HTML5_API:performance API 性能监控
PerformanceObserver 主要用于监听性能条目(如 paint、resource、longtask 等),比传统的 performance.getEntries() 更灵活,支持动态监测。两者均基于浏览器内部的性能时间线(Performance Timeline)获取数据,共享相同的性能条目类型(如 navigation、resource、paint 等)Performance
performance API
它是现代浏览器提供的一组用于测量和监控网页性能的接口,它能够帮助开发者获取高精度的性能数据,从而优化用户体验。
核心功能
Performance API 主要用于记录和分析网页加载、资源请求、脚本执行等关键性能指标。其核心功能包括:
1). 高精度时间测量:提供微秒级(最高可达5μs)的时间戳,远高于传统的 Date.now()。使用performance.now()
2). 性能条目记录:自动记录页面导航、资源加载、绘制事件等性能数据。
3). 关键指标监控:如首次绘制(FP)、首次内容绘制(FCP)、最大内容绘制(LCP)等
关键属性和方法
performance.timing(传统 API):
包含页面导航各阶段的时间戳,如 DNS 查询、TCP 连接、DOM 解析等(该接口已废弃,被PerformanceObserver替代,如果存在旧版浏览器兼容问题,timing该用还是得用)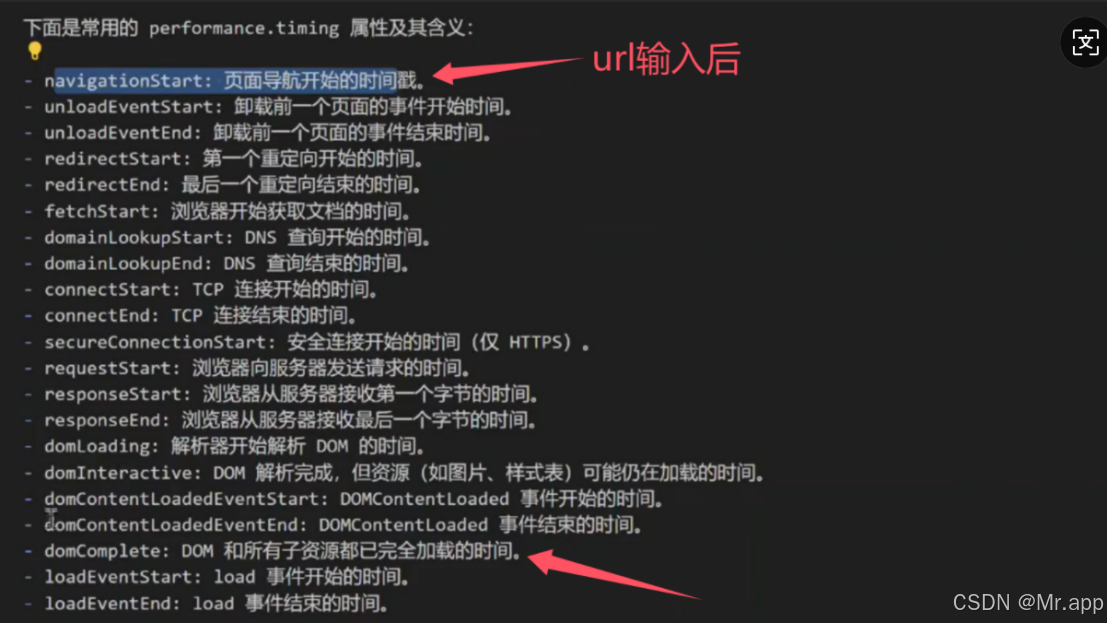
performance.getEntries():// return Array
返回所有性能条目,包括资源加载、导航时序等(避免直接调用,以减少性能开销)
performance.now():
返回当前时间的高精度时间戳,用于测量代码执行时间(替代了Date.now())
const start = performance.now();
console.log(`耗时:${performance.now() - start}ms`);
性能条目类型: getEntriesByType()
进一步过滤performance.getEntries()性能条目
调用方式: performance.getEntriesByType(“navigation”) // return Array
通过 performance.getEntriesByType() 可以获取特定类型的性能条目:

performance.getEntriesByType('resource').forEach(entry => {
console.log(entry.name, entry.duration);
});
PerformanceObserver(监测性能相关的指标)
PerformanceObserver 主要用于监听性能条目(如 paint、resource、longtask 等),比传统的 performance.getEntries() 更灵活,支持动态监测
Performance API 和 PerformanceObserver 是现代浏览器提供的两种性能监控工具,它们既有协同关系又有明显区别:
Performance API 提供静态性能数据采集能力(如 performance.getEntries())
PerformanceObserver 采用观察者模式动态监听性能事件,两者共同构成完整的性能监控体系
两者均基于浏览器内部的性能时间线(Performance Timeline)获取数据,共享相同的性能条目类型(如 navigation、resource、paint 等)
// 静态获取现有资源加载数据
const resources = performance.getEntriesByType('resource');
// 动态监听新产生的布局偏移
const observer = new PerformanceObserver(list => {
list.getEntries().forEach(entry => {
console.log('CLS:', entry.value);
});
});
observer.observe({type: 'layout-shift', buffered: true});
两者使用示例
一、监听首次内容渲染(FCP)
const timing = performance.timing;
const FCP = timing.domContentLoadedEventEnd - timing.navigationStart; // 首次内容渲染时间
console.log(`首次内容渲染时间FCP: ${FCP}`);
const TTFB = timing.responseStart - timing.requestStart; // 首字节时间
console.log(`首字节时间TTFB: ${TTFB}`);
// 计算页面完全加载时间(loadEventEnd到navigationStart)
const loadTime = performance.timing.loadEventEnd - this.startTime;
console.log(`计算页面完全加载时间: ${loadTime},`);
// 计算DOM解析完成时间(domComplete到navigationStart)
const domReadyTime =
performance.timing.domComplete - performance.timing.navigationStart;
console.log(`计算DOM解析完成时间: ${domReadyTime}`);
// 计算资源加载时间(loadEventStart到domLoading)
const resourceLoadTime =
performance.timing.loadEventStart - performance.timing.domLoading;
console.log(`计算资源加载时间: ${resourceLoadTime}`);
// 监听首次内容渲染(FCP)和最大内容渲染(LCP)
const observer = new PerformanceObserver((list) => {
list.getEntries().forEach((entry) => {
if (entry.entryType === "paint" && entry.name === "first-contentful-paint") {
console.log("FCP时间:", entry.startTime);
}
if (entry.entryType === "largest-contentful-paint") {
console.log("LCP时间:", entry.renderTime || entry.loadTime);
}
});
});
observer.observe({
entryTypes: ["paint", "largest-contentful-paint"],
});
二、资源加载耗时
// observer动态持续分析资源加载耗时
var observer = new PerformanceObserver(list => {
list.getEntries().forEach(entry => {
console.log(`${entry.name} 耗时: ${entry.duration.toFixed(2)}ms`);
});
});
observer.observe({type: 'resource', buffered: true});
// performance_api静态分析初始资源加载耗时
performance.getEntriesByType('resource').forEach(entry => {
console.log(`${entry.name} 耗时: ${entry.duration.toFixed(2)}ms`);
});
区别


更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)