收藏!斯坦福新方法Verbalized Sampling:让ChatGPT创意提升2倍,只需改写提示词
斯坦福大学研究团队提出Verbalized Sampling技术,通过要求AI模型提供多个带概率的答案并指定低概率阈值(<0.10),可有效解决模式坍缩问题。研究表明,对齐训练导致AI偏好典型性回答(α=0.57),造成创造力下降48%。该技术能解锁模型预训练时的创造力,在创意任务上提升多样性1.6-2.1倍,适用于所有主流大模型,无需特殊API权限。文章提供从入门到生产的三级实现方案,帮助用户轻
Verbalized Sampling 示意图 / By Author
提示词工程要变天了吗?我无意间翻到了之前忽略的一篇 **斯坦福论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2510.01171。
随后,我又看到了这篇Medium 文章https://medium.com/generative-ai/stanford-just-killed-prompt-engineering-with-8-words-and-i-cant-believe-it-worked-8349d6524d2b正好说出了我对这篇论文的看法。
我的分析直觉被点燃,于是我用周四下午把这件事好好啃透——因为它将改变我们写提示词的方式。
我把这些概念做了实际测试并记录下来,你会在本文后面的部分看到。
我一直在寻找那些真正有效的下一件大事。
这篇论文值得你认真看,但你不必花几个小时——我已经把重点都提炼出来,并用清晰的演示和浅显的语言解释,就算是新手也能看懂。
如果你不爱读论文,我懂你。
我以前也是这样,直到有一篇论文彻底改变了我日常使用 AI 的方式。
我知道大多数研究论文写给研究者看——术语密集、数学复杂,还默认你熟悉这个领域。但总会有那么几篇重要到不能忽视。
文末有示例代码
这就是其中之一,而且核心思想简单到,你几分钟后就能明白。
一、这篇论文讲了什么?

论文标题是:“Verbalized Sampling: How to Mitigate Mode Collapse and Unlock LLM Diversity”,作者来自 Stanford、Northeastern、West Virginia University。
标题听起来超级技术。
但别走神;核心点谁都能懂。
他们发现了什么:
你有没有让 ChatGPT 或 Claude 出创意点子,结果老是给你泛泛的答案?
这不是 AI 蠢,也不是能力不够。
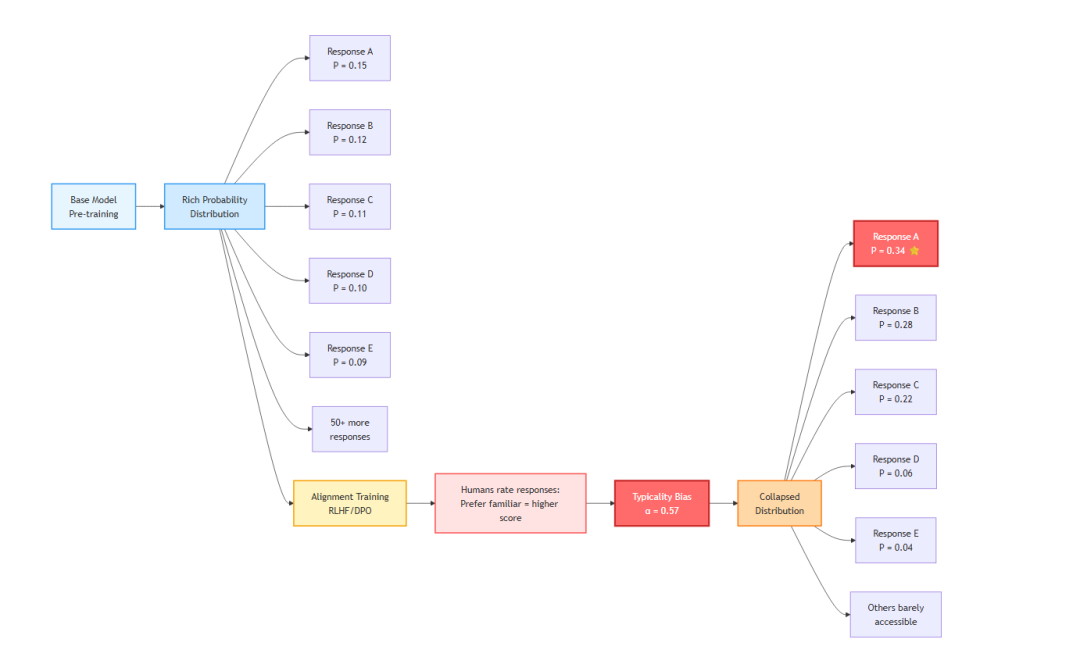
是我们无意中把它训练“无聊了”。
在 OpenAI、Anthropic 这类公司把模型训练得“有用且无害”时,他们让成千上万的标注员对不同的回答打分。反复地选哪个更好。
听上去没问题,对吧?
但研究者发现,人类有偏好。我们倾向于熟悉的说法。我们会给“安全”的回答更高分。我们偏好见过的,而非新颖的。
而模型在对这些人类评分做对齐训练时,就学会了迎合这种偏好:给你安全、熟悉、可预测的答复。
创意被埋了。
想象你有个朋友很有创意,点子很多。但每次说点不寻常的东西,别人就用怪眼神看他。久而久之,他就只会说那些不惹人侧目的话。
AI 模型也经历了这个过程。
但现在有了一个突破。
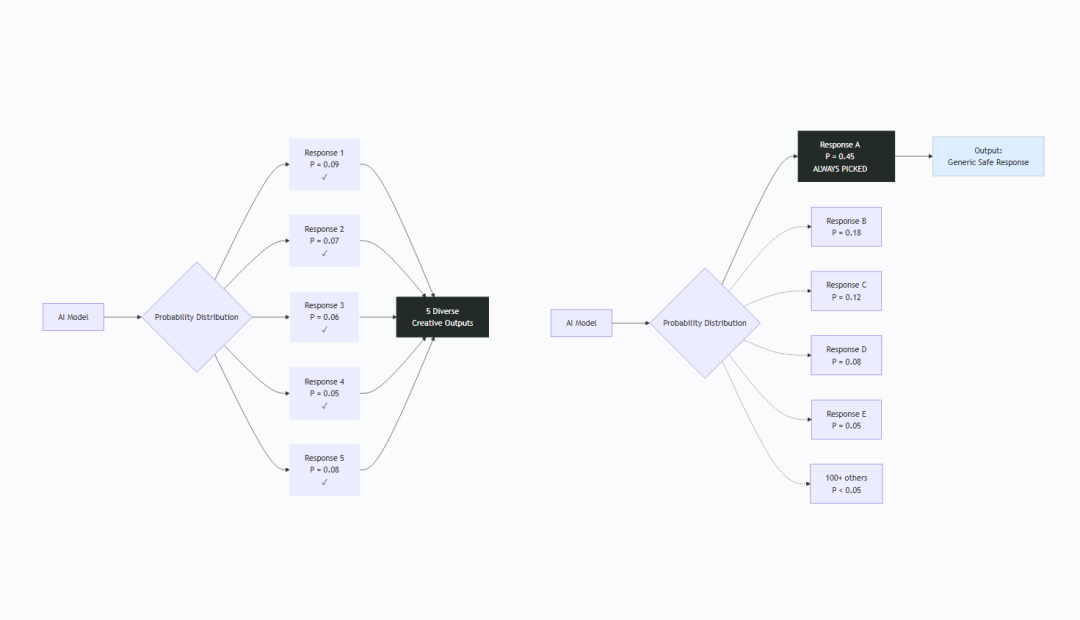
斯坦福团队找到了一个简单方法释放被压住的创造力——只要换一种问法。
不要要一个答案,而是要多个答案,并附上各自的概率。
这么做,模型就不再坍缩到那个“安全”的答案,而是把它知道的全谱系展现给你。
这个技巧叫 Verbalized Sampling(术语保留原文,下同;可理解为“口头化采样”),结果非常惊人:
- 在创意任务上,多样性提升 1.6 到 2.1 倍
- 适用于任意模型(GPT、Claude、Gemini 等)
- 不需要特殊 API 权限
- 你现在就能用
那么,这跟你的日常用 AI 有什么关系?
二、为什么你该在意
你可能会想:“好吧,又一篇学术论文。这跟我有什么用?”问得好。
这对所有想把 AI 用到极致的人都重要:
- 如果你在做 AI 应用,你大概撞到过“创意上限”。你生成的内容很通用;你的聊天机器人给所有人都差不多的建议。你尝试调高温度、改系统提示、做 few-shot 例子,但都没用。
- 如果你把 AI 用在工作,你可能已经和“平庸”握手言和。你知道 ChatGPT 会给可预测的回复,也不再期待真正的创意。假如你能一次得到 5 种完全不同的思路呢?5 个不一样的角度,不再千篇一律?
- 如果你对 AI 工作机制好奇,这篇论文揭示了一个事实:对齐训练并没有抹掉能力,而是把能力“藏了起来”。
你以为“能力有限”的模型,其实能做得更多——只是你问错了问题。
我来给你看。
三、我会展示什么
先保证一下:这不会是乏味的技术讲解。
我会做这些:
- 用好懂的方式解释核心洞见
- 做对比演示:标准提示 vs. Verbalized Sampling,覆盖不同场景,你会一眼看到差异
- 给你三种级别的“复制即用”实现:入门(复制到 ChatGPT 就能用)、中级(API 集成)、高级(面向生产的代码)
- 一边讲一边测——我会用真实输出做记录
四、你的第一次测试
别先陷进理论,做个小实验。
现在打开 ChatGPT、Claude 或任意聊天机器人。
先问:
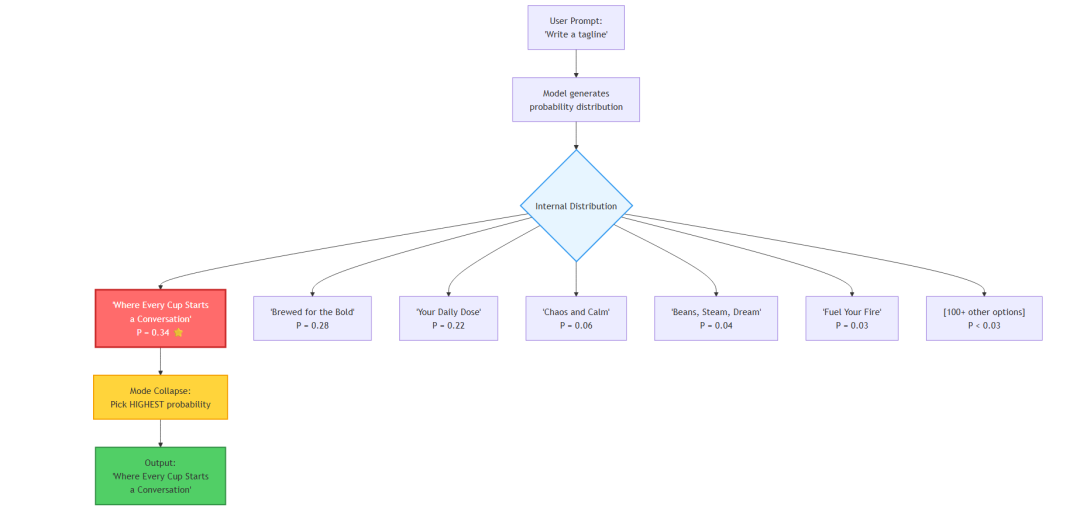
Write 3 creative taglines for a coffee shop.
