis[question] = answer
return analysis
# 使用示例
vqa_system = VisualQuestionAnswering()
image_path = "sample.jpg"
analysis = vqa_system.analyze_image_scene(image_path)
for question, answer in analysis.items():
print(f"问题: {question}")
print(f"回答: {answer}\n")
3.3 多模态数据处理流水线
python
import pandas as pd
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import List, Dict, Any
import base64
from io import BytesIO
@dataclass
class MultimodalData:
text: str = None
image: Image.Image = None
audio: np.ndarray = None
metadata: Dict[str, Any] = None
class MultimodalDataProcessor:
def __init__(self):
self.text_processor = TextProcessor()
self.image_processor = ImageProcessor()
self.audio_processor = AudioProcessor()
def process_batch(self, data_batch: List[MultimodalData]):
"""批量处理多模态数据"""
processed_batch = []
for data in data_batch:
processed_data = {}
if data.text:
processed_data['text_features'] = self.text_processor.process(data.text)
if data.image:
processed_data['image_features'] = self.image_processor.process(data.image)
if data.audio:
processed_data['audio_features'] = self.audio_processor.process(data.audio)
if data.metadata:
processed_data['metadata'] = data.metadata
processed_batch.append(processed_data)
return processed_batch
def align_modalities(self, processed_data):
"""对齐不同模态的特征"""
# 这里实现特征对齐逻辑
aligned_features = {}
if 'text_features' in processed_data and 'image_features' in processed_data:
# 对齐文本和图像特征
aligned_features['text_image'] = self._align_text_image(
processed_data['text_features'],
processed_data['image_features']
)
return aligned_features
class TextProcessor:
def process(self, text):
"""处理文本数据"""
# 文本清洗、分词、向量化等
return {
'tokens': self.tokenize(text),
'embeddings': self.get_embeddings(text),
'length': len(text)
}
class ImageProcessor:
def process(self, image):
"""处理图像数据"""
# 图像预处理、特征提取等
return {
'features': self.extract_features(image),
'size': image.size,
'format': image.format
}
3.4 多模态应用Mermaid架构图
graph TB
A[多模态输入] --> B[数据预处理]
B --> C[文本处理模块]
B --> D[图像处理模块]
B --> E[音频处理模块]
B --> F[视频处理模块]
C --> G[文本特征提取]
D --> H[视觉特征提取]
E --> I[音频特征提取]
F --> J[时序特征提取]
G --> K[多模态融合层]
H --> K
I --> K
J --> K
K --> L[跨模态注意力机制]
L --> M[任务特定头]
M --> N[文本生成]
M --> O[分类决策]
M --> P[检索匹配]
M --> Q[生成式任务]
N --> R[输出整合]
O --> R
P --> R
Q --> R
R --> S[多模态输出]
T[评估反馈] --> U[模型优化]
U --> G
U --> H
U --> I
U --> J
4. 企业级解决方案
4.1 企业级大模型架构设计
python
import os
import json
import redis
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Dict, List, Optional
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, BackgroundTasks
from pydantic import BaseModel
import uvicorn
from prometheus_client import Counter, Histogram, generate_latest
import logging
# 定义数据模型
class ChatRequest(BaseModel):
message: str
conversation_id: Optional[str] = None
user_id: str
model_config: Dict = {}
class ChatResponse(BaseModel):
response: str
conversation_id: str
timestamp: str
model_used: str
class EnterpriseLLMSolution:
def __init__(self):
self.app = FastAPI(title="企业级大模型服务平台")
self.redis_client = redis.Redis(
host=os.getenv('REDIS_HOST', 'localhost'),
port=int(os.getenv('REDIS_PORT', 6379)),
decode_responses=True
)
# 监控指标
self.request_counter = Counter('llm_requests_total', 'Total LLM requests', ['model', 'status'])
self.response_time = Histogram('llm_response_time_seconds', 'LLM response time')
