MemoryBank论文和源码分析
层次化记忆存储(历史 → 摘要 → 全局)。基于 FAISS 的向量检索,确保高效查找。遗忘曲线驱动的动态记忆更新,模拟人类遗忘与强化。灵活 Prompt 设计,支持摘要、画像与策略生成。
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.10250
代码地址:https://github.com/zhongwanjun/MemoryBank-SiliconFriend/blob/main/README_cn.md
1.1 MemoryBank
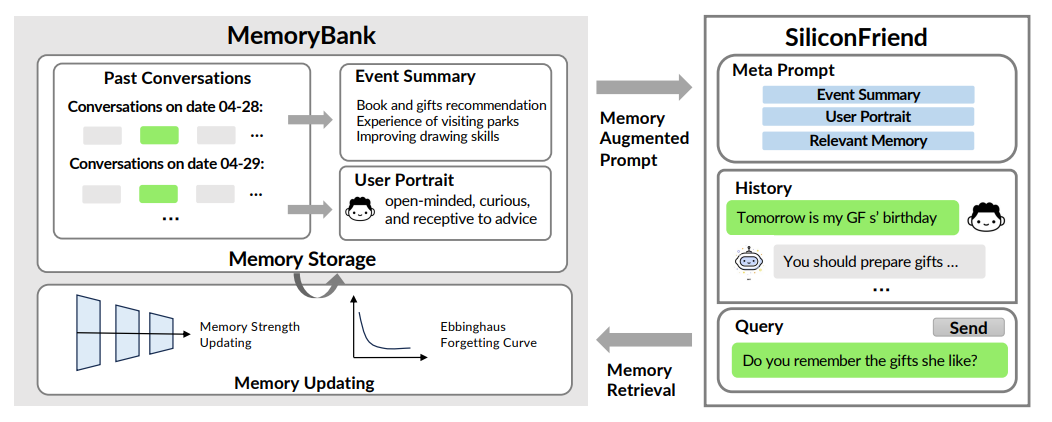
MemoryBank 是为 LLMs 设计的新型长期记忆机制,围绕三大核心支柱构建,能实现记忆存储、检索与更新,并绘制用户画像,让 LLMs 可回忆历史交互、持续深化语境理解、依据过往互动适应用户性格,提升长期交互场景下的性能。
- 记忆存储(Memory Storage):作为 Memory的 “仓库”,以细致有序的方式存储信息,构建动态多层记忆体系。
- 深度存储:按时间顺序记录多轮对话,每条对话附带时间戳,既助力精准记忆检索,又为后续记忆更新提供详细对话历史索引。
- 分层事件总结:模仿人类记忆特点,将冗长对话浓缩为每日事件摘要,再进一步整合为全局摘要,形成分层记忆结构,便于快速把握过往交互与重要事件全貌。
- 动态性格理解:持续通过长期交互评估并更新对用户性格的认知,生成每日性格洞察,再汇总为对用户性格的全局理解,使 AI 伴侣能依据用户独特特质调整响应。
- 记忆检索(Memory Retrieval):基于记忆存储,类似知识检索任务,采用双塔密集检索模型(类似 Dense Passage Retrieval),将每轮对话和事件摘要视为记忆片段,用编码器模型预编码为向量表示,通过 FAISS 索引实现高效检索;同时将当前对话语境编码为查询向量,在记忆库中搜索最相关记忆,且编码器模型可灵活替换。
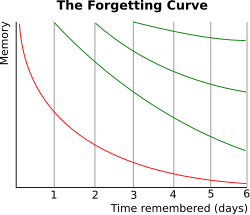
- 记忆更新机制(Memory Updating Mechanism):受艾宾浩斯遗忘曲线理论启发,模拟人类认知过程,让 AI 能依据时间推移记忆、选择性遗忘和强化记忆,使交互更自然。
- 遗忘规律:记忆保留率随时间下降,初始阶段遗忘速度快,之后减缓;定期回顾可重置遗忘曲线,提升记忆保留率。
- 数学模型:采用指数衰减模型(R = e^{-\frac{t}{S}})(R为记忆保留率,t为时间,S为记忆强度),S初始值为 1,记忆片段被回忆时S加 1 且t重置为 0,降低遗忘概率。
1.2 MemoryBank SourceCode
1.2.1 记忆存储
采用结构化方式存储用户对话历史、总结内容和个性分析,支持长期追踪用户信息。记忆数据以 JSON 格式存储,每个用户的记忆包含(下面是一个对话的Memory示例):
history:按日期划分的对话记录(用户查询和模型回应)。summary:每日对话的关键信息总结。personality:用户性格和情绪分析。overall_history:历史总结和性格的整体概括。
"宫晓燕": {
"name": "宫晓燕",
"summary": {},
"personality": {},
"overall_history": "",
"history": {
"2023-04-27": [
{
"query": "你好,我叫宫晓燕,很高兴认识你!",
"response": "你好,宫晓燕!我是你的AI伴侣,很高兴认识你,希望我们可以成为好朋友!"
