Spring 源码学习(十二)—— HandlerMapping(一)
HandlerMapping 接口的 HandlerExecutionChain 方法只有一个实现,即因此本文从 AbstractHandlerMapping 开始分析;static {
HandlerMapping 接口中只有一个获取 HandlerExecutionChain 执行链对象已经一些用于标识 HandlerMapping 中属性名的常量;
public interface HandlerMapping {
String BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".bestMatchingHandler";
String LOOKUP_PATH = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".lookupPath";
String PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".pathWithinHandlerMapping";
String BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".bestMatchingPattern";
String INTROSPECT_TYPE_LEVEL_MAPPING = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".introspectTypeLevelMapping";
String URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".uriTemplateVariables";
String MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".matrixVariables";
String PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".producibleMediaTypes";
@Nullable
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
} BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE 为当前请求最终匹配到的处理器对象(Handler)、LOOKUP_PATH 为 Spring MVC 实际用于处理器匹配的请求路径,可能与原始请求路径不同、PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE 为处理器映射内部路径,在模式匹配下值为实际匹配的模式路径,否则为全路径、BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE 为最佳匹配模式、INTROSPECT_TYPE_LEVEL_MAPPING 为是否检查类注解,即是否需要联合类注解进行匹配、URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE 为模版数据映射,其值为 Map、MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE 为矩阵变量映射、PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE 则是处理器可生成的 MediaType 集合。
1. WebApplicationObjectSupport
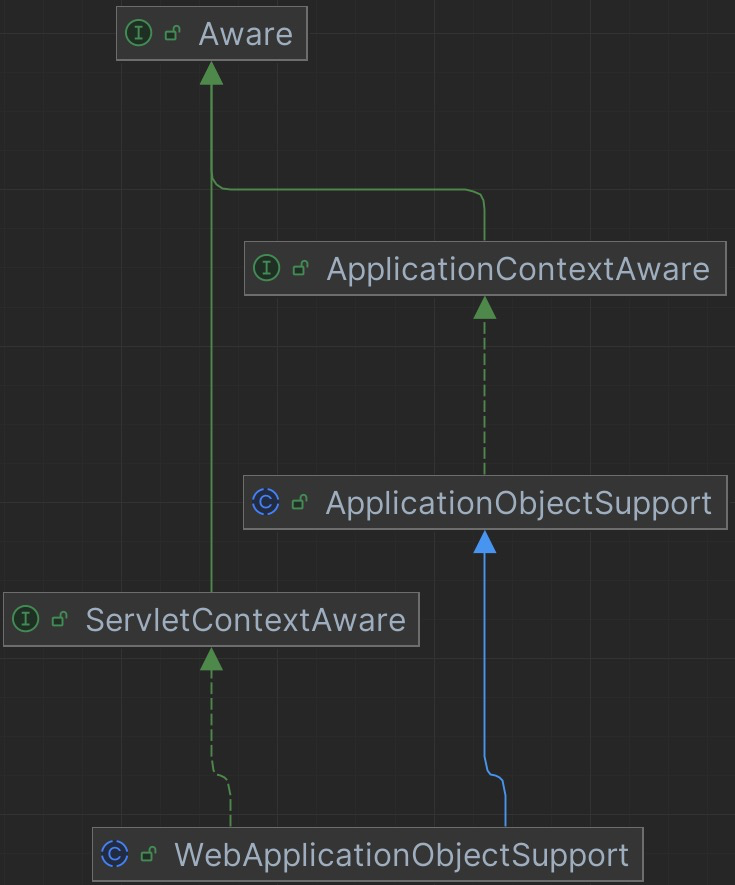
1.1 ApplicationObjectSupport
ApplicationObjectSupport 类为所有希望注入 applicationContext 应用上下文的对象提供一个通用父类;
1.1.1 变量
public abstract class ApplicationObjectSupport implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Nullable
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Nullable
private MessageSourceAccessor messageSourceAccessor;
@Nullable
public final ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() throws IllegalStateException {
if (this.applicationContext == null && isContextRequired()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"ApplicationObjectSupport instance [" + this + "] does not run in an ApplicationContext");
}
return this.applicationContext;
}
protected final ApplicationContext obtainApplicationContext() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = getApplicationContext();
Assert.state(applicationContext != null, "No ApplicationContext");
return applicationContext;
}
@Nullable
protected final MessageSourceAccessor getMessageSourceAccessor() throws IllegalStateException {
if (this.messageSourceAccessor == null && isContextRequired()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"ApplicationObjectSupport instance [" + this + "] does not run in an ApplicationContext");
}
return this.messageSourceAccessor;
}
}其有两个属性,分别为程序上下文 applicationContext 及消息接收器 messageSourceAccessor;然后为子类提供了两个用于获取应用程序上下文的方法 getApplicationContext 与 obtainApplicationContext 以及一个 getMessageSourceAccessor 方法用于获取 messageSourceAccessor 属性值。
1.1.2 setApplicationContext 方法
public abstract class ApplicationObjectSupport implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
public final void setApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
if (context == null && !isContextRequired()) {
// Reset internal context state.
this.applicationContext = null;
this.messageSourceAccessor = null;
}
else if (this.applicationContext == null) {
// Initialize with passed-in context.
if (!requiredContextClass().isInstance(context)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Invalid application context: needs to be of type [" + requiredContextClass().getName() + "]");
}
this.applicationContext = context;
this.messageSourceAccessor = new MessageSourceAccessor(context);
initApplicationContext(context);
}
else {
// Ignore reinitialization if same context passed in.
if (this.applicationContext != context) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Cannot reinitialize with different application context: current one is [" +
this.applicationContext + "], passed-in one is [" + context + "]");
}
}
}
protected boolean isContextRequired() {
return false;
}
protected Class<?> requiredContextClass() {
return ApplicationContext.class;
}
protected void initApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
initApplicationContext();
}
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
}
}setApplicationContext 方法在 context 为空且 isContextRequired 方法为 false 时,直接将 applicationContext 与 messageSourceAccessor 属性置为 null,否则在 applicationContext 属性为空但 context 参数不是需要的类型时直接抛出异常,否则将 applicationContext 属性设置为 context 参数值同时使用该参数创建 MessageSourceAccessor 对象并保存到 messageSourceAccessor 属性之中,最后调用 initApplicationContext 方法对上下文进行进一步处理;若 applicationContext 已赋值则会进行非重复性验证。
1.2 WebApplicationObjectSupport
WebApplicationObjectSupport 类为所有希望在 WebApplicationContext 上下文上运行的对象提供一个通用父类;
1.2.1 变量
public abstract class WebApplicationObjectSupport extends ApplicationObjectSupport implements ServletContextAware {
@Nullable
private ServletContext servletContext;
@Override
public final void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext != this.servletContext) {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
initServletContext(servletContext);
}
}
}WebApplicationObjectSupport 只有一个存储 Servlet 上下的 servletContext 属性,其是通过 setServletContext 方法注入的。
1.2.2 方法
public abstract class WebApplicationObjectSupport extends ApplicationObjectSupport implements ServletContextAware {
@Override
protected boolean isContextRequired() {
return true;
}
}isContextRequired 方法重写为直接返回 true;
public abstract class WebApplicationObjectSupport extends ApplicationObjectSupport implements ServletContextAware {
@Override
protected void initApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) {
super.initApplicationContext(context);
if (this.servletContext == null && context instanceof WebApplicationContext) {
this.servletContext = ((WebApplicationContext) context).getServletContext();
if (this.servletContext != null) {
initServletContext(this.servletContext);
}
}
}
protected void initServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
}
}initApplicationContext 方法在执行完父对象的 initApplicationContext 方法之后。若 servletContext 为空且 context 为 WebApplicationContext 上下文对象时,直接从上下文中获取 servletContext 上下文值保存到 servletContext 属性中并在其不为空时调用 initServletContext 方法让其子类对其初始化扩展;
public abstract class WebApplicationObjectSupport extends ApplicationObjectSupport implements ServletContextAware {
@Nullable
protected final WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext() throws IllegalStateException {
ApplicationContext ctx = getApplicationContext();
if (ctx instanceof WebApplicationContext) {
return (WebApplicationContext) getApplicationContext();
}
else if (isContextRequired()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("WebApplicationObjectSupport instance [" + this +
"] does not run in a WebApplicationContext but in: " + ctx);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
@Nullable
protected final ServletContext getServletContext() throws IllegalStateException {
if (this.servletContext != null) {
return this.servletContext;
}
ServletContext servletContext = null;
WebApplicationContext wac = getWebApplicationContext();
if (wac != null) {
servletContext = wac.getServletContext();
}
if (servletContext == null && isContextRequired()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("WebApplicationObjectSupport instance [" + this +
"] does not run within a ServletContext. Make sure the object is fully configured!");
}
return servletContext;
}
}WebApplicationObjectSupport 还提供了获取上下文的方法 getWebApplicationContext 与 getServletContext,分别用于获取 web 应用程序及 servlet 上下文,其都受到 isContextRequired 方法结果限制,若未获取到但该方法结果为 true 则会抛出异常;
public abstract class WebApplicationObjectSupport extends ApplicationObjectSupport implements ServletContextAware {
protected final File getTempDir() throws IllegalStateException {
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
Assert.state(servletContext != null, "ServletContext is required");
return WebUtils.getTempDir(servletContext);
}
}WebApplicationObjectSupport 还提供了一个用户获取Web 应用程序临时目录的 getTempDir 方法;
2. AbstractHandlerMapping
HandlerMapping 接口的 HandlerExecutionChain 方法只有一个实现,即 AbstractHandlerMapping;因此本文从 AbstractHandlerMapping 开始分析;
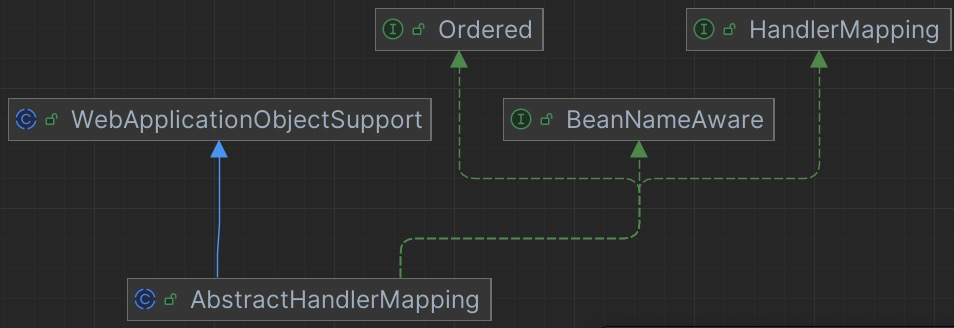
2.1 变量
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
@Nullable
private Object defaultHandler;
private UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper();
private PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
private final List<Object> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
private final List<HandlerInterceptor> adaptedInterceptors = new ArrayList<>();
@Nullable
private CorsConfigurationSource corsConfigurationSource;
private CorsProcessor corsProcessor = new DefaultCorsProcessor();
private int order = Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE; // default: same as non-Ordered
@Nullable
private String beanName;
public void setDefaultHandler(@Nullable Object defaultHandler) {
this.defaultHandler = defaultHandler;
}
@Nullable
public Object getDefaultHandler() {
return this.defaultHandler;
}
public void setInterceptors(Object... interceptors) {
this.interceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
public void setCorsProcessor(CorsProcessor corsProcessor) {
Assert.notNull(corsProcessor, "CorsProcessor must not be null");
this.corsProcessor = corsProcessor;
}
public CorsProcessor getCorsProcessor() {
return this.corsProcessor;
}
public void setOrder(int order) {
this.order = order;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return this.order;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
this.beanName = name;
}
}AbstractHandlerMapping 类拥有九个类变量,其中 defaultHandler 为默认处理器,urlPathHelper 为 url 匹配辅助器,pathMatcher 则是路径匹配器,interceptors 为拦截器列表,adaptedInterceptors 为处理器与拦截器适配器,corsConfigurationSource 为跨域配置源,corsProcessor 为跨域处理器,order 为执行顺序,默认为最后执行及一个存储当前对象名的 beanName;
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
public void setAlwaysUseFullPath(boolean alwaysUseFullPath) {
this.urlPathHelper.setAlwaysUseFullPath(alwaysUseFullPath);
if (this.corsConfigurationSource instanceof UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource) {
((UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource) this.corsConfigurationSource).setAlwaysUseFullPath(alwaysUseFullPath);
}
}
public void setUrlDecode(boolean urlDecode) {
this.urlPathHelper.setUrlDecode(urlDecode);
if (this.corsConfigurationSource instanceof UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource) {
((UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource) this.corsConfigurationSource).setUrlDecode(urlDecode);
}
}
public void setRemoveSemicolonContent(boolean removeSemicolonContent) {
this.urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(removeSemicolonContent);
if (this.corsConfigurationSource instanceof UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource) {
((UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource) this.corsConfigurationSource).setRemoveSemicolonContent(removeSemicolonContent);
}
}
public void setUrlPathHelper(UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper) {
Assert.notNull(urlPathHelper, "UrlPathHelper must not be null");
this.urlPathHelper = urlPathHelper;
if (this.corsConfigurationSource instanceof UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource) {
((UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource) this.corsConfigurationSource).setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper);
}
}
public UrlPathHelper getUrlPathHelper() {
return this.urlPathHelper;
}
}对于 urlPathHelper 属性,其不仅提供了直接设置的方法 setUrlPathHelper,还提供 3 个可以执行修改其属性的方法,分别为设置全路径匹配限制的 setAlwaysUseFullPath、设置 url 是否解码的 setUrlDecode 及是否需要直接移除 url 中 ;分号之后的内容的 setRemoveSemicolonContent 属性,值得注意的是这三个方法在 corsConfigurationSource 为 UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource 对象时,同时会在其中进行备份;
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
public void setPathMatcher(PathMatcher pathMatcher) {
Assert.notNull(pathMatcher, "PathMatcher must not be null");
this.pathMatcher = pathMatcher;
if (this.corsConfigurationSource instanceof UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource) {
((UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource) this.corsConfigurationSource).setPathMatcher(pathMatcher);
}
}
public PathMatcher getPathMatcher() {
return this.pathMatcher;
}
}setPathMatcher 方法会对入参进行非空验证,随后在为属性赋值的同时还是会将其值保存到 corsConfigurationSource 属性之中;
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
public void setCorsConfigurations(Map<String, CorsConfiguration> corsConfigurations) {
Assert.notNull(corsConfigurations, "corsConfigurations must not be null");
if (!corsConfigurations.isEmpty()) {
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
source.setCorsConfigurations(corsConfigurations);
source.setPathMatcher(this.pathMatcher);
source.setUrlPathHelper(this.urlPathHelper);
source.setLookupPathAttributeName(LOOKUP_PATH);
this.corsConfigurationSource = source;
}
else {
this.corsConfigurationSource = null;
}
}
public void setCorsConfigurationSource(CorsConfigurationSource corsConfigurationSource) {
Assert.notNull(corsConfigurationSource, "corsConfigurationSource must not be null");
this.corsConfigurationSource = corsConfigurationSource;
}
}AbstractHandlerMapping 类有两个 setCorsConfigurations 方法,一个入参为 CorsConfiguration Map 集合,该方法中会将 corsConfigurationSource 属性更新为 UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource 对象,并为其设置 corsConfigurations 、pathMatcher、urlPathHelper 以及 lookupPathAttributeName 属性,另一个方法直接传入 CorsConfiguration 对象,在通过非空验证后直接更新到 corsConfigurationSource 属性中;
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
@Nullable
protected final HandlerInterceptor[] getAdaptedInterceptors() {
return (!this.adaptedInterceptors.isEmpty() ?
this.adaptedInterceptors.toArray(new HandlerInterceptor[0]) : null);
}
@Nullable
protected final MappedInterceptor[] getMappedInterceptors() {
List<MappedInterceptor> mappedInterceptors = new ArrayList<>(this.adaptedInterceptors.size());
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
mappedInterceptors.add((MappedInterceptor) interceptor);
}
}
return (!mappedInterceptors.isEmpty() ? mappedInterceptors.toArray(new MappedInterceptor[0]) : null);
}
}getAdaptedInterceptors 方法将 adaptedInterceptors 属性转换为数组并返回,getMappedInterceptors 方法则是将 adaptedInterceptors 属性中的 MappedInterceptor 类型对象转化为数组然后返回;
2.2 方法
2.2.1 initApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
@Override
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
detectMappedInterceptors(this.adaptedInterceptors);
initInterceptors();
}
protected void extendInterceptors(List<Object> interceptors) {
}
protected void detectMappedInterceptors(List<HandlerInterceptor> mappedInterceptors) {
mappedInterceptors.addAll(BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
obtainApplicationContext(), MappedInterceptor.class, true, false).values());
}
protected void initInterceptors() {
if (!this.interceptors.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.interceptors.size(); i++) {
Object interceptor = this.interceptors.get(i);
if (interceptor == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Entry number " + i + " in interceptors array is null");
}
this.adaptedInterceptors.add(adaptInterceptor(interceptor));
}
}
}
protected HandlerInterceptor adaptInterceptor(Object interceptor) {
if (interceptor instanceof HandlerInterceptor) {
return (HandlerInterceptor) interceptor;
}
else if (interceptor instanceof WebRequestInterceptor) {
return new WebRequestHandlerInterceptorAdapter((WebRequestInterceptor) interceptor);
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Interceptor type not supported: " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
}
}initApplicationContext 方法依次调用 extendInterceptors 方法注册附加拦截器,detectMappedInterceptors 方法将上下文中的 MappedInterceptor 对象保存到 adaptedInterceptors 属性中,initInterceptors 方法调用 adaptInterceptor 方法对 interceptors 中所有拦截器值转化为 HandlerInterceptor 保存到 adaptedInterceptors 属性中。
2.2.2 getHandler
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
@Override
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = (this.corsConfigurationSource != null ? this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request) : null);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
config = (config != null ? config.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
@Nullable
protected abstract Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
}getHandler 方法首先使用 getHandlerInternal 方法获取子类中的内部处理器或 getDefaultHandler 方法获取默认处理器,未获取到时直接返回 null;若 handler 为字符串(对象名),直接从上下文中获取对应对象;之后调用 getHandlerExecutionChain 创建对应的处理器链 HandlerExecutionChain 对象,接下来若请求为跨域预检请求(带 ORIGIN 与 ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_METHOD 请求头的 OPTIONS 请求)或存在 CorsConfigurationSource 配置对象(handler 为 CorsConfigurationSource 或 corsConfigurationSource 属性不为空)时,将从 corsConfigurationSource 属性及 handler 关联 corsConfigurationSource 对象中获取到的 request 对应的 CorsConfiguration 跨域配置合并在一起并使用 getCorsHandlerExecutionChain 方法更新执行器链;最后返回 handler 对象。
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request, LOOKUP_PATH);
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
}getHandlerExecutionChain 方法在 handler 为 HandlerExecutionChain 对象时直接保存到 chain 变量中,否则将 chain 变量更新为使用 handler 创建的 HandlerExecutionChain 对象;随后使用 urlPathHelper 的 getLookupPathForRequest 方法从请求中获取实际用于匹配的路径值,随后将 adaptedInterceptors 与路径匹配的 MappedInterceptor 元素及其他类型元素全保存到 chain 变量之中并返回;
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
protected boolean hasCorsConfigurationSource(Object handler) {
if (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain) {
handler = ((HandlerExecutionChain) handler).getHandler();
}
return (handler instanceof CorsConfigurationSource || this.corsConfigurationSource != null);
}
}hasCorsConfigurationSource 方法用于判断 handler 对象是否为 CorsConfigurationSource 对象或当前 corsConfigurationSource 属性不为空;
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
@Nullable
protected CorsConfiguration getCorsConfiguration(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
Object resolvedHandler = handler;
if (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain) {
resolvedHandler = ((HandlerExecutionChain) handler).getHandler();
}
if (resolvedHandler instanceof CorsConfigurationSource) {
return ((CorsConfigurationSource) resolvedHandler).getCorsConfiguration(request);
}
return null;
}
}getCorsConfiguration 方法用于使用 handler 的关联 CorsConfigurationSource 对象获取 request 对应的 CorsConfiguration 配置,若不存在关联 CorsConfigurationSource 对象返回 null;
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(HttpServletRequest request,
HandlerExecutionChain chain, @Nullable CorsConfiguration config) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = chain.getInterceptors();
return new HandlerExecutionChain(new PreFlightHandler(config), interceptors);
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(0, new CorsInterceptor(config));
return chain;
}
}
}getCorsHandlerExecutionChain 方法用于向 chain 中扩展跨域处理,若 request 请求为跨域预检请求时,直接使用 HandlerExecutionChain 对 interceptors 拦截器数组进行封装然后返回,否则只是向拦截器链的头部添加 CorsInterceptor 拦截然后返回。
2.3 内部类
2.2.1 PreFlightHandler
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
private class PreFlightHandler implements HttpRequestHandler, CorsConfigurationSource {
@Nullable
private final CorsConfiguration config;
public PreFlightHandler(@Nullable CorsConfiguration config) {
this.config = config;
}
@Override
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
corsProcessor.processRequest(this.config, request, response);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public CorsConfiguration getCorsConfiguration(HttpServletRequest request) {
return this.config;
}
}
}PreFlightHandler 内部类实现了 HttpRequestHandler 与 CorsConfigurationSource 接口,其中 handleRequest 方法直接调用 corsProcessor 属性的 processRequest 方法处理请求,getCorsConfiguration 方法直接获取 config 属性。
2.2.2 CorsInterceptor
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
private class CorsInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter implements CorsConfigurationSource {
@Nullable
private final CorsConfiguration config;
public CorsInterceptor(@Nullable CorsConfiguration config) {
this.config = config;
}
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
// Consistent with CorsFilter, ignore ASYNC dispatches
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
return true;
}
return corsProcessor.processRequest(this.config, request, response);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public CorsConfiguration getCorsConfiguration(HttpServletRequest request) {
return this.config;
}
}
}CorsInterceptor 内部类继承了 HandlerInterceptorAdapter 类的同时实现了 CorsConfigurationSource 接口,重写了 HandlerInterceptorAdapter 类的 preHandle 方法,其首先判断是否已完成了异步处理,否则直接调用 corsProcessor 属性的 processRequest 方法处理请求。
2.3 UrlPathHelper
2.3.1 变量
- 静态变量
public class UrlPathHelper {
@Nullable
static volatile Boolean websphereComplianceFlag;
}UrlPathHelper 类只有一个 WebSphere 服务器是否移除 url 最后一个反斜杠的 websphereComplianceFlag 标识。
- 常量
public class UrlPathHelper {
private static final String WEBSPHERE_URI_ATTRIBUTE = "com.ibm.websphere.servlet.uri_non_decoded";
public static final UrlPathHelper defaultInstance = new UrlPathHelper();
static {
defaultInstance.setReadOnly();
}
public static final UrlPathHelper rawPathInstance = new UrlPathHelper() {
@Override
public String removeSemicolonContent(String requestUri) {
return requestUri;
}
};
static {
rawPathInstance.setAlwaysUseFullPath(true);
rawPathInstance.setUrlDecode(false);
rawPathInstance.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false);
rawPathInstance.setReadOnly();
}
}UrlPathHelper 类有一个保存服务器上的 请求转发(Forward) 时,用于 WebSphere 服务器获取原始客户端请求URI的特殊属性 WEBSPHERE_URI_ATTRIBUTE;还有两个 UrlPathHelper 实例,一个为 defaultInstance 默认值,其在声明后直接将其设置为只读;另一个为 rawPathInstance 实例,其 removeSemicolonContent 方法连 jsessionId 也不会处理,直接返回原始值,然后分别将其 AlwaysUseFullPath、UrlDecode 及 RemoveSemicolonContent 设置为 true、false 及 false,最后将其设置为只读。
- 类变量
public class UrlPathHelper {
private boolean alwaysUseFullPath = false;
private boolean urlDecode = true;
private boolean removeSemicolonContent = true;
private String defaultEncoding = WebUtils.DEFAULT_CHARACTER_ENCODING;
private boolean readOnly = false;
public void setAlwaysUseFullPath(boolean alwaysUseFullPath) {
checkReadOnly();
this.alwaysUseFullPath = alwaysUseFullPath;
}
public void setUrlDecode(boolean urlDecode) {
checkReadOnly();
this.urlDecode = urlDecode;
}
public boolean isUrlDecode() {
return this.urlDecode;
}
public void setRemoveSemicolonContent(boolean removeSemicolonContent) {
checkReadOnly();
this.removeSemicolonContent = removeSemicolonContent;
}
public boolean shouldRemoveSemicolonContent() {
return this.removeSemicolonContent;
}
public void setDefaultEncoding(String defaultEncoding) {
checkReadOnly();
this.defaultEncoding = defaultEncoding;
}
protected String getDefaultEncoding() {
return this.defaultEncoding;
}
private void setReadOnly() {
this.readOnly = true;
}
private void checkReadOnly() {
Assert.isTrue(!this.readOnly, "This instance cannot be modified");
}
}UrlPathHelper 类的类变量有是否只能进行全路径匹配的 alwaysUseFullPath 属性(默认为 false);是否需要对 url 进行解码的 urlDecode 属性(默认为 true);是否移除 url 中第一个 ; 号之后内容的 removeSemicolonContent 属性(默认 true);当前使用的编码方式 defaultEncoding 属性,默认使用 ISO-8859-1;属性是否只读 readOnly,默认为 false。
2.3.2 方法
- getLookupPathForRequest
public class UrlPathHelper {
public String getLookupPathForRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
String pathWithinApp = getPathWithinApplication(request);
// Always use full path within current servlet context?
if (this.alwaysUseFullPath) {
return pathWithinApp;
}
// Else, use path within current servlet mapping if applicable
String rest = getPathWithinServletMapping(request, pathWithinApp);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(rest)) {
return rest;
}
else {
return pathWithinApp;
}
}
public String getLookupPathForRequest(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable String lookupPathAttributeName) {
if (lookupPathAttributeName != null) {
String result = (String) request.getAttribute(lookupPathAttributeName);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
return getLookupPathForRequest(request);
}
}UrlPathHelper 类有两个 getLookupPathForRequest 方法,其中第一个直接调用 getPathWithinApplication 方法从请求中提取路径,并在 alwaysUseFullPath 为 true 时直接返回,否则返回通过 getPathWithinServletMapping 方法移除容器路径前缀后返回;第二个扩展了根据传入属性名直接从请求属性中获取,未获取到则会走第一个方法 。
- getPathWithinServletMapping
public class UrlPathHelper {
public String getPathWithinServletMapping(HttpServletRequest request) {
return getPathWithinServletMapping(request, getPathWithinApplication(request));
}
protected String getPathWithinServletMapping(HttpServletRequest request, String pathWithinApp) {
String servletPath = getServletPath(request);
String sanitizedPathWithinApp = getSanitizedPath(pathWithinApp);
String path;
// If the app container sanitized the servletPath, check against the sanitized version
if (servletPath.contains(sanitizedPathWithinApp)) {
path = getRemainingPath(sanitizedPathWithinApp, servletPath, false);
}
else {
path = getRemainingPath(pathWithinApp, servletPath, false);
}
if (path != null) {
// Normal case: URI contains servlet path.
return path;
}
else {
// Special case: URI is different from servlet path.
