《红黑树核心机制解析:C++ STL中map/set高效实现原理与工程实践》
为解决这个问题,我们在 map 和 set 这两个容器层,分别实现了仿函数 MapKeyOfT 和 SetKeyOfT,并将它们传递给红黑树的 KeyOfT 模板参数。,无法直接判断模板参数 T 具体是单纯的键类型 K(如:set 的场景 ),还是键值对类型 pair<K, V>(如:map 的场景 )这样一颗红黑树,既能适配 set 的 “纯 key 搜索场景”,也能适配 map 的 “key/
前言:
在C++标准库中,map和set凭借其稳定对数级查找复杂度(O(log n))成为高性能开发的关键组件。然而,它们的真正威力源于底层的红黑树自平衡机制,以及精心设计的迭代器体系。本文将以零依赖方式完整实现两套符合STL标准的容器:
Map<K, V>:键值映射容器
Set<T>:唯一键集合涵盖的核心技术细节包括:
✔ 红黑树节点结构设计(颜色标记、父子指针维护)
✔ 插入/删除的平衡修复策略(左旋、右旋及颜色调整)
✔ 迭代器失效机制(与STL标准的一致性保证)
✔ 性能基准测试(与std::map/std::set的对比分析)
目录

一、源码剖析
在 SGI - STL30 版本的源代码里,map 和 set 相关的实现代码分布在
map、set、stl_map.h、stl_set.h、stl_tree.h等几个头文件中。下面我们就看一看 map 和 set 实现结构框架的部分核心内容:
// set 容器相关声明与包含
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_TREE_H
#include <stl_tree.h>
#endif
#include <stl_set.h>
#include <stl_multiset.h>
// map 容器相关声明与包含
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_TREE_H
#include <stl_tree.h>
#endif
#include <stl_map.h>
#include <stl_multimap.h>
// stl_set.h 中 set 类模板定义
template <class Key, class Compare = less<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class set
{
public:
// typedefs:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Key value_type;
private:
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type,
identity<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t; // red-black tree representing set
};
// stl_map.h 中 map 类模板定义
template <class Key, class T, class Compare = less<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class map
{
public:
// typedefs:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef T mapped_type;
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;
private:
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type,
select1st<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t; // red-black tree representing map
};
/*----------------------红黑树 节点基类/类模板 定义----------------------*/
// stl_tree.h 中红黑树节点基类定义
struct __rb_tree_node_base
{
typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type;
typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;
color_type color;
base_ptr parent;
base_ptr left;
base_ptr right;
};
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc = alloc>
class rb_tree
{
protected:
typedef void* void_pointer;
typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node;
typedef rb_tree_node* link_type;
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Value value_type;
public:
// insert用的是第二个模板参数左形参
pair<iterator, bool> insert_unique(const value_type& x);
// erase和find用第一个模板参数做形参
size_type erase(const key_type& x);
