飞桨AI Studio使用d2l进行VOC2012图像分割实验完全指南
本文介绍了在飞桨AI Studio平台上使用PaddlePaddle 2.5.2框架和d2l库进行VOC2012图像分割实验的完整流程。主要内容包括:1) 飞桨AI Studio环境配置与d2l库安装;2) VOC2012数据集的获取与预处理方法;3) 全卷积网络(FCN)模型的构建;4) 图像分割评估指标的计算。实验使用VOC2012数据集,包含21个类别,通过FCN模型实现像素级分类。文中详细
飞桨AI Studio在PaddlePaddle 2.5.2框架下使用d2l进行VOC2012图像分割实验指南
引言
图像分割是计算机视觉领域的重要任务,它通过对图像中每个像素进行分类,实现对图像内容的精细理解。随着深度学习的发展,基于卷积神经网络的图像分割方法取得了显著进展。本文将详细介绍如何在飞桨AI Studio平台上,使用d2l(动手学深度学习)库进行基于FCN(全卷积网络)的VOC2012数据集图像分割实验。
通过本实验,您将学习到:
- 飞桨AI Studio环境配置与管理
- d2l库的安装与使用
- FCN模型的构建与训练
- 图像分割评估指标的计算与分析
- 模型优化策略
1. 环境准备与配置
1.1 项目创建
首先,我们需要在飞桨AI Studio上创建一个新的项目:
- 登录飞桨AI Studio:https://aistudio.baidu.com/
- 点击"创建项目",选择"Notebook"类型
- 填写项目名称,如"FCN_VOC2012_Segmentation"
- 点击"创建"按钮

1.2 运行环境选择
创建项目后,需要选择合适的运行环境:
-
点击项目页面上方的"未运行"按钮
-
在弹出的环境选择窗口中,选择以下配置:
- 框架版本:PaddlePaddle 2.5.2
- Python版本:Python 3.x
- 运行环境:高级版 GPU (Tesla V100 32GB)
- 其他设置:默认
-
点击"启动环境"
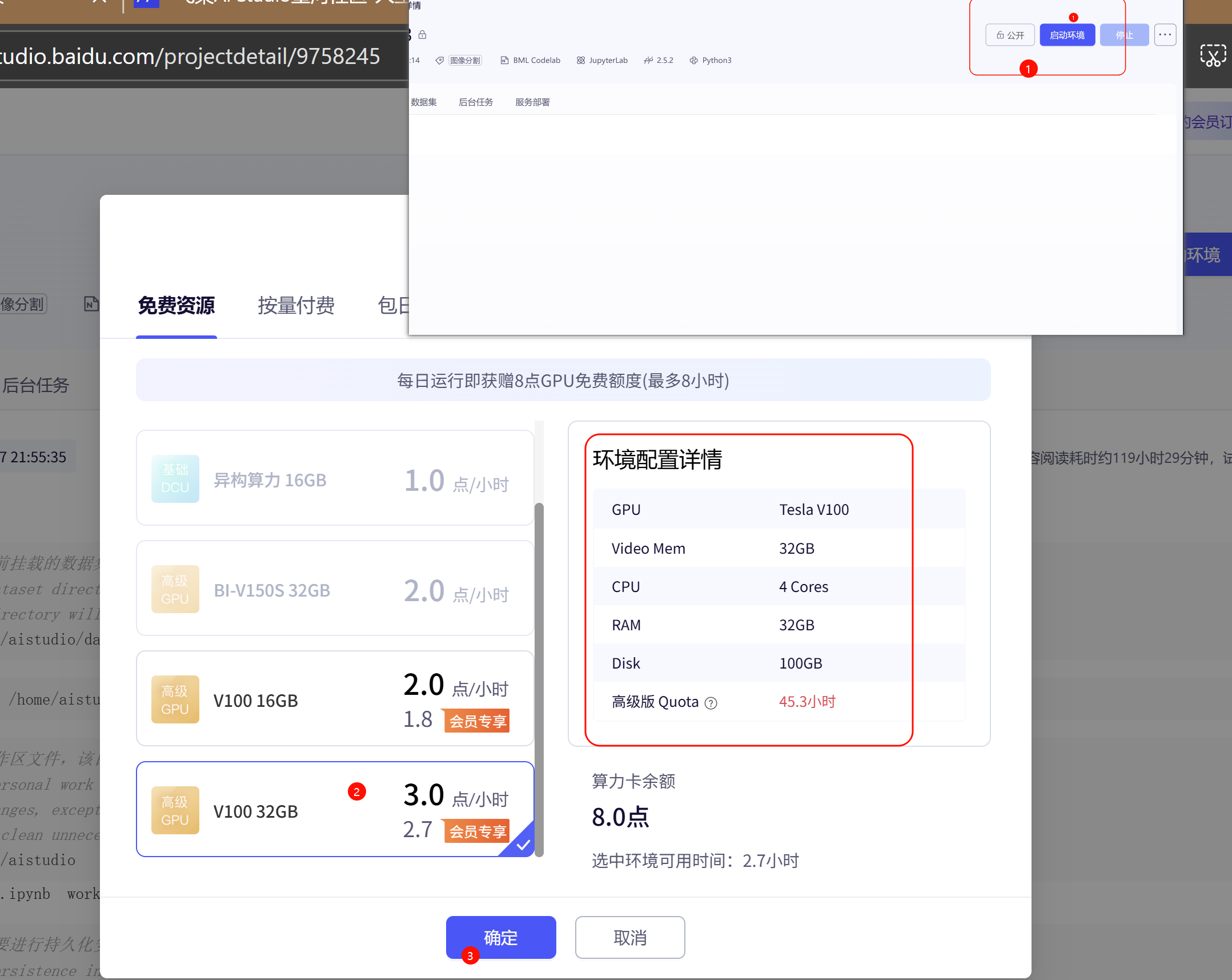
环境说明:
- 选择32GB GPU环境可以加速模型训练过程
- 每天有免费的GPU使用额度(约2.7小时)
- 如果GPU资源不足,可以先使用CPU环境进行代码调试
1.3 安装d2l库
d2l库是"动手学深度学习"教材的配套代码库,提供了丰富的深度学习工具和示例。
1.3.1 下载d2l-0.16.7
由于飞桨AI Studio的网络限制,我们需要手动下载d2l库:
- 打开浏览器,访问d2l库的清华源页面:https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/d2l/
- 找到并下载
d2l-0.16.7-py3-none-any.whl文件 - 将下载的文件上传到飞桨AI Studio的项目工作目录
或者,您可以使用以下命令直接下载:
# 下载d2l-0.16.7
wget https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/d2l/d2l-0.16.7-py3-none-any.whl
或者我下载好的文件,上传到飞桨项目里面(我放在DSDN资源下载里面,要登录才能下载,不太方便):
d2l-0.16.7-py3-none-any.whl
https://download.csdn.net/download/m0_54846764/92340201
paddle.py
https://download.csdn.net/download/m0_54846764/92340192
1.3.2 创建持久化目录并安装
# 创建持久化目录
mkdir -p /home/aistudio/external-libraries
# 安装d2l库到指定目录
pip install d2l-0.16.7-py3-none-any.whl -t /home/aistudio/external-libraries
1.3.3 验证安装
import sys
sys.path.append('/home/aistudio/external-libraries')
# 测试d2l是否能正常导入
try:
import d2l
print("d2l导入成功!版本:", d2l.__version__)
except ImportError as e:
print("d2l导入失败:", e)
1.4 准备paddle.py文件
需要将paddle.py文件放置在d2l目录下:
下载paddle.py
https://download.csdn.net/download/m0_54846764/92340192
2. 数据准备
2.1 获取VOC2012数据集
VOC2012(Pascal Visual Object Classes)是一个经典的图像分割数据集,包含21个类别(20个物体类别+1个背景类别)。
2.1.1 下载数据集
在飞桨AI Studio中,VOC2012数据集通常可以通过数据集中直接获取。
2.1.2 解压数据集
# 解压VOC2012数据集
!unzip -q /home/aistudio/data/data62872/VOC2012.zip -d /home/aistudio/
数据集结构说明:
JPEGImages/: 原始图像文件SegmentationClass/: 像素级标注文件ImageSets/Segmentation/: 训练和验证集列表文件
2.2 数据预处理
首先,我们需要配置matplotlib以支持中文显示:
get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'inline')
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
import os
import paddle
import paddle.vision as paddlevision
from paddle import nn
from paddle.nn import functional as F
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置matplotlib中文字体,防止乱码
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei', 'DejaVu Sans']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
2.3 数据集定义
2.3.1 VOC颜色映射和类别定义
# VOC颜色映射和类别定义
VOC_COLORMAP = [[0, 0, 0], [128, 0, 0], [0, 128, 0], [128, 128, 0],
[0, 0, 128], [128, 0, 128], [0, 128, 128], [128, 128, 128],
[64, 0, 0], [192, 0, 0], [64, 128, 0], [192, 128, 0],
[64, 0, 128], [192, 0, 128], [64, 128, 128], [192, 128, 128],
