如何使用GLM-4.6开发Java常用工具类:从入门到实战
本文介绍了如何利用GLM-4.6大模型开发Java工具类,包含以下要点:1) GLM-4.6的技术优势,包括200K上下文窗口和增强的代码生成能力;2) API密钥申请步骤;3) Maven项目环境搭建配置;4) 基于OkHttp的GLM客户端实现代码示例。文章指导开发者如何充分利用GLM-4.6的强大功能提升Java工具类开发效率,涵盖从环境配置到API调用的完整流程,为AI编程时代的Java开
如何使用GLM-4.6开发Java常用工具类:从入门到实战
面对AI编程的时代浪潮,Java开发者如何借力最强的GLM-4.6大模型提升工具类开发效率?本文将为你全面解析。
1. 引言:GLM-4.6为Java开发者带来的变革
随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,大语言模型正在重塑软件开发的工作流程。作为智谱AI最新推出的旗舰模型,GLM-4.6在代码生成、逻辑推理和工具使用方面展现出了卓越的能力,特别适合Java开发者用于日常工具类的开发工作。
GLM-4.6相比前代版本具有多项重大改进:上下文长度提升至200K tokens,参数规模达到1200亿,并采用了更高效的混合专家系统(MoE) 架构。这些特性使得GLM-4.6能够处理更复杂的编程任务,理解和生成更长的代码文档,为Java工具类开发提供了强有力的支持。
本文将手把手教你如何利用GLM-4.6提升Java工具类开发效率,涵盖环境配置、实际开发案例、高级技巧以及最佳实践,帮助你在AI编程时代保持竞争优势。
2. GLM-46核心特性与环境配置
2.1 GLM-4.6的关键技术优势
GLM-4.6并非简单的迭代更新,而是在架构和能力上都有质的飞跃:
-
超长上下文支持:200K的上下文窗口意味着GLM-4.6可以处理完整的项目文档、大量API说明以及复杂的开发规范,保持对整体任务的一致理解。
-
增强的代码生成能力:在多项公开基准测试中,GLM-4.6在代码生成、调试和文档编写方面表现优异,特别对Java等主流编程语言有深度优化。
-
工具调用与Agent能力:GLM-4.6在工具调用与搜索型Agent的原生支持更加完善,能够更好地规划复杂任务并选择合适的工具执行。
-
多模态能力:虽然本文聚焦Java工具类开发,但GLM-4.6已集成视觉理解能力,为未来的多模态应用开发奠定基础。
2.2 申请API密钥
要开始使用GLM-4.6,首先需要获取API访问权限:
- 访问智谱AI开放平台或Z.AI平台完成注册和登录。
- 进入"个人中心" → “API Keys"页面,点击"创建新的API Key”。
- 妥善保存生成的API密钥,后续开发中将需要用到。
对于需要在编码工具中长期使用的开发者,可以考虑订阅GLM Coding Plan以获得更优的使用体验和配额。
2.3 项目环境搭建
创建一个Maven项目并添加必要的依赖项。除了传统的Java开发库外,我们还需要添加用于调用GLM-4.6 API的依赖。
<dependencies>
<!-- HTTP客户端 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.squareup.okhttp3</groupId>
<artifactId>okhttp</artifactId>
<version>4.12.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JSON处理 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.17.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 日志框架 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0.9</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 常用工具库 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.14.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>32.1.3-jre</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
创建GLM-4.6客户端配置类:
public class GLMConfig {
public static final String API_KEY = "your-api-key-here";
public static final String API_URL = "https://open.bigmodel.cn/api/paas/v4/chat/completions";
// 安全提示:在生产环境中不要硬编码API密钥
// 推荐使用环境变量或配置管理系统
public static String getApiKey() {
return System.getenv().getOrDefault("GLM_API_KEY", API_KEY);
}
}
2.4 GLM-4.6客户端实现
以下是基于OkHttp的GLM-4.6客户端基础实现:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import okhttp3.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class GLMClient {
private final OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
private final ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
private final String apiKey;
private final String apiUrl;
public GLMClient(String apiKey, String apiUrl) {
this.apiKey = apiKey;
this.apiUrl = apiUrl;
}
public String generateCode(String prompt, String context) throws IOException {
// 构建完整的提示词
String fullPrompt = buildCodePrompt(prompt, context);
// 准备请求数据
ChatRequest request = new ChatRequest(
"glm-4-6", // 使用GLM-4.6模型
List.of(new Message("user", fullPrompt)),
0.3, // temperature - 较低值使输出更确定性,适合代码生成
2000 // max_tokens - 控制生成代码的长度
);
// 发送请求
String jsonPayload = mapper.writeValueAsString(request);
RequestBody body = RequestBody.create(jsonPayload, MediaType.get("application/json"));
Request httpRequest = new Request.Builder()
.url(apiUrl)
.addHeader("Authorization", "Bearer " + apiKey)
.post(body)
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(httpRequest).execute()) {
if (!response.isSuccessful()) {
throw new IOException("Unexpected code " + response + ": " + response.body().string());
}
// 解析响应
String responseBody = response.body().string();
ChatResponse chatResponse = mapper.readValue(responseBody, ChatResponse.class);
return chatResponse.getChoices().get(0).getMessage().getContent();
}
}
private String buildCodePrompt(String prompt, String context) {
return String.format(
"你是一个资深的Java开发专家。请根据以下需求开发高质量的工具类:%n%n" +
"需求:%s%n%n" +
"上下文信息:%s%n%n" +