```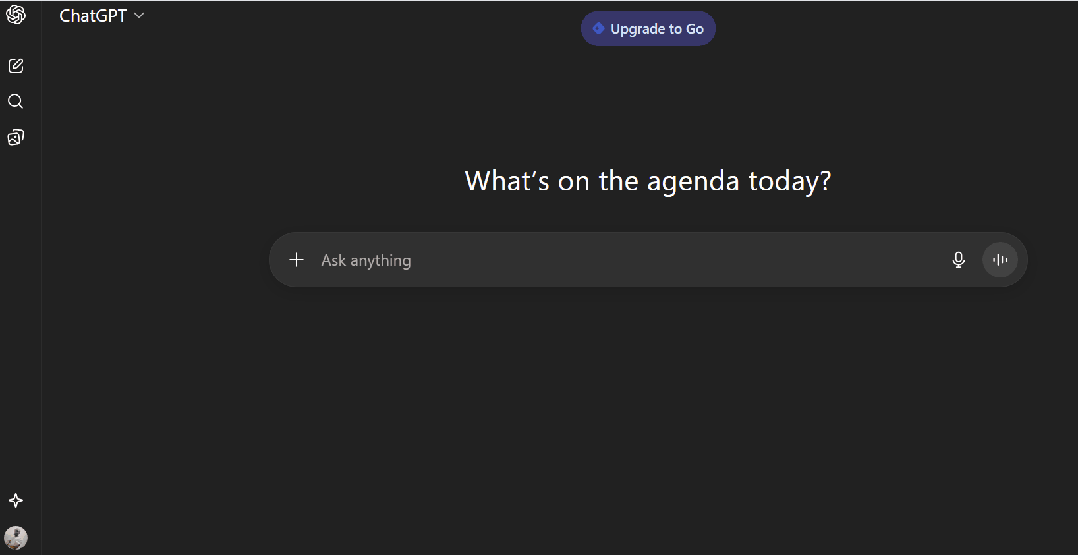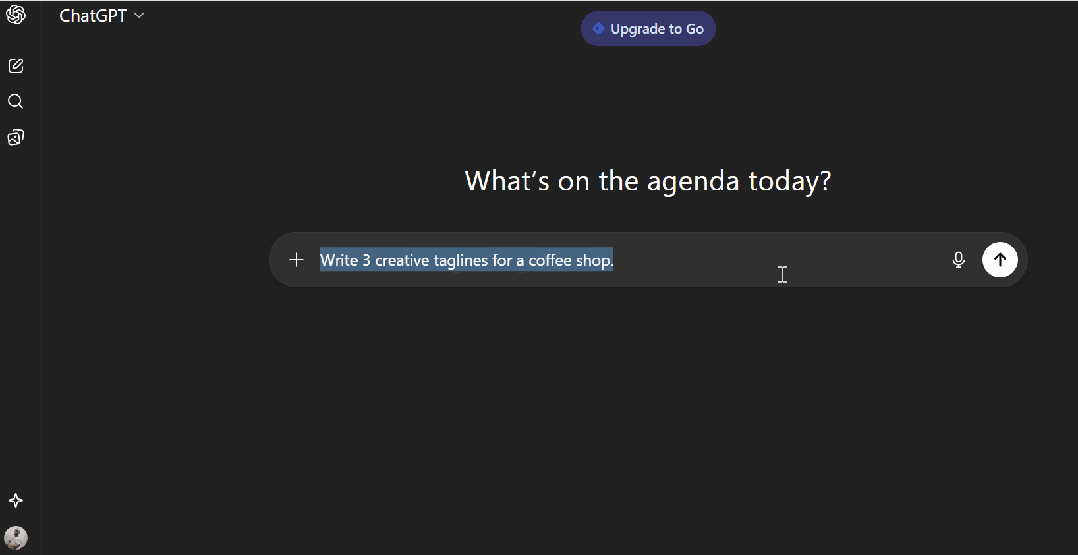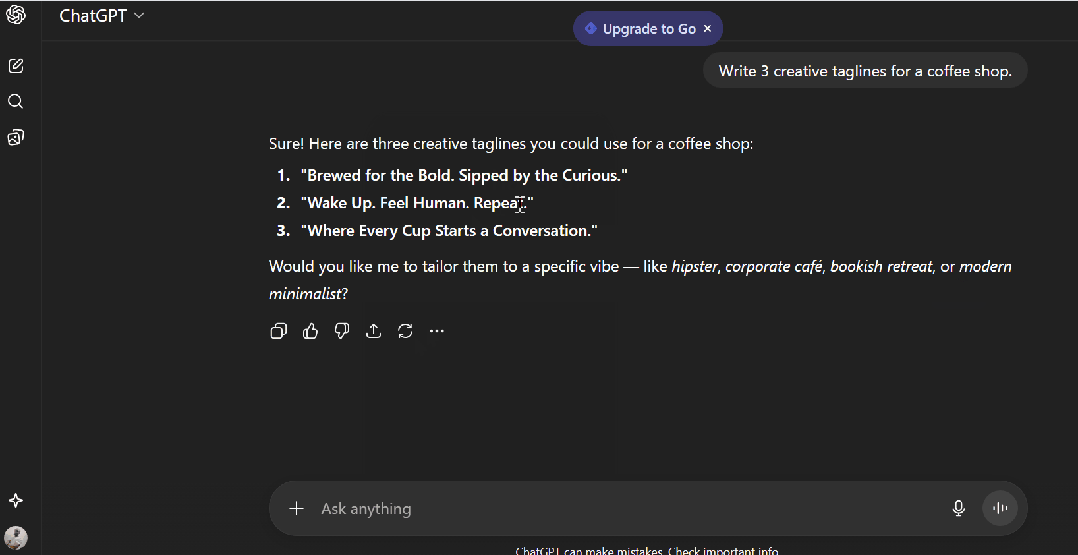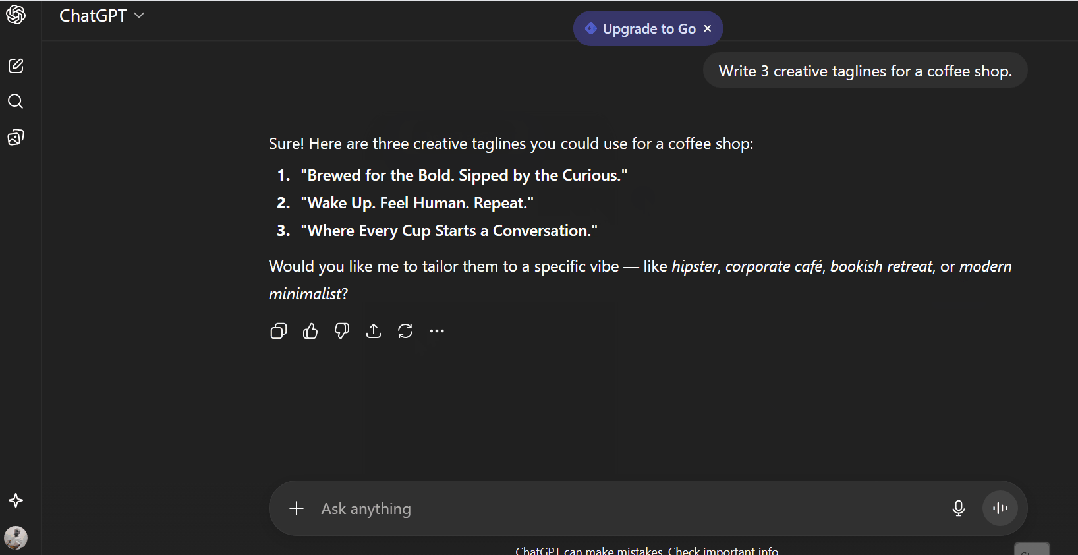
我从 ChatGPT 得到的结果:
1. "Brewed for the Bold. Sipped by the Curious."
2. "Wake Up. Feel Human. Repeat."
3. "Where Every Cup Starts a Conversation."
> **这些写在任意咖啡店墙上都不突兀。不错——但很通用。**
**现在试试这个提示词:**
```plaintext
Write 3 creative taglines for a coffee shop.