String pathInfo = request.getPathInfo();
if (pathInfo != null) {
// Use path info if available. Indicates index page within a servlet mapping?
// e.g. with index page: URI="/", servletPath="/index.html"
return pathInfo;
}
if (!this.urlDecode) {
// No path info... (not mapped by prefix, nor by extension, nor "/*")
// For the default servlet mapping (i.e. "/"), urlDecode=false can
// cause issues since getServletPath() returns a decoded path.
// If decoding pathWithinApp yields a match just use pathWithinApp.
path = getRemainingPath(decodeInternal(request, pathWithinApp), servletPath, false);
if (path != null) {
return pathWithinApp;
}
}
// Otherwise, use the full servlet path.
return servletPath;
}
}
}getPathWithinServletMapping 用于提取不包含 servlet 容器路径前缀的路径,用于后续 controller 控制器等的匹配。其首先调用 getServletPath 方法从 request 中获取 servlet 路径,同时使用 getSanitizedPath 方法移除 pathWithinApp 应用程序路径中的 // 替换为 /;之后尝试使用 getRemainingPath 方法从 sanitizedPathWithinApp 或 pathWithinApp 中移除 servletPath 前缀,若成功移除则直接返回处理后的路径;否则在 request 请求的 pathInfo 不为空时直接返回,在 pathInfo 也为空且 urlDecode 为 true 时直接返回 servlet 容器路径,在 urlDecode 为 false 时(禁用了 url 解码),则会使用 decodeInternal 方法尝试对 pathWithinApp 进行解码然后再调用 getRemainingPath 方法移除解码后的 url 中的容器路径前缀,成功移除后返回,否则也是返回 servlet 容器路径;
public class UrlPathHelper {
public String getServletPath(HttpServletRequest request) {
String servletPath = (String) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.INCLUDE_SERVLET_PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
if (servletPath == null) {
servletPath = request.getServletPath();
}
if (servletPath.length() > 1 && servletPath.endsWith("/") && shouldRemoveTrailingServletPathSlash(request)) {
// On WebSphere, in non-compliant mode, for a "/foo/" case that would be "/foo"
// on all other servlet containers: removing trailing slash, proceeding with
// that remaining slash as final lookup path...
servletPath = servletPath.substring(0, servletPath.length() - 1);
}
return servletPath;
}
}getServletPath 方法首先尝试从请求的 INCLUDE_SERVLET_PATH_ATTRIBUTE (javax.servlet.include.servlet_path)属性值中获取 servletPath 值,若未获取到则是从 request 参数的 getServletPath 方法中获取,之后根据需要移除或保留最后一个反斜杠然后返回。
public class UrlPathHelper {
private boolean shouldRemoveTrailingServletPathSlash(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (request.getAttribute(WEBSPHERE_URI_ATTRIBUTE) == null) {
// Regular servlet container: behaves as expected in any case,
// so the trailing slash is the result of a "/" url-pattern mapping.
// Don't remove that slash.
return false;
}
Boolean flagToUse = websphereComplianceFlag;
if (flagToUse == null) {
ClassLoader classLoader = UrlPathHelper.class.getClassLoader();
String className = "com.ibm.ws.webcontainer.WebContainer";
String methodName = "getWebContainerProperties";
String propName = "com.ibm.ws.webcontainer.removetrailingservletpathslash";
boolean flag = false;
try {
Class<?> cl = classLoader.loadClass(className);
Properties prop = (Properties) cl.getMethod(methodName).invoke(null);
flag = Boolean.parseBoolean(prop.getProperty(propName));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not introspect WebSphere web container properties: " + ex);
}
}
flagToUse = flag;
websphereComplianceFlag = flag;
}
// Don't bother if WebSphere is configured to be fully Servlet compliant.
// However, if it is not compliant, do remove the improper trailing slash!
return !flagToUse;
}
}shouldRemoveTrailingServletPathSlash 专门用于判断当前是否为 WebSphere 服务器且是否配置移除最后一个反斜杠;该方法首先从是否包含 WEBSPHERE_URI_ATTRIBUTE 属性判断是否为当前是否为 WebSphere 服务器,随后为了避免重复解析影响性能则会尝试从 websphereComplianceFlag 静态变量中获取,未加载则会通过反射机制器执行 com.ibm.ws.webcontainer.WebContainer 中的 getWebContainerProperties 方法并获取结果的 removetrailingservletpathslash 属性值,然后直接将该属性转化为 boolean 值保存到 websphereComplianceFlag 静态变量之中并返回。
public class UrlPathHelper {
private String getSanitizedPath(final String path) {
String sanitized = path;
while (true) {
int index = sanitized.indexOf("//");
if (index < 0) {
break;
}
else {
sanitized = sanitized.substring(0, index) + sanitized.substring(index + 1);
}
}
return sanitized;
}
}getSanitizedPath 方法用于将 url 中的 // 替换为 /。
public class UrlPathHelper {
@Nullable
private String getRemainingPath(String requestUri, String mapping, boolean ignoreCase) {
int index1 = 0;
int index2 = 0;
for (; (index1 < requestUri.length()) && (index2 < mapping.length()); index1++, index2++) {
char c1 = requestUri.charAt(index1);
char c2 = mapping.charAt(index2);
if (c1 == ';') {
index1 = requestUri.indexOf('/', index1);
if (index1 == -1) {
return null;
}
c1 = requestUri.charAt(index1);
}
if (c1 == c2 || (ignoreCase && (Character.toLowerCase(c1) == Character.toLowerCase(c2)))) {
continue;
}
return null;
}
if (index2 != mapping.length()) {
return null;
}
else if (index1 == requestUri.length()) {
return "";
}
else if (requestUri.charAt(index1) == ';') {
index1 = requestUri.indexOf('/', index1);
}
return (index1 != -1 ? requestUri.substring(index1) : "");
}
}getRemainingPath 方法用于从 requestUri 请求 uri 移除 mapping 字符串;当出现任意不匹配时直接返回 null,ignoreCase 为是否忽略大小写,值得注意的是若请求 uri 中存在 ; 分号,则会忽略匹配该分号到其下一 / 直接的内容;最后返回 完成匹配的剩余内容;
- getPathWithinServletMapping
public class UrlPathHelper {
public String getPathWithinApplication(HttpServletRequest request) {
String contextPath = getContextPath(request);
String requestUri = getRequestUri(request);
String path = getRemainingPath(requestUri, contextPath, true);
if (path != null) {
// Normal case: URI contains context path.
return (StringUtils.hasText(path) ? path : "/");
}
else {
return requestUri;
}
}
}getPathWithinServletMapping 用于用于获取请求中不带上下文路径前缀的解码路径,其首先分别通过 getContextPath 与 getRequestUri 两个方法分别获取解码后的上下文路径及完整路径,随后调用 getRemainingPath 方法移除完整路径中的上下文路径前缀;若其前缀与上下文不匹配则直接返回完整 uri 路径;否则返回移除上下文路径的剩余字符串值,值得注意的时,若完全匹配则直接返回一个 / 字符;
- getRequestUri
public class UrlPathHelper {
public String getRequestUri(HttpServletRequest request) {
String uri = (String) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.INCLUDE_REQUEST_URI_ATTRIBUTE);
if (uri == null) {
uri = request.getRequestURI();
}
return decodeAndCleanUriString(request, uri);
}
}getRequestUri 方法用于获取解码后的请求 uri 路径,其首先从 request 请求的 INCLUDE_REQUEST_URI_ATTRIBUTE(javax.servlet.include.request_uri)属性或请求中直接获取原始 uri 路径,然后调用 decodeRequestString 方法对其解码并返回。
- getContextPath
public class UrlPathHelper {
public String getContextPath(HttpServletRequest request) {
String contextPath = (String) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.INCLUDE_CONTEXT_PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
if (contextPath == null) {
contextPath = request.getContextPath();
}
if (StringUtils.matchesCharacter(contextPath, '/')) {
// Invalid case, but happens for includes on Jetty: silently adapt it.
contextPath = "";
}
return decodeRequestString(request, contextPath);
}
}getContextPath 用于获取当前上下文路径,其从 request 请求的 INCLUDE_CONTEXT_PATH_ATTRIBUTE(javax.servlet.include.context_path)属性或请求中直接获取原始上下文路径,若上下文路径为 /,则将其更新为空字符串,最后调用 decodeRequestString 方法为上下文路径进行解码并返回。
- getOriginatingRequestUri
public class UrlPathHelper {
public String getOriginatingRequestUri(HttpServletRequest request) {
String uri = (String) request.getAttribute(WEBSPHERE_URI_ATTRIBUTE);
if (uri == null) {
uri = (String) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.FORWARD_REQUEST_URI_ATTRIBUTE);
if (uri == null) {
uri = request.getRequestURI();
}
}
return decodeAndCleanUriString(request, uri);
}
}getOriginatingRequestUri 用于获取请求原始路径(特别是重定向请求);依次从 request 请求的 WEBSPHERE_URI_ATTRIBUTE(com.ibm.websphere.servlet.uri_non_decoded)、FORWARD_REQUEST_URI_ATTRIBUTE(javax.servlet.forward.request_uri)属性及 getRequestURI 方法获取原始 uri 路径,然后调用 decodeAndCleanUriString 方法为其进行解码并返回。
- getOriginatingContextPath
public class UrlPathHelper {
public String getOriginatingContextPath(HttpServletRequest request) {
String contextPath = (String) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.FORWARD_CONTEXT_PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
if (contextPath == null) {
contextPath = request.getContextPath();
}
return decodeRequestString(request, contextPath);
}
}getOriginatingContextPath 用于获取请求原始上下文路径(特别是重定向请求);依次从 request 请求的 FORWARD_SERVLET_PATH_ATTRIBUTE(javax.servlet.forward.servlet_path)与 getContextPath 方法获取原始上下文路径,然后调用 decodeRequestString 方法为其进行解码并返回。
- getOriginatingServletPath
public class UrlPathHelper {
public String getOriginatingContextPath(HttpServletRequest request) {
String contextPath = (String) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.FORWARD_CONTEXT_PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
if (contextPath == null) {
contextPath = request.getContextPath();
}
return decodeRequestString(request, contextPath);
}
}getOriginatingServletPath 用于获取请求原始 Servlet 容器上下文路径(特别是重定向请求);依次从 request 请求的 FORWARD_SERVLET_PATH_ATTRIBUTE(javax.servlet.forward.servlet_path)与 getServletPath 方法获取原始上下文路径,然后调用 decodeRequestString 方法为其进行解码并返回。
- getOriginatingQueryString
public class UrlPathHelper {
public String getOriginatingQueryString(HttpServletRequest request) {
if ((request.getAttribute(WebUtils.FORWARD_REQUEST_URI_ATTRIBUTE) != null) ||
(request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_REQUEST_URI_ATTRIBUTE) != null)) {
return (String) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.FORWARD_QUERY_STRING_ATTRIBUTE);
}
else {
return request.getQueryString();
}
}
}getOriginatingServletPath 用于获取请求原始请求参数(特别是重定向请求);在 request 请求为重定向请求时直接从请求的 FORWARD_QUERY_STRING_ATTRIBUTE (javax.servlet.forward.query_string)属性中获取,否则直接调用 getQueryString 方法返回当前请求参数。
- decodeAndCleanUriString
public class UrlPathHelper {
private String decodeAndCleanUriString(HttpServletRequest request, String uri) {
uri = removeSemicolonContent(uri);
uri = decodeRequestString(request, uri);
uri = getSanitizedPath(uri);
return uri;
}
}decodeAndCleanUriString 方法首先调用 removeSemicolonContent 方法清理 uri 路径,然后使用 decodeRequestString 方法对处理后的路径进行反编码,最后则调用 getSanitizedPath 方法将路径中所有的 // 替换为 / 并返回。
public class UrlPathHelper {
public String removeSemicolonContent(String requestUri) {
return (this.removeSemicolonContent ?
removeSemicolonContentInternal(requestUri) : removeJsessionid(requestUri));
}
}removeSemicolonContent 方法在 removeSemicolonContent 属性为 true 时,移除所有 ; 分号与 / 斜杠中的内容,否则只会移除 jsessionid 参数值。
public class UrlPathHelper {
private String removeSemicolonContentInternal(String requestUri) {
int semicolonIndex = requestUri.indexOf(';');
while (semicolonIndex != -1) {
int slashIndex = requestUri.indexOf('/', semicolonIndex);
String start = requestUri.substring(0, semicolonIndex);
requestUri = (slashIndex != -1) ? start + requestUri.substring(slashIndex) : start;
semicolonIndex = requestUri.indexOf(';', semicolonIndex);
}
return requestUri;
}
}removeSemicolonContentInternal 方法用于移除路径中所有 ; 分号与 / 斜杠中的所有内容。
public class UrlPathHelper {
private String removeJsessionid(String requestUri) {
String key = ";jsessionid=";
int index = requestUri.toLowerCase().indexOf(key);
if (index == -1) {
return requestUri;
}
String start = requestUri.substring(0, index);
for (int i = index + key.length(); i < requestUri.length(); i++) {
char c = requestUri.charAt(i);
if (c == ';' || c == '/') {
return start + requestUri.substring(i);
}
}
return start;
}
}removeJsessionid 方法用于移除 ;jsessionid= 与第一个 ; 分号或 / 反斜杠之间内容,即只移除 jsessionid 参数值。
- decodeRequestString
public class UrlPathHelper {
public String decodeRequestString(HttpServletRequest request, String source) {
if (this.urlDecode) {
return decodeInternal(request, source);
}
return source;
}
}decodeRequestString 方法在 urlDecode 属性为 true,即开启了 url 反编码时,调用 decodeInternal 方法对其进行反编码并返回,否则直接返回原始 url 路径。
public class UrlPathHelper {
private String decodeInternal(HttpServletRequest request, String source) {
String enc = determineEncoding(request);
try {
return UriUtils.decode(source, enc);
}
catch (UnsupportedCharsetException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not decode request string [" + source + "] with encoding '" + enc +
"': falling back to platform default encoding; exception message: " + ex.getMessage());
}
return URLDecoder.decode(source);
}
}
protected String determineEncoding(HttpServletRequest request) {
String enc = request.getCharacterEncoding();
if (enc == null) {
enc = getDefaultEncoding();
}
return enc;
}
}decodeInternal 方法实际对 source 原始路径进行解码,其首先通过 determineEncoding 方法获取当前请求所使用的编码模式,随后使用获取到的编码方式调用 UriUtils 工具类的 decode 方法对 source 进行反编码并返回,解码过程出现任意异常则直接利用 URLDecoder 类进行解码。
- decodePathVariables
public class UrlPathHelper {
public Map<String, String> decodePathVariables(HttpServletRequest request, Map<String, String> vars) {
if (this.urlDecode) {
return vars;
}
else {
Map<String, String> decodedVars = new LinkedHashMap<>(vars.size());
vars.forEach((key, value) -> decodedVars.put(key, decodeInternal(request, value)));
return decodedVars;
}
}
}decodePathVariables 方法用于反编码 restFul 路径请求参数,其在 urlDecode 开启时,即在对 url 反编码时已经对路径参数完成了反编码,因此直接返回原始值;否则将 vars 的所有 value 的替换为为调用 decodeInternal 反编码之后的值并返回。
- decodeMatrixVariables
public class UrlPathHelper {
public MultiValueMap<String, String> decodeMatrixVariables(
HttpServletRequest request, MultiValueMap<String, String> vars) {
if (this.urlDecode) {
return vars;
}
else {
MultiValueMap<String, String> decodedVars = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(vars.size());
vars.forEach((key, values) -> {
for (String value : values) {
decodedVars.add(key, decodeInternal(request, value));
}
});
return decodedVars;
}
}
}decodeMatrixVariables 方法用于反编码矩阵参数,其在 urlDecode 开启时,即在对 url 反编码时已经对路径参数完成了反编码,因此直接返回原始值;否则将 vars 的所有 value 的替换为为调用 decodeInternal 反编码之后的值并返回。
2.4 AntPathMatcher
2.4.1 PathMatcher 接口
PathMatcher 接口为字符串路径的匹配器接口,其提供了多种不同的匹配模式;
public interface PathMatcher {
boolean isPattern(String path);
}isPattern 方法用于判断指定字符串是否为模式表达式。
public interface PathMatcher {
boolean match(String pattern, String path);
boolean matchStart(String pattern, String path);
}match 与 matchStart 方法分别用于模式及前缀匹配。
public interface PathMatcher {
String extractPathWithinPattern(String pattern, String path);
Map<String, String> extractUriTemplateVariables(String pattern, String path);
}extractPathWithinPattern 与 extractUriTemplateVariables 方法则分别用于提取路径参数名及路径参数名与值映射。
public interface PathMatcher {
Comparator<String> getPatternComparator(String path);
}getPatternComparator 方法则是获取适配表达式的比较器。
public interface PathMatcher {
String combine(String pattern1, String pattern2);
}combine 方法将两个不同的表达式合并为 1 个。
2.4.2 变量
-
常量
public class AntPathMatcher implements PathMatcher {
/** Default path separator: "/". */
public static final String DEFAULT_PATH_SEPARATOR = "/";
private static final int CACHE_TURNOFF_THRESHOLD = 65536;
private static final Pattern VARIABLE_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("\\{[^/]+?\\}");
private static final char[] WILDCARD_CHARS = { '*', '?', '{' };
}AntPathMatcher 类有 4 个常量,分别为默认路径分隔符 DEFAULT_PATH_SEPARATOR、缓存关闭阈值 CACHE_TURNOFF_THRESHOLD、参数表达式 VARIABLE_PATTERN 及通配符数组 VARIABLE_PATTERN。
-
类变量
public class AntPathMatcher implements PathMatcher {
private String pathSeparator;
private PathSeparatorPatternCache pathSeparatorPatternCache;
private boolean caseSensitive = true;
private boolean trimTokens = false;
@Nullable
private volatile Boolean cachePatterns;
private final Map<String, String[]> tokenizedPatternCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
final Map<String, AntPathStringMatcher> stringMatcherCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
}AntPathMatcher 类拥有七个属性,其中 pathSeparator 与 pathSeparatorPatternCache 变量分别保存的是路径使用的分隔符及分隔符相关缓存;caseSensitive、trimTokens 及 cachePatterns 三个开关分别用于控制是否严格控制大小写、移除头尾多余空格及是否缓存表达式;最后两个属性为缓存,分别是表达式与字符串匹配器缓存。
2.4.3 方法
-
构造方法
public class AntPathMatcher {
public AntPathMatcher() {
this.pathSeparator = DEFAULT_PATH_SEPARATOR;
this.pathSeparatorPatternCache = new PathSeparatorPatternCache(DEFAULT_PATH_SEPARATOR);
}
public AntPathMatcher(String pathSeparator) {
Assert.notNull(pathSeparator, "'pathSeparator' is required");
this.pathSeparator = pathSeparator;
this.pathSeparatorPatternCache = new PathSeparatorPatternCache(pathSeparator);
}
}AntPathMatcher 有两个构造方法,都是利用分隔符为 pathSeparator 与 pathSeparatorPatternCache 两个属性赋值,差别在于分隔符是否从外部传入。
-
isPattern 方法
public class AntPathMatcher {
@Override
public boolean isPattern(@Nullable String path) {
if (path == null) {
return false;
}
boolean uriVar = false;
for (int i = 0; i < path.length(); i++) {
char c = path.charAt(i);
if (c == '*' || c == '?') {
return true;
}
if (c == '{') {
uriVar = true;
continue;
}
if (c == '}' && uriVar) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}AntPathMatcher 的 isPattern 方法通过判断字符串中是否有 * 与 ?通配符及封闭的 {} 对来判断是否为表达式。
-
doMatch 方法
public class AntPathMatcher {
@Override
public boolean match(String pattern, String path) {
return doMatch(pattern, path, true, null);
}
@Override
public boolean matchStart(String pattern, String path) {
return doMatch(pattern, path, false, null);
}
@Override
public Map<String, String> extractUriTemplateVariables(String pattern, String path) {
Map<String, String> variables = new LinkedHashMap<>();
boolean result = doMatch(pattern, path, true, variables);
if (!result) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Pattern \"" + pattern + "\" is not a match for \"" + path + "\"");
}
return variables;
}
}match、matchStart 及 extractUriTemplateVariables 三个方法都是调用的 doMatch 方法进行模式匹配。
public class AntPathMatcher {
protected boolean doMatch(String pattern, @Nullable String path, boolean fullMatch,
@Nullable Map<String, String> uriTemplateVariables) {
if (path == null || path.startsWith(this.pathSeparator) != pattern.startsWith(this.pathSeparator)) {
return false;
}
String[] pattDirs = tokenizePattern(pattern);
if (fullMatch && this.caseSensitive && !isPotentialMatch(path, pattDirs)) {
return false;
}
String[] pathDirs = tokenizePath(path);
int pattIdxStart = 0;
int pattIdxEnd = pattDirs.length - 1;
int pathIdxStart = 0;
int pathIdxEnd = pathDirs.length - 1;
// Match all elements up to the first **
while (pattIdxStart <= pattIdxEnd && pathIdxStart <= pathIdxEnd) {
String pattDir = pattDirs[pattIdxStart];
if ("**".equals(pattDir)) {
break;
}
if (!matchStrings(pattDir, pathDirs[pathIdxStart], uriTemplateVariables)) {
return false;
}
pattIdxStart++;
pathIdxStart++;
}
if (pathIdxStart > pathIdxEnd) {
// Path is exhausted, only match if rest of pattern is * or **'s
if (pattIdxStart > pattIdxEnd) {
return (pattern.endsWith(this.pathSeparator) == path.endsWith(this.pathSeparator));
}
if (!fullMatch) {
return true;
}
if (pattIdxStart == pattIdxEnd && pattDirs[pattIdxStart].equals("*") && path.endsWith(this.pathSeparator)) {
return true;
}
for (int i = pattIdxStart; i <= pattIdxEnd; i++) {
if (!pattDirs[i].equals("**")) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
else if (pattIdxStart > pattIdxEnd) {
// String not exhausted, but pattern is. Failure.