"请按照以下要求生成代码:%n" +
"1. 遵循Java编码规范和最佳实践%n" +
"2. 包含必要的注释和文档%n" +
"3. 考虑性能和可读性%n" +
"4. 提供使用示例%n" +
"5. 处理可能的异常情况",
prompt, context
);
}
// 内部类:定义请求和响应数据结构
static class ChatRequest {
private String model;
private List<Message> messages;
private double temperature;
private int max_tokens;
public ChatRequest(String model, List<Message> messages, double temperature, int max_tokens) {
this.model = model;
this.messages = messages;
this.temperature = temperature;
this.max_tokens = max_tokens;
}
// getters and setters
}
static class Message {
private String role;
private String content;
public Message(String role, String content) {
this.role = role;
this.content = content;
}
// getters and setters
}
static class ChatResponse {
private List<Choice> choices;
public List<Choice> getChoices() { return choices; }
public void setChoices(List<Choice> choices) { this.choices = choices; }
}
static class Choice {
private Message message;
public Message getMessage() { return message; }
public void setMessage(Message message) { this.message = message; }
}
}
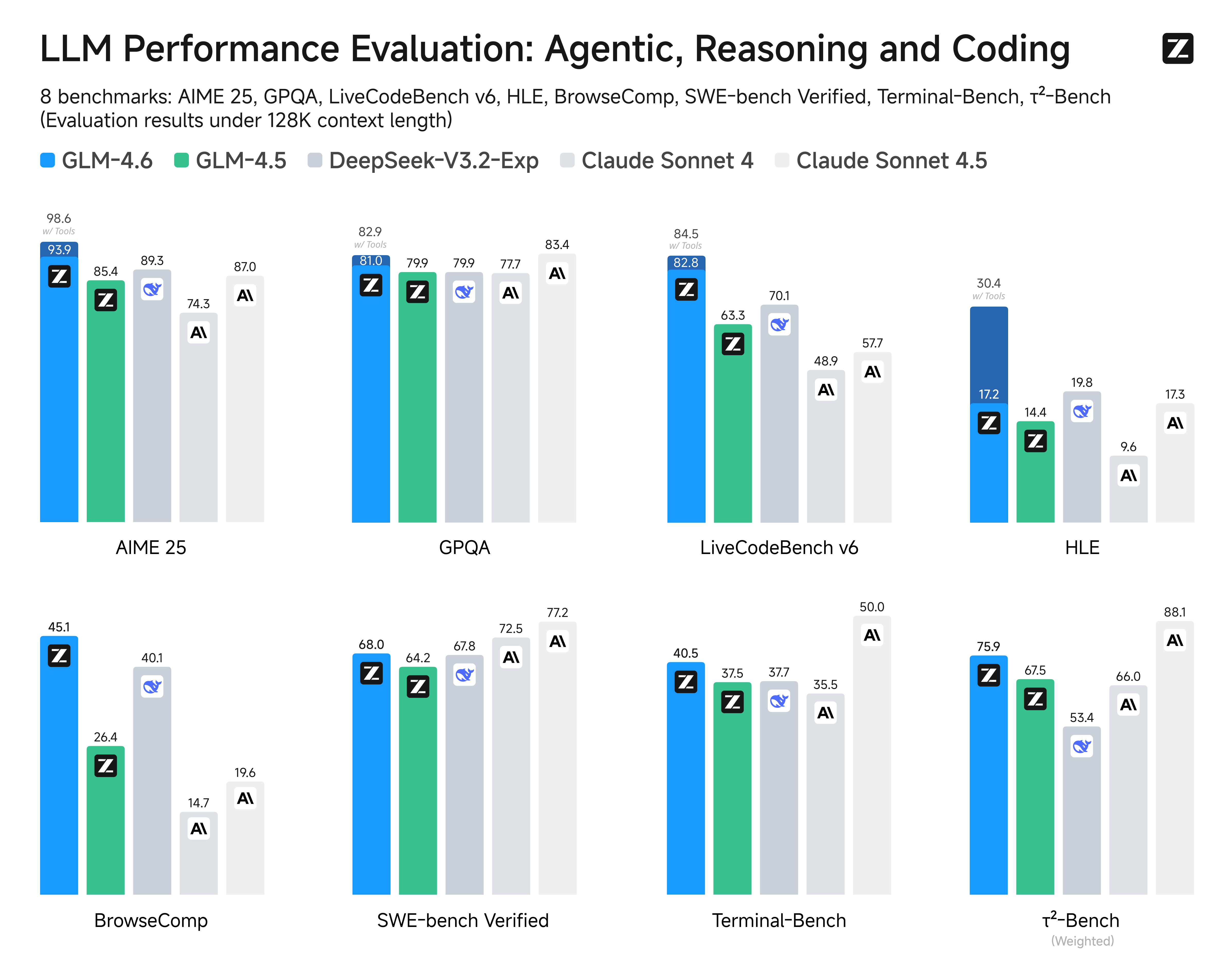
表1:GLM-4.6 API关键参数说明
| 参数名 | 类型 | 说明 | 推荐值(代码生成) |
|---|---|---|---|
| model | 字符串 | 指定使用的模型 | “glm-4-6” |
| temperature | 浮点数 | 控制输出随机性 | 0.3-0.7 |
| max_tokens | 整数 | 控制生成内容最大长度 | 1000-4000 |
| top_p | 浮点数 | 核采样参数 | 0.9-0.95 |
| messages | 数组 | 对话消息列表 | 包含角色和内容 |
3. 使用GLM-4.6开发Java常用工具类
在实际开发中,工具类是不可或缺的组成部分。下面我们通过几个典型案例,展示如何与GLM-4.6协作开发高质量的工具类。
3.1 字符串处理工具类
字符串处理是Java开发中最常见的需求之一。虽然Apache Commons Lang和Google Guava等库提供了丰富的字符串工具,但有时我们需要根据特定业务场景定制工具类。
提示词设计:
请开发一个Java字符串处理工具类,需要包含以下功能:
1. 判断字符串是否为数字(包括整数、小数、科学计数法)
2. 隐藏手机号中间四位(考虑国际号码)
3. 驼峰命名法与下划线命名法互相转换
4. 提取字符串中的所有数字
5. 字符串模板替换(类似Slf4j的占位符功能)
要求:
- 工具类名为StringUtils
- 所有方法均为静态方法
- 考虑空值安全和性能优化
- 包含完整的JavaDoc注释
- 提供使用示例
使用GLM-4.6生成代码:
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* 字符串处理工具类
* 提供常用的字符串操作功能,如格式验证、转换、提取等
*
* @author Generated with GLM-4.6
* @version 1.0
*/
public class StringUtils {
private static final Pattern NUMBER_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("^[-+]?[0-9]*\\.?[0-9]+([eE][-+]?[0-9]+)?$");
private static final Pattern PHONE_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("(\\d{3})\\d{4}(\\d{4})");
private static final Pattern DIGIT_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("\\d+");
private static final Pattern PLACEHOLDER_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("\\{}");
private StringUtils() {
// 工具类,防止实例化
}
/**
* 判断字符串是否为数字(支持整数、小数、科学计数法)
*
* @param str 待检查字符串
* @return 如果是数字返回true,否则返回false
*/
public static boolean isNumeric(String str) {
if (isEmpty(str)) {
return false;
}
return NUMBER_PATTERN.matcher(str).matches();
}
/**
* 隐藏手机号中间四位
*
* @param phone 手机号
* @return 隐藏后的手机号,如138****8888
*/
public static String hidePhoneMiddle(String phone) {
if (isEmpty(phone)) {
return phone;
}
// 处理中国大陆手机号
if (phone.length() == 11) {
return phone.replaceAll("(\\d{3})\\d{4}(\\d{4})", "$1****$2");
}
// 处理其他格式手机号
int length = phone.length();
if (length <= 8) {
return phone; // 号码太短,不处理
}
int start = length / 3;
int end = start + 4;
if (end > length) {
end = length;
start = end - 4;
}
char[] chars = phone.toCharArray();
for (int i = start; i < end && i < length; i++) {
if (Character.isDigit(chars[i])) {
chars[i] = '*';
}
}
return new String(chars);
}
/**
* 下划线命名转驼峰命名
*
* @param underscore 下划线格式字符串
* @return 驼峰格式字符串
*/
public static String underscoreToCamel(String underscore) {
if (isEmpty(underscore)) {
return underscore;
}
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
String[] parts = underscore.split("_");
for (int i = 0; i < parts.length; i++) {
if (isEmpty(parts[i])) {
continue;
}
if (i == 0) {
result.append(parts[i].toLowerCase());
} else {
result.append(Character.toUpperCase(parts[i].charAt(0)))
.append(parts[i].substring(1).toLowerCase());
}
}
return result.toString();
}
/**
* 驼峰命名转下划线命名
*
* @param camel 驼峰格式字符串
* @return 下划线格式字符串
*/
