[NN 2025]Multi-modal cross-domain self-supervised pre-training for fMRI and EEG fusion
计算机-人工智能-EEG和fMRI结合的跨域跨模态预训练精神疾病分类
论文网址:Multi-modal cross-domain self-supervised pre-training for fMRI and EEG fusion - ScienceDirect
目录
2.3.1. Deep learning for brain networks learning
2.3.2. Multi-modal fusion for neuroimaging integration
2.3.3. Self-supervised pre-training and multi-domain fusion
2.4.2. Domain-specific data construction
2.4.3. Domain-specific encoders and projectors
2.4.4. Cross-domain self-supervised loss
2.4.5. Cross-modal self-supervised loss
2.4.6. Cross-model distillation across domains
2.5. Data acquisition and preprocessing
2.5.2. Unified pre-training dataset construction
2.6.2. Justification of hyperparameters setting
2.6.3. Criteria of nodes/edges selection for fMRI/EEG graph construction
2.6.4. Overall comparison with other methods
2.6.5. Sensitivity analysis of domain-specific augmentation strategies
2.6.6. Ablation analysis of cross domains and modalities
2.6.7. Brain biomarker interpretation
2.6.8. Ablation study on the proposed self-supervised loss
2.6.9. Analysis of the potential universal pre-training abilities
2.6.10. Cross-model knowledge distillation across domains