self.setup_routes()
self.load_models()
def setup_routes(self):
"""设置API路由"""
@self.app.post("/chat", response_model=ChatResponse)
async def chat_endpoint(request: ChatRequest, background_tasks: BackgroundTasks):
start_time = datetime.now()
try:
response = await self.process_chat(request)
# 记录成功请求
self.request_counter.labels(
model=response.model_used,
status='success'
).inc()
return response
except Exception as e:
# 记录失败请求
self.request_counter.labels(
model=request.model_config.get('model', 'unknown'),
status='error'
).inc()
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
finally:
# 记录响应时间
processing_time = (datetime.now() - start_time).total_seconds()
self.response_time.observe(processing_time)
@self.app.get("/metrics")
async def metrics_endpoint():
return generate_latest()
@self.app.get("/health")
async def health_check():
return {"status": "healthy", "timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat()}
async def process_chat(self, request: ChatRequest) -> ChatResponse:
"""处理聊天请求"""
# 获取或创建会话ID
conversation_id = request.conversation_id or self.generate_conversation_id()
# 保存用户消息
self.save_conversation_turn(conversation_id, "user", request.message)
# 选择模型
model = self.select_model(request.model_config)
# 生成回复
response_text = await model.generate_response(
request.message,
self.get_conversation_history(conversation_id)
)
# 保存助手回复
self.save_conversation_turn(conversation_id, "assistant", response_text)
return ChatResponse(
response=response_text,
conversation_id=conversation_id,
timestamp=datetime.now().isoformat(),
model_used=model.name
)
def save_conversation_turn(self, conversation_id: str, role: str, content: str):
"""保存对话记录"""
turn_data = {
"role": role,
"content": content,
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat()
}
self.redis_client.rpush(
f"conversation:{conversation_id}",
json.dumps(turn_data)
)
# 设置过期时间(例如7天)
self.redis_client.expire(f"conversation:{conversation_id}", 7*24*3600)
# 启动服务
if __name__ == "__main__":
solution = EnterpriseLLMSolution()
uvicorn.run(solution.app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
4.2 模型管理与部署系统
python
import docker
import yaml
from kubernetes import client, config
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
import asyncio
class ModelManager:
def __init__(self):
self.load_k8s_config()
self.docker_client = docker.from_env()
def load_k8s_config(self):
"""加载Kubernetes配置"""
try:
config.load_incluster_config()
except config.ConfigException:
config.load_kube_config()
self.k8s_apps_v1 = client.AppsV1Api()
self.k8s_core_v1 = client.CoreV1Api()
def deploy_model(self, model_config: Dict) -> str:
"""部署模型服务"""
# 创建Docker镜像
image_name = self.build_model_image(model_config)
# 创建Kubernetes部署
deployment = self.create_deployment_manifest(model_config, image_name)
service = self.create_service_manifest(model_config)
# 应用部署
self.k8s_apps_v1.create_namespaced_deployment(
body=deployment,
namespace="llm-models"
)
self.k8s_core_v1.create_namespaced_service(
body=service,
namespace="llm-models"
)
return f"{model_config['name']}-deployed"
def build_model_image(self, model_config: Dict) -> str:
"""构建模型Docker镜像"""
dockerfile = f"""
FROM pytorch/pytorch:2.0.1-cuda11.7-cudnn8-runtime
WORKDIR /app
# 安装依赖
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
# 复制模型文件
COPY models/ ./models/
COPY app.py .
