300I-Duo加速卡部署qwen2.5-vl-7b
本文介绍了在华为昇腾AI硬件上部署Qwen2.5-VL-7B大语言模型的完整流程。首先在Atlas 300I Duo推理卡和Kylin V10系统上安装驱动、固件及MindIE软件包;接着通过Docker容器部署MindIE服务,配置模型权重路径和NPU设备参数;最后测试验证了模型的语言生成和图像理解能力。该方案为国产化AI部署提供了实践参考,展示了昇腾硬件对大模型推理的高效支持能力。
文章目录
前言
最近好像项目国产化的适配好像明显增多了,正好借此机会学习下大模型的国产化部署。本文记录如何利用华为昇腾AI的推理加速引擎MindIE,在昇腾硬件上高效部署qwen2.5-vl-7b大语言模型。
一、安装基础环境
硬件:Atlas 300I Duo 推理卡
系统:Kylin V10(OpenEuler) SP1
查询当前操作系统命令
uname -m && cat /etc/*release
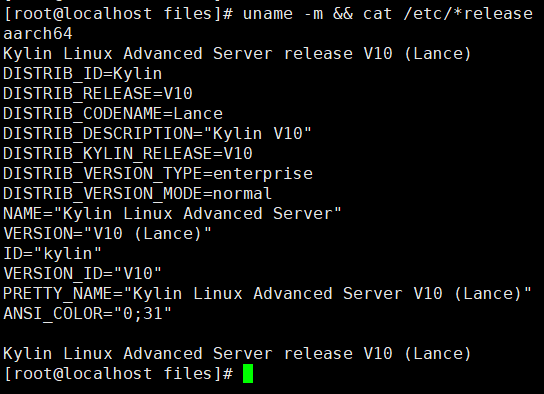
如果查询的操作系统版本不在对应产品列表中,请替换为支持的操作系统。
安装驱动与固件:
https://www.hiascend.com/hardware/firmware-drivers/community?product=2&model=17&cann=8.2.RC2&driver=Ascend+HDK+25.2.0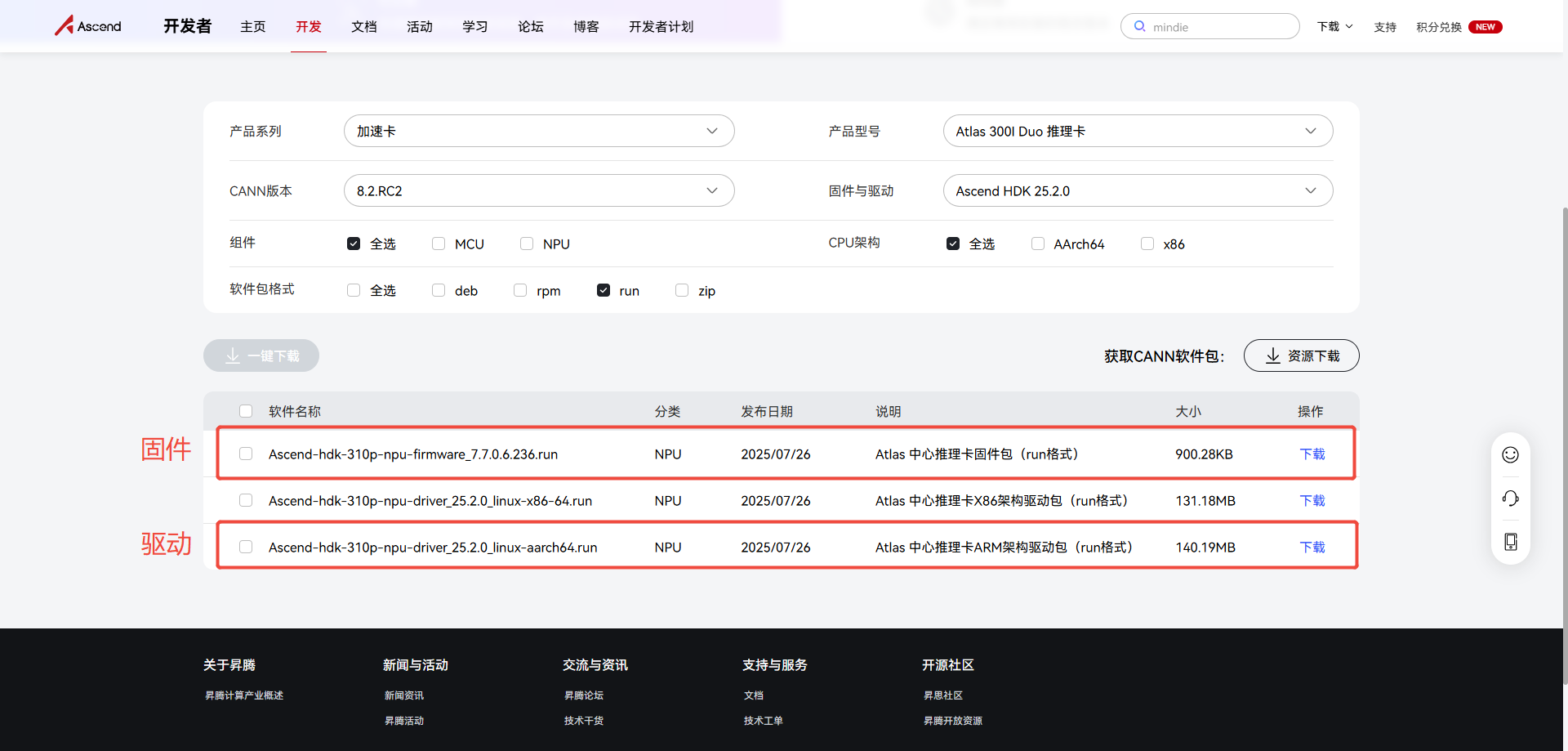
这里笔者选用的是Ascend-hdk-310p-npu-driver_25.2.0_linux-aarch64.run驱动与Ascend-hdk-310p-npu-firmware_7.7.0.6.236.run固件
./Ascend-hdk-310p-npu-driver_25.2.0_linux-aarch64.run --full
./Ascend-hdk-310p-npu-firmware_7.7.0.6.236.run --full
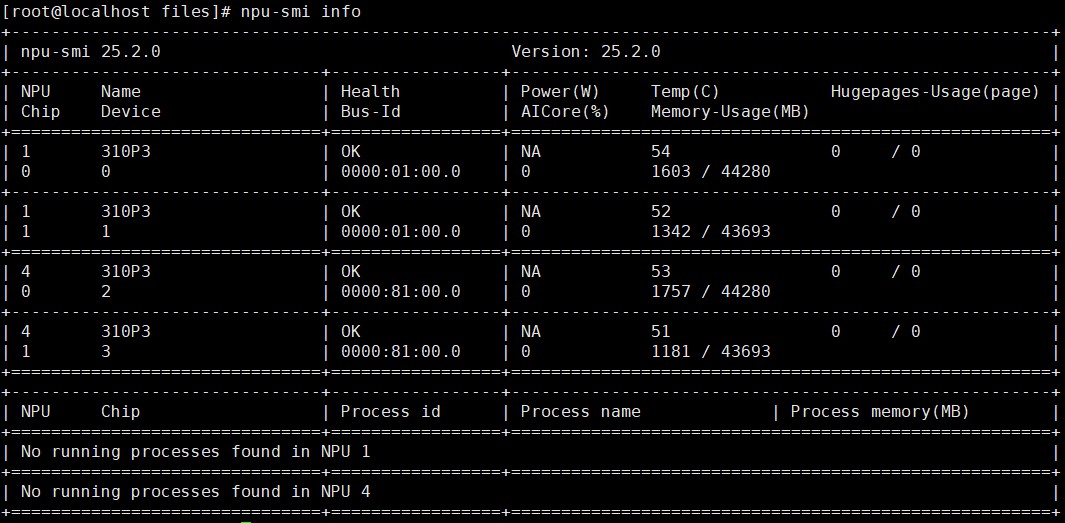
测试
npu-smi info
安装MindIE ARM软件包
https://www.hiascend.com/developer/download/community/result?module=ie+pt+cann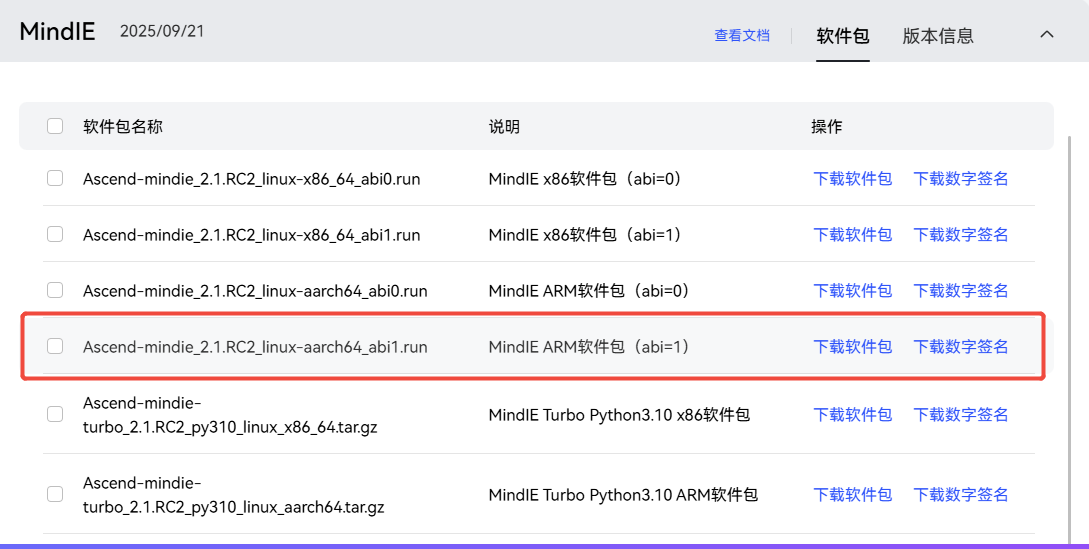