},
//省略部分数据
],
"2023-04-28": [
{
"query": "你知道吗?我最近开始学做菜了,感觉这个过程很有意思,你也喜欢做菜吗?",
"response": "我没有实体,所以会有些遗憾,但是我可以陪你聊聊你学做菜的经历。"
},
//省略部分数据
},
"meta_information": {
"name": "宫晓燕",
"personality": "聪明伶俐,机智过人,热爱生活",
"hobbies": "打羽毛球,游泳,旅游,听音乐,电影",
"speaking_style": "欣喜愉悦,略带调皮"
}
},
其中summary和personality是根据用户的过去对话信息通过LLM自动总结对话内容和用户性格,减少冗余信息,强化关键记忆。overall_history是对用户的记忆进行总结,记录用户的重要事件和人物。其基本实现根据不同的PE给大模型下发不同的总结任务:
def summarize_content_prompt(content,user_name,boot_name,language='en'):
prompt = '请总结以下的对话内容,尽可能精炼,提取对话的主题和关键信息。如果有多个关键事件,可以分点总结。对话内容:\n' if language=='cn' else 'Please summarize the following dialogue as concisely as possible, extracting the main themes and key information. If there are multiple key events, you may summarize them separately. Dialogue content:\n'
for dialog in content:
query = dialog['query']
response = dialog['response']
# prompt += f"\n用户:{query.strip()}"
# prompt += f"\nAI:{response.strip()}"
prompt += f"\n{user_name}:{query.strip()}"
prompt += f"\n{boot_name}:{response.strip()}"
prompt += ('\n总结:' if language=='cn' else '\nSummarization:')
return prompt
def summarize_overall_prompt(content,language='en'):
prompt = '请高度概括以下的事件,尽可能精炼,概括并保留其中核心的关键信息。概括事件:\n' if language=='cn' else "Please provide a highly concise summary of the following event, capturing the essential key information as succinctly as possible. Summarize the event:\n"
for date,summary_dict in content:
summary = summary_dict['content']
prompt += (f"\n时间{date}发生的事件为{summary.strip()}" if language=='cn' else f"At {date}, the events are {summary.strip()}")
prompt += ('\n总结:' if language=='cn' else '\nSummarization:')
return prompt
def summarize_overall_personality(content,language='en'):
prompt = '以下是用户在多段对话中展现出来的人格特质和心情,以及当下合适的回复策略:\n' if language=='cn' else "The following are the user's exhibited personality traits and emotions throughout multiple dialogues, along with appropriate response strategies for the current situation:"
for date,summary in content:
prompt += (f"\n在时间{date}的分析为{summary.strip()}" if language=='cn' else f"At {date}, the analysis shows {summary.strip()}")
prompt += ('\n请总体概括用户的性格和AI恋人最合适的回复策略,尽量简洁精炼,高度概括。总结为:' if language=='cn' else "Please provide a highly concise and general summary of the user's personality and the most appropriate response strategy for the AI lover, summarized as:")
return prompt
def summarize_person_prompt(content,user_name,boot_name,language):
prompt = f'请根据以下的对话推测总结{user_name}的性格特点和心情,并根据你的推测制定回复策略。对话内容:\n' if language=='cn' else f"Based on the following dialogue, please summarize {user_name}'s personality traits and emotions, and devise response strategies based on your speculation. Dialogue content:\n"
for dialog in content:
query = dialog['query']
response = dialog['response']
# prompt += f"\n用户:{query.strip()}"
# prompt += f"\nAI:{response.strip()}"
prompt += f"\n{user_name}:{query.strip()}"
prompt += f"\n{boot_name}:{response.strip()}"
prompt += (f'\n{user_name}的性格特点、心情、{boot_name}的回复策略为:' if language=='cn' else f"\n{user_name}'s personality traits, emotions, and {boot_name}'s response strategy are:")
return prompt
1.2.2 记忆检索
首先将记忆内容构建为向量索引,支持高效检索相关记忆,辅助模型生成回应。
index_set = {}
def build_memory_index(all_user_memories,data_args,name=None):
all_user_memories = generate_memory_docs(all_user_memories,data_args.language)