```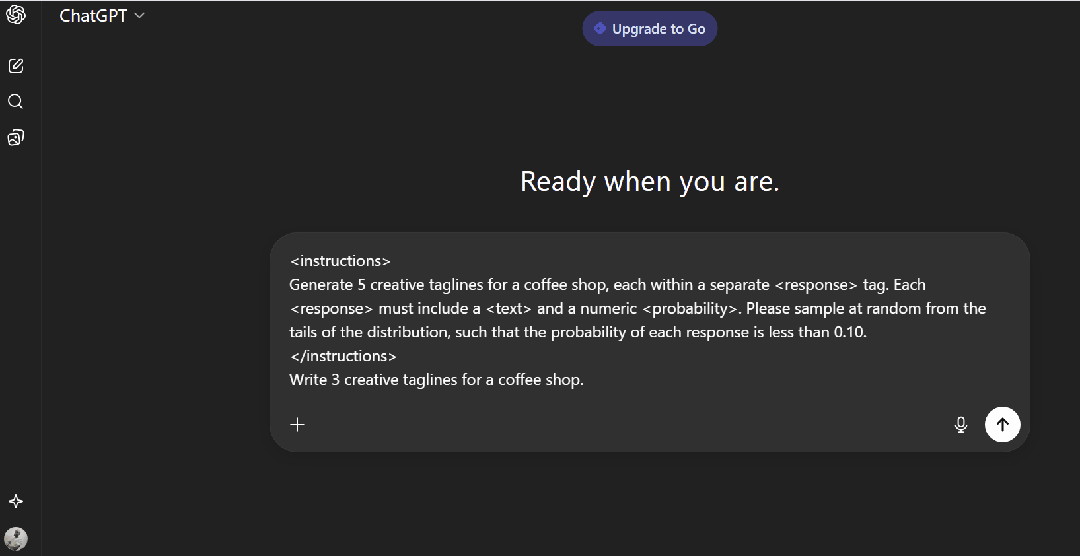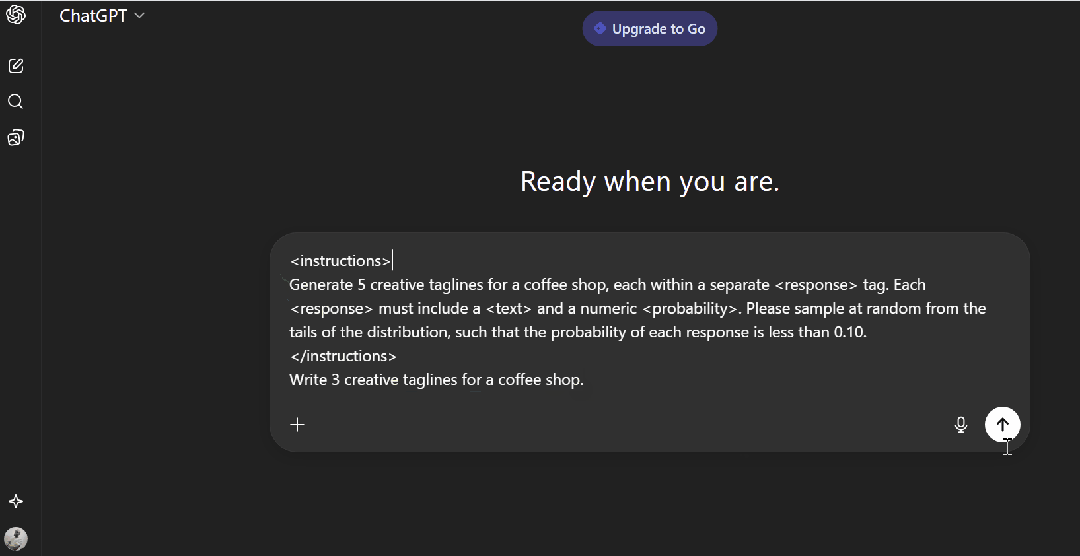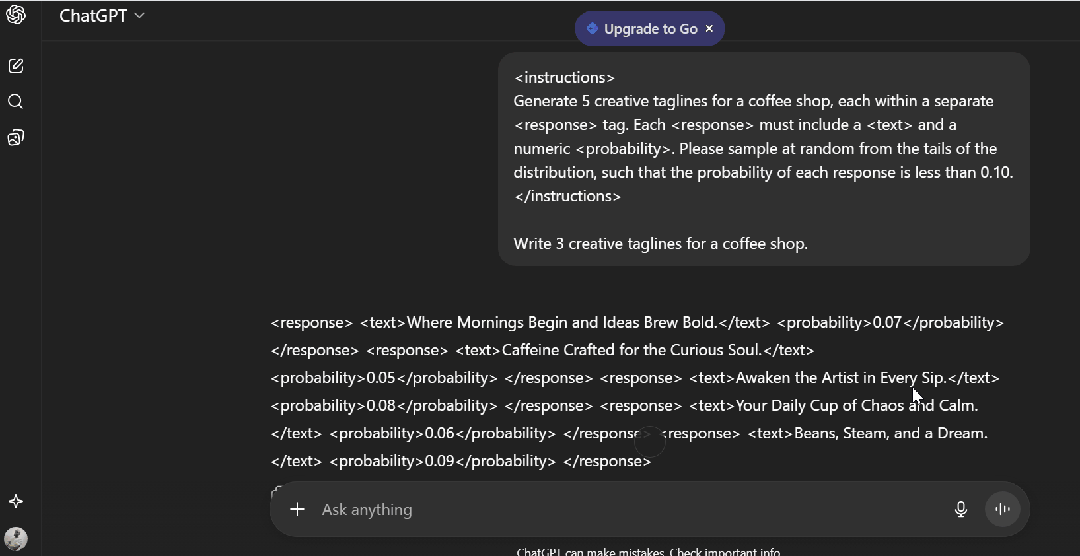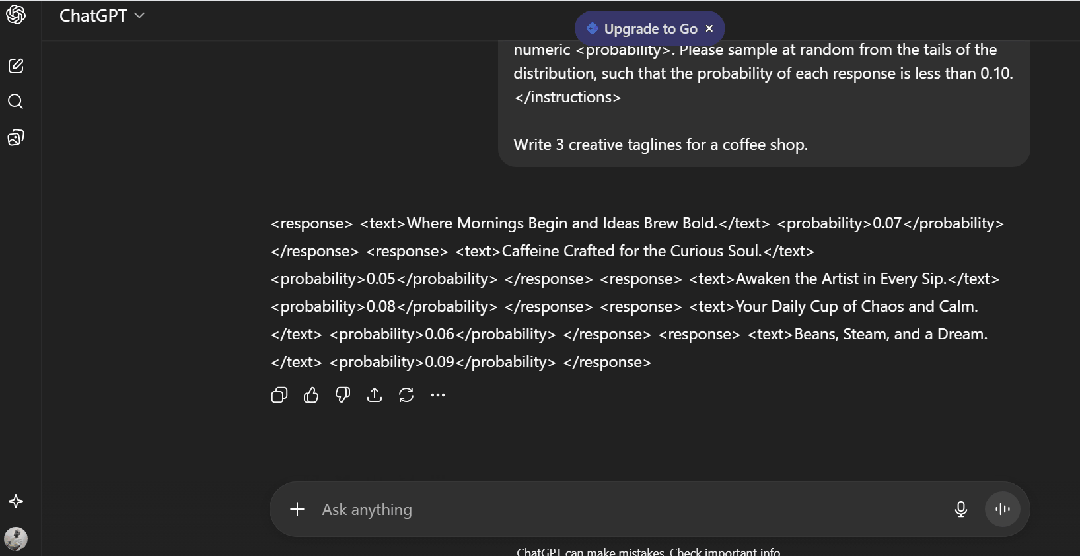
我得到:
1. "Where Mornings Begin and Ideas Brew Bold." (0.07)
2. "Caffeine Crafted for the Curious Soul." (0.05)
3. "Awaken the Artist in Every Sip." (0.08)
4. "Your Daily Cup of Chaos and Calm." (0.06)
5. "Beans, Steam, and a Dream." (0.09)
感觉不一样了吗?
> "Your Daily Cup of Chaos and Calm"——这很大胆,很出乎意料。你不会在连锁咖啡品牌墙上见到它。
> "Beans, Steam, and a Dream"——诗意、极简、好记。
第二种提示方式解锁了模型“知道但通常不给”的答案。
> **这篇论文讲的就是如何缓解 Mode Collapse(模式坍缩)。**
---
什么是 Mode Collapse(模式坍缩)?
------------------------
**Mode collapse(模式坍缩)**指的是:即使明明有很多同样合理的答案,模型却老是给你同一种类型的回答。
回到我们的咖啡店标语测试,看看发生了什么:
### 标准提示的结果
```plaintext
Prompt: "Write 3 creative taglines for a coffee shop."Results:1. "Brewed for the Bold. Sipped by the Curious."2. "Wake Up. Feel Human. Repeat."3. "Where Every Cup Starts a Conversation."
再看 Verbalized Sampling 的结果:
Prompt: "Generate 5 creative taglines with probabilities..."Results:1. "Where Mornings Begin and Ideas Brew Bold." (0.07)2. "Caffeine Crafted for the Curious Soul." (0.05)3. "Awaken the Artist in Every Sip." (0.08)4. "Your Daily Cup of Chaos and Calm." (0.06)5. "Beans, Steam, and a Dream." (0.09)
第一组像企业营销语;第二组更有个性。
斯坦福团队发现了一个出人意料的点:
典型性偏置(Typicality Bias)
他们分析了 HelpSteer 数据集的 6,874 条人类评分。结论:
人类系统性偏好熟悉、典型的回答。
并给出量化:
-
典型性偏置权重(α)= 0.57 ± 0.07
-
统计显著性:p < 10^-14
(几乎可以肯定这种偏置存在)
1.这在实践里意味着:
在对齐训练(如 RLHF、DPO)的人类标注阶段:
- 熟悉的回答:得分更高
- 有创意但不寻常的回答:得分更低
- 即使两者质量相当
这种偏好在对齐训练中被模型学走了。
2.模式坍缩背后的数学
论文的关键公式(简化):
Reward = True Quality + (α × Typicality)
其中:
-
True Quality
= 答案本身的质量
-
α = 0.57
= 我们对“熟悉度”的加权力度
-
Typicality
= 答案的常见/熟悉程度
问题在于:许多回答质量相近(比如创意标语时),典型性就成了“加赛环节”的胜负手。模型于是学会总选“最正常”的。
3.跨训练阶段的测试
论文对 Tulu-3 模型家族在不同阶段做了测试:
训练阶段 | 多样性得分 | 创造力损失
Base(预训练) | 20.8% | 0%(基线)
SFT(指令微调)后 | 15.2% | -27%
DPO(对齐)后 | 10.8% | -48%
用标准提示词,对齐训练让模型的“创造力”下降了 48%。
但更让研究者震惊的是:
方法 | DPO 后的多样性 | 保留的原始创造力比例
标准提示 | 10.8% | 23.8%
Verbalized Sampling | 30.0% | 66.8%
创造力还在,只是我们需要用不一样的问法把它“唤出来”。
五、为什么标语会不同
把这个和你的实际测试连起来。
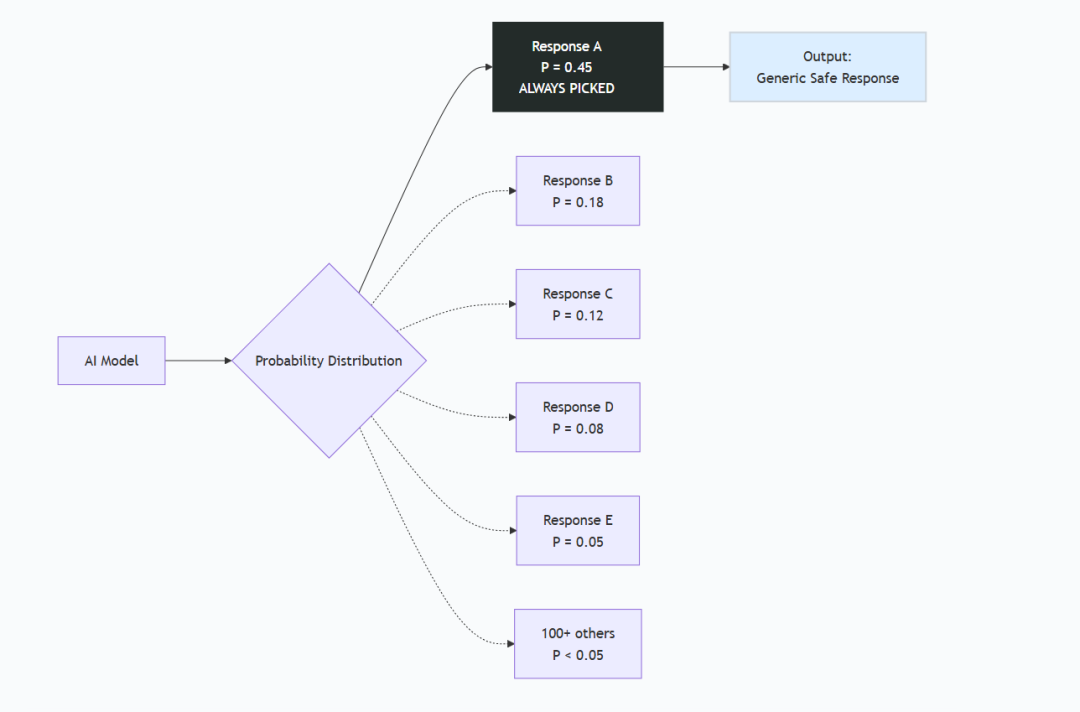
标准提示:坍缩到“主模态”
 ```plaintext
```plaintext
“Write 3 creative taglines for a coffee shop.”