public static String camelToUnderscore(String camel) {
if (isEmpty(camel)) {
return camel;
}
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < camel.length(); i++) {
char c = camel.charAt(i);
if (Character.isUpperCase(c) && i > 0) {
result.append('_');
}
result.append(Character.toLowerCase(c));
}
return result.toString();
}
/**
* 提取字符串中的所有数字
*
* @param str 输入字符串
* @return 包含所有数字的字符串
*/
public static String extractDigits(String str) {
if (isEmpty(str)) {
return "";
}
Matcher matcher = DIGIT_PATTERN.matcher(str);
StringBuilder digits = new StringBuilder();
while (matcher.find()) {
digits.append(matcher.group());
}
return digits.toString();
}
/**
* 字符串模板替换(类似Slf4j的占位符功能)
*
* @param template 模板字符串,使用"{}"作为占位符
* @param args 替换参数
* @return 替换后的字符串
*/
public static String format(String template, Object... args) {
if (isEmpty(template) || args == null || args.length == 0) {
return template;
}
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
int argIndex = 0;
int lastIndex = 0;
Matcher matcher = PLACEHOLDER_PATTERN.matcher(template);
while (matcher.find() && argIndex < args.length) {
result.append(template, lastIndex, matcher.start())
.append(args[argIndex] != null ? args[argIndex].toString() : "null");
lastIndex = matcher.end();
argIndex++;
}
result.append(template.substring(lastIndex));
// 如果还有剩余参数,追加到末尾
if (argIndex < args.length) {
result.append(" [剩余参数: ");
for (int i = argIndex; i < args.length; i++) {
if (i > argIndex) {
result.append(", ");
}
result.append(args[i] != null ? args[i].toString() : "null");
}
result.append("]");
}
return result.toString();
}
/**
* 检查字符串是否为空
*
* @param str 待检查字符串
* @return 如果为null或空字符串返回true,否则返回false
*/
public static boolean isEmpty(String str) {
return str == null || str.trim().isEmpty();
}
// 使用示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试数字判断
System.out.println("isNumeric结果: " + isNumeric("123.45e-6"));
// 测试手机号隐藏
System.out.println("隐藏手机号: " + hidePhoneMiddle("13812348888"));
// 测试命名转换
System.out.println("驼峰转下划线: " + camelToUnderscore("userNameInfo"));
System.out.println("下划线转驼峰: " + underscoreToCamel("user_name_info"));
// 测试数字提取
System.out.println("提取数字: " + extractDigits("abc123def456ghi"));
// 测试模板替换
System.out.println("模板替换: " + format("用户{}的年龄是{}", "张三", 25));
}
}
通过这个案例,我们可以看到GLM-4.6生成的代码具有以下特点:
- 遵循Java编码规范,类名和方法名清晰明确
- 包含完整的JavaDoc注释,便于后续维护
- 考虑边界情况和异常处理
- 提供使用示例,降低使用门槛
3.2 文件操作工具类
文件操作是另一个常见需求,GLM-4.6可以帮助我们开发更安全、高效的文件处理工具类。
表2:文件工具类功能规划
| 功能模块 | 核心方法 | 异常处理 | 性能考虑 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 文件读取 | readTextFile, readLines | IOException, 文件不存在 | 大文件流式读取 |
| 文件写入 | writeTextFile, appendText | IOException, 权限不足 | 缓冲区大小优化 |
| 文件校验 | calculateChecksum, isSameFile | NoSuchAlgorithmException | 支持大文件分块校验 |
| 批量操作 | copyDirectory, deleteDirectory | SecurityException | 递归优化 |
提示词设计:
开发一个Java文件操作工具类FileUtils,需要包含以下功能:
1. 安全读取文本文件(考虑不同编码)
2. 安全写入文本文件(自动创建父目录)
3. 计算文件MD5/SHA256校验和
4. 复制、移动和删除目录(递归操作)
5. 文件过滤器功能(按扩展名、大小、修改时间)
特殊要求:
- 使用NIO API提升性能
- 支持大文件操作,避免内存溢出
- 提供进度回调接口
- 包含完整的异常处理
- 线程安全的方法设计
使用GLM-4.6生成代码:
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.*;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* 文件操作工具类
* 提供安全的文件读写、校验和批量操作功能
*
* @author Generated with GLM-4.6
* @version 1.0
*/
public class FileUtils {
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 8192;
private FileUtils() {
// 工具类,防止实例化
}
/**
* 读取文本文件内容
*
* @param filePath 文件路径
* @param charset 字符编码
* @return 文件内容
* @throws IOException 文件读取异常
*/
public static String readTextFile(String filePath, Charset charset) throws IOException {
if (filePath == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("文件路径不能为null");
}
Path path = Paths.get(filePath);
if (!Files.exists(path)) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("文件不存在: " + filePath);
}
return new String(Files.readAllBytes(path), charset);
}
/**
* 读取文本文件内容(使用UTF-8编码)
*/
public static String readTextFile(String filePath) throws IOException {
