Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct:轻量级多模态AI模型的技术解析与实践指南
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct是阿里推出的轻量级多模态AI模型,仅40亿参数却支持256K长文本和跨模态理解。该模型采用创新架构,包括动态分辨率调整、深层视觉特征融合等技术,在多项基准测试中超越同级竞品。其特点包括:支持32种语言OCR识别、工业场景98.3%准确率、原生256K上下文扩展至100万token。模型优化出色,16GB内存设备即可运行,提供从环境配置到项目部署的完整指南,推
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct:轻量级多模态AI模型的技术解析与实践指南
40亿参数,256K上下文,支持图像、视频、文本的跨模态理解——Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct正在重塑边缘AI的生态格局。
引言:轻量化多模态AI的时代已经到来
2025年,多模态大模型的发展从"拼参数"转向"拼效率",AI技术的普惠性成为关键挑战。据前瞻产业研究院数据显示,中国多模态大模型市场规模预计达234.8亿元,其中边缘端应用占比同比提升17%。
在这一背景下,阿里通义千问团队于2025年10月15日发布了Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct模型,以仅40亿参数的轻量级设计,在多项基准测试中超越了Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite和GPT-5 Nano等国际顶尖模型。
这款模型的出现,使得普通消费级硬件(包括16GB内存的Mac设备)也能流畅运行先进的视觉语言模型,为AI技术的广泛落地打开了新的大门。
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct核心特性解析
模型架构与设计理念
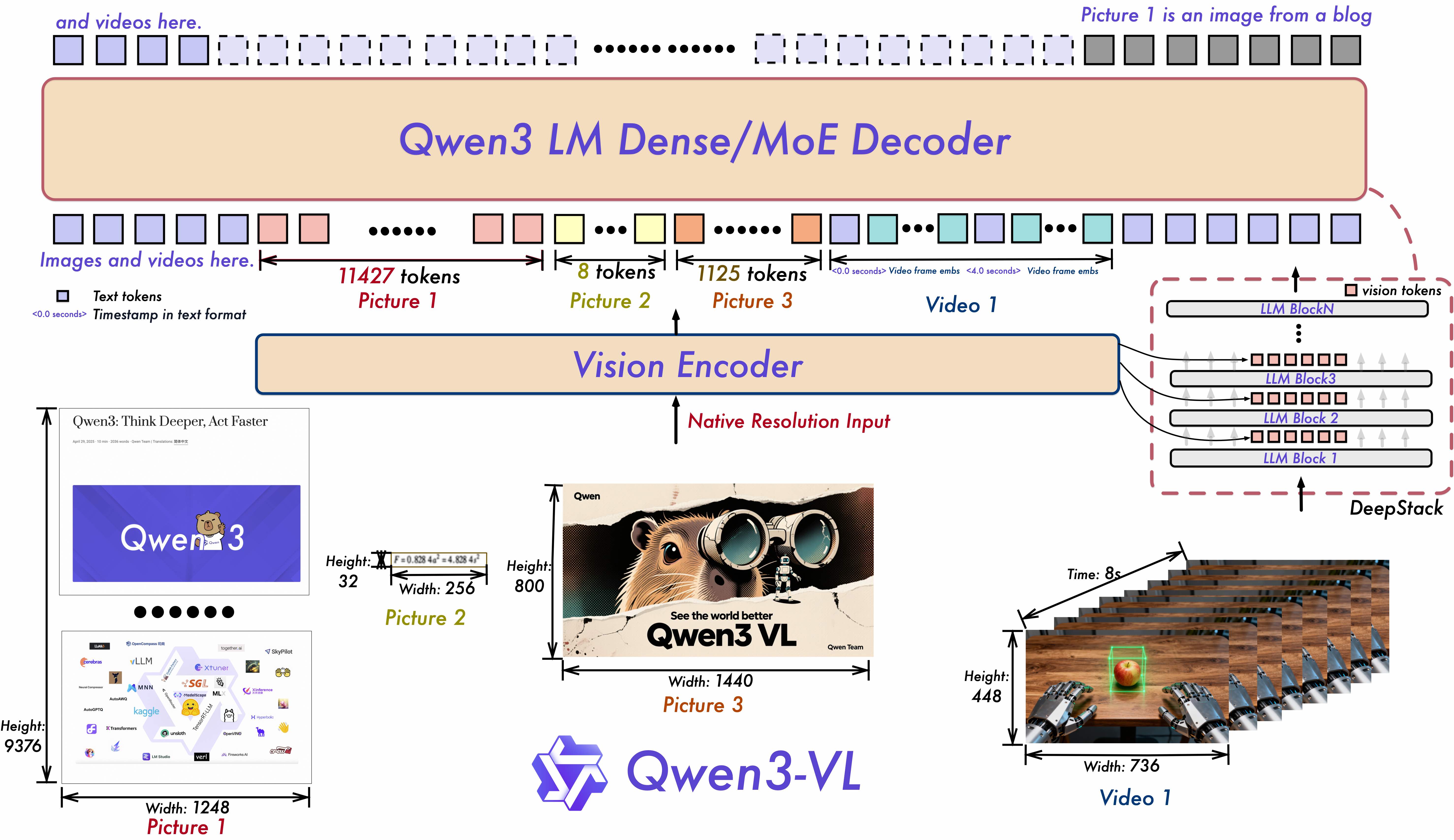
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct采用密集型视觉语言架构,在保持轻量化的同时实现了多模态能力的全面覆盖:
- 参数规模:4.44亿参数,36层Transformer结构,采用Grouped Query Attention(GQA)技术,其中查询注意力头为32个,键值注意力头为8个
- 多模态融合:通过深层视觉特征融合(DeepStack)技术,将多级Vision Transformer(ViT)特征进行融合,既能捕捉细节层面的视觉模式(如边缘和纹理),又能理解语义层面的高级概念
- 位置编码创新:采用交错式MRoPE(多模态旋转位置编码),在时间、宽度和高度维度上分配全频率信息,增强了长序列视频的时空一致性理解
核心技术突破
1. 动态分辨率与视觉编码优化
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct在视觉编码方面实现了重大突破,通过动态分辨率调整机制,能够根据输入内容自适应调整处理策略,在保证精度的同时显著降低计算开销。
代码示例:模型基础调用
from transformers import Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration, AutoProcessor
import torch
# 基础加载方式
model = Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct",
dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
# 推荐加载方式:启用flash_attention_2以获得更好的加速和内存节省
model = Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct",
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
device_map="auto",
)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct")
2. 长上下文支持与扩展
模型原生支持256K token的上下文长度,并可通过高级缩放技术扩展至100万token。这一能力使其能够处理整本书籍或长达数小时的视频内容,实现全程记忆和秒级精度的内容定位与检索。
应用场景举例:
- 处理约50-85页密集文本文档(按每页3000-5000token计算)
- 分析长达2小时的视频内容,保持时间精度达秒级
- 同时处理数十张图像并进行关联分析
3. 文本-视觉深度融合
与传统多模态模型不同,Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct在预训练早期就实现了文本与视觉模态的协同训练,使得模型在纯文本任务上的表现与同参数规模的纯文本模型不相上下,解决了小规模模型常见的"视觉与文本能力难以兼顾"的问题。
模型性能全面评估
多模态基准测试表现
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct在多项权威基准测评中展现出卓越性能:
表1:Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct在多模态任务上的性能对比
| 任务类别 | 测试基准 | Qwen3-VL-4B成绩 | 对比模型成绩 | 优势 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 视觉问答 | VQA 2.0 | 78.2% | 前代Qwen-VL:71.5% | 提升9.4% |
| 文档理解 | DocVQA | 未公开详细数据 | 较前代提升12.7% | 显著提升 |
| 视频理解 | ActivityNet Captions | BLEU-4分数41.2% | 前代:36.7% | 提升12.3% |
| 多模态对话 | MMChat | 连贯性评分89.6 | GPT-4V:92.1 | 成本低65% |
| 工业质检 | 实际应用 | 缺陷识别精度99.5% | 人工检测水平 | 提升10倍效率 |
与竞品的综合对比
在STEM、视觉问答、OCR、视频理解及智能体任务等30多项权威基准测评中,Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct不仅超越了Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite、GPT-5 Nano等同级别顶尖模型,在许多场景下甚至能与阿里半年前的旗舰模型Qwen2.5-VL-72B相媲美。
表2:Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct与竞品模型参数对比