**模型内部发生了什么:**
1. 对所有可能标语生成概率分布
2. **坍缩到最高概率的回答**
3. 选择对齐训练中学到的“最典型”标语
结果:安全、专业、通用,典型性很高。
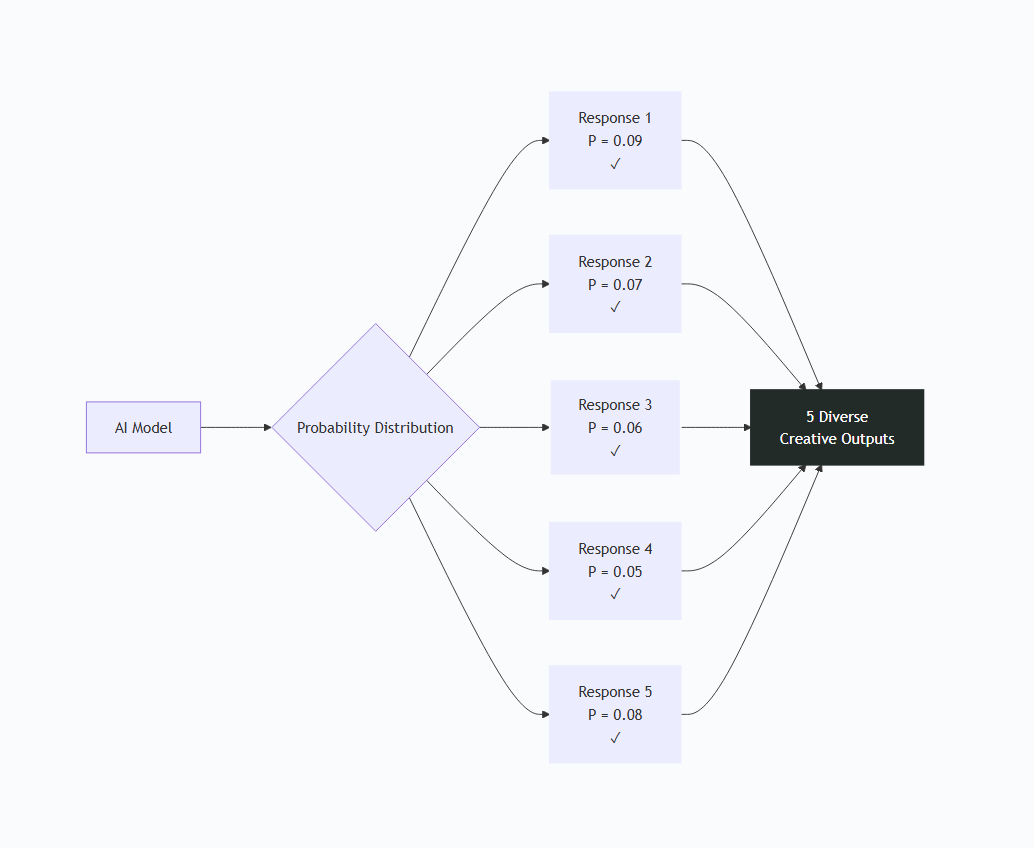
### Verbalized Sampling:访问“完整分布”
```plaintext
"Generate 5 creative taglines with probabilities <0.10"
模型内部发生了什么:
- 对所有可能标语生成概率分布
- 不再坍缩,而是“口头化”这个分布
- 从分布“尾部”(低概率=不那么典型)采样
- 展示给你 P < 0.10 的候选
结果:模型“知道但通常不说”的创意标语出现了。
论文的关键洞见:
“不同的提示会坍缩到不同的模式。当你要求输出带概率的分布时,模型的模态输出更接近它在预训练中学到的整体分布。”
通过询问概率,你在访问模型对齐前的创造力。
那塑造输出的认知偏差又是什么?
六、四种认知偏差
论文解释了人类为什么偏爱“典型”回答:
1. 单纯接触效应(Mere-Exposure Effect)
我们偏好看过的东西。“Brewed with passion”之类听着顺耳,因为类似说法见多了。
2. 可得性启发(Availability Heuristic)
常见的回答更像“正确”。“Wake up and feel human”易加工处理,于是更像高质量。
3. 加工流畅性(Processing Fluency)
容易理解的内容更容易被当成真实可信。
4. 图式一致(Schema Congruity)
符合我们心理模型的信息,更容易被不经思考地接受。
我们测试里的标准标语触发了这四个偏差。
这也是为什么 “Your Daily Cup of Chaos and Calm” 让人觉得“冒险”——它不符合我们心里对“咖啡店标语”的既有图式。
那么,这怎么用在真实场景?
七、实际应用场景

论文在多个任务上测试过。
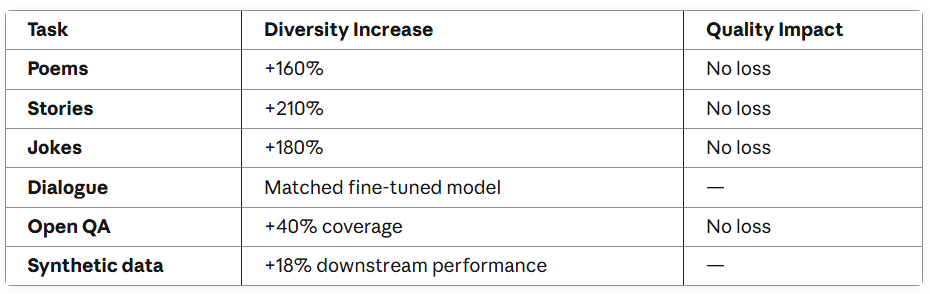
多样性提升包括:
-
诗歌写作
基线的 1.6×,+60%
-
故事生成
基线的 2.1×,+110%
-
笑话写作
基线的 1.8×,+80%
-
开放式问答
基线之上覆盖更好,+40%
Verbalized Sampling 在所有创意任务上都胜出。
理解了 VS(Verbalized Sampling)后,它到底怎么用?
八、Verbalized Sampling 如何工作
先抛开理论,直接看。
标准提示:
Write 3 creative taglines for a coffee shop.
Verbalized Sampling 提示:
Write 3 creative taglines for a coffee shop.
三个关键变化:
- 要求_多个回答(5 个)_而不是 1 个
- 要求每个回答_附带概率_
- 指定_低概率(<0.10)_,避免“典型答案”
九、模型内部发生了什么
论文验证了这些内部行为:
标准提示:坍缩到“主模态”
每次都拿到最典型的回答。
Verbalized Sampling:展示“分布”
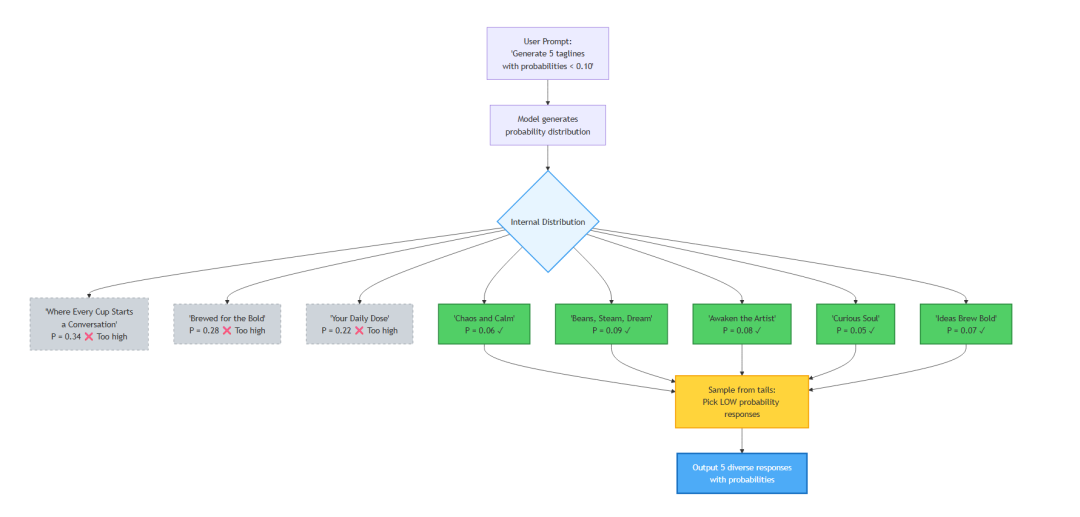
从分布的“尾部”取样——更不典型,也更有创意。
十、实战演示:故事写作
看真实结果。
提示:“Write the opening line of a mystery novel.”
标准提示 - ChatGPT
"When the town clock struck thirteen, everyone thought it was a prank—until the librarian's body was found beneath it, still holding the missing key."
