Jest: A Guide to Running Tests with Precision
Jest is a flexible testing framework. The package.json file helps us create simple commands for common testing tasks. By using flags like --coverage, --watch, --testPathPattern, and -t, we gain fine-g
Introduction
In modern software development, writing tests is very important. Tests help make sure our code works correctly. Jest is a popular JavaScript testing tool. It is simple and powerful. This article will look at a real package.json file. We will learn how to use Jest to run tests. We will see how to run all tests, or just specific ones. This helps make development faster and easier.
Understanding Test Scripts in package.json
A package.json file often has a scripts section. This section holds commands we can run. Let’s look at the test-related scripts from the example.
"scripts": {
"test": "jest",
"test:coverage": "jest --coverage",
"test:coverage:watch": "jest --coverage --watch",
"test:coverage:unit": "jest --coverage --testPathPattern='tests/unit'",
"test:coverage:integration": "jest --coverage --testPathPattern='tests/integration'",
"test:coverage:contract": "jest --coverage --testPathPattern='tests/contract'",
}
The test script is the simplest. Running npm test will execute the jest command. By default, Jest looks for test files in the project and runs them.
The test:coverage script runs jest --coverage. The --coverage flag tells Jest to collect information about which parts of our code the tests have run. It creates a report. This report shows how much of the code is tested.
The test:coverage:watch script adds the --watch flag. This is very useful during development. Jest will watch for file changes. When a file is saved, Jest automatically runs the tests related to that file. This gives fast feedback.
How to Run Specific Tests
Sometimes, we do not want to run all tests. Running all tests can be slow. We may only want to test the part of the code we are working on. Jest gives us tools to do this.
The --testPathPattern flag is a powerful tool. It tells Jest to only run tests in files that match a certain path. In the example, the script test:coverage:contract uses --testPathPattern='tests/contract'. When we run npm run test:coverage:contract, Jest will only run the test files inside the tests/contract/ directory. This is very efficient.
Let’s look at the files in the tests/contract directory:
auth-github-callback.test.tsauth-github.test.tsauth-refresh.test.ts- …and many others.
If we only want to run one specific file, like auth-signin.test.ts, we can run a command directly in the terminal:
npx jest tests/contract/auth-signin.test.ts
This command tells Jest to run only that single file.
What if a file has many test cases, and we only want to run one? Imagine the file auth-signin.test.ts has this code:
describe('Authentication sign-in', () => {
test('should fail with wrong password', () => {
// Test code here
});
test('should succeed with correct credentials', () => {
// Test code here
});
});
To run only the test named ‘should succeed with correct credentials’, we can use the -t flag. The -t flag stands for --testNamePattern.
npx jest -t 'should succeed with correct credentials'
This command will search all test files and run only the tests whose names match the text. Combining it with a file path is even more precise:
npx jest tests/contract/auth-signin.test.ts -t 'should succeed with correct credentials'
This is the most specific way to run a test. It helps developers focus on one small part of the system.
A Visual Guide to Running Tests
The following diagram shows the different ways to run tests, from general to specific.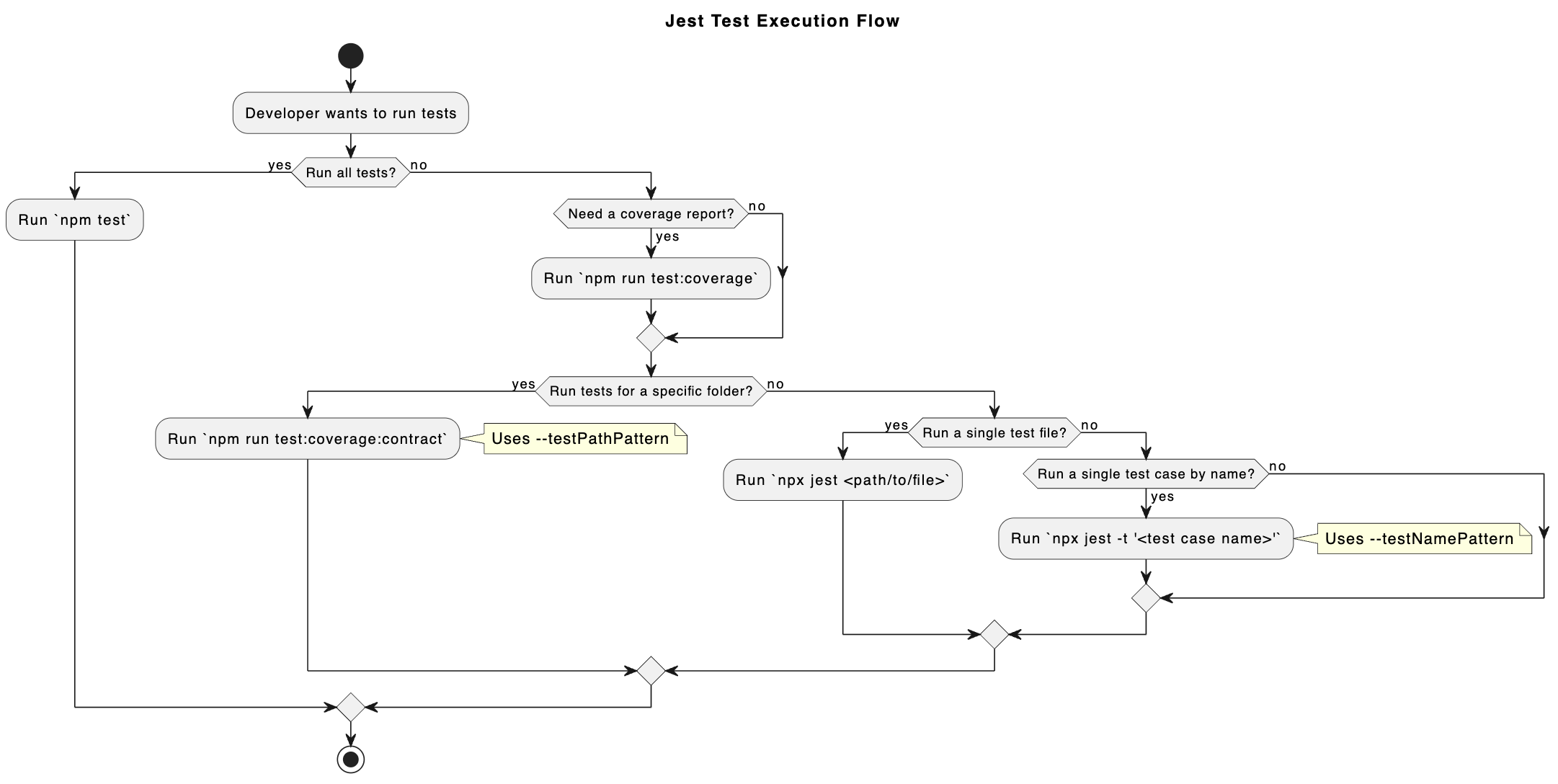
Conclusion
Jest is a flexible testing framework. The package.json file helps us create simple commands for common testing tasks. By using flags like --coverage, --watch, --testPathPattern, and -t, we gain fine-grained control over which tests to run. This ability to run specific tests is not just a convenience; it is a key practice for efficient and focused development. It allows developers to get quick feedback and fix problems faster.
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献30条内容
已为社区贡献30条内容






所有评论(0)