【AIE1001】Week9/10: 数据结构与算法
数据结构与算法综合摘要 本文涵盖数据结构与算法基础知识和实现方法。第一部分介绍算法基础概念,包括数据结构定义(组织和访问数据的系统方法)和算法定义(有限时间内执行任务的逐步过程)。重点讲解算法分析技术,提供了运行时间测量代码示例和大O表示法数学定义,比较了7种常见函数的复杂度增长趋势。 第二部分详细实现数据结构,包括: 栈(Stack)及其LIFO原则,实现代码和应用(网页历史、撤销操作) 队列(
·
数据结构与算法综合提纲(附英文原文和代码)
第一部分:算法基础 (Week 9)
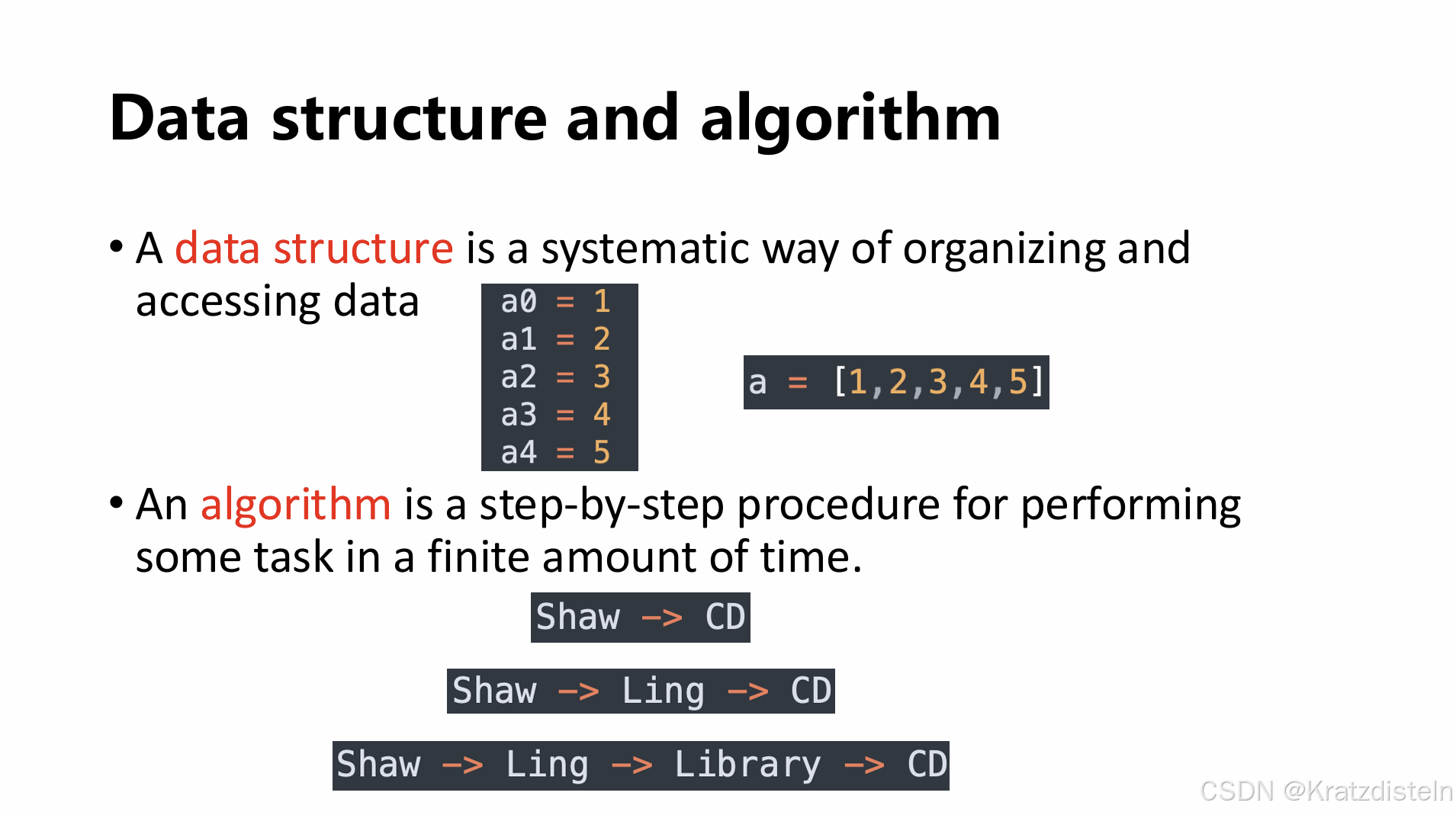
1. 数据结构和算法概述
英文原文:
- “A data structure is a systematic way of organizing and accessing data”(数据结构是组织和访问数据的系统化方法)
- “An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for performing some task in a finite amount of time”(算法是在有限时间内执行某些任务的逐步过程)
示例:
a = [1,2,3,4,5]
Shaw -> CD
Shaw -> Ling -> CD
Shaw -> Ling -> Library -> CD
2. 学习重要性
英文原文:
- “Important for all other branches of computer science”(对计算机科学的所有其他分支都很重要)
- “Plays a key role in modern technological innovation”(在现代技术创新中发挥关键作用)
- “Performance gains due to the improvements in algorithms have greatly exceeded even the dramatic performance gains due to increased processor speed”(由于算法改进带来的性能提升甚至大大超过了由于处理器速度提高带来的显著性能提升)
3. 算法分析基础
运行时间测量代码:
from time import time
startTime = time()
for i in range(1,20000):
if i%10 == 0:
print(i)
endTime = time()
print('The time elapsed is:', endTime - startTime,' seconds')
原始操作定义:
- ✓ Assigning an identifier to an object(为对象分配标识符)
- ✓ Determining the object associated with an identifier(确定与标识符关联的对象)
- ✓ Performing an arithmetic operation(执行算术运算)
- ✓ Comparing two numbers(比较两个数字)
- ✓ Accessing a single element of a Python list by index(通过索引访问Python列表的单个元素)
- ✓ Calling a function(调用函数)
- ✓ Returning from a function(从函数返回)
4. 时间复杂度分析
大O表示法定义:
- “Let f(n) and g(n) be functions mapping positive integers to positive real numbers. We say that f(n) is O(g(n)) if there is a real constant c > 0 and an integer constant n₀ ≥ 1 such that f(n) ≤ cg(n), for n ≥ n₀”(设f(n)和g(n)是将正整数映射到正实数的函数。如果存在实常数c > 0和整数常数n₀ ≥ 1,使得对于n ≥ n₀,f(n) ≤ cg(n),则我们说f(n)是O(g(n)))
7种函数比较:
n log n n n log n n² n³ 2ⁿ
8 3 8 24 64 512 256
16 4 16 64 256 4,096 65,536
第二部分:数据结构实现 (Week 10)
各数据结构知识点详细整理
1. 栈 (Stack)
核心概念英文原文:
- “A stack is a collection of objects that are inserted and removed according to the last-in, first-out (LIFO) principle”(栈是根据后进先出原则插入和移除对象的集合)
- “A user may insert objects into a stack at any time, but may only access or remove the most recently inserted object that remains (at the so-called ‘top’ of the stack)”(用户可以随时将对象插入栈中,但只能访问或移除保留的最远插入的对象(在所谓的栈"顶部"))
应用场景:
- “Internet Web browsers store the addresses of recently visited sites in a stack”(互联网网络浏览器将最近访问的站点地址存储在栈中)
- “Text editors usually provide an ‘undo’ mechanism that cancels recent editing operations”(文本编辑器通常提供"撤销"机制来取消最近的编辑操作)
栈类方法:
S.push(e): Add element e to the top of stack S(将元素e添加到栈S的顶部)S.pop(): Remove and return the top element from the stack S(移除并返回栈S的顶部元素)S.top(): Return a reference to the top element of stack S(返回栈S顶部元素的引用)S.is_empty(): Return True if stack S does not contain any elements(如果栈S不包含任何元素,则返回True)len(S): Return the number of elements in stack S(返回栈S中的元素数量)
基于列表的实现代码:
class ListStack:
def __init__(self):
self.__data = list()
def __len__(self):
return len(self.__data)
def is_empty(self):
return len(self.__data) == 0
def push(self, e):
self.__data.append(e)
def top(self):
if self.is_empty():
print('The stack is empty.')
else:
return self.__data[self.__len__()-1]
def pop(self):
if self.is_empty():
print('The stack is empty.')