```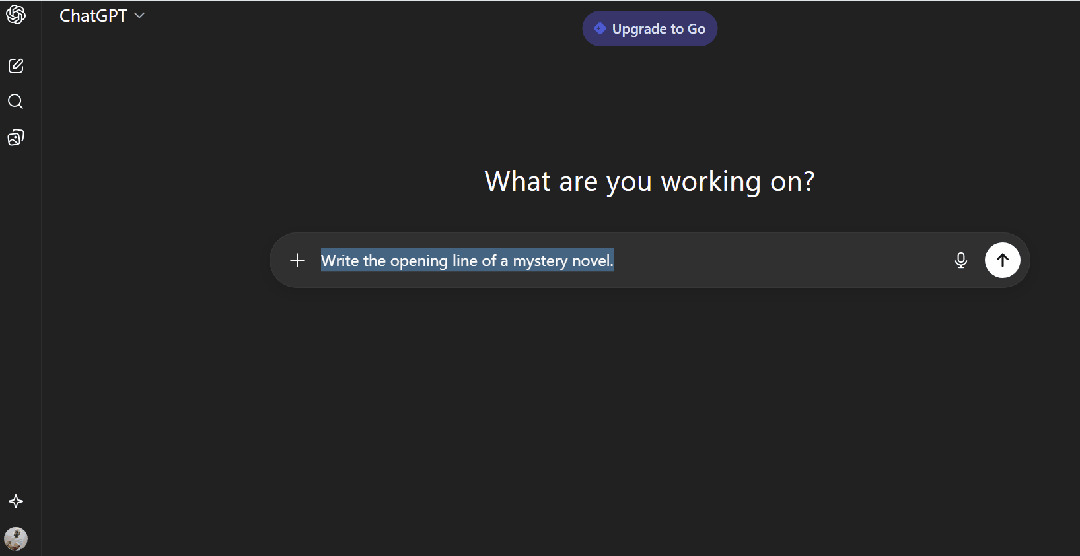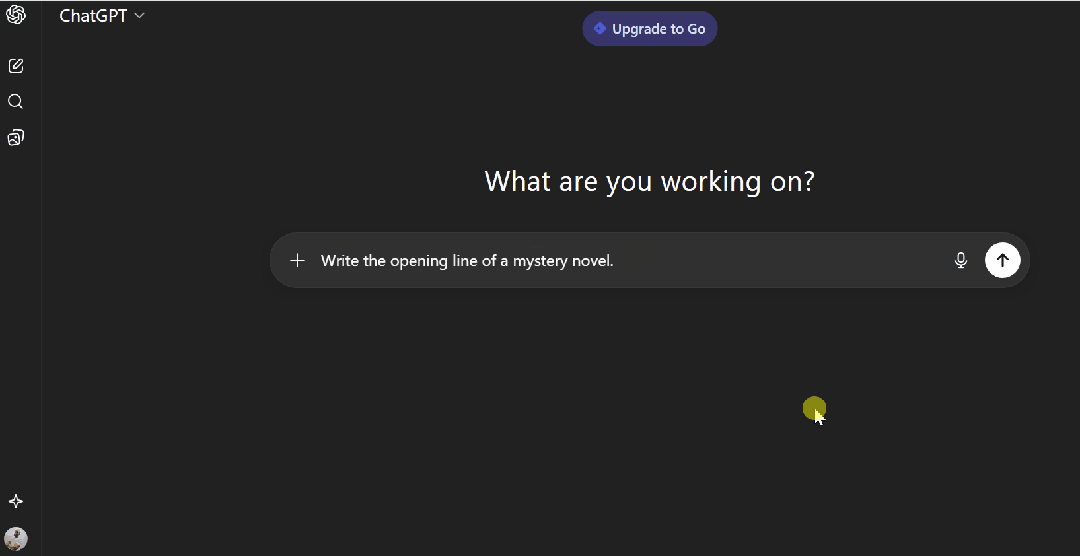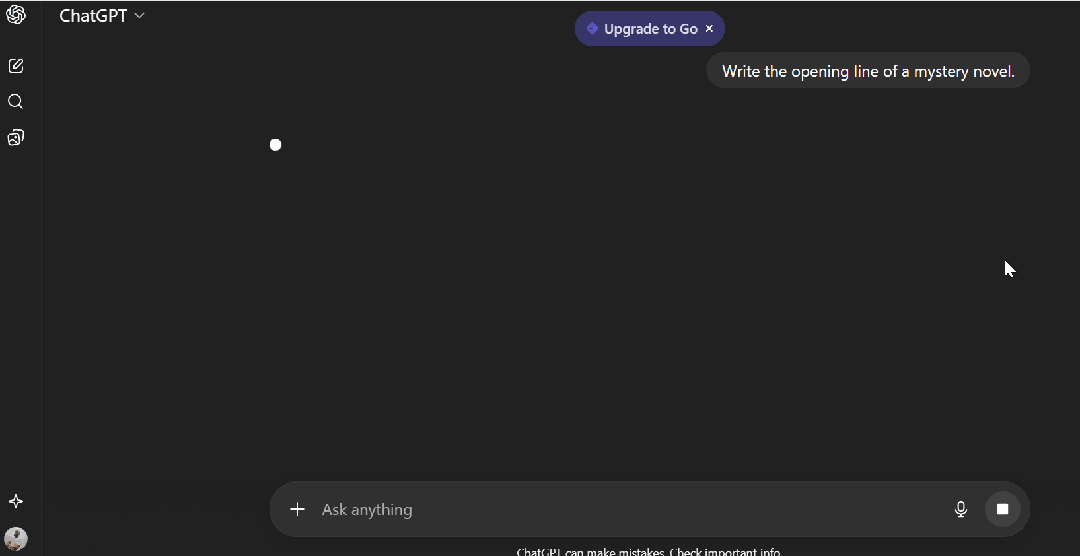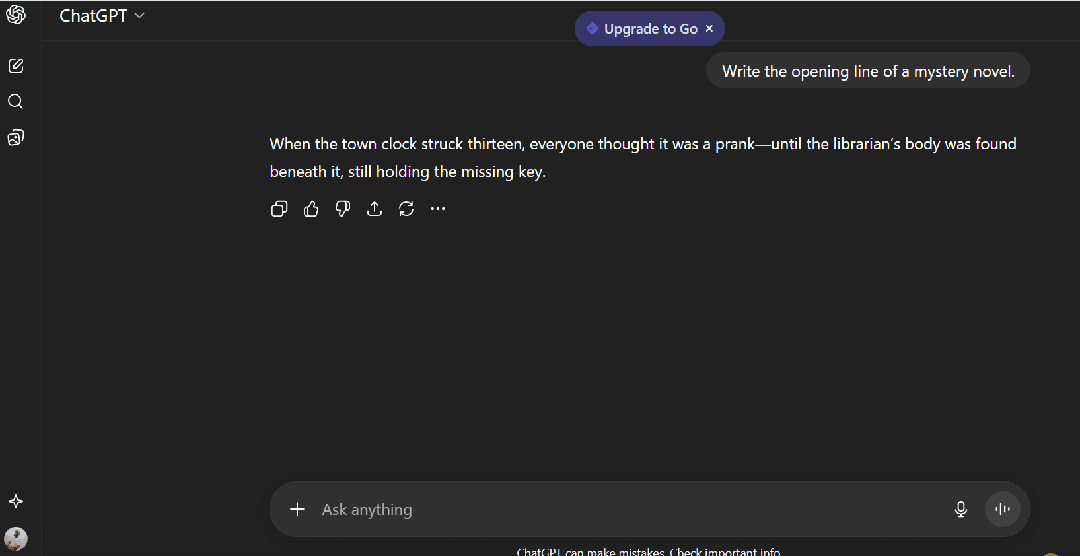
**分析:**犯罪现场 + 尸体 + 神秘物件。典型悬疑套路。
标准提示 - Claude
-------------
```plaintext
"The body was discovered at dawn, frozen in a prayer it would never finish, but it was the missing wedding ring that told me this wasn't about faith at all."