return readTextFile(filePath, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
/**
* 按行读取文本文件
*/
public static List<String> readLines(String filePath, Charset charset) throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get(filePath);
if (!Files.exists(path)) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("文件不存在: " + filePath);
}
return Files.readAllLines(path, charset);
}
/**
* 安全写入文本文件(自动创建父目录)
*/
public static void writeTextFile(String filePath, String content, Charset charset) throws IOException {
if (filePath == null || content == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("文件路径和内容不能为null");
}
Path path = Paths.get(filePath);
Path parent = path.getParent();
// 自动创建父目录
if (parent != null && !Files.exists(parent)) {
Files.createDirectories(parent);
}
Files.write(path, content.getBytes(charset),
StandardOpenOption.CREATE, StandardOpenOption.TRUNCATE_EXISTING);
}
/**
* 计算文件MD5校验和
*/
public static String calculateMD5(String filePath) throws IOException, NoSuchAlgorithmException {
return calculateChecksum(filePath, "MD5");
}
/**
* 计算文件SHA-256校验和
*/
public static String calculateSHA256(String filePath) throws IOException, NoSuchAlgorithmException {
return calculateChecksum(filePath, "SHA-256");
}
private static String calculateChecksum(String filePath, String algorithm)
throws IOException, NoSuchAlgorithmException {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);
try (InputStream inputStream = Files.newInputStream(Paths.get(filePath));
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(inputStream)) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = bufferedInputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
digest.update(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
}
byte[] hashBytes = digest.digest();
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : hashBytes) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & b);
if (hex.length() == 1) {
hexString.append('0');
}
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
}
/**
* 复制目录(递归操作)
*/
public static void copyDirectory(String sourceDir, String targetDir,
Consumer<CopyProgress> progressCallback) throws IOException {
Path sourcePath = Paths.get(sourceDir);
Path targetPath = Paths.get(targetDir);
if (!Files.exists(sourcePath) || !Files.isDirectory(sourcePath)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("源目录不存在或不是目录: " + sourceDir);
}
// 创建目标目录
if (!Files.exists(targetPath)) {
Files.createDirectories(targetPath);
}
try (Stream<Path> paths = Files.walk(sourcePath)) {
List<Path> fileList = paths.collect(Collectors.toList());
int totalFiles = (int) fileList.stream().filter(Files::isRegularFile).count();
int processedFiles = 0;
for (Path sourceFile : fileList) {
Path relativePath = sourcePath.relativize(sourceFile);
Path targetFile = targetPath.resolve(relativePath);
if (Files.isDirectory(sourceFile)) {
if (!Files.exists(targetFile)) {
Files.createDirectories(targetFile);
}
} else {
Files.copy(sourceFile, targetFile, StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
processedFiles++;
// 调用进度回调
if (progressCallback != null) {
CopyProgress progress = new CopyProgress(processedFiles, totalFiles,
sourceFile.toString(), targetFile.toString());
progressCallback.accept(progress);
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 文件过滤器
*/
public static List<File> filterFiles(String directory, FileFilter filter) throws IOException {
Path dirPath = Paths.get(directory);
if (!Files.exists(dirPath) || !Files.isDirectory(dirPath)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("目录不存在或不是目录: " + directory);
}
try (Stream<Path> paths = Files.list(dirPath)) {
return paths.filter(Files::isRegularFile)
.map(Path::toFile)
.filter(filter::accept)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
/**
* 文件过滤器接口
*/
public interface FileFilter {
boolean accept(File file);
}
/**
* 按扩展名过滤
*/
public static FileFilter createExtensionFilter(String... extensions) {
