aosp15命令行调节音量大小及service call源码剖析
这个问题大家可以回想一下,本质上音量设置也是一般设置app操作了UI最后跨进程调用到了AudioService服务,一般跨进程服务其实也是可以直接使用adb shell service call 方式进行调用,比如以前使用service call命令调用SurfaceFlinger进行Layer trace的导出。那么根据上面IAudioService.aidl文件中展示的各个接口方法,首先要确定
背景
在音量调节时候经常都是在设置的如下UI画面中进行调节,需要通过手动操作相对较为麻烦,有时候有系统可能还对音量这块画面进行了移除,可能都找不到如下图这种画面:
那么有没有什么命令行可以进行音量的设置呢?
这个问题大家可以回想一下,本质上音量设置也是一般设置app操作了UI最后跨进程调用到了AudioService服务,一般跨进程服务其实也是可以直接使用adb shell service call 方式进行调用,比如以前使用service call命令调用SurfaceFlinger进行Layer trace的导出。
开始和停止抓取sf的的layer
开始抓取:
SurfaceFlinger:adb shell su root service call SurfaceFlinger 1025 i32 1
停止抓取:
SurfaceFlinger:adb shell su root service call SurfaceFlinger 1025 i32 0
其中call后面的参数进行一一解释
SurfaceFlinger:代表服务名字
1025:代表方法序号,这个需要结合具体服务,sf来说他直接代码有具体数值
i32:代表整型变量
1,0:代表具体的值
这样service call命令就可以跨进程调用到SurfaceFlinger
frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
case 1025: { // Set layer tracing
n = data.readInt32();
bool tracingEnabledChanged;
if (n == 1) {
int64_t fixedStartingTime = data.readInt64();
ALOGD("LayerTracing enabled");
tracingEnabledChanged = mLayerTracing.enable();
if (tracingEnabledChanged) {
int64_t startingTime =
(fixedStartingTime) ? fixedStartingTime : systemTime();
mScheduler
->schedule([&]() FTL_FAKE_GUARD(mStateLock) {
mLayerTracing.notify("start", startingTime);
})
.wait();
}
} else if (n == 2) {
std::string filename = std::string(data.readCString());
ALOGD("LayerTracing disabled. Trace wrote to %s", filename.c_str());
tracingEnabledChanged = mLayerTracing.disable(filename.c_str());
} else {
ALOGD("LayerTracing disabled");
tracingEnabledChanged = mLayerTracing.disable();
}
mTracingEnabledChanged = tracingEnabledChanged;
reply->writeInt32(NO_ERROR);
return NO_ERROR;
}
那么就同样思路方法我们来尝试使用service call命令设置音量。
探索接口设置UI操作音量
frameworks/base/core/java/android/preference/SeekBarVolumizer.java
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_SET_STREAM_VOLUME:
//省略
mAudioManager.setStreamVolume(mStreamType, mLastProgress,
AudioManager.FLAG_SHOW_UI_WARNINGS);
break;
通过AudioManager的setStreamVolume接口进行音量的设置,setStreamVolume的实现如下:
frameworks/base/media/java/android/media/AudioManager.java
/**
* Sets the volume index for a particular stream.
* <p>This method has no effect if the device implements a fixed volume policy
* as indicated by {@link #isVolumeFixed()}.
* <p>From N onward, volume adjustments that would toggle Do Not Disturb are not allowed unless
* the app has been granted Do Not Disturb Access.
* See {@link NotificationManager#isNotificationPolicyAccessGranted()}.
* @param streamType The stream whose volume index should be set.
* @param index The volume index to set. See
* {@link #getStreamMaxVolume(int)} for the largest valid value.
* @param flags
* @see #getStreamMaxVolume(int)
* @see #getStreamVolume(int)
* @see #isVolumeFixed()
* @throws SecurityException if the volume change triggers a Do Not Disturb change
* and the caller is not granted notification policy access.