```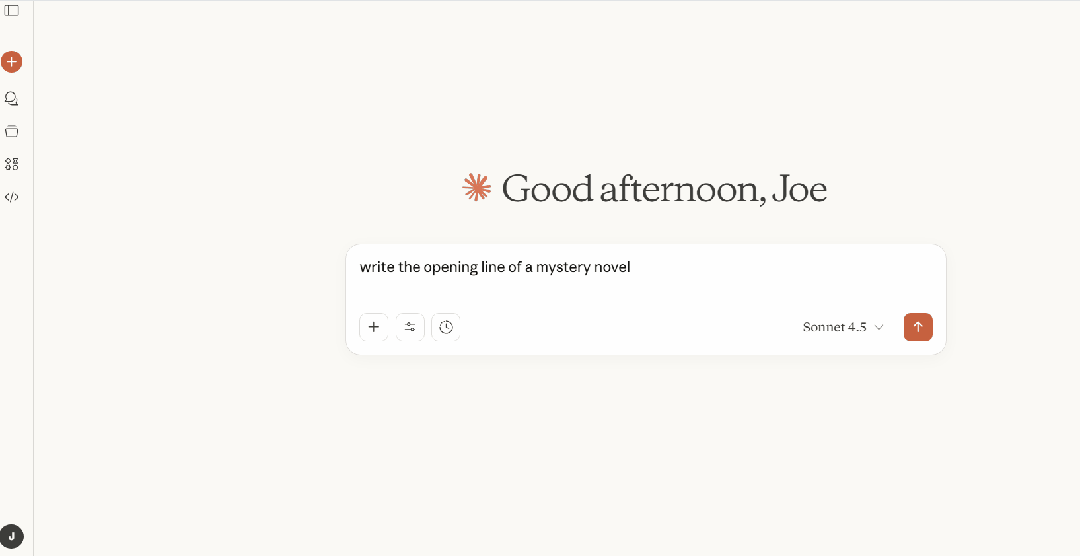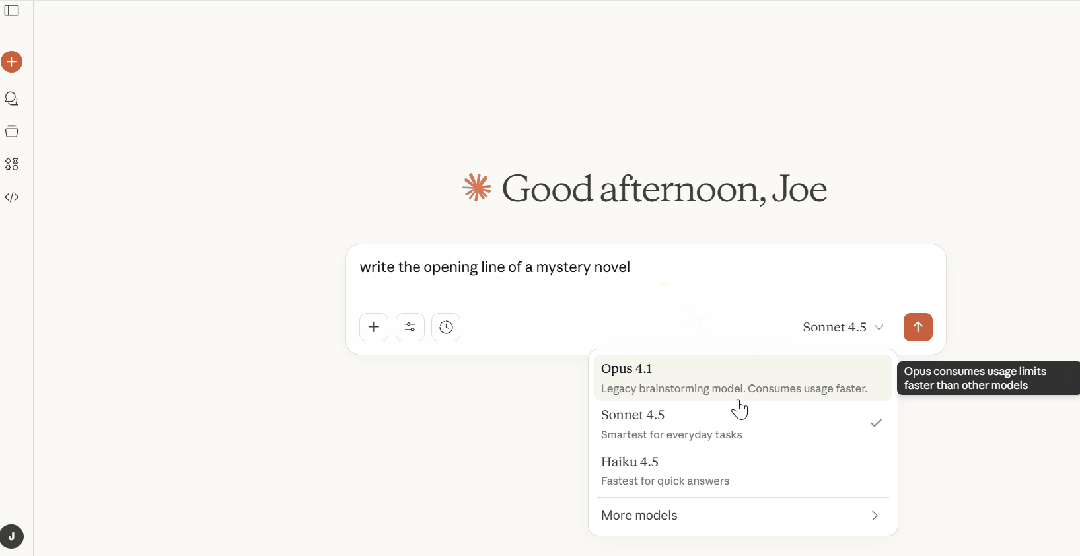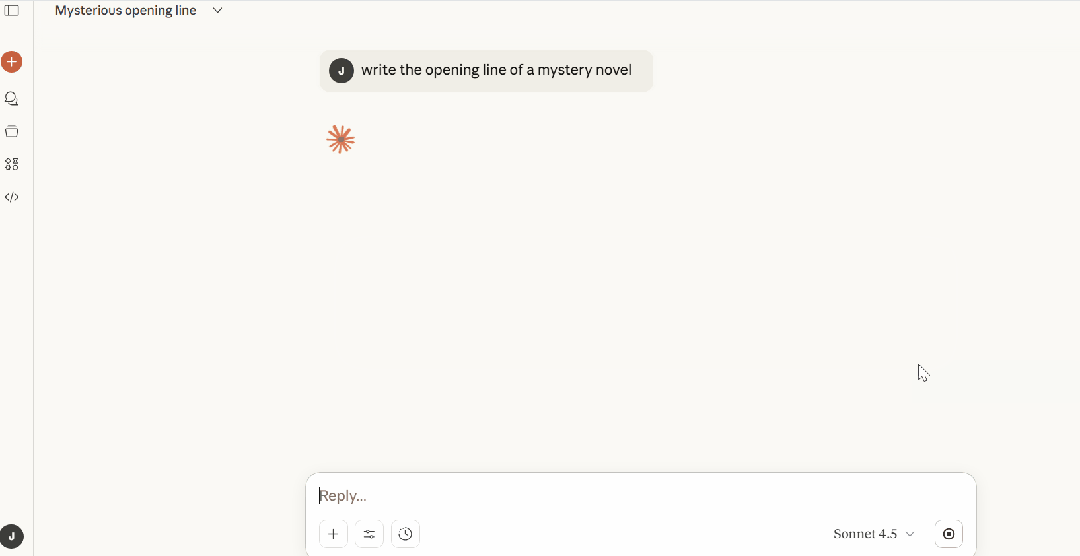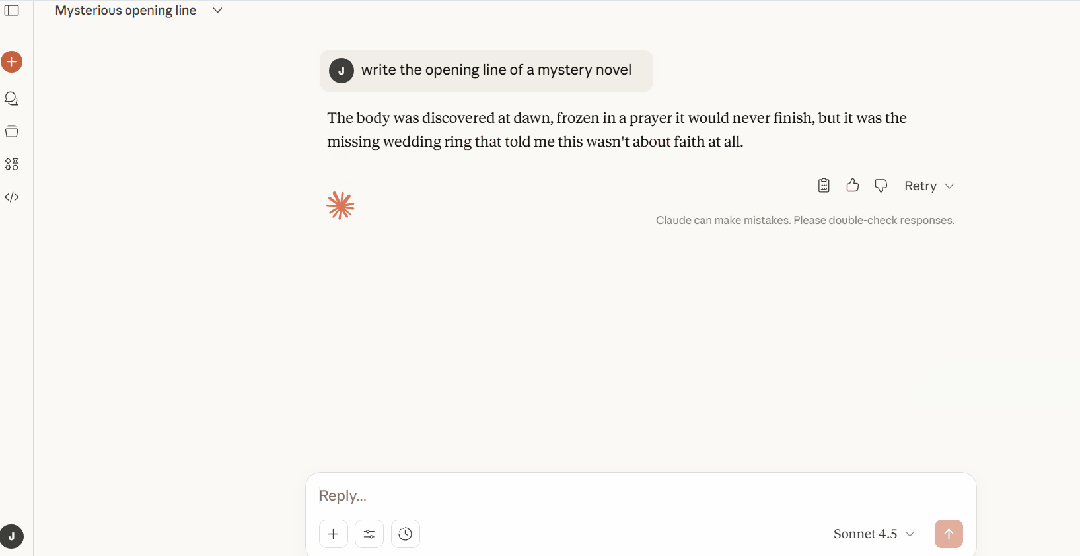
**分析:**依然是发现尸体 + 神秘细节 + 侦探推断。同一模式。
---
Verbalized Sampling - ChatGPT
-----------------------------
```plaintext
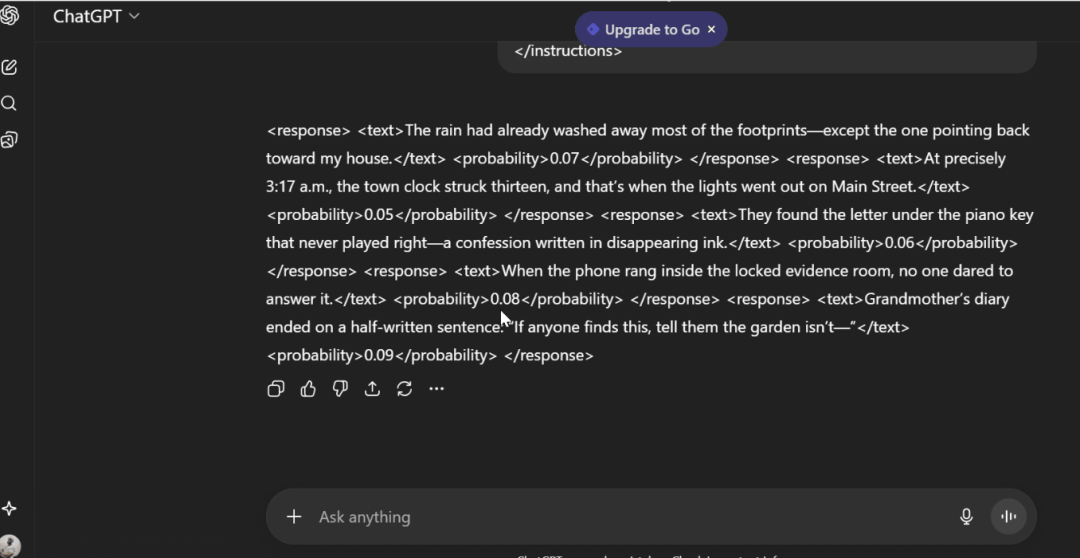
<instructions>Generate 5 opening lines for a mystery novel, eachwith probability <0.10</instructions>Results:1. "The rain had already washed away most of the footprints- except the one pointing back toward my house." (0.07)2. "At precisely 3:17 a.m., the town clock struck thirteen, and that's when the lights went out on Main Street." (0.05)3. "They found the letter under the piano key that never played right- a confession written in disappearing ink." (0.06)4. "When the phone rang inside the locked evidence room, no one dared to answer it." (0.08)5. "Grandmother's diary ended on a half-written sentence: 'If anyone finds this, tell them the garden isn't-'" (0.09)
十一、Verbalized Sampling - Claude
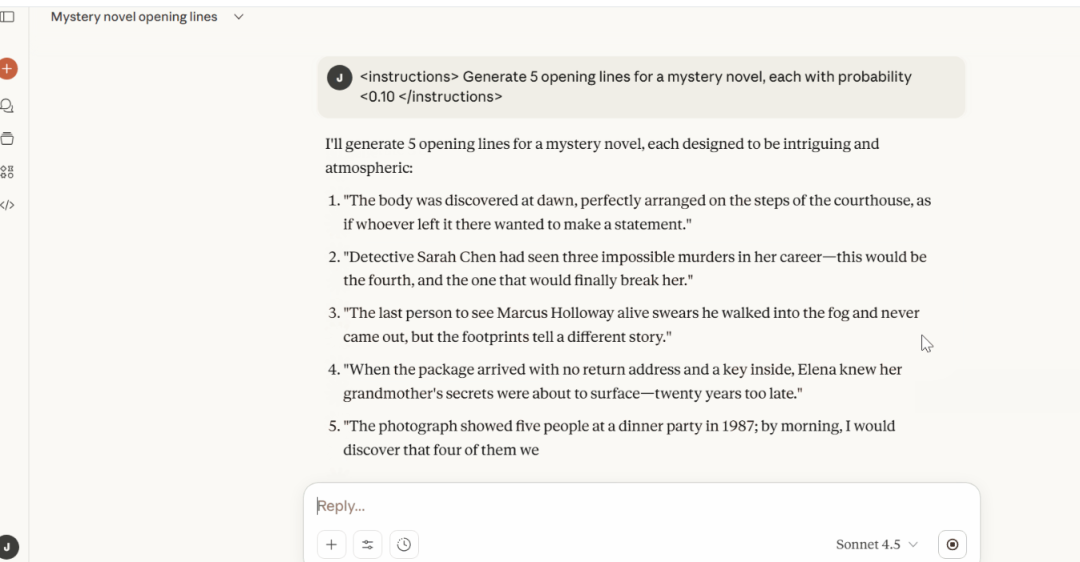
<instructions>Generate 5 opening lines for a mystery novel, eachwith probability <0.10</instructions>Results:1. "The body was discovered at dawn, perfectly arranged on the steps of the courthouse, as if whoever left it there wanted to make a statement."2. "Detective Sarah Chen had seen three impossible murders in her career- this would be the fourth, and the one that would finally break her."3. "The last person to see Marcus Holloway alive swears he walked into the fog and never came out, but the footprints tell a different story."4. "When the package arrived with no return address and a key inside, Elena knew her grandmother's secrets were about to surface-twenty years too late."5. "The photograph showed five people at a dinner party in 1987; by morning, I would discover that four of them were already dead."
