LoRA原理与PyTorch代码实现
无论是火热的大模型(LLM)还是文生图模型(Stable Diffusion)微调的时候,都需要大量的GPU显存,个人的显卡上很难实现, 因此各种参数高效(Parameter-Efficient)的方法层出不穷,最受大家欢迎的就是LoRA 《LoRA:Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Modules》LoRA有很多的优点,节约显存,训练快,效果损失小(相当
目录
矩阵都可以表示为若干个线性无关向量,最大的线性无关向量个数就是秩
背景
无论是火热的大模型(LLM)还是文生图模型(Stable Diffusion)微调的时候,都需要大量的GPU显存,个人的显卡上很难实现, 因此各种参数高效(Parameter-Efficient)的方法层出不穷,最受大家欢迎的就是LoRA 《LoRA:Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Modules》
LoRA有很多的优点,节约显存,训练快,效果损失小(相当于全参数微调),推理的时候不增加耗时,可以做一个插入式组件使用。 缺点当然也有,那就是还是会有一些效果的损失
核心原理
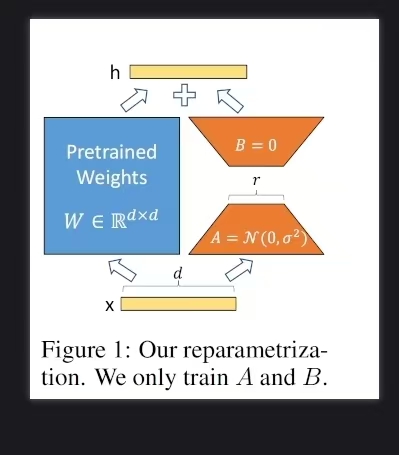
核心原理非常的简单,任意一个矩阵,都可以对它进行低秩分解,把一个很大的矩阵拆分成两个小矩阵
,在训练的过程中不去改变
参数,而是去改变
,具体可以表示为
最终在训练计算的时候是
其中, and
,r 甚至可以设置成1 为什么说只优化AB两个矩阵就可以了呢?这里面的假设是什么? W不是满秩的,里面有大量参数是冗余的,那么其实可以用更接近满秩的矩阵AB代替
矩阵都可以表示为若干个线性无关向量,最大的线性无关向量个数就是秩
PyTorch代码实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import math
class LinearLoRALayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_features,out_features,merge = False,rank = 8,lora_alpha = 16,dropout = 0.1):
super().__init__()
self.in_fatures = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.merge = merge
self.rank = rank
self.linear = nn.Linear(in_features,out_features)
# linear : weight shape is (out_features,in_features)
# input x shape is (batch_size,seq_len,in_features)
# 计算过程是 x @ weight.T
# 所以weight shape is (out_features,in_features)
if rank > 0:
# 这里是为了标注lora_a和lora_b是可训练参数
self.lora_a = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(out_features,rank))
# lora_a需要初始化为高斯分布
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.lora_a,a = 0.01)
# a表示leaky_relu的负斜率系数,一般是0.01这样的小值,不可能>1
self.lora_b = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(rank,in_features))
self.scale = lora_alpha / rank
# linear 需要设置为不可以训练
self.linear.weight.requires_grad = False
self.linear.bias.requires_grad = False
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) if dropout > 0 else nn.Identity()
# merge 是 bool 类型,如果为True,则将lora的权重和linear的权重合并
if merge:
self.merge_weight()
def merge_weight(self,):
if self.merge and self.rank > 0:
# (output_features,rank) @ (rank,input_features) = (output_features,input_features)
self.linear.weight.data += self.scale * (self.lora_a @ self.lora_b)
def unmerge_weight(self,):
if self.rank > 0:
self.linear.weight.data -= self.scale * (self.lora_a @ self.lora_b)
def forward(self,x):
# x shape is (batch_size,seq_len,in_features)
if self.rank > 0 and not self.merge:
output = self.linear(x) + self.scale * (x @ (self.lora_a @ self.lora_b).T)
elif self.rank > 0 and self.merge:
output = self.linear(x)
else:
output = self.linear(x)
output = self.dropout(output)
return output
# Test the LoRALinear layer
batch_size = 32
seq_len = 128
in_features = 768
out_features = 512
rank = 8
lora_alpha = 16
dropout = 0.1
X = torch.randn(batch_size,seq_len,in_features)
lora_layer = LinearLoRALayer(
in_features = in_features,
out_features = out_features,
rank = rank,
lora_alpha = lora_alpha,
dropout = dropout,
merge = False
)
# Forward pass
output = lora_layer(X)
print(f"Output shape (no merge):{output.shape}")
# Test weight merging/unmerging
lora_layer.merge_weight()
output_after_merge = lora_layer(X)
lora_layer.unmerge_weight()
output_after_unmerge = lora_layer(X)
print("Max difference after merge/unmerge cycle:",
torch.max(torch.abs(output - output_after_unmerge)).item())
致谢
由于本人水平有限,博客中如出现理解偏颇之处,欢迎大家指正
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容






所有评论(0)