*/
public void setStreamVolume(int streamType, int index, @PublicVolumeFlags int flags) {
final IAudioService service = getService();
try {
service.setStreamVolumeWithAttribution(streamType, index, flags,
getContext().getOpPackageName(), getContext().getAttributionTag());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
可以看到最后也是调用到了AudioService的setStreamVolumeWithAttribution方法。可以看看服务端的都有哪些方法:
frameworks/base/media/java/android/media/IAudioService.aidl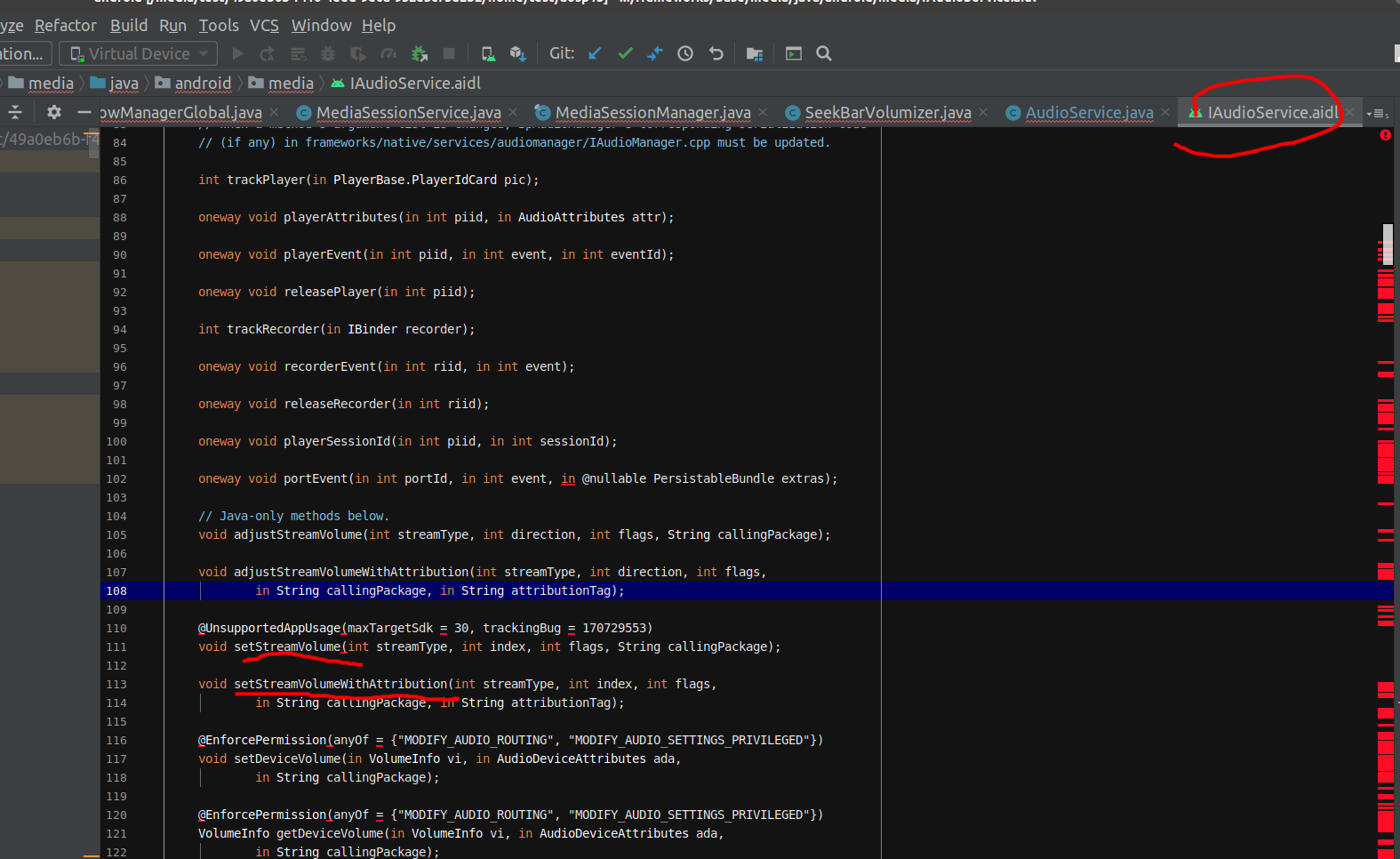 可以看到确实有相关的接口方法。
可以看到确实有相关的接口方法。
明显AudioService属于一个binder的服务stub端,那么是否可以参考类似使用命令service call SurfaceFlinger抓取SurfaceFlinger的Layer trace的方案来触发音量调节呢?