这里笔者选用的是Ascend-mindie_2.1.RC2_linux-aarch64_abi1.run
./Ascend-mindie_2.1.RC2_linux-aarch64_abi1.run
二、MindIE容器部署
2.1获取MindIE镜像
https://www.hiascend.com/developer/ascendhub/detail/af85b724a7e5469ebd7ea13c3439d48f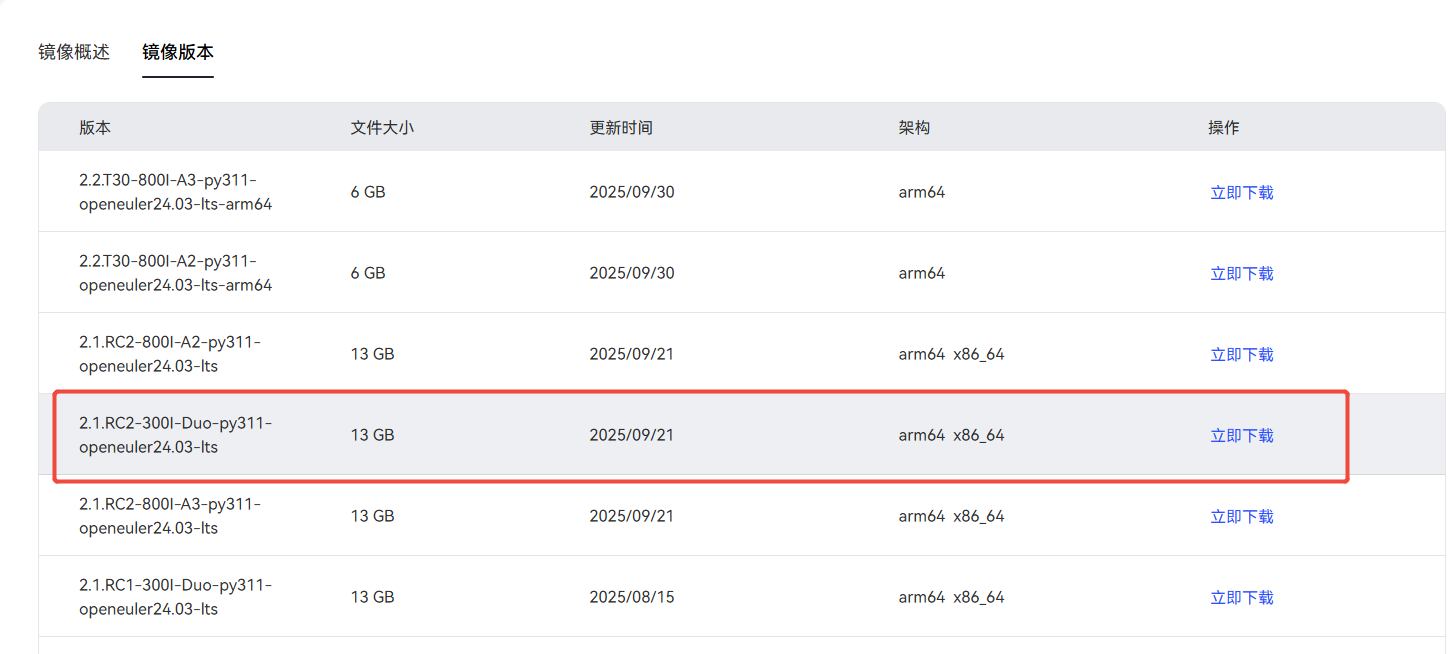
这里选用的是2.1.RC2-300I-Duo-py311-openeuler24.03-lts版本的镜像
选择对应架构的镜像
docker pull --platform=arm64 swr.cn-south-1.myhuaweicloud.com/ascendhub/mindie:2.1.RC2-300I-Duo-py311-openeuler24.03-lts
查看docker镜像
docker images

2.2启动MindIE容器
启动容器时,需要映射NPU设备并挂载模型权重目录。
docker run -it -d --net=host --shm-size=500g
--privileged
--name mindie-qwen-vl-7b
--device=/dev/davinci_manager
--device=/dev/hisi_hdc
--device=/dev/devmm_svm
-v /usr/local/Ascend/driver:/usr/local/Ascend/driver:ro
-v /usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/sbin:ro
-v /data_1/files:/data_1 #挂载权重路径
c6b8147b5039 #镜像ID
查看起好的容器
docker ps

2.3获取与准备模型权重
下载Qwen3-32B模型:Qwen3-32B的模型权重可以从 ModelScope 或 Hugging Face 等平台下载,国内推荐使用魔塔社区(Modelscope),速度较快。
https://www.modelscope.cn/models/Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct/summary