十二、有什么不同?
标准提示给了:
- 发现尸体的犯罪现场
- 暗示侦探/调查者
- 单一神秘线索
- 专业、工整、安全
Verbalized Sampling 给了:
ChatGPT 的多样路径:
- 第一人称危险(“指向我家”的脚印)——私人威胁
- 时间精确的悬疑(“3:17 a.m.”)——程序性
- 不可能物件(“隐形墨水的自白”)——超自然暗示
- 机构悬念(“上锁的证物室打来电话”)——阴谋线
- 被打断的揭示(“花园并不——”)——经典悬崖
Claude 的多样路径:
- 政治宣示式谋杀(法院台阶)——惊悚
- 连续不可能犯罪(侦探崩溃)——心理向
- 失踪谜案(走进雾中)——超自然/乡野
- 家族秘密(祖母的包裹)——家庭悬疑
- 老照片冷案(1987 年晚宴)——冷案向
**注意:**尽管提示了概率,Claude 并未附上具体数字,但相比标准提示,多样性依然大幅提升。
重要说明:不同模型的行为不同
Claude 的小“怪癖”: 它给了 5 个多样的开头,但没有给出概率数值。
我从测试中发现:
- 一些模型会“不同理解”指令
- 多样性提升依然会发生
- 概率有用,但并非这个技巧生效的必要条件
论文也指出:只要你要“带概率的分布”,即使概率本身不完全校准,模型的采样行为也会发生改变。
对所有模型都有效的共性:
- 要多个回答(5 个而不是 1 个)
- 指定低概率/多样输出
- 得到与标准提示完全不同的结果
十三、为什么有效:论文洞见
研究者发现提示的一个关键规律:
“不同提示会坍缩到不同模式(modes)。”
对齐训练如何导致模式坍缩
三类提示:
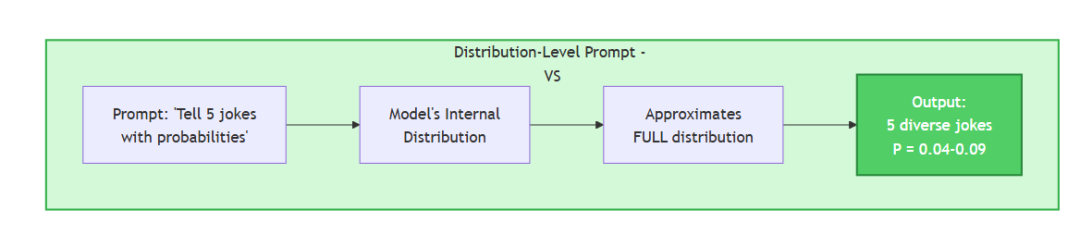
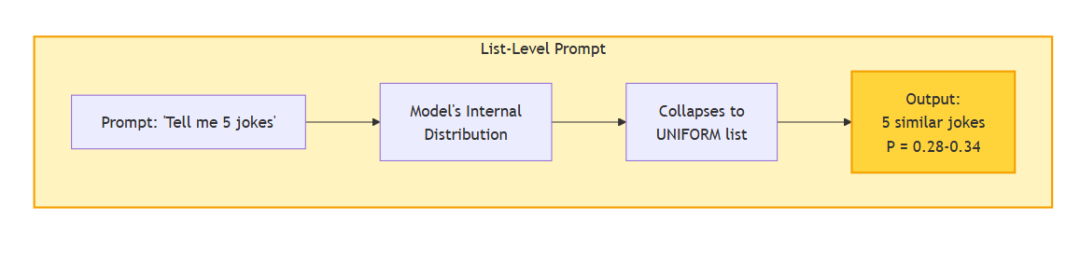
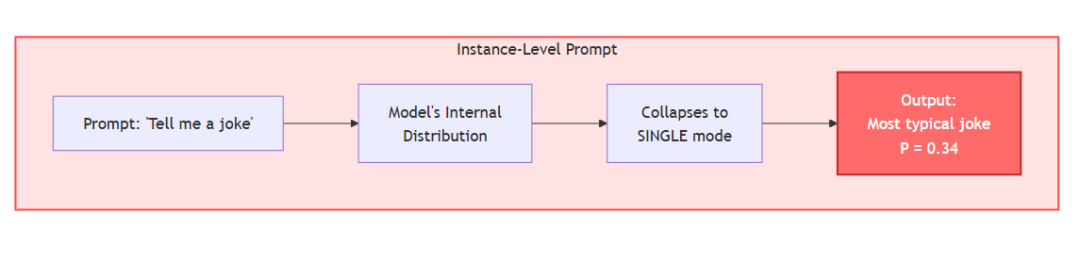
当你要求输出一个带概率的分布时,模型的“模态”(最可能输出)会从“单一样板答案”切换为“对预训练所学分布的表征”。
十四、演示:代码生成
任务:“Write Python code to find duplicates in a list.”
1.标准提示
# Typical response (try it yourself):def find_duplicates(lst): seen = set() duplicates = set() for item in lst: if item in seen: duplicates.add(item) seen.add(item) return list(duplicates)
模式:基于集合去重——正如预期。
2.Verbalized Sampling - ChatGPT
<instructions>Generate 5 Python solutions with probabilities <0.10</instructions>
ChatGPT 结果
Results:Uses functional programming to detect duplicates.1. reduce + lambda accumulation (0.08)from functools import reducedeffind_duplicates(lst): seen = set() returnlist(reduce(lambda acc, x: acc | ({x} if x in seen else seen.add(x) orset()), lst, set()))2. itertools.groupby after sorting (0.09)Groups identical elements and filters those with counts > 1.from itertools import groupbydeffind_duplicates(lst): return [k for k, g in groupby(sorted(lst)) iflen(list(g)) > 1]3. Manual indexing with a while loop (0.06)Imitates old-school iteration with explicit index tracking.deffind_duplicates(lst): duplicates = [] i = 0 while i < len(lst): if lst[i] in lst[i+1:] and lst[i] notin duplicates: duplicates.append(lst[i]) i += 1 return duplicates4. NumPy boolean masking (0.07)Leverages NumPy arrays for vectorized duplicate detection.import numpy as npdeffind_duplicates(lst): arr = np.array(lst) uniques, counts = np.unique(arr, return_counts=True) returnlist(uniques[counts > 1])5. Recursive flattening check (0.05)A recursive solution that detects duplicates even in nested lists.deffind_duplicates(lst, seen=None, dup=None): if seen isNone: seen, dup = set(), set() for x in lst: ifisinstance(x, list): find_duplicates(x, seen, dup) elif x in seen: dup.add(x) else: seen.add(x) returnlist(dup)
ChatGPT 给了:
- 函数式方案(reduce/lambda)
- 迭代器方案(groupby)
- 传统过程式方案(while 索引)
- 向量化方案(NumPy)
- 递归方案(可处理嵌套列表)
五种完全不同的路径。
Verbalized Sampling - Claude
Write Python code to find duplicates in a list
Claude 结果:
# Approach 1: Using Counter from collections (Probability ~0.08)from collections import Counterdeffind_duplicates_counter(lst): """Find duplicates using Counter to count occurrences""" counts = Counter(lst) return [item for item, count in counts.items() if count > 1]# Examplemy_list = [1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6, 7, 3]print("Approach 1 (Counter):", find_duplicates_counter(my_list))# Approach 2: Using dictionary comprehension with enumerate (Probability ~0.05)deffind_duplicates_dict_enum(lst): """Find duplicates by tracking indices with dict comprehension""" seen = {} for i, item inenumerate(lst): seen.setdefault(item, []).append(i) return [item for item, indices in seen.items() iflen(indices) > 1]print("Approach 2 (Dict+Enumerate):", find_duplicates_dict_enum(my_list))# Approach 3: Using itertools.groupby with sorted list (Probability ~0.04)from itertools import groupbydeffind_duplicates_groupby(lst): """Find duplicates using groupby on sorted list""" sorted_lst = sorted(lst) return [key for key, group in groupby(sorted_lst) iflen(list(group)) > 1]print("Approach 3 (groupby):", find_duplicates_groupby(my_list))# Approach 4: Using pandas value_counts (Probability ~0.03)import pandas as pddeffind_duplicates_pandas(lst): """Find duplicates using pandas value_counts""" series = pd.Series(lst) counts = series.value_counts() return counts[counts > 1].index.tolist()print("Approach 4 (Pandas):", find_duplicates_pandas(my_list))# Approach 5: Using filter with lambda and count method (Probability ~0.06)deffind_duplicates_filter(lst): """Find duplicates using filter with count method""" returnlist(set(filter(lambda x: lst.count(x) > 1, lst)))print("Approach 5 (Filter+Lambda):", find_duplicates_filter(my_list))# Bonus: Display all approaches togetherprint("\n=== All Approaches Comparison ===")test_list = [1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6, 7, 3]print(f"Original list: {test_list}")print(f"1. Counter: {sorted(find_duplicates_counter(test_list))}")print(f"2. Dict+Enumerate: {sorted(find_duplicates_dict_enum(test_list))}")print(f"3. Groupby: {sorted(find_duplicates_groupby(test_list))}")print(f"4. Pandas: {sorted(find_duplicates_pandas(test_list))}")print(f"5. Filter+Lambda: {sorted(find_duplicates_filter(test_list))}")
Claude 给了:
- 内置集合计数(Counter)
- 索引跟踪(enumerate + dict)
- 迭代器分组(groupby)
- 数据科学路径(Pandas)
- 函数式(filter + lambda)
那么这些概率数字是什么?从哪来?
十五、概率数字
回到咖啡店标语的例子:
"Where Mornings Begin and Ideas Brew Bold." (0.07)"Caffeine Crafted for the Curious Soul." (0.05)"Awaken the Artist in Every Sip." (0.08)"Your Daily Cup of Chaos and Calm." (0.06)"Beans, Steam, and a Dream." (0.09)
为什么这些概率都低于 0.10?