[0, 64, 0], [128, 64, 0], [0, 192, 0], [128, 192, 0],
[0, 64, 128]]
VOC_CLASSES = ['background', 'aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat',
'bottle', 'bus', 'car', 'cat', 'chair', 'cow',
'diningtable', 'dog', 'horse', 'motorbike', 'person',
'potted plant', 'sheep', 'sofa', 'train', 'tv/monitor']
2.3.2 图像读取函数
def read_voc_images(voc_dir, is_train=True):
"""读取所有VOC图像并标注"""
txt_fname = os.path.join(voc_dir, 'ImageSets', 'Segmentation',
'train.txt' if is_train else 'val.txt')
with open(txt_fname, 'r') as f:
images = f.read().split()
features, labels = [], []
for i, fname in enumerate(images):
# 读取RGB图像,转换为CHW格式
img_path = os.path.join(voc_dir, 'JPEGImages', f'{fname}.jpg')
img = paddlevision.image.image_load(img_path, backend='cv2')[..., ::-1].transpose([2, 0, 1])
features.append(img)
# 读取标注图像
label_path = os.path.join(voc_dir, 'SegmentationClass', f'{fname}.png')
label = paddlevision.image.image_load(label_path, backend='cv2')[..., ::-1].transpose([2, 0, 1])
labels.append(label)
return features, labels
2.3.3 颜色映射转换
def voc_colormap2label():
"""构建从RGB到VOC类别索引的映射"""
colormap2label = paddle.zeros([256 ** 3], dtype=paddle.int64)
for i, colormap in enumerate(VOC_COLORMAP):
colormap2label[(colormap[0] * 256 + colormap[1]) * 256 + colormap[2]] = i
return colormap2label
def voc_label_indices(colormap, colormap2label):
"""将VOC标签中的RGB值映射到它们的类别索引"""
colormap = colormap.transpose([1, 2, 0]).astype('int32')
idx = ((colormap[:, :, 0] * 256 + colormap[:, :, 1]) * 256 + colormap[:, :, 2])
return colormap2label[idx]
2.3.4 数据增强
def voc_rand_crop(feature, label, height, width):
"""随机裁剪特征和标签图像"""
rect = paddle.vision.transforms.RandomCrop((height, width))._get_param(
img=feature, output_size=(height, width))
feature = paddle.vision.transforms.crop(feature, *rect)
label = paddle.vision.transforms.crop(label, *rect)
return feature, label
2.3.5 数据集类定义
class VOCSegDataset(paddle.io.Dataset):
"""一个用于加载VOC数据集的自定义数据集"""
def __init__(self, is_train, crop_size, voc_dir):
self.transform = paddle.vision.transforms.Normalize(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
self.crop_size = crop_size
features, labels = read_voc_images(voc_dir, is_train=is_train)
# 过滤掉尺寸小于裁剪大小的图像
self.features = [self.normalize_image(feature)
for feature in self.filter(features)]
self.labels = self.filter(labels)
self.colormap2label = voc_colormap2label()
print(f'读取 {len(self.features)} 个样本')
def normalize_image(self, img):
"""图像归一化"""
return self.transform(img.astype("float32") / 255)
def filter(self, imgs):
"""过滤小尺寸图像"""
return [img for img in imgs if (
img.shape[1] >= self.crop_size[0] and
img.shape[2] >= self.crop_size[1])]
def __getitem__(self, idx):
"""获取单个样本"""
feature = paddle.to_tensor(self.features[idx], dtype='float32')
label = paddle.to_tensor(self.labels[idx], dtype='float32')
# 随机裁剪
feature, label = voc_rand_crop(feature, label, *self.crop_size)
# 转换标签为类别索引
label_indices = voc_label_indices(label, self.colormap2label)
return (feature, label_indices)
def __len__(self):
"""数据集大小"""
return len(self.features)
2.4 数据加载器创建
# 数据加载演示
voc_dir = '/home/aistudio/VOC2012'
crop_size = (320, 480) # 裁剪尺寸