iterator find(const key_type& x);
protected:
size_type node_count; // keeps track of size of tree
link_type header;
};
// stl_tree.h 中红黑树节点类模板定义
template <class Value>
struct __rb_tree_node : public __rb_tree_node_base
{
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value>* link_type;
Value value_field;
};
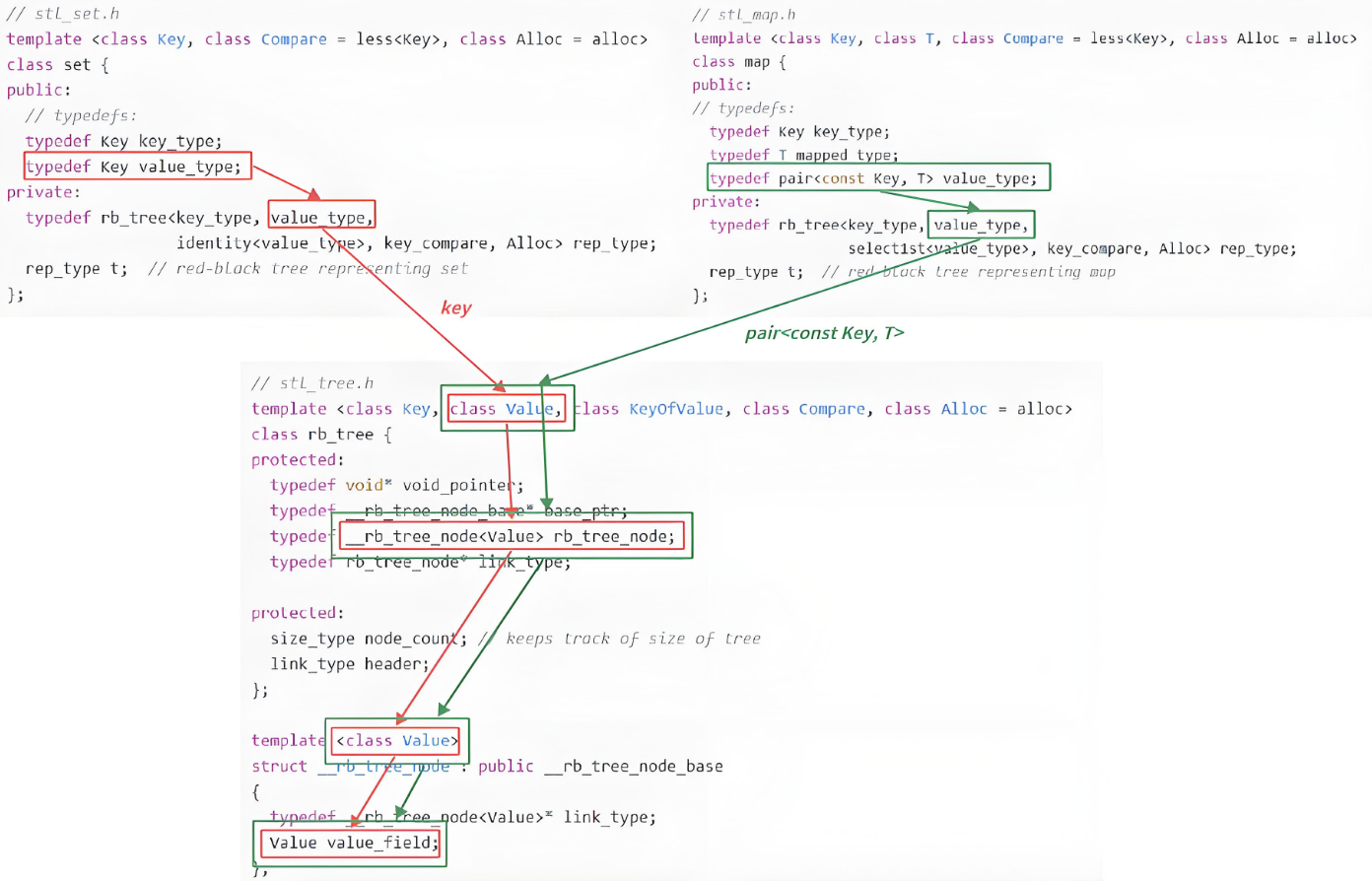
红黑树(rb_tree)泛型设计思想解析
通过对框架的分析,我们能看到 SGI STL 源码中 rb_tree 的泛型设计非常巧妙
- 它不直接写死“仅支持 key 搜索” 或 “仅支持 key/value 搜索”
- 而是通过第二个模板参数 Value 灵活控制:红黑树节点(__rb_tree_node)中实际存储的数据类型,由 Value 决定
这样一颗红黑树,既能适配 set 的 “纯 key 搜索场景”,也能适配 map 的 “key/value 搜索场景”。
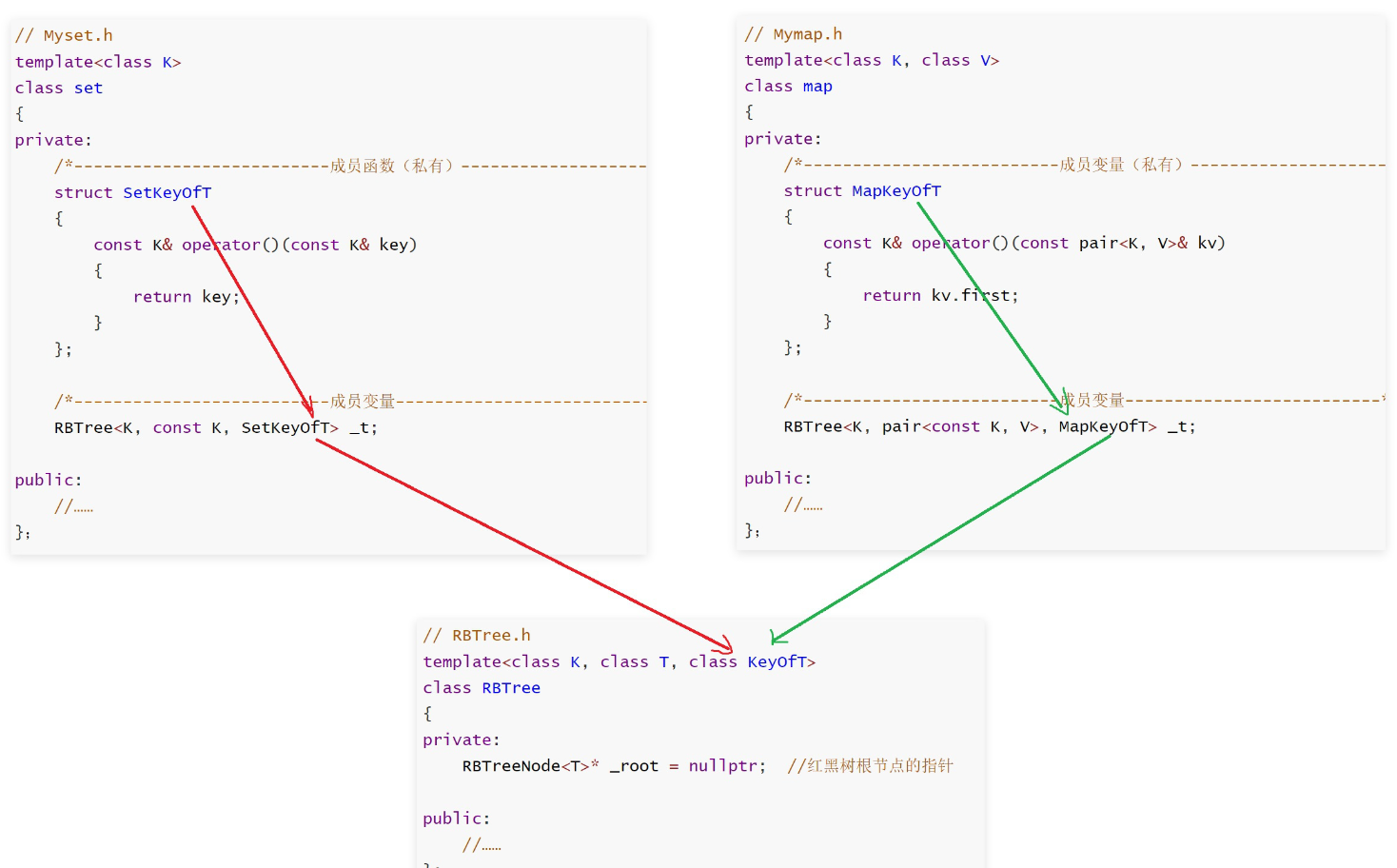
二、红黑树插入实现
由于红黑树(RBTree)采用泛型设计,无法直接判断模板参数 T 具体是单纯的键类型 K(如:set 的场景 ),还是键值对类型 pair<K, V>(如:map 的场景 )
- 这会导致一个问题:在 insert 逻辑里进行 “节点比较” 时,默认的比较规则无法满足需求
- 因为 pair 的默认比较会同时涉及 key 和 value,但我们实际需要只比较 key
为解决这个问题,我们在 map 和 set 这两个容器层,分别实现了仿函数 MapKeyOfT 和 SetKeyOfT,并将它们传递给红黑树的 KeyOfT 模板参数
这样,红黑树内部就能通过 KeyOfT 仿函数:
- 先从 T 类型对象中提取出 key
- 再用这个 key 进行比较
- 从而实现 “仅按 key 排序 / 插入” 的逻辑。
//插入
bool insert(const V& date)
{
if (root==nullptr)
{
root = new Node(date);
root->_co = Black;
return true;
}
//找插入位置
Node* cur = root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
Function Sort;
while (cur)
{
parent = cur;
if (Sort(cur->_date) > Sort(date))
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (Sort(cur->_date) < Sort(date))
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else//如果相等就退出
{
cout << "值相等无法插入" << endl;
return false;
}
}
//连接+插入
cur = new Node(date);
if (Sort(parent->_date) < Sort(date))
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//调整
Node* grandfather = nullptr;
Node* uncle = nullptr;
while (parent && parent->_co == Red)
{
grandfather = parent->_parent;
//左边调整
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
{
uncle = grandfather->_right;
//如果uncle存在且为红
if (uncle && uncle->_co == Red)
{
parent->_co = Black;
uncle->_co = Black;
grandfather->_co = Red;
//向上更新
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//根据cur的位置旋转
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
//右旋
Whirl_R(grandfather);
}
else
{
//左右双旋
Whirl_L_R(grandfather);
}
break;
}
}
else//右边调整
{
uncle = grandfather->_left;
//如果uncle存在且为红
if (uncle && uncle->_co == Red)
{
parent->_co = Black;
uncle->_co = Black;
grandfather->_co = Red;
//向上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else//如果uncle不存在或者存在为黑
{
//根据cur选择旋转
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
//左旋
Whirl_L(grandfather);
}
else
{
//右左双旋
Whirl_R_L(grandfather);
}
break;
}
}
}
root->_co = Black;
return true;
}
//左旋