2.6.11. Comparison among the parameters of different models
2.6.12. Analysis of computational complexity, efficiency and effectiveness
2.7. Explanation for our model architecture
2.8. Discussion on real-world clinical applicability and model interpretability
2.9. Limitations and future works
1. 心得
(1)作者脑回路和我不一样,使得我读起来有点艰难
(2)论文挺长的,实验ok,后面讲了一堆优势局限啥的感觉其实没必要
(3)根据不同模态选择不同训练方法
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①提出多模态跨域自监督预训练模型(Multi-modal Cross-domain Self-supervised Pre-training Model,MCSP)去同时提取fMRI和EEG的特征
2.2. Introduction
①EEG和fMRI可以实现时间和空间的互补
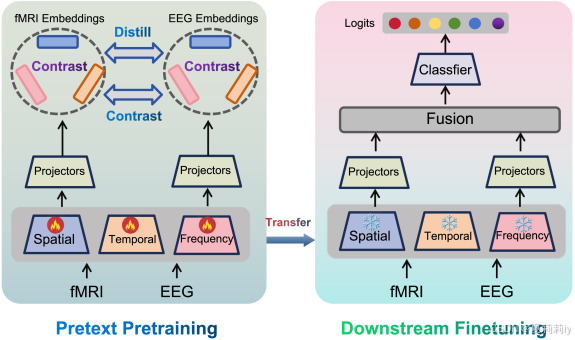
②MCSP模型的整体预训练和微调范式:
2.3. Related works
2.3.1. Deep learning for brain networks learning
①介绍一些EEG或fMRI精神疾病诊断的模型
2.3.2. Multi-modal fusion for neuroimaging integration
①介绍了各种各样多模态融合精神疾病检测
2.3.3. Self-supervised pre-training and multi-domain fusion
①介绍一些自监督模型
2.4. Methodology
2.4.1. Overall architecture
①MCSP的框架:
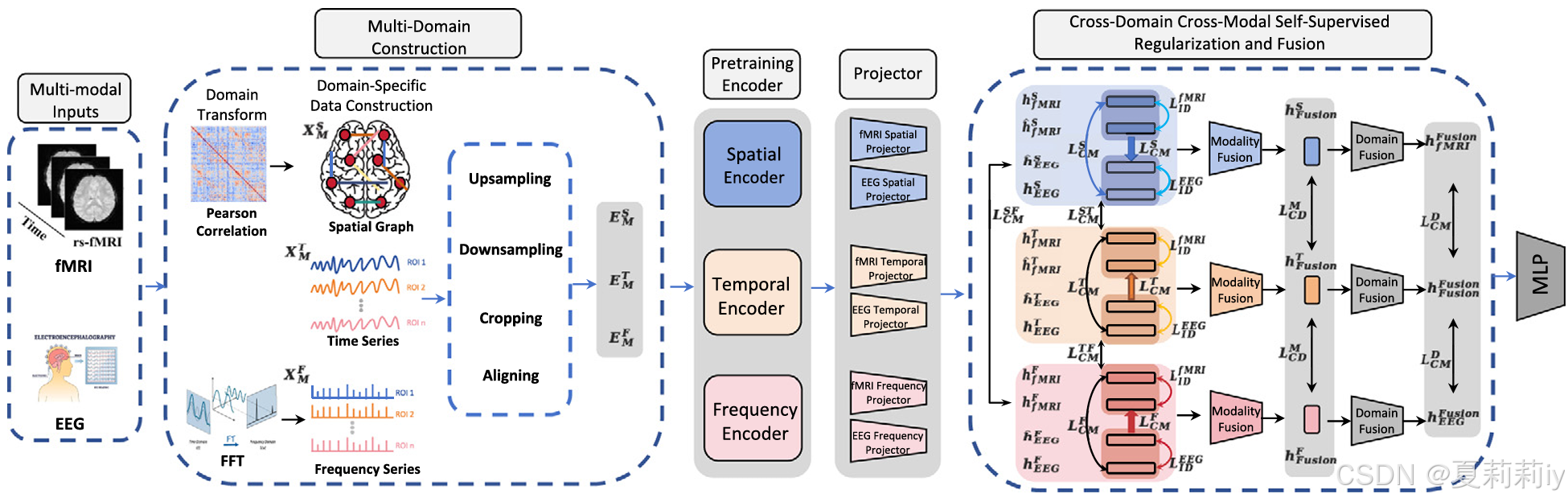
2.4.2. Domain-specific data construction
①fMRI FC构建方法:皮尔逊相关 “For fMRI, following Li et al. (2021), we construct functional connectome (FC) using the Pearson Correlation Coefficients as node features and adopt the correlation as edge connections.”(这句话写的...皮尔逊同时是节点特征和边缘连接吗)