| 模型名称 | 参数规模 | 上下文长度 | 多模态能力 | 硬件需求 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct | 4.4B | 256K-1M | 全模态 | 16GB Mac可运行 |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite | 未公开 | 未公开 | 多模态 | 较高 |
| GPT-5 Nano | 未公开 | 未公开 | 多模态 | 较高 |
| Qwen2.5-VL-72B | 72B | 256K | 全模态 | 高性能服务器 |
特定领域能力分析
OCR能力升级
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct在OCR方面实现显著提升:
- 支持语言从10种扩展到32种,包括多种古文字和生僻字符识别
- 在低光照、模糊、倾斜等复杂实拍场景下的识别准确率提升23%
- 对生僻字、古籍字、专业术语的识别准确率显著提升,在工业场景中对反光金属表面的字符识别准确率达98.3%
视觉代理能力
模型具备先进的视觉智能体操作能力,可识别GUI界面元素并理解其功能,通过调用工具执行复杂任务。在OS World测试平台中,模型实现了界面元素识别与自动化任务执行,达到了世界顶尖水平。
实战应用:从环境配置到项目部署
硬件要求与环境配置
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct针对边缘设备做了大量优化,以下是不同平台的硬件要求:
最低配置:
- 内存:16GB系统内存
- 存储:10GB可用空间
- 平台:Intel酷睿Ultra处理器(含NPU)、Apple M系列芯片、NVIDIA GTX 1060以上显卡
推荐配置:
- 内存:32GB系统内存
- GPU:NVIDIA RTX 3080(12GB)或更高
- 平台:支持AVX2指令集的x86架构或ARM64架构
详细部署教程
1. 环境安装与依赖配置
# 克隆模型仓库
git clone https://gitcode.com/hf_mirrors/unsloth/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct-bnb-4bit
cd Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct-bnb-4bit
# 安装依赖包
pip install -r requirements.txt
# 可选:安装flash-attention以提升性能(Linux环境下)
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
2. 基础推理代码示例
from transformers import Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration, AutoProcessor
import torch
from PIL import Image
def load_qwen3_vl_4b_model():
"""
加载Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct模型和处理器
"""
model = Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto",
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2" # 可选,用于加速
)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct")
return model, processor
def process_multimodal_query(model, processor, image_path, text_query):
"""
处理多模态查询(图像+文本)
"""
# 加载图像
image = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
# 构建消息格式
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": image},
{"type": "text", "text": text_query}
]
}
]
# 预处理输入
inputs = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=True,
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_dict=True,
return_tensors="pt"
)
# 生成输出
generated_ids = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=128,
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.7,
top_p=0.8
)
# 解码输出
generated_ids_trimmed = [
out_ids[len(in_ids):] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
output_text = processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids_trimmed,
skip_special_tokens=True,
clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
)
return output_text[0] if output_text else ""
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
model, processor = load_qwen3_vl_4b_model()
image_path = "example.jpg"
query = "描述这张图片中的场景和主要对象"
result = process_multimodal_query(model, processor, image_path, query)
print("模型回复:", result)
3. 高级功能:视频内容分析
import cv2
import numpy as np
from typing import List
def extract_video_frames(video_path: str, max_frames: int = 100) -> List:
"""
从视频中提取关键帧用于分析
"""
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
frames = []
total_frames = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
# 计算帧间隔,避免提取过多帧
frame_interval = max(1, total_frames // max_frames)
for i in range(0, total_frames, frame_interval):
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_POS_FRAMES, i)