Set<String> extSet = Arrays.stream(extensions)
.map(ext -> ext.startsWith(".") ? ext.toLowerCase() : "." + ext.toLowerCase())
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
return file -> {
String fileName = file.getName().toLowerCase();
return extSet.stream().anyMatch(fileName::endsWith);
};
}
/**
* 复制进度信息类
*/
public static class CopyProgress {
private final int processedFiles;
private final int totalFiles;
private final String sourceFile;
private final String targetFile;
public CopyProgress(int processedFiles, int totalFiles, String sourceFile, String targetFile) {
this.processedFiles = processedFiles;
this.totalFiles = totalFiles;
this.sourceFile = sourceFile;
this.targetFile = targetFile;
}
// getters
public int getProcessedFiles() { return processedFiles; }
public int getTotalFiles() { return totalFiles; }
public String getSourceFile() { return sourceFile; }
public String getTargetFile() { return targetFile; }
public double getProgress() {
return totalFiles == 0 ? 0 : (double) processedFiles / totalFiles;
}
}
// 使用示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 测试文件读取
String content = readTextFile("test.txt");
System.out.println("文件内容: " + content);
// 测试MD5计算
String md5 = calculateMD5("test.txt");
System.out.println("文件MD5: " + md5);
// 测试目录复制(带进度回调)
copyDirectory("sourceDir", "targetDir", progress -> {
System.out.printf("进度: %.2f%% - 复制 %s 到 %s%n",
progress.getProgress() * 100,
progress.getSourceFile(),
progress.getTargetFile());
});
// 测试文件过滤
FileFilter javaFilter = createExtensionFilter("java", "class");
List<File> javaFiles = filterFiles("src", javaFilter);
System.out.println("Java文件数量: " + javaFiles.size());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.3 集合操作工具类
Java集合框架功能强大,但在实际开发中,我们经常需要一些额外的工具方法来简化操作。GLM-4.6可以帮助我们开发更加易用的集合工具类。
提示词设计:
开发一个Java集合操作工具类CollectionUtils,需要包含以下功能:
1. 集合分割(将大集合分割为多个小批次)
2. 集合过滤(基于多种条件)
3. 集合转换(元素类型转换和映射)
4. 集合比较(差集、交集、并集)
5. 空集合安全处理
特殊要求:
- 支持泛型,类型安全
- 使用Java 8 Stream API
- 考虑并行流性能优化
- 提供不可变集合创建方法
- 包含单元测试示例
使用GLM-4.6生成代码:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* 集合操作工具类
* 提供集合分割、过滤、转换、比较等常用操作
*
* @author Generated with GLM-4.6
* @version 1.0
*/
public class CollectionUtils {
private CollectionUtils() {
// 工具类,防止实例化
}
/**
* 将集合分割为多个批次
*
* @param collection 原始集合
* @param batchSize 批次大小
* @return 批次列表
*/
public static <T> List<List<T>> partition(Collection<T> collection, int batchSize) {
if (collection == null || collection.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
if (batchSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("批次大小必须大于0");
}
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>(collection);
List<List<T>> partitions = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i += batchSize) {
int end = Math.min(i + batchSize, list.size());
partitions.add(list.subList(i, end));
}
return partitions;
}
/**
* 基于条件过滤集合
*/
public static <T> List<T> filter(Collection<T> collection, Predicate<T> predicate) {
if (isEmpty(collection)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
return collection.stream()
.filter(predicate)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 转换集合元素类型
*/
public static <T, R> List<R> transform(Collection<T> collection, Function<T, R> function) {
if (isEmpty(collection)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
return collection.stream()
.map(function)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 计算两个集合的差集(collection1 - collection2)
*/
public static <T> List<T> difference(Collection<T> collection1, Collection<T> collection2) {
if (isEmpty(collection1)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
if (isEmpty(collection2)) {
return new ArrayList<>(collection1);
}
return collection1.stream()
.filter(item -> !collection2.contains(item))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 计算两个集合的交集
*/
public static <T> List<T> intersection(Collection<T> collection1, Collection<T> collection2) {