void Whirl_L(Node* parent)
{
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
Node* cur = parent->_right;
Node* curleft = cur->_left;
//连接cur和parent
cur->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
//连接curleft和parent
parent->_right = curleft;
if (curleft)
{
curleft->_parent = parent;
}
//连接ppnode和cur
if (ppnode)
{
cur->_parent = ppnode;
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = cur;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = cur;
}
}
else
{
root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
//更新颜色
cur->_co = Black;
parent->_co = Red;
}
//右旋
void Whirl_R(Node* parent)
{
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
Node* cur = parent->_left;
Node* curright = cur->_right;
//连接cur和parent
cur->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
//连接curleft和parent
parent->_left = curright;
if (curright)
{
curright->_parent = parent;
}
//连接ppnode和cur
if (ppnode)
{
cur->_parent = ppnode;
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = cur;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = cur;
}
}
else
{
root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
//更新颜色
cur->_co = Black;
parent->_co = Red;
}
//左右双旋
void Whirl_L_R(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_left;
Node* curright = cur->_right;
//左旋
Whirl_L(cur);
//右旋
Whirl_R(parent);
//更新颜色
curright->_co = Black;
cur->_co = Red;
parent->_co = Red;
}
//右左双旋
void Whirl_R_L(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_right;
Node* curleft = cur->_left;
//右旋
Whirl_R(cur);
//左旋
Whirl_L(parent);
//更新颜色
curleft->_co = Black;
cur->_co = Red;
parent->_co = Red;
}三、红黑树Find查找
不论是map还是set都是根据Key查找的,因此map里面的仿函数需要重载
//Find查找
Node find(const V& date)
{
Function Find;
if (root == nullptr)
{
cout << "查找失败,根为空" << endl;
return nullptr;
}
Node* cur = root;
while (cur)
{
if (Find(cur->_date) > Find(date))
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if(Find(cur->_date) < Find(date))
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}四、Set的普通迭代器
template <typename T>
class RBTreeSet {
private:
struct Node {
T value;
Node* parent;
Node* left;
Node* right;
bool is_red;
// 查找子树最小节点(用于begin())
static Node* minimum(Node* x) noexcept {
while (x->left != nullptr) {
x = x->left;
}
return x;
}
// 查找子树最大节点(用于end()前驱)
static Node* maximum(Node* x) noexcept {
while (x->right != nullptr) {
x = x->right;
}
return x;
}
};
public:
// 迭代器类定义
class iterator {
using iterator_category = std::bidirectional_iterator_tag;
using value_type = T;
using difference_type = std::ptrdiff_t;
using pointer = const T*; // set元素不可修改