return false;
}
else if (!fullMatch && "**".equals(pattDirs[pattIdxStart])) {
// Path start definitely matches due to "**" part in pattern.
return true;
}
// up to last '**'
while (pattIdxStart <= pattIdxEnd && pathIdxStart <= pathIdxEnd) {
String pattDir = pattDirs[pattIdxEnd];
if (pattDir.equals("**")) {
break;
}
if (!matchStrings(pattDir, pathDirs[pathIdxEnd], uriTemplateVariables)) {
return false;
}
pattIdxEnd--;
pathIdxEnd--;
}
if (pathIdxStart > pathIdxEnd) {
// String is exhausted
for (int i = pattIdxStart; i <= pattIdxEnd; i++) {
if (!pattDirs[i].equals("**")) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
while (pattIdxStart != pattIdxEnd && pathIdxStart <= pathIdxEnd) {
int patIdxTmp = -1;
for (int i = pattIdxStart + 1; i <= pattIdxEnd; i++) {
if (pattDirs[i].equals("**")) {
patIdxTmp = i;
break;
}
}
if (patIdxTmp == pattIdxStart + 1) {
// '**/**' situation, so skip one
pattIdxStart++;
continue;
}
// Find the pattern between padIdxStart & padIdxTmp in str between
// strIdxStart & strIdxEnd
int patLength = (patIdxTmp - pattIdxStart - 1);
int strLength = (pathIdxEnd - pathIdxStart + 1);
int foundIdx = -1;
strLoop:
for (int i = 0; i <= strLength - patLength; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < patLength; j++) {
String subPat = pattDirs[pattIdxStart + j + 1];
String subStr = pathDirs[pathIdxStart + i + j];
if (!matchStrings(subPat, subStr, uriTemplateVariables)) {
continue strLoop;
}
}
foundIdx = pathIdxStart + i;
break;
}
if (foundIdx == -1) {
return false;
}
pattIdxStart = patIdxTmp;
pathIdxStart = foundIdx + patLength;
}
for (int i = pattIdxStart; i <= pattIdxEnd; i++) {
if (!pattDirs[i].equals("**")) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}doMatch 方法拥有 4 个参数,分别为 pattern 模式、path 匹配字符串、是否全路径匹配 fullMatch(用于前缀匹配)及路径参数值 uriTemplateVariables(用于提取路径参数值);其首先调用 isPotentialMatch 方法对路径进行预匹配,未匹配上直接返回 false;随后将使用表达式与路径使用 pathSeparator 进行分割并从前往后遍历直到表达式元素为 **,存在不匹配元素时直接返回 false;之后若遍历完了 path 路径的所有元素(pathIdxStart > pathIdxEnd) ,首先若表达式也完成了遍历(pattIdxStart > pattIdxEnd)则只需判断其结尾处是否一致,表达式未完成遍历时,表明 path 只是表达式的前缀,在不需要全部匹配时直接返回 true,若表达式已达到尾部(pattIdxStart == pattIdxEnd)、最后一个元素为 * 且路径是以分隔符结尾则表明完全匹配直接返回,最后判断剩余表达式元素中是否全为 **,全为 ** 时返回 true,否则返回 false;若表达式遍历完,但路径未完成遍历则直接返回 false;当表达式与路径都未完成遍历时,表明遍历的最后一个元素为 ** ,该条件下不需要全量匹配时直接返回 true,需要全量匹配则会从后向前遍历,也是直到遇到 ** 或元素不匹配时停止,遇到 ** 时直接中止遍历,元素不匹配则直接返回 false;随后又分成两种情况:完全完成了 path 路径元素的遍历(pathIdxStart > pathIdxEnd),这时需要确认的是未遍历到的表达式中部元素是否全为 **,是的话返回 true,否则返回 false;第二种情况则是遇到了 ** 中断了遍历,这时则会将中间部分以 ** 作为分割进行分段匹配,直到将 path 元素遍历完成或遇到无法匹配路径。
public class AntPathMatcher {
protected String[] tokenizePattern(String pattern) {
String[] tokenized = null;
Boolean cachePatterns = this.cachePatterns;
if (cachePatterns == null || cachePatterns.booleanValue()) {
tokenized = this.tokenizedPatternCache.get(pattern);
}
if (tokenized == null) {
tokenized = tokenizePath(pattern);
if (cachePatterns == null && this.tokenizedPatternCache.size() >= CACHE_TURNOFF_THRESHOLD) {
// Try to adapt to the runtime situation that we're encountering:
// There are obviously too many different patterns coming in here...
// So let's turn off the cache since the patterns are unlikely to be reoccurring.
deactivatePatternCache();
return tokenized;
}
if (cachePatterns == null || cachePatterns.booleanValue()) {
this.tokenizedPatternCache.put(pattern, tokenized);
}
}
return tokenized;
}
protected String[] tokenizePath(String path) {
return StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(path, this.pathSeparator, this.trimTokens, true);
}
private void deactivatePatternCache() {
this.cachePatterns = false;
this.tokenizedPatternCache.clear();
this.stringMatcherCache.clear();
}
}tokenizePattern 方法用于分割表达式,其返回分割完的表达式数组;其在 cachePatterns 属性为 true 时尝试从 tokenizedPatternCache 缓存中获取对应表达式数组,未获取到则调用 tokenizePath 方法按 pathSeparator 分割 pattern 参数并在需要缓存时将其缓存到 tokenizedPatternCache 属性之中,值得注意的是,在缓存数量达到 CACHE_TURNOFF_THRESHOLD 阈值时调用 deactivatePatternCache 方法关闭缓存。
public class AntPathMatcher {
private boolean isPotentialMatch(String path, String[] pattDirs) {
if (!this.trimTokens) {
int pos = 0;
for (String pattDir : pattDirs) {
int skipped = skipSeparator(path, pos, this.pathSeparator);
pos += skipped;
skipped = skipSegment(path, pos, pattDir);
if (skipped < pattDir.length()) {
return (skipped > 0 || (pattDir.length() > 0 && isWildcardChar(pattDir.charAt(0))));
}
pos += skipped;
}
}
return true;
}
private int skipSeparator(String path, int pos, String separator) {
int skipped = 0;
while (path.startsWith(separator, pos + skipped)) {
skipped += separator.length();
}
return skipped;
}
private int skipSegment(String path, int pos, String prefix) {
int skipped = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
char c = prefix.charAt(i);
if (isWildcardChar(c)) {
return skipped;
}
int currPos = pos + skipped;
if (currPos >= path.length()) {
return 0;
}
if (c == path.charAt(currPos)) {
skipped++;
}
}
return skipped;
}
private boolean isWildcardChar(char c) {
for (char candidate : WILDCARD_CHARS) {
if (c == candidate) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}isPotentialMatch 方法用于匹配的预判断,其在 trimTokens 为 true 时直接返回 true,否则对 pattDirs 表达式数组进行逐一排查,其首先调用 skipSeparator 方法跳过元素的分割符前缀,然后使用 skipSegment 获取匹配的字符数,在匹配字符数小于当前模式长度时,可能情况为路径长度小于模式的长度(已匹配字符串不包含任何通配符),存在通配符及非通配符完全匹配;路径长度小于模式的长度(已匹配字符串不包含任何通配符 skiped == 0)直接返回 false,拥有通配符直接返回 false (skiped < pattDir.length())及完全匹配(skiped == pattDir.length())继续匹配。
public class AntPathMatcher {
private boolean matchStrings(String pattern, String str,
@Nullable Map<String, String> uriTemplateVariables) {
return getStringMatcher(pattern).matchStrings(str, uriTemplateVariables);
}
protected AntPathStringMatcher getStringMatcher(String pattern) {
AntPathStringMatcher matcher = null;
Boolean cachePatterns = this.cachePatterns;
if (cachePatterns == null || cachePatterns.booleanValue()) {
matcher = this.stringMatcherCache.get(pattern);
}
if (matcher == null) {
matcher = new AntPathStringMatcher(pattern, this.caseSensitive);
if (cachePatterns == null && this.stringMatcherCache.size() >= CACHE_TURNOFF_THRESHOLD) {
// Try to adapt to the runtime situation that we're encountering:
// There are obviously too many different patterns coming in here...
// So let's turn off the cache since the patterns are unlikely to be reoccurring.
deactivatePatternCache();
return matcher;
}
if (cachePatterns == null || cachePatterns.booleanValue()) {
this.stringMatcherCache.put(pattern, matcher);
}
}
return matcher;
}
}matchStrings 方法用于字符串匹配及路径参数的提取,其通过 getStringMatcher 方法获取 AntPathStringMatcher 字符串匹配器进行字符串匹配;
-
extractPathWithinPattern 方法
public class AntPathMatcher {
@Override
public String extractPathWithinPattern(String pattern, String path) {
String[] patternParts = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(pattern, this.pathSeparator, this.trimTokens, true);
String[] pathParts = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(path, this.pathSeparator, this.trimTokens, true);
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
boolean pathStarted = false;
for (int segment = 0; segment < patternParts.length; segment++) {
String patternPart = patternParts[segment];
if (patternPart.indexOf('*') > -1 || patternPart.indexOf('?') > -1) {
for (; segment < pathParts.length; segment++) {
if (pathStarted || (segment == 0 && !pattern.startsWith(this.pathSeparator))) {
builder.append(this.pathSeparator);
}
builder.append(pathParts[segment]);
pathStarted = true;
}
}
}
return builder.toString();
}
}extractPathWithinPattern 方法用于提取 path 路径中与 pattern 表达式中模式匹配部分,即返回路径中与模式中的通配符相对应的部分(/docs/cvs/commit.html 与 /docs/cvs/commit.html 提取空字符串,/docs/* 与 /docs/cvs/commit 提取为 cvs/commit);其首先将 pattern 与 path 以 pathSeparator 分割成字符串数组,随后寻找表达式中带 * 或 ?的第一个元素,然后将该位置到 path 的最后一个元素拼接成字符串并返回。
-
combine 方法
public class AntPathMatcher {
@Override
public String combine(String pattern1, String pattern2) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(pattern1) && !StringUtils.hasText(pattern2)) {
return "";
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(pattern1)) {
return pattern2;
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(pattern2)) {
return pattern1;
}
boolean pattern1ContainsUriVar = (pattern1.indexOf('{') != -1);
if (!pattern1.equals(pattern2) && !pattern1ContainsUriVar && match(pattern1, pattern2)) {
// /* + /hotel -> /hotel ; "/*.*" + "/*.html" -> /*.html
// However /user + /user -> /usr/user ; /{foo} + /bar -> /{foo}/bar
return pattern2;
}
// /hotels/* + /booking -> /hotels/booking
// /hotels/* + booking -> /hotels/booking
if (pattern1.endsWith(this.pathSeparatorPatternCache.getEndsOnWildCard())) {
return concat(pattern1.substring(0, pattern1.length() - 2), pattern2);
}
// /hotels/** + /booking -> /hotels/**/booking
// /hotels/** + booking -> /hotels/**/booking
if (pattern1.endsWith(this.pathSeparatorPatternCache.getEndsOnDoubleWildCard())) {
return concat(pattern1, pattern2);
}
int starDotPos1 = pattern1.indexOf("*.");
if (pattern1ContainsUriVar || starDotPos1 == -1 || this.pathSeparator.equals(".")) {
// simply concatenate the two patterns
return concat(pattern1, pattern2);
}
String ext1 = pattern1.substring(starDotPos1 + 1);
int dotPos2 = pattern2.indexOf('.');
String file2 = (dotPos2 == -1 ? pattern2 : pattern2.substring(0, dotPos2));
String ext2 = (dotPos2 == -1 ? "" : pattern2.substring(dotPos2));
boolean ext1All = (ext1.equals(".*") || ext1.isEmpty());
boolean ext2All = (ext2.equals(".*") || ext2.isEmpty());
if (!ext1All && !ext2All) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot combine patterns: " + pattern1 + " vs " + pattern2);
}
String ext = (ext1All ? ext2 : ext1);
return file2 + ext;
}
}combine 方法用于合并两个表达式;若 pattern1 与 pattern2 参数不同、pattern1 不包含 {,且 pattern2 匹配 pattern1 则直接返回 pattern2;若 pattern1 以 * 结尾,则移除 * 后进行拼接,以 ** 结尾不做任何处理直接进行拼接;pattern 不包含 { 、*. 或以 . 作为分割符时也是直接进行拼接,即尝试合并扩展名("/*.html" + "/index" -> "/index.html","/*.html" + "/*.txt" -> 会抛出异常,因为不能合并两个不同的扩展名),其首先获取 pattern1 中 *. 后的部分与 pattern2 以 . 分割部分,在扩展名可匹配上时将 pattern2 的文件名与非空文件扩展名拼接然后返回。
public class AntPathMatcher {
private String concat(String path1, String path2) {
boolean path1EndsWithSeparator = path1.endsWith(this.pathSeparator);
boolean path2StartsWithSeparator = path2.startsWith(this.pathSeparator);
if (path1EndsWithSeparator && path2StartsWithSeparator) {
return path1 + path2.substring(1);
}
else if (path1EndsWithSeparator || path2StartsWithSeparator) {
return path1 + path2;
}
else {
return path1 + this.pathSeparator + path2;
}
}
}concat 方法用于直接拼接表达式,主要是在 path1 与 path2 之间移除或增加必要的 pathSeparator 分割符。
2.4.4 内部类
-
AntPathStringMatcher
public class AntPathMatcher {
protected static class AntPathStringMatcher {
private static final Pattern GLOB_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("\\?|\\*|\\{((?:\\{[^/]+?\\}|[^/{}]|\\\\[{}])+?)\\}");
private static final String DEFAULT_VARIABLE_PATTERN = "(.*)";
}
} AntPathStringMatcher 有拥有两个常量,GLOB_PATTERN 用于识别路径模式中的单字符通配符(?)、多字符通配符(*) 及 URI 变量({variable})三种特殊元素的正则表达式,DEFAULT_VARIABLE_PATTERN 则是 URI 变量的默认匹配模式。
public class AntPathMatcher {
protected static class AntPathStringMatcher {
private final Pattern pattern;
private final List<String> variableNames = new LinkedList<>();
}
}AntPathStringMatcher 有拥有存储匹配模式 pattern 与变量名数组 variableNames 两个变量。
public class AntPathMatcher {
protected static class AntPathStringMatcher {
public AntPathStringMatcher(String pattern) {
this(pattern, true);
}
public AntPathStringMatcher(String pattern, boolean caseSensitive) {
StringBuilder patternBuilder = new StringBuilder();
Matcher matcher = GLOB_PATTERN.matcher(pattern);
int end = 0;
while (matcher.find()) {
patternBuilder.append(quote(pattern, end, matcher.start()));
String match = matcher.group();
if ("?".equals(match)) {
patternBuilder.append('.');
}
else if ("*".equals(match)) {
patternBuilder.append(".*");
}
else if (match.startsWith("{") && match.endsWith("}")) {
int colonIdx = match.indexOf(':');
if (colonIdx == -1) {
patternBuilder.append(DEFAULT_VARIABLE_PATTERN);
this.variableNames.add(matcher.group(1));
}
else {
String variablePattern = match.substring(colonIdx + 1, match.length() - 1);
patternBuilder.append('(');
patternBuilder.append(variablePattern);
patternBuilder.append(')');
String variableName = match.substring(1, colonIdx);
this.variableNames.add(variableName);
}
}
end = matcher.end();
}
patternBuilder.append(quote(pattern, end, pattern.length()));
this.pattern = (caseSensitive ? Pattern.compile(patternBuilder.toString()) :
Pattern.compile(patternBuilder.toString(), Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE));
}
}
}AntPathStringMatcher 的构造方法拥有两个参数,其一为字符串表达式,另一个则是是否大小写敏感;其使用 GLOB_PATTERN 正则表达式将 pattern 参数(Ant 风格的路径模式)转换为正则表达式并保存至 pattern 属性之中;其将 pattern 中的 ? 替换为 . ,* 替换为 .*,使用 DEFAULT_VARIABLE_PATTERN 或定义的变量正则表达式(变量中间存在 :,即格式为 变量名:变量正则表达式)替换 uri 变量(使用 {} 包裹)并将变量名按顺序保存至 variableNames 属性之中;
public class AntPathMatcher {
protected static class AntPathStringMatcher {
public boolean matchStrings(String str, @Nullable Map<String, String> uriTemplateVariables) {
Matcher matcher = this.pattern.matcher(str);
if (matcher.matches()) {
if (uriTemplateVariables != null) {
// SPR-8455
if (this.variableNames.size() != matcher.groupCount()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The number of capturing groups in the pattern segment " +
this.pattern + " does not match the number of URI template variables it defines, " +
"which can occur if capturing groups are used in a URI template regex. " +
"Use non-capturing groups instead.");
}
for (int i = 1; i <= matcher.groupCount(); i++) {
String name = this.variableNames.get(i - 1);
String value = matcher.group(i);
uriTemplateVariables.put(name, value);
}
}
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
}
}matchStrings 方法用于正则模式匹配及参数提取;其中路径匹配上的变量值数必须与 variableNames 长度一致,然后将所有匹配的参数与结果值保存至 uriTemplateVariables 参数之中。
-
AntPatternComparator
AntPatternComparator 内部类用于表达式之间的比对,判断匹配的先后顺序;
public class AntPathMatcher {
protected static class AntPatternComparator implements Comparator<String> {
private final String path;
public AntPatternComparator(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
@Override
public int compare(String pattern1, String pattern2) {
PatternInfo info1 = new PatternInfo(pattern1);
PatternInfo info2 = new PatternInfo(pattern2);
if (info1.isLeastSpecific() && info2.isLeastSpecific()) {
return 0;
}
else if (info1.isLeastSpecific()) {
return 1;
}
else if (info2.isLeastSpecific()) {
return -1;
}
boolean pattern1EqualsPath = pattern1.equals(this.path);
boolean pattern2EqualsPath = pattern2.equals(this.path);
if (pattern1EqualsPath && pattern2EqualsPath) {
return 0;
}
else if (pattern1EqualsPath) {
return -1;
}
else if (pattern2EqualsPath) {
return 1;
}
if (info1.isPrefixPattern() && info2.isPrefixPattern()) {
return info2.getLength() - info1.getLength();
}
else if (info1.isPrefixPattern() && info2.getDoubleWildcards() == 0) {
return 1;
}
else if (info2.isPrefixPattern() && info1.getDoubleWildcards() == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (info1.getTotalCount() != info2.getTotalCount()) {
return info1.getTotalCount() - info2.getTotalCount();
}
if (info1.getLength() != info2.getLength()) {
return info2.getLength() - info1.getLength();
}
if (info1.getSingleWildcards() < info2.getSingleWildcards()) {
return -1;
}
else if (info2.getSingleWildcards() < info1.getSingleWildcards()) {
return 1;
}
if (info1.getUriVars() < info2.getUriVars()) {
return -1;
}
else if (info2.getUriVars() < info1.getUriVars()) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
}AntPatternComparator 比较器首先通过 isLeastSpecific 方法直接将 null 及 /** 全局表达式放在最后,之后将与 path 相等的表达式放在第一位执行,在两个表达式都是前缀表达式时,长度长的要比长度短的进行匹配,否则在只有其中一个表达式为前缀表达式,另一个表达式拥有 ** 时,直接先匹配前缀表达式;上述条件都无法判断时,将通过数量继续进行比对,其首先利用 getTotalCount 获取需要特殊匹配的总数(其中参数与单 * 占比为 1、双 * 占比为 2),先匹配数量多的;否则先匹配 Length 长度短、单 * 或路径参数少的表达式。
-
PatternInfo
PatternInfo 内部类用于解析表达式,提取其中主要元素;
public class AntPathMatcher {
protected static class AntPatternComparator implements Comparator<String> {
private static class PatternInfo {
@Nullable
private final String pattern;
private int uriVars;
private int singleWildcards;
private int doubleWildcards;
private boolean catchAllPattern;
private boolean prefixPattern;
@Nullable
private Integer length;
}
}PatternInfo 拥有 7 个属性,其中 pattern 保存的是原始表达式,uriVars 、singleWildcards 及 doubleWildcards 分别保存的是路径参数、单 * 及双 * 数量;catchAllPattern 与 prefixPattern 两个参数分别标识全局匹配还是前缀匹配表达式;length 属性保存的则是无参数路径表达式长度;
public class AntPathMatcher {
protected static class AntPatternComparator implements Comparator<String> {
private static class PatternInfo {
public PatternInfo(@Nullable String pattern) {
this.pattern = pattern;
if (this.pattern != null) {
initCounters();
this.catchAllPattern = this.pattern.equals("/**");
this.prefixPattern = !this.catchAllPattern && this.pattern.endsWith("/**");
}
if (this.uriVars == 0) {
this.length = (this.pattern != null ? this.pattern.length() : 0);
}
}
protected void initCounters() {
int pos = 0;
if (this.pattern != null) {
while (pos < this.pattern.length()) {
if (this.pattern.charAt(pos) == '{') {
this.uriVars++;
pos++;
}
else if (this.pattern.charAt(pos) == '*') {
if (pos + 1 < this.pattern.length() && this.pattern.charAt(pos + 1) == '*') {
this.doubleWildcards++;
pos += 2;
}
else if (pos > 0 && !this.pattern.substring(pos - 1).equals(".*")) {
this.singleWildcards++;
pos++;
}
else {
pos++;
}
}
else {
pos++;
}
}
}
}
public int getTotalCount() {
return this.uriVars + this.singleWildcards + (2 * this.doubleWildcards);
}
}
}
}PatternInfo 对象在创建过程中首先为 pattern 属性赋值;并在其不为空时调用 initCounters 方法为 uriVars 、singleWildcards 及 doubleWildcards 三个数量参数赋值,其中 uriVars 定义为 { 字符数同时为 catchAllPattern 与 prefixPattern 属性赋值,其中 catchAllPattern 属性直接通过是否与 /** 相等,prefixPattern 则是是否以 /** 结尾但不等于 /**;最后若表达式没有路径参数,其将 length 属性更新为 pattern 长度。
2.5 DefaultCorsProcessor
2.5.1 CorsProcessor 接口
CorsProcessor 接口为 cors 跨域请求处理的接口,其只有一个用于处理跨域请求的 processRequest 方法,该方法拥有三个参数,分别为跨域配置 configuration,request 请求及 response 响应对象;
public interface CorsProcessor {
boolean processRequest(@Nullable CorsConfiguration configuration, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException;
}2.5.2 方法
- processRequest 方法实现
public class DefaultCorsProcessor implements CorsProcessor {
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public boolean processRequest(@Nullable CorsConfiguration config, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
Collection<String> varyHeaders = response.getHeaders(HttpHeaders.VARY);
if (!varyHeaders.contains(HttpHeaders.ORIGIN)) {
response.addHeader(HttpHeaders.VARY, HttpHeaders.ORIGIN);
}
if (!varyHeaders.contains(HttpHeaders.ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_METHOD)) {
response.addHeader(HttpHeaders.VARY, HttpHeaders.ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_METHOD);
}
if (!varyHeaders.contains(HttpHeaders.ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_HEADERS)) {
response.addHeader(HttpHeaders.VARY, HttpHeaders.ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_HEADERS);
}
if (!CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
return true;
}
if (response.getHeader(HttpHeaders.ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_ORIGIN) != null) {
logger.trace("Skip: response already contains \"Access-Control-Allow-Origin\"");
return true;
}
boolean preFlightRequest = CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request);
if (config == null) {
if (preFlightRequest) {
rejectRequest(new ServletServerHttpResponse(response));
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
return handleInternal(new ServletServerHttpRequest(request), new ServletServerHttpResponse(response), config, preFlightRequest);
}
protected void rejectRequest(ServerHttpResponse response) throws IOException {
response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN);
response.getBody().write("Invalid CORS request".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
response.flush();
}
}DefaultCorsProcessor 类的 processRequest 方法实现本身只是对请求进行预处理,在通过处理后调用 handleInternal 对请求进行实际处理;在该方法之中,首先向 VARY 响应头中添加 ORIGIN、ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_METHOD 及 ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_HEADERS 三个内容表达在缓存响应时需要这三个请求头也作为联合缓存键;随后若不是跨域请求或拥有 ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_ORIGIN 响应头时直接返回 true;在 config 跨域配置为 null 时,根据是否为跨域预处理请求进行不同处理,是预请求时,直接调用 rejectRequest 方法拒绝跨域请求并返回 false,不是预请求则返回 true;而在 config 不为空时,调用 handleInternal 方法进行实际处理。
- handleInternal 方法
public class DefaultCorsProcessor implements CorsProcessor {
protected boolean handleInternal(ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response,
CorsConfiguration config, boolean preFlightRequest) throws IOException {
String requestOrigin = request.getHeaders().getOrigin();
String allowOrigin = checkOrigin(config, requestOrigin);
HttpHeaders responseHeaders = response.getHeaders();
if (allowOrigin == null) {
logger.debug("Reject: '" + requestOrigin + "' origin is not allowed");
rejectRequest(response);
return false;
}
HttpMethod requestMethod = getMethodToUse(request, preFlightRequest);
List<HttpMethod> allowMethods = checkMethods(config, requestMethod);
if (allowMethods == null) {
logger.debug("Reject: HTTP '" + requestMethod + "' is not allowed");
rejectRequest(response);
return false;
}
List<String> requestHeaders = getHeadersToUse(request, preFlightRequest);
List<String> allowHeaders = checkHeaders(config, requestHeaders);
if (preFlightRequest && allowHeaders == null) {
logger.debug("Reject: headers '" + requestHeaders + "' are not allowed");
rejectRequest(response);
return false;
}
responseHeaders.setAccessControlAllowOrigin(allowOrigin);
if (preFlightRequest) {
responseHeaders.setAccessControlAllowMethods(allowMethods);
}
if (preFlightRequest && !allowHeaders.isEmpty()) {
responseHeaders.setAccessControlAllowHeaders(allowHeaders);
}
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(config.getExposedHeaders())) {
responseHeaders.setAccessControlExposeHeaders(config.getExposedHeaders());
}
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(config.getAllowCredentials())) {
responseHeaders.setAccessControlAllowCredentials(true);
}
if (preFlightRequest && config.getMaxAge() != null) {
responseHeaders.setAccessControlMaxAge(config.getMaxAge());
}
response.flush();
return true;
}
@Nullable
protected String checkOrigin(CorsConfiguration config, @Nullable String requestOrigin) {
return config.checkOrigin(requestOrigin);
}
@Nullable
protected List<HttpMethod> checkMethods(CorsConfiguration config, @Nullable HttpMethod requestMethod) {
return config.checkHttpMethod(requestMethod);
}
@Nullable
private HttpMethod getMethodToUse(ServerHttpRequest request, boolean isPreFlight) {
return (isPreFlight ? request.getHeaders().getAccessControlRequestMethod() : request.getMethod());
}
@Nullable
protected List<String> checkHeaders(CorsConfiguration config, List<String> requestHeaders) {
return config.checkHeaders(requestHeaders);
}
private List<String> getHeadersToUse(ServerHttpRequest request, boolean isPreFlight) {
HttpHeaders headers = request.getHeaders();
return (isPreFlight ? headers.getAccessControlRequestHeaders() : new ArrayList<>(headers.keySet()));
}
} handleInternal 方法首先调用 config 参数的对应方法依次验证并获取允许的请求域名、方法及请求头,随后依次为响应头设置允许方法、请求头、Access-Control-Expose-Headers 自定义暴露响应头、ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_CREDENTIALS 是否允许跨域请求携带凭证及 ACCESS_CONTROL_MAX_AGE 预检请求的最大生存时间(单位为秒)。
2.6 CorsConfiguration
2.6.1 变量
-
常量
public class CorsConfiguration {
public static final String ALL = "*";
private static final List<HttpMethod> DEFAULT_METHODS = Collections.unmodifiableList(
Arrays.asList(HttpMethod.GET, HttpMethod.HEAD));
private static final List<String> DEFAULT_PERMIT_METHODS = Collections.unmodifiableList(
Arrays.asList(HttpMethod.GET.name(), HttpMethod.HEAD.name(), HttpMethod.POST.name()));
private static final List<String> DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL = Collections.singletonList(ALL);
