【018】Dubbo3从0到1系列之时间轮流程图解
Dubbo3时间轮机制采用HashedWheelTimer实现高效定时任务管理。其核心流程包括:1)初始化时间轮结构;2)通过队列接收任务并转移至对应时间槽;3)Worker线程周期性处理到期任务;4)支持多轮计数机制处理长延迟任务(如300秒任务分5轮处理)。系统采用生产者-消费者模式,通过时间轮算法优化海量定时任务调度,配合任务取消机制确保系统稳定性。典型场景中,通过remainingRoun
·
文章目录
Dubbo3时间轮
7.2.8 HashedWheelTimer图解
✅ 1. 架构图
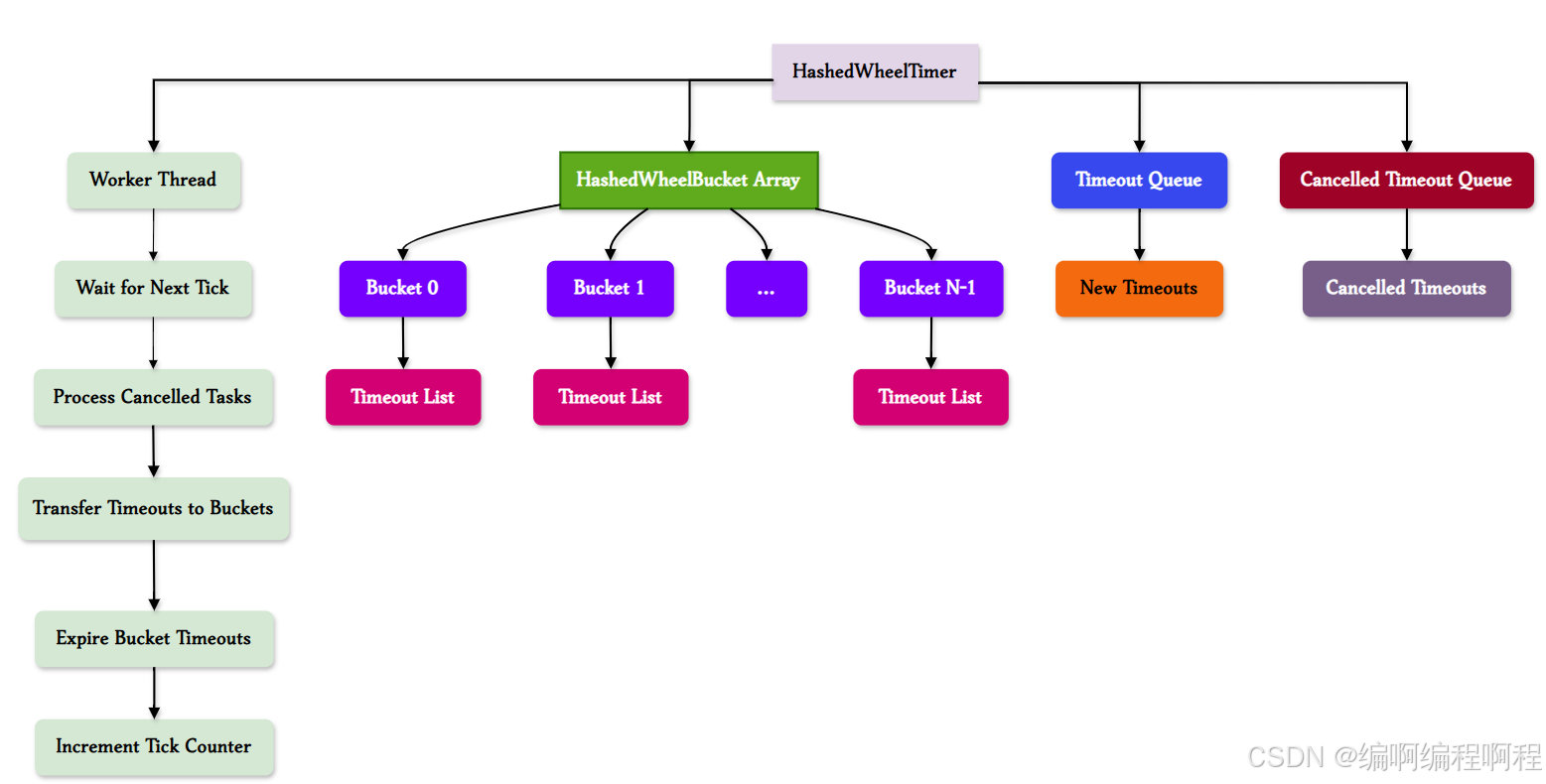