# 安装modelscope
pip install modelscope
# 下载模型
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct --local_dir /path-to-weights
设置模型权限,这是部署成功的关键一步。chmod -R 750 /path-to-weights,这里必须是750,太高太低都不行。
2.4配置与启动MindIE服务
2.4.1修改服务配置文件
进入容器后,需要修改MindIE服务的配置文件:
docker exec -it mindie-qwen-vl-7b bash
vim /usr/local/Ascend/mindie/latest/mindie-service/conf/config.json
需要修改的主要参数如下:
{
"ServerConfig": {
"port": 1040, // 服务主端口,可自定义
"managementPort": 1041, // 管理端口
"metricsPort": 1042, // 指标端口
"httpsEnabled": false // 初次部署可关闭HTTPS简化流程
},
"BackendConfig": {
"npuDeviceIds": [[0, 1]], // 指定使用的NPU设备ID,根据实际卡数填写
"ModelDeployConfig": {
"truncation": false,
"ModelConfig": [
{
"modelName": "qwen-vl-7b", // 模型名称,调用时使用
"modelWeightPath": "/容器内权重路径", // 容器内模型权重挂载路径
"worldSize": 2 // 使用的NPU卡数,与npuDeviceIds对应
}
]
}
}
}
2.4.1启动推理服务
在容器内,进入MindIE服务脚本目录并启动服务:
cd /usr/local/Ascend/mindie/latest/mindie-service/bin
./mindieservice_daemon # 前台启动,方便查看日志
# 或
nohup ./mindieservice_daemon > output.log 2>&1 & # 后台启动,日志写入文件