}CorsConfiguration 类的常量都是些默认值,其中 ALL 与 DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL 表明默认允许所有跨域请求,DEFAULT_METHODS 与 DEFAULT_PERMIT_METHODS 两个常量则分别为实际解析使用的默认方法(HttpMethod 枚举列表)及未设置时默认许可方法(字符串列表);
-
类变量
public class CorsConfiguration {
@Nullable
private List<String> allowedOrigins;
@Nullable
private List<String> allowedMethods;
@Nullable
private List<HttpMethod> resolvedMethods = DEFAULT_METHODS;
@Nullable
private List<String> allowedHeaders;
@Nullable
private List<String> exposedHeaders;
@Nullable
private Boolean allowCredentials;
@Nullable
private Long maxAge;
public void setAllowCredentials(@Nullable Boolean allowCredentials) {
this.allowCredentials = allowCredentials;
}
@Nullable
public Boolean getAllowCredentials() {
return this.allowCredentials;
}
public void setMaxAge(Duration maxAge) {
this.maxAge = maxAge.getSeconds();
}
public void setMaxAge(@Nullable Long maxAge) {
this.maxAge = maxAge;
}
@Nullable
public Long getMaxAge() {
return this.maxAge;
}
}CorsConfiguration 类中的类变量就是用于控制跨域访问权限的相关变量,他们分别为允许访问的源列表 allowedOrigins、允许访问方法配置 allowedMethods、实际解析使用的方法授权 resolvedMethods (默认为 DEFAULT_METHODS)、允许请求携带的请求头 allowedHeaders、允许浏览器暴露给 js 的头 exposedHeaders、是否携带认证凭据(cookie、TLS 证书及HTTP 认证头信息:Authorization: Basic 等)进行跨域的 allowCredentials 及预检请求最大生存时间 maxAge(秒)。
2.6.2 方法
-
构造方法
public class CorsConfiguration {
public CorsConfiguration() {
}
public CorsConfiguration(CorsConfiguration other) {
this.allowedOrigins = other.allowedOrigins;
this.allowedMethods = other.allowedMethods;
this.resolvedMethods = other.resolvedMethods;
this.allowedHeaders = other.allowedHeaders;
this.exposedHeaders = other.exposedHeaders;
this.allowCredentials = other.allowCredentials;
this.maxAge = other.maxAge;
}
}CorsConfiguration 类只有两个构造方法,一个是无参构造方法直接传家空对象,第二个直接复制已有的 CorsConfiguration 配置对象;
-
origin 方法
public class CorsConfiguration {
public void setAllowedOrigins(@Nullable List<String> allowedOrigins) {
this.allowedOrigins = (allowedOrigins != null ? new ArrayList<>(allowedOrigins) : null);
}
@Nullable
public List<String> getAllowedOrigins() {
return this.allowedOrigins;
}
public void addAllowedOrigin(String origin) {
if (this.allowedOrigins == null) {
this.allowedOrigins = new ArrayList<>(4);
}
else if (this.allowedOrigins == DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL) {
setAllowedOrigins(DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL);
}
this.allowedOrigins.add(origin);
}
}CorsConfiguration 类拥有三个 origin 相关方法,其中两个为 set 与 get 方法,其中 set 方法直接将 allowedOrigins 入参直接覆盖到 allowedOrigins 属性中而不会管起是否已有数据,addAllowedOrigin 方法在 allowedOrigins 属性为空时直接将其初始化为空列表,在其是 DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL 对象时,将 DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL 初始化为可变列表并保存到 allowedOrigins 属性之中,最后将传入的 origin 参数保存到 allowedOrigins 属性尾部。
-
method 方法
public class CorsConfiguration {
public void setAllowedMethods(@Nullable List<String> allowedMethods) {
this.allowedMethods = (allowedMethods != null ? new ArrayList<>(allowedMethods) : null);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(allowedMethods)) {
this.resolvedMethods = new ArrayList<>(allowedMethods.size());
for (String method : allowedMethods) {
if (ALL.equals(method)) {
this.resolvedMethods = null;
break;
}
this.resolvedMethods.add(HttpMethod.resolve(method));
}
}
else {
this.resolvedMethods = DEFAULT_METHODS;
}
}
@Nullable
public List<String> getAllowedMethods() {
return this.allowedMethods;
}
}setAllowedMethods 方法在传入的 allowedMethods 参数不为空时将 allowedMethods 初始化为 allowedMethods 参数创建的 ArrayList 列表对象,之后若入参为空,则会将 resolvedMethods 属性更新为 DEFAULT_METHODS 常量值,否则则会便利 allowedMethods 入参,若其中存在 ALL 常量通配符,则直接将 resolvedMethods 属性置为 null 并返回,否则将所有元素逐一转换为 HttpMethod 枚举值并保存到 resolvedMethods 属性之中。
public class CorsConfiguration {
public void addAllowedMethod(HttpMethod method) {
addAllowedMethod(method.name());
}
public void addAllowedMethod(String method) {
if (StringUtils.hasText(method)) {
if (this.allowedMethods == null) {
this.allowedMethods = new ArrayList<>(4);
this.resolvedMethods = new ArrayList<>(4);
}
else if (this.allowedMethods == DEFAULT_PERMIT_METHODS) {
setAllowedMethods(DEFAULT_PERMIT_METHODS);
}
this.allowedMethods.add(method);
if (ALL.equals(method)) {
this.resolvedMethods = null;
}
else if (this.resolvedMethods != null) {
this.resolvedMethods.add(HttpMethod.resolve(method));
}
}
}
}addAllowedMethod 方法在 method 入参为空时直接返回,否则若 allowedMethods 为 null 时直接将 allowedMethods 与 resolvedMethods 初始化为空列表,若 allowedMethods 为 DEFAULT_PERMIT_METHODS 常量值时,则会调用 setAllowedMethods 方法将 DEFAULT_PERMIT_METHODS 常量中所有元素保存到 allowedMethods 与 resolvedMethods 属性之中;随后在完成了 allowedMethods 与 resolvedMethods 初始化之后,直接将 method 参数保存到 allowedMethods 属性中,在入参为 ALL 时将 resolvedMethods 属性置为 null,否则也会将 method 参数值保存到 resolvedMethods 属性之中。
-
header 方法
public class CorsConfiguration {
public void setAllowedHeaders(@Nullable List<String> allowedHeaders) {
this.allowedHeaders = (allowedHeaders != null ? new ArrayList<>(allowedHeaders) : null);
}
@Nullable
public List<String> getAllowedHeaders() {
return this.allowedHeaders;
}
public void addAllowedHeader(String allowedHeader) {
if (this.allowedHeaders == null) {
this.allowedHeaders = new ArrayList<>(4);
}
else if (this.allowedHeaders == DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL) {
setAllowedHeaders(DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL);
}
this.allowedHeaders.add(allowedHeader);
}
public void setExposedHeaders(@Nullable List<String> exposedHeaders) {
this.exposedHeaders = (exposedHeaders != null ? new ArrayList<>(exposedHeaders) : null);
}
@Nullable
public List<String> getExposedHeaders() {
return this.exposedHeaders;
}
public void addExposedHeader(String exposedHeader) {
if (this.exposedHeaders == null) {
this.exposedHeaders = new ArrayList<>(4);
}
this.exposedHeaders.add(exposedHeader);
}
}allowedHeaders 与 exposedHeaders 属性也有三个相关方法,setAllowedHeaders、getAllowedHeaders 及 addAllowedHeader 方法;去逻辑与之前其他属性一致,这里就不做过多介绍了。
-
applyPermitDefaultValues 方法
public class CorsConfiguration {
public CorsConfiguration applyPermitDefaultValues() {
if (this.allowedOrigins == null) {
this.allowedOrigins = DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL;
}
if (this.allowedMethods == null) {
this.allowedMethods = DEFAULT_PERMIT_METHODS;
this.resolvedMethods = DEFAULT_PERMIT_METHODS
.stream().map(HttpMethod::resolve).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
if (this.allowedHeaders == null) {
this.allowedHeaders = DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL;
}
if (this.maxAge == null) {
this.maxAge = 1800L;
}
return this;
}
}applyPermitDefaultValues 方法用于初始化还未初始化的属性,其分别将 allowedOrigins、allowedMethods、resolvedMethods、allowedHeaders 及 maxAge 属性初始化为 DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL、DEFAULT_PERMIT_METHODS、DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL 及 1800。
-
combine 方法
public class CorsConfiguration {
@Nullable
public CorsConfiguration combine(@Nullable CorsConfiguration other) {
if (other == null) {
return this;
}
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration(this);
config.setAllowedOrigins(combine(getAllowedOrigins(), other.getAllowedOrigins()));
config.setAllowedMethods(combine(getAllowedMethods(), other.getAllowedMethods()));
config.setAllowedHeaders(combine(getAllowedHeaders(), other.getAllowedHeaders()));
config.setExposedHeaders(combine(getExposedHeaders(), other.getExposedHeaders()));
Boolean allowCredentials = other.getAllowCredentials();
if (allowCredentials != null) {
config.setAllowCredentials(allowCredentials);
}
Long maxAge = other.getMaxAge();
if (maxAge != null) {
config.setMaxAge(maxAge);
}
return config;
}
}combine 方法用于配置的合并,其首先逐一调用 setAllowedOrigins、setAllowedMethods、setAllowedHeaders 及 setExposedHeaders 方法将合并后的对应元素保存至对应元素之中,随后将 other 参数的 allowCredentials 与 maxAge 属性值更新到配置之中。
public class CorsConfiguration {
private List<String> combine(@Nullable List<String> source, @Nullable List<String> other) {
if (other == null) {
return (source != null ? source : Collections.emptyList());
}
if (source == null) {
return other;
}
if (source == DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL || source == DEFAULT_PERMIT_METHODS) {
return other;
}
if (other == DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL || other == DEFAULT_PERMIT_METHODS) {
return source;
}
if (source.contains(ALL) || other.contains(ALL)) {
return new ArrayList<>(Collections.singletonList(ALL));
}
Set<String> combined = new LinkedHashSet<>(source);
combined.addAll(other);
return new ArrayList<>(combined);
}
}字符串列表 combine 拼接方法,其直接将两个列表去重合并并返回,值得注意的是,若其中包含 ALL 常量元素直接将 ALL 单元素列表。
-
checkOrigin 方法
public class CorsConfiguration {
@Nullable
public String checkOrigin(@Nullable String requestOrigin) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(requestOrigin)) {
return null;
}
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.allowedOrigins)) {
return null;
}
if (this.allowedOrigins.contains(ALL)) {
if (this.allowCredentials != Boolean.TRUE) {
return ALL;
}
else {
return requestOrigin;
}
}
for (String allowedOrigin : this.allowedOrigins) {
if (requestOrigin.equalsIgnoreCase(allowedOrigin)) {
return requestOrigin;
}
}
return null;
}
}checkOrigin 方法验证请求源,在 allowedOrigins 属性包含 All 常量值时,allowCredentials 属性不为 true 时直接返回 ALL 常量,否则返回 requestOrigin 入参值;不包含 ALL 常量但存在与 requestOrigin 入参一致的参数时直接返回该入参值,否则返回 null。
-
checkHttpMethod 方法
public class CorsConfiguration {
@Nullable
public List<HttpMethod> checkHttpMethod(@Nullable HttpMethod requestMethod) {
if (requestMethod == null) {
return null;
}
if (this.resolvedMethods == null) {
return Collections.singletonList(requestMethod);
}
return (this.resolvedMethods.contains(requestMethod) ? this.resolvedMethods : null);
}
}checkHttpMethod 方法在 resolvedMethods 属性为 null 时直接返回入参值,否则在 resolvedMethods 属性中拥有 requestMethod 元素值时直接返该属性值,否则返回 null。
-
checkHeaders 方法
public class CorsConfiguration {
@Nullable
public List<String> checkHeaders(@Nullable List<String> requestHeaders) {
if (requestHeaders == null) {
return null;
}
if (requestHeaders.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.allowedHeaders)) {
return null;
}
boolean allowAnyHeader = this.allowedHeaders.contains(ALL);
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(requestHeaders.size());
for (String requestHeader : requestHeaders) {
if (StringUtils.hasText(requestHeader)) {
requestHeader = requestHeader.trim();
if (allowAnyHeader) {
result.add(requestHeader);
}
else {
for (String allowedHeader : this.allowedHeaders) {
if (requestHeader.equalsIgnoreCase(allowedHeader)) {
result.add(requestHeader);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
return (result.isEmpty() ? null : result);
}
}checkHeaders 方法在 requestHeaders 入参中与 allowedHeaders 参数匹配的所有请求头全保存返回。
2.7 CorsConfiguration
2.7.1 CorsConfigurationSource 接口
public interface CorsConfigurationSource {
@Nullable
CorsConfiguration getCorsConfiguration(HttpServletRequest request);
}CorsConfigurationSource 接口向外提供了一个 getCorsConfiguration 方法用于获取指定 request 请求对应的跨域配置 CorsConfiguration 对象;
2.7.2 变量
public class UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource implements CorsConfigurationSource {
private final Map<String, CorsConfiguration> corsConfigurations = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
private UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper();
@Nullable
private String lookupPathAttributeName;
public void setPathMatcher(PathMatcher pathMatcher) {
Assert.notNull(pathMatcher, "PathMatcher must not be null");
this.pathMatcher = pathMatcher;
}
public void setAlwaysUseFullPath(boolean alwaysUseFullPath) {
this.urlPathHelper.setAlwaysUseFullPath(alwaysUseFullPath);
}
public void setUrlDecode(boolean urlDecode) {
this.urlPathHelper.setUrlDecode(urlDecode);
}
public void setLookupPathAttributeName(@Nullable String lookupPathAttributeName) {
this.lookupPathAttributeName = lookupPathAttributeName;
}
public void setRemoveSemicolonContent(boolean removeSemicolonContent) {
this.urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(removeSemicolonContent);
}
public void setUrlPathHelper(UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper) {
Assert.notNull(urlPathHelper, "UrlPathHelper must not be null");
this.urlPathHelper = urlPathHelper;
}
public void setCorsConfigurations(@Nullable Map<String, CorsConfiguration> corsConfigurations) {
this.corsConfigurations.clear();
if (corsConfigurations != null) {
this.corsConfigurations.putAll(corsConfigurations);
}
}
public Map<String, CorsConfiguration> getCorsConfigurations() {
return Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.corsConfigurations);
}
public void registerCorsConfiguration(String path, CorsConfiguration config) {
this.corsConfigurations.put(path, config);
}
}UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource 属性拥有 4 个不同的属性,其中 corsConfigurations 属性保存的是路径模式与跨域配置硬伤、pathMatcher 为使用的路径匹配器,urlPathHelper 属性为路径帮助及 lookupPathAttributeName 保存的是请求 lookupPath 属性名。
2.7.3 getCorsConfiguration 方法实现
public class UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource implements CorsConfigurationSource {
@Override
@Nullable
public CorsConfiguration getCorsConfiguration(HttpServletRequest request) {
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request, this.lookupPathAttributeName);
for (Map.Entry<String, CorsConfiguration> entry : this.corsConfigurations.entrySet()) {
if (this.pathMatcher.match(entry.getKey(), lookupPath)) {
return entry.getValue();
}
}
return null;
}
}getCorsConfiguration 方法获取 corsConfigurations 属性中 key 与 request 路径匹配上的对应 CorsConfiguration 配置并返回。
3. RequestMappingHandlerMapping
RequestMappingHandlerMapping 类作为方法类请求(Controller)的核心处理类,因此本文随后将对其进行分析;
3.1 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
3.1.1 变量
-
常量
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
private static final String SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX = "scopedTarget.";
private static final HandlerMethod PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH =
new HandlerMethod(new EmptyHandler(), ClassUtils.getMethod(EmptyHandler.class, "handle"));
private static final CorsConfiguration ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG = new CorsConfiguration();
static {
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.addAllowedOrigin("*");
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.addAllowedMethod("*");
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.addAllowedHeader("*");
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.setAllowCredentials(true);
}
}AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 类的常量有 3 个,他们分别是标识 scope 作用域代理对象名前缀的 SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX,定义未匹配预检请求通用 HandlerMethod 的 PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH 及允许所有跨域请求的 ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG 常量;
-
类变量
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
private boolean detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts = false;
@Nullable
private HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy<T> namingStrategy;
private final MappingRegistry mappingRegistry = new MappingRegistry();
public void setDetectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts(boolean detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts) {
this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts = detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts;
}
public void setHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy(HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy<T> namingStrategy) {
this.namingStrategy = namingStrategy;
}
@Nullable
public HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy<T> getNamingStrategy() {
return this.namingStrategy;
}
MappingRegistry getMappingRegistry() {
return this.mappingRegistry;
}
}AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 类的 detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts 属性定义是否需要从父上下文中加载 Controller 类,namingStrategy 属性为 handler 处理器命名器以及 mappingRegistry 映射注册器。
3.1.2 方法
-
mappingRegistry 方法
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
public Map<T, HandlerMethod> getHandlerMethods() {
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
return Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings());
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
}getHandlerMethods 方法用于获取 mappingRegistry 注册器中现有的所有只读 HandlerMethod 对象映射;在获取映射的之前需要通过 mappingRegistry 属性的 acquireReadLock 方法获取对应锁,映射获取完成后使用 releaseReadLock 释放读锁。
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
@Nullable
public List<HandlerMethod> getHandlerMethodsForMappingName(String mappingName) {
return this.mappingRegistry.getHandlerMethodsByMappingName(mappingName);
}
}getHandlerMethodsForMappingName 方法用于获取 mappingName 对应的 HandlerMethod 对象列表。
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
public void registerMapping(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Register \"" + mapping + "\" to " + method.toGenericString());
}
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
}registerMapping 方法用于注册处理器,其直接调用 mappingRegistry 属性的 register 方法进行处理器注册。
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
public void unregisterMapping(T mapping) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Unregister mapping \"" + mapping + "\"");
}
this.mappingRegistry.unregister(mapping);
}
}unregisterMapping 方法用于注销处理器,其直接调用 mappingRegistry 属性的 unregister 方法进行注销。
-
afterPropertiesSet 方法
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
protected String[] getCandidateBeanNames() {
return (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
obtainApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
}
protected void handlerMethodsInitialized(Map<T, HandlerMethod> handlerMethods) {
// Total includes detected mappings + explicit registrations via registerMapping
int total = handlerMethods.size();
if ((logger.isTraceEnabled() && total == 0) || (logger.isDebugEnabled() && total > 0) ) {
logger.debug(total + " mappings in " + formatMappingName());
}
}
}afterPropertiesSet 方法在 spring 容器属性设置完成后,调用 initHandlerMethods 方法对处理器方法进行初始化;initHandlerMethods 方法遍历 getCandidateBeanNames 方法获取所有候选对象名(detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts 为 true 时会获取包含父上下文的所有对象名,否则只获取当前上下文的所有对象名),调用 processCandidateBean 依次处理非作用域代理对象并在处理完成后调用 handlerMethodsInitialized 方法对方法进行初始化。
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
protected abstract boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType);
}processCandidateBean 方法在获取上下文中 beanName 参数对应类型,若子类的 isHandler 判断该类为处理器时,进一步调用 detectHandlerMethods 方法来定义处理器方法;
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
@Nullable
protected abstract T getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType);
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
}detectHandlerMethods 方法用于获取并注册指定对象中属于处理器的方法;其通过 MethodIntrospector 类的 selectMethods 方法获取 handler 类型中通过 getMappingForMethod 方法获取到的方法映射; 最后逐一调用 registerHandlerMethod 方法将获取到的方法进行注册;
-
getHandlerInternal 方法
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
@Override
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
request.setAttribute(LOOKUP_PATH, lookupPath);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
}getHandlerInternal 方法首先使用 UrlPathHelper 获取 request 请求对应的 lookupPath 并保存到请求的 LOOKUP_PATH 属性中;随后调用 lookupHandlerMethod 方法获取对应的 HandlerMethod 对象,并在其不为空时直接调用其的 createWithResolvedBean 方法创建对象并返回,在查询 HandlerMethod 对象的过程中也会调用 acquireReadLock 方法加锁,并在获取完了之后调用 releaseReadLock 对读锁进行释放。
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod);
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
for (T mapping : mappings) {
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
if (match != null) {
matches.add(new Match(match, this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().get(mapping)));
}
}
}
protected void handleMatch(T mapping, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) {
request.setAttribute(HandlerMapping.PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE, lookupPath);
}
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod handleNoMatch(Set<T> mappings, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request)
throws Exception {
return null;
}
@Nullable
protected abstract T getMatchingMapping(T mapping, HttpServletRequest request);
}lookupHandlerMethod 方法首先尝试获取 mappingRegistry 中 lookupPath 对应的匹配器集合,获取到了之后通过 addMatchingMappings 方法将匹配上的 Match 对象保存至 matches 变量之中,未获取到则会将 mappingRegistry 属性中匹配的 Match 匹配器保存到 matches 变量之中;若通过上述处理,matches 变量为空时调用 handleNoMatch 方法进行不存在匹配器处理;否则通过 getMappingComparator 获取比较器并通过比较器获取最佳 Match 匹配器,值得注意的是,若存在多个匹配项且请求为跨域预检请求时直接返回 PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH 常量值;随后将最佳匹配的处理方法绑定到请求的 BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE 属性之中,并调用 handleMatch 方法进行处理并返回最佳匹配的处理方法。
-
hasCorsConfigurationSource 方法
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
@Override
protected boolean hasCorsConfigurationSource(Object handler) {
return super.hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) ||
(handler instanceof HandlerMethod && this.mappingRegistry.getCorsConfiguration((HandlerMethod) handler) != null);
}
}AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 类扩展了 hasCorsConfigurationSource 方法,其除了父类的 hasCorsConfigurationSource 方法判断是否拥有跨域配置源时,还扩展了对 mappingRegistry 中是否拥有 handler 对应的跨域配置源判断。
-
getCorsConfiguration 方法
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
@Override
protected CorsConfiguration getCorsConfiguration(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = super.getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
if (handler instanceof HandlerMethod) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
if (handlerMethod.equals(PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH)) {
return AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG;
}
else {
CorsConfiguration corsConfigFromMethod = this.mappingRegistry.getCorsConfiguration(handlerMethod);
corsConfig = (corsConfig != null ? corsConfig.combine(corsConfigFromMethod) : corsConfigFromMethod);
}
}
return corsConfig;
}
}getCorsConfiguration 方法在 handler 与 PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH 相等时,直接返回 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 类的 ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG 常量值;否则将通过父类的 getCorsConfiguration 方法获取到的跨域配置与通过 mappingRegistry 属性获取到的 handlerMethod 对应跨域配置进行合并然后返回。
3.1.3 内部类
-
MappingRegistry 类
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
class MappingRegistry {
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();
private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> mappingLookup = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> urlLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
private final Map<String, List<HandlerMethod>> nameLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Map<HandlerMethod, CorsConfiguration> corsLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
public Map<T, HandlerMethod> getMappings() {
return this.mappingLookup;
}
@Nullable
public List<T> getMappingsByUrl(String urlPath) {
return this.urlLookup.get(urlPath);
}
public List<HandlerMethod> getHandlerMethodsByMappingName(String mappingName) {
return this.nameLookup.get(mappingName);
}
@Nullable
public CorsConfiguration getCorsConfiguration(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
HandlerMethod original = handlerMethod.getResolvedFromHandlerMethod();
return this.corsLookup.get(original != null ? original : handlerMethod);
}
public void acquireReadLock() {
this.readWriteLock.readLock().lock();
}
public void releaseReadLock() {
this.readWriteLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
}MappingRegistry 内部类有 6 个属性,分别为处理器注册器映射 registry 属性,保存 T 类型 mapping 与 HandlerMethod 对象映射的 mappingLookup 属性,保存 url 路径与 T 类型 mapping 对象映射的 urlLookup 属性;nameLookup 属性保存名称与 HandlerMethod 对象映射;corsLookup 属性则为 HandlerMethod 对象与 CorsConfiguration 跨域配置映射,readWriteLock 为当前注册器的读写锁。
register 方法
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
class MappingRegistry {
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
// Assert that the handler method is not a suspending one.