那么下面就来介绍一下命令行如何调节音量。
命令行设置音量
那么根据上面IAudioService.aidl文件中展示的各个接口方法,首先要确定接口方法,然后数出对应方法的序号,再确认具体参数,确定使用的方法,下面两个方法其实都可以
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = 30, trackingBug = 170729553)
void setStreamVolume(int streamType, int index, int flags, String callingPackage);
void setStreamVolumeWithAttribution(int streamType, int index, int flags,
in String callingPackage, in String attributionTag);
他们的序号就是IAudioService.aidl中的方法,上到下从1开始进行数,发现setStreamVolume对应是12,setStreamVolumeWithAttribution对应是13,其实两个方法只相差一个attributionTag参数,这两个string参数其实不传递就默认为null。
一个是StreamType,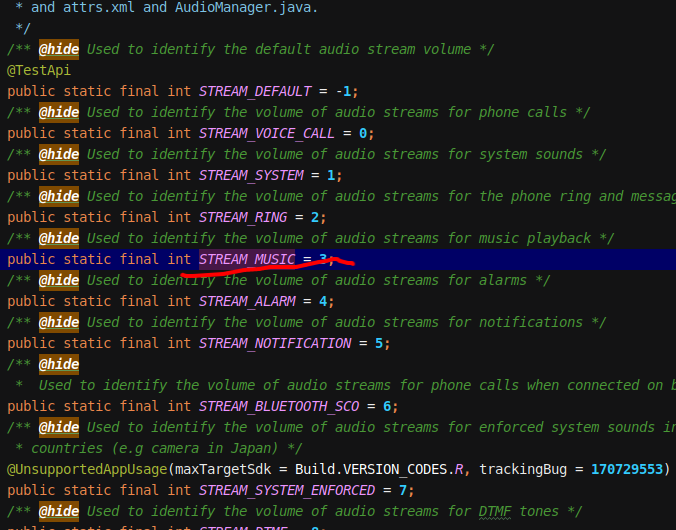
一个是direction,其实就是index,这里直接传递index数字,一般0-15
