Coze平台全面解析:测试工程师的AI智能体开发指南
Coze是字节跳动推出的新一代AI智能体开发平台,支持以低代码方式构建、部署和管理AI智能体。它不仅仅是另一个聊天机器人平台,而是完整的智能体开发生态系统。🧠科普小知识:什么是AI智能体?AI智能体是能够感知环境、做出决策并执行动作的软件实体。与传统程序不同,智能体具有自主性反应能力主动性和社交能力,能够根据目标灵活调整行为。Coze平台为测试工程师提供了强大的AI能力,能够显著提升测试效率和质
深入探索字节跳动Coze平台如何重塑测试工作流程,从零开始构建智能测试助手
一、引言:测试工程师面临的新挑战与机遇
在快速迭代的软件开发环境中,测试工程师经常面临这样的困境:
-
需求文档频繁变更,测试用例维护成本高
-
复杂系统难以全面覆盖,边缘场景易遗漏
-
缺陷分析依赖个人经验,排查效率低下
-
重复性工作占用大量时间,难以专注价值提升
传统的自动化测试工具虽然提高了执行效率,但在智能分析和自适应能力方面仍有局限。这就是Coze平台发挥作用的地方——它将AI能力引入测试全流程,让测试工程师能够构建专属的智能助手。
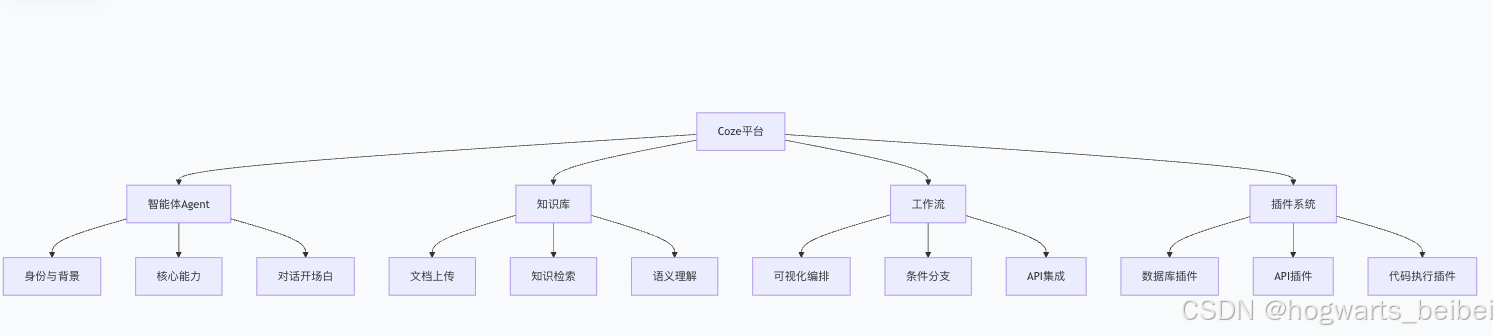
二、Coze平台核心架构解析
2.1 什么是Coze?
Coze是字节跳动推出的新一代AI智能体开发平台,支持以低代码方式构建、部署和管理AI智能体。它不仅仅是另一个聊天机器人平台,而是完整的智能体开发生态系统。
🧠 科普小知识:什么是AI智能体?
AI智能体是能够感知环境、做出决策并执行动作的软件实体。与传统程序不同,智能体具有自主性、反应能力、主动性和社交能力,能够根据目标灵活调整行为。
2.2 Coze的核心优势
与传统自动化工具相比,Coze具有明显优势:
| 特性 | 传统自动化工具 | Coze平台 |
|---|---|---|
| 学习曲线 | 需要编程技能 | 低代码/零代码 |
| 集成能力 | 需要单独开发集成 | 内置丰富插件和API |
| 适应性 | 规则固定,难适应变化 | AI驱动,适应新场景 |
| 维护成本 | 变更需要修改脚本 | 通过训练自动适应 |
| 分析能力 | 有限的数据分析 | 深度学习和模式识别 |
三、Coze在测试领域的应用场景
3.1 智能测试用例生成
传统测试用例设计依赖工程师经验,Coze可以分析需求文档自动生成测试场景:
python
# 测试用例生成工作流示例
def generate_test_cases(requirement_doc, testing_standard):
"""
基于需求文档和测试标准生成测试用例
"""
# 1. 需求分析
requirements = analyze_requirements(requirement_doc)
# 2. 提取测试关键点
test_points = extract_test_points(requirements, testing_standard)
# 3. 应用测试设计方法
test_cases = []
for point in test_points:
# 等价类划分
eq_classes = generate_equivalence_classes(point)
# 边界值分析
boundary_values = generate_boundary_values(point)
# 场景法
scenarios = generate_scenarios(point)
test_cases.extend(combine_test_cases(eq_classes, boundary_values, scenarios))
# 4. 格式化为标准模板
formatted_cases = format_to_template(test_cases)
return formatted_cases
# 使用示例
requirement = "用户登录功能,支持用户名密码和手机验证码两种方式"
test_standard = "需要覆盖正常流程、异常情况和安全测试"
cases = generate_test_cases(requirement, test_standard)
3.2 智能缺陷分析与管理
Coze可以改变缺陷管理方式,提供智能分析能力:
python
def intelligent_defect_analysis(new_bug_report):
"""
智能缺陷分析工作流
"""
# 1. 分析缺陷描述和上下文
bug_analysis = analyze_bug_description(new_bug_report)
# 2. 在知识库中搜索相似缺陷
similar_bugs = search_similar_bugs(bug_analysis.features)
if similar_bugs:
# 3. 提供可能的解决方案
solutions = extract_solutions(similar_bugs)
# 4. 推荐相关负责人员
recommended_assignee = recommend_assignee(similar_bugs)
result = {
"type": "known_issue",
"solutions": solutions,
"recommended_assignee": recommended_assignee
}
else:
# 5. 为新缺陷分类和优先级评估
category = categorize_bug(bug_analysis)
priority = assess_priority(bug_analysis)
result = {
"type": "new_issue",
"category": category,
"priority": priority,
"suggested_actions": ["详细日志分析", "环境对比测试"]
}
return result
# 使用示例
bug_report = {
"title": "登录页面点击提交后无响应",
"description": "在Chrome浏览器中,输入正确凭证后点击登录按钮,页面无任何反应",