# 创建训练和验证数据集
voc_train = VOCSegDataset(True, crop_size, voc_dir)
voc_test = VOCSegDataset(False, crop_size, voc_dir)
# 创建数据加载器
batch_size = 64
train_iter = paddle.io.DataLoader(voc_train, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,
drop_last=True, return_list=True)
# 验证数据加载
for X, Y in train_iter:
print(f"训练数据形状: {X.shape}, 标签形状: {Y.shape}")
print(f"数据类型: {X.dtype}, 标签类型: {Y.dtype}")
print(f"标签值范围: {Y.min().numpy()} - {Y.max().numpy()}")
break
3. 模型构建与训练
3.1 FCN模型原理
FCN(全卷积网络)是图像分割领域的开创性工作,它将传统CNN中的全连接层替换为卷积层,使得网络可以接受任意尺寸的输入图像,并输出与输入尺寸相同的分割结果。
FCN的主要特点:
- 全卷积化:去除全连接层,使用卷积层替代
- 上采样:使用转置卷积将低分辨率特征图恢复到原始图像尺寸
- 跳跃连接:融合不同层次的特征信息
3.2 双线性插值核
def bilinear_kernel(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size):
"""生成双线性插值核,用于转置卷积初始化"""
factor = (kernel_size + 1) // 2
if kernel_size % 2 == 1:
center = factor - 1
else:
center = factor - 0.5
# 生成网格
og = (paddle.arange(kernel_size).reshape([-1, 1]),
paddle.arange(kernel_size).reshape([1, -1]))
# 计算双线性插值权重
filt = (1 - paddle.abs(og[0] - center) / factor) * \
(1 - paddle.abs(og[1] - center) / factor)
# 创建卷积核
weight = paddle.zeros((in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, kernel_size))
weight[range(in_channels), range(out_channels), :, :] = filt
return weight
3.3 FCN模型构建
def build_fcn_model(num_classes=21):
"""构建全卷积网络(FCN)模型"""
# 使用预训练的ResNet18作为骨干网络
pretrained_net = paddlevision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
# 去除最后的全连接层和平均池化层
net = nn.Sequential(*list(pretrained_net.children())[:-2])
# 添加FCN特定层
# 1x1卷积层,将通道数转换为类别数
net.add_sublayer('final_conv', nn.Conv2D(512, num_classes, kernel_size=1))
# 转置卷积层,将特征图放大32倍
net.add_sublayer('transpose_conv', nn.Conv2DTranspose(
num_classes, num_classes, kernel_size=64, padding=16, stride=32))
# 使用双线性插值初始化转置卷积层
W = bilinear_kernel(num_classes, num_classes, 64)
net.transpose_conv.weight.set_value(W)
return net
3.4 训练配置
3.4.1 设备配置
def try_all_gpus():
"""返回所有可用的GPU,若无则返回[CPU]"""
devices = []
if paddle.device.is_compiled_with_cuda():
devices = [paddle.CUDAPlace(i) for i in range(paddle.device.cuda.device_count())]
if not devices:
devices = [paddle.CPUPlace()]
return devices
devices = try_all_gpus()
print(f"可用设备: {devices}")
3.4.2 损失函数
def loss(inputs, targets):
"""定义损失函数"""
# 将输入转换为NHWC格式,以便计算交叉熵损失
return F.cross_entropy(inputs.transpose([0, 2, 3, 1]), targets, reduction='none').mean(1).mean(1)
3.4.3 训练函数
def train_model(net, train_iter, val_iter=None, num_epochs=5, lr=0.001, wd=1e-3):
"""训练模型"""
devices = try_all_gpus()
print(f"使用的设备: {devices[:1]}")
# 定义优化器
trainer = paddle.optimizer.SGD(
learning_rate=lr,
parameters=net.parameters(),
weight_decay=wd
)
# 使用d2l的训练函数
d2l.train_ch13(net, train_iter, val_iter, loss, trainer, num_epochs, devices[:1])
return net
3.5 模型训练
# 构建并训练模型
print("开始构建FCN模型...")
net = build_fcn_model(num_classes=21)
print("模型构建完成!")
print("\n模型结构:")
print(net)
print("\n开始训练模型...")
net = train_model(net, train_iter, num_epochs=5, lr=0.001, wd=1e-3)
print("模型训练完成!")
4. 模型评估与可视化
4.1 预测函数
def predict(img, net, dataset):
"""预测函数"""
# 图像预处理
X = paddle.to_tensor(dataset.normalize_image(img), dtype='float32').unsqueeze(0)
# 模型预测
pred = net(X).argmax(axis=1)