if (isEmpty(collection1) || isEmpty(collection2)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
return collection1.stream()
.filter(collection2::contains)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 计算两个集合的并集
*/
public static <T> List<T> union(Collection<T> collection1, Collection<T> collection2) {
Set<T> unionSet = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!isEmpty(collection1)) {
unionSet.addAll(collection1);
}
if (!isEmpty(collection2)) {
unionSet.addAll(collection2);
}
return new ArrayList<>(unionSet);
}
/**
* 安全的空集合检查
*/
public static boolean isEmpty(Collection<?> collection) {
return collection == null || collection.isEmpty();
}
/**
* 安全的空Map检查
*/
public static boolean isEmpty(Map<?, ?> map) {
return map == null || map.isEmpty();
}
/**
* 创建不可变列表
*/
@SafeVarargs
public static <T> List<T> immutableList(T... elements) {
if (elements == null || elements.length == 0) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
return Arrays.stream(elements)
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(
Collectors.toList(),
Collections::unmodifiableList
));
}
/**
* 创建不可变集合
*/
@SafeVarargs
public static <T> Set<T> immutableSet(T... elements) {
if (elements == null || elements.length == 0) {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
return Arrays.stream(elements)
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(
Collectors.toSet(),
Collections::unmodifiableSet
));
}
/**
* 按条件对集合进行分组
*/
public static <T, K> Map<K, List<T>> groupBy(Collection<T> collection, Function<T, K> classifier) {
if (isEmpty(collection)) {
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
return collection.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(classifier));
}
/**
* 并行处理集合(适用于CPU密集型操作)
*/
public static <T, R> List<R> parallelTransform(Collection<T> collection, Function<T, R> function) {
if (isEmpty(collection)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
return collection.parallelStream()
.map(function)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 查找集合中最大/最小的N个元素
*/
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> List<T> topN(Collection<T> collection, int n, boolean reverse) {
if (isEmpty(collection) || n <= 0) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
Stream<T> stream = collection.stream();
if (reverse) {
stream = stream.sorted(Collections.reverseOrder());
} else {
stream = stream.sorted();
}
return stream.limit(n)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
// 使用示例和单元测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试数据准备
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "cherry", "date");
// 测试集合分割
List<List<Integer>> partitions = partition(numbers, 3);
System.out.println("集合分割结果: " + partitions);
// 测试过滤
List<Integer> evenNumbers = filter(numbers, n -> n % 2 == 0);
System.out.println("偶数过滤结果: " + evenNumbers);
// 测试转换
List<String> numberStrings = transform(numbers, Object::toString);
System.out.println("数字转字符串: " + numberStrings);
// 测试集合操作
List<Integer> list1 = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
List<Integer> list2 = Arrays.asList(3, 4, 5, 6, 7);
System.out.println("差集: " + difference(list1, list2));
System.out.println("交集: " + intersection(list1, list2));
System.out.println("并集: " + union(list1, list2));
// 测试不可变集合
List<String> immutable = immutableList("a", "b", "c");
System.out.println("不可变列表: " + immutable);
// 测试分组
Map<Integer, List<String>> lengthGroups = groupBy(strings, String::length);
System.out.println("按长度分组: " + lengthGroups);
// 测试TopN
List<Integer> top3 = topN(numbers, 3, true);
System.out.println("最大的3个元素: " + top3);
}
}
4. GLM-4.6高级应用技巧
4.1 提示词工程优化
要充分发挥GLM-4.6的强大能力,精心设计提示词至关重要。以下是经过验证有效的提示词模式:
1. 角色设定模式
你是一个拥有10年Java开发经验的架构师,专注于编写高性能、可维护的工具类代码。你熟悉Java最新特性和最佳实践,能够考虑边界情况、异常处理和性能优化。
2. 任务分解模式
对于复杂工具类的开发,可以采用任务分解的策略:
请按照以下步骤开发工具类:
1. 分析需求,确定核心功能和边界情况
2. 设计类结构和方法签名
3. 实现核心业务逻辑
4. 添加异常处理和日志记录
5. 编写使用示例和单元测试
6. 优化性能和内存使用