一个是flags,这里直接传递一个1就行
那么命令就确定了:
adb shell service call audio 12 i32 3 i32 15 i32 1
命令含义就是通过
执行结果如下: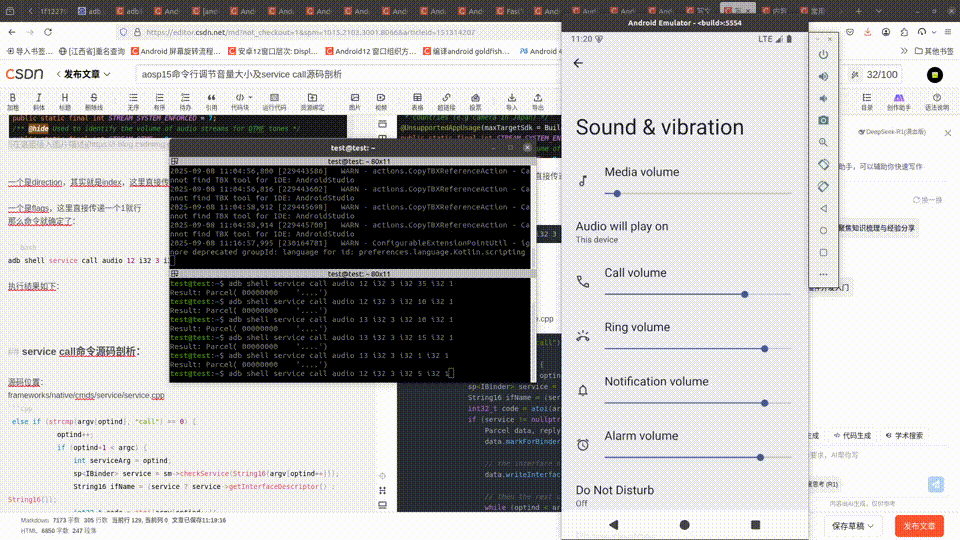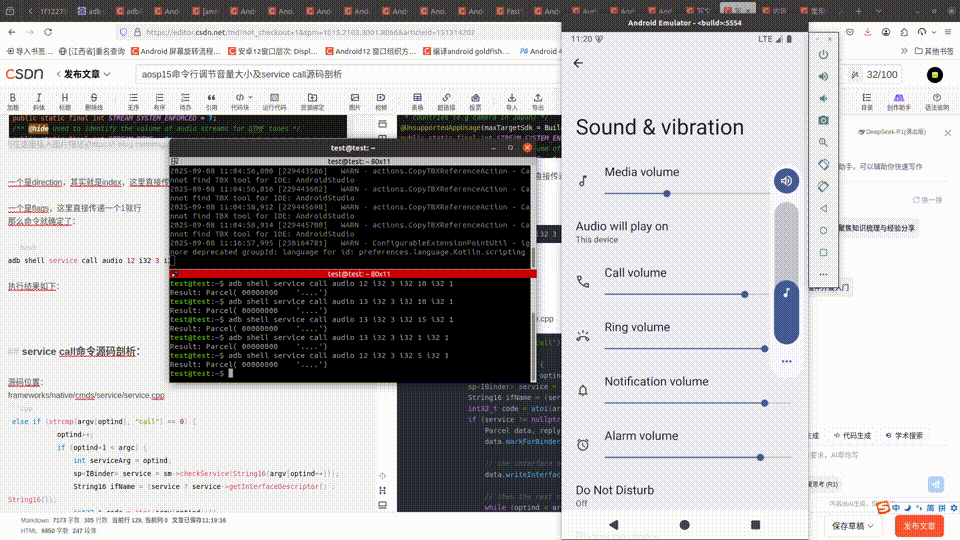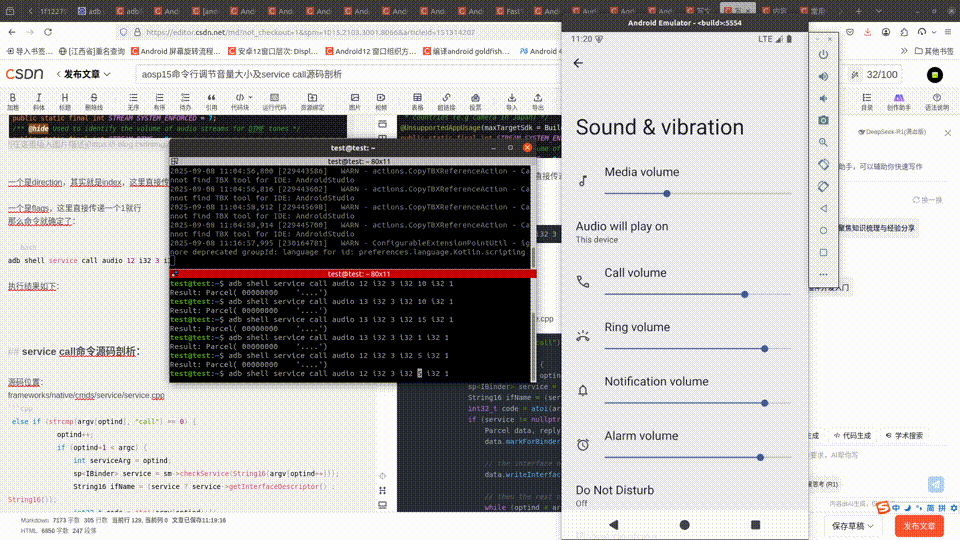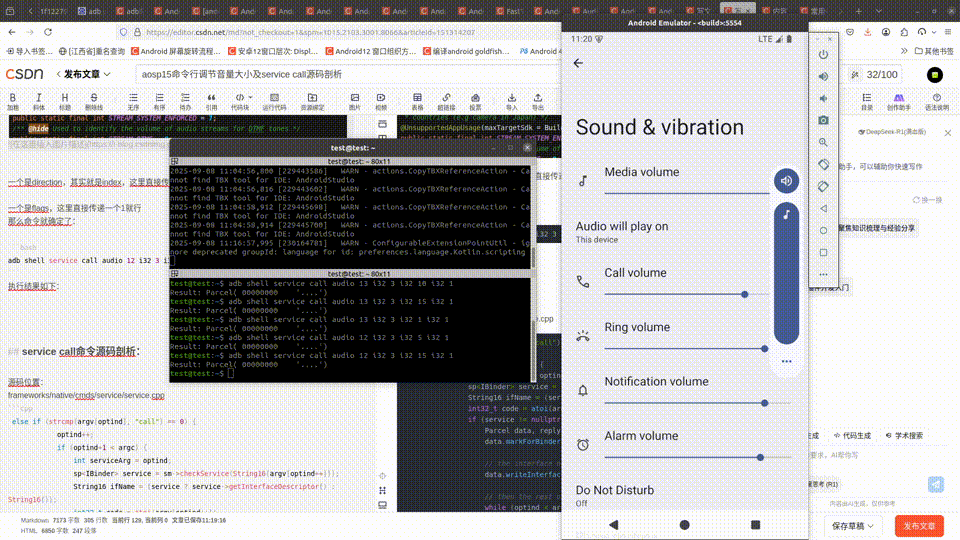
同样使用adjustStreamVolumeWithAttribution方法的话,就需要把12变成13既可以,后面两个参数不进行传递。
adb shell service call audio 13 i32 3 i32 5 i32 1
同样也可以获取音量,方法为:
int getStreamVolume(int streamType);
那么方法序号就是21,传递StreamType为Music即3就可以。
test@test:~$ adb shell service call audio 12 i32 3 i32 10 i32 1
Result: Parcel( 00000000 '....')
test@test:~$ adb shell service call audio 21 i32 3
Result: Parcel( 00000000 0000000a '........')