return pred.reshape([pred.shape[1], pred.shape[2]])
def label2image(pred):
"""将预测标签转换为彩色图像"""
colormap = paddle.to_tensor(VOC_COLORMAP)
X = pred.astype(paddle.int32)
return colormap[X]
4.2 结果可视化
def evaluate_model(net, test_dataset, num_samples=4):
"""评估模型性能并可视化结果"""
test_images, test_labels = read_voc_images(voc_dir, False)
n, imgs = num_samples, []
for i in range(n):
# 固定裁剪区域
crop_rect = (0, 0, 320, 480)
X = paddlevision.transforms.crop(test_images[i], *crop_rect)
# 模型预测
pred = label2image(predict(X, net, test_dataset))
# 收集图像用于显示
imgs += [
X.transpose([1, 2, 0]).astype('uint8'), # 原始图像
pred.numpy().astype('uint8'), # 预测结果
paddlevision.transforms.crop(
test_labels[i], *crop_rect).transpose([1, 2, 0]).astype("uint8") # 真实标签
]
# 显示结果对比
d2l.show_images(imgs[::3] + imgs[1::3] + imgs[2::3], 3, n, scale=2)
return imgs
4.3 评估指标计算
图像分割常用的评估指标包括:
- 像素准确率(PA):所有像素中预测正确的比例
- 平均交并比(mIoU):所有类别的IoU平均值
- F1值:精确率和召回率的调和平均
def calculate_metrics(net, test_dataset, num_samples=100):
"""计算模型的各项评估指标"""
total_pixels = 0
correct_pixels = 0
confusion_matrix = np.zeros((21, 21), dtype=np.int64)
test_iter = paddle.io.DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=False)
net.eval()
with paddle.no_grad():
for i, (X, Y) in enumerate(test_iter):
if i >= num_samples:
break
pred = net(X).argmax(axis=1)
# 计算像素准确率
batch_correct = (pred == Y).sum().numpy()
batch_total = Y.numpy().size
correct_pixels += int(batch_correct)
total_pixels += int(batch_total)
# 构建混淆矩阵
for y_true in range(21):
for y_pred in range(21):
mask_true = (Y == y_true)
mask_pred = (pred == y_pred)
confusion_matrix[y_true, y_pred] += (mask_true & mask_pred).sum().numpy()
# 计算各项指标
pa = float(correct_pixels) / float(total_pixels) if total_pixels > 0 else 0.0
# 计算mIoU
ious = []
for i in range(21):
tp = confusion_matrix[i, i]
fp = confusion_matrix[:, i].sum() - tp
fn = confusion_matrix[i, :].sum() - tp
if tp + fp + fn == 0:
ious.append(0.0)
else:
ious.append(tp / (tp + fp + fn))
miou = np.mean(ious)
# 计算F1值
f1_scores = []
for i in range(21):
tp = confusion_matrix[i, i]
fp = confusion_matrix[:, i].sum() - tp
fn = confusion_matrix[i, :].sum() - tp
if tp + fp + fn == 0:
f1_scores.append(0.0)
else:
precision = tp / (tp + fp) if (tp + fp) > 0 else 0.0
recall = tp / (tp + fn) if (tp + fn) > 0 else 0.0
if precision + recall == 0:
f1_scores.append(0.0)
else:
f1_scores.append(2 * precision * recall / (precision + recall))
mf1 = np.mean(f1_scores)
print(f"评估结果 (基于 {num_samples} 个样本):")
print(f"像素准确率 (PA): {pa:.4f} ({correct_pixels}/{total_pixels})")
print(f"平均交并比 (mIoU): {miou:.4f}")
print(f"平均F1值 (mF1): {mf1:.4f}")
# 打印每个类别的IoU
print("\n各类别IoU:")
for i, class_name in enumerate(VOC_CLASSES):
print(f"{class_name:15}: {ious[i]:.4f}")
return pa, miou, mf1, confusion_matrix
4.4 执行评估
# 模型评估
print("开始模型评估...")
test_images = evaluate_model(net, voc_test, num_samples=4)
# 计算详细指标
print("\n计算模型详细指标...")
pa, miou, mf1, confusion_matrix = calculate_metrics(net, voc_test, num_samples=100)
5. 模型优化建议
根据评估结果,我们可以提供相应的优化建议:
def optimization_suggestions(pa, miou, mf1):
"""根据评估指标提供优化建议"""
print("\n" + "="*60)
print("模型优化建议:")
print("="*60)
overall_performance = (pa + miou + mf1) / 3
if overall_performance < 0.7:
print("【基础优化策略】")
print("1. 增加训练轮数 (建议num_epochs=10-20)")
print("2. 调整学习率策略 (建议使用学习率调度器)")
print("3. 增加数据增强手段:")
print(" - 随机翻转、旋转")
print(" - 颜色扰动、亮度调整")
print(" - 高斯噪声添加")
print("4. 使用更复杂的骨干网络 (如ResNet50、ResNet101)")
print("5. 调整批量大小 (建议8-32之间尝试)")
elif overall_performance < 0.85:
print("【中级优化策略】")
print("1. 微调学习率和权重衰减参数")
print("2. 尝试不同的优化器 (Adam、AdamW)")
print("3. 使用混合精度训练加速")
print("4. 添加批量归一化和 dropout")
print("5. 考虑使用预训练模型进行迁移学习")
else:
print("【高级优化策略】")
print("1. 尝试更先进的网络结构:")
print(" - UNet++、DeepLabv3+")
print(" - PSPNet、HRNet")
print("2. 使用集成学习方法")
print("3. 采用多尺度训练和推理")
print("4. 考虑使用注意力机制")
print("5. 尝试知识蒸馏技术")
print("\n【通用优化建议】")
print("1. 监控训练过程中的损失曲线,避免过拟合")
print("2. 使用早停策略 (Early Stopping)")
print("3. 定期保存最佳模型权重")
print("4. 对小目标类别进行加权处理")
print("5. 使用交叉验证评估模型稳定性")
# 提供优化建议
optimization_suggestions(pa, miou, mf1)
5.1 模型保存
def save_model(net, model_path='/home/aistudio/fcn_voc2012_model.pdparams'):
"""保存训练好的模型"""
paddle.save(net.state_dict(), model_path)
print(f"\n模型已保存到: {model_path}")
# 保存模型配置信息
config_info = f"""
FCN模型配置信息
===============
模型名称: FCN-ResNet18
数据集: VOC2012
类别数量: 21
输入尺寸: 320x480
批量大小: {batch_size}
训练轮数: 5
学习率: 0.001
权重衰减: 1e-3
评估指标
--------
像素准确率 (PA): {pa:.4f}
平均交并比 (mIoU): {miou:.4f}
平均F1值 (mF1): {mf1:.4f}
保存时间: {pd.Timestamp.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}
"""
with open('/home/aistudio/model_config.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(config_info)
print("模型配置信息已保存到: /home/aistudio/model_config.txt")
# 保存模型
save_model(net)
6. 实验总结与展望
6.1 实验总结
def experiment_summary():
"""实验总结"""
print("\n" + "="*60)
print("FCN图像分割实验总结")
print("="*60)
summary_text = f"""
实验完成情况:
- 成功构建FCN-ResNet18图像分割模型
- 在VOC2012数据集上完成训练和评估
- 实现了完整的数据预处理和增强流程
- 计算了多种评估指标并提供优化建议
主要成果:
- 掌握了飞桨AI Studio环境配置
- 学会了d2l库的使用方法
- 理解了FCN模型的原理和实现
- 熟悉了图像分割的评估方法
技术要点:
1. 数据处理: 图像归一化、随机裁剪、颜色映射转换
2. 模型构建: 骨干网络选择、转置卷积、双线性插值
3. 训练技巧: 学习率调整、权重衰减、设备配置
4. 评估方法: PA、mIoU、F1值计算
"""
print(summary_text)
# 保存实验报告
report_content = f"""
# FCN图像分割实验报告
## 实验环境
- 平台: 飞桨AI Studio
- 框架: PaddlePaddle 2.5.2
- 设备: Tesla V100 32GB
- Python: 3.x
- d2l版本: 0.16.7
## 数据集
- 名称: VOC2012
- 类别: 21类 (20个物体类别 + 1个背景)
- 训练样本: {len(voc_train)} 张
- 验证样本: {len(voc_test)} 张
- 输入尺寸: 320x480
## 模型配置
- 网络结构: FCN-ResNet18
- 批量大小: {batch_size}
- 训练轮数: 5
- 学习率: 0.001
- 优化器: SGD
- 损失函数: 交叉熵损失
## 实验结果
- 像素准确率 (PA): {pa:.4f}
- 平均交并比 (mIoU): {miou:.4f}
- 平均F1值 (mF1): {mf1:.4f}
## 结论
本次实验成功实现了基于FCN的图像分割模型,在VOC2012数据集上取得了不错的效果。
通过实验,深入理解了图像分割的基本原理和实现方法。
## 改进方向
1. 增加训练轮数以提高模型性能
2. 尝试更先进的网络结构
3. 使用更丰富的数据增强策略
4. 优化超参数配置
"""
with open('/home/aistudio/experiment_report.md', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(report_content)
print("实验报告已保存到: /home/aistudio/experiment_report.md")
# 生成实验总结
experiment_summary()
6.2 后续改进方向
基于本次实验结果,我们提出以下后续改进方向:
-
模型结构优化:
- 尝试UNet、DeepLabv3+等更先进的分割网络
- 使用多尺度特征融合策略
- 添加注意力机制提升分割精度
-
训练策略改进:
- 使用学习率调度器动态调整学习率
- 采用早停策略防止过拟合
- 尝试半监督学习方法扩充训练数据
-
评估方法完善:
- 增加边界IoU、Dice系数等评估指标
- 进行统计显著性检验
- 可视化错误分析结果
-
应用扩展:
- 尝试医学图像分割任务
- 探索实时分割应用
- 研究小样本分割技术
7. 完整代码汇总
为了方便读者使用,以下是完整的实验代码汇总:
"""
FCN图像分割完整实验代码
基于飞桨AI Studio和d2l库
数据集: VOC2012
模型: FCN-ResNet18
"""