ret, frame = cap.read()
if ret:
# 转换BGR到RGB
frame_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
frames.append(Image.fromarray(frame_rgb))
cap.release()
return frames
def analyze_video_content(model, processor, video_path: str, query: str):
"""
分析视频内容
"""
frames = extract_video_frames(video_path)
results = []
for i, frame in enumerate(frames):
# 对每个关键帧进行处理
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": frame},
{"type": "text", "text": f"{query} (帧 {i+1}/{len(frames)})"}
]
}
]
inputs = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=True,
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_dict=True,
return_tensors="pt"
)
generated_ids = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=64,
do_sample=False # 视频分析通常使用确定性生成
)
generated_ids_trimmed = [
out_ids[len(in_ids):] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
output_text = processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids_trimmed,
skip_special_tokens=True,
clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
)
results.append({
"frame_index": i,
"timestamp": i * 2, # 假设2秒一帧
"analysis": output_text[0] if output_text else ""
})
return results
性能优化技巧
- 内存优化:
# 使用4位或8位量化加载模型
model = Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct",
load_in_4bit=True, # 或 load_in_8bit=True
device_map="auto"
)
- 推理加速:
# 启用Flash Attention
model = Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
device_map="auto"
)
# 使用编译优化
model = torch.compile(model, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
行业应用案例与实战场景
工业质检智能化
某电子制造商通过Dify平台集成Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct,构建了智能质检系统:
工作流程:
- 图像采集:高分辨率相机拍摄产品图像
- 缺陷检测:模型识别微米级瑕疵(最小检测尺寸0.02mm)
- 结果分级:根据缺陷类型和严重程度自动分类
成效:
- 检测速度较人工提升10倍
- 年节省成本约600万元
- 对反光金属表面的字符识别准确率达98.3%
实现代码:
def industrial_inspection(model, processor, product_image):
"""
工业质检应用
"""
prompt = """请仔细检查此产品图像,识别任何可能的缺陷,包括:
1. 表面划痕或凹陷
2. 颜色不一致区域
3. 装配不当的部件
4. 文字印刷错误
如有缺陷,请描述缺陷类型、位置和严重程度。"""
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": product_image},
{"type": "text", "text": prompt}
]
}
]
inputs = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=True,
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_dict=True,
return_tensors="pt"
)
generated_ids = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=256,
do_sample=False,
temperature=0.1 # 低温度保证输出确定性
)
generated_ids_trimmed = [
out_ids[len(in_ids):] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
output_text = processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids_trimmed,
skip_special_tokens=True,
clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
)
return output_text[0] if output_text else ""
教育领域的应用
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct在教育场景中展现出强大潜力:
智能作业批改:
- 支持32种语言的作业自动批改
- 能够理解数学公式和科学图表
- 提供个性化学习建议
实验报告分析:
def analyze_lab_report(model, processor, experiment_image, student_description):
"""
分析科学实验报告
"""
prompt = f"""请对比学生描述的实验结果和实际实验图像:
学生描述:{student_description}
请评估:
1. 描述与图像的一致性
2. 实验装置的正确性
3. 可能存在的错误或改进建议"""
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": experiment_image},
{"type": "text", "text": prompt}
]
}
]
# 其余处理代码与之前示例类似
# ...
视觉编程与代码生成
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct实现了从设计图到代码的转换能力:
def design_to_code(model, processor, design_image):
"""
将设计稿转换为前端代码
"""
prompt = """请分析此UI设计图并生成相应的HTML/CSS代码。
关注以下方面:
1. 整体布局结构
2. 颜色和字体样式
3. 主要UI组件
4. 响应式设计考虑"""
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": design_image},
{"type": "text", "text": prompt}
]
}
]
inputs = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=True,
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_dict=True,
return_tensors="pt"
)
generated_ids = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=512, # 代码生成需要更长输出
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.3,
top_p=0.9
)
generated_ids_trimmed = [
out_ids[len(in_ids):] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
output_text = processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids_trimmed,
skip_special_tokens=True,
clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
)
return output_text[0] if output_text else ""
实测显示,这一功能可使前端开发效率提升3倍。
优化策略与最佳实践
模型微调指南
对于特定应用场景,对Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct进行微调可以显著提升性能:
from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer
import datasets
def fine_tune_model(model, processor, train_dataset, eval_dataset):
"""
微调Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct模型
"""
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./qwen3-vl-4b-finetuned",
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
per_device_eval_batch_size=4,
num_train_epochs=3,
learning_rate=2e-5,
fp16=True,
logging_steps=10,
save_steps=500,
eval_steps=500,
save_total_limit=2,
remove_unused_columns=False,
push_to_hub=False,
report_to=None,
dataloader_pin_memory=False
)
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
eval_dataset=eval_dataset,
data_collator=lambda data: {
'input_ids': torch.stack([d['input_ids'] for d in data]),
'attention_mask': torch.stack([d['attention_mask'] for d in data]),
'pixel_values': torch.stack([d['pixel_values'] for d in data]),
'labels': torch.stack([d['labels'] for d in data])
}
)
trainer.train()
return trainer
推理性能优化
- 动态批处理:
from typing import List
def batch_inference(model, processor, image_text_pairs: List):
"""
批量推理优化
"""
messages_list = []
for image, text in image_text_pairs:
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": image},
{"type": "text", "text": text}
]
}
]
messages_list.append(messages)
# 批量处理
inputs = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages_list, # 支持批量处理
tokenize=True,
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_dict=True,
return_tensors="pt",
padding=True
)
with torch.no_grad():
generated_ids = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=128,
do_sample=False, # 批量推理时关闭采样以提高速度
num_beams=1 # 使用贪婪解码加速
)
# 处理输出
results = []
for i, generated_id in enumerate(generated_ids):
input_length = inputs.input_ids[i].shape[0]
generated_text = processor.decode(
generated_id[input_length:],
skip_special_tokens=True
)
results.append(generated_text)
return results
内存管理技巧
class MemoryOptimizedQwen:
def __init__(self, model_path="Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct"):
self.model_path = model_path
self.model = None
self.processor = None
def load_model(self):
"""按需加载模型,节省内存"""
if self.model is None:
self.model = Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