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if ((parameterTypes.length > 0) && "kotlin.coroutines.Continuation".equals(parameterTypes[parameterTypes.length - 1].getName())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unsupported suspending handler method detected: " + method);
}
}
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
private void validateMethodMapping(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, T mapping) {
// Assert that the supplied mapping is unique.
HandlerMethod existingHandlerMethod = this.mappingLookup.get(mapping);
if (existingHandlerMethod != null && !existingHandlerMethod.equals(handlerMethod)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous mapping. Cannot map '" + handlerMethod.getBean() + "' method \n" +
handlerMethod + "\nto " + mapping + ": There is already '" +
existingHandlerMethod.getBean() + "' bean method\n" + existingHandlerMethod + " mapped.");
}
}
}
@Nullable
protected CorsConfiguration initCorsConfiguration(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
return null;
}
}register 方法不支持 kotlin 的协程挂起方法,因此其首先判断方法是否为 kotlin 的协程挂起方法,若为则会抛出异常;随后调用 readWriteLock 属性加上写锁,随后调用依次调用 createHandlerMethod 、validateMethodMapping 方法创建 HandlerMethod 对象并进行重复添加验证,在通过后将 mapping 与 HandlerMethod 对象映射保存到 mappingLookup 属性之中;随后将通过 getDirectUrls 获取到的所有 url 路径与 mapping 参数映射保存到 urlLookup 属性之中;随后若 namingStrategy 属性不为空,则会调用其生成名称并将与 HandlerMethod 对象的映射关系保存到 nameLookup 属性之中;随后将 handlerMethod 对象与通过 initCorsConfiguration 方法初始化的 CorsConfiguration 跨域配置对象映射保存到 corsLookup 对象之中;最后将 mapping 参数与新建的 MappingRegistration 对象映射保存到 registry 属性之中后为 readWriteLock 属性的写锁进行解锁。
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
class MappingRegistry {
private List<String> getDirectUrls(T mapping) {
List<String> urls = new ArrayList<>(1);
for (String path : getMappingPathPatterns(mapping)) {
if (!getPathMatcher().isPattern(path)) {
urls.add(path);
}
}
return urls;
}
}
protected abstract Set<String> getMappingPathPatterns(T mapping);
}getDirectUrls 方法将 getMappingPathPatterns 方法获取到的 url 字符串路径列表通过 PathMatcher 属性的 isPattern 方法(非 pathMatcher 属性类型表达式)过滤后返回;
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
class MappingRegistry {
private void addMappingName(String name, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
List<HandlerMethod> oldList = this.nameLookup.get(name);
if (oldList == null) {
oldList = Collections.emptyList();
}
for (HandlerMethod current : oldList) {
if (handlerMethod.equals(current)) {
return;
}
}
List<HandlerMethod> newList = new ArrayList<>(oldList.size() + 1);
newList.addAll(oldList);
newList.add(handlerMethod);
this.nameLookup.put(name, newList);
}
}
}addMappingName 方法将 handlerMethod 参数保存到 nameLookup 中 name 对应的列表之中;其中若以保存则直接返回。
unregister 方法
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
class MappingRegistry {
public void unregister(T mapping) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
MappingRegistration<T> definition = this.registry.remove(mapping);
if (definition == null) {
return;
}
this.mappingLookup.remove(definition.getMapping());
for (String url : definition.getDirectUrls()) {
List<T> list = this.urlLookup.get(url);
if (list != null) {
list.remove(definition.getMapping());
if (list.isEmpty()) {
this.urlLookup.remove(url);
}
}
}
removeMappingName(definition);
this.corsLookup.remove(definition.getHandlerMethod());
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
private void removeMappingName(MappingRegistration<T> definition) {
String name = definition.getMappingName();
if (name == null) {
return;
}
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = definition.getHandlerMethod();
List<HandlerMethod> oldList = this.nameLookup.get(name);
if (oldList == null) {
return;
}
if (oldList.size() <= 1) {
this.nameLookup.remove(name);
return;
}
List<HandlerMethod> newList = new ArrayList<>(oldList.size() - 1);
for (HandlerMethod current : oldList) {
if (!current.equals(handlerMethod)) {
newList.add(current);
}
}
this.nameLookup.put(name, newList);
}
}
}unregister 方法首先也是调用 readWriteLock 属性加上写锁,随后依次移除 registry、mappingLookup、urlLookup、nameLookup 及 corsLookup 属性中对应映射值,在移除完成后释放写锁。
-
MappingRegistration 类
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
private static class MappingRegistration<T> {
private final T mapping;
private final HandlerMethod handlerMethod;
private final List<String> directUrls;
@Nullable
private final String mappingName;
public MappingRegistration(T mapping, HandlerMethod handlerMethod,
@Nullable List<String> directUrls, @Nullable String mappingName) {
Assert.notNull(mapping, "Mapping must not be null");
Assert.notNull(handlerMethod, "HandlerMethod must not be null");
this.mapping = mapping;
this.handlerMethod = handlerMethod;
this.directUrls = (directUrls != null ? directUrls : Collections.emptyList());
this.mappingName = mappingName;
}
public T getMapping() {
return this.mapping;
}
public HandlerMethod getHandlerMethod() {
return this.handlerMethod;
}
public List<String> getDirectUrls() {
return this.directUrls;
}
@Nullable
public String getMappingName() {
return this.mappingName;
}
}
}MappingRegistration 内部类用于保存处理器的相关属性值,其包含了 T 类型 mapping 映射对象、HandlerMethod 处理器方法对象、对应所有 url 字符串路径列表及 mappingName 处理器方法名称。
-
Match 类
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
private class Match {
private final T mapping;
private final HandlerMethod handlerMethod;
public Match(T mapping, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
this.mapping = mapping;
this.handlerMethod = handlerMethod;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.mapping.toString();
}
}
}Match 内部类用于对 mapping 与对应 HandlerMethod 对象的封装。
-
MatchComparator 类
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
private class MatchComparator implements Comparator<Match> {
private final Comparator<T> comparator;
public MatchComparator(Comparator<T> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
@Override
public int compare(Match match1, Match match2) {
return this.comparator.compare(match1.mapping, match2.mapping);
}
}
}MatchComparator 内部类用于 Match 封装类的比较器,其 compare 方法直接对应 Match 对象的 mapping 属性。
3.2 HandlerMethod
3.2.1 变量
public class HandlerMethod {
private final Object bean;
@Nullable
private final BeanFactory beanFactory;
private final Class<?> beanType;
private final Method method;
private final Method bridgedMethod;
private final MethodParameter[] parameters;
@Nullable
private HttpStatus responseStatus;
@Nullable
private String responseStatusReason;
@Nullable
private HandlerMethod resolvedFromHandlerMethod;
@Nullable
private volatile List<Annotation[][]> interfaceParameterAnnotations;
private final String description;
public Object getBean() {
return this.bean;
}
public Method getMethod() {
return this.method;
}
public Class<?> getBeanType() {
return this.beanType;
}
protected Method getBridgedMethod() {
return this.bridgedMethod;
}
public MethodParameter[] getMethodParameters() {
return this.parameters;
}
@Nullable
protected HttpStatus getResponseStatus() {
return this.responseStatus;
}
@Nullable
protected String getResponseStatusReason() {
return this.responseStatusReason;
}
@Nullable
public HandlerMethod getResolvedFromHandlerMethod() {
return this.resolvedFromHandlerMethod;
}
}HandlerMethod 类为处理器方法封装类,其保存了处理器方法的相关属性,其中 bean 保存的是处理器对象,beanFactory 为处理器对象工厂,处理器类型 beanType,保存处理器原始及桥接方法的 method 及 bridgedMethod 属性,方法封装参数数组 parameters;ResponseStatus 注解的 responseStatus 与 responseStatusReason 属性值,resolvedFromHandlerMethod 属性保存的则是重复创建的处理器方法的源 HandlerMethod 对象;interfaceParameterAnnotations 属性保存的是对应顶层接口方法的所有参数注解;description 则是保存了处理器类名、方法名及参数名的描述。
3.2.2 方法
-
构造方法
HandlerMethod 类拥有 5 个构造方法,其中前三个修饰符为 public,提供给外部创建对象,第四个则是提供给子类使用的 protected 修饰符修饰的构造方法;最后一个则是私有的,提供给 createWithResolvedBean 方法使用;
public class HandlerMethod {
public HandlerMethod(Object bean, Method method) {
Assert.notNull(bean, "Bean is required");
Assert.notNull(method, "Method is required");
this.bean = bean;
this.beanFactory = null;
this.beanType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(bean);
this.method = method;
this.bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
this.parameters = initMethodParameters();
evaluateResponseStatus();
this.description = initDescription(this.beanType, this.method);
}
public HandlerMethod(Object bean, String methodName, Class<?>... parameterTypes) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Assert.notNull(bean, "Bean is required");
Assert.notNull(methodName, "Method name is required");
this.bean = bean;
this.beanFactory = null;
this.beanType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(bean);
this.method = bean.getClass().getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
this.bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(this.method);
this.parameters = initMethodParameters();
evaluateResponseStatus();
this.description = initDescription(this.beanType, this.method);
}
public HandlerMethod(String beanName, BeanFactory beanFactory, Method method) {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name is required");
Assert.notNull(beanFactory, "BeanFactory is required");
Assert.notNull(method, "Method is required");
this.bean = beanName;
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
Class<?> beanType = beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot resolve bean type for bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
this.beanType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(beanType);
this.method = method;
this.bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
this.parameters = initMethodParameters();
evaluateResponseStatus();
this.description = initDescription(this.beanType, this.method);
}
}三个 public 修饰的构造方法在设置完其他属性后依次调用 initMethodParameters 方法获取方法参数保存到 parameters 属性之中,同时调用 evaluateResponseStatus 方法解析 ResponseStatus 注解。
public class HandlerMethod {
private MethodParameter[] initMethodParameters() {
int count = this.bridgedMethod.getParameterCount();
MethodParameter[] result = new MethodParameter[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
result[i] = new HandlerMethodParameter(i);
}
return result;
}
}initMethodParameters 方法利用 bridgedMethod 桥接方法创建 HandlerMethodParameter 对象数组并返回;
public class HandlerMethod {
private void evaluateResponseStatus() {
ResponseStatus annotation = getMethodAnnotation(ResponseStatus.class);
if (annotation == null) {
annotation = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(getBeanType(), ResponseStatus.class);
}
if (annotation != null) {
this.responseStatus = annotation.code();
this.responseStatusReason = annotation.reason();
}
}
}evaluateResponseStatus 方法获取方法或类上的 ResponseStatus 注解,并将其中的 code 与 reason 分别保存到 responseStatus 与 responseStatusReason 属性之中;
public class HandlerMethod {
protected HandlerMethod(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
Assert.notNull(handlerMethod, "HandlerMethod is required");
this.bean = handlerMethod.bean;
this.beanFactory = handlerMethod.beanFactory;
this.beanType = handlerMethod.beanType;
this.method = handlerMethod.method;
this.bridgedMethod = handlerMethod.bridgedMethod;
this.parameters = handlerMethod.parameters;
this.responseStatus = handlerMethod.responseStatus;
this.responseStatusReason = handlerMethod.responseStatusReason;
this.description = handlerMethod.description;
this.resolvedFromHandlerMethod = handlerMethod.resolvedFromHandlerMethod;
}
private HandlerMethod(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Object handler) {
Assert.notNull(handlerMethod, "HandlerMethod is required");
Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object is required");
this.bean = handler;
this.beanFactory = handlerMethod.beanFactory;
this.beanType = handlerMethod.beanType;
this.method = handlerMethod.method;
this.bridgedMethod = handlerMethod.bridgedMethod;
this.parameters = handlerMethod.parameters;
this.responseStatus = handlerMethod.responseStatus;
this.responseStatusReason = handlerMethod.responseStatusReason;
this.resolvedFromHandlerMethod = handlerMethod;
this.description = handlerMethod.description;
}
}其余构造方法直接复制 handlerMethod 参数中的大部分属性,其中 protected 修饰的构造方法是参数全量复制,而 private 修饰的则是将 bean 属性赋值为 handler 参数,resolvedFromHandlerMethod 属性赋值为 handlerMethod 参数值;
-
ReturnType 方法
public class HandlerMethod {
public MethodParameter getReturnType() {
return new HandlerMethodParameter(-1);
}
}getReturnType 方法用户获取方法返回类型的 MethodParameter 封装,其直接使用 -1 创建 HandlerMethodParameter 对象并返回(在 SynthesizingMethodParameter 属性中返回值索引为 -1)。
public class HandlerMethod {
public MethodParameter getReturnValueType(@Nullable Object returnValue) {
return new ReturnValueMethodParameter(returnValue);
}
}getReturnValueType 方法用于创建封装实际返回值的封装,直接使用 ReturnValueMethodParameter 封装 returnValue 参数值并返回。
public class HandlerMethod {
public boolean isVoid() {
return Void.TYPE.equals(getReturnType().getParameterType());
}
}isVoid 方法用于判断方法是否为无返参方法,直接判断返回参数类型是否为 Void。
-
MethodAnnotation 方法
public class HandlerMethod {
@Nullable
public <A extends Annotation> A getMethodAnnotation(Class<A> annotationType) {
return AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(this.method, annotationType);
}
public <A extends Annotation> boolean hasMethodAnnotation(Class<A> annotationType) {
return AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(this.method, annotationType);
}
}getMethodAnnotation 与 hasMethodAnnotation 方法分别用于获取方法指定注解与判断是否存在指定注解。
-
createWithResolvedBean 方法
public class HandlerMethod {
public HandlerMethod createWithResolvedBean() {
Object handler = this.bean;
if (this.bean instanceof String) {
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "Cannot resolve bean name without BeanFactory");
String beanName = (String) this.bean;
handler = this.beanFactory.getBean(beanName);
}
return new HandlerMethod(this, handler);
}
}createWithResolvedBean 方法用于将当前 HandlerMethod 对象复制为一个新的 HandlerMethod 对象并返回,其中若只提供了字符串类型的 bean 属性(对象名),则会首先从 beanFactory 对象工厂属性中解析获取出来。
3.2.3 内部类
-
HandlerMethodParameter
HandlerMethodParameter 类继承自 SynthesizingMethodParameter 类,专门用于封装处理器元方法参数,其扩展了 SynthesizingMethodParameter 类的一些注解获取功能,使其能更有效处理处理器方法参数;
public class HandlerMethod {
protected class HandlerMethodParameter extends SynthesizingMethodParameter {
@Nullable
private volatile Annotation[] combinedAnnotations;
}
}其只有一个用于缓存参数注解的 combinedAnnotations 注解;
public class HandlerMethod {
protected class HandlerMethodParameter extends SynthesizingMethodParameter {
public HandlerMethodParameter(int index) {
super(HandlerMethod.this.bridgedMethod, index);
}
protected HandlerMethodParameter(HandlerMethodParameter original) {
super(original);
}
}
}HandlerMethodParameter 类拥有两个构造方法,其一使用当前桥接方法及参数索引值调用父对象对应构造器创建 HandlerMethodParameter 对象,另一个则是直接使用已有 HandlerMethodParameter 对象进行创建;
public class HandlerMethod {
protected class HandlerMethodParameter extends SynthesizingMethodParameter {
@Override
public Class<?> getContainingClass() {
return HandlerMethod.this.getBeanType();
}
}
}HandlerMethodParameter 类首先重写了 getContainingClass 方法,其直接获取 beanType 对象类型属性;
public class HandlerMethod {
protected class HandlerMethodParameter extends SynthesizingMethodParameter {
@Override
public <T extends Annotation> T getMethodAnnotation(Class<T> annotationType) {
return HandlerMethod.this.getMethodAnnotation(annotationType);
}
@Override
public <T extends Annotation> boolean hasMethodAnnotation(Class<T> annotationType) {
return HandlerMethod.this.hasMethodAnnotation(annotationType);
}
@Override
public Annotation[] getParameterAnnotations() {
Annotation[] anns = this.combinedAnnotations;
if (anns == null) {
anns = super.getParameterAnnotations();
int index = getParameterIndex();
if (index >= 0) {
for (Annotation[][] ifcAnns : getInterfaceParameterAnnotations()) {
if (index < ifcAnns.length) {
Annotation[] paramAnns = ifcAnns[index];
if (paramAnns.length > 0) {
List<Annotation> merged = new ArrayList<>(anns.length + paramAnns.length);
merged.addAll(Arrays.asList(anns));
for (Annotation paramAnn : paramAnns) {
boolean existingType = false;
for (Annotation ann : anns) {
if (ann.annotationType() == paramAnn.annotationType()) {
existingType = true;
break;
}
}
if (!existingType) {
merged.add(adaptAnnotation(paramAnn));
}
}
anns = merged.toArray(new Annotation[0]);
}
}
}
}
this.combinedAnnotations = anns;
}
return anns;
}
}
}HandlerMethodParameter 类重写了三个注解相关方法,其中 getMethodAnnotation 与 hasMethodAnnotation 方法使用直接调用所属 HandlerMethod 对象的对应方法进行优化;getParameterAnnotations 方法则首先尝试从 combinedAnnotations 缓存中去获取,若还未缓存则会首先调用父类的 getParameterAnnotations 方法获取参数的直接注解,同时遍历处理器方法所实现的所有接口方法的注解,将指定索引处的所有注解与原始注解进行去重合并并保存到 combinedAnnotations 缓存之中然后返回;
public class HandlerMethod {
private List<Annotation[][]> getInterfaceParameterAnnotations() {
List<Annotation[][]> parameterAnnotations = this.interfaceParameterAnnotations;
if (parameterAnnotations == null) {
parameterAnnotations = new ArrayList<>();
for (Class<?> ifc : ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(this.method.getDeclaringClass())) {
for (Method candidate : ifc.getMethods()) {
if (isOverrideFor(candidate)) {
parameterAnnotations.add(candidate.getParameterAnnotations());
}
}
}
this.interfaceParameterAnnotations = parameterAnnotations;
}
return parameterAnnotations;
}
}getInterfaceParameterAnnotations 方法用户获取处理器所实现的顶级接口方法中的参数注解数组列表,一个元素保存的是一个所实现的接口方法的注解二维数组;
-
ReturnValueMethodParameter
public class HandlerMethod {
private class ReturnValueMethodParameter extends HandlerMethodParameter {
@Nullable
private final Class<?> returnValueType;
public ReturnValueMethodParameter(@Nullable Object returnValue) {
super(-1);
this.returnValueType = (returnValue != null ? returnValue.getClass() : null);
}
protected ReturnValueMethodParameter(ReturnValueMethodParameter original) {
super(original);
this.returnValueType = original.returnValueType;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getParameterType() {
return (this.returnValueType != null ? this.returnValueType : super.getParameterType());
}
@Override
public ReturnValueMethodParameter clone() {
return new ReturnValueMethodParameter(this);
}
}
}ReturnValueMethodParameter 类为方法返回参数封装类,其中 returnValueType 属性保存的是返参类型;
3.3 RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
3.3.1 变量
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
private static final Method HTTP_OPTIONS_HANDLE_METHOD;
static {
try {
HTTP_OPTIONS_HANDLE_METHOD = HttpOptionsHandler.class.getMethod("handle");
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
// Should never happen
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to retrieve internal handler method for HTTP OPTIONS", ex);
}
}
}RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping 类只有一个保存 http options 请求处理方法的 HTTP_OPTIONS_HANDLE_METHOD 常量,其在类加载时直接在静态代码块中赋值为 HttpOptionsHandler 类的 handle 方法。
3.3.2 方法
(1)构造方法
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
protected RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping() {
setHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy(new RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy());
}
}RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping 类只只提供了一个无参构造方法,其只是将 handlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy 命名策略属性设置为 RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy 对象。
(2)抽象方法实现
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
@Override
protected Set<String> getMappingPathPatterns(RequestMappingInfo info) {
return info.getPatternsCondition().getPatterns();
}
@Override
protected RequestMappingInfo getMatchingMapping(RequestMappingInfo info, HttpServletRequest request) {
return info.getMatchingCondition(request);
}
@Override
protected Comparator<RequestMappingInfo> getMappingComparator(final HttpServletRequest request) {
return (info1, info2) -> info1.compareTo(info2, request);
}
}getMappingPathPatterns、getMatchingMapping 及 getMappingComparator 三个抽象方法的实现,都是直接通过调用 RequestMappingInfo 类型 info 参数对应方法实现的;
(3)getHandlerInternal 方法扩展
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
@Override
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
request.removeAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
try {
return super.getHandlerInternal(request);
}
finally {
ProducesRequestCondition.clearMediaTypesAttribute(request);
}
}
}getHandlerInternal 方法扩展了 request 请求参数的 PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE 属性的移除及 MediaTypes 相关属性的清理;
(4)单 mapping 参数 handleMatch 方法扩展
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
@Override
protected void handleMatch(RequestMappingInfo info, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) {
super.handleMatch(info, lookupPath, request);
String bestPattern;
Map<String, String> uriVariables;
Set<String> patterns = info.getPatternsCondition().getPatterns();
if (patterns.isEmpty()) {
bestPattern = lookupPath;
uriVariables = Collections.emptyMap();
}
else {
bestPattern = patterns.iterator().next();
uriVariables = getPathMatcher().extractUriTemplateVariables(bestPattern, lookupPath);
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE, bestPattern);
if (isMatrixVariableContentAvailable()) {
Map<String, MultiValueMap<String, String>> matrixVars = extractMatrixVariables(request, uriVariables);
request.setAttribute(HandlerMapping.MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE, matrixVars);
}
Map<String, String> decodedUriVariables = getUrlPathHelper().decodePathVariables(request, uriVariables);
request.setAttribute(HandlerMapping.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE, decodedUriVariables);
if (!info.getProducesCondition().getProducibleMediaTypes().isEmpty()) {
Set<MediaType> mediaTypes = info.getProducesCondition().getProducibleMediaTypes();
request.setAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE, mediaTypes);
}
}
}handleMatch 方法扩展在调用了父类的 handleMatch 方法后,获取 info 参数中所有表达式集合,若获取到的集合不为空,则分别将 bestPattern 与 uriVariables 局部变量值更新为第一个表达式及从 lookupPath 路径中提取的路径参数值映射集合,否则分别将其更新为 lookupPath 参数及空映射集合,并在赋值完成后将 bestPattern 变量值绑定到 request 请求的 BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE 属性之中;之后若启用了矩阵传参,则需要调用 extractMatrixVariables 方法提取矩阵参数并与 MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE 属性绑定相绑定;最后分别将解码后的路径参数映射与媒体类型响应许可列表集合分别绑定到 URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE 与 PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE 属性上。
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
private boolean isMatrixVariableContentAvailable() {