"environment": "Chrome 115, Windows 10"
}
analysis_result = intelligent_defect_analysis(bug_report)
print(f"缺陷分析结果: {analysis_result}")
3.3 测试数据智能生成
测试数据准备是测试过程中的常见瓶颈,Coze可以智能生成和管理测试数据:
python
def generate_test_data(data_schema, constraints=None):
"""
根据数据模式和约束生成测试数据
"""
if constraints is None:
constraints = {}
test_data = []
# 生成正常数据
normal_data = generate_normal_data(data_schema)
test_data.extend(normal_data)
# 生成边界值数据
boundary_data = generate_boundary_data(data_schema, constraints)
test_data.extend(boundary_data)
# 生成异常数据
abnormal_data = generate_abnormal_data(data_schema)
test_data.extend(abnormal_data)
return test_data
# 使用示例
user_schema = {
"username": {"type": "string", "min_len": 6, "max_len": 20},
"password": {"type": "string", "min_len": 8, "patterns": ["[A-Z]", "[a-z]", "[0-9]"]},
"email": {"type": "string", "format": "email"},
"age": {"type": "integer", "min": 18, "max": 100}
}
constraints = {
"username": ["unique"],
"email": ["unique", "valid_format"]
}
test_users = generate_test_data(user_schema, constraints)
print(f"生成{len(test_users)}条测试数据")
四、实战:创建测试工程师智能体
4.1 环境准备与初始化
首先访问Coze官网注册账号,然后创建第一个测试智能体:
python
# Coze API客户端示例
class CozeClient:
def __init__(self, api_key):
self.api_key = api_key
self.base_url = "https://api.coze.cn/v1"
def create_agent(self, agent_config):
"""创建智能体"""
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
response = requests.post(
f"{self.base_url}/agents",
json=agent_config,
headers=headers
)
return response.json()
def upload_knowledge(self, agent_id, files):
"""上传知识库文档"""
# 实现文件上传逻辑
pass
# 智能体配置示例
test_agent_config = {
"name": "QA测试助手",
"description": "专注于软件测试的智能助手",
"role": "你是一名专业的测试工程师助手,擅长测试用例设计、缺陷分析和测试策略制定。",
"capabilities": [
"测试用例生成",
"缺陷分析",
"测试数据生成",
"测试报告分析"
],
"settings": {
"temperature": 0.3,
"max_tokens": 2000,
"context_rounds": 10
}
}
# 创建智能体
client = CozeClient("your_api_key")
agent_info = client.create_agent(test_agent_config)
print(f"智能体创建成功: {agent_info['id']}")
4.2 知识库构建与优化
为测试智能体上传专业知识文档:
python
def build_qa_knowledge_base(agent_id, documents):
"""
构建测试知识库
"""
knowledge_base = []
for doc in documents:
if doc['type'] == 'requirement':
# 处理需求文档
processed = process_requirement_doc(doc['content'])
knowledge_base.extend(processed)
elif doc['type'] == 'test_case':
# 处理测试用例
processed = process_test_cases(doc['content'])
knowledge_base.extend(processed)
elif doc['type'] == 'bug_report':
# 处理缺陷报告
processed = process_bug_reports(doc['content'])
knowledge_base.extend(processed)
# 上传到Coze知识库
upload_success = upload_to_coze_kb(agent_id, knowledge_base)
return upload_success
# 示例文档
documents = [
{
"type": "requirement",
"name": "用户管理系统需求文档",
"content": "用户管理系统需要支持用户注册、登录、个人信息管理等功能..."