②EEG节点特征:Power Envelope Coefficients,同样的相关性被当作边缘连接(...)
③fMRI时间序列都被“标准化”(emm这个描述,就不能讲讲具体的做法吗比如裁剪)成,其中
,
④脑电序列被下采样(说的这么高端...)为,其中
。然后把脑电序列竖着砍成125个段
让其与fMRI齐平
⑤对于频域序列的fMRI上采样和下采样获得均匀的,然后EEG对齐和分割获得
(这里写得太模糊了吧我的天哪)
2.4.3. Domain-specific encoders and projectors
(1)Modality-agnostic domain-specific encoders
①模态无关编码器:Graph Transformer:
其中是模态,
表示域,
表示用于三个域的编码器,
在空间域中表示节点数在时域和频域中表示ROI的数量,
是时域和频域的长度
(2)Modality-aware projection heads
①投影层:
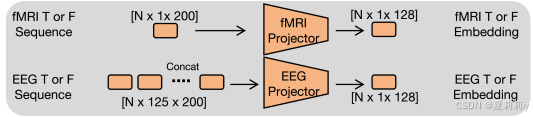
此时被分开的脑电切片又要全部连上再送进投影仪
2.4.4. Cross-domain self-supervised loss
①域内交叉视图一致性损失和跨域一致性损失
:
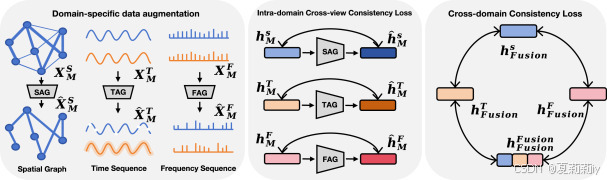
②对三个域的增强:
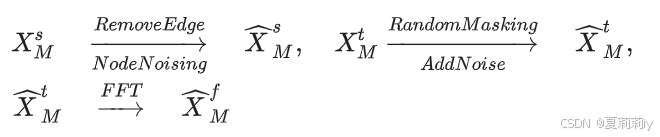
③把增强后的域特征投入域编码器和投影器之后得到(好混乱啊这里),对增强前后同域视图使用对比损失:
其中
④跨域一致性损失:
⑤总损失:
2.4.5. Cross-modal self-supervised loss
①跨模态自监督损失CM-SSL由域内跨模态蒸馏损失和跨模态一致性损失
组成:
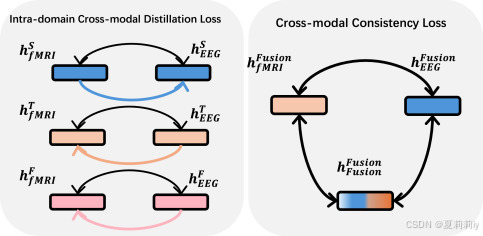
②不同域同样本损失:
③整体分布正则化:
④总损失:
作者把设置为0.8
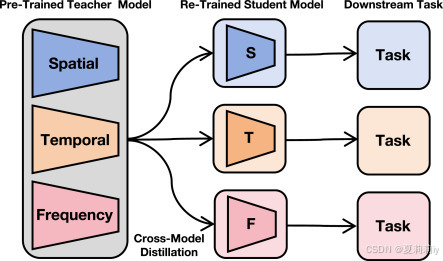
2.4.6. Cross-model distillation across domains
①下游分类损失:交叉熵
②蒸馏软损失和硬损失:
其中是领域融合教师模型(为什么要写
又不解释,只说
),
是单一域候选学生模型
③跨域预训练的跨模型蒸馏概念:
2.5. Data acquisition and preprocessing
2.5.1. Datasets
①数据集:ADHD-200,ABIDE I,ABIDE II,EMBARC,HBN
②统计数据:
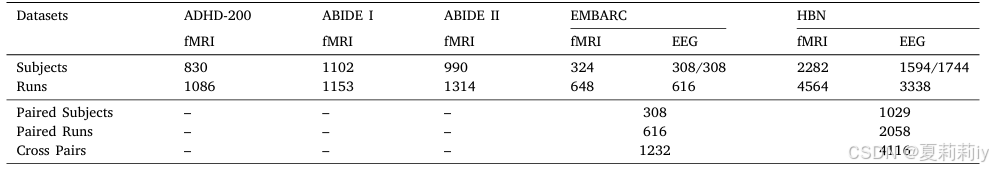
2.5.2. Unified pre-training dataset construction
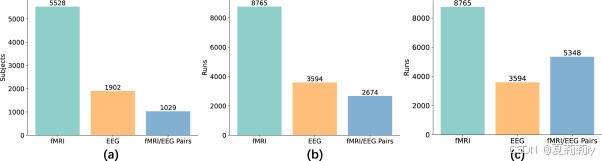
①EMBARC和HBN数据集每个人都采集了两次配对数据,即fMRI匹配睁眼/闭眼EEG。作者为了扩充数据进行交叉匹配得到四组数据
②(a)样本数量;(b)运行次数;(c)交叉匹配后的运行次数:
2.5.3. Data preprocessing
①fMRI预处理:fMRIPrep流程,脑模板为Schaefer100
②EEG预处理:utomated artifact rejection pipeline
2.6. Experiments
2.6.1. Implementation details
①设备:Nvidia RTX 4090 GPU
②epoch: 400 for pretraining, 50 for fine tuning, 80 for training
③学习率:动态,优化器为Adam
④交叉验证:十折
2.6.2. Justification of hyperparameters setting
①初始学习率:5e-4
②学习策略:余弦退火
③Batch size: 128 for pretraining and 32 for downstream training
2.6.3. Criteria of nodes/edges selection for fMRI/EEG graph construction
①上面写过了
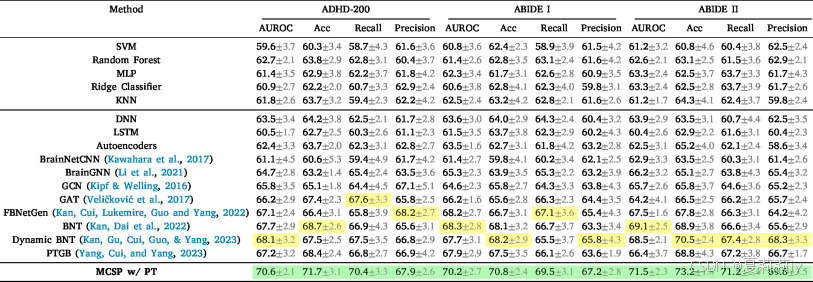
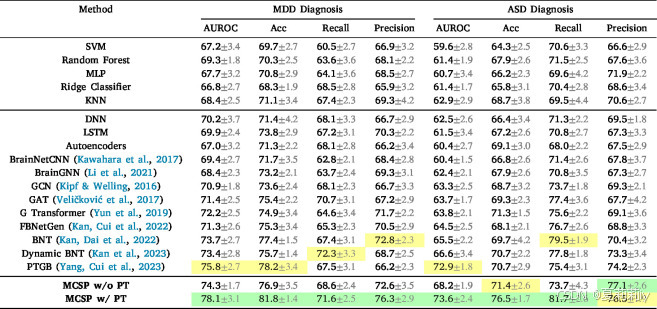
2.6.4. Overall comparison with other methods
①在fMRI数据集上的表现:
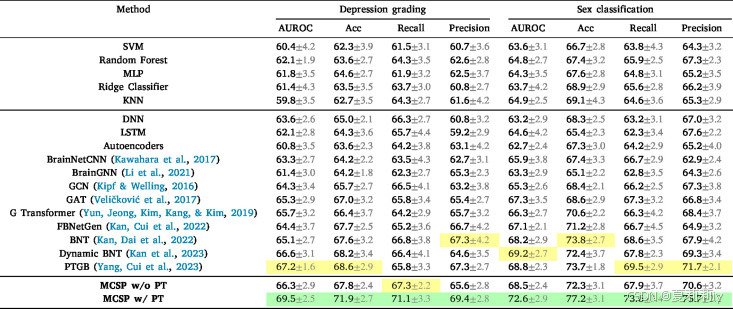
②在多模态数据集EMBARC上的表现:
③在多模态数据集HBN上的表现:
2.6.5. Sensitivity analysis of domain-specific augmentation strategies
①空间领域数据增强:随机节点和边的去除、节点级的噪声注入、边扰动、子图提取和图旋转;时域频域增强:随机移除数据点、序列噪声注入、序列翻转和随机裁剪
②数据增强在HBN上的实验:

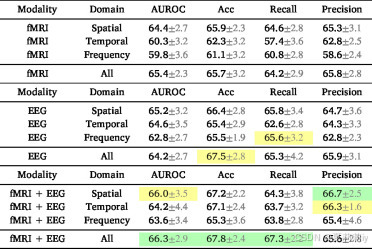
2.6.6. Ablation analysis of cross domains and modalities
①不同域在EMBARC数据集上的消融实验:
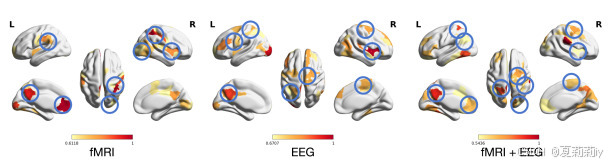
2.6.7. Brain biomarker interpretation
①EMBARC数据集上最重要的十个脑区:
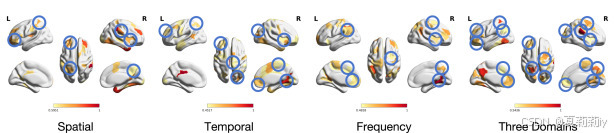
②不同域的重要脑区:
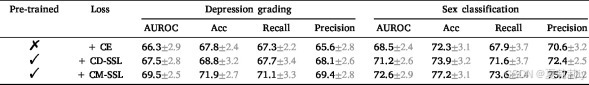
2.6.8. Ablation study on the proposed self-supervised loss
①EMBARC数据集上的损失实验:
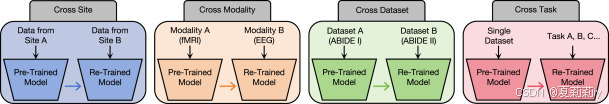
2.6.9. Analysis of the potential universal pre-training abilities
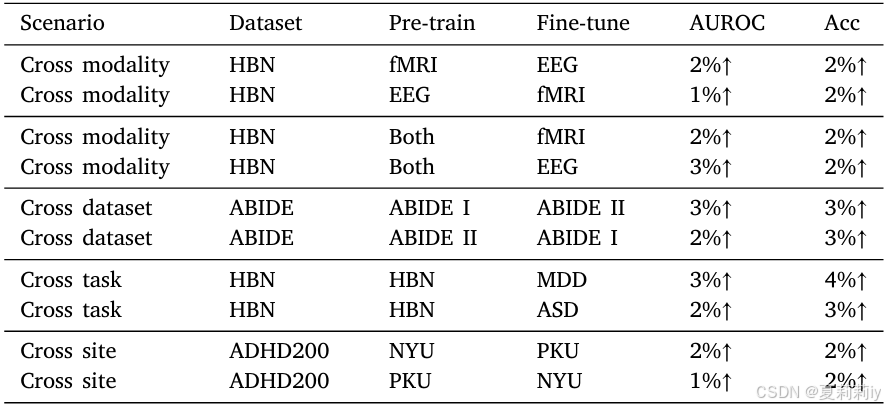
①四种训练模式:
②预训练实验:
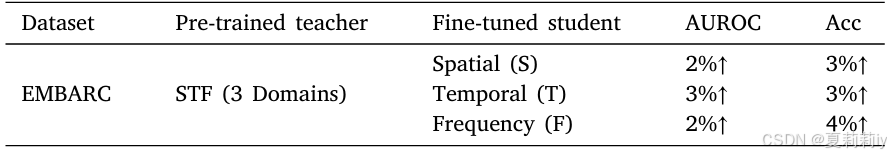
2.6.10. Cross-model knowledge distillation across domains
①知识蒸馏实验:
2.6.11. Comparison among the parameters of different models
①模型性能和参数(圆圈大小):
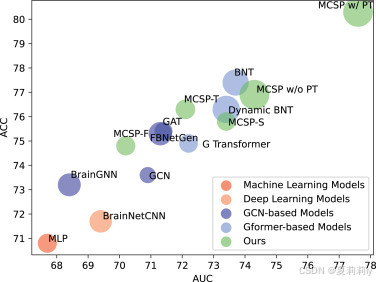
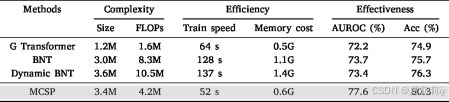
2.6.12. Analysis of computational complexity, efficiency and effectiveness
①参数分析:
2.6.13. Exploring why our method is effective and superior to existing methods and other self-supervised methods
①介绍模型优势
2.7. Explanation for our model architecture
①啊...
2.8. Discussion on real-world clinical applicability and model interpretability
①可以临床使用也有解释性
2.9. Limitations and future works
①局限:超参数选择,收敛问题,样本量少,没有动态学习
2.10. Conclusion
~
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献29条内容
已为社区贡献29条内容






所有评论(0)