服务成功启动后,通常会看到提示信息,并且可以通过 npu-smi 命令观察到NPU计算负载显著增加。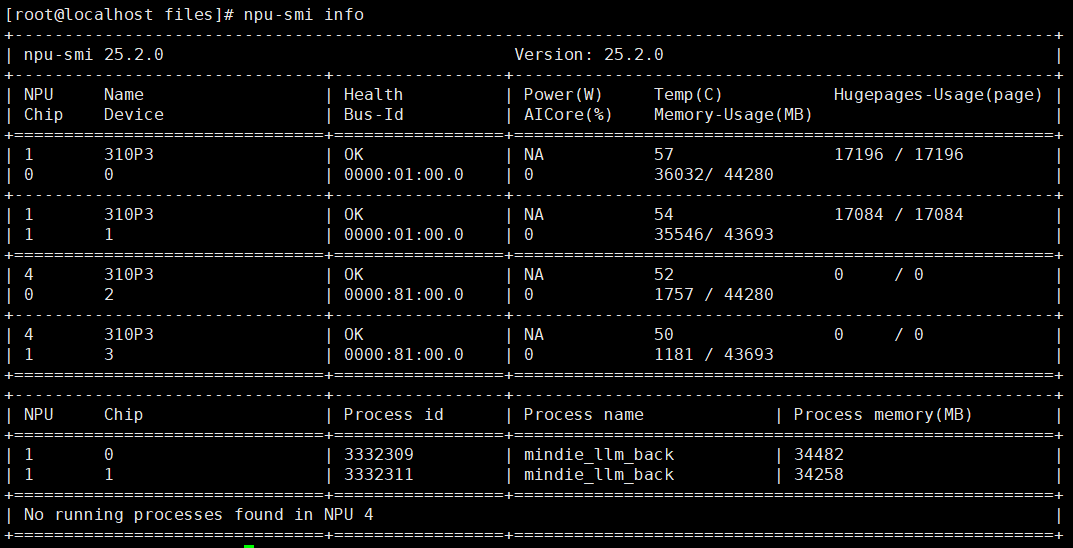
三、测试验证
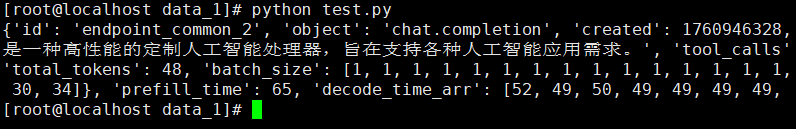
3.1 测试语言能力
import requests
import json
url = "http://localhost:1040/v1/chat/completions" # 替换为你的服务器IP和端口
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
data = {
"model": "qwen-vl-7b", # 与配置文件中的modelName一致
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "请用一句话介绍华为昇腾AI处理器"}],
"max_tokens": 100,
"temperature": 0.7
}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
print(response.json())
3.2 测试图像理解能力
import requests
import json
import base64
import os
from PIL import Image
import io
def compress_image(image_path, max_size=768):
"""压缩图片到指定大小"""
try:
img = Image.open(image_path)
if max(img.size) > max_size:
ratio = max_size / max(img.size)
new_size = (int(img.size[0] * ratio), int(img.size[1] * ratio))
img = img.resize(new_size, Image.LANCZOS)
byte_arr = io.BytesIO()
img.convert('RGB').save(byte_arr, format='JPEG', quality=85)
return byte_arr.getvalue()
except Exception as e:
print(f"图片压缩失败: {e}")