using reference = const T&; // set元素不可修改
Node* current;
const RBTreeSet* tree; // 用于边界检查
public:
explicit iterator(Node* node = nullptr, const RBTreeSet* t = nullptr)
: current(node), tree(t) {}
// 解引用操作符
reference operator*() const {
return current->value;
}
pointer operator->() const {
return &(operator*());
}
// 前置++
iterator& operator++() {
if (current == nullptr) {
// 处理end()++的情况
throw std::out_of_range("RBTreeSet iterator out of range");
}
if (current->right != nullptr) {
// 情况1:存在右子树,找右子树的最小节点
current = Node::minimum(current->right);
} else {
// 情况2:向上查找第一个是左子节点的祖先
Node* parent = current->parent;
while (parent != nullptr && current == parent->right) {
current = parent;
parent = parent->parent;
}
current = parent; // 可能为nullptr(到达end)
}
return *this;
}
// 后置++(标准实现方式)
iterator operator++(int) {
iterator tmp = *this;
++(*this);
return tmp;
}
// 前置--(逆向遍历)
iterator& operator--() {
if (current == nullptr) {
// 处理begin()--的情况
throw std::out_of_range("RBTreeSet iterator out of range");
}
if (current->left != nullptr) {
// 情况1:存在左子树,找左子树的最大节点
current = Node::maximum(current->left);
} else {
// 情况2:向上查找第一个是右子节点的祖先
Node* parent = current->parent;
while (parent != nullptr && current == parent->left) {
current = parent;
parent = parent->parent;
}
current = parent; // 必须非nullptr(已校验)
}
return *this;
}
// 比较操作符
bool operator==(const iterator& other) const noexcept {
return current == other.current;
}
bool operator!=(const iterator& other) const noexcept {
return !(*this == other);
}
// 允许从非const转为const迭代器
operator typename RBTreeSet::const_iterator() const {
return typename RBTreeSet::const_iterator(current, tree);
}
};
// const迭代器(继承自普通迭代器)
class const_iterator : public iterator {
public:
using iterator::iterator;
// 继承所有功能,元素始终保持只读
};
// 获取迭代器
iterator begin() noexcept {
return iterator(Node::minimum(root), this);
}
iterator end() noexcept {
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const_iterator cbegin() const noexcept {
return const_iterator(Node::minimum(root), this);
}
const_iterator cend() const noexcept {
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
};五、Map的普通迭代器
template <typename Key, typename Value>
class RBTreeMap {
private:
using value_type = std::pair<const Key, Value>; // 关键:Key必须为const
struct Node {
value_type data; // 存储pair<const Key, Value>
Node* parent;
Node* left;
Node* right;
bool is_red;
// 获取子树最小节点(用于begin())
static Node* minimum(Node* x) noexcept {
while (x->left != nullptr) {
x = x->left;
}
return x;
}
// 获取子树最大节点(用于rbegin())
static Node* maximum(Node* x) noexcept {