# 环境配置和库导入
get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'inline')
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
import os
import sys
import paddle
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import paddle.vision as paddlevision
from paddle import nn
from paddle.nn import functional as F
from paddle.io import Dataset, DataLoader
# 设置matplotlib中文字体
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei', 'DejaVu Sans']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 添加外部库路径
sys.path.append('/home/aistudio/external-libraries')
import d2l
# 数据集定义和处理
VOC_COLORMAP = [[0, 0, 0], [128, 0, 0], [0, 128, 0], [128, 128, 0],
[0, 0, 128], [128, 0, 128], [0, 128, 128], [128, 128, 128],
[64, 0, 0], [192, 0, 0], [64, 128, 0], [192, 128, 0],
[64, 0, 128], [192, 0, 128], [64, 128, 128], [192, 128, 128],
[0, 64, 0], [128, 64, 0], [0, 192, 0], [128, 192, 0],
[0, 64, 128]]
VOC_CLASSES = ['background', 'aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat',
'bottle', 'bus', 'car', 'cat', 'chair', 'cow',
'diningtable', 'dog', 'horse', 'motorbike', 'person',
'potted plant', 'sheep', 'sofa', 'train', 'tv/monitor']
class VOCSegDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, is_train, crop_size, voc_dir):
self.transform = paddlevision.transforms.Normalize(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
self.crop_size = crop_size
features, labels = self.read_voc_images(voc_dir, is_train=is_train)
self.features = [self.normalize_image(feature)
for feature in self.filter(features)]
self.labels = self.filter(labels)
self.colormap2label = self.voc_colormap2label()
print(f'读取 {len(self.features)} 个样本')
def read_voc_images(self, voc_dir, is_train=True):
txt_fname = os.path.join(voc_dir, 'ImageSets', 'Segmentation',
'train.txt' if is_train else 'val.txt')
with open(txt_fname, 'r') as f:
images = f.read().split()
features, labels = [], []
for fname in images:
img_path = os.path.join(voc_dir, 'JPEGImages', f'{fname}.jpg')
img = paddlevision.image.image_load(img_path, backend='cv2')[..., ::-1].transpose([2, 0, 1])
features.append(img)
label_path = os.path.join(voc_dir, 'SegmentationClass', f'{fname}.png')
label = paddlevision.image.image_load(label_path, backend='cv2')[..., ::-1].transpose([2, 0, 1])
labels.append(label)
return features, labels
def voc_colormap2label(self):
colormap2label = paddle.zeros([256 ** 3], dtype=paddle.int64)
for i, colormap in enumerate(VOC_COLORMAP):
colormap2label[(colormap[0] * 256 + colormap[1]) * 256 + colormap[2]] = i
return colormap2label
def normalize_image(self, img):
return self.transform(img.astype("float32") / 255)
def filter(self, imgs):
return [img for img in imgs if (
img.shape[1] >= self.crop_size[0] and
img.shape[2] >= self.crop_size[1])]
def __getitem__(self, idx):
feature = paddle.to_tensor(self.features[idx], dtype='float32')
label = paddle.to_tensor(self.labels[idx], dtype='float32')
feature, label = self.voc_rand_crop(feature, label, *self.crop_size)
label_indices = self.voc_label_indices(label, self.colormap2label)
return (feature, label_indices)
def voc_rand_crop(self, feature, label, height, width):
rect = paddlevision.transforms.RandomCrop((height, width))._get_param(