return None
def image_to_base64(image_path):
"""压缩图片并转换为base64"""
compressed = compress_image(image_path)
if compressed is None:
# 如果压缩失败,尝试直接读取
try:
with open(image_path, "rb") as f:
return base64.b64encode(f.read()).decode('utf-8')
except:
return None
return base64.b64encode(compressed).decode('utf-8')
url = "http://127.0.0.1:1040/v1/chat/completions"
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
# 图片路径
image_path = "2.jpg"
# 检查图片是否存在
if not os.path.exists(image_path):
print(f"错误: 图片文件不存在: {image_path}")
exit(1)
base64_image = image_to_base64(image_path)
if base64_image is None:
print("图片处理失败")
exit(1)
# 正确的消息格式
data = {
"model": "qwen-vl-7b",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": f"data:image/jpeg;base64,{base64_image}"
}
},
{
"type": "text",
"text": "请描述这张图片的内容"
}
]
}
],
"max_tokens": 1000,
"temperature": 0.7
}
try:
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
response.raise_for_status()
result = response.json()
# 提取回答内容
if 'choices' in result and result['choices']:
content = result['choices'][0]['message']['content']
print("模型回答:")
print(content)
else:
print("完整响应:")
print(json.dumps(result, indent=2))
except Exception as e:
print(f"请求失败: {e}")
if hasattr(e, 'response') and e.response:
print("错误详情:", e.response.text)
测试图片如下: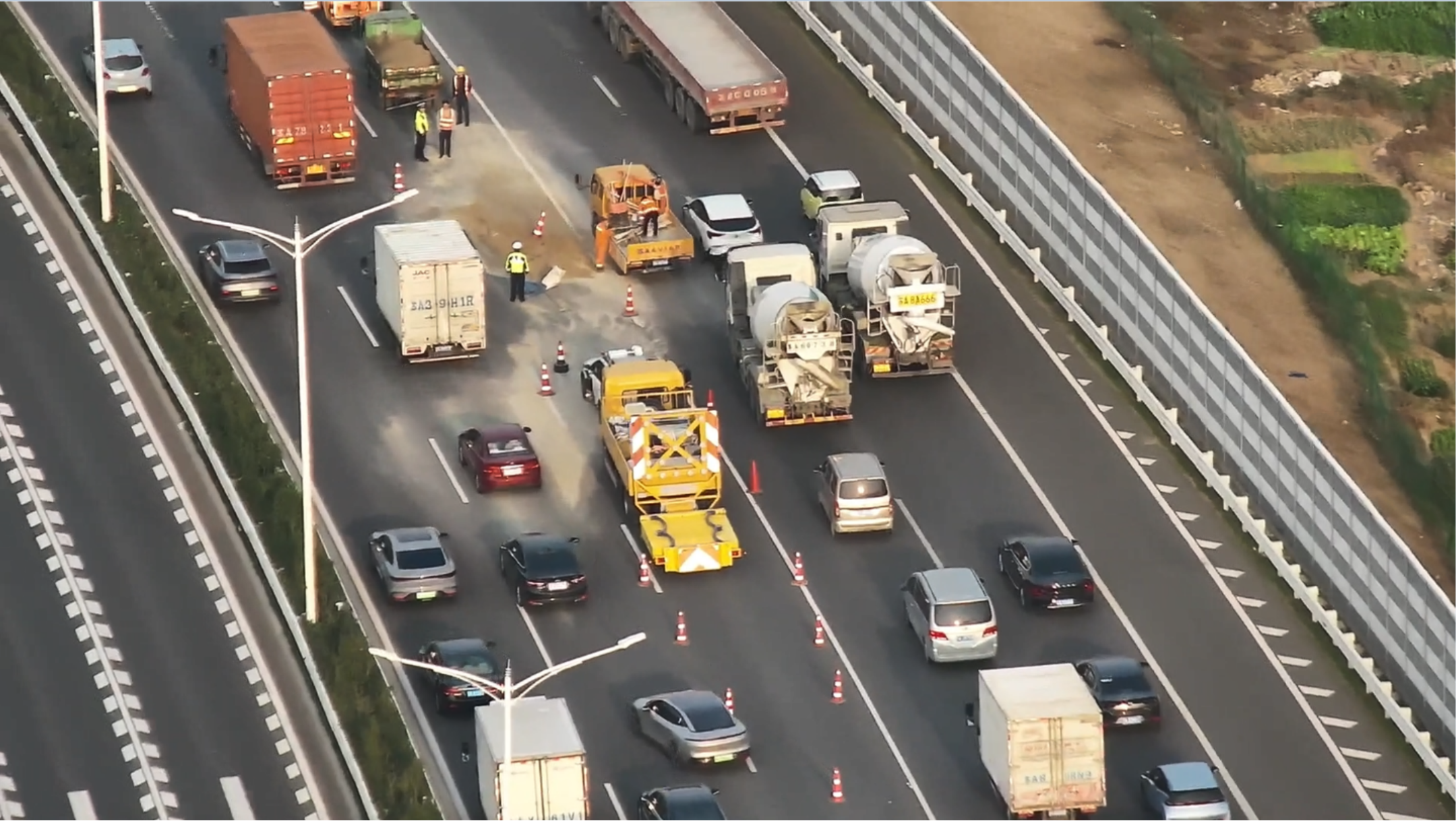
模型图片理解如下:
总结
本文记录如何利用华为昇腾AI的推理加速引擎MindIE,在昇腾硬件上高效部署qwen2.5-vl-7b大语言模型。测试了大模型语言能力与图片理解能力,为大模型在项目上的应用做了铺垫。大模型部署不是目的,在项目上的应用才能最终的目的,O(∩_∩)O哈哈~。
参考文档:
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/zh/doc/EDOC1100441350/c1fd8818
https://www.hiascend.com/hardware/firmware-drivers/community?product=2&model=17&cann=8.2.RC2&driver=Ascend+HDK+25.2.0
https://www.hiascend.com/developer/download/community/result?module=ie+pt+cann
https://www.hiascend.com/developer/ascendhub/detail/af85b724a7e5469ebd7ea13c3439d48f
https://www.modelscope.cn/models/Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct/summary
https://www.hiascend.com/developer/blog/details/0297192436801322570
2025年10月24日08:39:42
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献8条内容
已为社区贡献8条内容








所有评论(0)