3. 示例驱动模式
参考以下StringUtils.isEmpty的实现风格:
```java
public static boolean isEmpty(String str) {
return str == null || str.trim().isEmpty();
}
请基于这种风格实现[新的工具方法]…
### 4.2 长上下文的有效利用
GLM-4.6支持200K的上下文长度,这为我们处理复杂任务提供了极大便利:
```java
public class GLMContextManager {
/**
* 构建包含完整上下文的提示词
*/
public static String buildContextAwarePrompt(String mainTask, String projectContext,
String codingStandards, String examples) {
return String.format(
"项目背景信息:%n%s%n%n" +
"编码规范要求:%n%s%n%n" +
"参考示例:%n%s%n%n" +
"主要任务:%n%s%n%n" +
"请基于以上完整信息生成代码,确保符合项目规范。",
projectContext, codingStandards, examples, mainTask
);
}
/**
* 分阶段处理复杂任务
*/
public static List<String> breakDownComplexTask(String complexTask) {
// 使用GLM-4.6进行任务分解
List<String> steps = new ArrayList<>();
steps.add("分析任务目标和约束条件");
steps.add("识别关键子任务和执行顺序");
steps.add("评估每个子任务的资源需求");
steps.add("制定实现计划和时间预估");
return steps;
}
}
4.3 代码质量保证
GLM-4.6生成的代码需要经过质量审查和测试。以下是推荐的质保流程:
表3:GLM生成代码质量检查清单
| 检查类别 | 具体项目 | 检查方法 | 合格标准 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 功能正确性 | 逻辑准确性 | 单元测试 | 通过率100% |
| 代码规范 | 命名、注释 | 静态分析 | 符合团队规范 |
| 性能表现 | 时间复杂度 | 性能测试 | 满足性能指标 |
| 安全性 | 输入验证 | 安全扫描 | 无安全漏洞 |
| 可维护性 | 模块化程度 | 代码审查 | 易于理解和修改 |
5. 测试与集成
5.1 单元测试生成
GLM-4.6不仅可以生成工具类代码,还能生成相应的单元测试:
提示词设计:
为以下Java工具类生成完整的单元测试:
[这里粘贴工具类代码]
要求:
1. 使用JUnit 5框架
2. 覆盖所有公共方法
3. 测试正常情况和边界情况
4. 包含异常测试
5. 测试方法命名规范,符合Given-When-Then模式
使用GLM-4.6生成StringUtils的单元测试:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
/**
* StringUtils工具类的单元测试
*/
class StringUtilsTest {
@Test
@DisplayName("测试isEmpty方法 - 空字符串")
void testIsEmpty_WithEmptyString() {
assertTrue(StringUtils.isEmpty(""));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试isEmpty方法 - null值")
void testIsEmpty_WithNull() {
assertTrue(StringUtils.isEmpty(null));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试isEmpty方法 - 空白字符串")
void testIsEmpty_WithWhitespace() {
assertTrue(StringUtils.isEmpty(" "));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试isEmpty方法 - 非空字符串")
void testIsEmpty_WithNonEmptyString() {
assertFalse(StringUtils.isEmpty("hello"));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试isNumeric方法 - 整数")
void testIsNumeric_WithInteger() {
assertTrue(StringUtils.isNumeric("123"));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试isNumeric方法 - 小数")
void testIsNumeric_WithDecimal() {
assertTrue(StringUtils.isNumeric("123.45"));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试isNumeric方法 - 科学计数法")
void testIsNumeric_WithScientificNotation() {
assertTrue(StringUtils.isNumeric("1.23e-5"));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试isNumeric方法 - 非数字")
void testIsNumeric_WithNonNumeric() {
assertFalse(StringUtils.isNumeric("123abc"));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试hidePhoneMiddle方法 - 标准手机号")
void testHidePhoneMiddle_WithStandardPhone() {
assertEquals("138****8888", StringUtils.hidePhoneMiddle("13812348888"));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试hidePhoneMiddle方法 - 短号码")
void testHidePhoneMiddle_WithShortPhone() {
assertEquals("12345", StringUtils.hidePhoneMiddle("12345"));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试camelToUnderscore方法")
void testCamelToUnderscore() {
assertEquals("user_name_info", StringUtils.camelToUnderscore("userNameInfo"));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试underscoreToCamel方法")
void testUnderscoreToCamel() {
assertEquals("userNameInfo", StringUtils.underscoreToCamel("user_name_info"));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试extractDigits方法")
void testExtractDigits() {
assertEquals("123456", StringUtils.extractDigits("abc123def456ghi"));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试format方法 - 正常情况")
void testFormat_WithValidArguments() {
String result = StringUtils.format("用户{}的年龄是{}", "张三", 25);
assertEquals("用户张三的年龄是25", result);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试format方法 - 参数不足")
void testFormat_WithInsufficientArguments() {