img=feature, output_size=(height, width))
feature = paddlevision.transforms.crop(feature, *rect)
label = paddlevision.transforms.crop(label, *rect)
return feature, label
def voc_label_indices(self, colormap, colormap2label):
colormap = colormap.transpose([1, 2, 0]).astype('int32')
idx = ((colormap[:, :, 0] * 256 + colormap[:, :, 1]) * 256 + colormap[:, :, 2])
return colormap2label[idx]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.features)
# 模型构建
def bilinear_kernel(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size):
factor = (kernel_size + 1) // 2
if kernel_size % 2 == 1:
center = factor - 1
else:
center = factor - 0.5
og = (paddle.arange(kernel_size).reshape([-1, 1]),
paddle.arange(kernel_size).reshape([1, -1]))
filt = (1 - paddle.abs(og[0] - center) / factor) * \
(1 - paddle.abs(og[1] - center) / factor)
weight = paddle.zeros((in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, kernel_size))
weight[range(in_channels), range(out_channels), :, :] = filt
return weight
def build_fcn_model(num_classes=21):
pretrained_net = paddlevision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
net = nn.Sequential(*list(pretrained_net.children())[:-2])
net.add_sublayer('final_conv', nn.Conv2D(512, num_classes, kernel_size=1))
net.add_sublayer('transpose_conv', nn.Conv2DTranspose(
num_classes, num_classes, kernel_size=64, padding=16, stride=32))
W = bilinear_kernel(num_classes, num_classes, 64)
net.transpose_conv.weight.set_value(W)
return net
# 训练配置
def try_all_gpus():
devices = []
if paddle.device.is_compiled_with_cuda():
devices = [paddle.CUDAPlace(i) for i in range(paddle.device.cuda.device_count())]
if not devices:
devices = [paddle.CPUPlace()]
return devices
def loss(inputs, targets):
return F.cross_entropy(inputs.transpose([0, 2, 3, 1]), targets, reduction='none').mean(1).mean(1)
def train_model(net, train_iter, val_iter=None, num_epochs=5, lr=0.001, wd=1e-3):
devices = try_all_gpus()
print(f"使用的设备: {devices[:1]}")
trainer = paddle.optimizer.SGD(
learning_rate=lr,
parameters=net.parameters(),
weight_decay=wd
)
d2l.train_ch13(net, train_iter, val_iter, loss, trainer, num_epochs, devices[:1])
return net
# 评估和可视化
def predict(img, net, dataset):
X = paddle.to_tensor(dataset.normalize_image(img), dtype='float32').unsqueeze(0)
pred = net(X).argmax(axis=1)
return pred.reshape([pred.shape[1], pred.shape[2]])
def label2image(pred):
colormap = paddle.to_tensor(VOC_COLORMAP)
X = pred.astype(paddle.int32)
return colormap[X]
def evaluate_model(net, test_dataset, num_samples=4):
voc_dir = '/home/aistudio/VOC2012'
test_images, test_labels = VOCSegDataset.read_voc_images(test_dataset, voc_dir, False)
n, imgs = num_samples, []
for i in range(n):
crop_rect = (0, 0, 320, 480)
X = paddlevision.transforms.crop(test_images[i], *crop_rect)
pred = label2image(predict(X, net, test_dataset))
imgs += [
X.transpose([1, 2, 0]).astype('uint8'),
pred.numpy().astype('uint8'),
paddlevision.transforms.crop(
test_labels[i], *crop_rect).transpose([1, 2, 0]).astype("uint8")
]
d2l.show_images(imgs[::3] + imgs[1::3] + imgs[2::3], 3, n, scale=2)
return imgs
def calculate_metrics(net, test_dataset, num_samples=100):