✅ 2. 初始化流程图
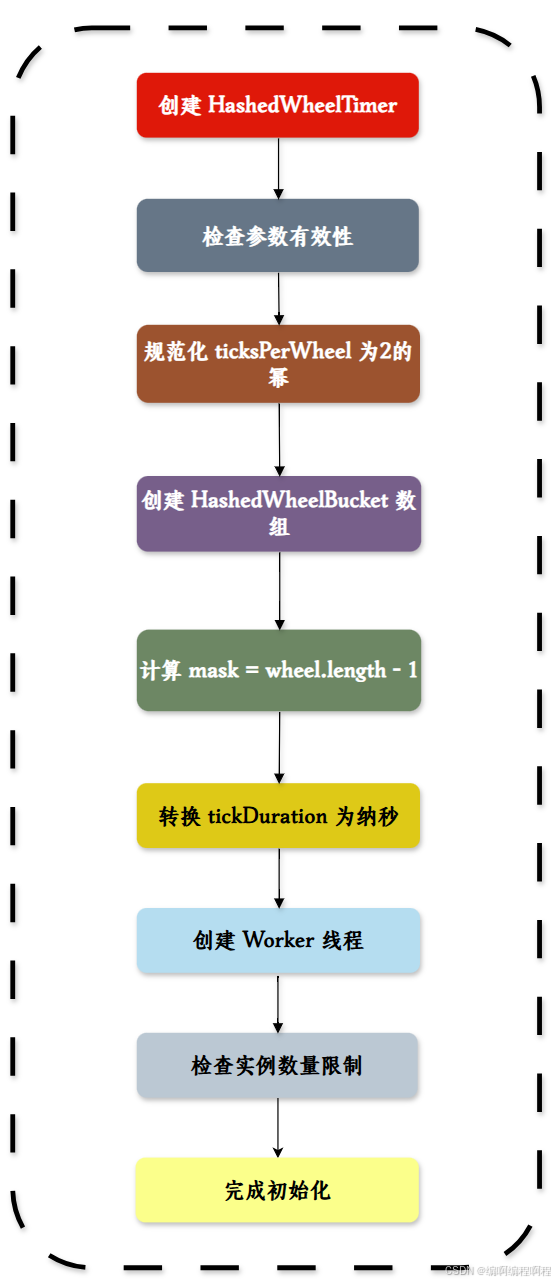
✅ 3. 添加定时任务流程图
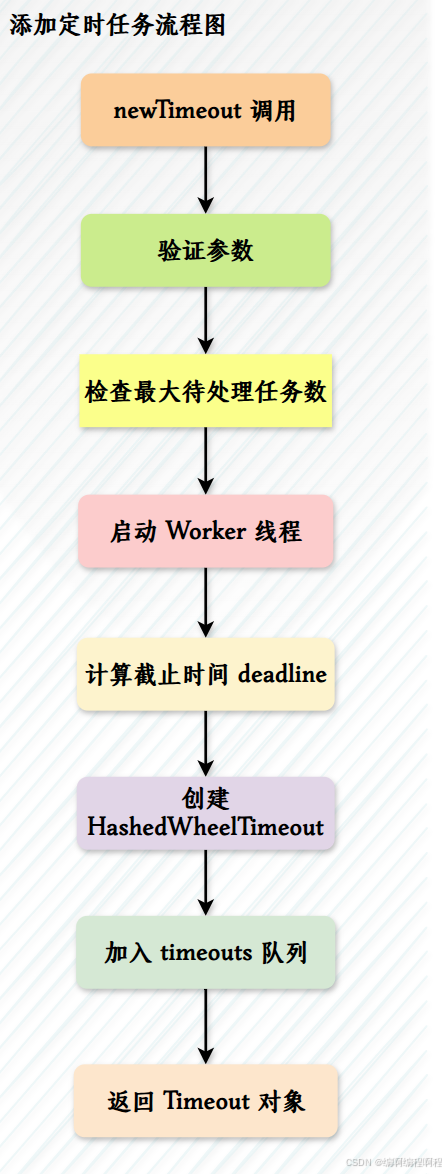
✅ 4. Worker 线程处理流程图
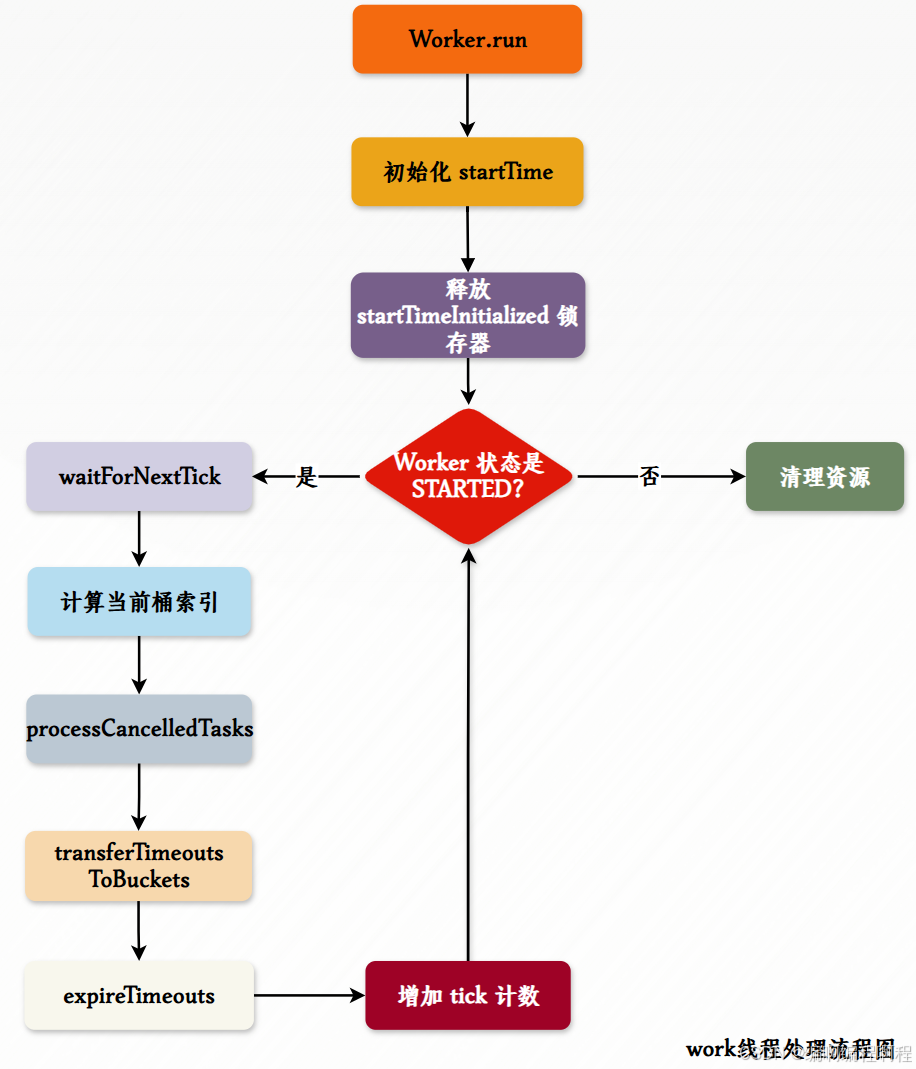
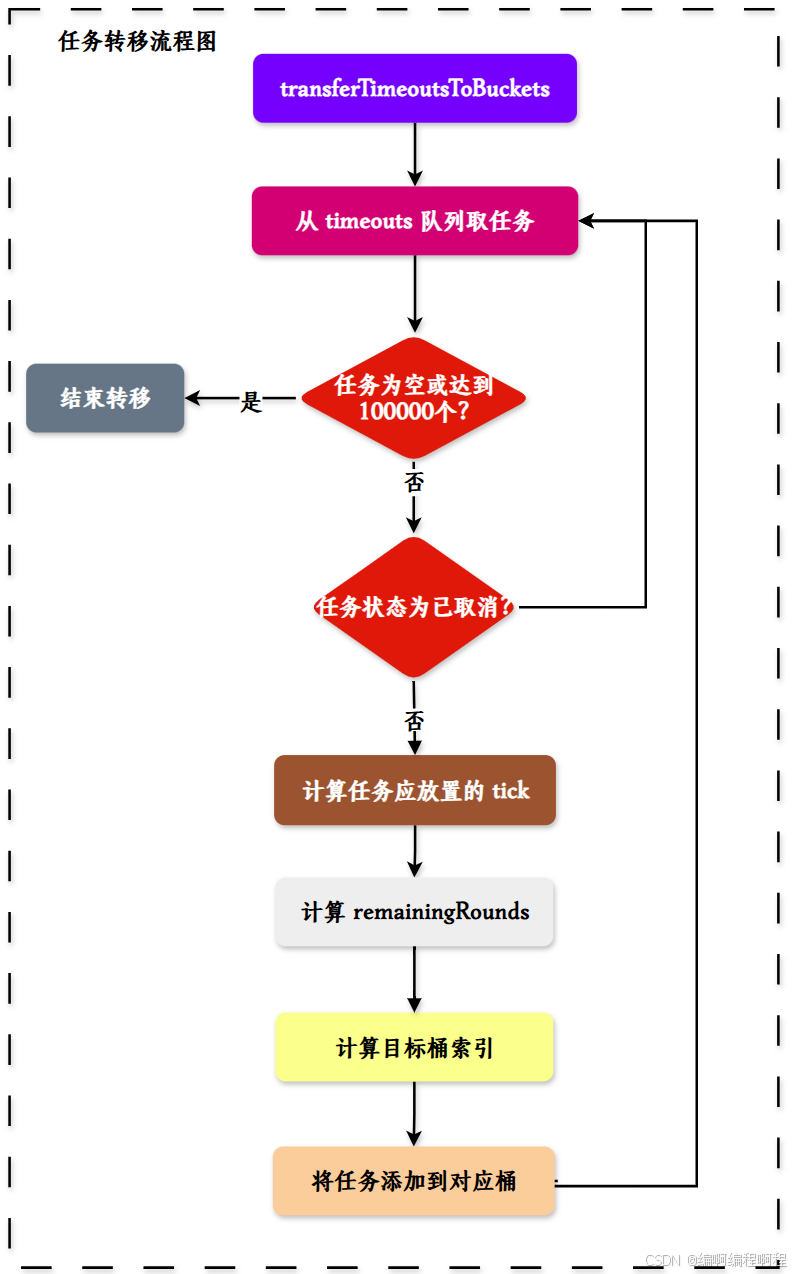
✅ 5. 任务转移流程图
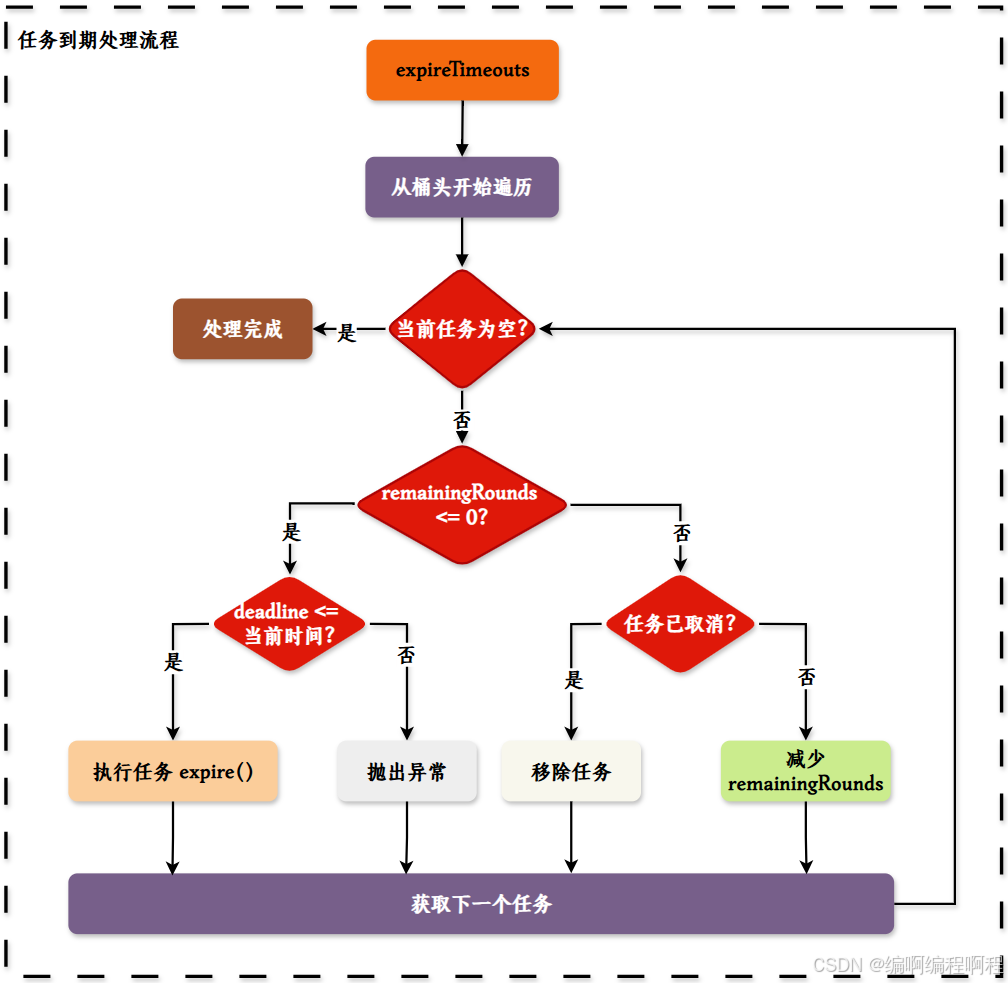
✅ 6. 任务到期处理流程
✅ 7. 时间轮工作时序图