return !getUrlPathHelper().shouldRemoveSemicolonContent();
}
private Map<String, MultiValueMap<String, String>> extractMatrixVariables(
HttpServletRequest request, Map<String, String> uriVariables) {
Map<String, MultiValueMap<String, String>> result = new LinkedHashMap<>();
uriVariables.forEach((uriVarKey, uriVarValue) -> {
int equalsIndex = uriVarValue.indexOf('=');
if (equalsIndex == -1) {
return;
}
int semicolonIndex = uriVarValue.indexOf(';');
if (semicolonIndex != -1 && semicolonIndex != 0) {
uriVariables.put(uriVarKey, uriVarValue.substring(0, semicolonIndex));
}
String matrixVariables;
if (semicolonIndex == -1 || semicolonIndex == 0 || equalsIndex < semicolonIndex) {
matrixVariables = uriVarValue;
}
else {
matrixVariables = uriVarValue.substring(semicolonIndex + 1);
}
MultiValueMap<String, String> vars = WebUtils.parseMatrixVariables(matrixVariables);
result.put(uriVarKey, getUrlPathHelper().decodeMatrixVariables(request, vars));
});
return result;
}
}isMatrixVariableContentAvailable 方法通过 urlPathHelper 属性的 shouldRemoveSemicolonContent 方法判断是否禁用矩阵参数。extractMatrixVariables 方法通过对路径参数中的 ; 分割来提取真正路径参数及矩阵参数,其中 ; 号前的部分就是实际路径参数值,后半部分则是矩阵参数,他的名称与值与 query 参数一样都是通过 = 进行分割的。
(5)mapping 集合参数 handleMatch 方法扩展
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
@Override
protected HandlerMethod handleNoMatch(
Set<RequestMappingInfo> infos, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws ServletException {
PartialMatchHelper helper = new PartialMatchHelper(infos, request);
if (helper.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
if (helper.hasMethodsMismatch()) {
Set<String> methods = helper.getAllowedMethods();
if (HttpMethod.OPTIONS.matches(request.getMethod())) {
HttpOptionsHandler handler = new HttpOptionsHandler(methods);
return new HandlerMethod(handler, HTTP_OPTIONS_HANDLE_METHOD);
}
throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(request.getMethod(), methods);
}
if (helper.hasConsumesMismatch()) {
Set<MediaType> mediaTypes = helper.getConsumableMediaTypes();
MediaType contentType = null;
if (StringUtils.hasLength(request.getContentType())) {
try {
contentType = MediaType.parseMediaType(request.getContentType());
}
catch (InvalidMediaTypeException ex) {
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException(ex.getMessage());
}
}
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException(contentType, new ArrayList<>(mediaTypes));
}
if (helper.hasProducesMismatch()) {
Set<MediaType> mediaTypes = helper.getProducibleMediaTypes();
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(new ArrayList<>(mediaTypes));
}
if (helper.hasParamsMismatch()) {
List<String[]> conditions = helper.getParamConditions();
throw new UnsatisfiedServletRequestParameterException(conditions, request.getParameterMap());
}
return null;
}
}mapping 集合参数 handleMatch 方法首先使用 mapping 集合与 request 请求对象创建 PartialMatchHelper 聚合匹配器对象;在 PartialMatchHelper 对象不匹配请求方法时,除了 OPTIONS 请求会使用 HTTP_OPTIONS_HANDLE_METHOD 值创建 HandlerMethod 对象并返回之外,都是直接抛出 HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException 异常;PartialMatchHelper 对象不支持当前请求的媒体类型时直接抛出 HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException 异常;PartialMatchHelper 对象不支持当前需要响应的媒体类型时则会直接抛出 HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException 异常;缺少必要参数时则会抛出 UnsatisfiedServletRequestParameterException 异常。
3.3.3 内部类
(1)PartialMatchHelper
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
private static class PartialMatchHelper {
private final List<PartialMatch> partialMatches = new ArrayList<>();
public PartialMatchHelper(Set<RequestMappingInfo> infos, HttpServletRequest request) {
for (RequestMappingInfo info : infos) {
if (info.getPatternsCondition().getMatchingCondition(request) != null) {
this.partialMatches.add(new PartialMatch(info, request));
}
}
}
}
}PartialMatchHelper 类只有一个 PartialMatch 列表属性用于保存所有 RequestMappingInfo 创建的 PartialMatch 对向。
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
private static class PartialMatchHelper {
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.partialMatches.isEmpty();
}
}
}PartialMatchHelper 类的 isEmpty 方法用于判断内部 partialMatches 属性是否为空;
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
private static class PartialMatchHelper {
public boolean hasMethodsMismatch() {
for (PartialMatch match : this.partialMatches) {
if (match.hasMethodsMatch()) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean hasConsumesMismatch() {
for (PartialMatch match : this.partialMatches) {
if (match.hasConsumesMatch()) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean hasProducesMismatch() {
for (PartialMatch match : this.partialMatches) {
if (match.hasProducesMatch()) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean hasParamsMismatch() {
for (PartialMatch match : this.partialMatches) {
if (match.hasParamsMatch()) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
}PartialMatchHelper 拥有 4 个属性判断方法,分别为判断是否所有 PartialMatch 元素的方法都不匹配的 hasMethodsMismatch 、方法与请求媒体类型都不匹配的 hasConsumesMismatch、方法、请求与响应媒体类型都不匹配的 hasProducesMismatch 以及方法、请求与响应媒体类型及参数都不匹配的 hasParamsMismatch 方法;他们都是依次调用元素中的对应方法,存在任何反例时直接返回 false,否则返回 true;
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
private static class PartialMatchHelper {
public Set<String> getAllowedMethods() {
Set<String> result = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (PartialMatch match : this.partialMatches) {
for (RequestMethod method : match.getInfo().getMethodsCondition().getMethods()) {
result.add(method.name());
}
}
return result;
}
public Set<MediaType> getConsumableMediaTypes() {
Set<MediaType> result = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (PartialMatch match : this.partialMatches) {
if (match.hasMethodsMatch()) {
result.addAll(match.getInfo().getConsumesCondition().getConsumableMediaTypes());
}
}
return result;
}
public Set<MediaType> getProducibleMediaTypes() {
Set<MediaType> result = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (PartialMatch match : this.partialMatches) {
if (match.hasConsumesMatch()) {
result.addAll(match.getInfo().getProducesCondition().getProducibleMediaTypes());
}
}
return result;
}
public List<String[]> getParamConditions() {
List<String[]> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (PartialMatch match : this.partialMatches) {
if (match.hasProducesMatch()) {
Set<NameValueExpression<String>> set = match.getInfo().getParamsCondition().getExpressions();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(set)) {
int i = 0;
String[] array = new String[set.size()];
for (NameValueExpression<String> expression : set) {
array[i++] = expression.toString();
}
result.add(array);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
}最后 PartialMatchHelper 拥有 4 个属性获取方法,分别为获取所有匹配方法名的 getAllowedMethods、获取支持的请求媒体类型的 getConsumableMediaTypes、获取支持的响应媒体类型的 getProducibleMediaTypes 及获取所有参数名集合的 getParamConditions 方法;都是依次调用元素中的对应方法并组合所有结果并返回。
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
private static class PartialMatchHelper {
private static class PartialMatch {
private final RequestMappingInfo info;
private final boolean methodsMatch;
private final boolean consumesMatch;
private final boolean producesMatch;
private final boolean paramsMatch;
public PartialMatch(RequestMappingInfo info, HttpServletRequest request) {
this.info = info;
this.methodsMatch = (info.getMethodsCondition().getMatchingCondition(request) != null);
this.consumesMatch = (info.getConsumesCondition().getMatchingCondition(request) != null);
this.producesMatch = (info.getProducesCondition().getMatchingCondition(request) != null);
this.paramsMatch = (info.getParamsCondition().getMatchingCondition(request) != null);
}
public RequestMappingInfo getInfo() {
return this.info;
}
public boolean hasMethodsMatch() {
return this.methodsMatch;
}
public boolean hasConsumesMatch() {
return (hasMethodsMatch() && this.consumesMatch);
}
public boolean hasProducesMatch() {
return (hasConsumesMatch() && this.producesMatch);
}
public boolean hasParamsMatch() {
return (hasProducesMatch() && this.paramsMatch);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.info.toString();
}
}
}
}PartialMatch 内部类用于 5 个属性,分别为 RequestMappingInfo 处理器及 4 个状态标识,其中状态标识通过创建时 info 与 request 请求综合计算所得。
(2)HttpOptionsHandler
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
private static class HttpOptionsHandler {
private final HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
public HttpOptionsHandler(Set<String> declaredMethods) {
this.headers.setAllow(initAllowedHttpMethods(declaredMethods));
}
private static Set<HttpMethod> initAllowedHttpMethods(Set<String> declaredMethods) {
Set<HttpMethod> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(declaredMethods.size());
if (declaredMethods.isEmpty()) {
for (HttpMethod method : HttpMethod.values()) {
if (method != HttpMethod.TRACE) {
result.add(method);
}
}
}
else {
for (String method : declaredMethods) {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.valueOf(method);
result.add(httpMethod);
if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.GET) {
result.add(HttpMethod.HEAD);
}
}
result.add(HttpMethod.OPTIONS);
}
return result;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public HttpHeaders handle() {
return this.headers;
}
}
}HttpOptionsHandler 类为 Options 请求的默认处理器,其只有一个保存请求头对象的 headers 属性用于 handle 请求处理时返回;其值根据对象创建时传入的方法集合进行初始化,在为传入任何方法时,会将除 TRACE 之外的所有 HTTP 方法保存至该属性之中,否则只是将传入的方法及 OPTIONS 保存至该属性之中。
3.4 RequestMappingHandlerMapping
3.4.1 实现接口
RequestMappingHandlerMapping 类在继承了 RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping 类之外,还实现了 MatchableHandlerMapping 与 EmbeddedValueResolverAware 接口。
(1)MatchableHandlerMapping 接口
public interface MatchableHandlerMapping extends HandlerMapping {
@Nullable
RequestMatchResult match(HttpServletRequest request, String pattern);
}MatchableHandlerMapping 接口只定义了一个 match 方法,用于判断 request 是否与 pattern 表达式相匹配。
(2)EmbeddedValueResolverAware 接口
public interface EmbeddedValueResolverAware extends Aware {
void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver resolver);
}EmbeddedValueResolverAware 接口用于注入 StringValueResolver 字符串值解析器。
3.4.2 变量
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
private boolean useSuffixPatternMatch = true;
private boolean useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch = false;
private boolean useTrailingSlashMatch = true;
private Map<String, Predicate<Class<?>>> pathPrefixes = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager = new ContentNegotiationManager();
@Nullable
private StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver;
private RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
@Deprecated
public void setUseSuffixPatternMatch(boolean useSuffixPatternMatch) {
this.useSuffixPatternMatch = useSuffixPatternMatch;
}
@Deprecated
public void setUseRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(boolean useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch) {
this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch = useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch;
this.useSuffixPatternMatch = (useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch || this.useSuffixPatternMatch);
}
public void setUseTrailingSlashMatch(boolean useTrailingSlashMatch) {
this.useTrailingSlashMatch = useTrailingSlashMatch;
}
public void setPathPrefixes(Map<String, Predicate<Class<?>>> prefixes) {
this.pathPrefixes = Collections.unmodifiableMap(new LinkedHashMap<>(prefixes));
}
public Map<String, Predicate<Class<?>>> getPathPrefixes() {
return this.pathPrefixes;
}
public void setContentNegotiationManager(ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager) {
Assert.notNull(contentNegotiationManager, "ContentNegotiationManager must not be null");
this.contentNegotiationManager = contentNegotiationManager;
}
public ContentNegotiationManager getContentNegotiationManager() {
return this.contentNegotiationManager;
}
@Override
public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver resolver) {
this.embeddedValueResolver = resolver;
}
@Deprecated
public boolean useSuffixPatternMatch() {
return this.useSuffixPatternMatch;
}
@Deprecated
public boolean useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch() {
return this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch;
}
public boolean useTrailingSlashMatch() {
return this.useTrailingSlashMatch;
}
@Nullable
@Deprecated
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public List<String> getFileExtensions() {
return this.config.getFileExtensions();
}
}RequestMappingHandlerMapping 类拥有三个开关类型属性,分别为是否开启后缀匹配的 useSuffixPatternMatc、是否开启注册的后缀模式匹配 useTrailingSlashMatch(开启时,只有注册的后缀才可用于后缀匹配)及匹配是否忽略尾部反斜杠的 useTrailingSlashMatch 属性;pathPrefixes 则是全剧配置的路径前缀与类预测器映射器(用于为指定类处理器设置路径前缀),ContentNegotiationConfigurer 属性则是内容协商配置,embeddedValueResolver 属性则是路径字符串解析器及最后一个 config 属性用于保存 RequestMappingInfo 对象建造配置。
3.4.3 方法
(1)afterPropertiesSet 方法的扩展
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
this.config.setUrlPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper());
this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher());
this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(useSuffixPatternMatch());
this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(useTrailingSlashMatch());
this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch());
this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager());
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
}afterPropertiesSet 方法扩展了 RequestMappingInfo 建造配置的构造;其在父 afterPropertiesSet 方法执行之前为 config 属性赋值,将其更新为 RequestMappingInfo 的 BuilderConfiguration 内部类对象的同时为其属性进行赋值。
(2)isHandler 方法的实现
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
}isHandler 方法只要类使用 Controller 或 RequestMapping 注解修饰,就返回 true (即所有使用 Controller 或 RequestMapping 注解修饰类都是处理器)。
(3)getMappingForMethod 方法的实现
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
@Override
@Nullable
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
@Nullable
String getPathPrefix(Class<?> handlerType) {
for (Map.Entry<String, Predicate<Class<?>>> entry : this.pathPrefixes.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue().test(handlerType)) {
String prefix = entry.getKey();
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
prefix = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(prefix);
}
return prefix;
}
}
return null;
}
}getMappingForMethod 方法调用 createRequestMappingInfo 方法依次为方法及处理器类型创建 RequestMappingInfo 对象,在他们都不为空时以方法 RequestMappingInfo 对象为主进行合并(若方法未能创建 RequestMappingInfo 对象,则直接返回 null );随后再将通过 getPathPrefix 方法获取到的处理器路径前缀合并到创建好的 RequestMappingInfo 对象之中再返回。
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
@Nullable
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
@Nullable
protected RequestCondition<?> getCustomTypeCondition(Class<?> handlerType) {
return null;
}
@Nullable
protected RequestCondition<?> getCustomMethodCondition(Method method) {
return null;
}
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
.methods(requestMapping.method())
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name());
if (customCondition != null) {
builder.customCondition(customCondition);
}
return builder.options(this.config).build();
}
}createRequestMappingInfo 方法首先获取元素的 RequestMapping 注解的同时获取对应的 RequestCondition 对象并进一步调用以 RequestMapping 注解作为参数的 createRequestMappingInfo 方法实际创建 RequestMappingInfo 对象并返回。
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
protected String[] resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(String[] patterns) {
if (this.embeddedValueResolver == null) {
return patterns;
}
else {
String[] resolvedPatterns = new String[patterns.length];
for (int i = 0; i < patterns.length; i++) {
resolvedPatterns[i] = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(patterns[i]);
}
return resolvedPatterns;
}
}
}resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns 方法逐一调用 embeddedValueResolver 的 resolveStringValue 字符串解析方法(设置环境变量值等)处理所有 path 然后返回;
(4)register 方法的扩展
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
@Override
public void registerMapping(RequestMappingInfo mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
super.registerMapping(mapping, handler, method);
updateConsumesCondition(mapping, method);
}
@Override
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, RequestMappingInfo mapping) {
super.registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mapping);
updateConsumesCondition(mapping, method);
}
private void updateConsumesCondition(RequestMappingInfo info, Method method) {
ConsumesRequestCondition condition = info.getConsumesCondition();
if (!condition.isEmpty()) {
for (Parameter parameter : method.getParameters()) {
MergedAnnotation<RequestBody> annot = MergedAnnotations.from(parameter).get(RequestBody.class);
if (annot.isPresent()) {
condition.setBodyRequired(annot.getBoolean("required"));
break;
}
}
}
}
}RequestMappingHandlerMapping 类为 registerMapping 与 registerHandlerMethod 方法扩展了 updateConsumesCondition 方法来更新 consumesCondition 属性;updateConsumesCondition 方法在 consumesCondition 属性不为空时,根据参数的 RequestBody 属性值更新其是否必须。
(5)match 方法的实现
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
@Override
public RequestMatchResult match(HttpServletRequest request, String pattern) {
RequestMappingInfo info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(pattern).options(this.config).build();
RequestMappingInfo matchingInfo = info.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (matchingInfo == null) {
return null;
}
Set<String> patterns = matchingInfo.getPatternsCondition().getPatterns();
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request, LOOKUP_PATH);
return new RequestMatchResult(patterns.iterator().next(), lookupPath, getPathMatcher());
}
}match 方法使用 pattern 表达式入参创建 RequestMappingInfo 对象然后尝试调用其 getMatchingCondition 方法获取 request 请求匹配的 RequestMappingInfo 对象,未获取到时直接返回空;随后使用从匹配的 RequestMappingInfo 对象中获取到的第一个表达式、请求路径及路径匹配器创建 RequestMatchResult 并返回。
(6)initCorsConfiguration 方法重构
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
@Override
protected CorsConfiguration initCorsConfiguration(Object handler, Method method, RequestMappingInfo mappingInfo) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
Class<?> beanType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
CrossOrigin typeAnnotation = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(beanType, CrossOrigin.class);
CrossOrigin methodAnnotation = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, CrossOrigin.class);
if (typeAnnotation == null && methodAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
updateCorsConfig(config, typeAnnotation);
updateCorsConfig(config, methodAnnotation);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(config.getAllowedMethods())) {
for (RequestMethod allowedMethod : mappingInfo.getMethodsCondition().getMethods()) {
config.addAllowedMethod(allowedMethod.name());
}
}
return config.applyPermitDefaultValues();
}
}initCorsConfiguration 方法使用 updateCorsConfig 方法依次使用修饰类型与方法的 CrossOrigin 注解值更新本地 CorsConfiguration 配置,在未手动配置任意许可方法时,则会将 mappingInfo 参数中的所有方法全保存为许可方法。
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
private void updateCorsConfig(CorsConfiguration config, @Nullable CrossOrigin annotation) {
if (annotation == null) {
return;
}
for (String origin : annotation.origins()) {
config.addAllowedOrigin(resolveCorsAnnotationValue(origin));
}
for (RequestMethod method : annotation.methods()) {
config.addAllowedMethod(method.name());
}
for (String header : annotation.allowedHeaders()) {
config.addAllowedHeader(resolveCorsAnnotationValue(header));
}
for (String header : annotation.exposedHeaders()) {
config.addExposedHeader(resolveCorsAnnotationValue(header));
}
String allowCredentials = resolveCorsAnnotationValue(annotation.allowCredentials());
if ("true".equalsIgnoreCase(allowCredentials)) {
config.setAllowCredentials(true);
}
else if ("false".equalsIgnoreCase(allowCredentials)) {
config.setAllowCredentials(false);
}
else if (!allowCredentials.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@CrossOrigin's allowCredentials value must be \"true\", \"false\", " +
"or an empty string (\"\"): current value is [" + allowCredentials + "]");
}
if (annotation.maxAge() >= 0) {
config.setMaxAge(annotation.maxAge());
}
}
private String resolveCorsAnnotationValue(String value) {
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
String resolved = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(value);
return (resolved != null ? resolved : "");
}
else {
return value;
}
}
}updateCorsConfig 方法用于将 annotation 注解中的所有属性值转换成配置值后保存到 config 配置参数之中。
3.5 RequestMappingInfo
3.5.1 RequestCondition 接口
public interface RequestCondition<T> {
T combine(T other);
@Nullable
T getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request);
int compareTo(T other, HttpServletRequest request);
}RequestCondition 接口为所有请求匹配条件类通用接口,其定义了三个方法,分别为合并参数的 combine 、获取指定 request 请求匹配信息的 getMatchingCondition 以及在判断指定请求上下文中与其他条件比较优先级的 compareTo 方法。
3.5.2 AbstractRequestCondition 抽象类
public abstract class AbstractRequestCondition<T extends AbstractRequestCondition<T>> implements RequestCondition<T> {
public boolean isEmpty() {
return getContent().isEmpty();
}
protected abstract Collection<?> getContent();
protected abstract String getToStringInfix();
}AbstractRequestCondition 抽象类扩展了三个方法,第一个为判断是否无任何内容的 isEmpty 方法、第二个则是获取所有条件内容集合的 getContent 方法最后一个则是返回用于打印的不同条件值之间使用如 && 、|| 等的连接符的 getToStringInfix 方法。
3.5.3 RequestMethodsRequestCondition 类
RequestMethodsRequestCondition 类用于存储 http 请求方法条件;
(1)变量
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
private static final Map<String, RequestMethodsRequestCondition> requestMethodConditionCache;
static {
requestMethodConditionCache = new HashMap<>(RequestMethod.values().length);
for (RequestMethod method : RequestMethod.values()) {
requestMethodConditionCache.put(method.name(), new RequestMethodsRequestCondition(method));
}
}
private final Set<RequestMethod> methods;
public Set<RequestMethod> getMethods() {
return this.methods;
}
}RequestMethodsRequestCondition 类拥有一个常量 requestMethodConditionCache (用于缓存单请求方法条件)及一个用于保存当前条件方法结合的 methods 类变量。
(2)方法
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
public RequestMethodsRequestCondition(RequestMethod... requestMethods) {
this.methods = (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(requestMethods) ?