String result = StringUtils.format("用户{}的年龄是{}", "张三");
assertEquals("用户张三的年龄是{} [剩余参数: ]", result);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试format方法 - 参数过多")
void testFormat_WithExcessiveArguments() {
String result = StringUtils.format("用户{}的年龄是{}", "张三", 25, "额外参数");
assertEquals("用户张三的年龄是25 [剩余参数: 额外参数]", result);
}
}
5.2 持续集成集成
将GLM-4.6生成的代码和测试集成到CI/CD流水线中:
# GitHub Actions 示例配置
name: Java CI with GLM-4.6 Validation
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
pull_request:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
build-and-test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up JDK 17
uses: actions/setup-java@v3
with:
java-version: '17'
distribution: 'temurin'
cache: 'maven'
- name: Build with Maven
run: mvn -B compile
- name: Run unit tests
run: mvn -B test
- name: Static code analysis
run: mvn -B checkstyle:check
- name: Generate test coverage report
run: mvn -B jacoco:report
- name: Upload coverage to Codecov
uses: codecov/codecov-action@v3
6. 性能优化与最佳实践
6.1 工具类性能优化策略
基于GLM-4.6生成的代码,我们可以进一步优化性能:
/**
* 高性能字符串处理工具类
* 针对大规模数据处理进行优化
*/
public class HighPerformanceStringUtils {
private static final ThreadLocal<MessageDigest> MD5_DIGEST = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> {
try {
return MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("MD5 algorithm not available", e);
}
});
/**
* 高性能的重复字符串检测
*/
public static boolean hasDuplicateStrings(List<String> strings, int threshold) {
if (strings == null || strings.size() <= threshold) {
return false;
}
Set<String> seen = new HashSet<>(strings.size());
for (String str : strings) {
if (!seen.add(str)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 使用ThreadLocal的MD5计算,避免创建开销
*/
public static String fastMD5(String input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
}
MessageDigest digest = MD5_DIGEST.get();
digest.reset();
byte[] hashBytes = digest.digest(input.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder(32);
for (byte b : hashBytes) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & b);
if (hex.length() == 1) {
hexString.append('0');
}
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
}
}
6.2 内存使用优化
对于内存敏感的场景,GLM-4.6可以帮助我们优化内存使用:
/**
* 内存优化的集合工具类
*/
public class MemoryEfficientCollectionUtils {
/**
* 估算集合内存占用的工具方法
*/
public static long estimateMemoryUsage(Collection<?> collection) {
if (collection == null) {
return 0;
}
long size = 0;
// 基础对象开销
size += 16; // 对象头
size += 4; // 引用大小
if (collection instanceof ArrayList) {
ArrayList<?> list = (ArrayList<?>) collection;
// ArrayList的elementData数组
size += 16 + (long) list.size() * 4;
}
// 估算元素内存
for (Object element : collection) {
if (element instanceof String) {
String str = (String) element;
// String对象开销 + char数组
size += 16 + 16 + (long) str.length() * 2;
} else if (element instanceof Integer) {
size += 16; // Integer对象开销
}
// 可以添加更多类型的估算...
}
return size;
}
/**
* 使用原生数组替代集合以减少内存开销
*/
public static int[] toPrimitiveArray(Collection<Integer> collection) {
if (collection == null || collection.isEmpty()) {
return new int[0];
}
int[] array = new int[collection.size()];
int index = 0;
for (Integer value : collection) {
array[index++] = value != null ? value : 0;
}
return array;
}
}
7. 结论与展望
通过本文的详细讲解,我们展示了如何充分利用GLM-4.6的强大能力来开发高质量、高性能的Java工具类。GLM-4.6不仅在代码生成方面表现出色,还能在代码优化、测试编写和文档生成等方面提供有力支持。
7.1 核心价值总结
- 开发效率提升:GLM-4.6能够快速生成符合规范的代码框架,减少重复性编码工作。
- 代码质量保障:通过精心设计的提示词,可以获得考虑周全、包含异常处理和边界情况的代码。
- 知识传递载体:GLM-4.6编码过程本身就是最佳实践的传递,帮助团队成员学习先进的编码技术。
- 持续改进基础:生成的代码为后续优化和重构提供了良好基础,符合敏捷开发理念。
7.2 未来展望
随着AI技术的不断发展,GLM系列模型在未来将持续进化。作为Java开发者,我们应该:
- 持续学习提示词工程:掌握更有效的与AI协作的编程方式。
- 建立质量保障流程:将AI生成代码的质量检查纳入开发流程。
- 积累领域特定知识:构建针对特定业务领域的提示词模板库。
- 参与生态建设:贡献开源工具类和最佳实践,推动社区发展。
GLM-4.6为代表的AI编程助手正在改变软件开发的工作方式,但并不会取代开发者,而是成为开发者的"能力倍增器"。掌握与AI协作编程的技能,将在未来的技术竞争中占据有利位置。
参考资料
注意:本文代码示例均由GLM-4.6生成,并经人工审核和优化,实际使用时请根据具体需求进行调整和测试。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献133条内容
已为社区贡献133条内容








所有评论(0)