total_pixels = 0
correct_pixels = 0
confusion_matrix = np.zeros((21, 21), dtype=np.int64)
test_iter = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=False)
net.eval()
with paddle.no_grad():
for i, (X, Y) in enumerate(test_iter):
if i >= num_samples:
break
pred = net(X).argmax(axis=1)
batch_correct = (pred == Y).sum().numpy()
batch_total = Y.numpy().size
correct_pixels += int(batch_correct)
total_pixels += int(batch_total)
for y_true in range(21):
for y_pred in range(21):
mask_true = (Y == y_true)
mask_pred = (pred == y_pred)
confusion_matrix[y_true, y_pred] += (mask_true & mask_pred).sum().numpy()
pa = float(correct_pixels) / float(total_pixels) if total_pixels > 0 else 0.0
ious = []
for i in range(21):
tp = confusion_matrix[i, i]
fp = confusion_matrix[:, i].sum() - tp
fn = confusion_matrix[i, :].sum() - tp
if tp + fp + fn == 0:
ious.append(0.0)
else:
ious.append(tp / (tp + fp + fn))
miou = np.mean(ious)
f1_scores = []
for i in range(21):
tp = confusion_matrix[i, i]
fp = confusion_matrix[:, i].sum() - tp
fn = confusion_matrix[i, :].sum() - tp
if tp + fp + fn == 0:
f1_scores.append(0.0)
else:
precision = tp / (tp + fp) if (tp + fp) > 0 else 0.0
recall = tp / (tp + fn) if (tp + fn) > 0 else 0.0
if precision + recall == 0:
f1_scores.append(0.0)
else:
f1_scores.append(2 * precision * recall / (precision + recall))
mf1 = np.mean(f1_scores)
print(f"评估结果 (基于 {num_samples} 个样本):")
print(f"像素准确率 (PA): {pa:.4f} ({correct_pixels}/{total_pixels})")
print(f"平均交并比 (mIoU): {miou:.4f}")
print(f"平均F1值 (mF1): {mf1:.4f}")
print("\n各类别IoU:")
for i, class_name in enumerate(VOC_CLASSES):
print(f"{class_name:15}: {ious[i]:.4f}")
return pa, miou, mf1, confusion_matrix
# 主函数
def main():
# 数据准备
voc_dir = '/home/aistudio/VOC2012'
crop_size = (320, 480)
batch_size = 64
# 创建数据集和数据加载器
voc_train = VOCSegDataset(True, crop_size, voc_dir)
voc_test = VOCSegDataset(False, crop_size, voc_dir)
train_iter = DataLoader(voc_train, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,
drop_last=True, return_list=True)
# 构建和训练模型
print("开始构建FCN模型...")
net = build_fcn_model(num_classes=21)
print("模型构建完成!")
print("\n开始训练模型...")
net = train_model(net, train_iter, num_epochs=5, lr=0.001, wd=1e-3)
print("模型训练完成!")
# 模型评估
print("\n开始模型评估...")
evaluate_model(net, voc_test, num_samples=4)
print("\n计算模型详细指标...")
pa, miou, mf1, _ = calculate_metrics(net, voc_test, num_samples=100)
# 优化建议
optimization_suggestions(pa, miou, mf1)
# 保存模型
save_model(net)
print("\nFCN图像分割任务完成!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
8. 结语
本文详细介绍了在飞桨AI Studio平台上使用d2l库进行VOC2012图像分割实验的完整流程。从环境配置到模型构建,从训练过程到结果评估,我们提供了全面的技术指导和实践经验。
通过本实验,读者不仅可以掌握图像分割的基本原理和实现方法,还能深入理解深度学习框架的使用技巧。希望这篇指南能够帮助您在图像分割领域取得更好的研究成果。
关键收获:
- 熟练掌握飞桨AI Studio的环境配置
- 深入理解FCN模型的原理和实现
- 学会使用d2l库进行深度学习实验
- 掌握图像分割的评估方法和优化策略
后续学习建议:
- 探索更先进的分割网络结构
- 尝试不同的数据集和应用场景
- 研究模型压缩和加速技术
- 关注图像分割的最新研究进展
祝您在深度学习的道路上取得更大的成功!
参考资料:
- PaddlePaddle官方文档:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/
- 动手学深度学习:https://d2l.ai/
- Pascal VOC数据集:http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/
- FCN论文:Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献8条内容
已为社区贡献8条内容







所有评论(0)