},
{
"type": "test_case",
"name": "登录功能测试用例",
"content": "测试用例ID: LOGIN-001, 名称: 有效用户名密码登录..."
},
{
"type": "bug_report",
"name": "历史缺陷报告",
"content": "缺陷ID: BUG-1234, 标题: 登录页面XSS漏洞..."
}
]
# 构建知识库
success = build_qa_knowledge_base(agent_info['id'], documents)
print(f"知识库构建{'成功' if success else '失败'}")
4.3 工作流设计与集成
创建测试相关的工作流:
python
def create_test_workflow(workflow_config):
"""
创建测试工作流
"""
workflow = {
"name": workflow_config["name"],
"description": workflow_config["description"],
"steps": []
}
# 添加工作流步骤
for step in workflow_config["steps"]:
workflow["steps"].append({
"name": step["name"],
"action": step["action"],
"parameters": step.get("parameters", {}),
"conditions": step.get("conditions", [])
})
return workflow
# 测试用例生成工作流配置
test_case_workflow_config = {
"name": "测试用例生成工作流",
"description": "根据需求描述自动生成测试用例",
"steps": [
{
"name": "需求分析",
"action": "analyze_requirements",
"parameters": {"detail_level": "high"}
},
{
"name": "测试点提取",
"action": "extract_test_points",
"conditions": ["previous_step_success"]
},
{
"name": "用例生成",
"action": "generate_test_cases",
"parameters": {"techniques": ["equivalence", "boundary", "scenario"]}
},
{
"name": "用例优化",
"action": "optimize_cases",
"conditions": ["has_test_cases"]
},
{
"name": "格式输出",
"action": "format_output",
"parameters": {"template": "standard_test_case"}
}
]
}
# 创建工作流
workflow = create_test_workflow(test_case_workflow_config)
print(f"工作流创建成功: {workflow['name']}")
五、Coze与现有测试工具集成
5.1 与测试管理系统集成
python
def integrate_with_test_management(coze_agent, tm_system):
"""
与测试管理系统集成
"""
integration_config = {
"jira": {
"api_endpoint": tm_system["url"] + "/rest/api/2",
"auth_type": "basic",
"mappings": {
"test_case": {"create": "/testcase", "update": "/testcase/{id}"},
"defect": {"create": "/issue", "update": "/issue/{id}"}
}
},
"testrail": {
"api_endpoint": tm_system["url"] + "/index.php?/api/v2",
"auth_type": "basic",
"mappings": {
"test_case": {"create": "/add_case/{section_id}", "get": "/get_case/{id}"},
"test_run": {"create": "/add_run/{project_id}", "get": "/get_run/{id}"}
}
}
}
# 配置Webhook和API连接
setup_integration(coze_agent, integration_config[tm_system["type"]])
return True
# 使用示例
tm_system = {
"type": "jira",
"url": "https://your-company.atlassian.net",
"credentials": {"username": "user", "password": "pass"}
}
integrate_with_test_management(agent_info['id'], tm_system)
print("测试管理系统集成完成")
5.2 与CI/CD管道集成
python
def integrate_with_ci_cd(coze_agent, ci_system):
"""
与CI/CD系统集成
"""
integration_points = {
"jenkins": {
"webhook_url": f"{ci_system['url']}/generic-webhook-trigger/invoke",
"triggers": {
"on_build_start": "触发测试分析",
"on_build_complete": "生成测试报告",
"on_deployment": "执行冒烟测试"
}
},
"gitlab": {
"webhook_url": f"{ci_system['url']}/api/v4/projects/{ci_system['project_id']}/hooks",
"triggers": {
"on_push": "代码变更分析",
"on_merge_request": "差异测试评估"
}
}
}
# 设置CI/CD集成
setup_ci_cd_integration(coze_agent, integration_points[ci_system["type"]])
return True
# 使用示例
ci_system = {
"type": "jenkins",
"url": "https://jenkins.your-company.com",
"project_id": "test-automation"