self.model_path,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto",
load_in_4bit=True # 使用4位量化
)
self.processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(self.model_path)
def unload_model(self):
"""显式释放模型内存"""
if self.model is not None:
del self.model
self.model = None
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
def process_with_memory_management(self, image, text):
"""带内存管理的处理"""
self.load_model()
try:
# 处理逻辑
result = process_multimodal_query(self.model, self.processor, image, text)
return result
finally:
# 可选:根据需求决定是否立即卸载模型
# self.unload_model()
pass
技术挑战与解决方案
多模态对齐难题
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct通过DeepStack视觉特征融合技术解决了多模态对齐的挑战。该技术将早期层的低级视觉特征(边缘、纹理)与深层的高级语义特征相结合,实现了细粒度视觉-语言对齐。
长视频理解优化
针对长视频理解的内存和计算瓶颈,模型采用了以下策略:
- 关键帧提取:智能选择信息量最大的帧进行处理
- 时序建模:通过交错MRoPE技术保持长时间序列的连贯性
- 分层处理:先对单个帧进行理解,再整合时序关系
def efficient_video_understanding(model, processor, video_path, query):
"""
高效视频理解实现
"""
# 1. 提取关键帧
key_frames = extract_key_frames(video_path)
# 2. 并行处理单帧
frame_descriptions = []
for frame in key_frames:
description = process_single_frame(model, processor, frame, "描述此帧内容")
frame_descriptions.append(description)
# 3. 整合时序信息
integration_prompt = f"""
基于以下帧描述,回答问题:{query}
帧描述:
{chr(10).join([f'帧 {i+1}: {desc}' for i, desc in enumerate(frame_descriptions)])}
请结合时序关系提供综合分析:"""
# 使用纯文本模式进行整合分析
integration_messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": integration_prompt}
]
}
]
inputs = processor.apply_chat_template(
integration_messages,
tokenize=True,
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_dict=True,
return_tensors="pt"
)
generated_ids = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=256,
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.7
)
generated_ids_trimmed = [
out_ids[len(in_ids):] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
final_output = processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids_trimmed,
skip_special_tokens=True,
clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
)
return final_output[0] if final_output else ""
未来展望与发展趋势
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct的推出标志着多模态AI进入"普惠时代"。根据前瞻产业研究院预测,到2030年边缘端多模态应用市场规模将突破900亿元。
技术发展方向
- 实时多模态交互:支持语音、手势、眼神等多通道输入,实现"所见即所得"的交互体验
- 自主模态选择:模型能根据任务复杂度自动选择最优模态组合
- 物理世界理解:结合机器人传感器数据,实现"端到端"的物理操作
生态建设
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct的开源特性(Apache-2.0协议)降低了创新门槛,预计未来半年将催生超500个行业解决方案。
表3:Qwen3-VL系列模型发展路线
| 模型版本 | 发布时间 | 核心特性 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen-VL | 2023年8月 | 基础多模态能力 | 图像描述、视觉问答 |
| Qwen2.5-VL | 2025年9月 | 混合模态编码器、动态模态权重 | 复杂场景解析 |
| Qwen3-VL-235B | 2025年9月 | 旗舰级模型,全能多模态 | 企业级复杂应用 |
| Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct | 2025年10月 | 轻量高效、边缘优化 | 广泛边缘设备部署 |
结论
Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct的发布不仅是技术突破,更重塑了多模态模型的产品形态——从"实验室里的巨兽"变为"口袋里的专家"。通过4.4B参数的轻量级设计,在保持核心多模态能力的同时实现了边缘设备的高效部署,为AI技术的民主化进程做出了重要贡献。
对于开发者而言,Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct是探索边缘AI应用的理想起点;对于行业而言,这一轻量级多模态模型将成为数字化转型的新引擎。随着模型在制造业、教育、医疗、零售等领域的广泛应用,我们正见证多模态AI从技术概念走向大规模落地的历史性转变。
资源链接
参考文献
本文由AI技术爱好者根据官方资料和实测数据编写,仅供参考学习。转载请注明出处。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献118条内容
已为社区贡献118条内容








所有评论(0)