# 暴露端口
EXPOSE 8000
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
"""
# 构建镜像
image, logs = self.docker_client.images.build(
fileobj=dockerfile.encode('utf-8'),
tag=f"llm-model-{model_config['name']}:latest",
rm=True
)
return image.tags[0]
class ModelServingTemplate:
"""模型服务模板"""
@staticmethod
def get_fastapi_template(model_class: str) -> str:
"""生成FastAPI服务模板"""
return f'''
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
import uvicorn
from transformers import pipeline
app = FastAPI()
# 加载模型
model = pipeline("text-generation", model="{model_class}")
class Request(BaseModel):
text: str
max_length: int = 100
class Response(BaseModel):
generated_text: str
@app.post("/generate")
async def generate_text(request: Request):
result = model(request.text, max_length=request.max_length)
return Response(generated_text=result[0]["generated_text"])
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
'''
class AutoScalingManager:
"""自动扩缩容管理"""
def __init__(self):
self.metrics_server = "http://prometheus:9090"
async def check_scaling_need(self, deployment_name: str) -> bool:
"""检查是否需要扩缩容"""
# 获取当前指标
cpu_usage = await self.get_cpu_usage(deployment_name)
memory_usage = await self.get_memory_usage(deployment_name)
request_rate = await self.get_request_rate(deployment_name)
# 扩缩容决策逻辑
if (cpu_usage > 80 or memory_usage > 80 or request_rate > 1000):
return True
elif (cpu_usage < 20 and memory_usage < 20 and request_rate < 100):
return False
return None
async def scale_deployment(self, deployment_name: str, replicas: int):
"""执行扩缩容"""
patch = {
"spec": {
"replicas": replicas
}
}
apps_v1 = client.AppsV1Api()
apps_v1.patch_namespaced_deployment_scale(
name=deployment_name,
namespace="llm-models",
body=patch
)
4.3 安全与权限管理
python
from jose import JWTError, jwt
from passlib.context import CryptContext
from fastapi.security import HTTPBearer, HTTPAuthorizationCredentials
from fastapi import Depends, HTTPException, status
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import secrets
class SecurityManager:
def __init__(self):
self.pwd_context = CryptContext(schemes=["bcrypt"], deprecated="auto")
self.security = HTTPBearer()
self.SECRET_KEY = os.getenv("SECRET_KEY", secrets.token_urlsafe(32))
self.ALGORITHM = "HS256"
self.ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES = 30
def verify_password(self, plain_password, hashed_password):
return self.pwd_context.verify(plain_password, hashed_password)
def get_password_hash(self, password):
return self.pwd_context.hash(password)
def create_access_token(self, data: dict, expires_delta: timedelta = None):
to_encode = data.copy()
if expires_delta:
expire = datetime.utcnow() + expires_delta
else:
expire = datetime.utcnow() + timedelta(minutes=15)
to_encode.update({"exp": expire})
encoded_jwt = jwt.encode(to_encode, self.SECRET_KEY, algorithm=self.ALGORITHM)
return encoded_jwt
async def get_current_user(self, credentials: HTTPAuthorizationCredentials = Depends(HTTPBearer())):
credentials_exception = HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
detail="Could not validate credentials",
headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
)
try:
payload = jwt.decode(credentials.credentials, self.SECRET_KEY, algorithms=[self.ALGORITHM])
username: str = payload.get("sub")
if username is None:
raise credentials_exception
except JWTError:
raise credentials_exception
user = self.get_user(username)
if user is None:
raise credentials_exception
return user
class RateLimiter:
"""速率限制器"""
def __init__(self, redis_client, max_requests: int = 100, window_seconds: int = 3600):
self.redis = redis_client
self.max_requests = max_requests
self.window = window_seconds
async def is_rate_limited(self, user_id: str, endpoint: str) -> bool:
key = f"rate_limit:{user_id}:{endpoint}"
current = self.redis.get(key)