else:
return self.__data.pop()
使用示例:
def main():
s = ListStack()
print('The stack is empty? ', s.is_empty())
s.push(100)
s.push(200)
s.push(300)
print(s.top())
print(s.pop())
print(s.top())
反转列表应用:
from stack import ListStack
def reverse_data(oldList):
s = ListStack()
newList = list()
for i in oldList:
s.push(i)
while (not s.is_empty()):
mid = s.pop()
newList.append(mid)
return newList
括号匹配检查:
from stack import ListStack
def is_matched(expr):
leftv = '([{'
rightv = ')]}'
s = ListStack()
for c in expr:
if c in leftv:
s.push(c)
elif c in rightv:
if s.is_empty():
return False
if rightv.index(c) != leftv.index(s.pop()):
return False
return s.is_empty()
HTML标签匹配:
from stack import ListStack
def is_matched_html(raw):
s = ListStack()
j = raw.find('<')
while j != -1:
k = raw.find('>', j+1)
if k == -1:
return False
tag = raw[j+1:k]
if not tag.startswith('/'):
s.push(tag)
else:
if s.is_empty():
return False
if tag[1:] != s.pop():
return False
j = raw.find('<', k+1)
return s.is_empty()
2. 队列 (Queue)
核心概念英文原文:
- “A queue is a collection of objects that are inserted and removed according to the first-in, first-out (FIFO) principle”(队列是根据先进先出原则插入和移除对象的集合)
- “Elements can be inserted at any time, but only the element that has been in the queue the longest can be next removed”(元素可以随时插入,但只有进入队列时间最长的元素才能被下一个移除)
队列类方法:
Q.enqueue(e): Add element e to the back of queue Q(将元素e添加到队列Q的尾部)Q.dequeue(): Remove and return the first element from queue Q(移除并返回队列Q的第一个元素)Q.first(): Return a reference to the element at the front of queue Q(返回队列Q前端元素的引用)Q.is_empty(): Return True if queue Q does not contain any elements(如果队列Q不包含任何元素,则返回True)len(Q): Return the number of elements in queue Q(返回队列Q中的元素数量)
基于列表的实现代码:
class ListQueue:
default_capacity = 5
def __init__(self):
self.__data = [None] * ListQueue.default_capacity
self.__size = 0
self.__front = 0
self.__end = 0
def __len__(self):
return self.__size
def is_empty(self):
return self.__size == 0
def first(self):
if self.is_empty():
print('Queue is empty.')
else:
return self.__data[self.__front]
def dequeue(self):
if self.is_empty():
print('Queue is empty.')
return None
answer = self.__data[self.__front]
self.__data[self.__front] = None
self.__front = (self.__front + 1) % ListQueue.default_capacity
self.__size -= 1
return answer
def enqueue(self, e):
if self.__size == ListQueue.default_capacity:
print('The queue is full.')
return None
self.__data[self.__end] = e
self.__end = (self.__end + 1) % ListQueue.default_capacity
self.__size += 1
def outputQ(self):
print(self.__data)
Web服务模拟应用:
from ListQueue import ListQueue
from random import random
from math import floor
class WebService():
default_capacity = 5
def __init__(self):
self.nameQ = ListQueue()
self.timeQ = ListQueue()
def taskArrive(self, taskName, taskTime):
if self.nameQ.__len__() < WebService.default_capacity:
self.nameQ.enqueue(taskName)
self.timeQ.enqueue(taskTime)
print('A new task 《'+taskName+'》 has arrived and is waiting for processing...')
else:
print('The service queue of our website is full, the new task is dropped.')
def taskProcess(self):
if (self.nameQ.is_empty() == False):
taskName = self.nameQ.dequeue()
taskTime = self.timeQ.dequeue()
print('Task 《'+taskName+'》 has been processed, it costs '+str(taskTime)+' seconds.')
3. 链表 (Linked List)
核心概念英文原文:
- “A singly linked list, in its simplest form, is a collection of nodes that collectively form a linear sequence”(单向链表,最简单的形式是共同形成线性序列的节点集合)
- “Each node stores a reference to an object that is an element of the sequence, as well as a reference to the next node of the list”(每个节点存储对作为序列元素的对象的引用,以及对列表中下一个节点的引用)
- “The first and last nodes of a linked list are known as the head and tail of the list, respectively”(链表的第一个和最后一个节点分别称为列表的头部和尾部)
节点类定义:
class Node:
def __init__(self, element, pointer):
self.element = element
self.pointer = pointer
3.1 基于链表的栈实现
class LinkedStack:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.size = 0
def __len__(self):
return self.size
def is_empty(self):
return self.size == 0
def push(self, e):
self.head = Node(e, self.head)
self.size += 1
def top(self):
if self.is_empty():
print('Stack is empty.')
else:
return self.head.element
def pop(self):
if self.is_empty():
print('Stack is empty.')
else:
answer = self.head.element
self.head = self.head.pointer
self.size -= 1
return answer
3.2 基于链表的队列实现
class LinkedQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
self.size = 0
def __len__(self):
return self.size
def is_empty(self):
return self.size == 0
def first(self):
if self.is_empty():
print('Queue is empty.')
else:
return self.head.element
def dequeue(self):
if self.is_empty():
print('Queue is empty.')