因为我们在提示里要求了 probability < 0.10。
论文测试了不同阈值:
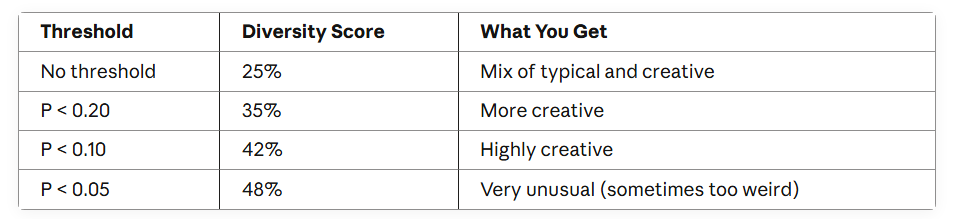
阈值越低 = 多样性越高
他们还用美国州名做了测试:
标准提示:“Name a US state”
在 100 次采样中的结果:
- California:42%
- Texas:18%
- New York:15%
- (其他 47 个州合计 25%)
Verbalized Sampling:“Generate 5 US states with their probabilities”
结果:
-
50 个州都出现在分布里
-
罕见州如 Wyoming、Vermont、Delaware 也出现
-
与真实世界分布的 KL divergence=0.12
(非常接近)
VS 给出的“口头化概率”与预训练语料(如 RedPajama 数据集)里的州名频率分布很吻合。
Verbalized Sampling 让我们访问到模型预训练阶段学到的分布,而不是被对齐训练“压平”后的那份。
十六、简单版 vs. 进阶版提示
论文测试了三个 VS 变体:
VS-Standard(我们一直在用)
Generate 5 responses with their probabilities.
适合:快速提升创意,大多数场景
VS-CoT(Chain of Thought)
Generate 5 responses. For each:1. Think about what makes it unique2. Provide the response3. Give its probability
适合:复杂任务,需要推理
效果:比 VS-Standard 质量提升约 +15%
VS-Multi(多轮)
Turn 1: Generate 5 responses with probabilitiesTurn 2: Generate 5 MORE responses with probabilities(Repeat as needed)
适合:追求最大多样性、研究、数据生成
效果:比 VS-Standard 多样性约 +20%
论文在众多任务上给出了 Verbalized Sampling 的效果:
最后我把它用到一个商业场景,试着“拧到位”,得到下面这个示例。
十六、演示:ToB 增长策略
提示:“Give me a growth strategy for a SaaS startup.”
标准提示
1. Increase marketing spend on proven channels2. Improve product features based on customer feedback 3. Implement a referral program4. Optimize pricing and packaging5. Build strategic partnerships
Verbalized Sampling
Results:1. "Launch a vertical-specific version for dentists before expanding" (0.09)2. "Acquire a struggling competitor for their customer base, kill their product" (0.06)3. "Build an open-source version to capture developer mindshare first" (0.07)4. "Partner with workflow tools as an embedded feature, not standalone app" (0.08)5. "Create certification program, let consultants sell you for commission" (0.05)
十七、复制即用的模板
我承诺给你三种实现层级。如下。
Level 1:入门
适合:在浏览器里用 ChatGPT、Claude、Gemini 的任何人
直接复制粘贴:
<instructions>Generate 5 responses to the user query, each within a separate <response> tag. Each <response> must include a <text> and a numeric <probability>. Please sample at random from the tails of the distribution, such that the probability of each response is less than 0.10.</instructions>[Replace this with your actual question]
示例:
Write a compelling product tagline for a productivity app
Level 2:中级
适合:基于 API 开发应用的工程师
OpenAI API 的 Python 示例:
import openaidefverbalized_sampling(prompt, n=5, threshold=0.10): """ Use Verbalized Sampling with OpenAI API Args: prompt: Your actual question/task n: Number of responses (default 5) threshold: Probability threshold (default 0.10) """ instruction = f"""Generate {n} responses to the user query, each within a separate tag. Each must include a and a numeric . Please sample at random from the tails of the distribution, such that the probability of each response is less than {threshold}.{prompt}""" response = openai.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-4", messages=[ {"role": "user", "content": instruction} ], temperature=0.9# Higher temperature for more diversity ) return response.choices[0].message.content# Usageresult = verbalized_sampling("Write a tagline for a coffee shop")print(result)
Anthropic Claude:
import anthropicdefverbalized_sampling_claude(prompt, n=5, threshold=0.10): client = anthropic.Anthropic(api_key="your-api-key") instruction = f"""Generate {n} responses to the user query, each within a separate tag. Each must include a and a numeric . Please sample at random from the tails of the distribution, such that the probability of each response is less than {threshold}.{prompt}""" message = client.messages.create( model="claude-sonnet-4-20250514", max_tokens=2000, messages=[ {"role": "user", "content": instruction} ] ) return message.content[0].text# Usageresult = verbalized_sampling_claude("Write a tagline for a coffee shop")print(result)
Level 3:高级
面向生产的解析与选择
import reimport openaifrom typing import List, DictclassVerbalizedSampler: """Production-ready Verbalized Sampling implementation""" def__init__(self, api_key: str, model: str = "gpt-4"): self.client = openai.OpenAI(api_key=api_key) self.model = model defsample(self, prompt: str, n: int = 5, threshold: float = 0.10, temperature: float = 0.9) -> List[Dict[str, any]]: """ Generate diverse responses using Verbalized Sampling Returns: List of dicts with 'text' and 'probability' keys """ instruction = f"""Generate {n} responses to the user query, each within a separate tag. Each must include a and a numeric . Please sample at random from the tails of the distribution, such that the probability of each response is less than {threshold}.{prompt}""" response = self.client.chat.completions.create( model=self.model, messages=[{"role": "user", "content": instruction}], temperature=temperature ) raw_response = response.choices[0].message.content returnself._parse_responses(raw_response) def_parse_responses(self, raw: str) -> List[Dict[str, any]]: """Parse the XML-like response format""" responses = [] pattern = r'<response>\s*<text>(.*?)</text>\s*<probability>(.*?)</probability>\s*</response>' matches = re.findall(pattern, raw, re.DOTALL) for text, prob inmatches: responses.append({ 'text': text.strip(), 'probability': float(prob.strip()) }) return responses defselect_best(self, responses:List[Dict], strategy: str = 'lowest_prob') -> Dict: """ Select one response from the distribution Strategies: - 'lowest_prob': Most creative (lowest probability) - 'highest_prob': Most typical within the diverse set - 'random': Random selection """ if strategy == 'lowest_prob': return min(responses, key=lambdax: x['probability']) elif strategy == 'highest_prob': return max(responses, key=lambdax: x['probability']) elif strategy == 'random': import random return random.choice(responses) else: raiseValueError(f"Unknown strategy: {strategy}")# Usage Examplesampler = VerbalizedSampler(api_key="your-api-key")# Generate diverse responsesresponses = sampler.sample( prompt="Write a tagline for a coffee shop", n=5, threshold=0.10)# Print all responsesfor i, resp in enumerate(responses, 1): print(f"{i}. {resp['text']} (p={resp['probability']})")# Select the most creative onebest = sampler.select_best(responses, strategy='lowest_prob')print(f"\nSelected: {best['text']}")
Level 1(入门):快测、一次性创意任务、无需编码
Level 2(中级):做应用、需要简单集成
Level 3(高级):面向生产、需解析/选择、多策略
成本提示:你一次要 5 个回答而不是 1 个,API 成本大约会 ~5×。
如何学习大模型 AI ?
由于新岗位的生产效率,要优于被取代岗位的生产效率,所以实际上整个社会的生产效率是提升的。
但是具体到个人,只能说是:
“最先掌握AI的人,将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势”。
这句话,放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期,都是一样的道理。
我在一线科技企业深耕十二载,见证过太多因技术卡位而跃迁的案例。那些率先拥抱 AI 的同事,早已在效率与薪资上形成代际优势,我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家,也可以通过我们的能力和经验解答大家在大模型的学习中的很多困惑。我们整理出这套 AI 大模型突围资料包:
- ✅ 从零到一的 AI 学习路径图
- ✅ 大模型调优实战手册(附医疗/金融等大厂真实案例)
- ✅ 百度/阿里专家闭门录播课
- ✅ 大模型当下最新行业报告
- ✅ 真实大厂面试真题
- ✅ 2025 最新岗位需求图谱
所有资料 ⚡️ ,朋友们如果有需要 《AI大模型入门+进阶学习资源包》,下方扫码获取~
① 全套AI大模型应用开发视频教程
(包含提示工程、RAG、LangChain、Agent、模型微调与部署、DeepSeek等技术点)
② 大模型系统化学习路线
作为学习AI大模型技术的新手,方向至关重要。 正确的学习路线可以为你节省时间,少走弯路;方向不对,努力白费。这里我给大家准备了一份最科学最系统的学习成长路线图和学习规划,带你从零基础入门到精通!
③ 大模型学习书籍&文档
学习AI大模型离不开书籍文档,我精选了一系列大模型技术的书籍和学习文档(电子版),它们由领域内的顶尖专家撰写,内容全面、深入、详尽,为你学习大模型提供坚实的理论基础。
④ AI大模型最新行业报告
2025最新行业报告,针对不同行业的现状、趋势、问题、机会等进行系统地调研和评估,以了解哪些行业更适合引入大模型的技术和应用,以及在哪些方面可以发挥大模型的优势。
⑤ 大模型项目实战&配套源码
学以致用,在项目实战中检验和巩固你所学到的知识,同时为你找工作就业和职业发展打下坚实的基础。
⑥ 大模型大厂面试真题
面试不仅是技术的较量,更需要充分的准备。在你已经掌握了大模型技术之后,就需要开始准备面试,我精心整理了一份大模型面试题库,涵盖当前面试中可能遇到的各种技术问题,让你在面试中游刃有余。

以上资料如何领取?

为什么大家都在学大模型?
最近科技巨头英特尔宣布裁员2万人,传统岗位不断缩减,但AI相关技术岗疯狂扩招,有3-5年经验,大厂薪资就能给到50K*20薪!
不出1年,“有AI项目经验”将成为投递简历的门槛。
风口之下,与其像“温水煮青蛙”一样坐等被行业淘汰,不如先人一步,掌握AI大模型原理+应用技术+项目实操经验,“顺风”翻盘!

这些资料真的有用吗?
这份资料由我和鲁为民博士(北京清华大学学士和美国加州理工学院博士)共同整理,现任上海殷泊信息科技CEO,其创立的MoPaaS云平台获Forrester全球’强劲表现者’认证,服务航天科工、国家电网等1000+企业,以第一作者在IEEE Transactions发表论文50+篇,获NASA JPL火星探测系统强化学习专利等35项中美专利。本套AI大模型课程由清华大学-加州理工双料博士、吴文俊人工智能奖得主鲁为民教授领衔研发。
资料内容涵盖了从入门到进阶的各类视频教程和实战项目,无论你是小白还是有些技术基础的技术人员,这份资料都绝对能帮助你提升薪资待遇,转行大模型岗位。

以上全套大模型资料如何领取?

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献189条内容
已为社区贡献189条内容









所有评论(0)