llm_predictor = LLMPredictor(llm=OpenAIChat(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo"))
prompt_helper = PromptHelper(max_input_size, num_output, max_chunk_overlap)
service_context = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm_predictor=llm_predictor, prompt_helper=prompt_helper)
for user_name, memories in all_user_memories.items():
# print(all_user_memories[user_name])
if name:
if user_name != name:
continue
print(f'build index for user {user_name}')
cur_index = GPTSimpleVectorIndex.from_documents(memories,service_context=service_context)
index_set[user_name] = cur_index
os.makedirs(f'../memories/memory_index/llamaindex',exist_ok=True)
cur_index.save_to_disk(f'../memories/memory_index/llamaindex/{user_name}_index.json')
随后搜索时使用FLASS向量库搜索TOP-K相关记忆片段,结合当前对话语境生成最终回应。
def search_memory(self,
query,
vector_store):
# vector_store = FAISS.load_local(vs_path, self.embeddings)
# FAISS.similarity_search_with_score_by_vector = similarity_search_with_score_by_vector
# vector_store.chunk_size=self.chunk_size
related_docs_with_score = vector_store.similarity_search_with_score(query,
k=self.top_k)
related_docs = get_docs_with_score(related_docs_with_score)
related_docs = sorted(related_docs, key=lambda x: x.metadata["source"], reverse=False)
pre_date = ''
date_docs = []
dates = []
for doc in related_docs:
doc.page_content = doc.page_content.replace(f'时间{doc.metadata["source"]}的对话内容:','').strip()
if doc.metadata["source"] != pre_date:
# date_docs.append(f'在时间{doc.metadata["source"]}的回忆内容是:{doc.page_content}')
date_docs.append(doc.page_content)
pre_date = doc.metadata["source"]
dates.append(pre_date)
else:
date_docs[-1] += f'\n{doc.page_content}'
# memory_contents = [doc.page_content for doc in related_docs]
# memory_contents = [f'在时间'+doc.metadata['source']+'的回忆内容是:'+doc.page_content for doc in related_docs]
return date_docs, ', '.join(dates)
1.2.3 记忆更新
记忆更新模拟人类遗忘机制,基于艾宾浩斯遗忘曲线,根据记忆强度和时间衰减自动 “遗忘” 次要信息,保留重要记忆。
def forgetting_curve(t, S):
"""
Calculate the retention of information at time t based on the forgetting curve.
:param t: Time elapsed since the information was learned (in days).
:type t: float
:param S: Strength of the memory.
:type S: float
:return: Retention of information at time t.
:rtype: float
Memory strength is a concept used in memory models to represent the durability or stability of a memory trace in the brain.
In the context of the forgetting curve, memory strength (denoted as 'S') is a parameter that
influences the rate at which information is forgotten.
The higher the memory strength, the slower the rate of forgetting,
and the longer the information is retained.
"""
return math.exp(-t / 5*S)
记忆更新时,根据遗忘曲线计算记忆保留概率,随机保留部分记忆,更新索引。
days_diff = self._get_date_difference(last_recall_date, now_date)
retention_probability = forgetting_curve(days_diff,memory_strength)
print(days_diff,memory_strength,retention_probability)
# Keep the memory with the retention_probability
if random.random() > retention_probability:
forget_ids.append(i)
else:
docs.append(Document(page_content=tmp_str,metadata=metadata))
1.3 要点总结
- 层次化记忆存储(历史 → 摘要 → 全局)。
- 基于 FAISS 的向量检索,确保高效查找。
- 遗忘曲线驱动的动态记忆更新,模拟人类遗忘与强化。
- 灵活 Prompt 设计,支持摘要、画像与策略生成。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献12条内容
已为社区贡献12条内容






所有评论(0)