else:
answer = self.head.element
self.head = self.head.pointer
self.size -= 1
if self.is_empty():
self.tail = None
return answer
def enqueue(self, e):
newest = Node(e, None)
if self.is_empty():
self.head = newest
else:
self.tail.pointer = newest
self.tail = newest
self.size += 1
3.3 循环链表
概念英文原文:
- “The tail of a linked list can use its next reference to point back to the head of the list”(链表的尾部可以使用其下一个引用指向列表的头部)
- “Such a structure is usually called a circularly linked list”(这种结构通常称为循环链表)
应用:
- “A round-robin scheduler iterates through a collection of elements in a circular fashion and ‘serves’ each element by performing a given action on it”(轮询调度器以循环方式遍历元素集合,并通过对其执行给定操作来"服务"每个元素)
循环队列实现:
class CQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.__tail = None
self.__size = 0
def __len__(self):
return self.__size
def is_empty(self):
return self.__size == 0
def first(self):
if self.is_empty():
print("Queue is empty.")
else:
head = self.__tail.pointer
return head.element
def dequeue(self):
if self.is_empty():
print('Queue is empty.')
else:
oldhead = self.__tail.pointer
if self.__size == 1:
self.__tail = None
else:
self.__tail.pointer = oldhead.pointer
self.__size -= 1
return oldhead.element
def enqueue(self, e):
newest = Node(e, None)
if self.is_empty():
newest.pointer = newest
else:
newest.pointer = self.__tail.pointer
self.__tail.pointer = newest
self.__tail = newest
self.__size += 1
3.4 双向链表
概念英文原文:
- “We can define a linked list in which each node keeps an explicit reference to the node before it and a reference to the node after it”(我们可以定义一个链表,其中每个节点都保持对其前一个节点和后一个节点的显式引用)
- “This kind of data structure is called doubly linked list”(这种数据结构称为双向链表)
- “Header node at the beginning of the list, and a trailer node at the end of the list. These ‘dummy’ nodes are known as sentinels”(列表开头的头节点和列表末尾的尾节点。这些"虚拟"节点称为哨兵节点)
实现代码:
class Node:
def __init__(self, element, prev, nxt):
self.element = element
self.prev = prev
self.nxt = nxt
class DLList:
def __init__(self):
self.header = Node(None, None, None)
self.trailer = Node(None, None, None)
self.header.nxt = self.trailer
self.trailer.prev = self.header
self.size = 0
def __len__(self):
return self.size
def is_empty(self):
return self.size == 0
def insert_between(self, e, predecessor, successor):
newest = Node(e, predecessor, successor)
predecessor.nxt = newest
successor.prev = newest
self.size += 1
return newest
def delete_node(self, node):
predecessor = node.prev
successor = node.nxt
predecessor.nxt = successor
successor.prev = predecessor
self.size -= 1
element = node.element
node.prev = node.nxt = node.element = None
return element
def iterate(self):
pointer = self.header.nxt
print('The elements in the list:')
while pointer != self.trailer:
print(pointer.element)
pointer = pointer.nxt
4. 排序算法
4.1 冒泡排序 - 标准列表
def bubble(bubbleList):
listLength = len(bubbleList)
while listLength > 0:
for i in range(listLength - 1):
if bubbleList[i] > bubbleList[i+1]:
buf = bubbleList[i]
bubbleList[i] = bubbleList[i+1]
bubbleList[i+1] = buf
listLength -= 1
return bubbleList
4.2 冒泡排序 - 链表
from LinkedQueue import LinkedQueue
def LinkedBubble(q):
listLength = q.size
while listLength > 0:
index = 0
pointer = q.head
while index < listLength-1:
if pointer.element > pointer.pointer.element:
buf = pointer.element
pointer.element = pointer.pointer.element
pointer.pointer.element = buf
index += 1
pointer = pointer.pointer
listLength -= 1
return q
4.3 快速排序
def quickSort(L, low, high):
i = low
j = high
if i >= j:
return L
key = L[i]
while i < j:
while i < j and L[j] >= key:
j = j-1
L[i] = L[j]
while i < j and L[i] <= key:
i = i+1
L[j] = L[i]
L[i] = key
quickSort(L, low, i-1)
quickSort(L, j+1, high)
return L
5. 树 (Tree)
核心概念英文原文:
- “A tree is a data structure that stores elements hierarchically”(树是一种分层存储元素的数据结构)
- “With the exception of the top element, each element in a tree has a parent element and zero or more children elements”(除了顶部元素外,树中的每个元素都有一个父元素和零个或多个子元素)
- “We typically call the top element the root of the tree”(我们通常称顶部元素为树的根)
有序树定义:
- “A tree is ordered if there is a meaningful linear order among the children of each node; such an order is usually visualized by arranging siblings from left to right, according to their order”(如果每个节点的子节点之间存在有意义的线性顺序,则树是有序的;这种顺序通常通过根据它们的顺序从左到右排列兄弟节点来可视化)
应用示例:
- 公司组织架构
- 算术表达式表示
- 迷宫路径搜索
- 游戏最佳移动决策
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献9条内容
已为社区贡献9条内容







所有评论(0)