}
integrate_with_ci_cd(agent_info['id'], ci_system)
print("CI/CD集成完成")
六、最佳实践与优化建议
6.1 提示词工程优化
python
def optimize_prompt_for_testing(base_prompt, testing_domain):
"""
为测试领域优化提示词
"""
domain_specific_additions = {
"web_testing": """
你专注于Web应用测试,特别关注:
- 跨浏览器兼容性问题
- 响应式设计测试
- 前端性能问题
- Web安全漏洞(XSS、CSRF等)
""",
"api_testing": """
你专注于API测试,特别关注:
- HTTP状态码和错误处理
- 请求/响应格式验证
- 性能和安全测试
- 接口契约一致性
""",
"mobile_testing": """
你专注于移动应用测试,特别关注:
- 设备兼容性问题
- 触摸交互测试
- 电池和性能优化
- 移动网络适应性
"""
}
optimized_prompt = base_prompt + domain_specific_additions.get(testing_domain, "")
# 添加测试特定约束
constraints = """
Constraints:
- 优先考虑测试覆盖率和缺陷发现能力
- 提供的解决方案需要可执行和可验证
- 对于不确定的领域,建议进一步测试方案
- 始终保持客观和基于证据的分析
"""
return optimized_prompt + constraints
# 使用示例
base_prompt = "你是一名专业的测试工程师助手,擅长分析测试需求和设计测试用例。"
optimized_prompt = optimize_prompt_for_qa(base_prompt, "web_testing")
print("优化后的提示词长度:", len(optimized_prompt))
6.2 性能监控与优化
python
def monitor_agent_performance(agent_id, time_window="7d"):
"""
监控智能体性能指标
"""
performance_metrics = {
"response_times": get_response_times(agent_id, time_window),
"accuracy_rates": get_accuracy_rates(agent_id, time_window),
"user_satisfaction": get_user_feedback(agent_id, time_window),
"resource_usage": get_resource_usage(agent_id, time_window)
}
# 分析性能问题
issues = analyze_performance_issues(performance_metrics)
# 生成优化建议
recommendations = generate_optimization_recommendations(issues)
return {
"metrics": performance_metrics,
"issues": issues,
"recommendations": recommendations
}
# 使用示例
performance_report = monitor_agent_performance(agent_info['id'])
print("性能监控报告生成完成")
七、总结与展望
Coze平台为测试工程师提供了强大的AI能力,能够显著提升测试效率和质量。通过本文介绍的方法和实践,你可以:
-
快速构建测试智能体:利用低代码平台创建专属测试助手
-
智能生成测试用例:基于需求文档自动生成全面测试场景
-
高效分析缺陷:利用AI能力快速定位和解决质量问题
-
无缝集成现有工具:连接测试管理系统和CI/CD管道
随着AI技术的不断发展,Coze在测试领域的应用前景包括:
-
自适应测试策略:根据系统变更自动调整测试重点
-
预测性质量分析:提前识别潜在质量风险
-
自然语言测试:使用自然语言描述生成可执行测试
-
全自动测试运维:实现测试环境的自维护和自优化
🚀 现在就开始你的Coze智能体开发之旅,体验AI带来的测试革命吧!

---人工智能学习交流群----
推荐阅读
* https://blog.csdn.net/chengzi_beibei/article/details/150393633?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
* https://blog.csdn.net/chengzi_beibei/article/details/150393354?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
* https://blog.csdn.net/chengzi_beibei/article/details/150393354?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
学社精选
- 测试开发之路 大厂面试总结 - 霍格沃兹测试开发学社 - 爱测-测试人社区
- 【面试】分享一个面试题总结,来置个顶 - 霍格沃兹测试学院校内交流 - 爱测-测试人社区
- 测试人生 | 从外包菜鸟到测试开发,薪资一年翻三倍,连自己都不敢信!(附面试真题与答案) - 测试开发 - 爱测-测试人社区
- 人工智能与自动化测试结合实战-探索人工智能在测试领域中的应用
- 爱测智能化测试平台
- 自动化测试平台
- 精准测试平台
- AI测试开发企业技术咨询服务
技术成长路线
系统化进阶路径与学习方案
- 人工智能测试开发路径
- 名企定向就业路径
- 测试开发进阶路线
- 测试开发高阶路线
- 性能测试进阶路径
- 测试管理专项提升路径
- 私教一对一技术指导
- 全日制 / 周末学习计划
- 公众号:霍格沃兹测试学院
- 视频号:霍格沃兹软件测试
- ChatGPT体验地址:霍格沃兹测试开发学社
- 霍格沃兹测试开发学社
企业级解决方案
测试体系建设与项目落地
- 全流程质量保障方案
- 按需定制化测试团队
- 自动化测试框架构建
- AI驱动的测试平台实施
- 车载测试专项方案
- 测吧(北京)科技有限公司
技术平台与工具
自研工具与开放资源
- 爱测智能化测试平台 - 测吧(北京)科技有限公司
- ceshiren.com 技术社区
- 开源工具 AppCrawler
- AI测试助手霍格沃兹测试开发学社
- 开源工具Hogwarts-Browser-Use
人工智能测试开发学习专区
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献17条内容
已为社区贡献17条内容







所有评论(0)