if current and int(current) >= self.max_requests:
return True
pipeline = self.redis.pipeline()
pipeline.incr(key, 1)
pipeline.expire(key, self.window)
pipeline.execute()
return False
class ContentFilter:
"""内容过滤器"""
def __init__(self):
self.sensitive_words = self.load_sensitive_words()
def filter_text(self, text: str) -> tuple[str, bool]:
"""过滤敏感内容"""
contains_sensitive = False
filtered_text = text
for word in self.sensitive_words:
if word in text.lower():
filtered_text = filtered_text.replace(word, "*" * len(word))
contains_sensitive = True
return filtered_text, contains_sensitive
def load_sensitive_words(self) -> list:
"""加载敏感词库"""
# 可以从文件或数据库加载
return ["敏感词1", "敏感词2", "违规内容"]
4.4 企业级解决方案Mermaid架构图
graph TB
A[客户端 Web/Mobile/API] --> B[负载均衡器]
B --> C[API网关]
C --> D[身份认证]
C --> E[速率限制]
C --> F[请求路由]
F --> G[业务逻辑层]
G --> H[会话管理]
G --> I[内容审核]
G --> J[计费计量]
H --> K[模型调度层]
I --> K
J --> K
K --> L[模型服务A]
K --> M[模型服务B]
K --> N[模型服务C]
L --> O[GPU集群1]
M --> P[GPU集群2]
N --> Q[GPU集群3]
R[监控系统] --> S[日志收集]
R --> T[性能指标]
R --> U[业务指标]
S --> V[中央日志]
T --> W[指标数据库]
U --> X[业务数据库]
Y[配置中心] --> Z[动态配置]
AA[注册中心] --> BB[服务发现]
CC[安全管理] --> DD[访问控制]
CC --> EE[数据加密]
CC --> FF[合规审计]
GG[CI/CD流水线] --> HH[自动部署]
GG --> II[版本管理]
GG --> JJ[回滚机制]

5. 性能优化与监控
5.1 模型推理优化
python
import torch
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizer
import onnxruntime as ort
import time
from contextlib import contextmanager
class ModelOptimizer:
def __init__(self, model_name: str):
self.model_name = model_name
self.original_model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
def convert_to_onnx(self, output_path: str):
"""转换为ONNX格式"""
dummy_input = self.tokenizer(
"样例文本",
return_tensors="pt",
padding=True,
truncation=True,
max_length=512
)
torch.onnx.export(
self.original_model,
tuple(dummy_input.values()),
output_path,
input_names=['input_ids', 'attention_mask'],
output_names=['logits'],
dynamic_axes={
'input_ids': {0: 'batch_size', 1: 'sequence_length'},
'attention_mask': {0: 'batch_size', 1: 'sequence_length'},
'logits': {0: 'batch_size'}
},
opset_version=13
)
def quantize_model(self, model_path: str):
"""模型量化"""
# 动态量化
quantized_model = torch.quantization.quantize_dynamic(
self.original_model,
{torch.nn.Linear},
dtype=torch.qint8
)
return quantized_model
def optimize_with_tensorrt(self, onnx_path: str, trt_path: str):
"""使用TensorRT优化"""
import tensorrt as trt
logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
builder = trt.Builder(logger)
network = builder.create_network(1 << int(trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH))
parser = trt.OnnxParser(network, logger)
with open(onnx_path, 'rb') as model:
if not parser.parse(model.read()):
for error in range(parser.num_errors):
print(parser.get_error(error))
config = builder.create_builder_config()
config.set_memory_pool_limit(trt.MemoryPoolType.WORKSPACE, 1 << 30)
serialized_engine = builder.build_serialized_network(network, config)
with open(trt_path, 'wb') as f:
f.write(serialized_engine)
class PerformanceMonitor:
def __init__(self):
self.metrics = {
'inference_time': [],
'memory_usage': [],
'throughput': []
}
@contextmanager
def track_inference(self):
"""跟踪推理性能"""
start_time = time.time()
start_memory = torch.cuda.memory_allocated() if torch.cuda.is_available() else 0
try:
yield
finally:
end_time = time.time()
end_memory = torch.cuda.memory_allocated() if torch.cuda.is_available() else 0
inference_time = end_time - start_time
memory_used = end_memory - start_memory
self.metrics['inference_time'].append(inference_time)
self.metrics['memory_usage'].append(memory_used)
def get_performance_report(self) -> dict:
"""生成性能报告"""
return {
'avg_inference_time': sum(self.metrics['inference_time']) / len(self.metrics['inference_time']),
'max_inference_time': max(self.metrics['inference_time']),
'min_inference_time': min(self.metrics['inference_time']),