✅ 8. 任务取消时序图
这些图表展示了 HashedWheelTimer 的核心工作机制,包括初始化过程、任务添加、任务处理以及任务取消等关键环节。整体设计采用了生产者-消费者模式,通过队列解耦了任务提交和任务处理的过程,并利用时间轮算法优化了大量定时任务的管理效率。
7.2.9 举例说明
- 用户提交一个延迟为 T = 300 秒(5 分钟) 的任务;
- 计算总 tick 数:totalTicks = T / tickDuration = 300_000ms / 100ms = 3000 ticks. (时间轮的指针,是一个步长为 1 的单调递增计数器)
- 由于 wheel 只有 512 个槽,计算:
- remainingRounds = totalTicks / ticksPerWheel = 3000 / 512 ≈ 5 轮
- remainingRounds ,剩余的轮数
- stopIndex = (currentTick + totalTicks) % ticksPerWheel
- 某个槽位停止下来
- remainingRounds = totalTicks / ticksPerWheel = 3000 / 512 ≈ 5 轮
- 将任务封装为 HashedWheelTimeout,记录ticksPerWheel
- 时间轮工作线程每 tick 一次:
- 当指针到达
stopIndex时,检查该槽位所有任务; - 若 remainingRounds > 0,则
remainingRounds--,不执行任务,继续等待下一轮; - 直到
remainingRounds == 0,才真正执行任务。
- 当指针到达
✅ 这就是 “多轮计数”机制,无需多级时间轮,也能支持任意长时间任务。
🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉
- Enjoy it
🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容









所有评论(0)