Collections.emptySet() : new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(requestMethods)));
}
private RequestMethodsRequestCondition(Set<RequestMethod> methods) {
this.methods = methods;
}
}RequestMethodsRequestCondition 类的构造方法都是直接将传入的所有请求方法对象全保存至 methods 属性之中。
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected Collection<RequestMethod> getContent() {
return this.methods;
}
}getContent 方法直接返回 methods 属性值。
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected String getToStringInfix() {
return " || ";
}
}getToStringInfix 方法直接返回 || 字符串。
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Override
public RequestMethodsRequestCondition combine(RequestMethodsRequestCondition other) {
if (isEmpty() && other.isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
else if (other.isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
else if (isEmpty()) {
return other;
}
Set<RequestMethod> set = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.methods);
set.addAll(other.methods);
return new RequestMethodsRequestCondition(set);
}
}combine 方法直接将两个 RequestMethodsRequestCondition 的 methods 属性值合并为一个 Set 集合然后返回。
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Override
@Nullable
public RequestMethodsRequestCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return matchPreFlight(request);
}
if (getMethods().isEmpty()) {
if (RequestMethod.OPTIONS.name().equals(request.getMethod()) &&
!DispatcherType.ERROR.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) {
return null; // We handle OPTIONS transparently, so don't match if no explicit declarations
}
return this;
}
return matchRequestMethod(request.getMethod());
}
}getMatchingCondition 方法直在请求为跨域预检请求时,调用 matchPreFlight 方法并返回;在 methds 属性为空时,只要不是 OPTIONS 请求或错误直接返回当前对象;最后才会调用 matchRequestMethod 方法。
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Nullable
private RequestMethodsRequestCondition matchPreFlight(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (getMethods().isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
String expectedMethod = request.getHeader(HttpHeaders.ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_METHOD);
return matchRequestMethod(expectedMethod);
}
}matchPreFlight 方法在 methods 属性为空时直接返回,否则使用期望方法执行 matchRequestMethod 方法并返回。
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Nullable
private RequestMethodsRequestCondition matchRequestMethod(String httpMethodValue) {
RequestMethod requestMethod;
try {
requestMethod = RequestMethod.valueOf(httpMethodValue);
if (getMethods().contains(requestMethod)) {
return requestMethodConditionCache.get(httpMethodValue);
}
if (requestMethod.equals(RequestMethod.HEAD) && getMethods().contains(RequestMethod.GET)) {
return requestMethodConditionCache.get(HttpMethod.GET.name());
}
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
// Custom request method
}
return null;
}
}matchRequestMethod 方法在 methods 属性包含传入的 httpMethodValue 参数时,直接喊回缓存中该参数的对应值;在请求为 HEAD 且当前支持 GET 方法时则会返回 Get 方法对应缓存;除此之外,直接返回 null。
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Override
public int compareTo(RequestMethodsRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
if (other.methods.size() != this.methods.size()) {
return other.methods.size() - this.methods.size();
}
else if (this.methods.size() == 1) {
if (this.methods.contains(RequestMethod.HEAD) && other.methods.contains(RequestMethod.GET)) {
return -1;
}
else if (this.methods.contains(RequestMethod.GET) && other.methods.contains(RequestMethod.HEAD)) {
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
}compareTo 方法首先会比较 methods 元素多少,直接返回他们之间的差值;在大小一致时,则会判断 GET 与 HEAD 之间的关系,GET 优先级要高于 HEAD;其余情况返回 0。
3.5.4 PatternsRequestCondition 类
PatternsRequestCondition 类用于存储 http 请求路径表达式条件;
(1)变量
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
private final static Set<String> EMPTY_PATH_PATTERN = Collections.singleton("");
}PatternsRequestCondition 类只有一个保存空字符集合的常量;
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
private final Set<String> patterns;
private final UrlPathHelper pathHelper;
private final PathMatcher pathMatcher;
private final boolean useSuffixPatternMatch;
private final boolean useTrailingSlashMatch;
private final List<String> fileExtensions = new ArrayList<>();
public Set<String> getPatterns() {
return this.patterns;
}
}PatternsRequestCondition 类的属性包含了模式表达式集合 patterns,url 辅助匹配器 pathHelper,路径匹配器 pathMatcher、文件扩展名列表 fileExtensions 以及 useSuffixPatternMatch 与 useTrailingSlashMatch 两个开关属性;
(2)方法
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
public PatternsRequestCondition(String... patterns) {
this(patterns, null, null, true, true, null);
}
public PatternsRequestCondition(String[] patterns, @Nullable UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper,
@Nullable PathMatcher pathMatcher, boolean useTrailingSlashMatch) {
this(patterns, urlPathHelper, pathMatcher, false, useTrailingSlashMatch, null);
}
@Deprecated
public PatternsRequestCondition(String[] patterns, @Nullable UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper,
@Nullable PathMatcher pathMatcher, boolean useSuffixPatternMatch, boolean useTrailingSlashMatch) {
this(patterns, urlPathHelper, pathMatcher, useSuffixPatternMatch, useTrailingSlashMatch, null);
}
@Deprecated
public PatternsRequestCondition(String[] patterns, @Nullable UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper,
@Nullable PathMatcher pathMatcher, boolean useSuffixPatternMatch,
boolean useTrailingSlashMatch, @Nullable List<String> fileExtensions) {
this.patterns = initPatterns(patterns);
this.pathHelper = urlPathHelper != null ? urlPathHelper : UrlPathHelper.defaultInstance;
this.pathMatcher = pathMatcher != null ? pathMatcher : new AntPathMatcher();
this.useSuffixPatternMatch = useSuffixPatternMatch;
this.useTrailingSlashMatch = useTrailingSlashMatch;
if (fileExtensions != null) {
for (String fileExtension : fileExtensions) {
if (fileExtension.charAt(0) != '.') {
fileExtension = "." + fileExtension;
}
this.fileExtensions.add(fileExtension);
}
}
}
private static Set<String> initPatterns(String[] patterns) {
if (!hasPattern(patterns)) {
return EMPTY_PATH_PATTERN;
}
Set<String> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(patterns.length);
for (String pattern : patterns) {
pattern = PathPatternParser.defaultInstance.initFullPathPattern(pattern);
result.add(pattern);
}
return result;
}
private static boolean hasPattern(String[] patterns) {
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(patterns)) {
for (String pattern : patterns) {
if (StringUtils.hasText(pattern)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}PatternsRequestCondition 类创建的过程中首先使用 initPatterns 方法对传入 patterns 参数进行初始化(主要为每个缺少 / 前缀的路径添加 / 前缀),将 urlPathHelper 属性初始为传入 urlPathHelper 参数值,为空时则设置默认值,将 pathMatcher 属性初始为传入 pathMatcher 参数值,为空时则初始化为新建的 AntPathMatcher 对象,useSuffixPatternMatch 与 useTrailingSlashMatch 属性都初始化为传入值最后为传入的 fileExtensions 路径元素添加必要的 . 前缀并保存到 fileExtensions 属性之中。
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected Collection<String> getContent() {
return this.patterns;
}
}getContent 方法直接返回 patterns 属性值。
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected String getToStringInfix() {
return " || ";
}
}getToStringInfix 方法直接返回 || 字符串。
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Override
public PatternsRequestCondition combine(PatternsRequestCondition other) {
if (isEmptyPathPattern() && other.isEmptyPathPattern()) {
return this;
}
else if (other.isEmptyPathPattern()) {
return this;
}
else if (isEmptyPathPattern()) {
return other;
}
Set<String> result = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!this.patterns.isEmpty() && !other.patterns.isEmpty()) {
for (String pattern1 : this.patterns) {
for (String pattern2 : other.patterns) {
result.add(this.pathMatcher.combine(pattern1, pattern2));
}
}
}
return new PatternsRequestCondition(result, this);
}
private boolean isEmptyPathPattern() {
return this.patterns == EMPTY_PATH_PATTERN;
}
}combine 方法会将两个 PatternsRequestCondition 对象中的所有 patterns 属性表达式列表全部使用当前 pathMatcher 属性重新合并然后通过私有构造方法新建并返回
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Override
@Nullable
public PatternsRequestCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
String lookupPath = this.pathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request, HandlerMapping.LOOKUP_PATH);
List<String> matches = getMatchingPatterns(lookupPath);
return !matches.isEmpty() ? new PatternsRequestCondition(new LinkedHashSet<>(matches), this) : null;
}
}getMatchingCondition 方法会通过 getMatchingPatterns 方法将与 request 请求匹配的所有表达式查询出来,然后新建 PatternsRequestCondition 对象并返回。
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
public List<String> getMatchingPatterns(String lookupPath) {
List<String> matches = null;
for (String pattern : this.patterns) {
String match = getMatchingPattern(pattern, lookupPath);
if (match != null) {
matches = (matches != null ? matches : new ArrayList<>());
matches.add(match);
}
}
if (matches == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
if (matches.size() > 1) {
matches.sort(this.pathMatcher.getPatternComparator(lookupPath));
}
return matches;
}
}getMatchingPatterns 方法会通过 getMatchingPatterns 方法将与 request 请求匹配的所有表达式查询出来,然后新建 PatternsRequestCondition 对象并返回。
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Nullable
private String getMatchingPattern(String pattern, String lookupPath) {
if (pattern.equals(lookupPath)) {
return pattern;
}
if (this.useSuffixPatternMatch) {
if (!this.fileExtensions.isEmpty() && lookupPath.indexOf('.') != -1) {
for (String extension : this.fileExtensions) {
if (this.pathMatcher.match(pattern + extension, lookupPath)) {
return pattern + extension;
}
}
}
else {
boolean hasSuffix = pattern.indexOf('.') != -1;
if (!hasSuffix && this.pathMatcher.match(pattern + ".*", lookupPath)) {
return pattern + ".*";
}
}
}
if (this.pathMatcher.match(pattern, lookupPath)) {
return pattern;
}
if (this.useTrailingSlashMatch) {
if (!pattern.endsWith("/") && this.pathMatcher.match(pattern + "/", lookupPath)) {
return pattern + "/";
}
}
return null;
}
}getMatchingPattern 方法首先判断是否启用了后缀匹配,若启用了则首先会判断路径是否与可以匹配上指定类型文件的表达式,若能匹配则会返回对应表达式与对应 extendsion 文件扩展名的拼接结果,若不存在文件匹配的选项,则会通过向每个表达式添加 .* 的方式判断是否满足后缀匹配;若上述无法匹配,则会判断直接使用 pathMatcher 判断是否匹配,最后则会在 useTrailingSlashMatch 开关开启时,尝试为表达式添加 / 后缀来进行匹配,若实在无法匹配才会返回 null;
public final class RequestMethodsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestMethodsRequestCondition> {
@Override
public int compareTo(PatternsRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
String lookupPath = this.pathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request, HandlerMapping.LOOKUP_PATH);
Comparator<String> patternComparator = this.pathMatcher.getPatternComparator(lookupPath);
Iterator<String> iterator = this.patterns.iterator();
Iterator<String> iteratorOther = other.patterns.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext() && iteratorOther.hasNext()) {
int result = patternComparator.compare(iterator.next(), iteratorOther.next());
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
}
if (iterator.hasNext()) {
return -1;
}
else if (iteratorOther.hasNext()) {
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
}compareTo 方法首先使用当前 pathMatcher 匹配器获取请求路径对应的 Comparator 比较器,然后使用该比较器依次对对应位置的表达式进行比较,一直到出现不是同级别表达式或其中一个完成了遍历,若出现了不是同一级别的表达式则直接返回比较结果,否则结果偏向与表达式更少的条件;
3.5.5 ParamsRequestCondition 类
(1)变量
public final class ParamsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ParamsRequestCondition> {
private final Set<ParamExpression> expressions;
public Set<NameValueExpression<String>> getExpressions() {
return new LinkedHashSet<>(this.expressions);
}
}ParamsRequestCondition 类只有一个保存参数表达式的 expressions 属性;
(2)方法
public final class ParamsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ParamsRequestCondition> {
public ParamsRequestCondition(String... params) {
this.expressions = parseExpressions(params);
}
private static Set<ParamExpression> parseExpressions(String... params) {
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(params)) {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
Set<ParamExpression> expressions = new LinkedHashSet<>(params.length);
for (String param : params) {
expressions.add(new ParamExpression(param));
}
return expressions;
}
private ParamsRequestCondition(Set<ParamExpression> conditions) {
this.expressions = conditions;
}
}ParamsRequestCondition 对象创建时,依次将利用传入的 params 表达式参数元素创建 ParamExpression 表达式对象保存至 expressions 属性之中;
public final class ParamsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ParamsRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected Collection<ParamExpression> getContent() {
return this.expressions;
}
}getContent 方法直接返回 expressions 属性值。
public final class ParamsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ParamsRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected String getToStringInfix() {
return " && ";
}
}getToStringInfix 方法直接返回 && 字符串。
public final class ParamsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ParamsRequestCondition> {
@Override
public ParamsRequestCondition combine(ParamsRequestCondition other) {
if (isEmpty() && other.isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
else if (other.isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
else if (isEmpty()) {
return other;
}
Set<ParamExpression> set = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.expressions);
set.addAll(other.expressions);
return new ParamsRequestCondition(set);
}
}combine 方法直接将两个 ParamsRequestCondition 对象的 expressions 合并为一个 Set 集合并返回。
public final class ParamsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ParamsRequestCondition> {
@Override
@Nullable
public ParamsRequestCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
for (ParamExpression expression : this.expressions) {
if (!expression.match(request)) {
return null;
}
}
return this;
}
}getMatchingCondition 方法遍历所有 expressions 表达式,在其中存在任意不匹配时直接返回 null,否则返回当前对象。
public final class ParamsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ParamsRequestCondition> {
@Override
public int compareTo(ParamsRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
int result = other.expressions.size() - this.expressions.size();
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
return (int) (getValueMatchCount(other.expressions) - getValueMatchCount(this.expressions));
}
private long getValueMatchCount(Set<ParamExpression> expressions) {
long count = 0;
for (ParamExpression e : expressions) {
if (e.getValue() != null && !e.isNegated()) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}compareTo 方法在 expressions 属性长度不一致时直接返回其中的差值,否则返回他们之间的 getValueMatchCount 方法结果差值;getValueMatchCount 方法用于获取非空且正向表达式的数量;
3.5.6 ConsumesRequestCondition 类
(1)变量
public final class ConsumesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ConsumesRequestCondition> {
private static final ConsumesRequestCondition EMPTY_CONDITION = new ConsumesRequestCondition();
private final List<ConsumeMediaTypeExpression> expressions;
private boolean bodyRequired = true;
public Set<MediaTypeExpression> getExpressions() {
return new LinkedHashSet<>(this.expressions);
}
public Set<MediaType> getConsumableMediaTypes() {
Set<MediaType> result = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (ConsumeMediaTypeExpression expression : this.expressions) {
if (!expression.isNegated()) {
result.add(expression.getMediaType());
}
}
return result;
}
public void setBodyRequired(boolean bodyRequired) {
this.bodyRequired = bodyRequired;
}
public boolean isBodyRequired() {
return this.bodyRequired;
}
}ConsumesRequestCondition 类用于保存接受媒体类型条件,其拥有一个空条件常量 EMPTY_CONDITION、允许的媒体类型表达式列表 expressions 以及是否需要请求体的 bodyRequired 属性;
(2)方法
public final class ConsumesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ConsumesRequestCondition> {
public ConsumesRequestCondition(String... consumes) {
this(consumes, null);
}
public ConsumesRequestCondition(String[] consumes, @Nullable String[] headers) {
this.expressions = parseExpressions(consumes, headers);
if (this.expressions.size() > 1) {
Collections.sort(this.expressions);
}
}
private static List<ConsumeMediaTypeExpression> parseExpressions(String[] consumes, @Nullable String[] headers) {
Set<ConsumeMediaTypeExpression> result = null;
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(headers)) {
for (String header : headers) {
HeaderExpression expr = new HeaderExpression(header);
if ("Content-Type".equalsIgnoreCase(expr.name) && expr.value != null) {
result = (result != null ? result : new LinkedHashSet<>());
for (MediaType mediaType : MediaType.parseMediaTypes(expr.value)) {
result.add(new ConsumeMediaTypeExpression(mediaType, expr.isNegated));
}
}
}
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(consumes)) {
result = (result != null ? result : new LinkedHashSet<>());
for (String consume : consumes) {
result.add(new ConsumeMediaTypeExpression(consume));
}
}
return (result != null ? new ArrayList<>(result) : Collections.emptyList());
}
private ConsumesRequestCondition(List<ConsumeMediaTypeExpression> expressions) {
this.expressions = expressions;
}
}ConsumesRequestCondition 对象创建时,首先调用 parseExpressions 将传入的 consumes 与 headers 参数转换为 ConsumeMediaTypeExpression 集合,并在完成后对其进行排序;parseExpressions 方法首先将 headers 参数中的 Content-Type 元素转化为 ConsumeMediaTypeExpression 对象保存,随后逐一将 consumes 参数中的所有元素转换为 ConsumeMediaTypeExpression 对象并与之前创建的 ConsumeMediaTypeExpression 对象糅合在一起保存并返回。
public final class ConsumesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ConsumesRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected Collection<ConsumeMediaTypeExpression> getContent() {
return this.expressions;
}
}getContent 方法直接返回 expressions 属性值。
public final class ConsumesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ConsumesRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected String getToStringInfix() {
return " || ";
}
}getToStringInfix 方法直接返回 || 字符串。
public final class ConsumesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ConsumesRequestCondition> {
@Override
public ConsumesRequestCondition combine(ConsumesRequestCondition other) {
return (!other.expressions.isEmpty() ? other : this);
}
}combine 方法在 other 参数为空时直接返回 other 参数值,否则返回当前对象值。
public final class ConsumesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ConsumesRequestCondition> {
@Override
@Nullable
public ConsumesRequestCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return EMPTY_CONDITION;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
if (!hasBody(request) && !this.bodyRequired) {
return EMPTY_CONDITION;
}
// Common media types are cached at the level of MimeTypeUtils
MediaType contentType;
try {
contentType = StringUtils.hasLength(request.getContentType()) ?