可以看到这里的值为0a,也就是上面设置的10.
service call命令源码剖析:
源码位置:
frameworks/native/cmds/service/service.cpp
else if (strcmp(argv[optind], "call") == 0) {
optind++;
if (optind+1 < argc) {
int serviceArg = optind;
sp<IBinder> service = sm->checkService(String16(argv[optind++]));
String16 ifName = (service ? service->getInterfaceDescriptor() : String16());
int32_t code = atoi(argv[optind++]);
if (service != nullptr && ifName.size() > 0) {
Parcel data, reply;
data.markForBinder(service);
// the interface name is first
data.writeInterfaceToken(ifName);
// then the rest of the call arguments
while (optind < argc) {
//把参数都通过Parcel的方法进行write写入
if (strcmp(argv[optind], "i32") == 0) {
optind++;
data.writeInt32(atoi(argv[optind++]));
} else if (strcmp(argv[optind], "i64") == 0) {
optind++;
data.writeInt64(atoll(argv[optind++]));
} else if (strcmp(argv[optind], "s16") == 0) {
optind++;
data.writeString16(String16(argv[optind++]));
} else if (strcmp(argv[optind], "f") == 0) {
optind++;
data.writeFloat(atof(argv[optind++]));
} else if (strcmp(argv[optind], "d") == 0) {
optind++;
data.writeDouble(atof(argv[optind++]));
} else if (strcmp(argv[optind], "null") == 0) {
optind++;
data.writeStrongBinder(nullptr);
} else if (strcmp(argv[optind], "fd") == 0) {
optind++;
const char *path = argv[optind++];
int fd = open(path, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
aerr << prog_name << ": could not open '" << path << "'" << endl;
wantsUsage = true;
result = 10;
break;
}
data.writeFileDescriptor(fd, true /* take ownership */);
} else if (strcmp(argv[optind], "afd") == 0) {
optind++;
const char *path = argv[optind++];
int fd = open(path, O_RDONLY);
struct stat statbuf;
int afd = ashmem_create_region("test", statbuf.st_size);
void* ptr = mmap(NULL, statbuf.st_size,
PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, afd, 0);
(void)read(fd, ptr, statbuf.st_size);
close(fd);
data.writeFileDescriptor(afd, true /* take ownership */);
} else if (strcmp(argv[optind], "nfd") == 0) {
optind++;
data.writeFileDescriptor(
atoi(argv[optind++]), true /* take ownership */);
} else if (strcmp(argv[optind], "intent") == 0) {
char* action = nullptr;
char* dataArg = nullptr;
char* type = nullptr;
int launchFlags = 0;
char* component = nullptr;
int categoryCount = 0;
char* categories[16];
char* context1 = nullptr;
optind++;
while (optind < argc)
{
char* key = strtok_r(argv[optind], "=", &context1);
char* value = strtok_r(nullptr, "=", &context1);
// we have reached the end of the XXX=XXX args.
if (key == nullptr) break;
if (strcmp(key, "action") == 0)
{
action = value;
}
else if (strcmp(key, "data") == 0)
{
dataArg = value;
}
else if (strcmp(key, "type") == 0)
{
type = value;
}
else if (strcmp(key, "launchFlags") == 0)
{
launchFlags = atoi(value);
}
else if (strcmp(key, "component") == 0)
{
component = value;
}
else if (strcmp(key, "categories") == 0)
{
char* context2 = nullptr;
categories[categoryCount] = strtok_r(value, ",", &context2);
while (categories[categoryCount] != nullptr)
{
categoryCount++;
categories[categoryCount] = strtok_r(nullptr, ",", &context2);
}
}
optind++;
}
writeString16(data, action);
writeString16(data, dataArg);
writeString16(data, type);
data.writeInt32(launchFlags);
writeString16(data, component);
if (categoryCount > 0)
{
data.writeInt32(categoryCount);
for (int i = 0 ; i < categoryCount ; i++)
{
writeString16(data, categories[i]);
}
}
else
{
data.writeInt32(0);
}
// for now just set the extra field to be null.
data.writeInt32(-1);
} else {
aerr << prog_name << ": unknown option " << argv[optind] << endl;
wantsUsage = true;
result = 10;
break;
}
}
service->transact(code, data, &reply);
aout << "Result: " << reply << endl;
} else {
aerr << prog_name << ": Service " << argv[serviceArg]
<< " does not exist" << endl;
result = 10;
}
} else {
wantsUsage = true;
result = 10;
}
}
本质上service call的原理,就是组装好相关参数到Parcel,然后通过transact方法进行跨进程通讯。
原文地址:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/YTXL0VNsyazyb-KvXnKXnQ
更多framework实战开发,请关注“千里马学框架”
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献8条内容
已为社区贡献8条内容






所有评论(0)