while (x->right != nullptr) {
x = x->right;
}
return x;
}
};
public:
// 迭代器类(支持->和*操作符访问pair)
class iterator {
using iterator_category = std::bidirectional_iterator_tag;
using difference_type = std::ptrdiff_t;
using reference = value_type&;
using pointer = value_type*;
Node* current;
const RBTreeMap* tree; // 用于边界检查
public:
explicit iterator(Node* node = nullptr, const RBTreeMap* t = nullptr)
: current(node), tree(t) {}
// 解引用为pair<const Key, Value>&
reference operator*() const {
return current->data;
}
// 箭头操作符返回pair指针
pointer operator->() const {
return &(current->data);
}
// 前置++(中序后继)
iterator& operator++() {
if (current == nullptr) {
throw std::out_of_range("RBTreeMap iterator out of range");
}
if (current->right != nullptr) {
current = Node::minimum(current->right);
} else {
Node* parent = current->parent;
while (parent != nullptr && current == parent->right) {
current = parent;
parent = parent->parent;
}
current = parent;
}
return *this;
}
// 后置++
iterator operator++(int) {
iterator tmp = *this;
++(*this);
return tmp;
}
// 前置--(中序前驱)
iterator& operator--() {
if (tree->empty()) {
throw std::out_of_range("RBTreeMap iterator out of range");
}
if (current == nullptr) {
// end()--时指向最大节点
current = Node::maximum(tree->root);
} else if (current->left != nullptr) {
current = Node::maximum(current->left);
} else {
Node* parent = current->parent;
while (parent != nullptr && current == parent->left) {
current = parent;
parent = parent->parent;
}
current = parent;
}
return *this;
}
// 比较操作符
bool operator==(const iterator& other) const noexcept {
return current == other.current;
}
bool operator!=(const iterator& other) const noexcept {
return !(*this == other);
}
};
// const迭代器(禁止修改value)
class const_iterator : public iterator {
public:
using const_reference = const value_type&;
using const_pointer = const value_type*;
const_iterator(Node* node = nullptr, const RBTreeMap* t = nullptr)
: iterator(node, t) {}
// 重载解引用操作符返回const引用
const_reference operator*() const {
return iterator::operator*();
}
// 重载箭头操作符返回const指针
const_pointer operator->() const {
return iterator::operator->();
}
};
// 迭代器获取方法
iterator begin() noexcept {
return iterator(Node::minimum(root), this);
}
iterator end() noexcept {
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const_iterator cbegin() const noexcept {
return const_iterator(Node::minimum(root), this);
}
const_iterator cend() const noexcept {
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
};
祝大家1024程序员节快乐!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容









所有评论(0)