MediaType.parseMediaType(request.getContentType()) :
MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM;
}
catch (InvalidMediaTypeException ex) {
return null;
}
List<ConsumeMediaTypeExpression> result = getMatchingExpressions(contentType);
return !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(result) ? new ConsumesRequestCondition(result) : null;
}
private boolean hasBody(HttpServletRequest request) {
String contentLength = request.getHeader(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_LENGTH);
String transferEncoding = request.getHeader(HttpHeaders.TRANSFER_ENCODING);
return StringUtils.hasText(transferEncoding) ||
(StringUtils.hasText(contentLength) && !contentLength.trim().equals("0"));
}
@Nullable
private List<ConsumeMediaTypeExpression> getMatchingExpressions(MediaType contentType) {
List<ConsumeMediaTypeExpression> result = null;
for (ConsumeMediaTypeExpression expression : this.expressions) {
if (expression.match(contentType)) {
result = result != null ? result : new ArrayList<>();
result.add(expression);
}
}
return result;
}
}getMatchingCondition 方法在 request 为跨域预检请求或需要请求体但请求没有时,返回 EMPTY_CONDITION 常量值;随后获取请求使用请求媒体类型,若为空则取 APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM;最后通过 getMatchingExpressions 方法获取 expressions 属性中匹配的元素集合并返回。
public final class ConsumesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ConsumesRequestCondition> {
@Override
public ConsumesRequestCondition combine(ConsumesRequestCondition other) {
return (!other.expressions.isEmpty() ? other : this);
}
}combine 方法在 other 参数为空时直接返回 other 参数值,否则返回当前对象值。
public final class ConsumesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ConsumesRequestCondition> {
@Override
public int compareTo(ConsumesRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
if (this.expressions.isEmpty() && other.expressions.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
else if (this.expressions.isEmpty()) {
return 1;
}
else if (other.expressions.isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
else {
return this.expressions.get(0).compareTo(other.expressions.get(0));
}
}
}compareTo 方法直接比较两个 ConsumesRequestCondition 对象的第一个表达式。
3.5.7 ProducesRequestCondition 类
(1)变量
public final class ProducesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ProducesRequestCondition> {
private static final ContentNegotiationManager DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_MANAGER =
new ContentNegotiationManager();
private static final ProducesRequestCondition EMPTY_CONDITION = new ProducesRequestCondition();
private static final List<ProduceMediaTypeExpression> MEDIA_TYPE_ALL_LIST =
Collections.singletonList(new ProduceMediaTypeExpression(MediaType.ALL_VALUE));
private static final String MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE = ProducesRequestCondition.class.getName() + ".MEDIA_TYPES";
private final List<ProduceMediaTypeExpression> expressions;
private final ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager;
}ProducesRequestCondition 类用于保存响应限制条件,其拥有四个常量:DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_MANAGER 为默认内容协商控制器、EMPTY_CONDITION 为空 ProducesRequestCondition 对象、 MEDIA_TYPE_ALL_LIST 保存的则是匹配所有媒体类型列表及与请求绑定的当前需要提供的媒体类型属性名;拥有两个类属性:可提供的表达式列表 expressions 与使用的内容协商控制器 contentNegotiationManager;
(2)方法
public final class ProducesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ProducesRequestCondition> {
public ProducesRequestCondition(String... produces) {
this(produces, null, null);
}
public ProducesRequestCondition(String[] produces, @Nullable String[] headers) {
this(produces, headers, null);
}
public ProducesRequestCondition(String[] produces, @Nullable String[] headers,
@Nullable ContentNegotiationManager manager) {
this.expressions = parseExpressions(produces, headers);
if (this.expressions.size() > 1) {
Collections.sort(this.expressions);
}
this.contentNegotiationManager = manager != null ? manager : DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_MANAGER;
}
private List<ProduceMediaTypeExpression> parseExpressions(String[] produces, @Nullable String[] headers) {
Set<ProduceMediaTypeExpression> result = null;
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(headers)) {
for (String header : headers) {
HeaderExpression expr = new HeaderExpression(header);
if ("Accept".equalsIgnoreCase(expr.name) && expr.value != null) {
for (MediaType mediaType : MediaType.parseMediaTypes(expr.value)) {
result = (result != null ? result : new LinkedHashSet<>());
result.add(new ProduceMediaTypeExpression(mediaType, expr.isNegated));
}
}
}
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(produces)) {
for (String produce : produces) {
result = (result != null ? result : new LinkedHashSet<>());
result.add(new ProduceMediaTypeExpression(produce));
}
}
return (result != null ? new ArrayList<>(result) : Collections.emptyList());
}
private ProducesRequestCondition(List<ProduceMediaTypeExpression> expressions, ProducesRequestCondition other) {
this.expressions = expressions;
this.contentNegotiationManager = other.contentNegotiationManager;
}
}创建 ProducesRequestCondition 对象时,将 header 参数中的 Accept 元素与 produces 中所有元素转换为 ProduceMediaTypeExpression 对象列表然后排序后保存到 expressions 属性中,同时为 contentNegotiationManager 属性赋值,在 manager 参数不为空时初始化为该参数值,否则使用 DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_MANAGER 常量值;
public final class ProducesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ProducesRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected List<ProduceMediaTypeExpression> getContent() {
return this.expressions;
}
}getContent 方法直接返回 expressions 属性值。
public final class ProducesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ProducesRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected String getToStringInfix() {
return " || ";
}
}getToStringInfix 方法直接返回 || 字符串。
public final class ProducesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ProducesRequestCondition> {
@Override
public ProducesRequestCondition combine(ConsumesRequestCondition other) {
return (!other.expressions.isEmpty() ? other : this);
}
}combine 方法在 other 参数为空时直接返回 other 参数值,否则返回当前对象值。
public final class ProducesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ProducesRequestCondition> {
@Override
@Nullable
public ProducesRequestCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return EMPTY_CONDITION;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
List<MediaType> acceptedMediaTypes;
try {
acceptedMediaTypes = getAcceptedMediaTypes(request);
}
catch (HttpMediaTypeException ex) {
return null;
}
List<ProduceMediaTypeExpression> result = getMatchingExpressions(acceptedMediaTypes);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(result)) {
return new ProducesRequestCondition(result, this);
}
else if (MediaType.ALL.isPresentIn(acceptedMediaTypes)) {
return EMPTY_CONDITION;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
@Nullable
private List<ProduceMediaTypeExpression> getMatchingExpressions(List<MediaType> acceptedMediaTypes) {
List<ProduceMediaTypeExpression> result = null;
for (ProduceMediaTypeExpression expression : this.expressions) {
if (expression.match(acceptedMediaTypes)) {
result = result != null ? result : new ArrayList<>();
result.add(expression);
}
}
return result;
}
}getMatchingCondition 方法通过 getMatchingExpressions 方法获取条件中与 request 请求参数所匹配的可接受的响应媒体类型列表;在其不为空时直接使用当前对象与匹配列表创建 ProducesRequestCondition 对象并返回,否则在 request 所能接受的媒体类型包含 ALL 值时,直接返回 EMPTY_CONDITION 常量值,否则直接返回 null。
public final class ProducesRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ProducesRequestCondition> {
@Override
public int compareTo(ProducesRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
try {
List<MediaType> acceptedMediaTypes = getAcceptedMediaTypes(request);
for (MediaType acceptedMediaType : acceptedMediaTypes) {
int thisIndex = this.indexOfEqualMediaType(acceptedMediaType);
int otherIndex = other.indexOfEqualMediaType(acceptedMediaType);
int result = compareMatchingMediaTypes(this, thisIndex, other, otherIndex);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
thisIndex = this.indexOfIncludedMediaType(acceptedMediaType);
otherIndex = other.indexOfIncludedMediaType(acceptedMediaType);
result = compareMatchingMediaTypes(this, thisIndex, other, otherIndex);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
}
return 0;
}
catch (HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException ex) {
// should never happen
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot compare without having any requested media types", ex);
}
}
private int indexOfEqualMediaType(MediaType mediaType) {
for (int i = 0; i < getExpressionsToCompare().size(); i++) {
MediaType currentMediaType = getExpressionsToCompare().get(i).getMediaType();
if (mediaType.getType().equalsIgnoreCase(currentMediaType.getType()) &&
mediaType.getSubtype().equalsIgnoreCase(currentMediaType.getSubtype())) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
private int indexOfIncludedMediaType(MediaType mediaType) {
for (int i = 0; i < getExpressionsToCompare().size(); i++) {
if (mediaType.includes(getExpressionsToCompare().get(i).getMediaType())) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
private int compareMatchingMediaTypes(ProducesRequestCondition condition1, int index1,
ProducesRequestCondition condition2, int index2) {
int result = 0;
if (index1 != index2) {
result = index2 - index1;
}
else if (index1 != -1) {
ProduceMediaTypeExpression expr1 = condition1.getExpressionsToCompare().get(index1);
ProduceMediaTypeExpression expr2 = condition2.getExpressionsToCompare().get(index2);
result = expr1.compareTo(expr2);
result = (result != 0) ? result : expr1.getMediaType().compareTo(expr2.getMediaType());
}
return result;
}
private List<ProduceMediaTypeExpression> getExpressionsToCompare() {
return (this.expressions.isEmpty() ? MEDIA_TYPE_ALL_LIST : this.expressions);
}
}compareTo 方法通过对比 request 请求可接受媒体列表在两个 ProducesRequestCondition 对象 expressions 属性中所在索引。
3.5.8 HeadersRequestCondition 类
(1)变量
public final class HeadersRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<HeadersRequestCondition> {
private static final HeadersRequestCondition PRE_FLIGHT_MATCH = new HeadersRequestCondition();
private final Set<HeaderExpression> expressions;
public Set<NameValueExpression<String>> getExpressions() {
return new LinkedHashSet<>(this.expressions);
}
}HeadersRequestCondition 类用于保存请求头限制条件,其只有一个保存用于跨域预请求条件常量 PRE_FLIGHT_MATCH 以及一个内部请求头表达式集合;
(2)方法
public final class HeadersRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<HeadersRequestCondition> {
public HeadersRequestCondition(String... headers) {
this.expressions = parseExpressions(headers);
}
private static Set<HeaderExpression> parseExpressions(String... headers) {
Set<HeaderExpression> result = null;
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(headers)) {
for (String header : headers) {
HeaderExpression expr = new HeaderExpression(header);
if ("Accept".equalsIgnoreCase(expr.name) || "Content-Type".equalsIgnoreCase(expr.name)) {
continue;
}
result = (result != null ? result : new LinkedHashSet<>(headers.length));
result.add(expr);
}
}
return (result != null ? result : Collections.emptySet());
}
private HeadersRequestCondition(Set<HeaderExpression> conditions) {
this.expressions = conditions;
}
}HeadersRequestCondition 对象创建过程中,会逐一将 headers 参数中除 Accept 与 Content-Type 表达式外的所有元素转换为 HeaderExpression 对象保存到 expressions 属性之中;
public final class HeadersRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<HeadersRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected Collection<ParamExpression> getContent() {
return this.expressions;
}
}getContent 方法直接返回 expressions 属性值。
public final class HeadersRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<HeadersRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected String getToStringInfix() {
return " && ";
}
}getToStringInfix 方法直接返回 && 字符串。
public final class HeadersRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<HeadersRequestCondition> {
@Override
public HeadersRequestCondition combine(HeadersRequestCondition other) {
if (isEmpty() && other.isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
else if (other.isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
else if (isEmpty()) {
return other;
}
Set<HeaderExpression> set = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.expressions);
set.addAll(other.expressions);
return new HeadersRequestCondition(set);
}
}combine 方法直接将两个 HeadersRequestCondition 对象的 expressions 属性值合并到一起并返回。
public final class HeadersRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<HeadersRequestCondition> {
@Override
@Nullable
public HeadersRequestCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PRE_FLIGHT_MATCH;
}
for (HeaderExpression expression : this.expressions) {
if (!expression.match(request)) {
return null;
}
}
return this;
}
}getMatchingCondition 方法在 request 请求为跨域预检请求时直接返回 PRE_FLIGHT_MATCH 常量值;否则只有在 request 参数与 expressions 属性中所有表达式都匹配时才会返回当前对象,一旦出现不匹配则返回 null。
public final class HeadersRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<HeadersRequestCondition> {
@Override
public int compareTo(HeadersRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
int result = other.expressions.size() - this.expressions.size();
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
return (int) (getValueMatchCount(other.expressions) - getValueMatchCount(this.expressions));
}
private long getValueMatchCount(Set<HeaderExpression> expressions) {
long count = 0;
for (HeaderExpression e : expressions) {
if (e.getValue() != null && !e.isNegated()) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}compareTo 方法首先比较 expressions 属性的元素数量,在其数量相同时则会比较他们的正向头条件数量。
3.5.9 RequestConditionHolder 类
(1)变量
public final class RequestConditionHolder extends AbstractRequestCondition<RequestConditionHolder> {
@Nullable
private final RequestCondition<Object> condition;
@Nullable
public RequestCondition<?> getCondition() {
return this.condition;
}
}RequestConditionHolder 类用于封装一些自定义请求条件,其只有一个用于保存被封装的条件的 condition 属性;
(2)方法
public final class HeadersRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<HeadersRequestCondition> {
public RequestConditionHolder(@Nullable RequestCondition<?> requestCondition) {
this.condition = (RequestCondition<Object>) requestCondition;
}
}RequestConditionHolder 直接使用外部传入的自定义验证条件进行创建;
public final class HeadersRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<HeadersRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected Collection<?> getContent() {
return (this.condition != null ? Collections.singleton(this.condition) : Collections.emptyList());
}
@Override
protected String getToStringInfix() {
return " ";
}
@Override
public RequestConditionHolder combine(RequestConditionHolder other) {
if (this.condition == null && other.condition == null) {
return this;
}
else if (this.condition == null) {
return other;
}
else if (other.condition == null) {
return this;
}
else {
assertEqualConditionTypes(this.condition, other.condition);
RequestCondition<?> combined = (RequestCondition<?>) this.condition.combine(other.condition);
return new RequestConditionHolder(combined);
}
}
private void assertEqualConditionTypes(RequestCondition<?> thisCondition, RequestCondition<?> otherCondition) {
Class<?> clazz = thisCondition.getClass();
Class<?> otherClazz = otherCondition.getClass();
if (!clazz.equals(otherClazz)) {
throw new ClassCastException("Incompatible request conditions: " + clazz + " and " + otherClazz);
}
}
@Override
@Nullable
public RequestConditionHolder getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (this.condition == null) {
return this;
}
RequestCondition<?> match = (RequestCondition<?>) this.condition.getMatchingCondition(request);
return (match != null ? new RequestConditionHolder(match) : null);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(RequestConditionHolder other, HttpServletRequest request) {
if (this.condition == null && other.condition == null) {
return 0;
}
else if (this.condition == null) {
return 1;
}
else if (other.condition == null) {
return -1;
}
else {
assertEqualConditionTypes(this.condition, other.condition);
return this.condition.compareTo(other.condition, request);
}
}
}RequestConditionHolder 类其余方法都是直接对内部封装对象进行处理,值得注意的是,其中对于两个 RequestConditionHolder 对象操作的方法(combine 与 compareTo)都会首先调用 assertEqualConditionTypes 方法判断封装对象类型是否一致,不一致会直接抛出异常;
3.5.10 RequestConditionHolder 类
(1)变量
public class CompositeRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<CompositeRequestCondition> {
private final RequestConditionHolder[] requestConditions;
public List<RequestCondition<?>> getConditions() {
return unwrap();
}
private List<RequestCondition<?>> unwrap() {
List<RequestCondition<?>> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (RequestConditionHolder holder : this.requestConditions) {
result.add(holder.getCondition());
}
return result;
}
}CompositeRequestCondition 类用于封装组合请求条件,其只有一个用于保存被封装的条件列表的 requestConditions 属性;
(2)方法
public class CompositeRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<CompositeRequestCondition> {
public CompositeRequestCondition(RequestCondition<?>... requestConditions) {
this.requestConditions = wrap(requestConditions);
}
private CompositeRequestCondition(RequestConditionHolder[] requestConditions) {
this.requestConditions = requestConditions;
}
private RequestConditionHolder[] wrap(RequestCondition<?>... rawConditions) {
RequestConditionHolder[] wrappedConditions = new RequestConditionHolder[rawConditions.length];
for (int i = 0; i < rawConditions.length; i++) {
wrappedConditions[i] = new RequestConditionHolder(rawConditions[i]);
}
return wrappedConditions;
}
}CompositeRequestCondition 对象在创建过程之中,直接调用 wrap 逐一封装 requestConditions 参数中的所有元素并保存到 requestConditions 属性之中;
public class CompositeRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<CompositeRequestCondition> {
@Override
protected Collection<?> getContent() {
return (!isEmpty() ? getConditions() : Collections.emptyList());
}
@Override
protected String getToStringInfix() {
return " && ";
}
}RequestConditionHolder 的 getToStringInfix 方法直接返回 && ;
public class CompositeRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<CompositeRequestCondition> {
@Override
public CompositeRequestCondition combine(CompositeRequestCondition other) {
if (isEmpty() && other.isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
else if (other.isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
else if (isEmpty()) {
return other;
}
else {
assertNumberOfConditions(other);
RequestConditionHolder[] combinedConditions = new RequestConditionHolder[getLength()];
for (int i = 0; i < getLength(); i++) {
combinedConditions[i] = this.requestConditions[i].combine(other.requestConditions[i]);
}
return new CompositeRequestCondition(combinedConditions);
}
}
private void assertNumberOfConditions(CompositeRequestCondition other) {
Assert.isTrue(getLength() == other.getLength(),
"Cannot combine CompositeRequestConditions with a different number of conditions. " +
ObjectUtils.nullSafeToString(this.requestConditions) + " and " +
ObjectUtils.nullSafeToString(other.requestConditions));
}
}combine 方法将当前对象与 other 对象的 requestConditions 属性中相同位置元素进行合并之后返回;
public class CompositeRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<CompositeRequestCondition> {
@Override
@Nullable
public CompositeRequestCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
RequestConditionHolder[] matchingConditions = new RequestConditionHolder[getLength()];
for (int i = 0; i < getLength(); i++) {
matchingConditions[i] = this.requestConditions[i].getMatchingCondition(request);
if (matchingConditions[i] == null) {
return null;
}
}
return new CompositeRequestCondition(matchingConditions);
} ObjectUtils.nullSafeToString(other.requestConditions));
}
}getMatchingCondition 方法则是对所有元素执行 getMatchingCondition 方法,若出现了未能获取到任何的条件的元素则直接返回 null;否则将所有获取到的条件合并到一起并返回。
public class CompositeRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<CompositeRequestCondition> {
@Override
public int compareTo(CompositeRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
if (isEmpty() && other.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
else if (isEmpty()) {
return 1;
}
else if (other.isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
else {
assertNumberOfConditions(other);
for (int i = 0; i < getLength(); i++) {
int result = this.requestConditions[i].compareTo(other.requestConditions[i], request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
}compareTo 方法返回 requestConditions 属性中一个不想等的比较结果值。
3.5.11 变量
(1)常量
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {
private static final PatternsRequestCondition EMPTY_PATTERNS = new PatternsRequestCondition();
private static final RequestMethodsRequestCondition EMPTY_REQUEST_METHODS = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition();
private static final ParamsRequestCondition EMPTY_PARAMS = new ParamsRequestCondition();
private static final HeadersRequestCondition EMPTY_HEADERS = new HeadersRequestCondition();
private static final ConsumesRequestCondition EMPTY_CONSUMES = new ConsumesRequestCondition();
private static final ProducesRequestCondition EMPTY_PRODUCES = new ProducesRequestCondition();
private static final RequestConditionHolder EMPTY_CUSTOM = new RequestConditionHolder(null);
}RequestMappingInfo 类有 7 个常量,对应的是 7 个请求判断条件,保存的对应空判断条件;
(2)类变量
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {
@Nullable
private final String name;
private final PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition;
private final RequestMethodsRequestCondition methodsCondition;
private final ParamsRequestCondition paramsCondition;
private final HeadersRequestCondition headersCondition;
private final ConsumesRequestCondition consumesCondition;
private final ProducesRequestCondition producesCondition;
private final RequestConditionHolder customConditionHolder;
private final int hashCode;
@Nullable
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public PatternsRequestCondition getPatternsCondition() {
return this.patternsCondition;
}
public RequestMethodsRequestCondition getMethodsCondition() {
return this.methodsCondition;
}
public ParamsRequestCondition getParamsCondition() {
return this.paramsCondition;
}
public HeadersRequestCondition getHeadersCondition() {
return this.headersCondition;
}
public ConsumesRequestCondition getConsumesCondition() {
return this.consumesCondition;
}
public ProducesRequestCondition getProducesCondition() {
return this.producesCondition;
}
@Nullable
public RequestCondition<?> getCustomCondition() {
return this.customConditionHolder.getCondition();
}
}RequestMappingInfo 类拥有 9 个类变量,除了 7 个请求条件之外,还有保存请求名称的 name 及 hashcode 值两个属性;
3.5.12 方法
(1)构造方法
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {
public RequestMappingInfo(@Nullable String name, @Nullable PatternsRequestCondition patterns,
@Nullable RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods, @Nullable ParamsRequestCondition params,
@Nullable HeadersRequestCondition headers, @Nullable ConsumesRequestCondition consumes,
@Nullable ProducesRequestCondition produces, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> custom) {
this.name = (StringUtils.hasText(name) ? name : null);
this.patternsCondition = (patterns != null ? patterns : EMPTY_PATTERNS);
this.methodsCondition = (methods != null ? methods : EMPTY_REQUEST_METHODS);
this.paramsCondition = (params != null ? params : EMPTY_PARAMS);
this.headersCondition = (headers != null ? headers : EMPTY_HEADERS);
this.consumesCondition = (consumes != null ? consumes : EMPTY_CONSUMES);
this.producesCondition = (produces != null ? produces : EMPTY_PRODUCES);
this.customConditionHolder = (custom != null ? new RequestConditionHolder(custom) : EMPTY_CUSTOM);
this.hashCode = calculateHashCode(
this.patternsCondition, this.methodsCondition, this.paramsCondition, this.headersCondition,
this.consumesCondition, this.producesCondition, this.customConditionHolder);
}
public RequestMappingInfo(@Nullable PatternsRequestCondition patterns,
@Nullable RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods, @Nullable ParamsRequestCondition params,
@Nullable HeadersRequestCondition headers, @Nullable ConsumesRequestCondition consumes,
@Nullable ProducesRequestCondition produces, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> custom) {
this(null, patterns, methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom);
}
public RequestMappingInfo(RequestMappingInfo info, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customRequestCondition) {
this(info.name, info.patternsCondition, info.methodsCondition, info.paramsCondition, info.headersCondition,
info.consumesCondition, info.producesCondition, customRequestCondition);
}
private static int calculateHashCode(
PatternsRequestCondition patterns, RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods,
ParamsRequestCondition params, HeadersRequestCondition headers,
ConsumesRequestCondition consumes, ProducesRequestCondition produces,
RequestConditionHolder custom) {
return patterns.hashCode() * 31 + methods.hashCode() + params.hashCode() +
headers.hashCode() + consumes.hashCode() + produces.hashCode() + custom.hashCode();
}
}在 RequestMappingInfo 对象创建时,在为对应属性赋值之后,调用 calculateHashCode 方法计算 hash 值并保存到 hashCode 属性之中;
(2)combine
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {
@Override
public RequestMappingInfo combine(RequestMappingInfo other) {
String name = combineNames(other);
PatternsRequestCondition patterns = this.patternsCondition.combine(other.patternsCondition);
RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.combine(other.methodsCondition);
ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.combine(other.paramsCondition);
HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.combine(other.headersCondition);
ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.combine(other.consumesCondition);
ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.combine(other.producesCondition);
RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.combine(other.customConditionHolder);
return new RequestMappingInfo(name, patterns,
methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom.getCondition());
}
@Nullable
private String combineNames(RequestMappingInfo other) {
if (this.name != null && other.name != null) {
String separator = RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy.SEPARATOR;
return this.name + separator + other.name;
}
else if (this.name != null) {
return this.name;
}
else {
return other.name;
}
}
}combine 方法逐一调用各属性的 combine 方法合并所有属性;
(3)getMatchingCondition
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {
@Override
@Nullable
public RequestMappingInfo getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (methods == null) {
return null;
}
ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (params == null) {
return null;
}
HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (headers == null) {
return null;
}
ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (consumes == null) {
return null;
}
ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (produces == null) {
return null;
}
PatternsRequestCondition patterns = this.patternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (patterns == null) {
return null;
}
RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (custom == null) {
return null;
}
return new RequestMappingInfo(this.name, patterns,
methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom.getCondition());
}
}getMatchingCondition 方法逐一调用 methodsCondition、paramsCondition、headersCondition、consumesCondition、producesCondition、patternsCondition 及 customConditionHolder 属性的 getMatchingCondition 方法获取对应的条件值,若存在任何属性没有对应条件直接返回 null,否则将所有获取到的条件对象组合成新的 RequestMappingInfo 对象并返回。
3.5.13 DefaultBuilder 建造器
(1)paths 方法
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {
public static Builder paths(String... paths) {
return new DefaultBuilder(paths);
}
}paths 方法用于创建 DefaultBuilder 默认建造器,其只传了可变路径数组;
(2)Builder 接口
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {
public interface Builder {
Builder paths(String... paths);
Builder methods(RequestMethod... methods);
Builder params(String... params);
Builder headers(String... headers);
Builder consumes(String... consumes);
Builder produces(String... produces);
Builder mappingName(String name);
Builder customCondition(RequestCondition<?> condition);
Builder options(BuilderConfiguration options);
RequestMappingInfo build();
}
}Builder 内部接口只定义设置属性的各种方法及一个 build 建造方法;
(3)属性及属性设置方法
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {
private static class DefaultBuilder implements Builder {
private String[] paths;
private RequestMethod[] methods = new RequestMethod[0];
private String[] params = new String[0];
private String[] headers = new String[0];
private String[] consumes = new String[0];
private String[] produces = new String[0];
private boolean hasContentType;
private boolean hasAccept;
@Nullable
private String mappingName;
@Nullable
private RequestCondition<?> customCondition;
private BuilderConfiguration options = new BuilderConfiguration();
public DefaultBuilder(String... paths) {
this.paths = paths;
}
@Override
public Builder paths(String... paths) {
this.paths = paths;
return this;
}
@Override
public DefaultBuilder methods(RequestMethod... methods) {
this.methods = methods;
return this;
}
@Override
public DefaultBuilder params(String... params) {
this.params = params;
return this;
}
@Override
public DefaultBuilder headers(String... headers) {
for (String header : headers) {
this.hasContentType = this.hasContentType ||
header.contains("Content-Type") || header.contains("content-type");
this.hasAccept = this.hasAccept ||
header.contains("Accept") || header.contains("accept");
}
this.headers = headers;
return this;
}
@Override
public DefaultBuilder consumes(String... consumes) {
this.consumes = consumes;
return this;
}
@Override
public DefaultBuilder produces(String... produces) {
this.produces = produces;
return this;
}
@Override
public DefaultBuilder mappingName(String name) {
this.mappingName = name;
return this;
}
@Override
public DefaultBuilder customCondition(RequestCondition<?> condition) {
this.customCondition = condition;
return this;
}
@Override
public Builder options(BuilderConfiguration options) {
this.options = options;
return this;
}
}
}DefaultBuilder 内部类的所有方法直接为属性赋值,值得注意的是 headers 方法,在拥有 Content-Type 类型头时才会将 hasContentType 属性置为 true,在拥有 Accept 类型头时才会将 hasAccept 属性置为 true;
(4)build 方法
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {
private static class DefaultBuilder implements Builder {
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public RequestMappingInfo build() {
PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition = ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.paths) ? null :
new PatternsRequestCondition(
this.paths, this.options.getUrlPathHelper(), this.options.getPathMatcher(),
this.options.useSuffixPatternMatch(), this.options.useTrailingSlashMatch(),
this.options.getFileExtensions());
ContentNegotiationManager manager = this.options.getContentNegotiationManager();
return new RequestMappingInfo(this.mappingName, patternsCondition,
ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.methods) ?
null : new RequestMethodsRequestCondition(this.methods),
ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.params) ?
null : new ParamsRequestCondition(this.params),
ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.headers) ?
null : new HeadersRequestCondition(this.headers),
ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.consumes) && !this.hasContentType ?
null : new ConsumesRequestCondition(this.consumes, this.headers),
ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.produces) && !this.hasAccept ?
null : new ProducesRequestCondition(this.produces, this.headers, manager),
this.customCondition);
}
}
}build 方法依次使用对应属性及 options 构建器配置创建对应条件信息并封装为 RequestMappingInfo 对象并返回;
(5)BuilderConfiguration 类
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {
public static class BuilderConfiguration {
@Nullable
private UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper;
@Nullable
private PathMatcher pathMatcher;
private boolean trailingSlashMatch = true;
private boolean suffixPatternMatch = true;
private boolean registeredSuffixPatternMatch = false;
@Nullable
private ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager;
public void setUrlPathHelper(@Nullable UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper) {
this.urlPathHelper = urlPathHelper;
}
@Nullable
public UrlPathHelper getUrlPathHelper() {
return this.urlPathHelper;
}
public void setPathMatcher(@Nullable PathMatcher pathMatcher) {
this.pathMatcher = pathMatcher;
}
@Nullable
public PathMatcher getPathMatcher() {
return this.pathMatcher;
}
public void setTrailingSlashMatch(boolean trailingSlashMatch) {
this.trailingSlashMatch = trailingSlashMatch;
}
public boolean useTrailingSlashMatch() {
return this.trailingSlashMatch;
}
@Deprecated
public void setSuffixPatternMatch(boolean suffixPatternMatch) {
this.suffixPatternMatch = suffixPatternMatch;
}
@Deprecated
public boolean useSuffixPatternMatch() {
return this.suffixPatternMatch;
}
@Deprecated
public void setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(boolean registeredSuffixPatternMatch) {
this.registeredSuffixPatternMatch = registeredSuffixPatternMatch;
this.suffixPatternMatch = (registeredSuffixPatternMatch || this.suffixPatternMatch);
}
@Deprecated
public boolean useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch() {
return this.registeredSuffixPatternMatch;
}
@Nullable
@Deprecated
public List<String> getFileExtensions() {
if (useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch() && this.contentNegotiationManager != null) {
return this.contentNegotiationManager.getAllFileExtensions();
}
return null;
}
public void setContentNegotiationManager(ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager) {
this.contentNegotiationManager = contentNegotiationManager;
}
@Nullable
public ContentNegotiationManager getContentNegotiationManager() {
return this.contentNegotiationManager;
}
}
}BuilderConfiguration 类保存了相关配置,分别为 url 路径协助器 urlPathHelper、路径匹配器 pathMatcher、匹配时是否忽略尾部反斜杠 trailingSlashMatch(默认为 true)、是否进行后缀匹配 suffixPatternMatch(默认为 true)、是否只针对注册的后缀进行匹配的 registeredSuffixPatternMatch 属性以及内容协商控制器;
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)