'avg_memory_usage': sum(self.metrics['memory_usage']) / len(self.metrics['memory_usage']),
'total_inferences': len(self.metrics['inference_time'])
}
5.2 缓存与批处理系统
python
from functools import lru_cache
from threading import Lock
import threading
import queue
import time
class InferenceBatcher:
def __init__(self, model, max_batch_size: int = 32, max_wait_time: float = 0.1):
self.model = model
self.max_batch_size = max_batch_size
self.max_wait_time = max_wait_time
self.batch_queue = queue.Queue()
self.results = {}
self.lock = Lock()
self.batch_counter = 0
# 启动批处理线程
self.batch_thread = threading.Thread(target=self._process_batches, daemon=True)
self.batch_thread.start()
def infer(self, input_data):
"""异步推理接口"""
batch_id = self.batch_counter
self.batch_counter += 1
future = FutureResult()
with self.lock:
self.results[batch_id] = future
self.batch_queue.put((batch_id, input_data, time.time()))
return future
def _process_batches(self):
"""批处理线程"""
current_batch = []
batch_ids = []
last_batch_time = time.time()
while True:
try:
# 获取新请求,最多等待max_wait_time
item = self.batch_queue.get(timeout=self.max_wait_time)
batch_id, input_data, arrival_time = item
current_batch.append(input_data)
batch_ids.append(batch_id)
except queue.Empty:
item = None
# 检查是否应该处理当前批次
should_process = (
len(current_batch) >= self.max_batch_size or
(item is None and len(current_batch) > 0) or
(time.time() - last_batch_time) >= self.max_wait_time
)
if should_process and len(current_batch) > 0:
# 处理批次
try:
batch_results = self.model(current_batch)
# 分发结果
for batch_id, result in zip(batch_ids, batch_results):
if batch_id in self.results:
self.results[batch_id].set_result(result)
del self.results[batch_id]
except Exception as e:
# 处理错误
for batch_id in batch_ids:
if batch_id in self.results:
self.results[batch_id].set_exception(e)
del self.results[batch_id]
# 重置批次
current_batch = []
batch_ids = []
last_batch_time = time.time()
class FutureResult:
"""异步结果容器"""
def __init__(self):
self._result = None
self._exception = None
self._event = threading.Event()
def set_result(self, result):
self._result = result
self._event.set()
def set_exception(self, exception):
self._exception = exception
self._event.set()
def result(self, timeout=None):
if not self._event.wait(timeout):
raise TimeoutError("等待结果超时")
if self._exception:
raise self._exception
return self._result
class ResponseCache:
"""响应缓存"""
def __init__(self, max_size: int = 10000, ttl: int = 3600):
self.cache = {}
self.max_size = max_size
self.ttl = ttl
self.access_order = []
self.lock = Lock()
def get(self, key: str):
"""获取缓存值"""
with self.lock:
if key in self.cache:
entry = self.cache[key]
if time.time() - entry['timestamp'] < self.ttl:
# 更新访问顺序
self.access_order.remove(key)
self.access_order.append(key)
return entry['value']
else:
# 删除过期条目
del self.cache[key]
self.access_order.remove(key)
return None
def set(self, key: str, value):
"""设置缓存值"""
with self.lock:
# 如果缓存已满,删除最久未使用的条目
if len(self.cache) >= self.max_size and key not in self.cache:
oldest_key = self.access_order.pop(0)
del self.cache[oldest_key]
self.cache[key] = {
'value': value,
'timestamp': time.time()
}
self.access_order.append(key)
def generate_cache_key(self, prompt: str, model_config: dict) -> str:
"""生成缓存键"""
import hashlib
key_data = prompt + str(sorted(model_config.items()))
return hashlib.md5(key_data.encode()).hexdigest()
总结
大模型落地是一个系统工程,涉及从模型微调、提示词工程、多模态应用到企业级解决方案的完整链条。本文详细介绍了各个环节的技术实现和最佳实践:
-
模型微调:介绍了全参数微调、LoRA等参数高效微调方法,提供了完整的代码示例
-
提示词工程:系统阐述了提示词设计原则、优化方法和评估体系
-
多模态应用:展示了视觉语言模型的集成方法和数据处理流水线
-
企业级解决方案:提供了完整的架构设计、安全管理和部署方案
成功的大模型落地需要综合考虑技术可行性、业务需求、资源约束和运营成本。通过本文介绍的方法和工具,企业可以构建稳定、高效、安全的大模型应用系统,真正发挥大模型在业务场景中的价值。
随着技术的不断发展,大模型落地将变得更加简单和高效,但核心的工程原则和架构设计思想将长期适用。希望本文能为读者在大模型落地实践中提供有价值的参考和指导。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献173条内容
已为社区贡献173条内容






所有评论(0)